Abstract
Pakistan is facing a severe energy crisis due to its heavy dependency on the import of costly fossil fuels, which ultimately leads to expansive electricity generation, a low power supply, and interruptive load shedding. In this regard, the utilization of available renewable energy resources within the country for production of electricity can lessen this energy crisis. Livestock waste/manure is considered the most renewable and abundant material for biogas generation. Pakistan is primarily an agricultural country, and livestock is widely kept by the farming community, in order to meet their needs. According to the 2016–2018 data on the livestock population, poultry held the largest share at 45.8%, followed by buffaloes (20.6%), cattle (12.7%), goats (10.8%), sheep (8.4%), asses (1.3%), camels (0.25%), horses (0.1%), and mules (0.05%). Different animals produce different amounts of manure, based upon their size, weight, age, feed, and type. The most manure is produced by cattle (10–20 kg/day), while poultry produce the least (0.08–0.1 kg/day). Large quantities of livestock manure are produced from each province of Pakistan; Punjab province was the highest contributor (51%) of livestock manure in 2018. The potential livestock manure production in Pakistan was 417.3 million tons (Mt) in 2018, from which 26,871.35 million m3 of biogas could be generated—with a production potential of 492.6 petajoules (PJ) of heat energy and 5521.5 MW of electricity. Due to its favorable conditions for biodigester technologies, and through the appropriate development of anaerobic digestion, the currently prevailing energy crises in Pakistan could be eliminated.
1. Introduction
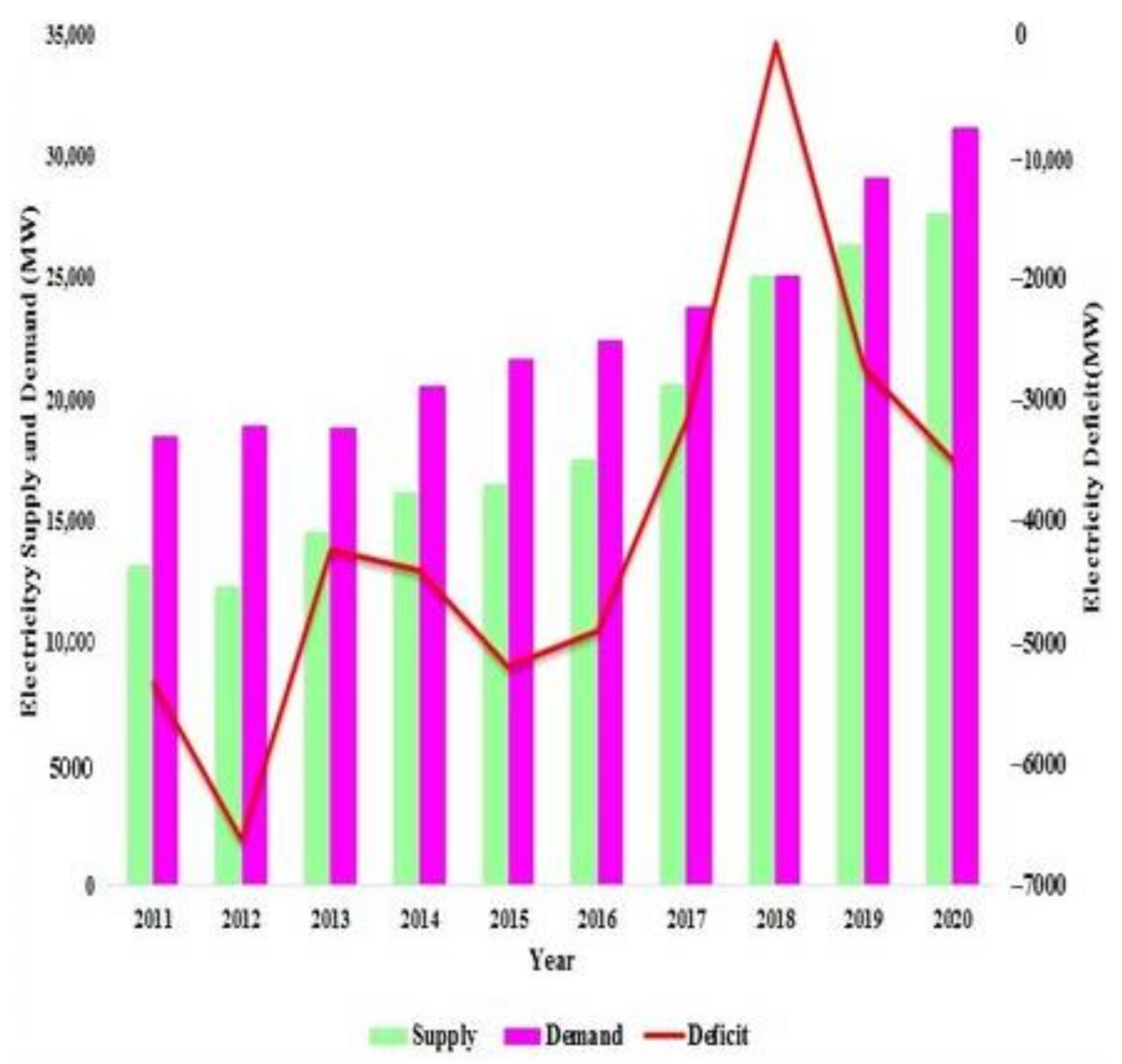
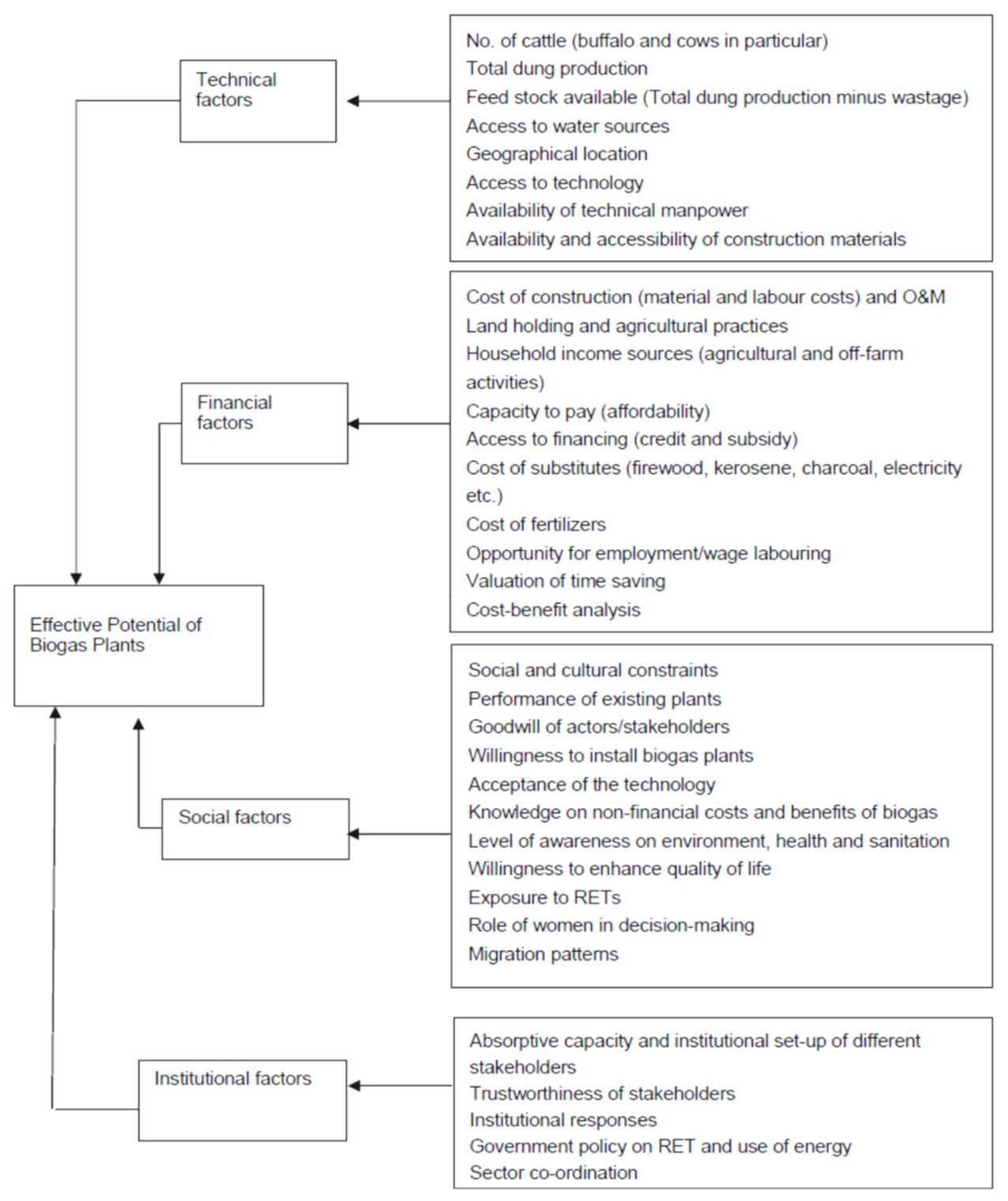
The production of cheap, green energy has been considered a prime objective for a country heading towards sustainable development. Pakistan, as a developing country, needs an enormous amount of energy, around 25,000 megawatts (MW), for its industrial, agricultural, and household needs (Figure 1). However, this energy demand has not been met, which has led to electricity crises [1,2,3]. Due to these severe energy crises, Pakistan is currently facing tremendous electricity load shedding (10–14 h/day) [4,5,6,7]. Energy consumption has increased due to the growth in industrialization and the increasing urban population. For example, the per capita energy consumption of Pakistan has shown an increasing trend from the year 2000, from 373.13 to 484.45 kWh [8].
