Abstract
The sustainability of agroecosystems is at risk owing to continuous anthropogenic disturbance. As such, there is a need to evaluate indicator taxa that may be used to monitor the health of agricultural management systems. Carabid beetles are ubiquitous and functionally crucial in agroecosystems while at the same time are sensitive to the changes caused by management practices. Their quick response to anthropogenic disturbances has been proposed as a practical and realistic tool for monitoring the sustainability of agricultural practices. However, there is still disagreement about carabids as possible indicators of agroecosystem sustainability. We conducted a systematic review of the responses of carabid beetles to agricultural systems in different biogeographical areas. We examined whether these beetles could serve as potential indicators of agroecosystem sustainability. The ISI Web of Science, Google Scholar, and Scopus were used to search for papers published from 2000–2019. In total, we included 69 studies indicating the use of carabids to monitor the impact of management practices in agroecosystems. Most studies were conducted in European countries (n = 37), while Southern Africa and East Asia countries were significantly under-represented (n = 10). Carabid beetle response to agroecosystems varied between management practices, with biodiversity indices (n = 41: positive 60%, negative 19%, and neutral 19%) being the most measured response variable, followed by functional diversity (n = 28: positive 67%, negative 25%, and neutral 7%). Overall, our findings highlight the need for more research in underdeveloped countries, to investigate the potential of overlooked carabids and include response variables measuring functional diversity in assessing the sustainability of agricultural management. This will assist policy makers and land managers in making active and informed decisions about agroecological disturbances and management.
1. Introduction
Agricultural intensification is one of the main causes of the biodiversity crisis [1], with repercussions for the functioning and sustainability of agroecosystems [2,3]. Agricultural management systems that involve the continuous use of pesticides result in habitat degradation, the conversion of semi-natural habitats to cropland, and the dominance of a few plant species in ever larger areas [4,5,6]. These significant challenges impact the ecological processes that provide the functions necessary for sustainable production [7]. Moreover, management practices are confronted with numerous challenges on multiple fronts, ranging from meeting the food demand for the growing population to dealing with climate change effects [8,9]. Concerns about the negative effects of high-input, industrially managed agriculture have prompted a call for sustainable management practices [10].
The implementation of sustainable agricultural practices should include cost-effective monitoring techniques that can be used to detect environmental changes, assess management performance, and provide warning signals for imminent ecological transitions [11]. Indicators are species or groups of species that are easily monitored and whose status reflects or predicts the condition(s) of the environment where they are found [12]. Indicator species may be a helpful tool for addressing agricultural intensification difficulties [13]. For decades, changes in key indicator species have been used to underpin increasing concern about the necessity of biodiversity conservation and sustainability in the face of accelerated environmental change induced by human activities. Subsequently, the use of indicators has been extended to aquatic and terrestrial invertebrates used to detect environmental impacts in freshwater [14,15,16] and different ecosystems [12,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Despite the extensive history of prospective indicator species, surprisingly, few studies have been conducted on indicators for sustainable agroecosystems [24,25]. Therefore, using taxonomic or functional groups that are sensitive to ecological change in agroecosystems might be a helpful tool to monitor the resilience and health of management practices.
