Abstract
Phytosociological research on aquatic and marsh vegetation was conducted in Rzeszów Reservoir (SE Poland): 134 relevés according to the Braun-Blanquet method were collected there in 2016 and compared to 91 relevés published in 1994 (225 relevés in total). Changes in vegetation type, diversity measures, species composition, and Ellenberg Indicator Values (EIVs) for light, moisture, reaction, and nitrogen were analysed. Over the 22 years (1994–2016), the greatest changes were noted in communities of the classes Lemnetea and Potametea and the alliance Salicion albae. The long-term observations demonstrated the disappearance of 14 phytocoenoses and the occurrence of 12 new ones. An expansion of marsh communities (Typhetum latifoliae, Typhetum angustifoliae, Glycerietum maximae, Leersietum oryzoidis) was noted, causing a decline of several species and vegetation types. According to canonical correspondence analysis (CCA), four environmental variables (light, moisture, nitrogen, and pH) were related to plant distribution. The strong disturbances reflected in intensive eutrophication were due to human activity, which is the main factor shaping the ecological succession and overgrowing of the reservoir.
1. Introduction
Reservoirs, as artificial water bodies, play an important role in the human economy and at the same time they are extremely valuable components of the natural environment, they have mostly been built by the damming of rivers [1,2]. They have changed the original river habitat considerably, not corresponding to flowing waters but more resembling natural lakes. These altered habitat conditions are reflected by the vegetation communities. Reservoirs may be of particular interest as they provide various ecosystem services, such as a supply of drinking water, industrial water supplies, power generation, flood control, water retention, and recreation, while contributing to the improvement of landscape aesthetics and increasing habitat diversity [3,4,5]. Water and marsh ecosystems are of particular importance in the urban landscape. They are a habitat for many plant species, including protected and rare ones, and maintaining a diverse landscape is important for improving local biodiversity [6]. Changes that occur as a result of human activity in aquatic ecosystems contribute to the degradation of these areas, and as a result, the withdrawal of species with narrow ecological requirements and the impoverishment of the flora.
In recent years, the importance of the aquatic ecosystem has been emphasized in the context of the relationship between plant-associated and communities of microbes (the phytomicrobiome). The plant microbiome plays multiple roles, can stimulate plants growth by helping them with the necessary nutrients, enhance the resistance of the plant to stress, as well as be used for bioremediation, help to clean water reservoirs from nutrient contamination. Using microorganisms from the environment supports sustainable development [7,8].
Like all water ecosystems, reservoirs are polluted with municipal wastewater, discharged directly or indirectly (from the catchment area). Besides, reservoirs are affected by the non-point source of pollution resulting from agriculture [9,10]. Rzeszów Reservoirs come under intensive human impacts, which degrade their water quality [11,12,13]. Eutrophication of water by nitrogen and phosphorus compounds is known to cause changes in the plant community composition, where macrophytes may eventually be replaced by green macroalgae or phytoplankton as a consequence of light deficiency [14,15].
Urbanization is one of the most important causes of degradation of natural habitats and it simplifies species composition of aquatic plants and disrupts hydrological systems [16,17]. The intensity and types of human impact, as well as accumulation of alluvial deposits carried by the current, affect the rate and range of transformation of aquatic and marsh vegetation. This is closely linked with the decline and appearance of new communities [18], and also with changes in the diversity of plant communities [14,19,20,21]. Vegetation dynamics in aquatic ecosystems could be fast and intense, especially in river ecosystems, because they are naturally disturbed ecosystems, and available sites are continuously created and destroyed by flow alterations, invasive species, and recreational use. Transformations usually concern the littoral zone–areas with great contrasts and heterogeneous environment (e.g., temperature, physical forces, disturbance regimes) [22,23]. Reservoirs have asymmetrical basins: they are the deeper at the dam, and shallow at the inflow. Their hydrological regime is intermediate between rivers and lakes, which causes instability and the disturbance of ecosystems occurring there [24]. The small depth and large area make the reservoirs particular habitats, where abiotic factors determine the functioning of the ecosystem, and in which homeostatic processes are poorly developed, given their artificiality [25,26].
The relationships between different environmental factors and the distribution of aquatic vegetation have been discussed in numerous publications [27,28,29]. Thus, aquatic macrophytes and communities have frequently been used in vegetation ecology as reliable indicators of habitat conditions in waters, as they seem to be directly correlated with specific environmental conditions and can reflect changes in trophic status [30,31,32]. Aquatic macrophytes are one of the biological quality elements for monitoring the ecological status of surface waters in view of the provisions of the EU Water Framework Directive 2000/60/CE. Therefore, they are widely used for environmental monitoring and water quality assessment throughout Europe [33,34]. Moreover, multitemporal analyses of aquatic vegetation could be an instrument to assess the direction of environmental changes, both over a short period [35] or over a long period [21].
Phytosociological studies are extremely useful as they make it possible to determine the current state and diversity of the vegetation cover and recognise the degree of naturalness and dynamism of communities in a given ecosystem. On their basis it is possible to draw conclusions about changes taking place in entire ecosystems, to follow the pace and directions of changes in flora and vegetation, which makes it possible to identify potential threats to the ecosystem and take protective measures.
The aim of this study was to analyse the transformation of the vegetation in Rzeszów Reservoir during the last 22 years (1994–2016) in case of changes, to explain the possible drivers of change.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Rzeszów Reservoir is located in south-eastern Poland (50°02′ N, 21°59′ E) at the boundary of two large geographical regions, the Carpathian Mountains and their foothills [36] with a temperate continental bioclimate [37]. In 1994 and 2016, the annual mean air temperature was 9.1/9.5 °C and precipitation reached 693/720 mm, respectively, the long-term mean annual air temperature in 1994–2016 was 8.8 °C (min. 6.9 °C, max. 10.2 °C). The observation of temperature changes over a more than 150-years period (1851–2010) indicates an increase in mean annual air temperature reaching 1.5 °C. Average annual precipitation is 680 mm (min. 471 mm–max. 981 mm) [36,38].