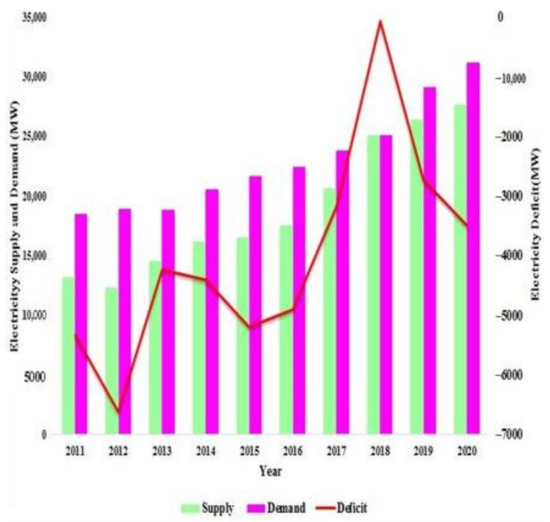
Figure 1.
Electricity supply, demand, and deficit of the country.
The current determined capacity of Pakistan is 22,000 MW of electricity (Figure 1). Mismanagement at transmission and distribution networks and high discharges have resulted in high losses that consequently increase load shedding. This is the foremost reason that Pakistan is facing energy shortfalls of 4000–6000 MW, as presented in Figure 1 [9,10,11,12,13,14]. The industrial, agricultural, and domestic sectors are suffering badly due to the ongoing energy shortfall [6]. A recent survey—conducted by the Private Power and Infrastructure Board, Government of Pakistan, Ministry of Energy (Power Division)—indicated that electricity consumption of 90.36 terawatt-hours (TWh) was recorded in Pakistan during 2015–2016, with 6.01% electricity export and 0.49% electricity import.
The electricity demand of the country is increasing at an annual rate of 11–13% [15] because of the increase in growth centers and the industrialization process. Pakistan is likely to follow the same trend in the future, as well. The energy demand for Pakistan is projected to rise to 54,000 MW in 2020 and 113,000 MW in 2030 [16,17,18].
It was found that 70% of Pakistan’s population lives in rural areas, and that 96.6% of rural people have no access to modern energy facilities. Thus, they are facing energy poverty. In this regard, it was also found that about 45% of their energy expenditure is spent on solid biomass such as dung cakes, firewood, and crop residues, with an additional 12% spent on natural gas, LPG, kerosene, and candles used for lighting and cooking purposes in rural areas [19].
Natural gas, firewood, kerosene, livestock dung, liquid petroleum gas (LPG), firewood, and electricity are the most common fuels currently being used for cooking purposes in Pakistan [20]. Natural gas (supplied through pipes) is the cheapest fuel for cooking purposes. However, due to the limited reserves and insufficient supply systems, it cannot be a promising fuel for cooking [21]. The limited reserves and high prices of fossil fuels have resulted in the fact that kerosene and LPG are not viable options for cooking purposes in Pakistan. On the other hand, the most common cooking fuels such as firewood, crop residues, and animal dung have lower efficiency with higher heating values as compared to the other fuels [22].
Raising livestock is one of the major agricultural activities in Pakistan which contributes to the agricultural economy of Pakistan. In this context, the agriculture-based economy has a 24.5% share of the gross domestic product (GDP) and provides 60% of export earnings in Pakistan. Likewise, 55.6% of the economy is from the livestock sector and contributes 11.8% of Pakistan’s GDP. Cattle raising is one of the major agricultural activities in Pakistan, meaning that a large quantity of livestock waste is produced in Pakistan which could be utilized as an appropriate source of sustainable energy. Cattle manure in most villages is used to prepare dried dung cakes that are burned for cooking energy.
People living in hilly areas of Pakistan are in difficult conditions to fulfill their energy demands, and they spend a lot of time collecting animal dung and woody biomass. In this regard, the use of livestock waste for energy production will be a worthwhile approach for providing an energy supply to the rural areas which in turn is beneficial for the economic development of the country, with a reduction in environment concerns [23,24].
Moreover, the use of biogas as a clean energy source will also reduce the utilization of conventional fossil fuels which in turn will lower GHG, and other hazardous gas emissions which are detrimental to the environment [25,26]. In this view, the development of biodigester technology will provide a manure management facility for dairy farms as well as for poultry farms. Digested manure is a natural fertilizer which can be applied to crops as a cost-effective alternative to synthetic fertilizers [26]. On the other hand, the development of biodigester technology will result in the conservation of resources and protection of the environment [27]. Considering the large quantity of livestock manure production in rural areas of Pakistan, it has potential to be utilized for energy production in order to overcome prevailing energy crises. The biogas produced from cattle manure is a unique sustainable energy supply due to its high availability as a decentralized energy source [28]. However, currently, the main issue with anaerobic digestion of livestock manure is the ammonia toxicity due to the higher concentrations of nitrogen as well as lower degradation during anaerobic digestion due to the higher concentrations of lignocellulosic materials [29,30]. This problem can be tackled by co-digestion of manure with material having a lower concentration of nitrogen [31,32].
Some studies have already been carried out to show the role of agro-industrial waste for biogas generation as an important source of sustainable energy in Pakistan [10,33,34]. Currently, about 8000 biogas plants are operative in Pakistan [35]. However, there is a lack of scientific study to evaluate the potential of livestock manure as a pivotal bioresource and the potential of biogas generation via anaerobic digestion of the available livestock manure in different provinces of Pakistan. Furthermore, it is also not clear how the potential of biogas from animal manure can contribute to the heat and electrical energy supply in Pakistan. Hence, it is essential to find out the potential of biogas, methane, and electricity generation using animal manure for enhancing biodigester technology in the country as well as for overcoming the prevailing energy and environmental issues.
Herein, we studied the potential of renewable energy production (e.g., biogas, methane, electricity, heat energy) from livestock manure in Pakistan by spatially analyzing and characterizing the data (from 1960 to 2018) that were collected from the Pakistan Bureau of Statistics and Ministry of National Food Security & Research. The results of this study will be useful for developing biogas-based electricity projects in all provinces of Pakistan which will not only be helpful in overcoming the ongoing energy crises but will also create employment opportunities, particularly in rural areas. This analysis will also be useful to the policymakers of developing countries that can change the lives of many villagers.
2. Methodology
2.1. Calculation of Livestock Population
The livestock population and density records were extracted from the archives of livestock census data (collected by the Pakistan Bureau of Statistics from 1960 to 2018) and arrayed provincially [36,37]. However, in this study, livestock populations were estimated for 2016, 2017, and 2018, using the annual growth rate of 8–10% [38].
2.2. Calculation and Measurement of Total Amount of Livestock Manure in Pakistan
The amount of manure produced by an animal depends on many parameters, including body weight, size, age, amount of feed, and type of animal [39]. The reference study found that the amount of manure produced by cattle and camels is 10–20 kg/day and 15–17 kg/day, respectively [39]. For sheep/goats, it is 2 kg/day, whereas, for mules, horses, and asses, it ranges from 10 to 15 kg/day [39]. Similarly, for poultry, daily manure generation is estimated to be 0.08–0.1 kg [39]. Keeping in view the effect of influential parameters, in this study, the average manure production for cattle/buffalo, goats/sheep, camels, and mules/horses/asses was considered 10 kg/day, 2 kg/day, 15 kg/day, 10 kg/day, and 0.1 kg/day, respectively.
2.3. Calculation of Total Potential of Biogas Production from Livestock Manure
The potential of biogas generation from livestock manure in the country was calculated using manure produced annually. The biogas production from animal manure can be affected by various factors such as the amount of manure, the availability of manure, and the total solids content in animal manure [39]. A variable coefficient of manure availability was introduced to concede the manure collection and transportation losses in the calculation. Table 1 summarizes the numeric values of influential parameters that were considered in this study. The theoretical potential of biogas (TPB) generated from animal manure was determined by the following Equation (1).
where TPB is the theoretical potential of biogas (million m3 year−1), M is the quantity of livestock manure/year/province (million kg year−1), AC denotes the availability coefficient of animal manure for selected species, TS is the total solids content of animal manure, and BY is the biogas yield of animal manure for each kilogram of total solids (m3 kg−1 TS).

Table 1.
Amount of animal manure produced, manure availability coefficient, biogas yield, and ratio of the total solids of animal manure for selected species [25,40,41].
