Site Characterization and Liquefaction Hazard Assessment for the Erenler Settlement Area (Sakarya Province, Turkey) Based on Integrated SPT-Vs Data
Abstract
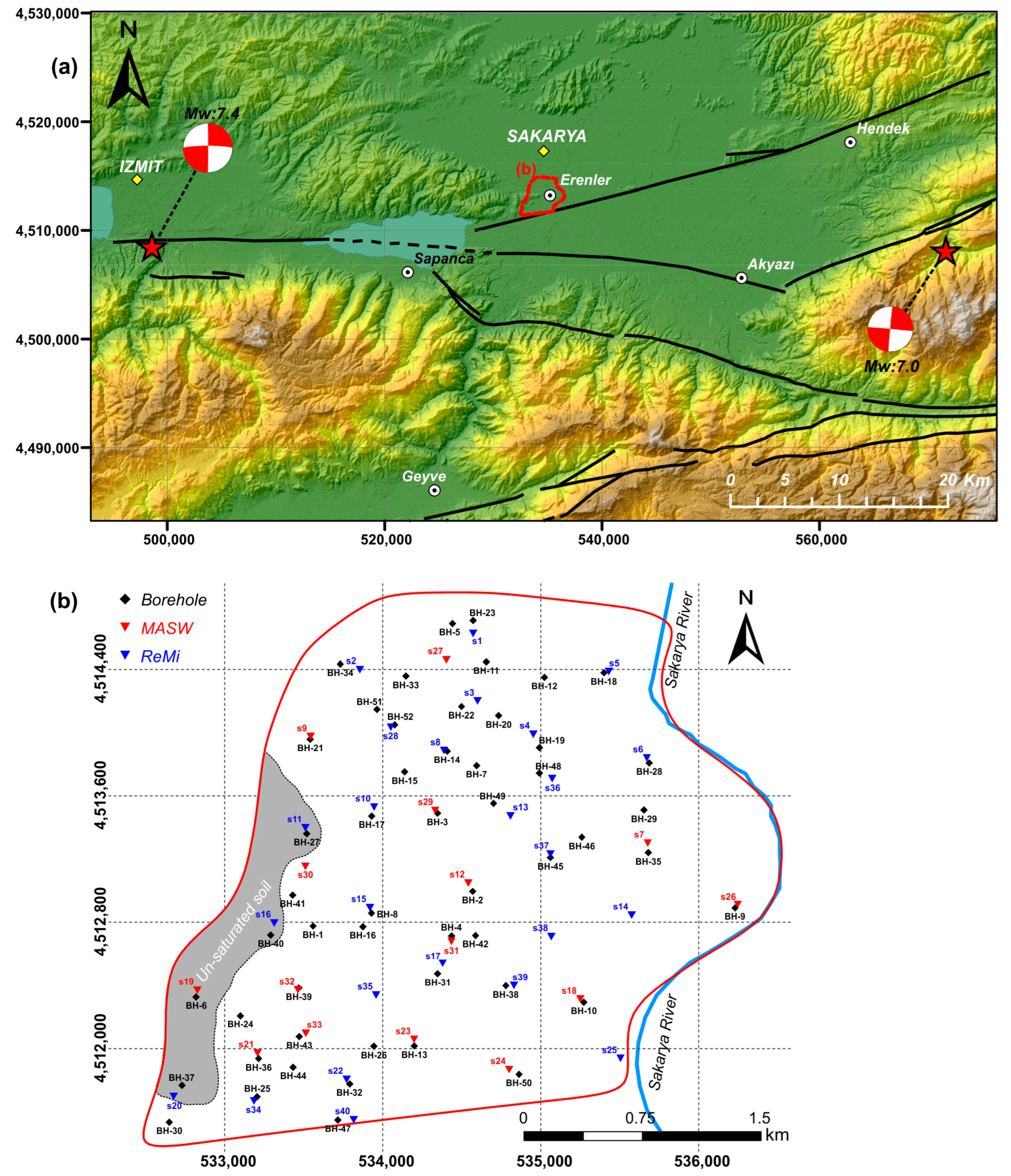
:1. Introduction
2. Geological and Tectonic Features
3. Liquefaction Approaches
3.1. Earthquake Selection and PGA Estimation
3.2. Liquefaction Probability Based on SPT-N
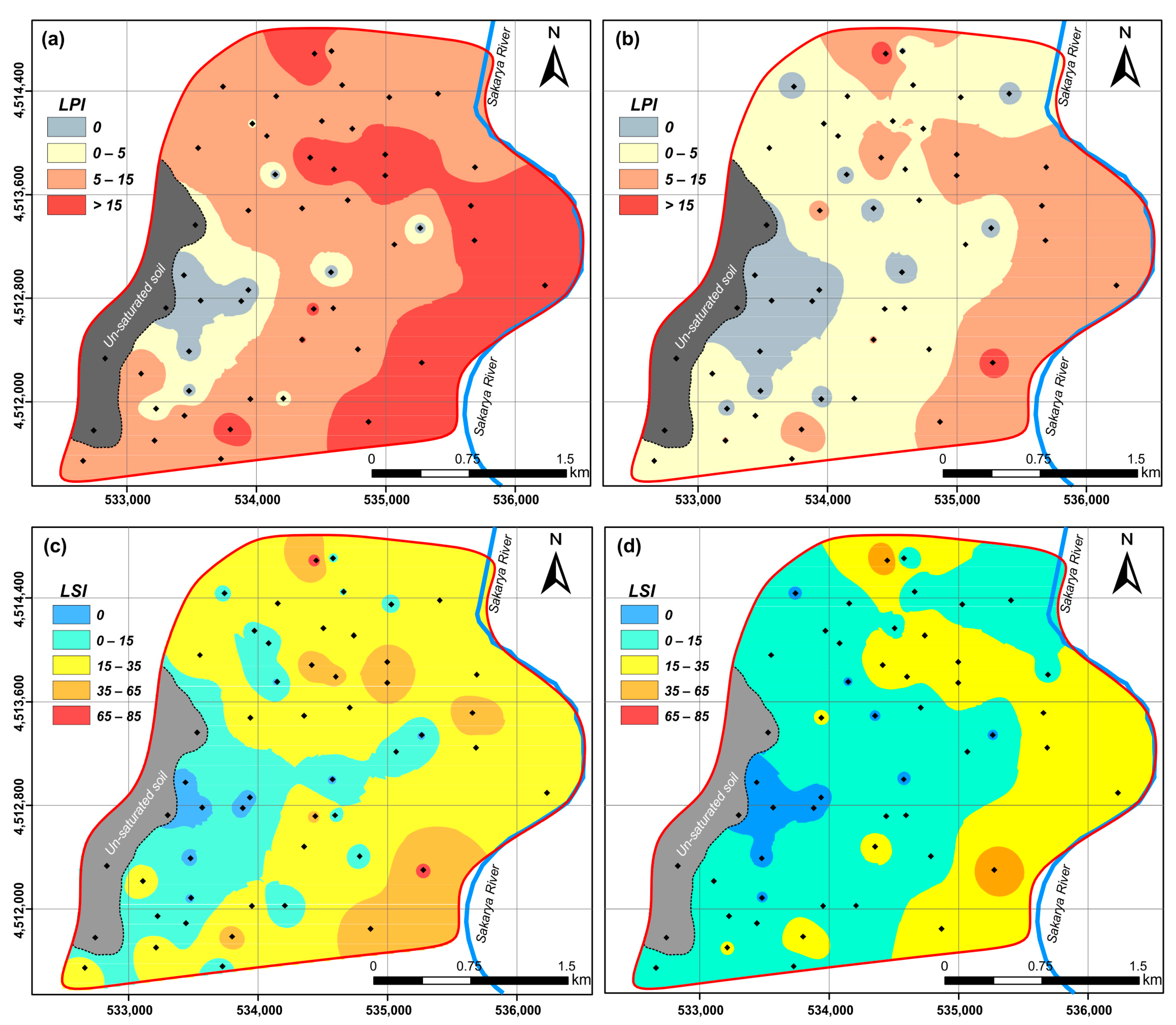
3.2.1. Liquefaction Potential Index (LPI)
3.2.2. Liquefaction Severity Index (LSI)
3.2.3. Ishihara Boundary Curve (IB)
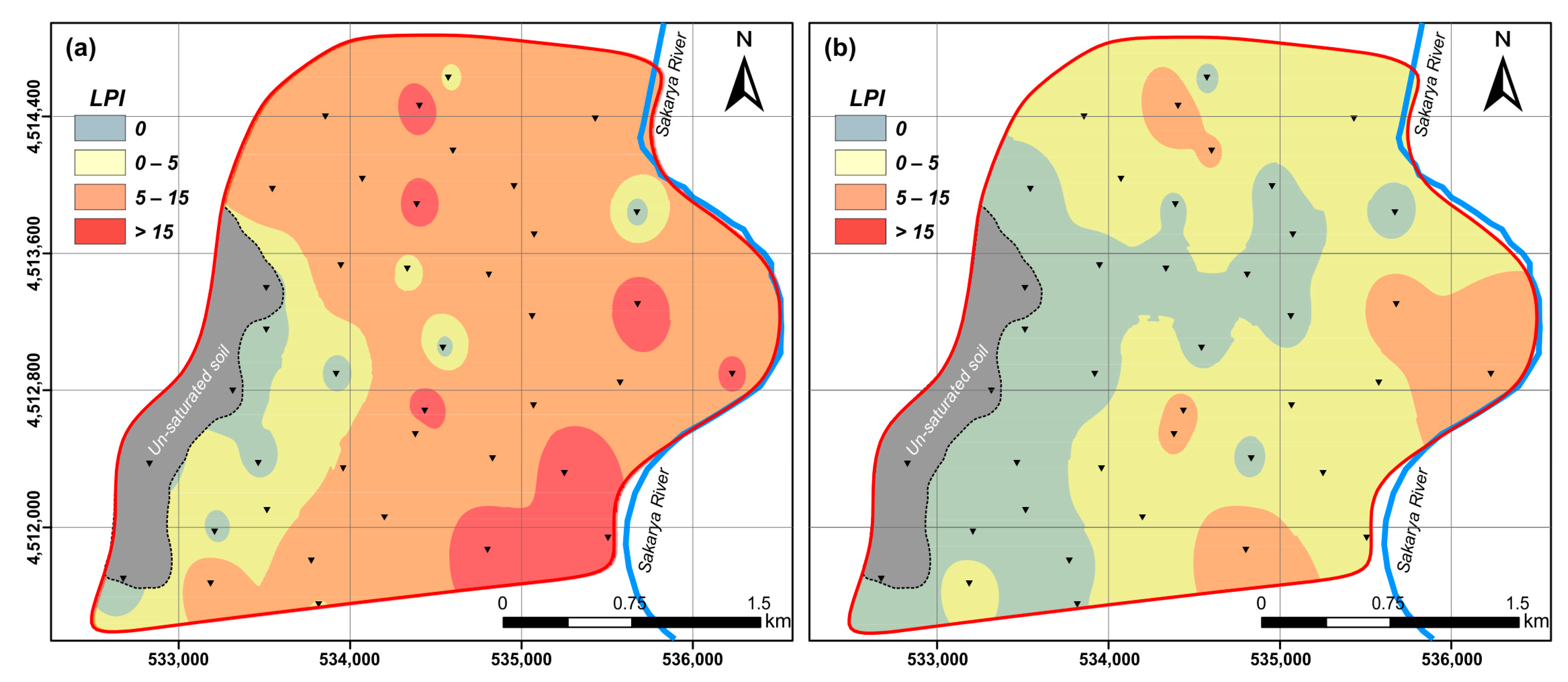
3.2.4. Ishihara-Inspired Index (LPIISH)
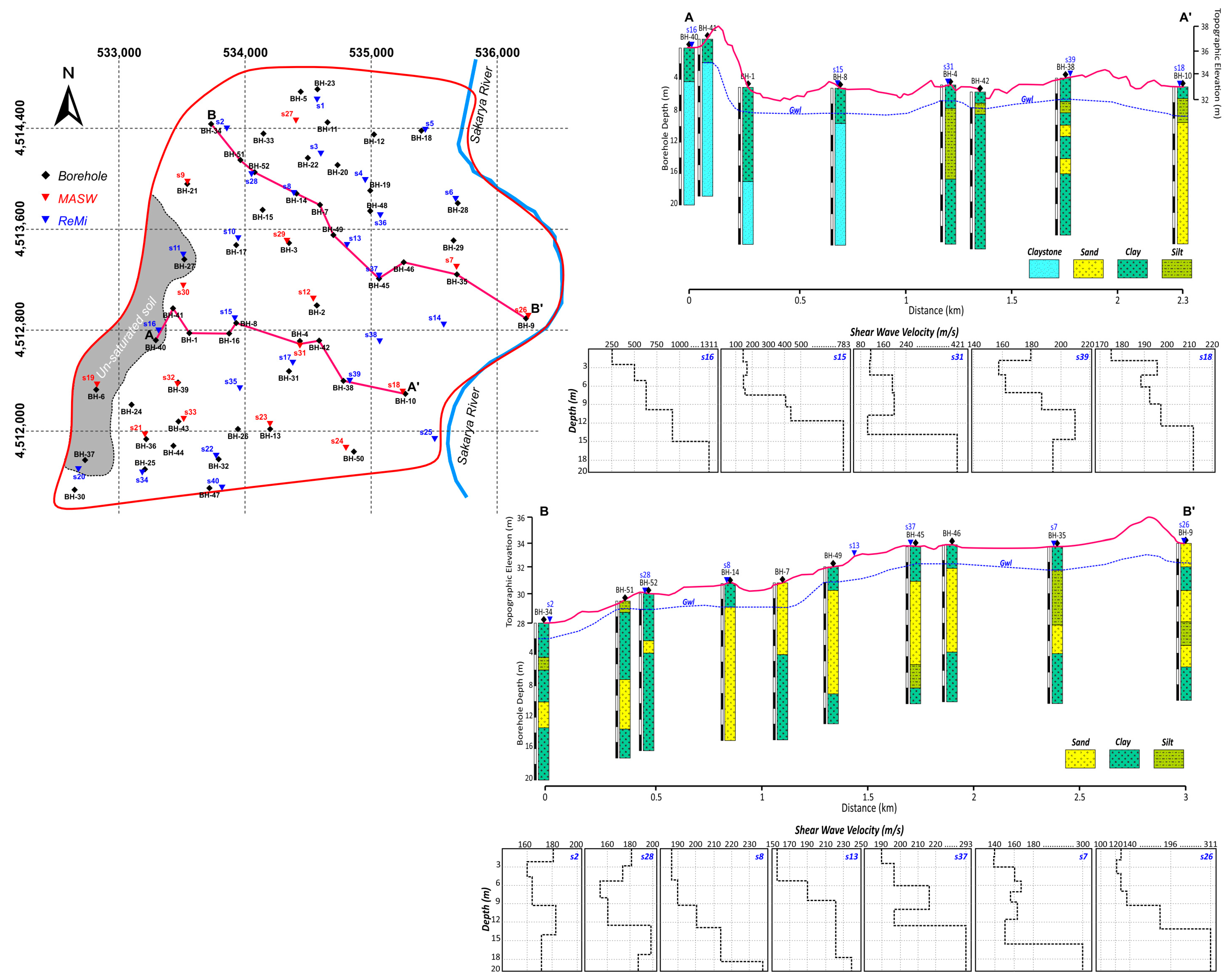
3.3. Shear Wave-Based Liquefaction Analysis
3.3.1. Surface Wave Data Acquisition
3.3.2. Liquefaction Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seed, H.B.; Idriss, I.M. Simplified Procedure for Evaluating Soil Liquefaction Potential. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1971, 97, 1249–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, H.B. Soil Liquefaction and Cyclic Mobility Evaluation for Level Ground during Earthquakes. J. Geotech. Eng. Div. 1979, 105, 201–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, H.B.; Idriss, I.M. Ground Motions and Soil Liquefaction during Earthquakes; Earthquake Engineering Research Insititue: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1982; p. 134. [Google Scholar]
- Youd, T.L.; Idriss, I.M.; Andrus, R.D.; Arango, I.; Castro, G.; Christian, J.T.; Dobry, R.; Finn, W.D.L.; Harder, L.F.; Hynes, M.E.; et al. Liquefaction Resistance of Soils: Summary Report from the 1996 NCEER and 1998 NCEER/NSF Workshops on Evaluation of Liquefaction Resistance of Soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2001, 127, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seed, H.B.; Idriss, I.M.; Arango, I. Evaluation of Liquefaction Potential Using Field Performance Data. J. Geotech. Eng. 1983, 109, 458–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, K.O.; Seed, R.B.; Der Kiureghian, A.; Tokimatsu, K.; Harder, L.F., Jr.; Kayen, R.E.; Moss, R.E. Standard Penetration Test-Based Probabilistic and Deterministic Assessment of Seismic Soil Liquefaction Potential. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 1314–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixit, J.; Dewaikar, D.M.; Jangid, R.S. Assessment of Liquefaction Potential Index for Mumbai City. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 2759–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cetin, K.O.; Seed, R.B.; Kayen, R.E.; Moss, R.E.; Bilge, H.T.; Ilgac, M.; Chowdhury, K. SPT-Based Probabilistic and Deterministic Assessment of Seismic Soil Liquefaction Triggering Hazard. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 115, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobry, R.; Stokoe, K.H.; Ladd, R.S.; Youd, T.L. Liquefaction Susceptibility from S-Wave Velocity. In Proceedings of the In-Situ Tests to Evaluate Liquefaction Susceptibility, ASCE National Convention, St. Louis, MO, USA, 26–30 October 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, P.K.; Woeller, D.J.; Finn, W.D.L. Seismic Cone Penetration Test for Evaluating Liquefaction Potential under Cyclic Loading. Can. Geotech. J. 1992, 29, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrus, R.D.; Stokoe, K.H. Liquefaction Resistance Based on Shear Wave Velocity: Report to the NCEER Workshop on Evaluation of Liquefaction Resistance (NCEER-97-0022); National Center for Earthquake Engineering Research: Buffalo, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 89–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kayen, R.; Moss, R.; Thompson, E.M.; Seed, R.; Cetin, K.; Kiureghian, A.D.; Tanaka, Y.; Tokimatsu, K. Shear-Wave Velocity–Based Probabilistic and Deterministic Assessment of Seismic Soil Liquefaction Potential. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2013, 139, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrus, R.D.; Stokoe, K.H.; Hsein Juang, C. Guide for Shear-Wave-Based Liquefaction Potential Evaluation. Earthq. Spectra 2004, 20, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.-G.; Chen, Y.-M. Laboratory Investigation on Assessing Liquefaction Resistance of Sandy Soils by Shear Wave Velocity. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2007, 133, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyanık, O. Soil Liquefaction Analysis Based on Soil and Earthquake Parameters. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 176, 104004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T. A Practical Method for Assessing Soil Liquefaction Potential Based on Case Studies at Various Sites in Japan. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference Microzonation Safer Construction Research Application, San Francisco, CA, USA, 26 November–1 December 1978; Volume 2, pp. 885–896. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, T.; Tokida, K.; Tatsuoka, F.; Watanabe, S.; Yasuda, S.; Sato, H. Microzonation for Soil Liquefaction Potential Using Simplified Methods. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Microzonation, Seattle, WA, USA, 28 June–1 July 1982; Volume 3, pp. 1310–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.J.; Juang, C.H. Calibration of SPT-and CPT-Based Liquefaction Evaluation Methods. In Innovations and Applications in Geotechnical Site Characterization; ASCE Geo-Institute: Denver, CO, USA, 2000; pp. 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Juang, C.H.; Yuan, H.; Lee, D.-H.; Lin, P.-S. Simplified Cone Penetration Test-Based Method for Evaluating Liquefaction Resistance of Soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2003, 129, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Ku, C.-S.; Yuan, H. A Study of the Liquefaction Risk Potential at Yuanlin, Taiwan. Eng. Geol. 2004, 71, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, H.; Gokceoglu, C. A Liquefaction Severity Index Suggested for Engineering Practice. Environ. Geol. 2005, 48, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, M.; Ozvan, A.; Akin, M.K.; Topal, T. Evaluation of Liquefaction in Karasu River Floodplain after the October 23, 2011, Van (Turkey) Earthquake. Nat. Hazards 2013, 69, 1551–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunusluoglu, M.C.; Karaca, O. Liquefaction Severity Mapping Based on SPT Data: A Case Study in Canakkale City (NW Turkey). Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K. Stability of Natural Deposits during Earthquakes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–16 August 1985; pp. 321–376. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, B.W.; Green, R.A.; Taylor, O.-D.S. Moving towards an Improved Index for Assessing Liquefaction Hazard: Lessons from Historical Data. Soils Found. 2015, 55, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sancio, R.B.; Bray, J.D.; Stewart, J.P.; Youd, T.L.; Durgunoǧlu, H.T.; Önalp, A.; Seed, R.B.; Christensen, C.; Baturay, M.B.; Karadayılar, T. Correlation between Ground Failure and Soil Conditions in Adapazari, Turkey. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2002, 22, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, E.; Önalp, A.; Arel, E.; Sert, S.; Özocak, A. Liquefaction of Silts: The Adapazari Criteria. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2010, 8, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, R.W.; Munter, S.K.; Krage, C.P.; DeJong, J.T. Liquefaction Evaluation of Interbedded Soil Deposit: Çark Canal in 1999 M7. 5 Kocaeli Earthquake. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2019, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, K.O.; Youd, T.L.; Seed, R.B.; Bray, J.D.; Sancio, R.; Lettis, W.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Durgunoglu, H.T. Liquefaction-Induced Ground Deformations at Hotel Sapanca during Kocaeli (Izmit), Turkey Earthquake. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2002, 22, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, Ö.; Duman, T.Y.; Özalp, S.; Şaroğlu, F.; Olgun, Ş.; Elmacı, H.; Çan, T. Active Fault Database of Turkey. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 16, 3229–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariaslan, M.M.; Yurdakul, M.E.; Osmancelebioglu, R.; Kecer, M.; Basa, F.; Senturk, K. Environmental Geology of Sakarya City and Its Natural Resources; MTA: Geology Research Department: Ankara, Turkey, 1998; pp. 1–144. [Google Scholar]
- Barka, A.A.; Kadinsky-Cade, K. Strike-Slip Fault Geometry in Turkey and Its Influence on Earthquake Activity. Tectonics 1988, 7, 663–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilinger, R.; McClusky, S.; Vernant, P.; Lawrence, S.; Ergintav, S.; Cakmak, R.; Ozener, H.; Kadirov, F.; Guliev, I.; Stepanyan, R.; et al. GPS Constraints on Continental Deformation in the Africa-Arabia-Eurasia Continental Collision Zone and Implications for the Dynamics of Plate Interactions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2006, 111, B5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkucu, M.; Budakoğlu, E.; Durmuş, H. Marmara Bölgesinde (KB Türkiye) Depremsellik ve Deprem Tehlikesi Üzerine Bir Tartışma. Yerbilimleri 2011, 32, 141–168. [Google Scholar]
