Vermicompost: An Eco-Friendly and Cost-Effective Alternative for Sustainable Agriculture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design and Procedures
2.1. Digested Biogas Slurry and Agricultural Residues
2.2. Initial Preparation of Varied Fresh Solid Wastes
2.3. Experimental Design for Vermicomposting
2.4. Physico-Chemical Analysis
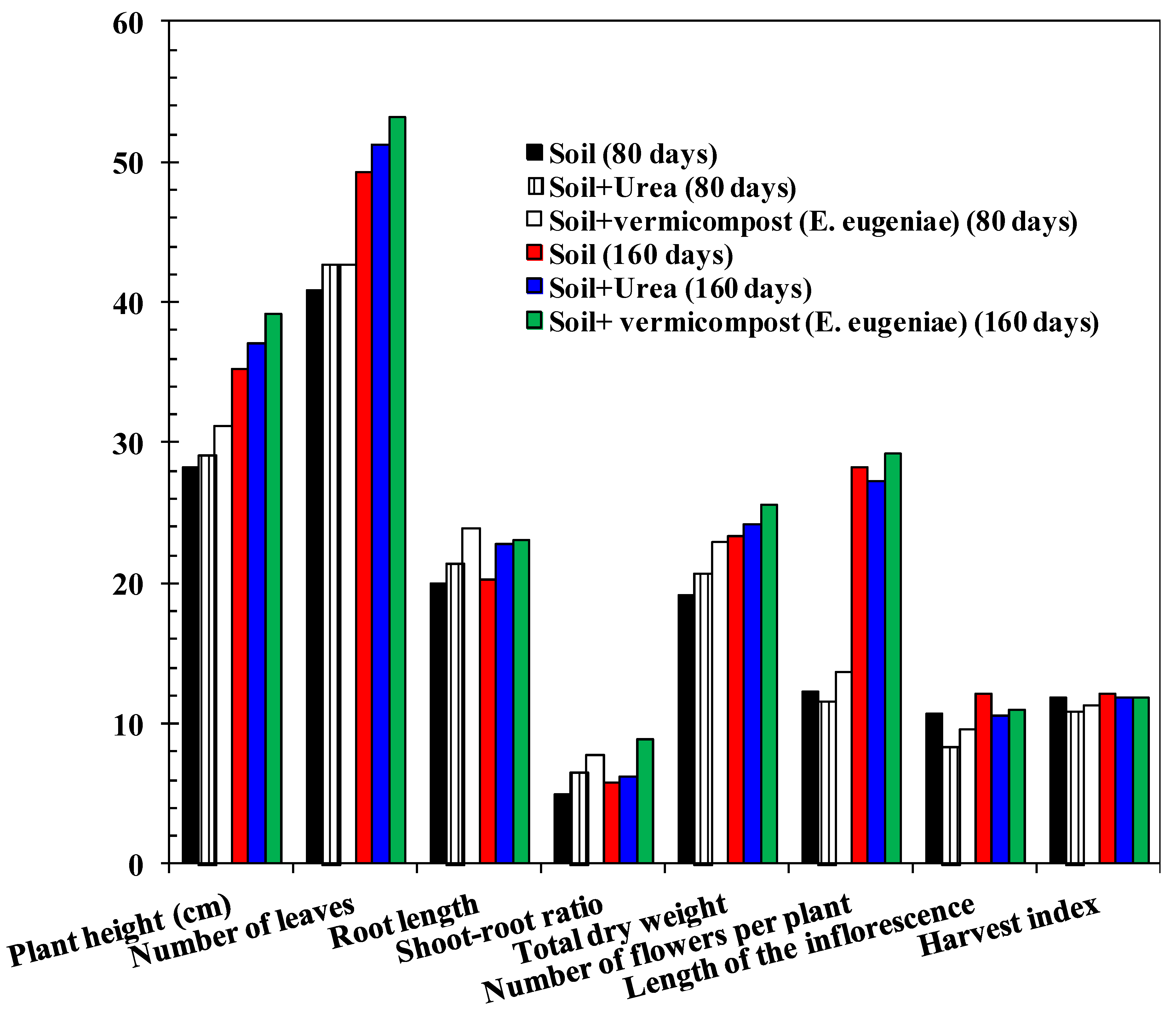
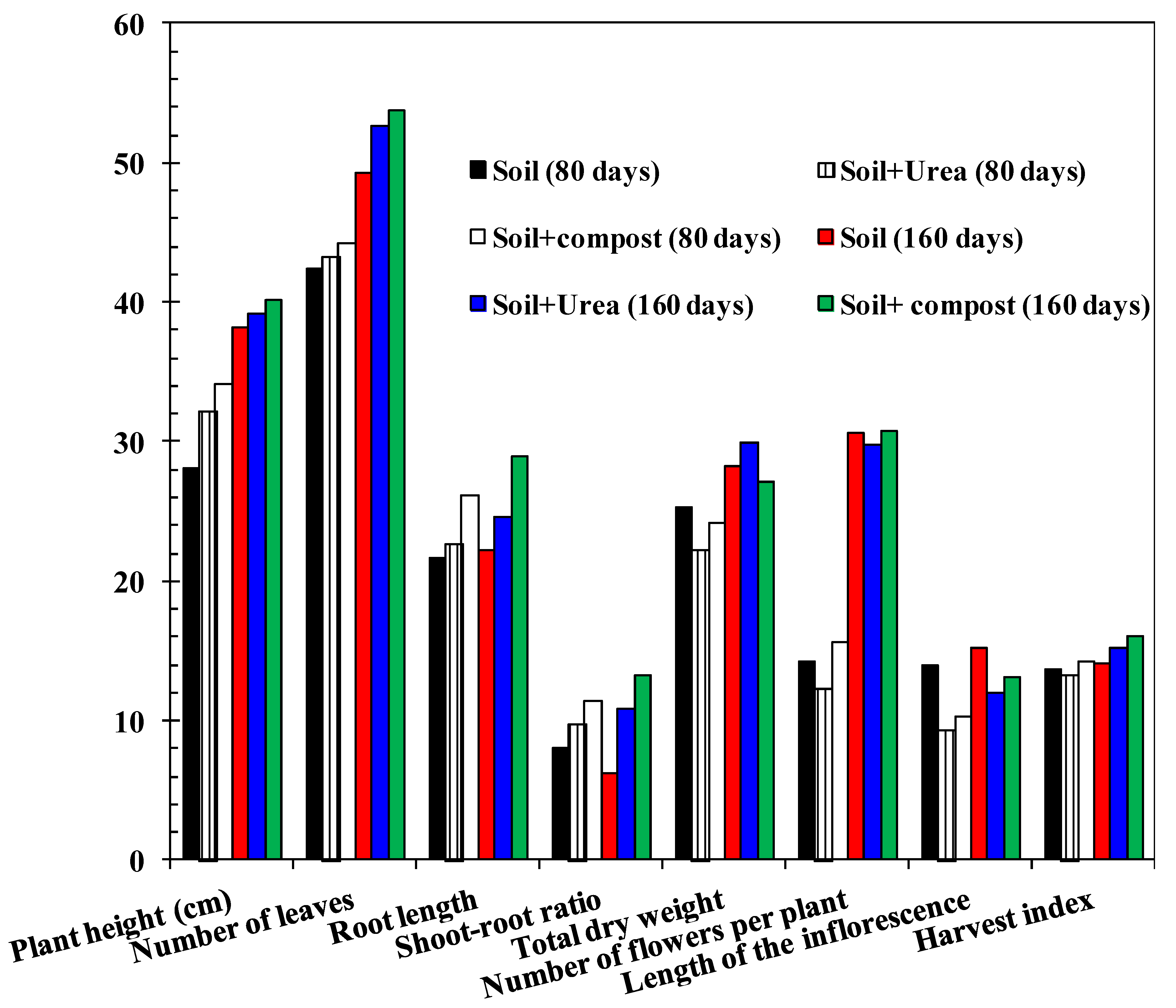
2.5. Plant Growth
2.6. Tests of Significance
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- One notable observation was the marked influence of worm density on the increase in zoomass. The most substantial growth occurred at a worm density of 125 animals/L, which outperformed densities of 62.5, 250, and 350 animals/L.
- The resultant NPK values ranged between 1.5 and 1.7% (N), 0.98 and 1.19% (P), and 1.1 and 1.49% (K) across various composted–vermicomposted wastes, underscoring the potential of the final vermicompost product as a marketable soil fertility enhancer.