Among edaphic arthropods, carabid beetles are regarded as excellent indicator species due to their abundance and diversity, well-known taxonomy, ease of sampling, and cost-effectiveness [12,26]. Carabids are particularly suitable for examining subtle effects of agroecosystem management practices such as pesticide use, depth of tillage, soil quality, moisture, and landscape heterogeneity, because certain species are stenotopic and thus intrinsically sensitive to environmental conditions [18,27,28,29]. Other biodiversity assessments have reported carabid responses to grassland management practices [30,31,32,33]. The importance of carabids in agroecosystems is critical due to their economic and functional value, acting as natural enemies of pests or components of trophic chains that support biodiversity [34,35]. Though carabids have been well studied taxonomically and ecologically in agroecosystems worldwide [36], most studies in Africa have documented the carabid beetle diversity in savanna biomes [37], forest–grassland mosaics [38], vineyards [39], and few in cereal agroecosystems [30,40]. Notably, their use as indicators of agroecosystem sustainability remains a challenge due to a lack of data on their ecological response, particularly under different agricultural management scenarios [21,36,41,42,43,44]. A detailed knowledge of the response of carabids in various management practices can provide insight into the health of agroecosystems. This review aims to provide a global and comprehensive overview of the use of carabid beetles in agroecosystems and assesses their inclusion as sustainability indicators. The focus is on conservation and biodiversity studies, with a geographical emphasis on agroecosystems where most research has been conducted, namely across semi-natural grasslands and field crops.
2. Materials and Methods
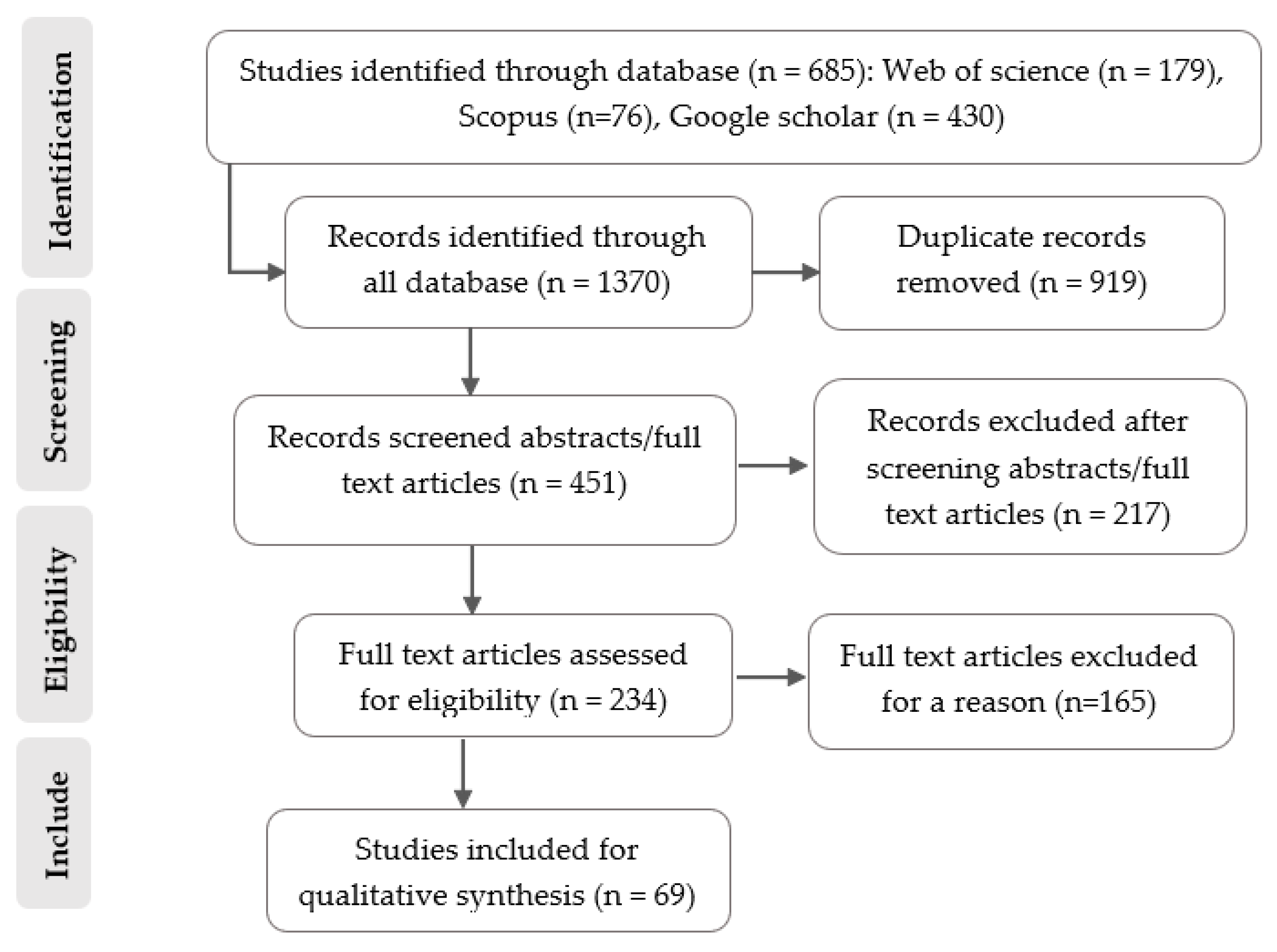
To summarize the ecological response of carabid beetles to agricultural management practices in different geographical regions, we conducted a systematic review using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews (PRISMA) statement [45], and checklists [46], (Figure 1, see Supplementary Information PRISMA checklists 2020—Tables S2 and S3). PRISMA is a standard protocol for conducting objective and reproducible systematic reviews to improve scientific transparency. We selected studies that examined cropland and semi-natural grassland because these agroecosystems are managed differently (from semi-natural habitats to homogeneous monocultures, crop rotations, pastures, organic farming, and diversified and conventional tillage), which affects carabid beetle biodiversity and functionality (Table 1, see Supplementary Information—Table S1).

Table 1.
Categories used to classify studies found in the literature search.
2.1. Search and Selection of Publications
We searched the ISI Web of Science Core Collection (http://www.isiwebofknowledge.com), Scopus (https://www.scopus.com), and Google Scholar (https://scholar.google.ca) for peer-reviewed publications published on all continents. We used the following search term to find studies on the effects of agroecosystem management practices on carabid beetles: (“agri-environmental programmes” OR “organic farming” OR “sustainable farming” OR “diversified farming” OR “integrated farming” OR “conservation farming” OR “conventional tillage” OR “intensive farming” OR “semi-natural grassland AND *Beetles”, AND *Carabidae”, AND “ground beetles” AND *Indicator”). To find the response variables, we used the following search term: (“abundance” OR “richness” OR “diversity” OR “composition” OR “functional diversity” OR “weed predator” OR “generalist” OR “specialist” OR “morphological traits” OR “trophic guilds”). All journal citations and abstracts were imported into the Mendeley online importer reference management software (https://www.mendeley.com) and their titles, keywords, and abstracts were checked.
2.2. Data Extraction and Synthesis
We focused on extracting data on language (English), year of publication (March 2000 to April 2019), biogeographic region (country/continents), agricultural management type (conventional tillage, organic farming, diversified farming, conservation agriculture, and grazing), diversity (richness, evenness, composition, abundance, and active density), functional traits (body size and dispersal ability), and trophic guilds (predators, granivores, and omnivores) (Table 1). We also evaluated each publication according to whether the authors reported negative, positive, or neutral effects of different agroecosystem management practices on carabid beetles. Grey literature, books, conference proceedings, technical reports, and unpublished data were not considered in the review conducted here.
3. Results
3.1. General Overview
The initial search for relevant articles resulted in 1370 articles. After eliminating duplicates (919 articles), the search criteria yielded 451 articles across all databases. The titles, abstracts, and keywords of 451 articles were screened, with 217 excluded. Critical appraisal of the 234 studies that met the relevance criteria led to the exclusion of 165 studies due to low or unclear validity. Consequently, 69 studies showing the response of carabid beetles to different management practices in agroecosystems were used for the qualitative synthesis. The search, screening, and inclusion of studies are schematically summarized in the flow chart below (Figure 1).
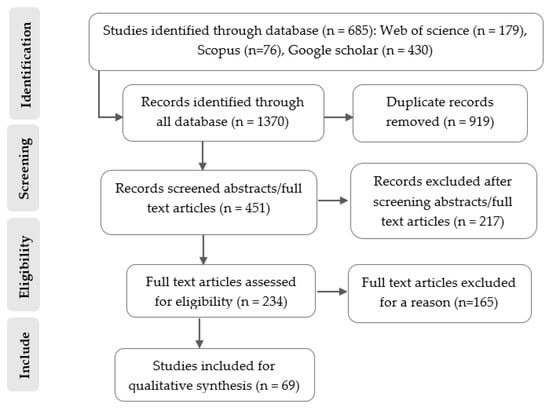
Figure 1.
A flow diagram showing the systematic review process (adapted from PRISMA guidelines).