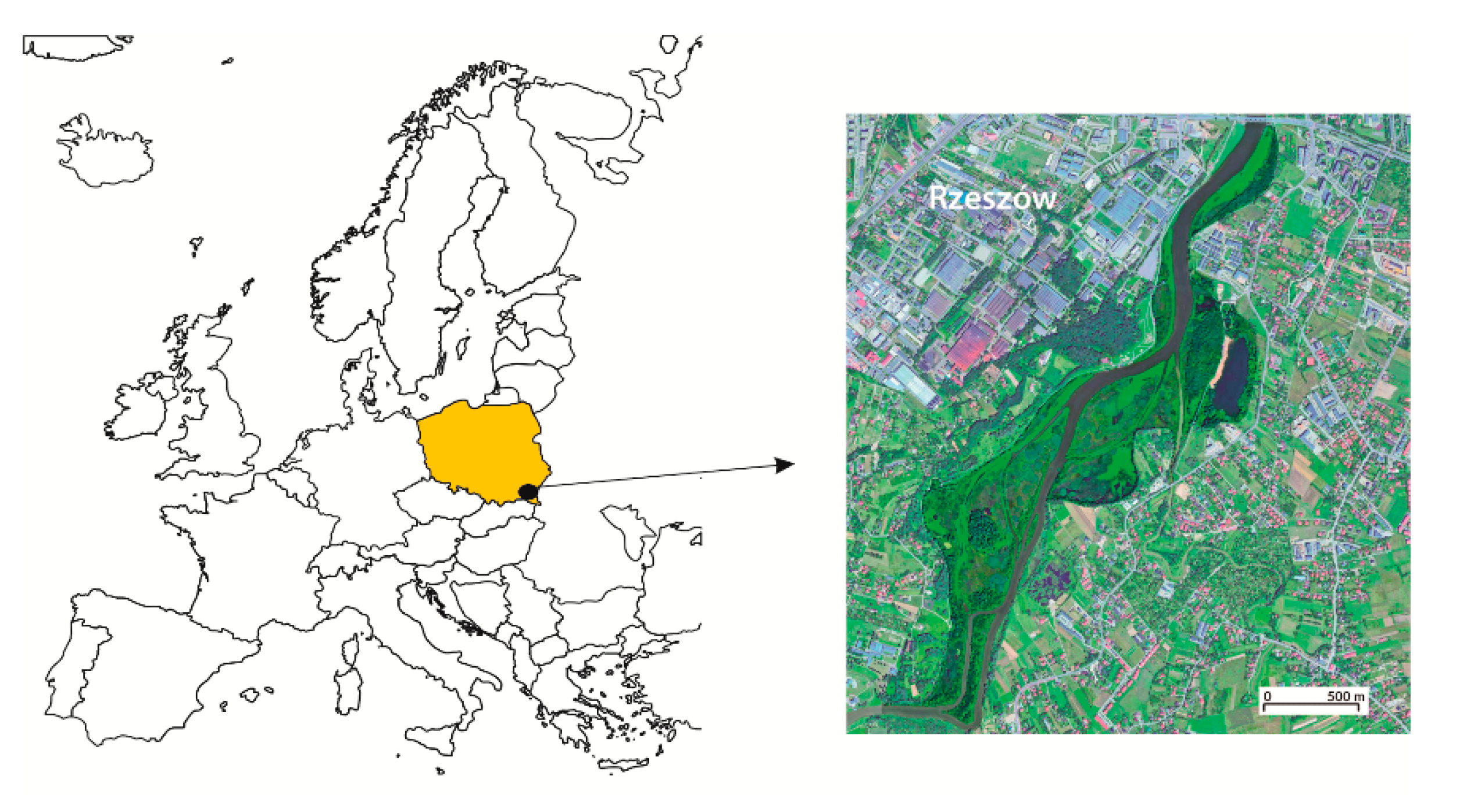
It is part of the protected Natura 2000 area with code PLH 180030 (Figure 1). The reservoir was established in 1973 by building a dam on the 64th km of the Wisłok River. It was set up to protect the functioning of industry and to serve as a municipal drinking water intake and a reservoir for recreation and sport purposes. Originally, it covered an area of 68 ha and had a volume of 1.8 mln m3. Over the last 20 years, however, the reservoir was greatly transformed. As a result of intensive sedimentation of the materials carried by the Wisłok River and its tributary, the Strug River, the surface area of the reservoir was reduced, its volume decreased to ca. 0.5 mln m3, and the average depth declined from 1.5 to 0.5 m, so that large parts of the water body are much shallower now [39].
Figure 1.
Location of the study area (source: Google Earth 2018).
2.2. Data Collection
The phytosociological relevés used for the study come from two periods: (i) 1994—the first description of 91 relevés by Kwiatkowska [40]; and (ii) 2016-134 relevés collected by our research team. The geographic position of our relevés was recorded with a differential GPS. Historical and recent relevés were made in aquatic and bank vegetation as well as plant communities directly adjacent to the reservoir, using the standard Braun-Blanquet method [41], during the period of maximum vegetation development (June–August). The names of vascular species follow Mirek et al. [42], and the names of liverworts follow Szweykowski [43]. Taxa were classified into vegetation units according to Matuszkiewicz [44].
2.3. Data Analysis
To identify the general pattern of variation in species composition within the entire data set an indirect ordination method (detrended correspondence analysis, DCA) was used. The species data show a clear unimodal response (length gradient > 3), enabling us to use canonical correspondence analysis (CCA). The significance of the environmental variables was calculated using a Monte Carlo test (499 permutations) and only predictors with p < 0.05 were included in the CCA model. CANOCO for Windows 5.0 software was used for the ordination [45].
The ecological indicator values (EIVs) were calculated for all the species recognized in each relevés, using Ellenberg et al. system [46] adopted for Polish conditions by Zarzycki et al. [47]. We took into account 4 environmental variables related to ecological indicator values describing the most typical habitat conditions–light (L), moisture (F), reaction pH (R), and nitrogen (N). The share of species with a specific indicator value in each relevés was determined using a modified formula for the weighted average (1):
where: WA—weighted average, Ai—abundance of cover of the i-th species in relevé, Ii—ecological indicator value for the i-th species, n—number of species in relevé.
The non-parametric Mann-Whitney test was applied to analyse the differences between the old and new relevés in EIV, the number of species, and the coverage of vegetation layers. The synoptic table was made for both periods, with the number of species and cover index, calculated as a total of the mean percentages of coverage of species in all relevés, divided by the total number of relevés and multiplied by 100. The value of the cover index gives a good estimation of the role of species in the communities.
The flora of the relevés was also compared based on a few other indices, focusing on (i) species richness (S = number of species); (ii) species diversity measured as the Shannon index (2):
where pi = frequency of species i; (iii) species evenness measured as the Pielou index: J’ = H’/lnS, defined as a ratio of the observed diversity to the maximum diversity, where S = number of species and Hmax = lnS [48,49]. The multivariate statistical package (MVSP 3.1) was used for these analyses [50]. The mean values of indices and SD (standard deviation) were computed, and the values obtained were compared. The original Braun-Blanquet [41] scale for species occurrence in phytosociological relevés was transformed as follows: r = 0.1%; + = 0.5%; 1 = 5%; 2 = 17.5%; 3 = 37.5%; 4 = 62.5%; and 5 = 87.5% [51]. The level of statistical significance of differences between the means for all the analyses was p = 0.05. Statistical tests were performed with STATISTICA 10.0 software [52].
H’ = −Σpi lognpi,
In order to investigate the differences in macrophyte species composition, an Indicator Species Analysis (ISA) [53] was performed on the species per species matrix, after removing rare species, that is, low-frequency species that appeared in only one relevé. For each species i in each site group j, the relative abundance RAij and the relative frequency RFij, are computer as follows (3):
where Aij = the mean abundance of species i across sites of the group j, Ai = the sum of the mean abundance of species i over all groups. RFij = Sij/Sj, where Sij = the number of sites in group j where species i is present, Sj = the total number of sites in that group. Then the Indicator Value (IV) of species i in the group j are: IVij = RAij × RFij × 100. Indicator Values range from 0 (no indication) to 100 (perfect indication). The ISA values were tested for significance using a Monte Carlo test (4999 permutations, α = 0.05). The ISA was performed using the PC-ORD software [54].