- Barka, A.; Akyuz, H.S.; Altunel, E.; Sunal, G.; Cakir, Z.; Dikbas, A.; Yerli, B.; Armijo, R.; Meyer, B.; De Chabalier, J.B. The Surface Rupture and Slip Distribution of the 17 August 1999 Izmit Earthquake (M 7.4), North Anatolian Fault. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2002, 92, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graizer, V.; Kalkan, E. Summary of the GK15 Ground-Motion Prediction Equation for Horizontal PGA and 5% Damped PSA from Shallow Crustal Continental Earthquakes. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2016, 106, 687–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, K.O.; Seed, R.B. Nonlinear Shear Mass Participation Factor (Rd) for Cyclic Shear Stress Ratio Evaluation. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2004, 24, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.-W.; Rogers, J.D. Simplified Method for Spatial Evaluation of Liquefaction Potential in the St. Louis Area. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.Z.; Siddiqua, S.; Kamal, A.S.M.M. Liquefaction Hazard Mapping by Liquefaction Potential Index for Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Eng. Geol. 2015, 188, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kim, M.; Baise, L.G.; Kim, B. Local and Regional Evaluation of Liquefaction Potential Index and Liquefaction Severity Number for Liquefaction-Induced Sand Boils in Pohang, South Korea. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 141, 106459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, B.; Ulusay, R.; Sonmez, H. A Study on the Identification of Liquefaction-Induced Failures on Ground Surface Based on the Data from the 1999 Kocaeli and Chi-Chi Earthquakes. Eng. Geol. 2008, 97, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ballegooy, S.; Green, R.A.; Lees, J.; Wentz, F.; Maurer, B.W. Assessment of Various CPT Based Liquefaction Severity Index Frameworks Relative to the Ishihara (1985) H1–H2 Boundary Curves. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2015, 79, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-G.; Xia, P.; Ling, D.-S.; Chen, Y.-M. Liquefaction Case Studies of Gravelly Soils during the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake. Eng. Geol. 2020, 274, 105691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.A.; Bommer, J.J.; Rodriguez-Marek, A.; Maurer, B.W.; Stafford, P.J.; Edwards, B.; Kruiver, P.P.; De Lange, G.; Van Elk, J. Addressing Limitations in Existing ‘Simplified’Liquefaction Triggering Evaluation Procedures: Application to Induced Seismicity in the Groningen Gas Field. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 17, 4539–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyin, M.; Baird, A.J.; Maurer, B.W. Field Assessment of Liquefaction Prediction Models Based on Geotechnical versus Geospatial Data, with Lessons for Each. Earthq. Spectra 2020, 36, 1386–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Miller, R.; Xia, J. Multichannel Analysis of Surface Waves (MASW). Geophysics 1999, 64, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louie, J.N. Faster, Better: Shear-Wave Velocity to 100 Meters Depth from Refraction Microtremor Arrays. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2001, 91, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, S.; Parolai, S.; Albarello, D.; Picozzi, M. Application of Surface-Wave Methods for Seismic Site Characterization. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 777–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.Z.; Siddiqua, S.; Kamal, A.S.M.M. Shear Wave Velocity Estimation of the Near-Surface Materials of Chittagong City, Bangladesh for Seismic Site Characterization. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 134, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silahtar, A.; Kanbur, M.Z.; Beyhan, G. Analysis of Seismic Site Characterization of the Isparta Basin (Southwestern Turkey) Using Passive Surface-Wave Method (ReMiTM) and Borehole Data. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Miller, R.D.; Park, C.B.; Hunter, J.A.; Harris, J.B.; Ivanov, J. Comparing Shear-Wave Velocity Profiles Inverted from Multichannel Surface Wave with Borehole Measurements. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2002, 22, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorson, J.R.; Claerbout, J.F. Velocity-stack and Slant-stack Stochastic Inversion. Geophysics 1985, 50, 2727–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.B.; Miller, R.D.; Miura, H. Optimum Field Parameters of an MASW Survey. Jpn. Soc. Explor. Geophys. Ext. Abstr. 2002, 36, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Louie, J.N.; Pancha, A.; Kissane, B. Guidelines and Pitfalls of Refraction Microtremor Surveys. J. Seismol. 2022, 26, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobry, R.; Abdoun, T.; Stokoe, K.H.; Moss, R.E.S.; Hatton, M.; El Ganainy, H. Liquefaction Potential of Recent Fills versus Natural Sands Located in High-Seismicity Regions Using Shear-Wave Velocity. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakir, B.S.; Sucuoglu, H.; Yilmaz, T. An Overview of Local Site Effects and the Associated Building Damage in Adapazari during the 17 August 1999 Izmit Earthquake. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2002, 92, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, M.; Acharya, I.P. Liquefaction Hazard Assessment and Ground Failure Probability Analysis in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal. Geoenviron. Disasters 2022, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.Z.; Siddiqua, S. Evaluation of Liquefaction-Resistance of Soils Using Standard Penetration Test, Cone Penetration Test, and Shear-Wave Velocity Data for Dhaka, Chittagong, and Sylhet Cities in Bangladesh. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Method | Masw | ReMi |
|---|---|---|
| Number of channels | 24 | 24 |
| Sample rate (ms) | 0.5 | 2 |
| Record length (sec) | 1 | 30 |
| Receiver spacing (m) | 3 | 3 |
| Minimal offset (m) | 12 | - |
| Array length (m) | 72 | 69 |
| Geophone frequency (Hz) | 4.5 | 4.5 |
| Number of stacks | 8–10 | 8–10 |
| Source | 10 kg sledgehammer | Ambient noise |