3.2. Trends in Carabid Beetle Studies and Status in Agricultural Management Systems
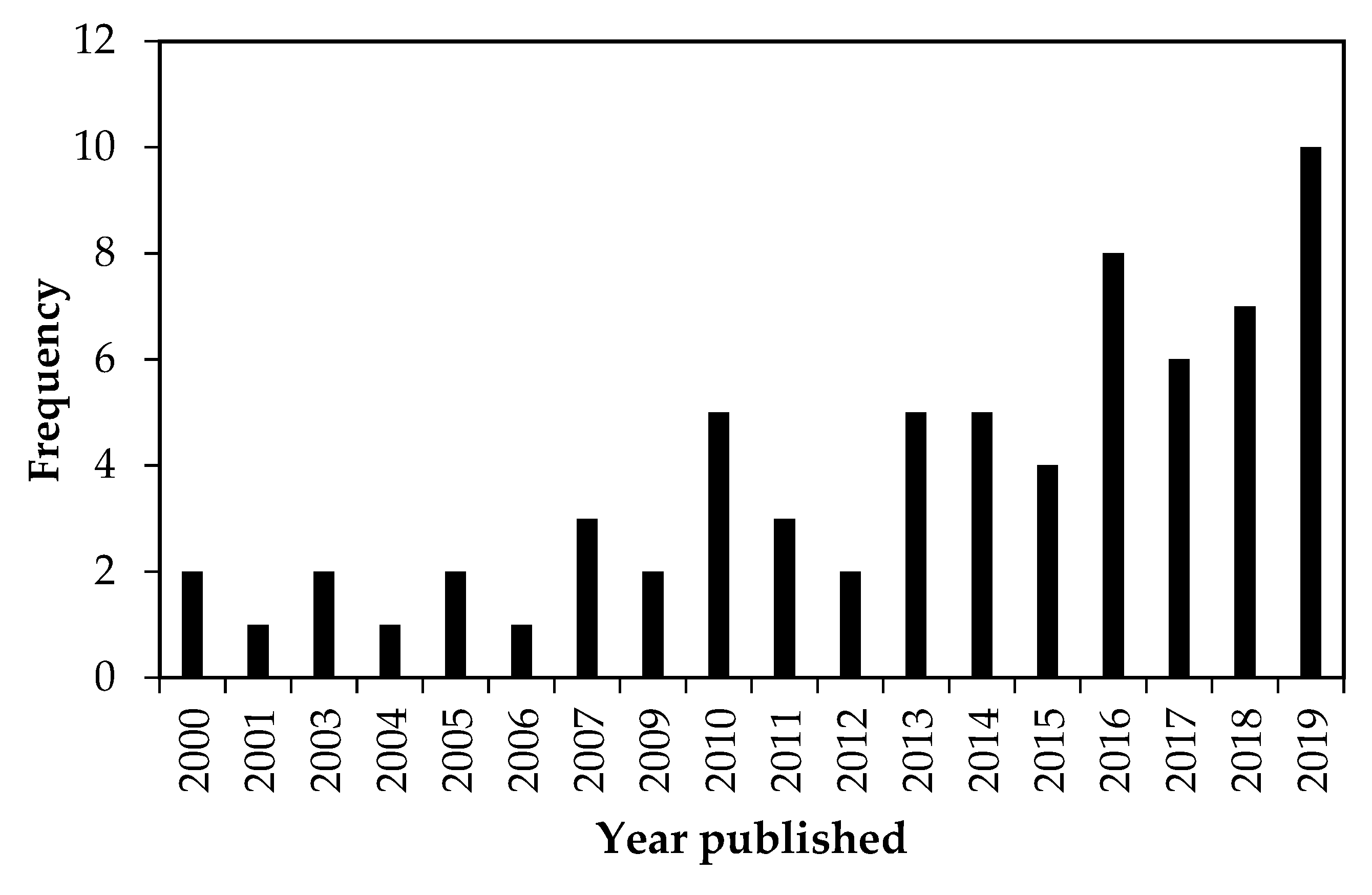
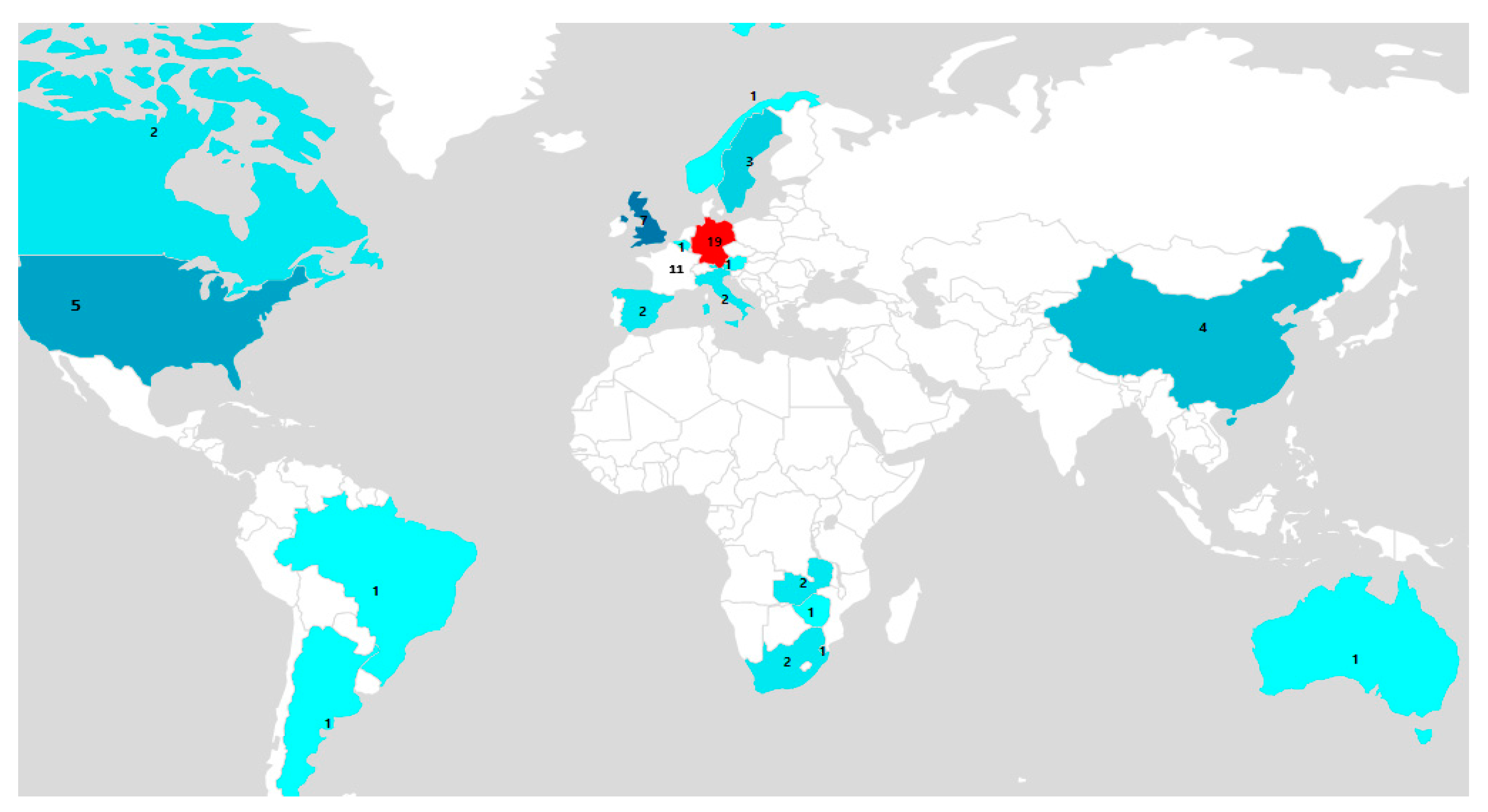
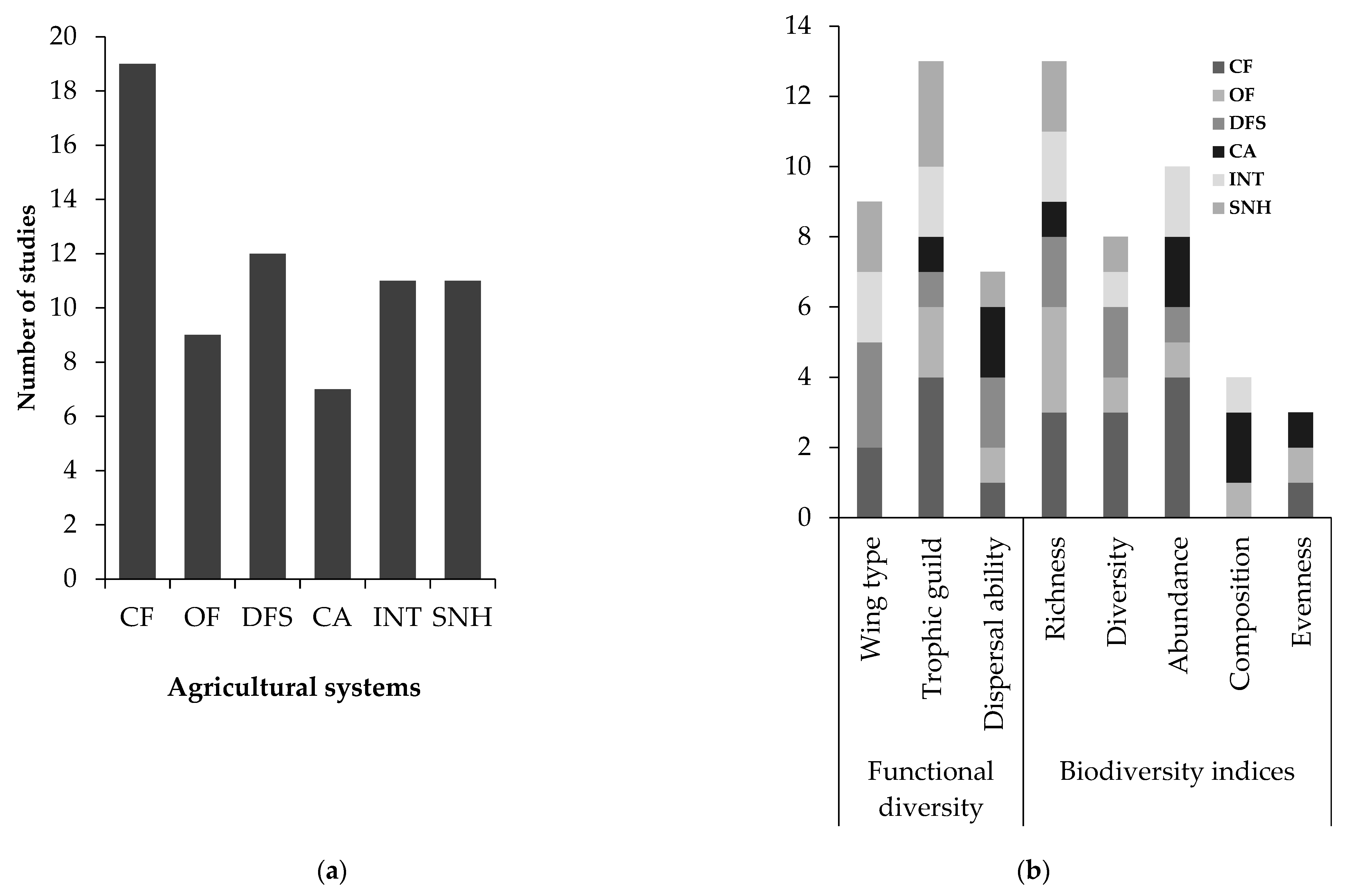
According to the systematic review, the first papers addressing the response of carabid beetles to agricultural management were published from 2000 to 2009, with no articles found in 2002. Since then, the temporal trend of studies dealing with this topic has shown a steadily increasing rate, indicating that it is an emerging field of research. This was found when 55 articles were published between 2010 and 2019, respectively (Figure 2). Overall, the selected papers show that most of the studies were conducted mainly in developed countries, particularly in Germany (n = 19), France (n = 11), the United Kingdom (n = 7), and the United States (n = 5), while few studies were conducted in developing countries in Southern Africa (n = 6) and