In this study, the biogas potential determined for the manure obtained from the selected animal species was calculated by considering AC and BY values of 50% and 0.6 m3 kg−1 TS, respectively, for cattle, buffaloes, camels, horses, asses, and mules. Moreover, AC and BY values of 33% and 0.30 m3 kg−1 TS were considered for sheep/goats, whereas for poultry, 99% and 0.15 m3 kg−1 TS, respectively, were considered. Similarly, the TS value was considered 25% for cattle, buffaloes, camels, horses, asses, and mules, whereas 20% was considered for sheep/goats and 29% for poultry [42].
2.4. Calculation of Potential of Methane and Electricity Production from Livestock Manure
In this section, a few assumptions were considered to estimate the methane and electricity production potential from the available livestock manure. However, it has been well documented that the proportion of methane content in goat/sheep manure ranges between 40 and 50%, whereas it ranges between 50 and 70% for poultry [43]. Biogas production has been significantly dependent upon the amount of methane production. It has been found that approximately 50–70% of the methane content transforms into biogas [44]. For this study, the biogas generation through anaerobic digestion of manure for the specified livestock was assumed to be 60% of methane, while methane was considered to form 50% of the biogas content for poultry manure. The heating value of methane was calculated by considering a conversion efficiency of 85% in the boiler, and the calorific value of methane was considered as 36 MJ/m3. The annual electricity generation potential using biogas was determined by Equation (2):
where ebiogas = amount of electricity generated using biogas (kWh year−1), Ebiogas = total amount of energy in biogas which has not been converted, and η = efficiency of the power plant for conversion of biogas to electricity (~30%). The unconverted energy content of the biogas was determined by the following Equation (3):
where C.Vbiogas = caloric value of the biogas, ~6 kWh m−3 [45], and mbiogas = annual amount of biogas produced from the selected species of livestock.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Livestock Population and Potential of Biodigester Technology
The livestock growth rate was calculated, and influential parameters were evaluated accordingly. Table 2 shows the provincial livestock population record of Pakistan from 1960 to 2018. From Table 2, it is summarized that the total livestock population achieved the highest number of 362,111,000 in 2018. Poultry exhibited the largest share, i.e., 45.8%, followed by goats, cattle, buffaloes, sheep, asses, camels, horses, and mules, with shares of 20.6%, 12.7%, 10.8%, 8.4%, 1.3%, 0.25%, 0.1%, and 0.05%, respectively. Punjab ranked at the top with a livestock population share of 39.7% on the regional scale, and Balochistan had the lowest population share, i.e., 13.6%. The temporal increment in the livestock population (4.9 times from 1960) emphasizes the potential of biogas origination and, consequently, biodigester technology development in the country.

Table 2.
Livestock population in different provinces of Pakistan for the years 1960–2018 (×1000 heads) [36,37].
3.2. Suitability of Livestock Manure as a Potential Substrate for Biodigester Technology
The livestock manure potential of the country in 2018 increases approximately 2.6 times from 1960 due to accretion in the livestock population. The gradual increase in livestock manure indicates that waste management through anaerobic digestion could be a viable solution, which also assists in overcoming the prevailing energy crises of the country. Moreover, manure management through anaerobic digestion will also reduce the consumption of synthetic fertilizers and increase crop yields due to the utilization of organic fertilizer, resulting in revenue generation.
Table 3 shows the temporal increment in animal manure production from 1960 to 2018. Based on calculations, ~417.3 million tons (Mt) of animal manure was produced in 2018. At the regional level, Punjab manifested the highest livestock manure potential with a 51% share of the total manure in 2018, followed by Sindh, KPK, and Balochistan, with shares of 24.1%, 14.85%, and 10.04%, respectively, whereas among animals species, cattle showed the highest contribution of 40.21% to the total manure produced in 2018, followed by buffaloes, goats, sheep, asses, poultry, camels, horses, and mules, with shares of 34.08%, 13.02%, 5.34%, 4.19%, 1.44%, 1.20%, 0.3%, and 0.14%, respectively.

Table 3.
Animal manure production potential in Pakistan from 1960 to 2018 (Mt/year).
3.3. Potential of Biogas Production from the Utilization of Biodigester Technology
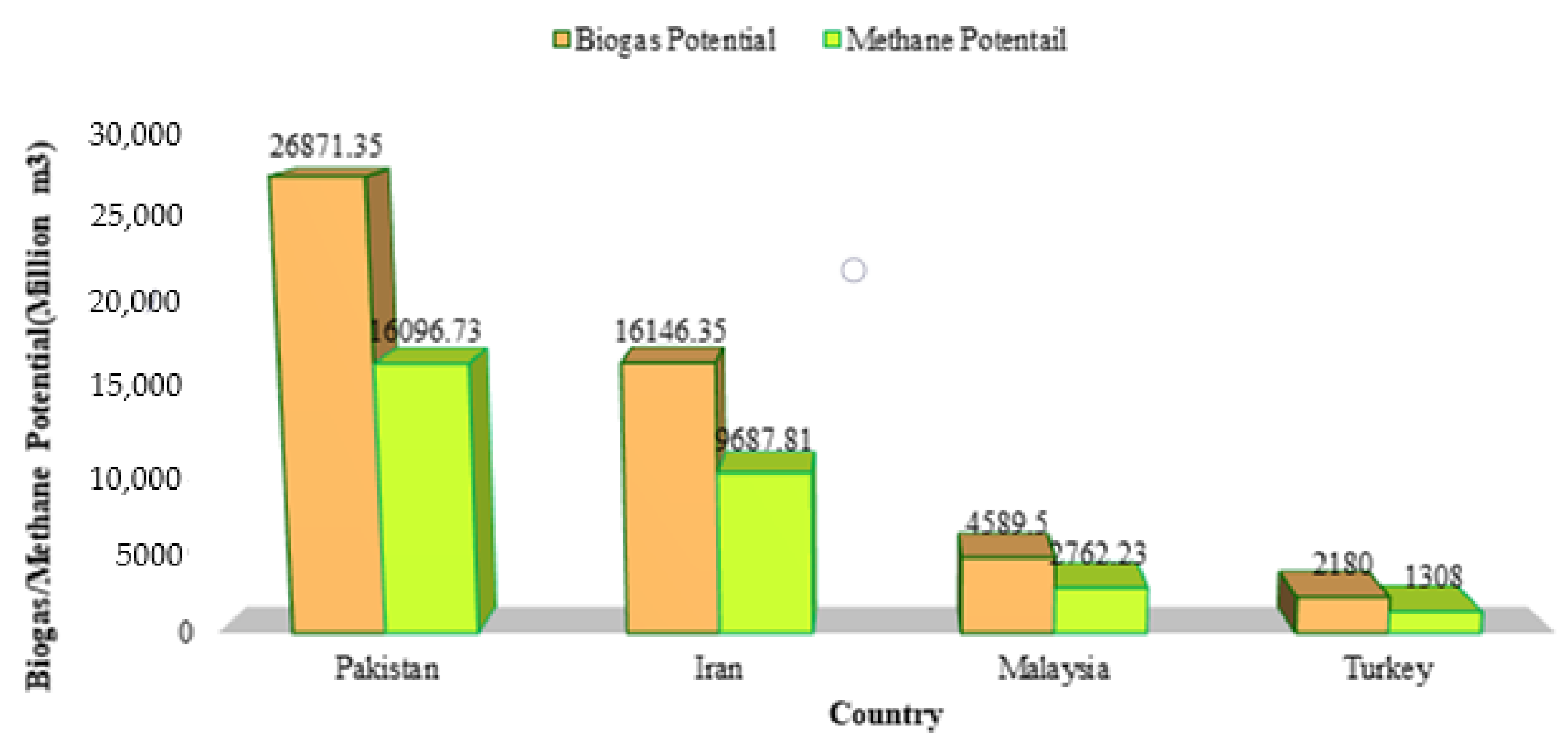
Table 4 shows the regional increase in biogas production from 1960 to 2018. It is found that 417.3 Mt of manure possesses the potential of producing 26,871.35 Mm3 of biogas. Due to the province having the highest population and manure production, Punjab is leading in biogas generation with a 53.92% share, followed by Sindh, KPK, and Balochistan, with 24.64%, 14.45%, and 6.97% shares in total biogas generation, respectively. Moreover, large animals such as cattle and buffaloes showed the highest biogas production potential with 46.83% and 39.70% shares of the total biogas generation, respectively. The other large animals such as camels, horses, asses, and mules revealed 1.41%, 0.35%, 4.89%, and 0.17% shares in the total biogas production, respectively. At the same time, smaller animals such as goats and sheep were found to have 4% and 1.64% shares, respectively. Similarly, poultry contributes 0.97%. In comparison to other agricultural countries, Pakistan leads in the biogas production potential (26,871.35 Mm3/year), followed by Iran (16,146.35 Mm3/year), Malaysia (4589.5 Mm3/year), and Turkey (2180 Mm3/year), as shown in Figure 2 [25,39,46,47,48].

Table 4.
Potential of biogas generation from livestock manure in Pakistan from 1960 to 2018 (Mt/year).
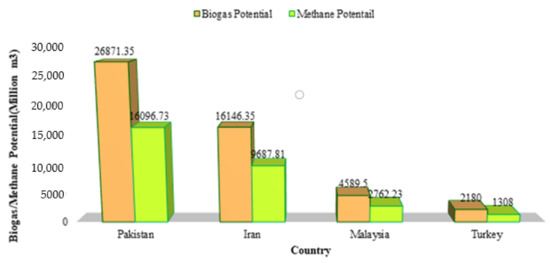
Figure 2.
