Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale Emissions Based on Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Areas and Data Sources
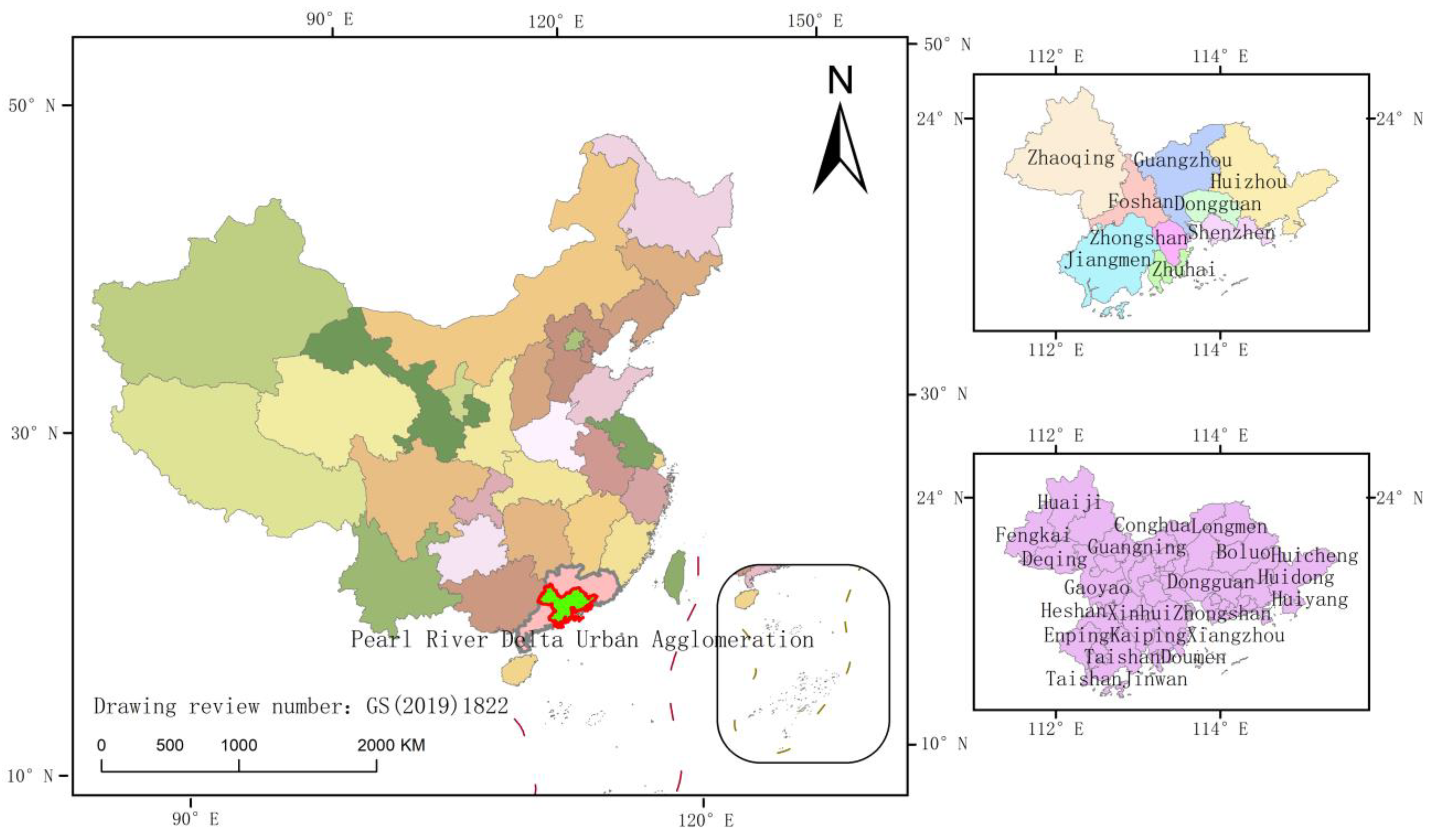
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. NTL
2.2.2. Statistical Data and Administrative Boundary Data
3. Methodology
3.1. NTL Fitting
3.2. Estimation of Energy Carbon Emissions
3.3. Carbon Emission Estimation Models
3.4. Corrected Simulated Grid Unit Pixel Carbon Emissions
3.5. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity Analysis of Carbon Emissions
3.5.1. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
3.5.2. Local Outlier Analysis Using Space–Time Cube (STC-LOF) and ES-THA
3.5.3. Analysis of Regional Differences in Multi-Scale Urban Carbon Emissions
3.6. Research on Influencing Factors of Carbon Emission
4. Results
4.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Tertiary Carbon Emissions
4.2. Spatial Simulation of Carbon Emissions at Grid-Cell Scale
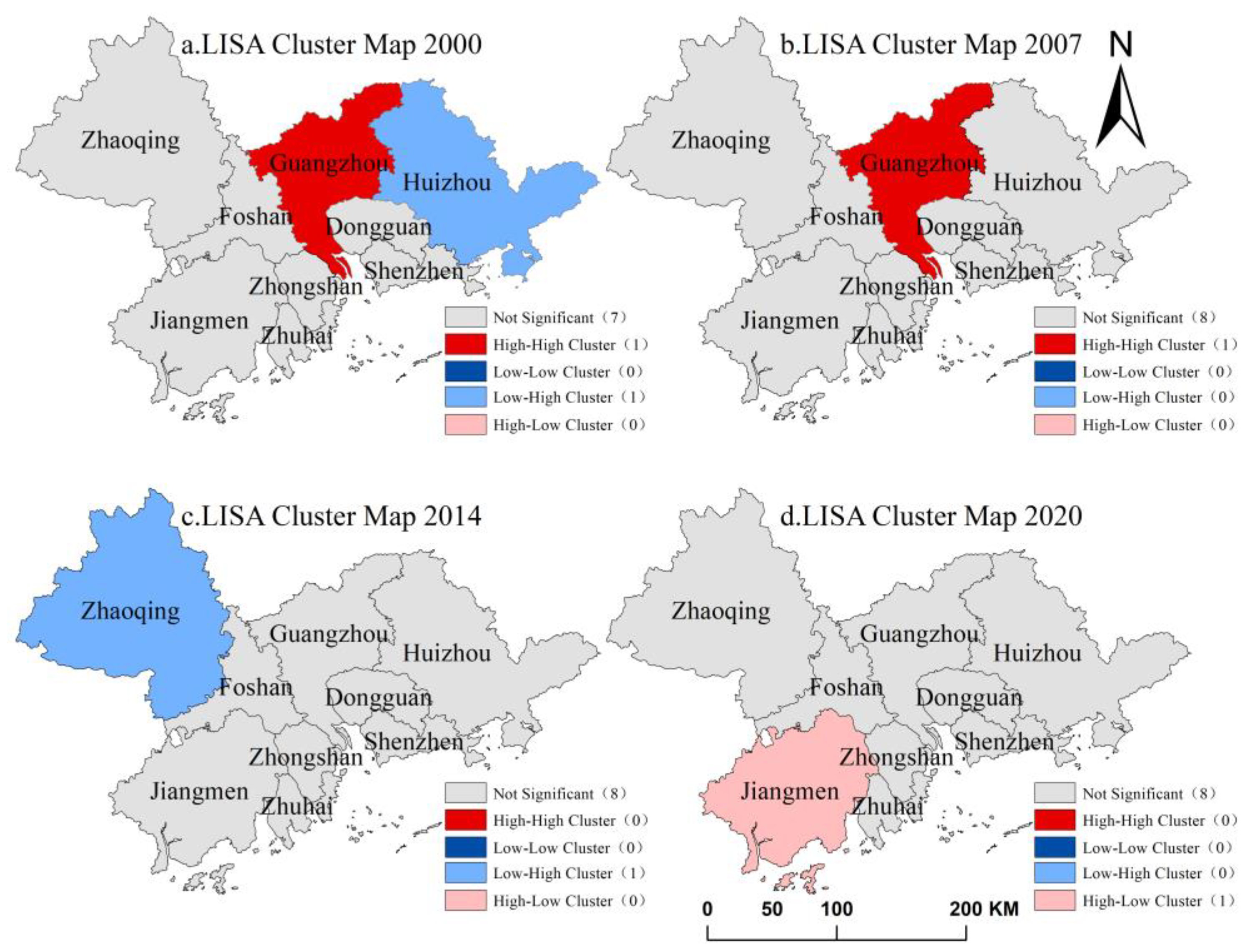
4.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis of Carbon Emissions
4.3.1. Moran’s I Exponential Spatial Autocorrelation
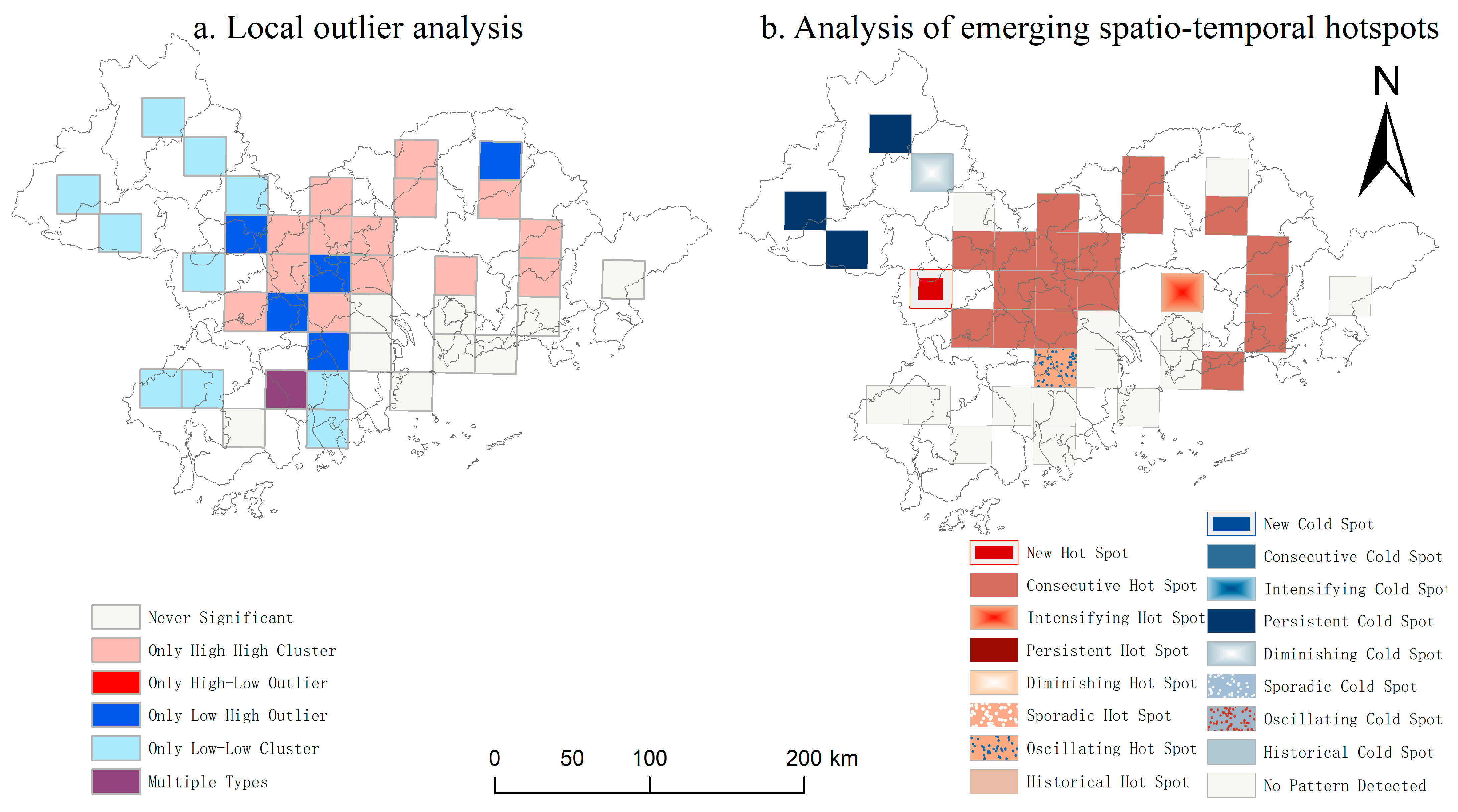
4.3.2. County-Level STC-LOF and ES-THA
4.3.3. Inequality of Carbon Emission Spatial Distribution at Multiple Scales
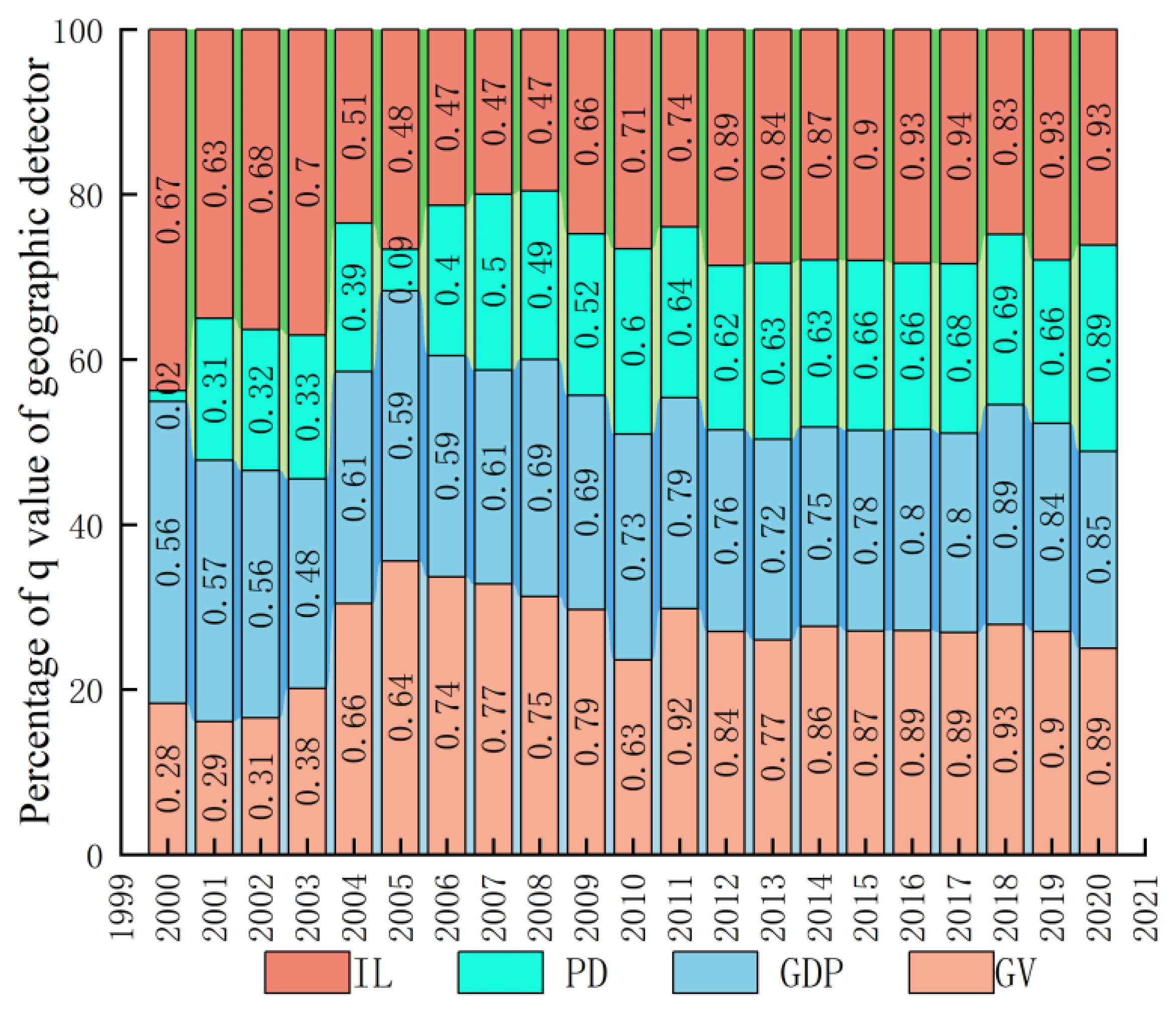
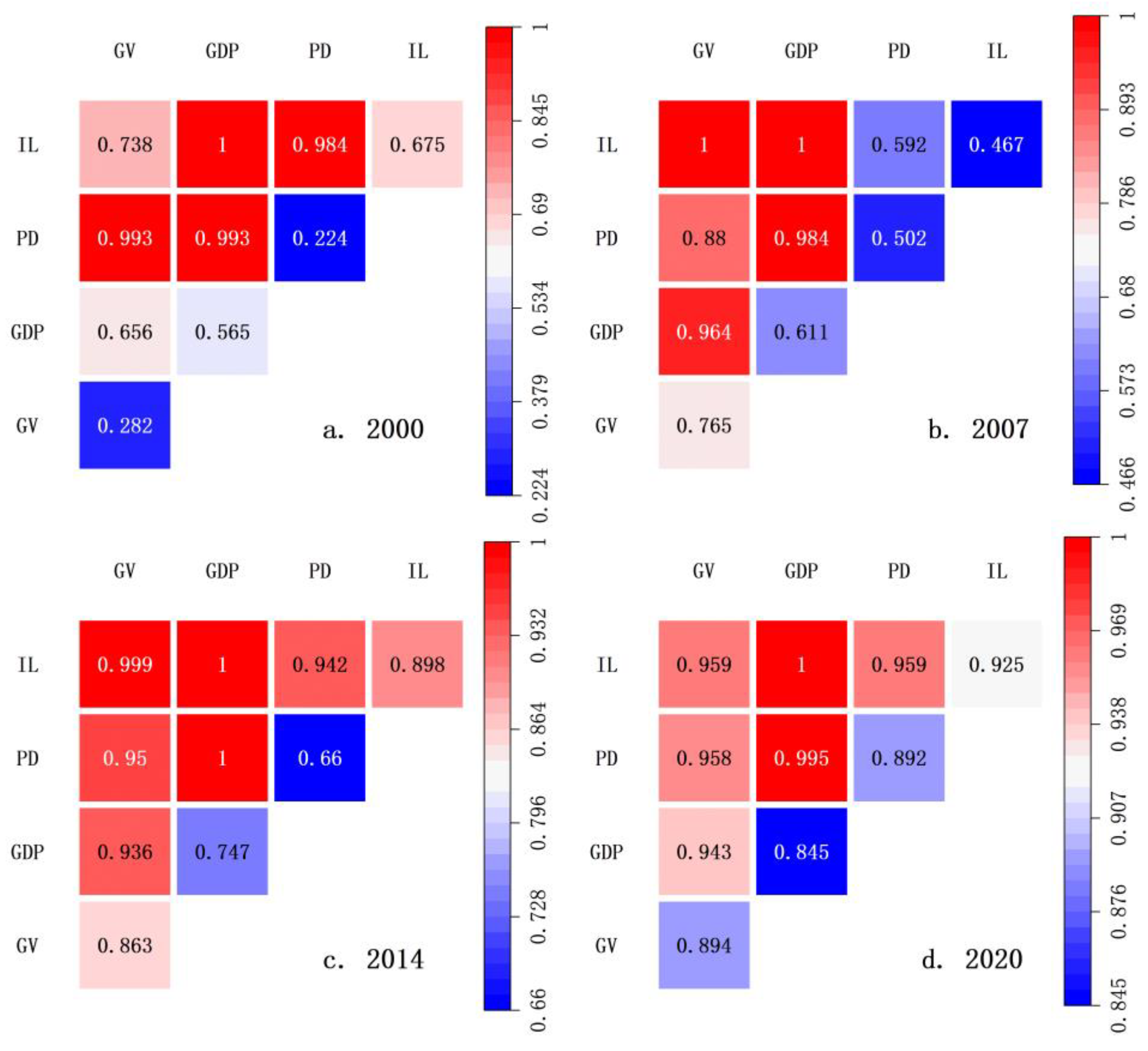
4.4. Analysis of Influencing Factors of Carbon Emission
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harvey, L.D.D. Allowable CO2 concentrations under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change as a function of the climate sensitivity probability distribution function. Environ. Res. Lett. 2007, 2, 14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichele, R.; Felbermayr, G. The Effect of the Kyoto Protocol on Carbon Emissions. J. Policy Anal. Manag. 2013, 32, 731–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, R.S. Inside UN Climate Change Negotiations: The Copenhagen Conference. Rev. Policy Res. 2010, 27, 795–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinghua, L.; Peng, L.; Bin, R.R.; Shengbin, L.; Xiaoping, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Yao, H. Carbon Emission Characteristics of Resource-Based Cities in China. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2022, 46, 4579–4591. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. The impact of China’s carbon trading market on regional carbon emission efficiency. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 29, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Lin, Y. Analyzing the spatiotemporal differences of carbon emission in the PearlRiver Delta using DMSP/OLS nighttime light images. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 26, 1824–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Jia, X.; Bai, B. Accounting and Characteristics Analysis of CO2 Emissions in Chinese Cities. Chin. J. Urban Environ. Stud. 2020, 8, 2050004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Tian, L.; Wang, J. Trend Forecast of Energy Production and Consuumption in China and Research of Carbon Emissions. J. Nat. Resour. 2010, 25, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Peng, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Spatial-temporal pattern and influence factors of county carbon emissions in Hunan Province based on nightlight data. Ecol. Sci. 2022, 41, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X. Carbon Dioxide Emissions Estimation and Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Gd Province Based on Nighttime Light Data; Chengdu University of Technology: Chengdu, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Dai, J. Spatio-temporal characteristics of carbon emission in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration derived from integrated DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023. Available online: https://x.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?filename=HKWZ202302001&dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDTEMP&v=sZmz0fHCQ4uDUSBUyvD75d3Iim1RLQqCwq0c1YmsO72e2AO3cFhoVjGCc4tWE5ca (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Xu, L. A Study on the Spatial-Temporal Pattern and Influence Factors of Prefecture-Level Cities Resident’s per Capita Carbon Emissions in China; Lanzhou University: Lanzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, B.; Zhou, Y. Urbanization, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A panel cointegration and causality analysis. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 26, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kuang, Y.; Huang, N. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis on Energy-Related CarbonEmission in Gd. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 180–187+193. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Jiao, W.; Chen, X.; Pang, J. The Dynamics and Spatial Differentiation Research of Carbon Emission from Energy Consumption in Henan Province. Areal Res. Dev. 2017, 36, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Zou, S.; Zhao, J.; Wen, Q.; Mi, W. Temporal-Spatial Difference Analysis of Carbon Emission from EnergyConsumption and Its Regional Type Division in Northwest China. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 36, 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Ji, S.; Wang, C.; Streets, D.G. Investigating the spatially heterogeneous impacts of urbanization on city-level industrial SO2 emissions: Evidence from night-time light data in China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, X. Accuracy analysis of inverting provincial-level carbon emissions from night-time light data in China: Comparison based on international carbon emission data. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 601, p. 012046. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.-H.; Xie, Y.-L.; Ji, L.; Cai, Y.-P.; Yang, Z.-F.; Xia, D.-H. Spatial-temporal evolution and driving forces of provincial carbon footprints in China: An integrated EE-MRIO and WA-SDA approach. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 176, 106543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, X.; Chuai, X.; Yang, H. The impact of land urbanization on carbon dioxide emissions in the Yangtze River Delta, China: A multiscale perspective. Cities 2021, 116, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Wang, M. Carbon dioxide emissions allocation: A review. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 125, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Yi, Z.; Liu, W.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F. Mapping population density in China between 1990 and 2010 using remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll CN, H.; Muller, J.P.; Elvidge, C.D. Night-time Imagery as a Tool for Global Mapping of Socioeconomic Parameters and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Ambio A J. Hum. Environ. 2000, 29, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ziskin, D.; Tuttle, B.T. Creating a Global Grid of Distributed Fossil Fuel CO2 Emissions from Nighttime Satellite Imagery. Energies 2010, 3, 1895–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.R.; Rayner, P.J.; Paget, M. Regional variations in spatial structure of nightlights, population density and fossil-fuel CO2 emissions. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 4756–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Graus, W.; Worrell, E.; Huang, B. Estimating CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions at urban scales by DMSP/OLS (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System) nighttime light imagery: Methodological challenges and a case study for China. Energy 2014, 71, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, D. Correlations