RAij = Aij/Ai,
3. Results
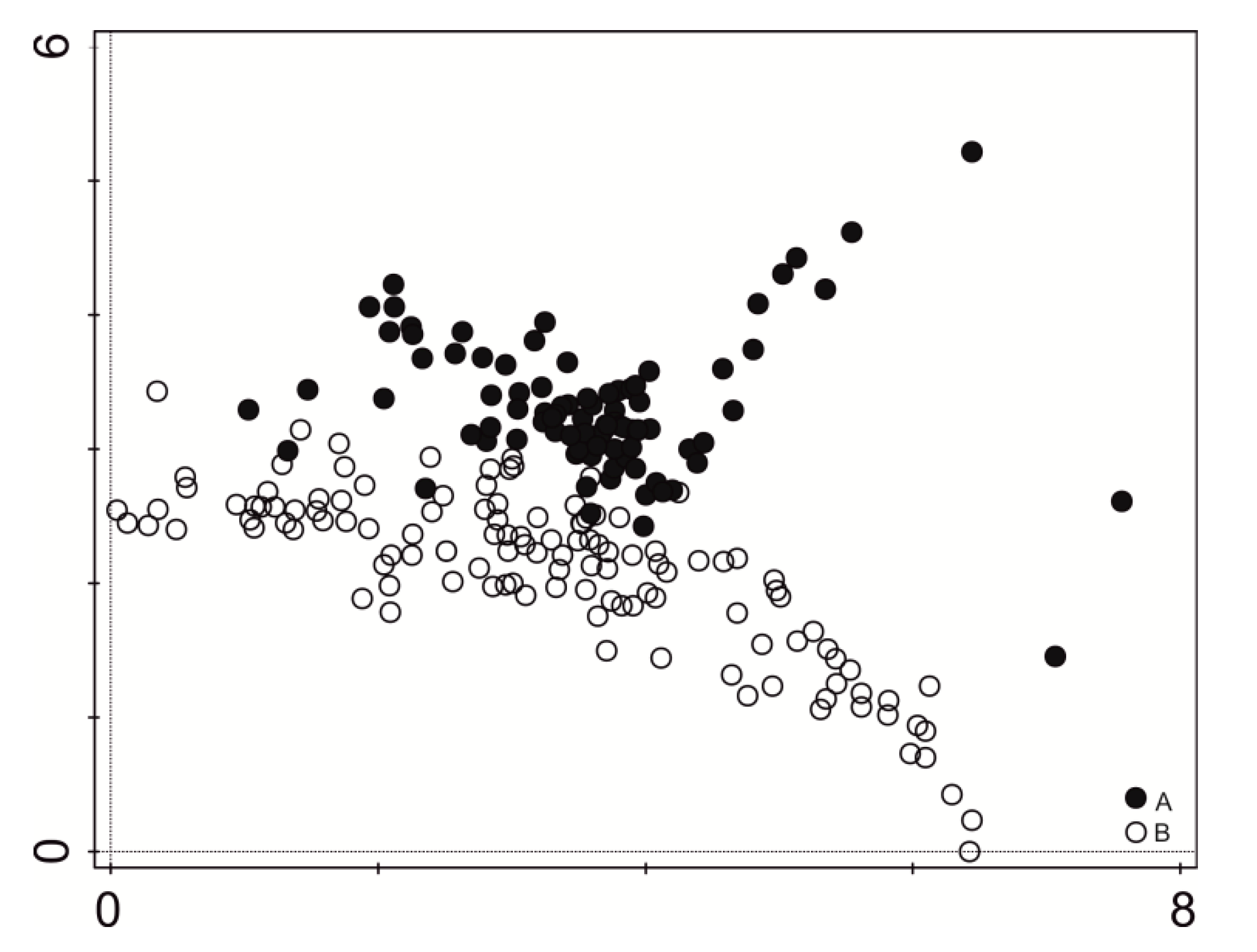
The vegetation units represented four major ecological groups: aquatic vegetation (Lemnetea and Potametea classes), marsh plants (Phragmitetea class), meadow plants (Molinio-Arrhenatheretea class), and shrubs (Salicetea purpurea, Alnetea glutinosae classes). Results of the vegetation composition analysis show that the studied communities have changed. The DCA diagram clearly distinguishes two major specifically concentrated sets of data (Figure 2).
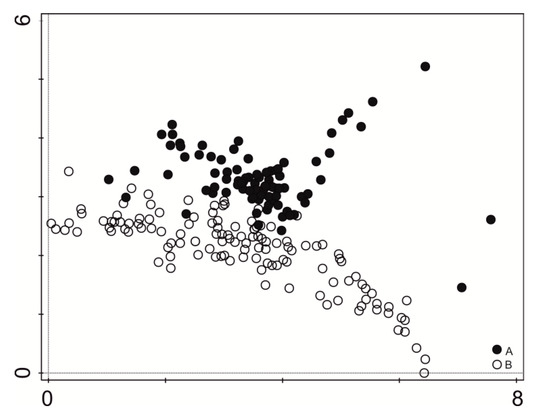
Figure 2.
Indirect ordination analyses (DCA) of all relevés. A—indicates relevés made in 1994, B—indicates relevés made in 2016.
In 1994, 23 types of plant communities comprising 125 species were distinguished [40], while now there are 21 phytocoenoses with 107 species. Overall, there were eight common plant communities in both study periods (Table 1). However, no differences in mean species diversity were noted (H’ = 1.4–3.28, mean 2.01 in 1994, and H’ = 0.68–2.21, mean 2.03 in 2016). Only the value of species evenness increased slightly, from 0.954 to 0.972 (Table 2).

Table 1.
Syntaxonomic composition of communities in the Rzeszów Reservoir of each period studied.

Table 2.
Mean values of particular indexes during period 1994–2016; ns—statistically not significant; U—statistic value, p—probability (Mann-Whitney test).
High variability was noted in communities of the classes Lemnetea and Potametea and of the alliance Salicion albae. Among permanent components of vegetation, there was a growing tendency in the vegetation surface area in the class Phragmitetea (Figure 3). The observations demonstrated disappearance of 14 phytocoenoses, e.g., Lemnetum gibbae, community with Potamogeton crispus, Potametum pectinati, Ranunculetum circinati, Elodeetum canadensis, Myriophylletum verticilati, and Oenantho-Rorippetum, and appearance of 12 new to this study area and yet undescribed communities, with special emphasis on the association Trapetum natantis (the largest local population of this species in south-eastern Poland), which occupies a significant area of the reservoir (Table 1).

Figure 3.
Vegetation succession in the Rzeszów Reservoir ((a,b) A—1994, (c,d) B—2016).