Biogas and methane potential of Pakistan in comparison to Iran, Turkey, and Malaysia.
3.4. Potential of Methane Production from the Utilization of Biodigester Technology
The methane production potential using farm animal manure in Pakistan is shown in Table 5. The results proclaim that the total methane production potential in 2018 showed the highest amount of 16,096.73 Mm3. The methane production potential in 2018 was estimated to be 2.45, 2.35, 2.12, 1.41, 0.96, 0.45, 0.06, and 0.03 times higher than the methane production potential in 1960, 1972, 1976, 1986, 1996, 2006, 2016, and 2017, respectively. Punjab had the highest methane potential with a 53.95% share, while Sindh, KPK, and Balochistan had 24.65, 14.41, and 6.97% shares in the total methane production potential, respectively. In comparison, it was found from cited studies that the potential of methane generation from livestock manure in Iran, Canada, Malaysia, Turkey, and Indonesia was 5160, 2310, 2289, 1308, and 5758 Mm3 year−1, respectively [25,39,46,47,48].

Table 5.
Potential of methane generation from livestock manure in Pakistan from 1960 to 2018 (Mt/year).
The gradual increase in methane production from livestock manure will reduce the energy imports of the country, which are currently at 34%, and the government is spending about USD 1.27 billion annually on these imports.
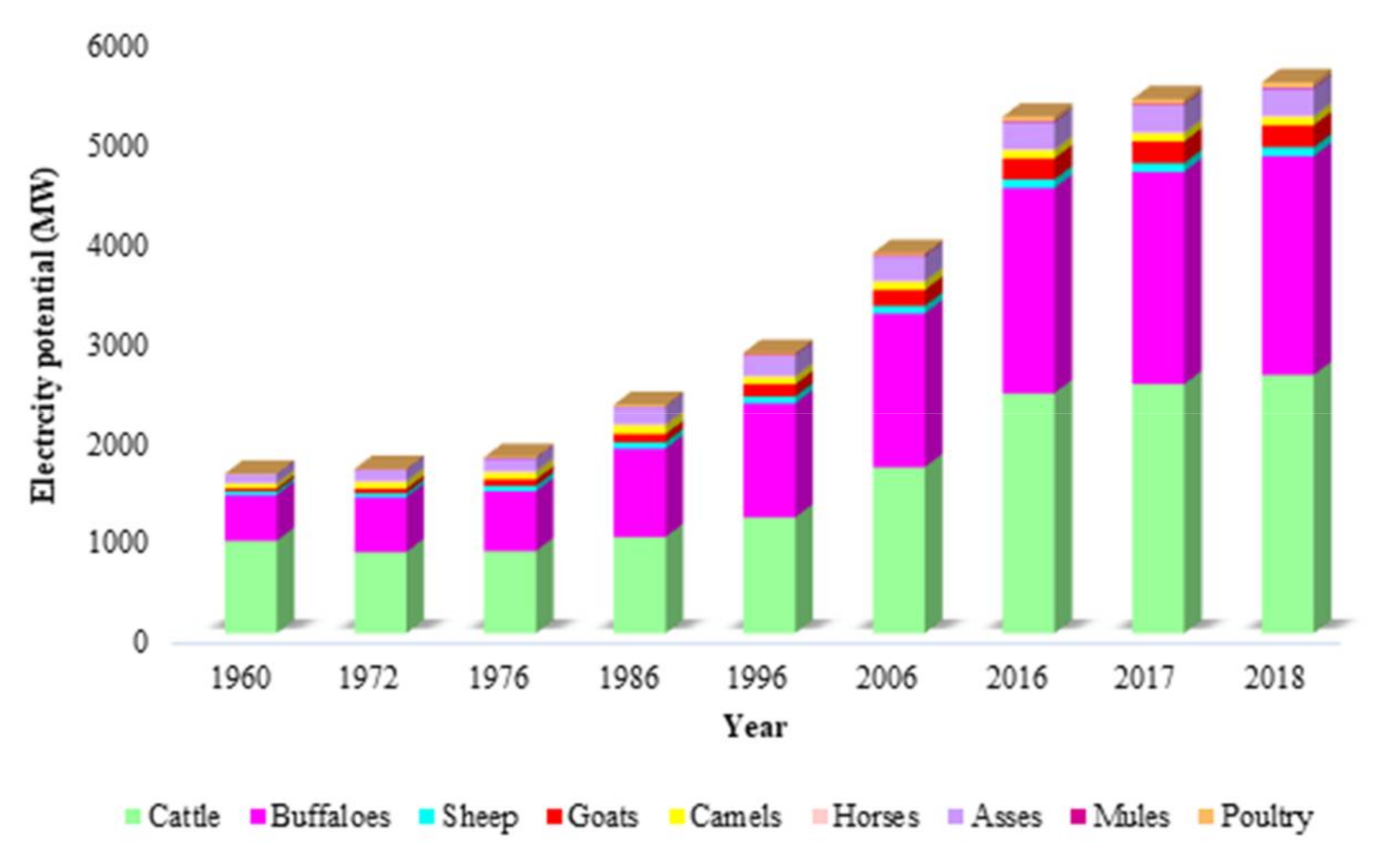
3.5. Potential of Heat Energy and Electricity Production from Biodigester Technology
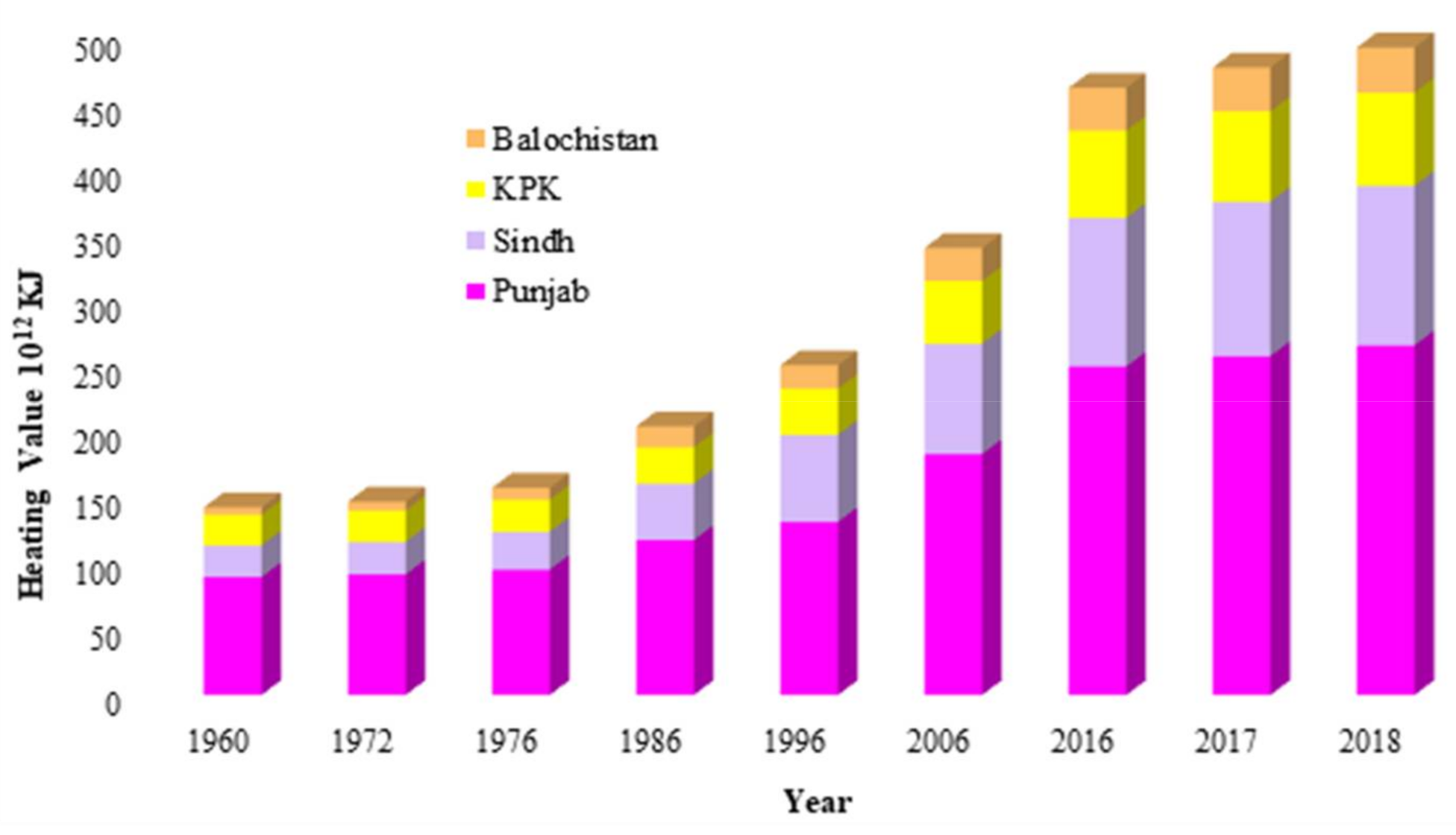
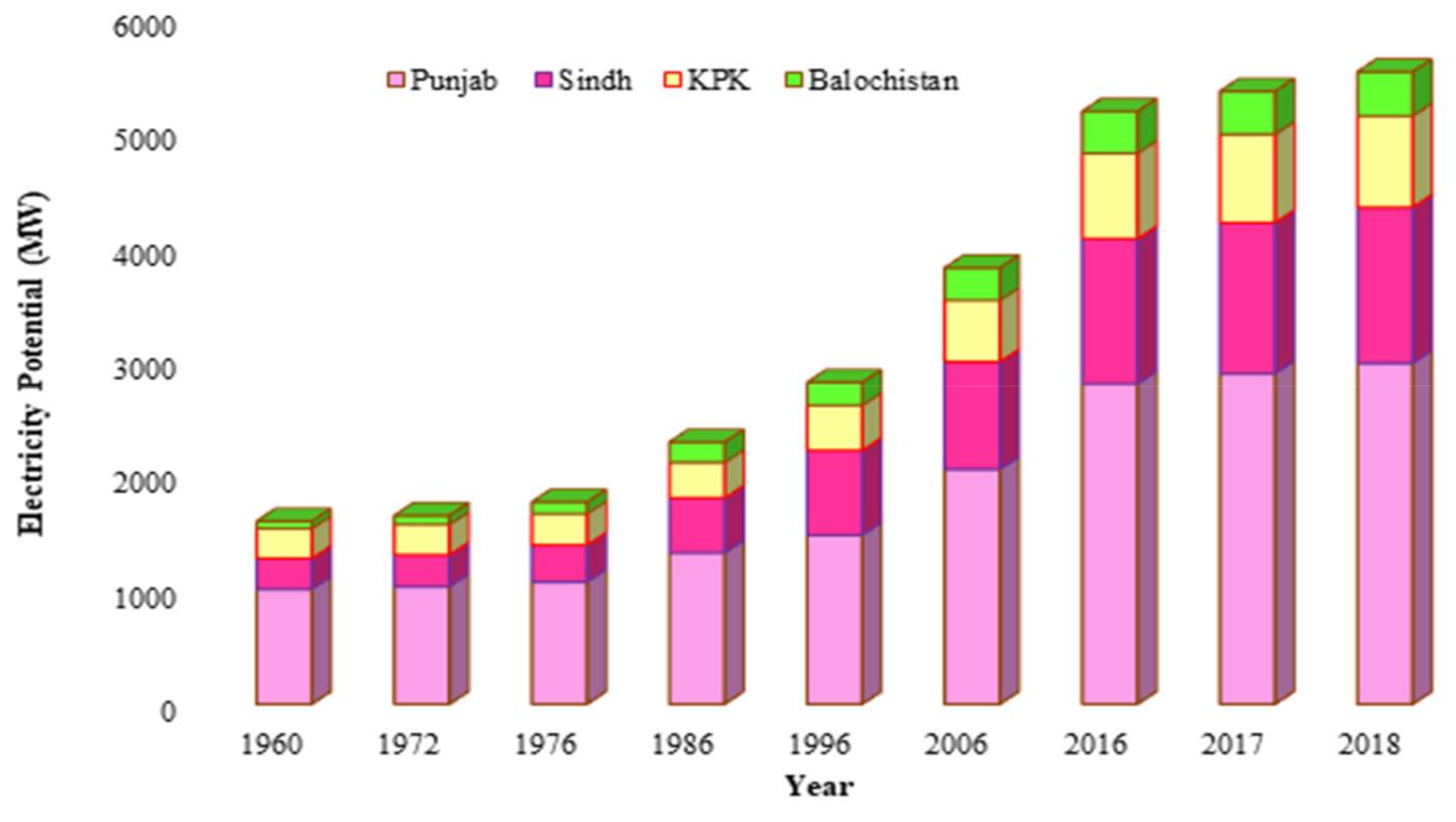