East Asia (n = 4), (Figure 3). In terms of agricultural management systems, conventional farming predominated in 28% of studies, followed by diversified farming systems (17%), integrated agriculture (16%) and semi-natural habitats (16%). Only a few studies were conducted on organic farming (13%) and conservation agriculture (10%) (Table 2; Figure 4a).
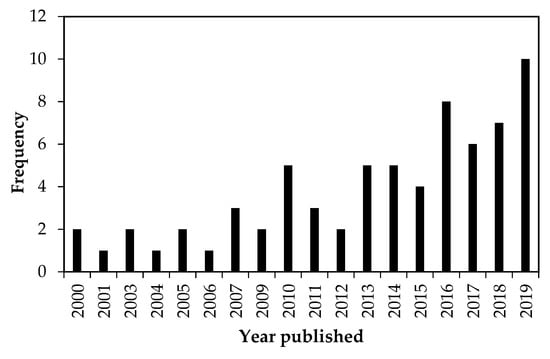
Figure 2.
Publications (n = the total of 69 screened articles) that investigated the response of carabid beetles to agricultural management practices between 2000 and 2019.
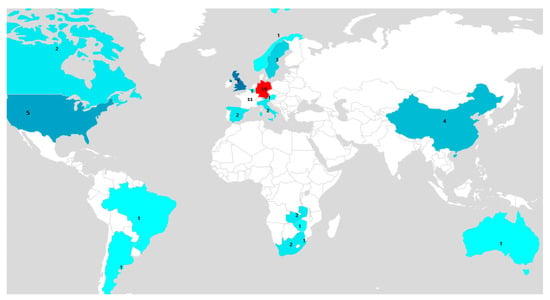
Figure 3.
Geographic locations of the 69 included peer-reviewed studies on the word map.
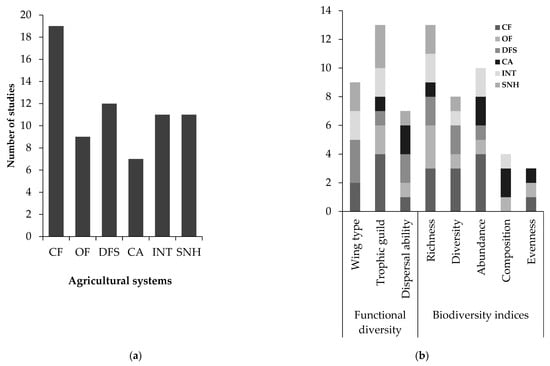
Figure 4.
Summary of number of papers published on (a) agricultural management type and (b) carabid functional diversity and biodiversity indices included in the systematic review (see Table 2 for abbreviations).