- Exploring the effects of worm loading, a recovery of 64.4% was noted with E. fetida at 62.5 animals per liter, whereas E. eugeniae achieved 45.6%. Increasing the density to 125 animals per liter resulted in recoveries of 89.7% and 68.2% for E. fetida and E. eugeniae reactors, respectively on vermicast production.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rehman, Z.U.; Ijaz, N.; Ye, W.; Ijaz, Z. Design optimization and statistical modeling of recycled waste-based additive for a variety of construction scenarios on heaving ground. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 39783–39802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, V. A review on current status of municipal solid waste management in India. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, R.B.; Suresh, S.; Sharma, A.K. Solid waste management in Bhopal (India): Present and future challenges. Ultra Chem. 2013, 9, 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Benitez, E.; Nogales, R.; Elvira, C.; Masciandaro, G.; Ceccanti, B. Enzyme activities as indicators of the stabilization of sewage sludge composting with Eisenia foetida. Biores. Technol. 1999, 67, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, A.; Thangaraj, R.; Ravindran, B.; Chang, S.W.; Karmegam, N. Centrality of cattle solid wastes in vermicomposting technology—A cleaner resource recovery and biowaste recycling option for agricultural and environmental sustainability. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 1156882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soobhany, N.; Mohee, R.; Garg, V.K. Recovery of nutrient from municipal solid waste by composting and vermicomposting using earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2931–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulcu, R.; Yaldiz, O. Composting of goat manure and wheat straw using pine cones as a bulking agent. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2700–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Suresh, S.; Chauhan, M.S.; Subbaramaiah, V.; Gosu, V. Recent Progress in Carbonaceous Materials for the NitrateAdsorption. J. Hazardous Toxic. Radioact. Waste 2022, 26, 04022013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Suresh, S.; Arisutha, S.; Sudhakar, K. Anaerobic Co-digestion of different wastes in a UASB. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon, J.; Cadena, E.; Pognani, M.; Barrena, R.; Sanchez, A.; Font, X.; Artola, A. Determination of the energy and environmental burdens associated with the biological treatment of source-separated Municipal Solid Wastes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5731–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndegwa, P.M.; Thompson, S.A. Integrating composting and Vermicomposting in the treatment and bioconversion of biosolids. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 76, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Jain, A.; Sarma, B.K.; Abhilash, P.C.; Singh, H.B. Solid waste management of temple floral offerings by vermicomposting using Eisenia fetida. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajalakshmi, S.; Abbasi, S.A. Effect of the application of water hyacinth compost/vermicompost on the growth and flowering of Crossandra undulaefolia, and on several vegetables. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 85, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Xia, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Cui, G.; Li, F.; Bai, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, N. Elimination of antibiotic resistance genes and human pathogenic bacteria by earthworms during vermicomposting of dewatered sludge by metagenomicanalysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khwairakpam, M.; Bhargava, R. Vermitechnology for sewage sludge recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, P.S.; Gajalakshmi, S.; Abbasi, S.A. Vermicomposting of the leaf litter of acacia (Acacia auriculiformis): Possible roles of reactor geometry, polyphenols, and lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, W.P.; Taylor, M.; Cossins, R. Evaluation of respirometry of the loading capacity of a high rate vermicompost bed for treating sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 98, 2611–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndegwa, P.M.; Thompson, S.A.; Das, K.C. Effects of stocking density and feeding rate on vermicomposting of biosolids. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 71, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Keshav, A. Textbook of Separation Processes; Studium Press (India) Pvt. Ltd.: Delhi, India, 2012; pp. 1–459. ISBN 978-93-80012-32-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Chauhan, M.S.; Sundaramurthy, S. Assessment of Groundwater Trends in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh: A Statistical Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Eaton, A.D. (Eds.) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pigatin, L.B.F.; Atoloye, I.A.; Obikoya, O.A.; Borsato, A.V.; Rezende, M.O.O. Chemical study of vermicomposted agro industrial wastes. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2016, 5, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.; Edwards, C.A. Effects of stocking rate and moisture content on the growth and maturation of Eisenia andrei (Oligochaeta) in pig manure. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1997, 29, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Das, S.; Goswami, L.; Das, P.; Sahariah, B.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Intensification of vermitechnology for kitchen vegetable waste and paddy straw employing earthworm consortium: Assessment of maturity time, microbial community structure, and economic benefit. J. Clean. Produc. 2018, 182, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthavalli, R.; Ramadas, V.; Paula, J.A.J.; Selvi, B.K.; Karmegam, N. Seaweeds as bioresources for vermicompost production using the earthworm, Perionyx excavatus (Perrier). Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, H.; Deka, S.; Baruah, C.K.; Das, J.; Hoque, S.; Sarma, H.; Sarma, N.S. Vermicomposting potentiality of Perionyx excavatus for recycling of waste biomass of java citronella—An aromatic oil yielding plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 11212–11217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnarain, Y.I.; Ansari, A.A.; Ori, L. Vermicomposting of different organic materials using the epigeic earthworm Eisenia foetida. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2018, 8, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.M.; Haynes, R.J. Evaluation of potting media for commercial nursery production of container grown plants. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 1977, 20, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndegwa, P.M.; Thompson, S.A. Effects of C-to-N ratio on vermicomposting of biosolids. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 75, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatua, C.; Sengupta, S.; Krishna Balla, V.; Kundu, B.; Chakraborti, A.; Tripathi, S. Dynamics of organic matter decomposition during vermicomposting of banana stem waste using Eisenia fetida. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, M.; Nandal, M.; Khosla, B. Microbes as vital additives for solid waste composting. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Smith, J.E. Reducing pathogen and vector attraction for biosolids. Biocycle 1999, 40, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, D.W.; Chalmers, J.A.; Storey, J.A. Evaluation of in-vessel composting of university postconsumer food wastes. Comp. Sci. Util. 1998, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepthi, M.P.; Kathireswari, P.; Rini, J.; Saminathan, K.; Karmegam, N. Vermitransformation of monogastric Elephas maximus and ruminant Bos taurus excrements into vermicompost using Eudrilus eugeniae. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320 Pt A, 124302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhiday, M.R. Earthworms in agriculture. Indian Farm. 1994, 43, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pathma, J.; Sakthivel, N. Microbial diversity of vermicompost bacteria that exhibit useful agricultural traits and waste management potential. Springer Plus 2012, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorinen, A.H.; Saharinen, M.H. Evolution of microbiological and chemical parameters during manure and straw co-composting in a drum com- posting system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1997, 66, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aynehband, A.; Gorooei, A.; Moezzi, A.A. Management in Organic Agriculture Vermicompost: An Eco-Friendly Technology for Crop Residue Management in Organic Agriculture. Energy Procedia 2017, 141, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewulo, B.S.; Hassan, K.O.; Ojeniyi, S.O. Comparative effect of cowdung manure on soil and leaf nutrient and yield of pepper. Int. J. Agri. Res. 2007, 2, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, S. Bioconversion of post-harvest crop residues and cattle shed manure into value-added products using earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae Kinberg. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 32, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuntawut, C.-N.; Chuleemas, B.I.; Mongkon, T.-O. Vermicompost: Tool for agro-industrial waste management and sustainable agriculture. Int. J. Environ. Rural. Develop. 2010, 1, 38–43. [Google Scholar]










| Parameter | Fresh DBS | Agricultural Residues | Composting | Vermicomposting (E. fetida) | Vermicomposting (E. eugeniae) | Control 3 | SEM 1 | p-Value 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vf | Ve | Vf XC | VeXC | ||||||||
| Moisture (%) | 76.3 e | 15.1 e | 63 e,a,b | 55 a,e,c | 58 b,e,d | 35.3 | 1.21 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
| C:N ratio | 8.4 e | 6.2 e | 10.1 e,a,b | 8.1 a,e,c | 9.3 b,e,d | 8.31 | 1.43 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.12 |
| pH | 0.94 e | 2.4 e | 7.5 e,a,b | 7.2 a,e,c | 8.0 b,e,d | 7.54 | 1.32 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| EC (dS/m) | 16.3 e | 27.3 e | 2.71 e,a,b | 1.62 a,e,c | 2.01 b,e,d | 3.21 | 0.93 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.21 |
| N (%) | 1.98 e | 1.9 e | 12.2 e,a,b | 17.2 a,e,c | 11.3 b,e,d | 9.33 | 1.72 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 0.31 |
| P (%) | 0.28 e | 0.6 e | 2.8 e,a,b | 9.3 a,e,c | 4.8 b,e,d | 3.82 | 1.77 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.21 |
| K (%) | 1.3 e | 0.7 e | 2.41 e,a,b | 13.91 a,e,c | 6.8 b,e,d | 2.51 | 1.45 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.33 | 0.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katiyar, R.B.; Sundaramurthy, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Arisutha, S.; Pratap-Singh, A.; Mishra, S.; Ayub, R.; Jeon, B.-H.; Khan, M.A. Vermicompost: An Eco-Friendly and Cost-Effective Alternative for Sustainable Agriculture. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152014701
Katiyar RB, Sundaramurthy S, Sharma AK, Arisutha S, Pratap-Singh A, Mishra S, Ayub R, Jeon B-H, Khan MA. Vermicompost: An Eco-Friendly and Cost-Effective Alternative for Sustainable Agriculture. Sustainability. 2023; 15(20):14701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152014701
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatiyar, Rajesh Babu, Suresh Sundaramurthy, Anil Kumar Sharma, Suresh Arisutha, Anubhav Pratap-Singh, Satyam Mishra, Rashid Ayub, Byong-Hun Jeon, and Moonis Ali Khan. 2023. "Vermicompost: An Eco-Friendly and Cost-Effective Alternative for Sustainable Agriculture" Sustainability 15, no. 20: 14701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152014701
APA StyleKatiyar, R. B., Sundaramurthy, S., Sharma, A. K., Arisutha, S., Pratap-Singh, A., Mishra, S., Ayub, R., Jeon, B.-H., & Khan, M. A. (2023). Vermicompost: An Eco-Friendly and Cost-Effective Alternative for Sustainable Agriculture. Sustainability, 15(20), 14701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152014701