between Urbanization and Vegetation Degradation across the World’s Metropolises Using DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2067–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, M.; Atkinson, P.M. Three-fold urban expansion in Saudi Arabia from 1992 to 2013 observed using calibrated DMSP-OLS night-time lights imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, N.; Kuang, Y. China’s 19-year city-level carbon emissions of energy consumptions, driving forces and regionalized mitigation guidelines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 35, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Wu, J. Modeling spatiotemporal CO2 (carbon dioxide) emission dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data using panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, T.K.; Badarinath, K.; Elvidge, C.; Tuttle, B. Spatial characterization of electrical power consumption patterns over India using temporal DMSP-OLS night-time satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Su, Y.; Zhao, Y. Regional inequality, spatial spillover effects and influencingfactors of China’s city-level energy-related carbon emissions. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 414–428. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Xian, W.; Shao, Q.; Yin, Z.; Qi, J. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale CO2 Emissions by Integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS Data: A Case Study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yun, C.; Li, L.; Huang, C. Spatiotemporal variations of urban CO2 emissions in China: A multiscale perspective. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, G. Spatial effects of carbon dioxide emissions from residential energy consumption: A county-level study using enhanced nocturnal lighting. Appl. Energy 2014, 131, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, X. The Accuracy of Nighttime Light Data to Estimate China’s Provincial Carbon Emissions: A Comparison with Carbon Emissions Allocated by International Carbon Database. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2022, 37, 319–332. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, T.; Shao, G.; Tang, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, W.; Liu, L. Quantifying Spatiotemporal Changes in Human Activities Induced by COVID-19 Pandemic Using Daily Nighttime Light Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 2740–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xiu, T.