In 1994, only 11 species exceeded 20% of frequency in the relevés. The most abundant were: Phalaris arundinacea L. (75 records), Lemna minor L. (73), Rorippa amphibia (L.) Besser (62), Typha latifolia L. (58), Alisma plantago-aquatica L. (51), Bidens tripartita L. (31), Salix viminalis L. (24), S. purpurea L. (24), Lycopus europaeus L. (24), Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleid. (23), and Lythrum salicaria L. (23). After 22 years, 15 species reached a high frequency (>20%): Typha latifolia (77 records), Glyceria maxima (Hartm.) Holmb. (74), Lemna minor (61), Berula erecta (Huds.) Coville (55), Spirodela polyrhiza (54), Phalaris arundinacea (52), Hydrocharis morsus-ranae L. (47), Mentha aquatica L. (42), Lycopus europaeus (41), Lythrum salicaria (38), Lemna trisulca L. (38), Trapa natans L. s. l. (37), Rumex hydrolapathum Huds. (35), Ceratophyllum demersum L. s. str. (34), and Poa palustris L. (32).
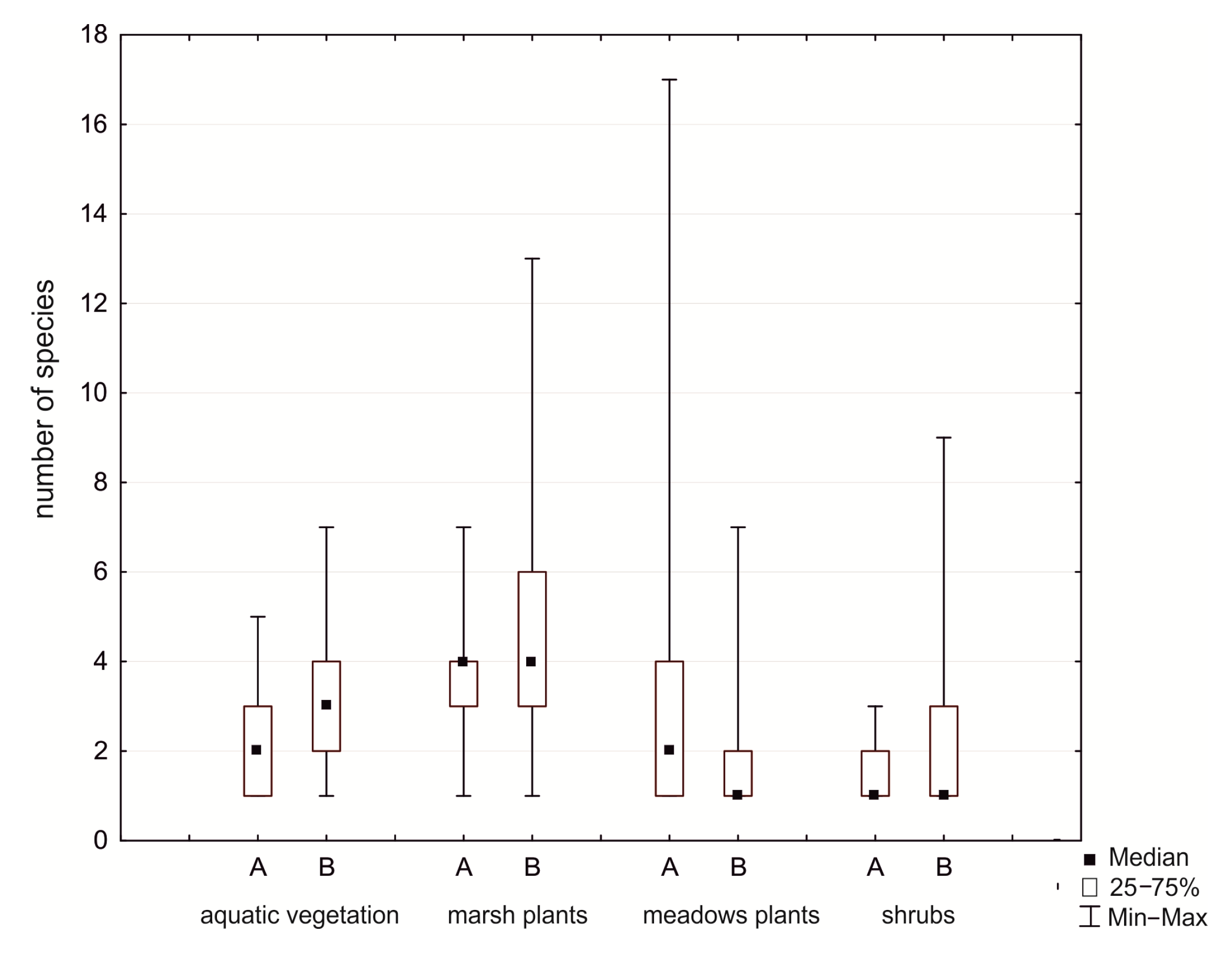
In spite of significant changes in the composition of aquatic communities (Lemnetea and Potametea classes), the number of species in plant communities remains similar, but the cover index decreased 74% and 68%, respectively. We observed an increase in the number of species from marsh communities (Phragmitetea class), and the cover index increased by 8%. In the Molinio-Arrhenatheretea class, the number of species and cover index decreased by 23%. Marsh communities in 2016 were the major components of vegetation in the study area, and the largest surfaces were covered by Typhetum latifoliae, Typhetum angustifoliae, Glycerietum maximae, and Leersietum oryzoidis. At the edges of the reservoir, contributions of species of the classes Artemisietea, Salicetea purpurea, and Alnetea glutinosa substantially increased, while the cover index of aquatic plants was lower than in 1994 (Table 3, Figure 4).

Table 3.
Comparison of changes of diagnostics species and cover index from 1994 to 2016.
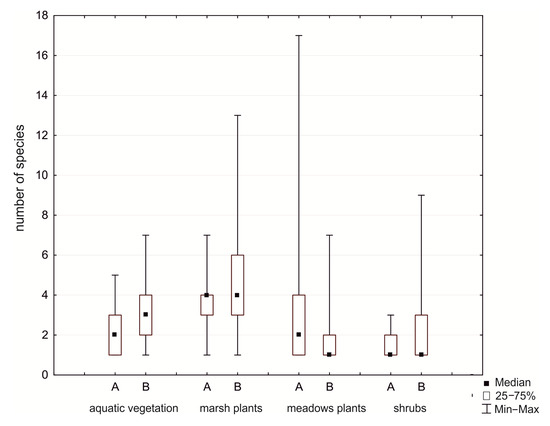
Figure 4.
Number of species on different ecological groups in the Rzeszów Reservoir (A—1994, B—2016). Explanation: aquatic vegetation (Lemnetea and Potametea classes), marsh plants (Phragmitetea class), meadow plants (Molinio-Arrhenatheretea class), and shrubs (Salicetea purpurea and Alnetea glutinosae classes).
