Abstract
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) has significantly transformed transportation, offering environmental advantages by curbing greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel dependency. However, their increasing adoption poses challenges for power systems, especially distribution systems, due to the direct connection of EVs with them. It requires robust infrastructure development, smart grid integration, and effective charging solutions to mitigate issues like overloading and peak demand to ensure grid stability, reliability, and sustainability. To prevent local equipment overloading during peak load intervals, the management of EV charging demand is carried out in this study, considering both the time to deadline and the energy demand of EVs. Initially, EVs are prioritized based on these two factors (time and energy)—those with shorter deadlines and lower energy demands receive higher rankings. This prioritization aims to maximize the number of EVs with their energy demands met. Subsequently, energy allocation to EVs is determined by their rankings while adhering to the transformer’s capacity limits. The process begins with the highest-ranked EV and continues until the transformer nears its limit. To this end, an index is proposed to evaluate the performance of the proposed method in terms of unserved EVs during various peak load intervals. Comparative analysis against the earliest deadline first approach demonstrates the superior ability of the proposed method to fulfill the energy demand of a larger number of EVs. By ensuring sustainable energy management, the proposed method supports the widespread adoption of EVs and the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable transportation system. Comparative analysis shows that the proposed method fulfills the energy needs of up to 33% more EVs compared to the earliest deadline method, highlighting its superior performance in managing network loads.
1. Introduction
The increasing use of electric vehicles (EVs) has brought about substantial changes in transportation, offering environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels [1]. EVs contribute to cleaner air and a more sustainable future. However, their growing presence presents challenges for power systems [2]. Handling the added electricity demand necessitates strong infrastructure development, effective grid integration, and intelligent charging solutions to prevent issues like overloading and peak demand [3]. Maintaining grid stability and reliability while managing this increased load poses a significant ongoing challenge [4].
This presents a notable challenge for residential distribution circuits as EVs directly connect to them. Peak electricity demand in residential areas often coincides with residents beginning to charge their EVs upon arriving home [5]. For example, a single EV charger can cause a household to consume three times more electricity than usual in various places [6]. Shared parking stations in communities, like residential apartment parking lots, exacerbate this issue as multiple residents charge their EVs simultaneously. This scenario can strain the local transformer, resulting in overloading and reliability concerns. This increased demand for electricity from EV charging can lead to voltage fluctuations and increased losses in the distribution system, affecting the overall efficiency and reliability of the grid [7]. Additionally, without proper management strategies in place, the increased load from EV charging can necessitate costly infrastructure upgrades to accommodate the growing number of EVs in residential areas [8]. The assessment of public EV charging station accessibility in King County, Washington, is carried out in [9], revealing significant spatial disparities and equity implications that inform sustainable urban planning. Similarly, research on photovoltaic-powered electric vehicle charging stations is carried out in [10], highlighting their potential for economic growth and decentralized energy systems. It also discussed the energy usage, costs, and payback periods that support their viability and guide future advancements in sustainable transportation. Therefore, effective management of EV charging is essential to ensure the stability and sustainability of residential distribution circuits [11].
Therefore, various studies have been proposed in the literature to address the load management of shared charging stations, broadly categorized into two groups. The first category focuses on EV load management through demand-side management and renewable integration. For instance, in [12], demand response strategies are employed for shared EV planning, considering power grid overload and charging service operations. In another study [13], transactive energy methods are applied to shared parking lots equipped with EV charging and rooftop PV systems. Additionally, a planning framework for gridable parking lots is explored in [14], considering uncertainties in user behavior while accommodating EVs. A data-driven demand-side management approach for a solar-powered electric vehicle charging station connected to a microgrid is proposed in [15], utilizing solar power to reduce conventional energy use during peak demand and addressing obstacles to EV adoption. A customer feedback-based EV charging scheduling method is proposed in [16] to reduce peak loads. A deep reinforcement learning method is used for the maintenance scheduling of distribution transformers. A hierarchical coordination framework is proposed in [17] for EVs to optimize domestic load, demonstrating significant peak demand reduction in a real distribution network. A reliability-driven time-of-use tariff is proposed in [18] for EV integration, enhancing grid stability through optimized pricing and advanced stochastic modeling. A two-layer optimization framework based on the Stackelberg leader-follower model is proposed in [19] to manage a tri-level energy management strategy for coordinating EV charging, incorporating decentralized energy requirement collection by aggregators, centralized optimization by microgrids, and upper-level coordination with a system operator.