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Jiao, L. Lockdown induced night-time light dynamics during the COVID-19 epidemic in global megacities. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Huang, N. Correction of DMSP/OLS Night-time Light Images and Its Application in China. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2015, 17, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X. Research on Correction and Fusion of DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS Nighttime Light Data; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y. Study on the Carbon Emissions from Energy Consumption in China Using DMSP/OLS Night Light Imageries; Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Guizhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Fan, L.; Guan, Z.; Feng, D.; Gao, Y. Spatial analysis of carbon emissions from region energy consumption based on night light data. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2017, 42, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.; Shen, L.; Zhong, S. Spatio-temporal Pattern of Carbon Emissions based on Nightlight Data of the Shanxi-Shaanxi-Inner Mongolia Region of China. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G. Spatiotemporal Evolution Pattern and Influencing factors of Energy Consumption Carbon Emissions in Lanzhou-Xining City Group; Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics: Lanzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, E.P.; Pires, M.A.; Matos, R.S.; Zamora, R.R.M.; Menezes, R.P.; Araújo, R.S.; de Souza, T.M. Lacunarity exponent and Moran index: A complementary methodology to analyze AFM images and its application to chitosan films. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2021, 581, 126192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Remote Sensing Monitoring and Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Forest Change Characteristics in Southwest China in Recent 20 Years; Southwest University: Chongqing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cuba, N.; Sauls, L.A.; Bebbington, A.J.; Bebbington, D.H.; Chicchon, A.; Marimón, P.D.; Diaz, O.; Hecht, S.; Kandel, S.; Osborne, T.; et al. Emerging hot spot analysis to indicate forest conservation priorities and efficacy on regional to continental scales: A study of forest change in Selva Maya 2000–2020. Environ. Res. Commun. 2022, 4, 71004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Fan, W.; Lv, Y. Analysis Methods of Spatio-temporal Patterns and Its Empirical Applications——A Case Study of Manufacturing Industry of Shandong Province. J. Geomat. Sci. Technol. 2021, 38, 624–630+638. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Chen, S.; Pan, K. Analysis on Spatial Imbalance and Dynamic Evolution of Carbon Lock-in: Taking Jiangsu Province as an Example. J. Zhejiang Shuren Univ. 2022, 22, 50–59+75. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Zou, S. Regional Differences, Convergence and Influencing Factors of Carbon Emissions Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. Yellow River 2022, 44, 6–12+56. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Khan, S.U.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, M. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity, convergence and its impact factors: Perspective of carbon emission intensity and carbon emission per capita considering carbon sink effect. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 92, 106699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liao, M.; Jiang, J. Research on Agricultural Carbon Emissions and Regional Carbon Emissions Reduction Strategies in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhang, K.; Dou, J. Comparisons on the Income Measurements in Chinese Household Survey Data. Manag. World 2019, 35, 36–60+226. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Responses of Suomi-NPP VIIRS-derived nighttime lights to socioeconomic activity in China’s cities. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, C.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Q.; Tian, Y. Temporal-spatial carbon emission patterns caused by fossil energy consumption at the city level in Hunan Province, China and the factors driving their composition. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 2476–2487. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X. System Analysis and Regulation of Energy Consumption Carbon Emissions of Hunan Province; Hunan Normal University: Changsha, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, Y. An LMDI-based investigation of the changes in carbon emissions of the transportation sector in the Yangtze River Economic. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 4817–4826. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Huang, Y. Spatial spillover effect and driving forces of carbon emission intensity at city level in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1131–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector:Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y. Spatial evolution and driving force analysis of ecological-production-living spaces on the Loess Plateau. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2022, 49, 112–121. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y.; Guan, D.; Liu, J.; Mi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Schroeder, H.; Cai, B.; Chen, Y.; Shao, S.; et al. Methodology and applications of city level CO2 emission accounts in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Type | Conversion Coefficient of Standard Coal (t/t) | Carbon Emission Factor/(104 t/104 t) |