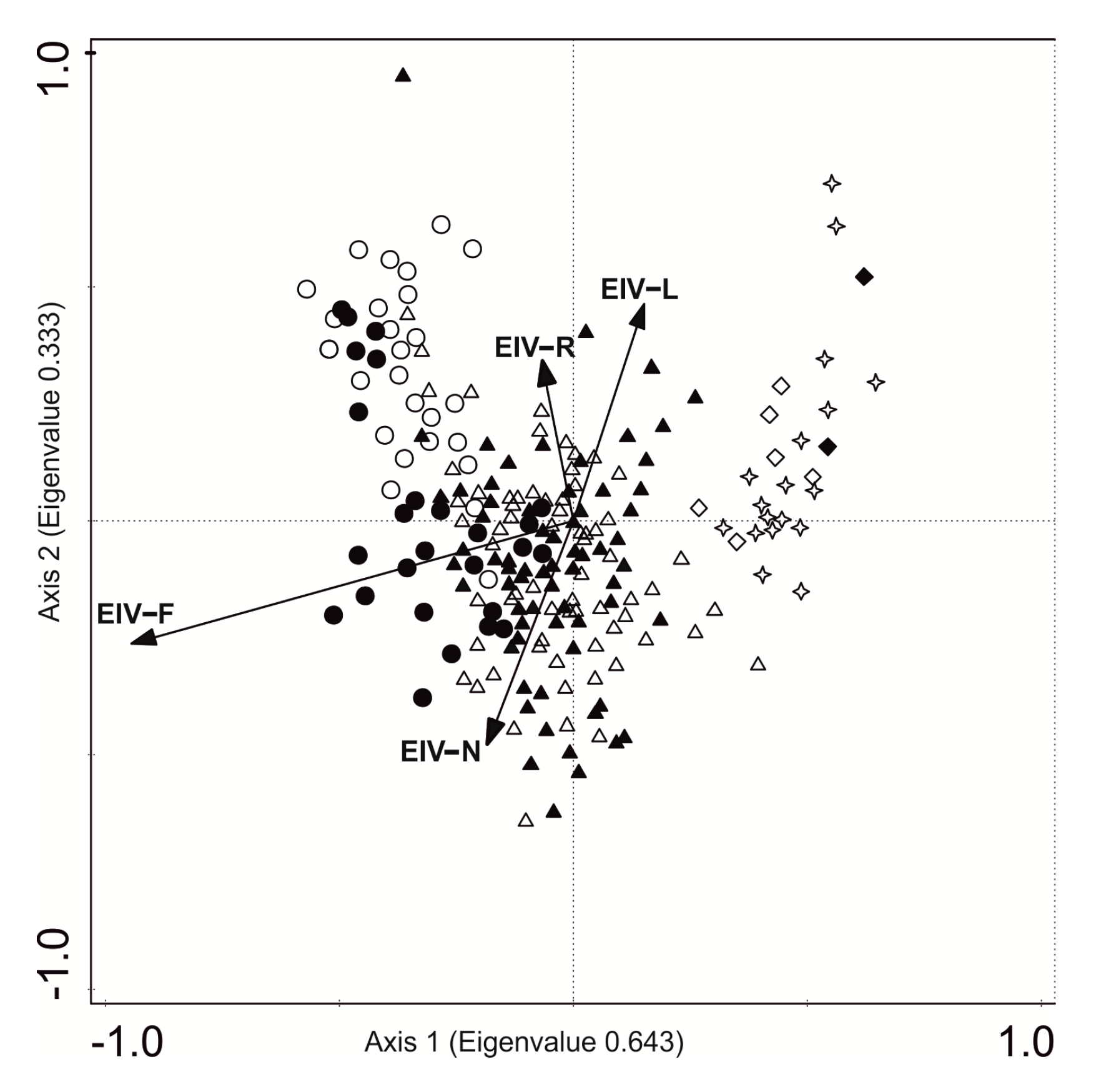
The CCA analysis, based on 225 relevés that were sampled in two periods (in the 1994s and 2016s), revealed two main axes (eigenvalues 0.643 and 0.333) with the first axis sharing a close positive correlation with EIVs for moisture (F) and second axis correlated positively with EIVs for reaction (pH) (Figure 5).
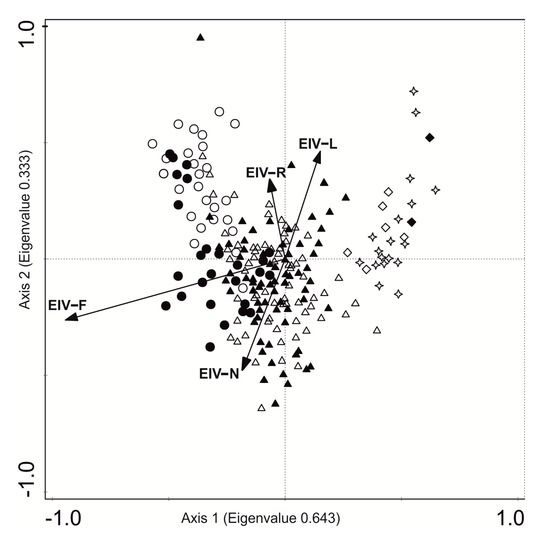
Figure 5.
Ordination biplot diagram of the canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) for the 1994 (black points) and 2016 (white points) years based on species matrix. The diagram explains 14.7% of total variance: EIV-F—5.8%, p = 0.002; EIV-N—3.7%, p = 0.002; EIV-R—3.1%, p = 0.032; EIV-L—2.1, p = 0.008. Abbreviation for vegetation ecological groups: circle—aquatic plants (Lemnetea and Potametea classes), triangle—marsh plants (Phragmitetea class), diamond—meadow plants (Molinio-Arrhenatheretea class), star—shrubs (Salicetea purpurea and Alnetea glutinosae classes); EIVs abbreviations: L—light, R—reaction pH, N—nitrogen, F—moisture.
The ISA results (Table 4) showed that from the 45 macrophyte species in 1994, only four were found to be diagnostics (Rorippa amphibia, Phalaris arundinaceae, Lemna minor, Alisma plantago-aquatica). In 2016, they were represented by 13 species (28.8% of the macrophyte) (Glyceria maxima, Berula erecta, Mentha aquatica, Typha latifolia, Rumex hydrolapathum, Galium palustre, Hydrocharis morsus-ranae, Leersia oryzoides, Carex pseudocyperus, Phragmites australis, Spirodela polyrhiza, Trapa natans, Sparganium erectum).

Table 4.
ISA results: show here are the indicator value and p-value for macrophyte species in both study periods (A—1994, B—2016).
4. Discussion
Freshwater resources, including reservoirs, provide a wide range of ecosystem services, such as flood control, climate change mitigation, river flow regulation, energy provision, as well as water storage. As, such they play crucial roles in human societies (drinking water provision, recreation), and economic development. Therefore all freshwater ecosystems exploited by human activities demand management. This may involve regular monitoring and include efforts to protect the system as well as restoration of damaged natural habitats. In the case of lakes and reservoirs, due to their economic benefits, there is an increasing requirement for policy for the sustainable exploitation of lakes and reservoirs, to sustain their beneficial uses over the long term [55,56].