The second category revolves around local demand management of EVs in shared parking lots. For example, ref. [20] considers vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) service to locally manage EV load in shared parking stations. Similarly, another study [21] examines EV charging at a parking garage with limited power capacity, utilizing the least laxity approach to address fairness concerns. Game-theoretic approaches are also employed for local EV load management. For example, a game-theory-based distributed charging control method for EVs is proposed in [22], utilizing price-driven charging models to minimize individual EV costs while ensuring network security. Additionally, in [23], Stackelberg’s game model is utilized to manage EV load, considering their utility for charging and discharging against set prices. A methodology for fair management of local energy communities with EVs in V2G programs is proposed in [24]. Results show that clustering EVs based on characteristics results in significant peak demand reduction. Non-linear charging profiles and the use of an augmented Lagrangian-based decentralized model predictive control are used in [25] for efficient and scalable power management in smart parking lots. A game-based coordinated charging price mechanism for parking clusters is proposed in [26], emphasizing vehicle aggregation and bi-directional power flow modeling. A dynamic pricing model for managing EV loads is proposed in [27] to mitigate transformer overloading in distribution systems. Finally, the Internet of Things and deep learning are used in [28] to manage EV loads in residential communities.
It is evident that existing studies have mainly focused on either energy demand [20,22,23] or flexibility in charging deadlines (laxity) [21] when allocating energy to EVs. This approach may lead to inefficient utilization of available local equipment capacity. For instance, allocating most capacity to a lower laxity customer with higher demand might cause dissatisfaction among numerous EV owners. Similarly, solely prioritizing energy demand could result in discontent among consumers with lower laxity. In addition, consideration of only one of these factors will result in energy demand fulfillment of a lesser number of EVs. Therefore, considering both factors in energy allocation becomes crucial to maximize the number of EVs with met energy demands, ensuring satisfaction for the maximum number of EV owners while adhering to local equipment limitations, such as avoiding transformer overloading.
To overcome issues in existing literature, this study employs both the time to deadline and the required energy of EVs to allocate energy effectively. Considering these factors maximizes the number of EVs having their energy demands met while adhering to local equipment capacity constraints. Initially, EVs are ranked based on these factors, and energy allocation commences with the highest-ranked EV. The transformer’s remaining capacity is updated after each allocation, and the subsequent EV is selected accordingly. Additionally, an index called the unserved index is introduced to evaluate the method’s performance, measuring the percentage of unserved EVs across various intervals. Using this index, the performance of the proposed method is compared with the earliest deadline first approach. The major contributions of this study can be summarized as follows:
- The study introduces a novel energy allocation method that considers both the time to deadline and required energy of EVs, maximizing the number of EVs with met energy demands while adhering to local equipment capacity constraints;
- An unserved index is proposed to evaluate the effectiveness of the energy allocation method, measuring the percentage of unserved EVs across various intervals;
- The proposed method demonstrates improved efficiency in energy distribution and higher satisfaction among EV owners compared to traditional approaches, such as the earliest deadline first method.
2. Network Configuration and EV Load Estimation