3.3. Carabid Response Variables to Agricultural Systems
We recorded five carabid biodiversity indices (41 studies: 25 positive, 8 negative, and 8 neutral) used to assess the effects of agricultural management type. Richness (13 studies) and abundance (10 studies), followed by diversity (9 studies), were the three most frequently assessed indices. The next frequently used measure was community composition (i.e., the assemblage of the different species comprising the studied community), followed by evenness. Functional diversity was measured in only a small proportion of papers (28 studies: 19 positive, 7 negative, and 2 neutral) and mainly concerned trophic guilds (13 studies), body size (9 studies), dispersal ability, and wing type (6 studies) across agricultural management type (Table 2, Figure 4b).

Table 2.
Carabid functional diversity and biodiversity indices in different agricultural management types (CF–conventional farming; OF–organic farming; DFS–diversified farming system; CA–conservation agriculture; INT–integrated farming; SNH–semi-natural habitats).
Table 2.
Carabid functional diversity and biodiversity indices in different agricultural management types (CF–conventional farming; OF–organic farming; DFS–diversified farming system; CA–conservation agriculture; INT–integrated farming; SNH–semi-natural habitats).
| Response Variables | Agricultural Management Type | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | CF | OF | DFS | CA | INT | SNH | Total | % Total | |
| Functional diversity | |||||||||
| Body size: small, medium, and large | Positive | 1 | - | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | 6 | 8.7 |
| Negative | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | 2.9 | |
| Neutral | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1.4 | |
| Trophic guilds: predators, omnivores, and granivores | Positive | 2 | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 11.6 |
| Negative | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | 2 | 4 | 5.8 | |
| Neutral | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.4 | |
| Dispersal ability (wing type): flightless, immobile, | Positive | 1 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 1 | 5 | 7.2 |
| macropterous, brachypterous, wingless, and apterous | Negative | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.4 |
| Neutral | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Biodiversity indices | |||||||||
| Richness | Positive | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 9 | 13.0 |
| Negative | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | 2.9 | |
| Neutral | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 2.9 | |
| Diversity | Positive | - | - | 3 | - | - | 1 | 4 | 5.8 |
| Negative | 2 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 4 | 5.8 | |
| Neutral | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.4 | |
| Abundance/active density | Positive | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 7 | 10.1 |
| Negative | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.4 | |
| Neutral | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - | 2 | 2.9 | |
| Composition | Positive | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 3 | 4.3 |
| Negative | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.4 | |
| Neutral | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | 2 | 2.9 | |
| Evenness | Positive | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2.9 |
| Negative | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.0 | |
| Neutral | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1.4 | |
| Grand total | 19 | 9 | 12 | 7 | 11 | 11 | 69 | 100 | |
4. Discussion
This review highlights the need to increase our knowledge of the use of carabid beetles as indicators of agroecosystem sustainability. The use of monitoring techniques such as indicator species to assess environmental change in agroecosystems is an emerging topic in research [43,44,47,48]. Because carabids clearly respond to agricultural management practices, they can play an important role in determining which practices in agroecosystems bring us closest to our goal of agroecosystem sustainability [36]. Despite the fact that the number of studies on carabids in agricultural systems is increasing globally, we have found that there is a clear geographical preponderance of studies from the most developed countries in Europe, with a large gap in the developing countries of Southern Africa and East Asia [49,50,51,52]. This implies that indicator species are prioritized in developed countries for monitoring the status of management practices in agroecosystems [53,54].
Carabid beetles are ubiquitous, stenotopic, and influenced by different agroecosystem management practices [55,56,57,58]. Conventional agricultural management has repeatedly been linked to negative effects on carabid diversity and functional traits [59,60,61,62,63]. The detrimental effects of this management can be explained by the fact that the synchronization of tillage timing and agrochemical application reduces carabid diversity by causing direct mortality and disturbance of overwintering sites [64,65,66]. This disturbance indirectly eliminates food sources and alters the habitat by changing the density, distribution, and composition of weeds [67,68]. According to Schröter et al. [65], these provide foliage and seeds to different species, control microclimate and soil moisture, and determine the degree of physical protection from predators and freedom of movement. For example, species that breed in autumn and overwinter as larvae in the soil are vulnerable to having their abundance affected by conventional tillage [69,70,71]. However, not all species decline due to such disturbance; certain species may be resistant or sensitive [72,73]. Studies conducted in conventional systems have shown that carabids can be used as indicators for monitoring ecological changes caused by management practices such as pesticide use and tillage methods [74,75,76].
Furthermore, our results show some preferences in using biodiversity indices, i.e., species richness and abundance as indicators of agricultural management conditions [77,78]. Species richness is one of the simplest measures of species diversity, and along with species abundance, it provides useful information about the state of different management practices [79]. However, there is a significant gap in the use of carabid functional diversity metrics. Trait-based information should also be included when assessing the sustainability of agroecosystems because measures of species richness and abundance are clearly insufficient to explain ecosystem functioning [50,52,80]. Dispersal ability, which is linked to functional traits such as body size, may be a key factor when assessing the health of agricultural management practices [81,82,83,84]. Body size has a greater influence on prey consumption [40]. This shows that functional traits, rather than broad community descriptors such as species richness, can better indicate ecosystem services of pest control for agricultural systems [43,50,85]. The dominance of key indicator species with high feeding rates can be used to assess the efficiency of a predator community in controlling pests [68]. For instance, larger carabids are a predictor of pest consumption, with larger species consuming large pests [21,47,63]. However, due to their limited dispersal ability, larger brachypterous predators are thought to be at greater risk of extinction than smaller macropterous species in severely disturbed and fragmented homogenized agroecosystems [57,73]. Smaller species thrive in open habitats because they can disperse when conditions are unfavorable [29,77,78], whereas species with restricted dispersal ability can only colonize new areas by running [36,56,86,87].
Carabid species that benefit from intact agroecosystems are considered indicators of sustainable management practices [88]. This implies that ecological, conservation, and integrated farming systems with a diverse crop mix and a diversity of field edges and strips are critical for the survival of carabid species [89,90]. Over time, these agroecosystems will provide shelter and more diverse food supplies, perhaps promoting carabid functioning and biodiversity [72,91]. Carabid species that occur in various habitats benefit from different management practices than specialists that occur in just one or a few habitats [92]. Each agroecosystem has its unique set of species, including both generalists and specialists, that can be used to track the effectiveness of management strategies [57,86].