A vast majority of European aquatic ecosystems are under the strong influence of long-term human activity. Reservoirs as artificial ecosystems are relatively less stable and exposed to the processes of more rapid ageing. Water bodies located within urban agglomeration undergo strong anthropogenic pressure, which influences the floristic and community structure of aquatic vegetation. The most important anthropogenic factors are the intensity of agriculture and wastewater discharges within the catchment that affect the eutrophication process [14,15,57,58].
Human activity has a significant impact on the species richness of aquatic ecosystems, directly and indirectly causing the loss of aquatic vegetation and/or limiting their diversity [59]. Reduction of heterogeneous habitats eliminates sensitive plant communities and species of the varied littoral zone, resulting in the appearance of anthropogenic communities with numerous synanthropic and invasive species [24,60,61]. On the other hand, reservoirs built on rivers may provide new artificial habitats for macrophytes [18]. A study by Hrivnác et al. [62] showed that species richness may be higher in artificial than natural aquatic habitats in different regions typical for the Central Europe landscape. Man-made habitats such as water reservoirs also provide suitable environmental conditions for the potential establishment and growth of macrophytes. Species richness did not change significantly in the studied area (H’ = 2.01, H’ = 2.03, respectively), and a similar indicator of diversity follow from the replacement of one phytocoenosis with another, visible within Lemnetea and Potametea classes. Similar results were observed by Sand-Jensen et al. [63] in the lakes of North-West Europe. The richness and species composition of aquatic plant communities are decisive by environmental variables, substrate, and chemical characteristics, nutrients availability and light conditions, etc. [25,26]. In our research, the depth of water determined the regression of submergent and floating-leaved macrophytes (Lemnetea, Potametea classes) and increase tall emergent macrophytes (Phragmitetea class) [64]. These results confirm the findings reported by Bakker et al. [65] and Lukács et al. [18], who indicated a relationship between species composition and various environmental variables, thus showing that depth and nutrient levels are the two most important factors. In addition, shallow water reservoirs are exposed to rapid heating and an increase in water temperature. As reported by Baláži et al. [24], the strongest factors influencing the composition of macrophyte communities are associated with water temperature.
The major factor modifying the aquatic and marsh vegetation of the study reservoir seems to be eutrophication. Increased discharge of domestic wastewaters and non-point pollution agricultural practices and urban development have recently led to excessive nutrient loading, which is considered to be one of the major causes of reservoir eutrophication. The reservoir characterised by stagnation of water has limited possibilities of neutralization of contaminants flowing from the catchment. This process leads to significant changes in species composition and cover of aquatic vegetation. Eutrophication enhances the density and height of tall emergent plants (Phragmitetea class) and floating-leaved species (e.g., Trapa natans), thereby increasing their ability to competitively exclude submerged communities (e.g., with Potamogeton crispus, Potametum pectinati, Myriophylletum verticillati). A similar trend in changes has been reported by many authors [10,15,66,67]. The inflow of nitrogen and phosphorus compounds from the catchment area was shown to result in the accelerated growth of algae and higher plants. This, in turn, leads to a disturbed balance of the rate of processes of production and decomposition of organic matter [68]. Eutrophication progress is linked with a decline of submerged vegetation, probably because increased water turbidity (low transparency) leads to light limitation in turn, and these features enable emerged vegetation to be dominant [18,69]. As argued by Sand-Jensen et al. [63], the development of aquatic vegetation depends on the extent of nutrient enrichment. The relationship is explained by increased competition at higher nitrate availability resulting in a shift towards floating-leaved macrophytes and thus light limitation [65]. The field observation in European lakes has confirmed that submerged aquatic macrophytes recover and increase in abundance in response to nutrient loading reduction, especially in small and shallow lakes [65,70].
Many studies confirm that the occurrence of some macrophytes is an indicator of eutrophication [33,71]. Significant quantitative bioindicators, suggesting that Rzeszów Reservoir is eutrophic, are the presence of Ceratophyllum demersum and the high frequency and abundance of Trapa natans, which are fast-growing, nutrient demanding species capable of forming a dense canopy on the water surface. Similarly, the development of hydrophilic vegetation (e.g., Ceratophyllum demersum L. s. str., Polygonum amphibium L., Mentha longifolia (L.) L., Bidens cernua L., Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud.) indicates that the water is rich in nutrients and the reservoir is, to a certain extent, eutrophic [72].
Particularly noteworthy in recent years is the appearance of water chestnut Trapa natans (threat status VU in Poland) [61,62,73,74]. The community Trapetum natantis covers a large area and spreads to new areas, mostly colonising the places where a lot of muddy sediments have accumulated. Its occurrence is probably related to human activity (transfer of seeds), as its presence is not mentioned in earlier reports [75].
The depth of reservoirs and the intensifying eutrophication process increase the sedimentation rate, thereby causing overgrowth [22,29,58]. Excessive eutrophication for many years has contributed to ecological succession and overgrowing of Rzeszów Reservoir. Currently, in terms of space, the dominant role is played by species from the Phragmitetea class (e.g., Glyceria maxima, Berula erecta, Typha latifoliae, Leersia oryzoides, Phragmites australis) characterised by high viability and resistance, which is confirmed by the ISA results of macrophytes. The accumulation of biomass for 22 years and eutrophic sediments of Wisłok River support stands of Typha spp. and P. australis, which clearly benefit from these processes. Their density and widespread nature could cause the loss of rare species, which show a significant decrease in abundance and species richness after 22 years [61]. As with the present results, the research observed by Svitok et al. [32] show to dominant Typha latifolia, i.e., the most widespread species that appear soon after disturbance in wet habitats and occurs early in the succession of open water. The abundance of Typha spp. and P. australis is probably related to the increased availability of nitrogen and phosphates in the substrate [22,76]. Our research confirms the relationship between the decreasing water depth and progressing ecological succession, and the decrease in water level has uncovered a part of the littoral zone. Similar directions of changes were observed in another reservoir [77]. All authors emphasize the importance of decomposition of submerged vegetation, as it contributes to shallowing, which can stimulate succession. Arthaud et al. [78] explain the consecutive stages of succession with progressive enrichment of ruderal phytocenosis that generally have high fecundity and good dispersal ability. In eutrophic lakes, the competitive exclusion of aquatic plants is particularly rapid. A further succession process facilitates the colonisation of woody vegetation on the edges (Salicetea and Alnetea classes).