|---|---|---|
| Coal | 0.7143 | 0.7559 |
| Coke | 0.9714 | 0.8550 |
| Crude oil | 1.4286 | 0.5857 |
| Gasoline | 1.4714 | 0.5538 |
| Kerosene | 1.4714 | 0.5714 |
| Diesel | 1.4571 | 0.5921 |
| Fuel oil | 1.4286 | 0.6185 |
| Liquefied petroleum gas | 1.6198 | 0.5042 |
| Natural gas | 1.3300 | 0.4483 |
| The thermal | 34.1200 | 0.6700 |
| Electric power | 0.3450 | 0.2720 |
| Region/Year | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gd | 9.4178% | 5.1477% | 10.7713% | 8.4456% | |
| 2000 | 2007 | 2014 | 2020 | ||
| Gz | 7.1487% | 3.2479% | 6.7489% | 7.1678% | 6.5783% |
| Sz | 6.8972% | 4.0125% | 7.1148% | 6.9715% | 6.7490% |
| Zq | 7.9615% | 7.3103% | 7.7214% | 7.3872% | 7.3451% |
| Dg | 5.4179% | 6.1024% | 7.9015% | 6.1078% | 6.1324% |
| 2000 | 2007 | 2014 | 2020 | ||
| County average | 15.4781% | 9.4713% | 17.1329% | 18.7385% | 15.4552% |
| Scale | Variable | 2000 | 2003 | 2006 | 2009 | 2012 | 2015 | 2018 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Municipal | Moran’s I | 0.0591 | 0.0818 | 0.1122 | 0.1187 | 0.1274 | 0.1552 | 0.1447 | 0.1391 |
| Z | 1.0187 | 1.2044 | 1.3905 | 1.4313 | 1.5120 | 1.1149 | 0.9948 | 0.9241 | |
| P | 0.16401 | 0.1224 | 0.0943 | 0.0889 | 0.0775 | 0.1372 | 0.1630 | 0.1775 | |
| County level | Moran’s I | 0.2224 | 0.2476 | 0.2702 | 0.2732 | 0.271 | 0.287 | 0.314 | 0.323 |
| Z | 2.5540 | 3.0759 | 3.3097 | 3.3764 | 3.3403 | 3.4676 | 3.7042 | 3.5020 | |
| P | 0.0139 | 0.0052 | 0.0033 | 0.0024 | 0.0012 | 0.0017 | 0.0014 | 0.0033 |
| Time | TP | TbP | wbP | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gz | Sz | Zh | Fs | Hz | Dg | Zs | Jm | Zq | |||
| 2000 | 0.5600 0.2632 0.4775 0.3613 | 0.0580 | 0.0770 | 0.0334 | 0.1945 | 0.0415 | 0.0482 | 0.0168 | 0.1086 | 0.0046 | 0.4042 |
| 2007 | 0.0104 | 0.0252 | 0.0238 | 0.0783 | 0.0755 | 0.0538 | 0.0203 | 0.0213 | 0.0057 | 0.3957 | |
| 2014 | 0.0457 | 0.0311 | 0.0611 | 0.0879 | 0.1292 | 0.0489 | 0.0202 | 0.0638 | 0.0236 | 0.3842 | |
| 2020 | 0.0321 | 0.0567 | 0.0332 | 0.0229 | 0.1676 | 0.0481 | 0.0221 | 0.1041 | 0.0422 | 0.5842 | |
| TwP | wwP | ||||||||||
| Gz | Sz | Zh | Fs | Hz | Dg | Zs | Jm | Zq | |||
| 2000 | 0.5747 | 0.2638 | 0.0218 | 0.0336 | 0.0233 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.1282 | 0.2193 | 0.5958 | |