Figure 3 shows that the potential of heat energy acquired from the burning of methane in 2018 was 492.6 PJ. Compared to 1960, heat energy increased 245.46% in 2018 due to the higher livestock manure production, thereby exalting methane production. On the regional scale, Punjab yielded more heating energy (266 PJ/year), followed by Sindh (121.71 PJ/year), KPK (510.5 PJ/year), and Balochistan (34.4 PJ/year). Consequently, Pakistan is leading in heat energy production from methane as compared to Malaysia, Turkey, and Iran due to the high livestock population [25,39,46,47,48,49]. In addition, the potential of heat energy produced in Pakistan is higher than in Canada [25]. Similarly, the potential of electricity generation from biogas was computed and is showcased in Figure 4. The highest potential of electricity generation by manure-based biogas obtained was 5521.5 MW in 2018. This value accounts for ~22% of the country’s electricity requirement which is an indication of the considerable energy share from livestock waste. A similar study was conducted in Canada which showed that biogas electricity could fulfill ~22% of the country’s electricity demands using agricultural waste such as wood waste and municipal solid waste [25].
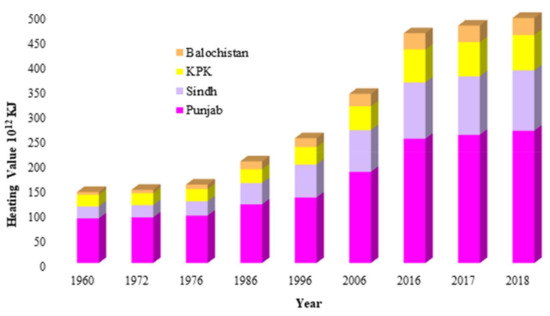
Figure 3.
Potential of heat energy obtained from the methane produced by livestock manure in different provinces of Pakistan.
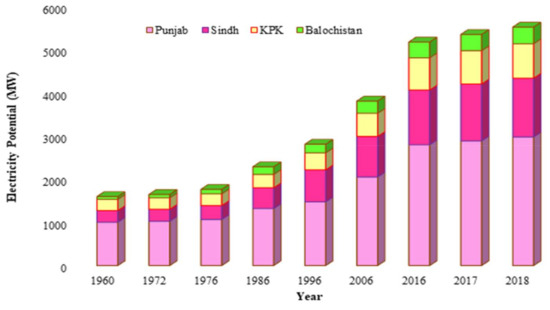
Figure 4.
Potential of electricity generation from manure-based biogas in different provinces of Pakistan.
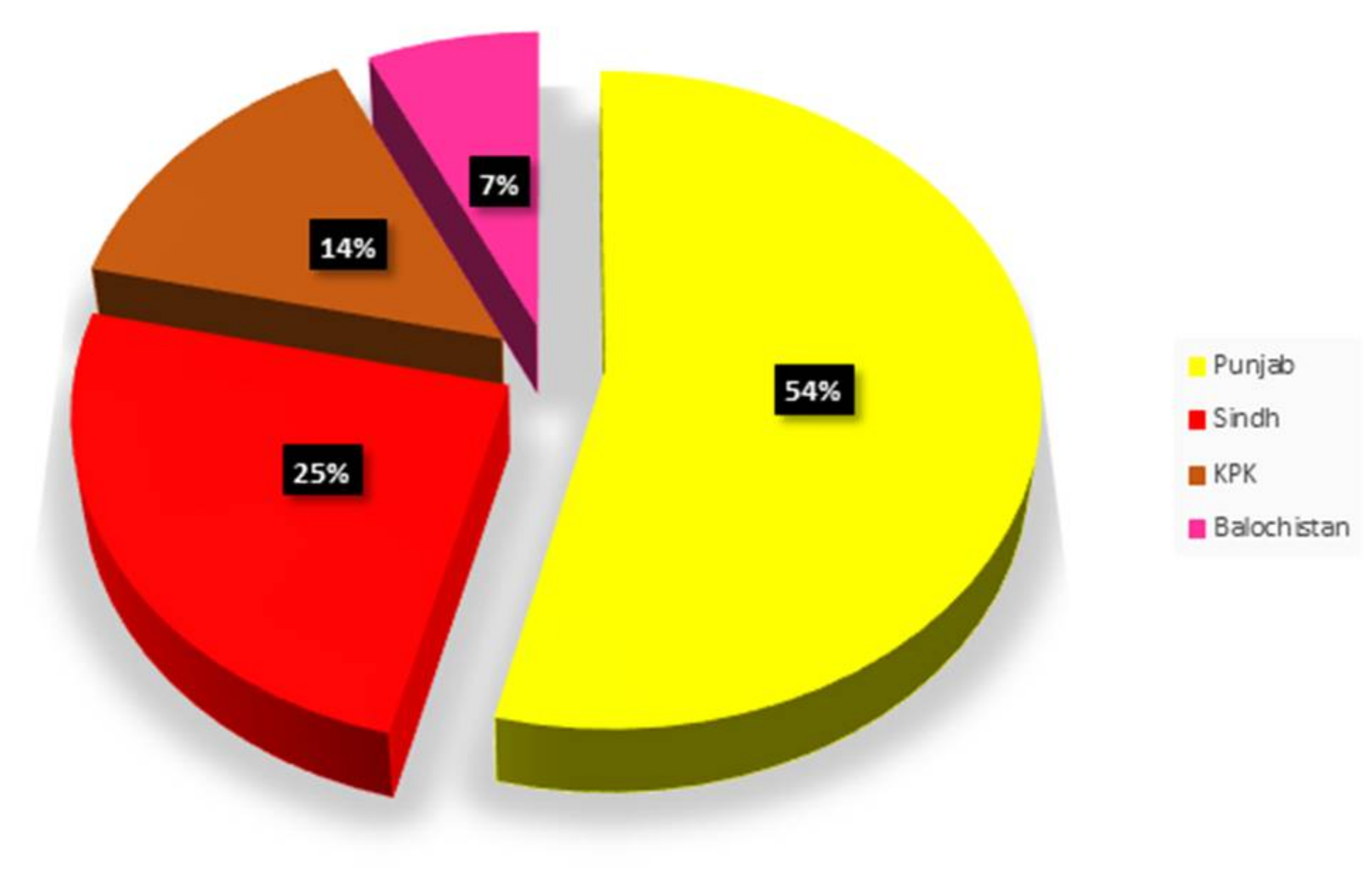
Punjab province had the highest electricity generation potential, with a value of 2977.3 MW, followed by Sindh, KPK, and Balochistan, with values of 1360.9, 798.0, and 385.1 MW, respectively. Furthermore, Punjab province had the highest electricity generation potential in 2018, contributing 54% of the total electricity generation, followed by Sindh, KPK, and Balochistan, with 25%, 14%, and 7% shares in electricity generation, respectively, as shown in Figure 5.