5. Conclusions
The artificial water bodies are sensitive and unstable ecosystems with constantly changing abiotic conditions. They play an important role in maintaining biodiversity, especially in areas affected by strong anthropopressure in urban areas (land-use changes, pollution, landscape fragmentation). The ongoing changes are reflected in the vegetation of the reservoir. Within two decades, intensive development of marsh communities (class Phragmitetea) took place, with the simultaneous disappearance of submerged and floating communities (classes Lemnetea and Potametea). The intensive development of rushes (Phragmition) indicates progressive eutrophication of the reservoir and leads to further ecological succession towards shrub communities. The study made it possible to determine the directions of changes and the degree of plant cover degradation. Knowledge of processes and factors affecting species diversity in such water reservoirs may prevent their further depletion and contribute to the effective protection of aquatic ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization M.Z. and T.W.; methodology M.Z., T.W. and M.W.; investigation M.Z. and T.W.; writing—original draft preparation M.Z. and M.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Rzeszow University, Institute of Agricultural Sciences (500-3-80-805/ZOPiEK/2021).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The Authors thank the three anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schmieder, K. European lake shores in danger-concepts for a sustainable development. Limnologica 2004, 34, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouillard, J.; Lago, M.; Abhold, K.; Röschel, L.; Kafyeke, T.; Mattheiß, V.; Klimmek, H. Protecting aquatic biodiversity in Europe: How much do EU environmental policies support ecosystem-based management? Ambio 2018, 47, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordević, B.; Dašić, T. Water storage reservoirs and their role in the development, utilization and protection of catchment. Spatium 2011, 24, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, A. Vascular flora of eight water reservoir areas in southern Italy. Check List 2015, 11, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatius, A.R.; Rasmussen, T.C. Small reservoir effects on headwater water quality in the rural-urban fringe, Georgia Piedmont, USA. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 8, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, M.; Quinto-Canas, R.; Cano-Ortiz, A.; Spampinato, G.; Pinto-Gomes, C. Originalities of Willow of Salix atrocinerea Brot. in Mediterranean Europe. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.L.; Gravel, V.; Yergeau, E. Editorial: Signaling in the Phytomicrobiome. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendrihan, S.; Pop, C.E. Biotechnological potential of plant associated microorganisms. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 26, 2700–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanik, A.; Baykal, B.B.; Gonenc, I.E. The impact of agricultural pollutants in six drinking water reservoirs. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egertson, C.J.; Kopaska, J.A.; Downing, J.A. A century of change in macrophyte abundance and composition in response to agricultural eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 2004, 524, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszelnik, P. Atmospheric deposition as a source of nitrogen and phosphorus loads into the Rzeszow reservoir, SE Poland. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2007, 33, 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Gruca-Rokosz, R.; Tomaszek, J.A.; Koszelnik, P.; Czerwieniec, E. Methane and carbon dioxide emission from some reservoirs in SE Poland. Limnol. Rev. 2010, 10, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruca-Rokosz, R. Quantitative fluxes of the greenhouse gases CH4 and CO2 from the surfaces of selected Polish reservoirs. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołdyn, H. Changes in plant species diversity of aquatic ecosystems in the agricultural landscape in West Poland in the last 30 years. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand-Jensen, K.; Bruun, H.H.; Baastrup-Spohr, L. Decade-long time delays in nutrient and plant species dynamics during eutrophication and reoligotrophication of Lake Fure 1900–2015. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.P.; Clements, S.E.; Corlett, R.T.; Hahs, A.K.; McCarthy, M.A.; McDonnell, M.J.; Schartz, M.W.; Thompson, K.; Vesk, P.A.; Williams, N.S.G. Plant traits and extinction in urban areas: A meta-analysis of 11 cities. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, G.; Bondallaz, L. Urban aquatic ecosystems: Habitat loss and depletion of native macrophyte diversity during the 20th century in four Swiss cities. Urban Ecosyst. 2013, 16, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukács, B.A.; Tóthmérész, B.; Borics, G.; Várbíró, G.; Juhász, P.; Kiss, B.; Müller, Z.; G-Tóth, L.; Erős, T. Macrophyte diversity of lakes in the Pannon Ecoregion (Hungary). Limnologica 2015, 53, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuzović, M.; Pavlović, D. Physical organization of two reservoirs in Serbia as a crucial factor in development of their hydrophilic flora: A comparative study. Hydrobiologia 2004, 525, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappuis, E.; Ballesteros, E.; Gacia, E. Distribution and richness of aquatic plants across Europe and Mediterranean countries: Patterns, environmental driving factors and comparison with total plant richness. J. Veg. Sci. 2012, 23, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzella, M.M.; Rostai, L.; Iberite, M.; Bolpagni, R.; Blasi, C. Changes in aquatic plants in the Italian volcanic-lake system detected using current data and historical records. Aquat. Bot. 2014, 112, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołdyn, H.; Arczyńska-Chudy, E.; Pińskwar, P.; Jezierska-Madziar, M. Natural and anthropogenic transformations of water and marsh vegetation in Lake Zbęchy (Wielkopolska Region). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2008, 37, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capers, R.S.; Selsky, R.; Bugbee, G.J. The relative importance of local conditions and regional processes in structuring aquatic plant communities. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 55, 952–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláži, P.; Hrivnák, R.; Ot’ahelová, H. The relationship between macrophyte assemblages and selected environmental variables in reservoirs of Slovakia examined for the purpose of ecological assessment. Pol. J. Ecol. 2014, 62, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornette, G.; Puijalon, S. Response of aquatic plants to abiotic factors: A review. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, N.A.; Pandit, A.K.; Ganai, B.A. Factors affecting the distribution patterns of aquatic macrophytes. Limnol. Rev. 2014, 14, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, S.I.; Arnott, S.E.; Cottingham, K.L. The relationship in lake communities between primary productivity and species richness. Ecology 2000, 81, 2662–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, O.; Sand-Jensen, K. Aquatic macrophyte richness in Danish lakes in relation to alkalinity, transparency and lake area. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N.; Willby, N.J. The influence of hydrological and land use indicators on macrophyte richness in lakes—A comparison of catchment and landscape buffers across multiple scales. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłosowski, S. The relationships between environmental factors and the submerged Potametea associations in lakes of north-eastern Poland. Hydrobiologia 2006, 560, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoul, P.; Freedman, B. Environmental influences on aquatic plants in freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Rev. 2006, 14, 89–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svitok, M.; Hrivnák, R.; Oťaheľová, H.; Dúbravková, D.; Paľove-Balang, P.; Slobodník, V. The Importance of Local and Regional Factors on the Vegetation of Created Wetlands in Central Europe. Wetlands 2011, 31, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, W.E.; Mjelde, M.; Dudley, B.; Hellsten, S.; Hanganu, J.; Kolada, A.; van den Berg, M.; Poikane, S.; Phillips, G.; Willby, N.; et al. Classifying aquatic macrophytes as indicators of eutrophication in European lakes. Aquat. Ecol. 2008, 42, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolada, A. The use of helophytes in assessing eutrophication of temperate lowland lakes: Added value? Aquat. Bot. 2016, 129, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolpagni, R.; Laini, A.; Azella, M.M. Short-term dynamics of submerged aquatic vegetation diversity and abundance in deep lakes. App. Veg. Sci. 2016, 19, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, A.; Ustrnul, Z.; Schmatz, D.R. Long-term variability of air temperature and precipitation conditions in the Polish Carpathians. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Martínez, S.; Rivas Sáenz, S.; Penas, A. Worldwide bioclimatic classification system. Glob. Geobot. 2011, 1, 1–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutiempo. Available online: http://en.tutiempo.net/ (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Gruca-Rokosz, R. Stan troficzny zbiornika zaporowego Rzeszów. JCEEA 2013, 30, 279–291. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska, M. Roślinność wodna i nadbrzeżna Zalewu Rzeszowskiego. Ann. UMCS Sect. C 1995, 50, 145–171. [Google Scholar]