| Borehole | Coordinates Turef-TM30 | Gwl | 1999 Izmit | 1967 Mudurnu | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | LPI | LSI | LPIISH | LPI | LSI | LPIISH | ||
| BH-1 | 533,554 | 4,510,978 | 3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-2 | 534,561 | 4,511,197 | 2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-3 | 534,340 | 4,511,691 | 3 | 8.85 | 24.09 | 5.32 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-4 | 534,427 | 4,510,913 | 2 | 16.59 | 38.95 | 8.36 | 2.50 | 13.43 | 0 |
| BH-5 | 534,435 | 4,512,886 | 2 | 43.98 | 73.77 | 34.72 | 21.99 | 59.02 | 16.62 |
| BH-6 | 532,817 | 4,510,531 | - | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-7 | 534,586 | 4,511,991 | 3 | 16.68 | 37.23 | 11.26 | 0.96 | 15.66 | 0 |
| BH-8 | 533,923 | 4,511,060 | 3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-9 | 536,216 | 4,511,094 | 2.5 | 6.84 | 9.88 | 16.12 | 4.71 | 9.32 | 11.1 |
| BH-10 | 535,262 | 4,510,498 | 3.5 | 38.00 | 67.20 | 22.01 | 17.38 | 47.81 | 6.76 |
| BH-11 | 534,647 | 4,512,644 | 2 | 7.25 | 14.39 | 4.73 | 1.66 | 8.94 | 0 |
| BH-12 | 535,013 | 4,512,548 | 2.5 | 6.57 | 11.75 | 5.58 | 2.70 | 8.77 | 0 |
| BH-13 | 534,192 | 4,510,223 | 2 | 4.26 | 7.45 | 0 | 1.90 | 5.76 | 0 |
| BH-14 | 534,399 | 4,512,082 | 3 | 27.96 | 50.90 | 18.08 | 13.36 | 34.06 | 8.51 |
| BH-15 | 534,132 | 4,511,951 | 1.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-16 | 533,867 | 4,510,975 | 2.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-17 | 533,924 | 4,511,673 | 1.8 | 14.82 | 28.05 | 8.92 | 5.87 | 16.40 | 1.92 |
| BH-18 | 535,389 | 4,512,576 | 1.8 | 10.76 | 28.81 | 11.33 | 0.26 | 6.34 | 0 |
| BH-19 | 534,982 | 4,512,105 | 2.5 | 23.45 | 42.99 | 16.15 | 10.01 | 26.47 | 6.31 |
| BH-20 | 534,725 | 4,512,306 | 3 | 13.96 | 26.06 | 0 | 4.74 | 18.08 | 0 |
| BH-21 | 533,536 | 4,512,157 | 1.7 | 8.33 | 17.18 | 0 | 1.53 | 6.34 | 0 |
| BH-22 | 534,490 | 4,512,363 | 1.5 | 9.83 | 16.83 | 0 | 4.60 | 13.10 | 0 |
| BH-23 | 534,564 | 4,512,905 | 3.5 | 5.13 | 11.05 | 4.36 | 0.27 | 5.84 | 0 |
| BH-24 | 533,095 | 4,510,413 | 2.5 | 11.89 | 25.63 | 0 | 2.73 | 13.10 | 0 |
| BH-25 | 533,199 | 4,509,899 | 2 | 12.18 | 21.70 | 0 | 5.09 | 16.28 | 0 |
| BH-26 | 533,939 | 4,510,220 | 2 | 6.34 | 17.61 | 0 | 0.08 | 4.09 | 0 |
| BH-27 | 533,514 | 4,511,562 | - | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-28 | 535,674 | 4,512,007 | 2 | 10.51 | 15.27 | 6.87 | 7.15 | 14.31 | 4.68 |
| BH-29 | 535,641 | 4,511,710 | 3 | 27.27 | 53.72 | 15.44 | 8.26 | 23.16 | 2.5 |
| BH-30 | 532,647 | 4,509,742 | 2 | 10.76 | 19.92 | 6.75 | 3.72 | 13.90 | 0 |
| BH-31 | 534,340 | 4,510,677 | 2 | 15.19 | 28.27 | 0 | 5.12 | 19.54 | 0 |
| BH-32 | 533,785 | 4,509,983 | 2.5 | 26.13 | 48.06 | 17.23 | 9.83 | 30.30 | 4.53 |
| BH-33 | 534,140 | 4,512,555 | 2.5 | 7.78 | 16.38 | 0 | 2.37 | 7.35 | 0 |
| BH-34 | 533,726 | 4,512,632 | 2 | 5.66 | 14.49 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-35 | 535,669 | 4,511,442 | 3 | 10.93 | 20.91 | 8.05 | 3.22 | 13.89 | 0 |
| BH-36 | 533,211 | 4,510,142 | 3 | 2.01 | 4.03 | 0 | 0.43 | 2.46 | 0 |
| BH-37 | 532,728 | 4,509,975 | - | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-38 | 534,770 | 4,510,602 | 3 | 5.79 | 11.43 | 4.92 | 1.38 | 7.17 | 0 |