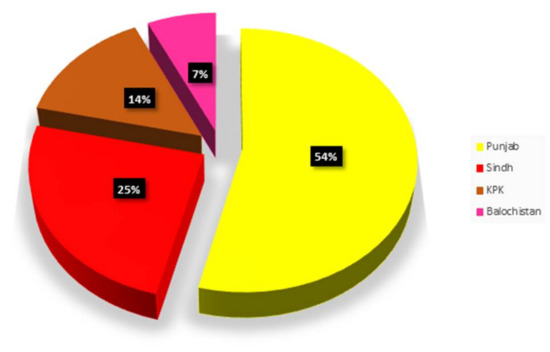
Figure 5.
Province-wise share of biogas-based electricity.
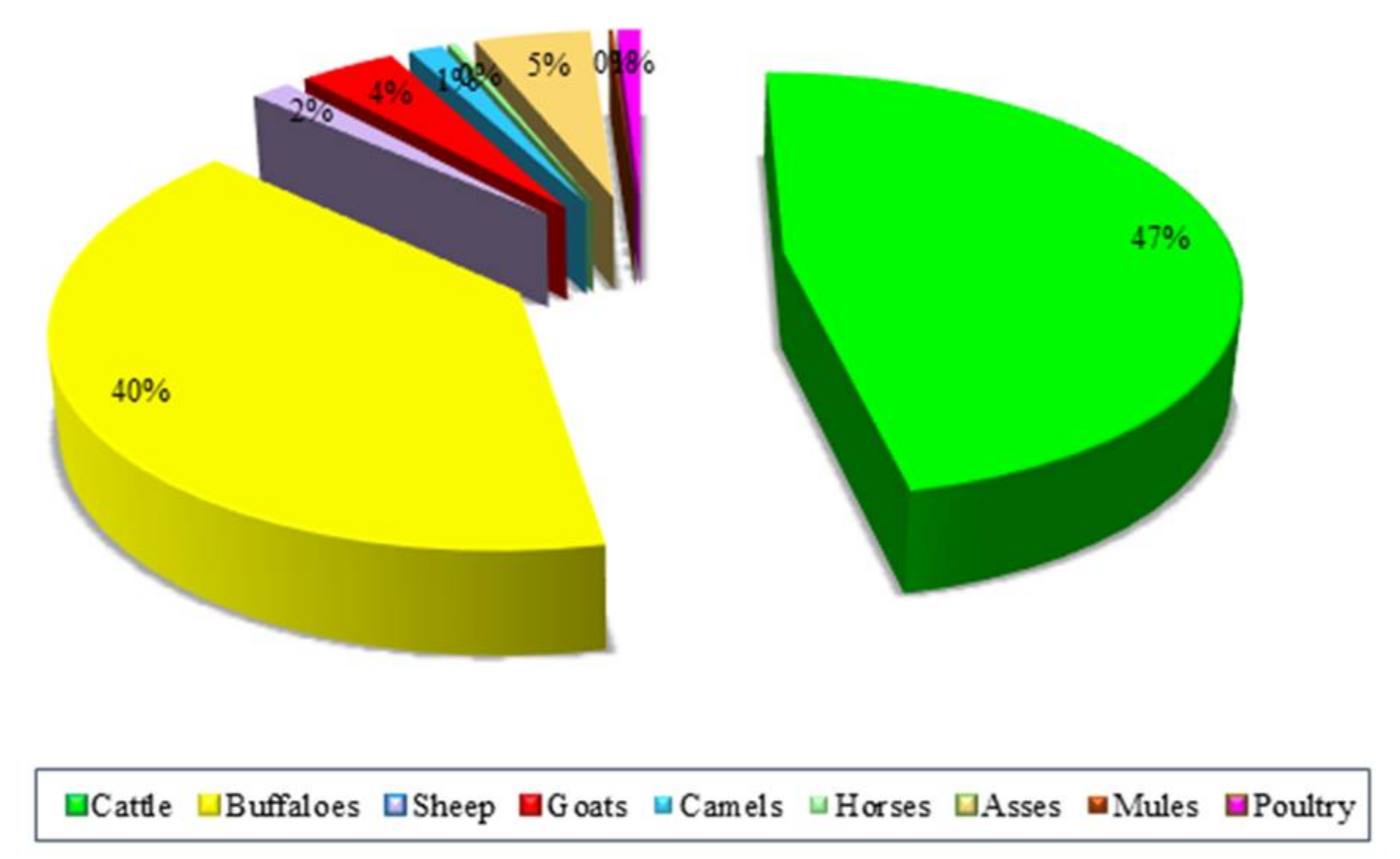
Figure 6 and Figure 7 illustrate the potential of electricity generation by manure-based biogas from different livestock animals. It is found that large ruminants, namely, cattle and buffaloes, had the highest potential for electricity generation, followed by asses and goats. The potential of electricity generated from cattle manure-based biogas had the maximum share, meaning that in 2018, it had a percentage value of 47%, followed by buffaloes, asses, goats, sheep, camels, poultry, horses, and mules, with percentage values of 40%, 5%, 4%, 2%, 1%, 1%, 0.35%, and 0.17%, respectively. It has previously been found that the potential of electricity generation by manure-based biogas in Malaysia, Turkey, and Iran could be 944 MW year−1, 448 MW year−1, and 3317 MW year−1, respectively [25,39,46,47,48].
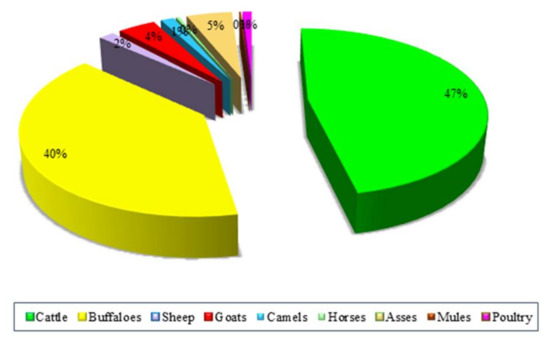
Figure 6.
Share of selected livestock species in biogas-based electricity.
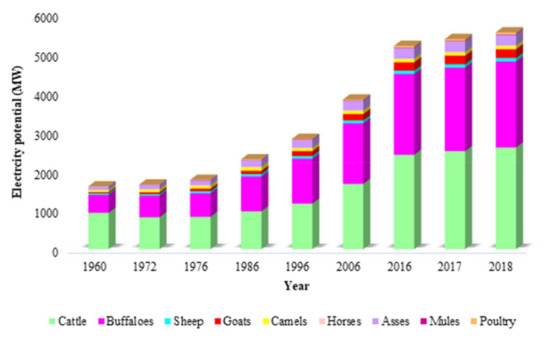
Figure 7.
Potential of electricity generation from manure-based biogas by different farm animals in Pakistan.
3.6. Feasibility and Suitability of Biodigester Technology in Pakistan
Studies conducted in many countries such as China [50], Malaysia [47], Turkey [39], Brazil [51], Serbia [52], Ecuador [42], Nepal [53], Indonesia [54], and Ethiopia [55] have indicated that biodigester technology is becoming popular because of its user-friendliness, cost-effectiveness, and robustness.