| 2007 | 0.3552 | 0.2206 | 0.0607 | 0.0741 | 0.0458 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0278 | 0.2447 | 0.6043 | |
| 2014 | 0.3621 | 0.1394 | 0.1146 | 0.1000 | 0.0722 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0848 | 0.2859 | 0.6158 | |
| 2020 | 0.3482 | 0.1407 | 0.1217 | 0.1287 | 0.0187 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0462 | 0.2110 | 0.4158 | |
| Time | TG | TbG | wbG | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gz | Sz | Zh | Fs | Hz | Dg | Zs | Jm | Zq | |||
| 2000 | 0.3791 | 0.0807 | 0.1557 | 0.0108 | 0.1105 | 0.0969 | 0.0279 | 0.0113 | 0.0651 | 0.0639 | 0.6145 |
| 2007 | 0.4953 | 0.0097 | 0.1202 | 0.0220 | 0.0538 | 0.1644 | 0.0429 | 0.0162 | 0.1048 | 0.1044 | 0.5646 |
| 2014 | 0.5474 | 0.0050 | 0.1069 | 0.0358 | 0.0364 | 0.1426 | 0.0418 | 0.0189 | 0.1349 | 0.0802 | 0.4881 |
| 2020 | 0.6391 | 0.0426 | 0.1126 | 0.0254 | 0.0345 | 0.2352 | 0.0390 | 0.0113 | 0.1877 | 0.1158 | 0.6149 |
| TwG | WwG | ||||||||||
| Gz | Sz | Zh | Fs | Hz | Dg | Zs | Jm | Zq | |||
| 2000 | 0.2947 | 0.2805 | 0.0186 | 0.0310 | 0.1046 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0383 | 0.1006 | 0.3855 | |
| 2007 | 0.5264 | 0.1600 | 0.1142 | 0.0855 | 0.2506 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0426 | 0.0862 | 0.4354 | |
| 2014 | 0.5154 | 0.2843 | 0.2154 | 0.0905 | 0.5041 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0520 | 0.1116 | 0.5119 | |
| 2020 | 0.5556 | 0.2572 | 0.2896 | 0.1003 | 0.2069 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0784 | 0.1257 | 0.3851 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, G. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale Emissions Based on Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108234
Liu Y, Zhou S, Zhang G. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale Emissions Based on Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability. 2023; 15(10):8234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108234
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yajing, Shuai Zhou, and Ge Zhang. 2023. "Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale Emissions Based on Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration" Sustainability 15, no. 10: 8234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108234
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhou, S., & Zhang, G. (2023). Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale Emissions Based on Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability, 15(10), 8234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108234