5. Conclusions
Given the constraints associated with implementing sustainable measures in agroecosystems, we suggest that carabid beetles can aid in monitoring the recovery and health of agricultural management practices. Continuous monitoring of indicator species in agroecosystems can reveal the pace and direction of change within management practices [24,93]. Though carabids are receiving remarkably more attention as indicators of agroecosystem sustainability worldwide, there is still a need to quantify diversity or composition and the impact of species functioning on agroecosystems. Determining the functional diversity of carabid beetles in agroecosystems can help us better understand their ability to provide ecosystem services of pest control [94]. Therefore, selecting indices or descriptors that integrate functional diversity information is crucial for future sustainable agricultural efficiency.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su15053936/s1, Table S1: Studies included in the systematic review. Table S2: PRISMA 2020 for Abstracts Checklist; Table S3: PRISMA 2020 Checklist.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization of the review was performed by M.M.M., R.S. and T.C.M.; methodology, M.M.M.; data collection, M.M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.M.; writing—review and editing, R.S., T.C.M. and M.M.M.; supervision, R.S. and T.C.M.; funding acquisition, R.S. and T.C.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by DAAD-National Research Foundation In-Country Doctoral Scholarships (grant number MND190627451172/123279) and the Sustainable and Healthy Food Systems (SHEFs) supported by the Wellcome Trust’s Our Planet, our Health programme (grant number, 205200/Z/16/Z. The University of KwaZulu-Natal: Centre for Functional Biodiversity is acknowledged for financial support of the project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G. Worldwide Decline of the Entomofauna: A Review of Its Drivers. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 232, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basedow, T. Conventional Agriculture (in Its Present Form) or Ecological Agriculture? - For the Maximal Biodiversity Both Are Necessary | Konventionelle Landwirtschaft (in Ihrer Gegenwärtigen Ausprägung) Oder Ökologische Landwirtschaft? - Für Die Maximale Biodiversit. Gesunde Pflanz. 2002, 54, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscharntke, T.; Tylianakis, J.M.; Rand, T.A.; Didham, R.K.; Fahrig, L.; Batáry, P.; Bengtsson, J.; Clough, Y.; Crist, T.O.; Dormann, C.F.; et al. Landscape Moderation of Biodiversity Patterns and Processes - Eight Hypotheses. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 661–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, T.G.; Vickery, J.A.; Wilson, J.D. Farmland Biodiversity: Is Habitat Heterogeneity the Key? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purtauf, T.; Roschewitz, I.; Dauber, J.; Thies, C.; Tscharntke, T.; Wolters, V. Landscape Context of Organic and Conventional Farms: Influences on Carabid Beetle Diversity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 108, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallé, R.; Happe, A.A.-K.A.K.; Baillod, A.B.A.B.; Tscharntke, T.; Batáry, P. Landscape Configuration, Organic Management, and within-Field Position Drive Functional Diversity of Spiders and Carabids. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, A.; Birkhofer, K.; Rusch, A.; Andersson, G.K.S.; Bommarco, R. A Framework to Identify Indicator Species for Ecosystem Services in Agricultural Landscapes A Framework to Identify Indicator Species for Ecosystem Services in Agricultural Landscapes. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Chami, D.; Daccache, A.; El Moujabber, M. How Can Sustainable Agriculture Increase Climate Resilience? A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2020. Transforming Food Systems for Affordable Healthy Diets. Rome. 2020. Available online: https://doi.org/10.4060/ca9692en (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Massaloux, D.; Sarrazin, B.; Roume, A.; Tolon, V.; Wezel, A. Complementarity of Grasslands and Cereal Fields Ensures Carabid Regional Diversity in French Farmlands. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 2861–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajaiba, R.L.; Périco, E.; da Silva, W.B.; Vieira, T.B.; Dalzochio, M.S.; Bastos, R.; Cabral, J.A.; Santos, M. How Informative Is the Response of Ground Beetles’ (Coleoptera: Carabidae) Assemblages to Anthropogenic Land Use Changes? Insights for Ecological Status Assessments from a Case Study in the Neotropics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainio, J.; Niemela, J. Ground Beetles ( Coleoptera: Carabidae ) as Bioindicators. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 487–506. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, J.; Samways, M.; Pryke, J. Terrestrial Invertebrates as Bioindicators: An Overview of Available Taxonomic Groups. J. Insect Conserv. 2013, 17, 831–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioria, M.; Schaffers, A.; Bacaro, G.; Feehan, J. The Conservation Value of Farmland Ponds: Predicting Water Beetle Assemblages Using Vascular Plants as a Surrogate Group. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, A.; Willows-Munro, S. The Utility of DNA Barcoding as a Tool to Assess the Success of Ecological Restoration Using Hemiptera as a Biological Indicator. Restor. Ecol. 2019, 27, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus-Freer, J.; Pyron, M. Concordance among Fish and Macroinvertebrate Assemblages in Streams of Indiana, USA. Hydrobiologia 2015, 758, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.N.; Hoffmann, B.D.; Müller, W.J.; Griffiths, A.D. Using Ants as Bioindicators in Land Management: Simplifying Assessment of Ant Community Responses. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 39, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, P.A. Carabids as Potential Indicators of Sustainable Farming Systems. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2007, 47, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work, T.T.; Koivula, M.; Klimaszewski, J.; Langor, D.; Spence, J.; Sweeney, J.; Hébert, C. Evaluation of Carabid Beetles as Indicators of Forest Change in Canada. Can. Entomol. 2008, 140, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriga, J.C.; Lassaletta, L.; Moreno, A.G. Ground-Living Spider Assemblages from Mediterranean Habitats under Different Management Conditions. J. Arachnol. 2010, 38, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivula, M.J. Carabidae Reflecting Environmental Conditions Useful Model Organisms, Indicators, or Both ? Ground Beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) Reflecting Environmental Conditions. Zookeys 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, G.S.; Mauda, E.V.; Seymour, C.L.; Munyai, T.C.; Dippenaar-Schoeman, A.; Foord, S.H. Landuse Change in Savannas Disproportionately Reduces Functional Diversity of Invertebrate Predators at the Highest Trophic Levels: Spiders as an Example. Ecosystems 2018, 21, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, G.S.; Muluvhahothe, M.M.; Seymour, C.L.; Munyai, T.C.; Bishop, T.R.; Foord, S.H. Stability of Afromontane Ant Diversity Decreases across an Elevation Gradient. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, e00596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyl, M. Carabid Beetles as Biodiversity and Ecological Indicators. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Tasminia, Tasminia, Australia, 1999. Available online: https://eprints.utas.edu.au/20894/ (accessed on 3 March 2019).