| BH-39 | 533,465 | 4,510,588 | 2.5 | 7.81 | 18.39 | 0 | 0.93 | 7.06 | 0 |
| BH-40 | 533,287 | 4,510,922 | - | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-41 | 533,425 | 4,511,173 | 3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-42 | 534,579 | 4,510,919 | 2 | 7.72 | 13.00 | 10.27 | 3.87 | 10.59 | 5.14 |
| BH-43 | 533,467 | 4,510,282 | 2.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-44 | 533,428 | 4,510,088 | 1.5 | 6.80 | 11.67 | 0 | 3.22 | 9.25 | 0 |
| BH-45 | 535,052 | 4,511,410 | 2.5 | 5.15 | 9.02 | 0 | 2.38 | 6.01 | 0 |
| BH-46 | 535,249 | 4,511,539 | 2.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| BH-47 | 533,706 | 4,509,708 | 2.3 | 6.22 | 9.80 | 0 | 3.67 | 8.63 | 0 |
| BH-48 | 534,982 | 4,511,944 | 2.5 | 26.50 | 48.65 | 24.21 | 9.77 | 26.63 | 9.32 |
| BH-49 | 534,693 | 4,511,753 | 2 | 10.36 | 25.23 | 6.26 | 1.36 | 5.02 | 0 |
| BH-50 | 534,853 | 4,510,043 | 2.5 | 24.49 | 51.96 | 10.6 | 5.53 | 23.13 | 0 |
| BH-51 | 533,956 | 4,512,344 | 1 | 4.66 | 14.27 | 0 | 2.89 | 12.89 | 0 |
| BH-52 | 534,066 | 4,512,249 | 2 | 6.10 | 9.77 | 0 | 3.46 | 8.45 | 0 |
| Data Acquisition Point | Coordinates Turef-TM30 | Vs30 (m/s) | Vs12 (m/s) | Data Acquisition Point | Coordinates Turef-TM30 | Vs30 (m/s) | Vs12 (m/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | X | Y | ||||||
| s1 | 534,565 | 4,512,821 | 208 | 195 | s21 | 533,204 | 4,510,176 | 264 | 168 |
| s2 | 533,850 | 4,512,593 | 185 | 170 | s22 | 533,766 | 4,510,008 | 203 | 189 |
| s3 | 534,593 | 4,512,396 | 198 | 171 | s23 | 534,192 | 4,510,260 | 226 | 150 |
| s4 | 534,945 | 4,512,187 | 216 | 193 | s24 | 534,792 | 4,510,072 | 178 | 146 |
| s5 | 535,420 | 4,512,582 | 200 | 193 | s25 | 535,494 | 4,510,141 | 204 | 151 |
| s6 | 535,660 | 4,512,037 | 235 | 229 | s26 | 536,216 | 4,511,094 | 216 | 159 |
| s7 | 535,666 | 4,511,500 | 211 | 166 | s27 | 534,396 | 4,512,656 | 215 | 173 |
| s8 | 534,380 | 4,512,082 | 202 | 180 | s28 | 534,064 | 4,512,231 | 187 | 193 |
| s9 | 533,540 | 4,512,171 | 193 | 154 | s29 | 534,325 | 4,511,706 | 238 | 668 |
| s10 | 533,940 | 4,511,726 | 230 | 188 | s30 | 533,506 | 4,511,352 | 1098 | 150 |
| s11 | 533,506 | 4,511,595 | 374 | 266 | s31 | 534,428 | 4,510,880 | 207 | 301 |
| s12 | 534,534 | 4,511,248 | 438 | 242 | s32 | 533,460 | 4,510,573 | 421 | 153 |
| s13 | 534,800 | 4,511,672 | 211 | 184 | s33 | 533,509 | 4,510,300 | 269 | 170 |
| s14 | 535,564 | 4,511,045 | 193 | 192 | s34 | 533,182 | 4,509,874 | 205 | 184 |
| s15 | 533,913 | 4,511,093 | 362 | 550 | s35 | 533,953 | 4,510,542 | 197 | 202 |
| s16 | 533,311 | 4,510,997 | 806 | 181 | s36 | 535,064 | 4,511,908 | 231 | 181 |
| s17 | 534,372 | 4,510,742 | 230 | 194 | s37 | 535,053 | 4,511,429 | 253 | 203 |
| s18 | 535,241 | 4,510,515 | 226 | 216 | s38 | 535,059 | 4,510,910 | 211 | 168 |
| s19 | 532,825 | 4,510,571 | 363 | 997 | s39 | 534,821 | 4,510,601 | 193 | 189 |
| s20 | 532,655 | 4,509,903 | 1068 | 195 | s40 | 533,799 | 4,509,698 | 219 | 150 |
| NEHRP Site Class | Rock/Soil Type | Vs30 (m/s) |
| A | Hard rock | >1500 |
| B | Rock | 760–1500 |