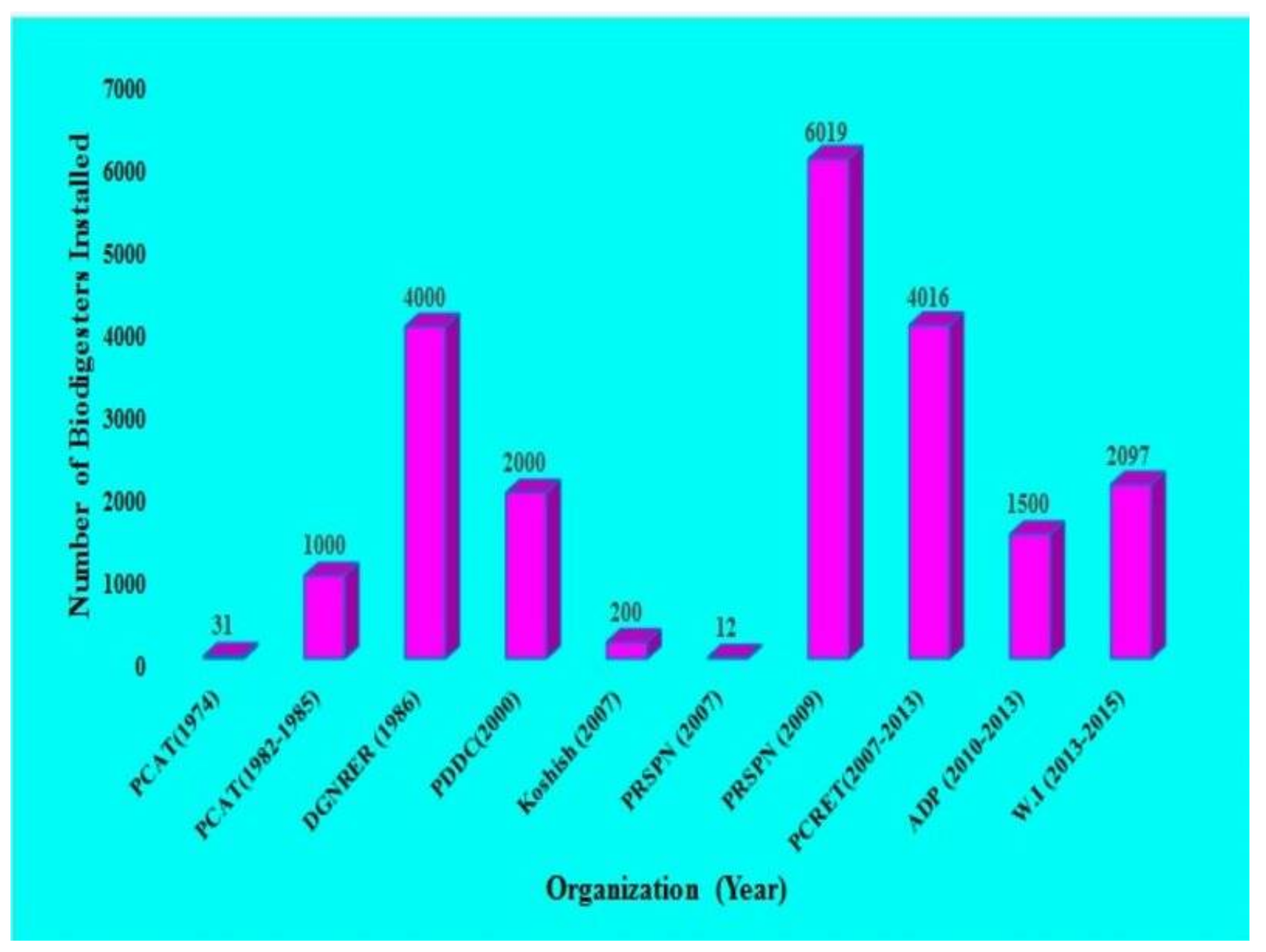
The prevailing energy crises of Pakistan can be eliminated by the appropriate development of biodigester technology. Biodigester technology in Pakistan has been considered over recent decades. In this regard, the first biogas plant was installed in Sindh in 1959 [19,56]. The government of Pakistan focused on the development of biodigester technology during the year 1974; the Pakistan Council for Appropriate Technology (PCAT) constructed 31 fixed dome digesters in different areas of Pakistan. Figure 8 depicts the biodigesters installed by different organizations in Pakistan during 1974–2015 [56].
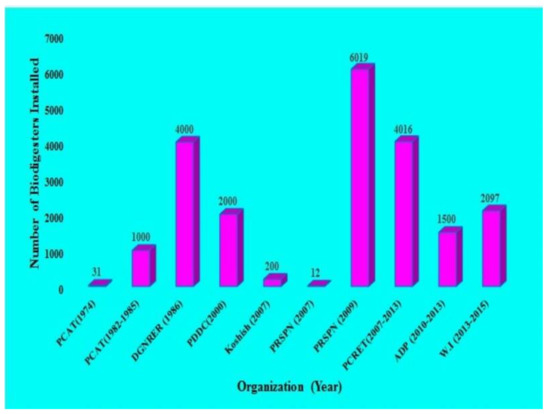
Figure 8.
The number of biodigesters that have already been installed by different organizations in Pakistan between 1974 and 2015.
According to Ghimire and Nepal, 2009 [56], many factors can drastically affect the potential of biodigesters, including technical factors, economic and financial factors, social factors, and institutional factors. Figure 9 shows all the main factors mentioned along with their classification. These inhibiting factors could be minimized if special attention is paid during the program implementation phase.
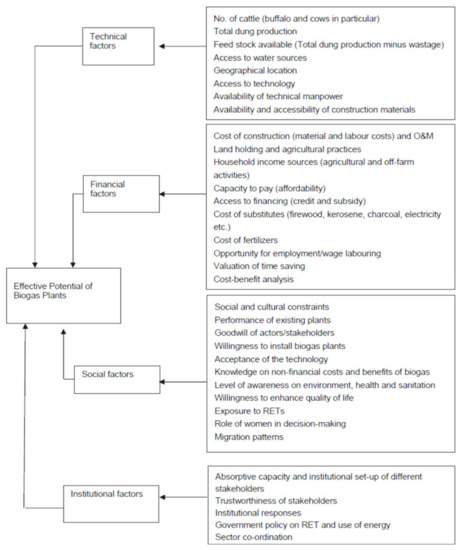
Figure 9.
Factors affecting biodigester technology development in Pakistan.
Most parts of Pakistan have favorable conditions for biodigesters. It is clear from the country’s livestock population that most of these animals are found in Punjab, Sindh, and KPK. It has been estimated that 10 million households are involved in raising livestock. In most parts of Punjab and Sindh, the temperature is favorable for the production of biogas. Construction materials and the labor force are easily available. Moreover, the land for installing biogas plants is not a problem for most farmers in Pakistan. However, about 30% of farmers in the country do not have favorable conditions for installing biodigesters due to the non-availability of land or harsh temperature conditions [56,57].
From Table 6, it is found that Pakistan has a capacity of 5 million biodigesters which can be easily installed in different farming areas. In this regard, the annual increase in the livestock population (as presented in Table 2) indicates a promising technology for biodigester development, especially in rural areas of Pakistan.

Table 6.
Potential for biogas plants in Pakistan [56].