- Niemelä, J. Biodiversity Monitoring for Decision-Making. Ann. Zool. Fennici 2000, 37, 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Döring, T.F.F.; Hiller, A.; Wehke, S.; Schulte, G.; Broll, G. Biotic Indicators of Carabid Species Richness on Organically and Conventionally Managed Arable Fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 98, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.M.; Frampton, G.K.; Brink van den, P.J. Carabids as Indicators within Temperate Arable Farming Systems: Implications from SCARAB and LINK Integrated Farming Systems Projects. In The Agroecology of Carabid Beetles; Holland, J.M., Ed.; Intercept: Andover, UK, 2002; pp. 251–277. ISBN 1898298769. [Google Scholar]
- Döring, T.F.T.F.; Kromp, B. Which Carabid Species Benefit from Organic Agriculture? - A Review of Comparative Studies in Winter Cereals from Germany and Switzerland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 98, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearin, A.F.; Reberg-Horton, S.C.; Gallandt, E.R. Direct Effects of Tillage on the Activity Density of Ground Beetle (Coleoptera: Carabidae) Weed Seed Predators. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botha, M. Arthropod and Plant Diversity in Maize Agro-Ecosystems of South Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, NorthWest University, Potchefstroom, South Africa, 2017. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10394/25058 (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Lemic, D.; Čačija, M.; Virić Gašparić, H.; Drmić, Z.; Bažok, R.; Pajač Živković, I. The Ground Beetle (Coleoptera: Carabidae) Community in an Intensively Managed Agricultural Landscape. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, A.; Mullen, C.; Wallace, J.; Barbercheck, M. Cover Crop-Based Reduced Tillage System Influences Carabidae (Coleoptera) Activity, Diversity and Trophic Group during Transition to Organic Production. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2017, 32, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, A.; Oxbrough, A.; Ashton, P. Managing Biodiversity in Upland Calcareous Grassland Landscapes: A Case Study of Spiders and Ground Beetles; Edge Hill University: Lancashire, UK, 2018; ISBN 9781900230629. [Google Scholar]
- Trichard, A.; Ricci, B.; Ducourtieux, C.; Petit, S. The Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Weed Seed Predation Differs between Conservation Agriculture and Conventional Tillage. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 188, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmler, U. Which Carabid Species (Coleoptera: Carabidae) Profit from Organic Farming after a Succession of 15 Years? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 263, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotze, D.J.; O’Hara, R.B. Species Decline - But Why? Explanations of Carabid Beetle (Coleoptera, Carabidae) Declines in Europe. Oecologia 2003, 135, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeman, C.S.; Foord, S.; Hamer, M. Annotated Checklist of Carabidae (Insecta: Coleoptera) of the Vhembe Biosphere Reserve, South Africa. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Yekwayo, I.; Pryke, J.S.; Roets, F.; Samways, M.J. Contrast and Context in a Forest-Grassland Mosaic. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 631–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaigher, R. The Effect of Different Vineyard Management Systems on the Epigaeic Arthropod Assemblages in the Cape Floristic Region. Msc Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2008. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10019.1/1565 (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- Makwela, M.M. Biodiversity of Predatory Beetle Groups, Carabidae and Coccinellidae and Their Role as Bioindicators. Msc Thesis, University of South Africa, Pretoria, South Africa, 2019. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10500/26902 (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Taboada, A.; Kotze, D.J.; Salgado, J.M.; Tárrega, R. The Value of Semi-Natural Grasslands for the Conservation of Carabid Beetles in Long-Term Managed Forested Landscapes. J. Insect Conserv. 2011, 15, 573–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailis, J.; Turka, I. The Diversity and Structure of Ground Beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) Assemblages in Differently Managed Winter Wheat Fields The Diversity and Structure of Ground Beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) Assemblages in Differently Managed Winter Wheat Fields. Balt. J. Coleopterol. 2014, 14, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Eyre, M.D.; Mcmillan, S.D.; Critchley, C.N.R. Ground Beetles ( Coleoptera, Carabidae ) as Indicators of Change and Pattern in the Agroecosystem: Longer Surveys Improve Understanding. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 68, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowett, K.; Milne, A.E.; Metcalfe, H.; Hassall, K.L.; Potts, S.G.; Senapathi, D.; Storkey, J. Species Matter When Considering Landscape Effects on Carabid Distributions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 285, 106631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, T.P. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Mckenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, M.D.; Luff, M.L.; Leifert, C. Crop, Field Boundary, Productivity and Disturbance Influences on Ground Beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in the Agroecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 165, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, A.; Ashton, P.A.; Powell, I.; Oxbrough, A. Habitat Associations of Epigeal Spiders in Upland Calcareous Grassland Landscapes: The Importance for Conservation. Biodivers. Conserv. 2018, 27, 1201–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmel, J.; Thiele, J.; Entling, M.H.; Buchholz, S. Trait Composition and Functional Diversity of Spiders and Carabids in Linear Landscape Elements. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 235, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, B.A.; Redhead, J.; Vanbergen, A.J.; Hulmes, L.; Hulmes, S.; Peyton, J.; Nowakowski, M.; Pywell, R.F.; Heard, M.S. Impact of Habitat Type and Landscape Structure on Biomass, Species Richness and Functional Diversity of Ground Beetles. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, E.; Wolters, V.; Birkhofer, K. Arable Weeds in Organically Managed Wheat Fields Foster Carabid Beetles by Resource- and Structure-Mediated Effects. Arthropod. Plant. Interact. 2012, 6, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayer, C.; Lövei, G.L.; Magura, T.; Dieterich, M.; Batáry, P. Carabid Functional Diversity Is Enhanced by Conventional Flowering Fields, Organic Winter Cereals and Edge Habitats. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 284, 106579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.S.; Renner, K.A.; Menalled, F.D.; Landis, D.A. Feeding Preferences of Weed Seed Predators and Effect on Weed Emergence. Weed Sci. 2007, 55, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, S.; Trichard, A.; Biju-Duval, L.; McLaughlin, B.; Bohan, D.A.A.; McLaughlin, Ó.B.; Bohan, D.A.A. Interactions between Conservation Agricultural Practice and Landscape Composition Promote Weed Seed Predation by Invertebrates. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 240, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrec, R.; Badenhausser, I.; Bretagnolle, V.; Börger, L.; Roncoroni, M.; Guillon, N.; Gauffre, B. Crop Succession and Habitat Preferences Drive the Distribution and Abundance of Carabid Beetles in an Agricultural Landscape. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 199, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, G.; Marrec, R.; Gauffre, B.; Roncoroni, M.; Augiron, S.; Bretagnolle, V. Multi-Scale Effects of Agri-Environment Schemes on Carabid Beetles in Intensive Farmland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 229, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviron, S.; Lalechère, E.; Duflot, R.; Parisey, N.; Poggi, S.; Du, R.; Parisey, N.; Poggi, S. Connectivity of Cropped vs. Semi-Natural Habitats Mediates Biodiversity: A Case Study of Carabid Beetles Communities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 268, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djoudi, E.A.; Marie, A.; Mangenot, A.; Puech, C.; Aviron, S.; Plantegenest, M.; Pétillon, J. Farming System and Landscape Characteristics Differentially Affect Two Dominant Taxa of Predatory Arthropods. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 259, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonason, D.; Smith, H.G.; Bengtsson, J.; Birkhofer, K. Landscape Simplification Promotes Weed Seed Predation by Carabid Beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnychuk, N.A.; Olfert, O.; Youngs, B.; Gillott, C. ScienceDirect.Com—Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment—Abundance and Diversity of Carabidae (Coleoptera) in Different Farming Systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 95, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, A.; Eltun, R. Long-Term Developments in the Carabid and Staphylinid (Col., Carabidae and Staphylinidae) Fauna during Conversion from Conventional to Biological Farming. J. Appl. Entomol. 2000, 124, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Ulrich, R.; Ranjha, M.H.; Irmler, U. Movement of Carabids from Grassy Strips to Crop Land in Organic Agriculture. J. Insect Conserv. 2014, 18, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chungu, D. Converting Forests to Agriculture Decreases Body Size of Carabid Assemblages Converting Forests to Agriculture Decreases Body Size of Carabid Assemblages in Zambia. Afr. J. Ecol. 2018, 56, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Barton, P.S.; Blanchard, W.; Evans, M.J.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Macfadyen, S.; McIntyre, S.; Driscoll, D.A. Disentangling the Effects of Farmland Use, Habitat Edges, and Vegetation Structure on Ground Beetle Morphological Traits. Oecologia 2018, 188, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröter, L.; Irmler, U. Organic Cultivation Reduces Barrier Effect of Arable Fields on Species Diversity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfiffner, L.; Luka, H. Effects of Low-Input Farming Systems on Carabids and Epigeal Spiders - A Paired Farm Approach. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2003, 4, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boetzl, F.A.; Krimmer, E.; Krauss, J.; Steffan-Dewenter, I. Agri-Environmental Schemes Promote Ground-Dwelling Predators in Adjacent Oilseed Rape Fields: Diversity, Species Traits and Distance-Decay Functions. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouabah, A.; Villerd, J.; Amiaud, B.; Plantureux, S.; Lasserre-Joulin, F. Response of Carabid Beetles Diversity and Size Distribution to the Vegetation Structure within Differently Managed Field Margins. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 200, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labruyere, S.; Ricci, B.; Lubac, A.; Petit, S. Crop Type, Crop Management and Grass Margins Affect the Abundance and the Nutritional State of Seed-Eating Carabid Species in Arable Landscapes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Duan, M.; Yu, Z.; Axmacher, J.C. Different Response Patterns of Epigaeic Spiders and Carabid Beetles to Varying Environmental Conditions in Fields and Semi-Natural Habitats of an Intensively Cultivated Agricultural Landscape. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 264, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Duan, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.I.N. Effects of Plant Diversity, Habitat and Agricultural Landscape Structure on the Functional Diversity of Carabid Assemblages in the North China Plain. Insect Conserv. Divers. 2015, 8, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, H.I.; Palmu, E.; Birkhofer, K.; Smith, H.G.; Hedlund, K. Agricultural Land Use Determines the Trait Composition of Ground Beetle Communities. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, C.; Burel, F.; Baudry, J. Spatial and Temporal Heterogeneity of the Crop Mosaic Influences Carabid Beetles in Agricultural Landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashavakure, N.; Mashingaidze, A.B.; Musundire, R.; Nhamo, N.; Gandiwa, E.; Thierfelder, C.; Muposhi, V.K. Soil Dwelling Beetle Community Response to Tillage, Fertilizer and Weeding Intensity in a Sub-Humid Environment in Zimbabwe. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, A.R.; Bright, P.W. The Impact of Grassy Field Margins on Macro-Invertebrate Abundance in Adjacent Arable Fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekötter, T.; Wamser, S.; Wolters, V.; Birkhofer, K. Landscape and Management Effects on Structure and Function of Soil Arthropod Communities in Winter Wheat. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardon, P.; Reheul, D.; Mertens, J.; Reubens, B.; De Frenne, P.; De Smedt, P.; Proesmans, W.; Van Vooren, L.; Verheyen, K. Gradients in Abundance and Diversity of Ground Dwelling Arthropods as a Function of Distance to Tree Rows in Temperate Arable Agroforestry Systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 270–271, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardarelli, E.; Bogliani, G. Effects of Grass Management Intensity on Ground Beetle Assemblages in Rice Field Banks. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, J.D.; Dosdall, L.M.; Clayton, G.W.; Harker, K.N.; O’Donovan, J.T. Ground Beetle (Coleoptera: Carabidae) Diversity, Activity Density, and Community Structure in a Diversified Agroecosystem. Environ. Entomol. 2012, 41, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatten, T.D.; Bosque-Pérez, N.A.; Labonte, J.R.; Guy, S.O.; Eigenbrode, S.D. Effects of Tillage on the Activity Density and Biological Diversity of Carabid Beetles in Spring and Winter Crops. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonhaute, J.-É.É.; Peres-Neto, P.; Lucas, É. Influence of Agronomic Practices, Local Environment and Landscape Structure on Predatory Beetle Assemblage. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, N.A.; Lamagdeleine-Dent, K.A.; Willand, J.E.; Jones, H.P.; McCravy, K.W. Species and Functional Trait Re-Assembly of Ground Beetle Communities in Restored Grasslands. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 3481–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alignier, A.; Aviron, S. Time-Lagged Response of Carabid Species Richness and Composition to Past Management Practices and Landscape Context of Semi-Natural Field Margins. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 204, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.; Řezáč, M. Even the Smallest Non-Crop Habitat Islands Could Be Beneficial: Distribution of Carabid Beetles and Spiders in Agricultural Landscape. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.A.; Brooks, D.R.; Ashby, J.E.; Perry, J.N.; Woiwod, I.P. Diversity and Abundance of the Coleopteran Fauna from Organic and Conventional Management Systems in Southern England. Agric. For. Entomol. 2003, 5, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.J.; McCracken, D.I.; Dennis, P.; Downie, I.S.; Griffin, A.L.; Foster, G.N.; Murphy, K.J.; Waterhouse, T. Relationships between Agricultural Management and Ecological Groups of Ground Beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) on Scottish Farmland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 93, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, M.; Fontaneto, D. Biodiversity of Ground Beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in Different Habitats of the Italian Po Lowland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 127, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duflot, R.; Ernoult, A.; Burel, F.; Aviron, S. Landscape Level Processes Driving Carabid Crop Assemblage in Dynamic Farmlands. Popul. Ecol. 2016, 58, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibull, A.; Östman, Ö. Basic and Applied Ecology Species Composition in Agroecosystems: The Effect of Landscape, Habitat, and Farm Management. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 361, 349–361. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, S.S.; Dosdall, L.M.; Spence, J.R.; Willenborg, C.J. Field Density and Distribution of Weeds Are Associated with Spatial Dynamics of Omnivorous Ground Beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekroos, J.; Hyvönen, T.; Tiainen, J.; Tiira, M. Responses in Plant and Carabid Communities to Farming Practises in Boreal Landscapes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 135, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menalled, F.D.; Smith, R.G.; Dauer, J.T.; Fox, T.B. Impact of Agricultural Management on Carabid Communities and Weed Seed Predation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purtauf, T.; Dauber, J.; Wolters, V. The Response of Carabids to Landscape Simplification Differs between Trophic Groups. Oecologia 2005, 142, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, H.I.; Birkhofer, K.; Smith, H.G.; Palmu, E.; Hedlund, K. Agricultural Land Use Affects Abundance and Dispersal Tendency of Predatory Arthropods. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2017, 18, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).