- Braun-Blanquet, J. Pflanzensoziologie. Grundzüge der Vegetationskunde, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Mirek, Z.; Piękoś-Mirkowa, H.; Zając, A.; Zając, M. Flowering plants and pteridophytes of Poland–A checklist. In Biodiversity of Poland; Mirek, Z., Ed.; W. Szafer Institute of Botany, Polish Academy of Sciences: Krakow, Poland, 2002; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Szweykowski, J. An annotated checklist of Polish liverworts and hornworst. In Biodiversity of Poland; Mirek, Z., Ed.; W. Szafer Institute of Botany, Polish Academy of Sciences: Krakow, Poland, 2006; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Matuszkiewicz, W. Przewodnik do Oznaczania Zbiorowisk Roślinnych; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012; p. 500. [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberg, H.; Weber, H.E.; Düll, R.; Wirth, V.; Werner, W.; Paulissen, D. Zeigerwerte von Pflanzen in Mitteleuropa. Scr. Geobot. 1992, 18, 1–258. [Google Scholar]
- Zarzycki, K.; Trzcińska-Tacik, H.; Różański, W.; Szeląg, Z.; Wołek, J.; Korzeniak, U. Ecological Indicator Values of Vascular Plants of Poland. In Biodiversity of Poland; Mirek, Z., Ed.; W. Szafer Institute of Botany, Polish Academy of Sciences: Krakow, Poland, 2002; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Illinois, IL, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. Ecological Diversity; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1975; p. 165. [Google Scholar]
- Kovach, W.L. MVSP–A MultiVariate Statistical Package for Windows, Version 3.1; Kovach Computing Services: Wales, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- van der Maarel, E. Transformation of cover-abundance values in phytosociology and its effects on community similarity. Vegetatio 1979, 39, 97–114. [Google Scholar]
- StatSoft. STATISTICA for Windows; Computer Program Manual. StatSoft: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dufrêne, M.; Legendre, P. Species Assemblages and Indicator Species: The Need for a Flexible Asymmetrical Approach. Ecol. Monogr. 1997, 67, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCune, B.; Mefford, M.J. PC-ORD Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data. Version 4; MjM Software Design: Gleneden Beach, OR, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, L.T.; Goethals, P.L.M. Opportunities and Challenges for the Sustainability of Lakes and Reservoirs in Relation to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Water 2019, 11, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, Y.; Dimitriou, E. A Large-Scale Nature-Based Solution in Agriculture for Sustainable Water Management: The Lake Karla Case. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappuis, E.; Gacia, E.; Ballesteros, E. Changes in aquatic macrophyte flora over the last century in Catalani water bodies (NE Spain). Aquat. Bot. 2011, 95, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choiński, A.; Ławniczak, A.; Ptak, M.; Sobkowiak, L. Causes of lake area changes in Poland. J. Resour. Ecol. 2011, 2, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ot’ahel’owá, H.; Ot’ahel’, J.; Pazúr, R.; Hrivnák, R.; Valachovič, M. Spatio-temporal changes in land cover and aquatic macrophytes of the Dunabe floodplain lake. Limnologica 2011, 41, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta, P.; Toivonen, H. Changes in Aquatic Macrophytes since 1933 in an Urban Lake, Idesjärvi, SW Finland. Ann. Bot. Fennici. 2008, 45, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaja, M.; Wójcik, T. Changes in vascular flora of the Rzeszow Reservoir after 20 years (SE Poland). Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrivnák, R.; Kochjarová, J.; Oťaheľová, H.; Paľove-Balang, P.; Slezák, M.; Slezák, P. Environmental drivers of macrophyte species richness in artificial and natural aquatic water bodies—Comparative approach from two central European regions. Ann. Limnol.-Int. J. Lim. 2014, 50, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand-Jensen, K.; Riis, T.; Vestergaard, O.; Larsen, S.E. Macrophyte decline in Danish lakes and streams over the past 100 years. J. Ecol. 2000, 88, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaja, M.; Wójcik, T. Występowanie Leersia oryzoides (Poaceae) w zbiorowiskach szuwarowych Zalewu Rzeszowskiego. Fragm. Flor. Geobot. Polon. 2014, 21, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, E.S.; Sarneel, J.M.; Gulati, R.D.; Liu, Z.; van Donk, E.V. Restoring macrophyte diversity in shallow temperate lakes: Biotic versus abiotic constraints. Hydrobiologia 2013, 710, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.J. Plant communities and plant diversity in softwater lakes of northern Europe. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 73, 287–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäemets, H.; Palmik, K.; Haldna, M.; Sudnitsyna, D.; Melnik, M. Eutrophication and macrophyte species richness in the large shallow North-European Lake Peipsi. Aquat. Bot. 2010, 92, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naselli-Flores, L. Mediterranean Climate and Eutrophication of Reservoirs: Limnological Skills to Improve Management. In Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences and Control; Ansari, A.A., Gill, S.S., Lanza, G.R., Rast., W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, G.; Willby, N.; Moss, B. Submerged macrophyte decline in shallow lakes: What have we learnt in the last forty years? Aquat. Bot. 2016, 135, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, T.L.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M. Response of submerged macrophytes in Danish lakes to nutrient loading reductions and biomanipulation. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506–509, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Johansson, L.S.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jørgensen, T.B.; Liboriussen, L.; Jeppesen, E. Submerged macrophytes as indicators of the ecological quality of lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuzović, M.; Pavlović, D.; Ostojić, A. Temporal and habitat distribution of macrophytes in lowland eutrophic reservoir Gruža in Serbia. Period. Biol. 2015, 117, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilz, M.; Kell, S.P.; Maxted, N.; Lansdown, R.V. European Red List of Vascular Plants; Publication Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kaźmierczakowa, R.; Bloch-Orłowska, J.; Celka, Z.; Cwener, A.; Dajdok, Z.; Michalska-Hejduk, D.; Pawlikowski, P.; Szczęśniak, E.; Ziarnek, K. Polish Red List of Pteridophytes and Flowering Plants; Institute of Nature Conservation, Polish Academy of Sciences: Krakow, Poland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kukuła, K.; Bylak, A. Expansion of water chestnut in a small dam reservoir: From pioneering colony to dense floating mat. Period. Biol. 2017, 119, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zerbe, S.; Han, W.; Thevs, N.; Li, W.; He, P.; Schmitt, A.O.; Liu, Y.; Ji, C. Nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of common reed (Phragmites australis) and its relationship to nutrient availability in northern China. Aquat. Bot. 2014, 112, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddubnyi, A.; Papchenkov, V.G.; Chemeris, E.V.; Bobro, A.A. Overgrowing of Protected Shallow Waters in the Upper Volga Reservoirs in Relation to Their Morphometry. Inland Water Biol. 2017, 10, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthaud, F.; Vallod, D.; Robin, J.; Wezel, A.; Bornette, G. Short-term succession of aquatic plant species richness along ecosystem productivity and dispersal gradients in shallow lakes. J. Veg. Sci. 2013, 24, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).