4. Conclusions
This study accentuates the livestock manure production potential and its utilization in different areas of Pakistan. This study found that livestock manure is a sustainable bioresource for energy generation in Pakistan. The highest population of livestock in Pakistan is found in Punjab province, followed by Sindh, KPK, and Balochistan. Livestock is mainly managed in almost 10 million households. The total potential of animal manure in the country for 2018 was 417.3 Mt, and 26,871.35 million m3 of biogas, 492.6 PJ of heat energy, and 5521.5 MW of electricity could potentially be produced from animal manure in 2018 to reduce the ongoing energy crises in Pakistan. Moreover, there are ample opportunities to harness biodigester technologies in Pakistan because of the space available for installing 5 million biodigesters in different farming areas. Considering the huge potential of biodigester technology, the country has a high need for the development and implementation of national programs focusing on disseminating domestic biodigesters in Pakistan.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.U.K. and M.S.; data curation, M.U.K., M.A., and A.Z.; formal analysis, M.U.K., M.A., I.S., and P.C.G.; funding acquisition, M.S. and I.S.; investigation, P.C.G., A.Z., A.S., M.F., U.S., and M.Y.; methodology, M.U.K., M.A., M.S., I.S., A.Z., U.S., and P.A.; project administration, M.U.K. and M.S.; resources, M.U.K., P.C.G., M.F., U.S., and P.A.; software, M.U.K., M.A., A.S., M.F., and M.Y.; supervision, M.U.K. and M.S.; validation, M.U.K., M.A., M.S., I.S., and A.Z.; visualization, I.S., P.C.G., A.Z., A.S., P.A., and M.Y.; writing—original draft, M.U.K.; writing—review and editing, M.A., M.S., I.S., P.C.G., A.Z., A.S., M.F., U.S., P.A., and M.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Pakistan [No:21-1830/SRGP/R&D/HEC/2018]. Publishing fees were supported by the funding program *Open Access Publishing* of Hamburg University of Technology (TUHH), Hamburg, Germany. Moreover, the authors express their gratitude towards Washington State University, Peking University, China, and the University of Agriculture Faisalabad, Pakistan, for providing all opportunities to conduct this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Uddin, W.; Zeb, K.; Haider, A.; Khan, B.; Islam, S.U.; Ishfaq, M.; Khan, I.; Adil, M.; Kim, H.J. Current and future prospects of small hydro power in Pakistan: A survey. Energy Strat. Rev. 2019, 24, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, S.R.; Takala, J.; Shakeel, W. Renewable energy sources in power generation in Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, U.; Khan, B.; Ali, S.; Arshad, C.; Farid, U.; Zeb, K.; Rehman, F.; Mehmood, C.A.; Vaccaro, A. Pakistan geothermal renewable energy potential for electric power generation: A survey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 63, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessides, I.N. Chaos in power: Pakistan’s electricity crisis. Energy Policy 2013, 55, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, C.A.; Zhang, F. Electricity shortages and manufacturing productivity in Pakistan. Energy Policy 2019, 132, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, M.H.; Chauhdary, S.T.; Ishak, D.; Kaloi, G.S.; Nadeem, M.H.; Wattoo, W.A.; Younas, T.; Hamid, H.T. Hybrid energy sources status of Pakistan: An optimal technical proposal to solve the power crises issues. Energy Strat. Rev. 2019, 24, 132–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, N.; Ali, U. An analysis of the effects of residential uninterpretable power supply systems on Pakistan’s power sector. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2017, 36, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Iqbal, W.; Shaikh, G.M.; Iqbal, N.; Solangi, Y.A.; Fatima, A. Measuring Energy Efficiency and Environmental Performance: A Case of South Asia. Processes 2019, 7, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, W.; Soban, M.; Akhtar, F.; Zaffar, N.A. Smart meters for industrial energy conservation and efficiency optimization in Pakistan: Scope, technology and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.R.; Jamshaid, S.; Naqvi, M.R.; Farooq, W.; Niazi, M.B.; Aman, Z.; Zubair, M.; Ali, M.; Shahbaz, M.; Inayat, A.; et al. Potential of biomass for bioenergy in Pakistan based on present case and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Abbas, F. The dynamics of electricity demand in Pakistan: A panel cointegration analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 1159–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, K.; Bajwa, S.U.; Ansted, R.B.; Mamoon, D.; Rehman, K.-U. Evaluating human resource management capacity for effective implementation of advanced metering infrastructure by electricity distribution companies in Pakistan. Util. Policy 2016, 41, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, H.; Murtaza, A.F.; Addoweesh, K.E.; Chiaberge, M. Pakistan’s progress in solar PV based energy generation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasti, S. Economic Survey of Pakistan 2014–2015; Government of Pakistan: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, S.A.U.; Cai, Y.; Fazal, R.; Das Walasai, G.; Mirjat, N.H. An integrated modeling approach for forecasting long-term energy demand in Pakistan. Energies 2017, 10, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, U.; Jahanzaib, M.; Ahmad, W.; Hussain, S. An institutional framework for the development of sustainable and competitive power market in Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuberi, M.J.S.; Torkmahalleh, M.A.; Ali, S.H. A comparative study of biomass resources utilization for power generation and transportation in Pakistan. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 11154–11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M. Current status and future success of renewable energy in Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, W.; Khan, B.; Shaukat, N.; Majid, M.; Mujtaba, G.; Mehmood, C.A.; Ali, S.; Younas, U.; Anwar, M.; Almeshal, A.M. Biogas potential for electric power generation in Pakistan: A survey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahut, D.B.; Ali, A.; Mottaleb, K.A.; Aryal, J.P. Wealth, education and cooking-fuel choices among rural households in Pakistan. Energy Strat. Rev. 2019, 24, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.N.; Sukhera, O.R. Management of natural gas resources and search for alternative renewable energy resources: A case study of Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Özçatalbaş, O.; Bakhsh, K. Rural household preferences for cleaner energy sources in Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 22783–22793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, N.; Grundmann, P. Adoption and diffusion of renewable energy—The case of biogas as alternative fuel for cooking in Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 101, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Luqman, M.; Hassan, Z.Y.; Yaqoob, A. Determinants of Biogas Technology Adoption in Pakistan. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. Ser. A Phys. Sci. 2019, 62, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, D.B.; Zhu, H.; Beland, M.; Cicek, N.; Holbein, B.E. Potential for hydrogen and methane production from biomass residues in Canada. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, G.K.; Kim, S.H. Effects of chemical compositions and ensiling on the biogas productivity and degradation rates of agricultural and food processing by-products. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TR, Y.S.S.; Kohli, S.; Rana, V. Enhancement of biogas production from solid substrates using different techniques. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, K.; Zaidi, A.A.; Askari, S.J. Design and performance analysis of floating dome type portable biogas plant for domestic use in Pakistan. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2016, 14, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.; Ahring, B.K. Improving the biogas yield of manure: Effect of pretreatment on anaerobic digestion of the recalcitrant fraction of manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.; Ahring, B.K. Anaerobic Digestion of Digested Manure Fibers: Influence of Thermal and Alkaline Thermal Pretreatment on the Biogas Yield. BioEnergy Res. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Khan, M.U.; Dai, Y.; Tong, Y.W.; Ahring, B.K. Influence of wet oxidation pretreatment with hydrogen peroxide and addition of clarified manure on anaerobic digestion of oil palm empty fruit bunches. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.; Ahring, B.K. Anaerobic digestion of biorefinery lignin: Effect of different wet explosion pretreatment conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjid, S.S.; Bilal, M.Q.; Nazir, M.S.; Hussain, A. Biogas, renewable energy resource for Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2833–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.; Hassan, M.Y.; Shakoor, R. Bioenergy from anaerobic digestion in Pakistan: Potential, development and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, N.; Khan, B.; Khan, T.; Younis, M.N.; ul Faris, N.; Javed, A.; Iqbal, M.N. A comprehensive review of biogas sector for electric power generation in Pakistan. PSM Biol. Res. 2016, 1, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Pakistan Livestock Census. Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, Government of Pakistan. 2006. Available online: https://www.pbs.gov.pk/content/pakistan-livestock-census-2006 (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Livestock Census Report 2006, Ministry of National Food Security & Research, Ismamabad. 2006. Available online: https://phkh.nhsrc.pk/sites/default/files/2019-06/All%20Pakistan%20Report%20Livestock%20Census%2006.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2019).
- Ministry of Finance, Government of Pakistan. Pakistan Economic Survey 2016–2017. Available online: http://www.finance.gov.pk/survey_1617.html (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Avcioğlu, A.O.; Türker, U. Status and potential of biogas energy from animal wastes in Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedrenne, F.; Béline, F.; Dabert, P.; Bernet, N. The effect of incubation conditions on the laboratory measurement of the methane producing capacity of livestock wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, R.; El-Mashad, H.M.; Dong, R. Effect of feed to inoculum ratios on biogas yields of food and green wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5103–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, C.; Wilkie, A.C. Greenhouse gas emissions and biogas potential from livestock in Ecuador. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2010, 14, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, I.M.; Ghazi, T.I.M.; Omar, R.; Idris, A. Anaerobic digestion of cattle manure: Influence of inoculums concentration. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2013, 10, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Igliński, B.; Buczkowski, R.; Cichosz, M. Biogas production in Poland—Current state, potential and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimnejad, M.; Adhami, A.; Darvari, S.; Zirepour, A.; Oh, S.-E. Microbial fuel cell as new technology for bioelectricity generation: A review. Alex. Eng. J. 2015, 54, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghanaki, M.M.; Ghobadian, B.; Najafi, G.; Galogah, R.J. Potential of biogas production in Iran. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeshahian, P.; Lim, J.S.; Ho, W.S.; Hashim, H.; Lee, C.T. Potential of biogas production from farm animal waste in Malaysia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Berawi, M.A.; Heryanto, R.; Rizalie, A. Waste to energy technology: The potential of sustainable biogas production from animal waste in Indonesia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 105, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidmamatov, O.; Rudenko, I.; Baier, U.; Khodjaniyazov, E. Challenges and Solutions for Biogas Production from Agriculture Waste in the Aral Sea Basin. Processes 2021, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Li, Z.; Mang, H.-P.; Huba, E.-M. A review of prefabricated biogas digesters in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra-Araújo, C.H.; Mariane, L.; Júnior, C.B.; Frigo, E.P.; Frigo, M.S.; Araújo, I.R.C.; Alves, H.J. Brazilian case study for biogas energy: Production of electric power, heat and automotive energy in condominiums of agroenergy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkovic, S.; Radoičić, T.K.; Vukadinović, B.; Kijevčanin, M. Potentials and status of biogas as energy source in the Republic of Serbia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 31, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katuwal, H.; Bohara, A.K. Biogas: A promising renewable technology and its impact on rural households in Nepal. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2668–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, A.; Liu, Z.; Lund, M. The impact of biogas technology adoption for farm households—Empirical evidence from mixed crop and livestock farming systems in Indonesia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, M.; Simane, B.; Eshete, G.; Workneh, T. A review on biogas technology and its contributions to sustainable rural livelihood in Ethiopia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 48, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, P.C. Final Report on Technical Study of Biogas Plants Installed in Pakistan; Prepared by: Asia/Africa Biogas Programme, Netherlands Development Organisation (SNV). 2007, pp. 1–74. Available online: https://bibalex.org/baifa/Attachment/Documents/172360.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Farooq, M.K.; Kumar, S. An assessment of renewable energy potential for electricity generation in Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 20, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).