| C | Dense soil/soft rock | 360–760 |
| D | Stiff soil | 180–360 |
| E | Soft soil | <180 |
| Data Acquisition Point | Coordinates Turef-TM30 | LPI | Data Acquisition Point | Coordinates Turef-TM30 | LPI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | 1999 Izmit | 1967 Mudurnu | X | Y | 1999 Izmit | 1967 Mudurnu | ||
| s1 | 534,565 | 4,512,821 | 3.48 | 0 | s21 | 533,204 | 4,510,176 | 0 | 0 |
| s2 | 533,850 | 4,512,593 | 9.92 | 2.04 | s22 | 533,766 | 4,510,008 | 9.22 | 0 |
| s3 | 534,593 | 4,512,396 | 10.5 | 5.65 | s23 | 534,192 | 4,510,260 | 5.38 | 3.77 |
| s4 | 534,945 | 4,512,187 | 10.34 | 0.27 | s24 | 534,792 | 4,510,072 | 23.5 | 10.45 |
| s5 | 535,420 | 4,512,582 | 12.86 | 3.12 | s25 | 535,494 | 4,510,141 | - | - |
| s6 | 535,660 | 4,512,037 | 0 | 0 | s26 | 536,216 | 4,511,094 | 15.16 | 9.5 |
| s7 | 535,666 | 4,511,500 | 18.73 | 7.25 | s27 | 534,396 | 4,512,656 | 19.96 | 10.63 |
| s8 | 534,380 | 4,512,082 | 19.84 | 0.48 | s28 | 534,064 | 4,512,231 | 5.72 | 2.77 |
| s9 | 533,540 | 4,512,171 | 6.4 | 0 | s29 | 534,325 | 4,511,706 | 3.27 | 0 |
| s10 | 533,940 | 4,511,726 | 9.48 | 0.1 | s30 | 533,506 | 4,511,352 | 0 | 0 |
| s11 | 533,506 | 4,511,595 | 0 | 0 | s31 | 534,428 | 4,510,880 | 20.36 | 6.07 |
| s12 | 534,534 | 4,511,248 | 0 | 0 | s32 | 533,460 | 4,510,573 | 0 | 0 |
| s13 | 534,800 | 4,511672 | 10.52 | 0.8 | s33 | 533,509 | 4,510,300 | 4.48 | 0.65 |
| s14 | 535,564 | 4,511,045 | - | - | s34 | 533,182 | 4,509,874 | 9.04 | 1.74 |
| s15 | 533,913 | 4,511,093 | 0 | 0 | s35 | 533,953 | 4,510,542 | - | - |
| s16 | 533,311 | 4,510,997 | 0 | 0 | s36 | 535,064 | 4,511,908 | 12.03 | 0 |
| s17 | 534,372 | 4,510,742 | 11.86 | 5.46 | s37 | 535,053 | 4,511,429 | 6.2 | 0.58 |
| s18 | 535,241 | 4,510,515 | 18.58 | 3.25 | s38 | 535,059 | 4,510,910 | - | - |
| s19 | 532,825 | 4,510,571 | 0 | 0 | s39 | 534,821 | 4,510,601 | 6.93 | 0 |
| s20 | 532,655 | 4,509,903 | 0 | 0 | s40 | 533,799 | 4,509,698 | 4.64 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silahtar, A.; Karaaslan, H.; Kocaman, K. Site Characterization and Liquefaction Hazard Assessment for the Erenler Settlement Area (Sakarya Province, Turkey) Based on Integrated SPT-Vs Data. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021534
Silahtar A, Karaaslan H, Kocaman K. Site Characterization and Liquefaction Hazard Assessment for the Erenler Settlement Area (Sakarya Province, Turkey) Based on Integrated SPT-Vs Data. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021534
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilahtar, Ali, Hasan Karaaslan, and Kadir Kocaman. 2023. "Site Characterization and Liquefaction Hazard Assessment for the Erenler Settlement Area (Sakarya Province, Turkey) Based on Integrated SPT-Vs Data" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021534
APA StyleSilahtar, A., Karaaslan, H., & Kocaman, K. (2023). Site Characterization and Liquefaction Hazard Assessment for the Erenler Settlement Area (Sakarya Province, Turkey) Based on Integrated SPT-Vs Data. Sustainability, 15(2), 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021534