2.1. System Configuration
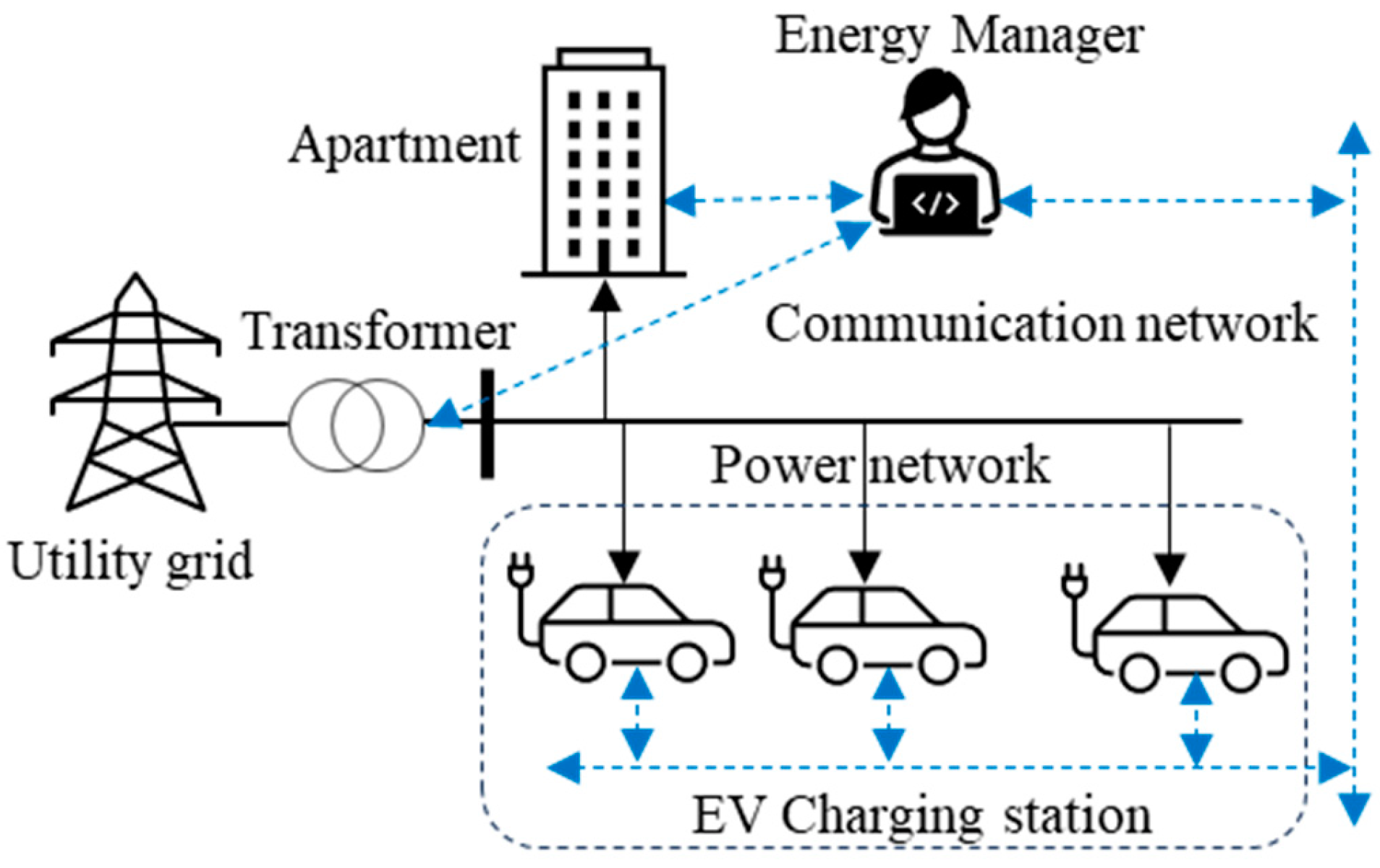
In this study, a residential apartment complex with a shared parking station is considered. However, the proposed method is adaptable for other shared parking locations, such as those in commercial and industrial buildings. The illustration of a typical apartment complex with a shared parking station is depicted in Figure 1. The principal stakeholders in this setup include the energy manager (EM), distribution system operator (DSO), and EV owners. It is important to note that flexibility and management of building loads are not within the scope of this study and are not considered.
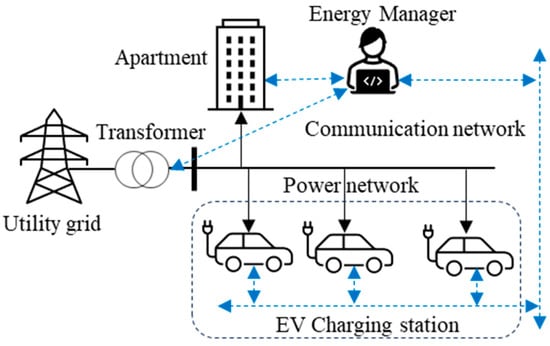
Figure 1.
Configuration of a residential apartment with a shared parking station.
The EM holds the responsibility of managing the load for both the building and the charging station. Additionally, the EM is also responsible for estimating the daily load of EVs, which will be further discussed in the following section. The EM establishes communication with the distribution system operators to acquire transformer-related information, including rated capacity and loading settings. Utilizing this information along with the combined load of the building and EVs, the EM estimates the available capacity of the transformer within each time interval throughout the day. Subsequently, the EM allocates energy to EVs considering both the remaining time to the deadline and the required energy by the EVs. In cases where the required energy by the EVs exceeds the available capacity of the transformer, the proposed allocation strategy is adapted accordingly.
2.2. EV Load Estimation
The section discusses a three-step method for determining the load profile of EVs, including feature extraction, pre-processing, and estimation. It emphasizes the challenge of realistic EV load profile estimation due to uncertainties and complex interdependencies among factors, highlighting the use of National Household Travel Survey (NHTS) data for behavior analysis [29,30]. Pre-processing of the NHTS data is crucial to avoid errors, and the proposed model can be applied to other localities if similar data are available. The study selected ten features from the NHTS data to calculate parameters for estimating power density functions for arrival time, departure time, and mileage of EVs. The analysis focused on four classes of vehicles: passenger cars, pickup trucks, sport utility vehicles, and vans. Details about the process can be found in [31].
Based on the load profiles of individual EVs, the load of the EV fleet can be determined. The net load of the EV fleet is necessary for each interval to maintain the normal operation of the transformer and prevent overloading. The daily EV load relies on various factors, such as the daily mileage of EVs, the energy efficiency of the vehicles, and the state-of-charge (SOC) upon the EVs’ return [32]. These parameters are inherently stochastic and are dependent on the behavior of the EV driver. As a result, most of these parameters, including daily mileage and SOC, are typically estimated using lognormal distributions [33,34]. Mathematically, daily mileage can be written as
where d is the daily mileage. µ and σ, respectively, represent the mean and standard deviation of daily mileage. Similar to [13], it is assumed that SOC reduces linearly with the traveled distance, and the initial SOC at the arrival time () can be computed as
where is the SOC at the start of the day, and D is the distance traveled by the EV and is the mileage efficiency of the EV. Details about individual EV load estimation can be found in [13]. After determining individual EV load, the EV fleet load is estimated as
where is the load of an individual EV and N is the total number of EVs in the parking station during interval t. is the load of the EV fleet during interval t. The net EV load is used in the following section to compare and allocate the available power capacity of the transformer among different EVs available in the parking station at that time.
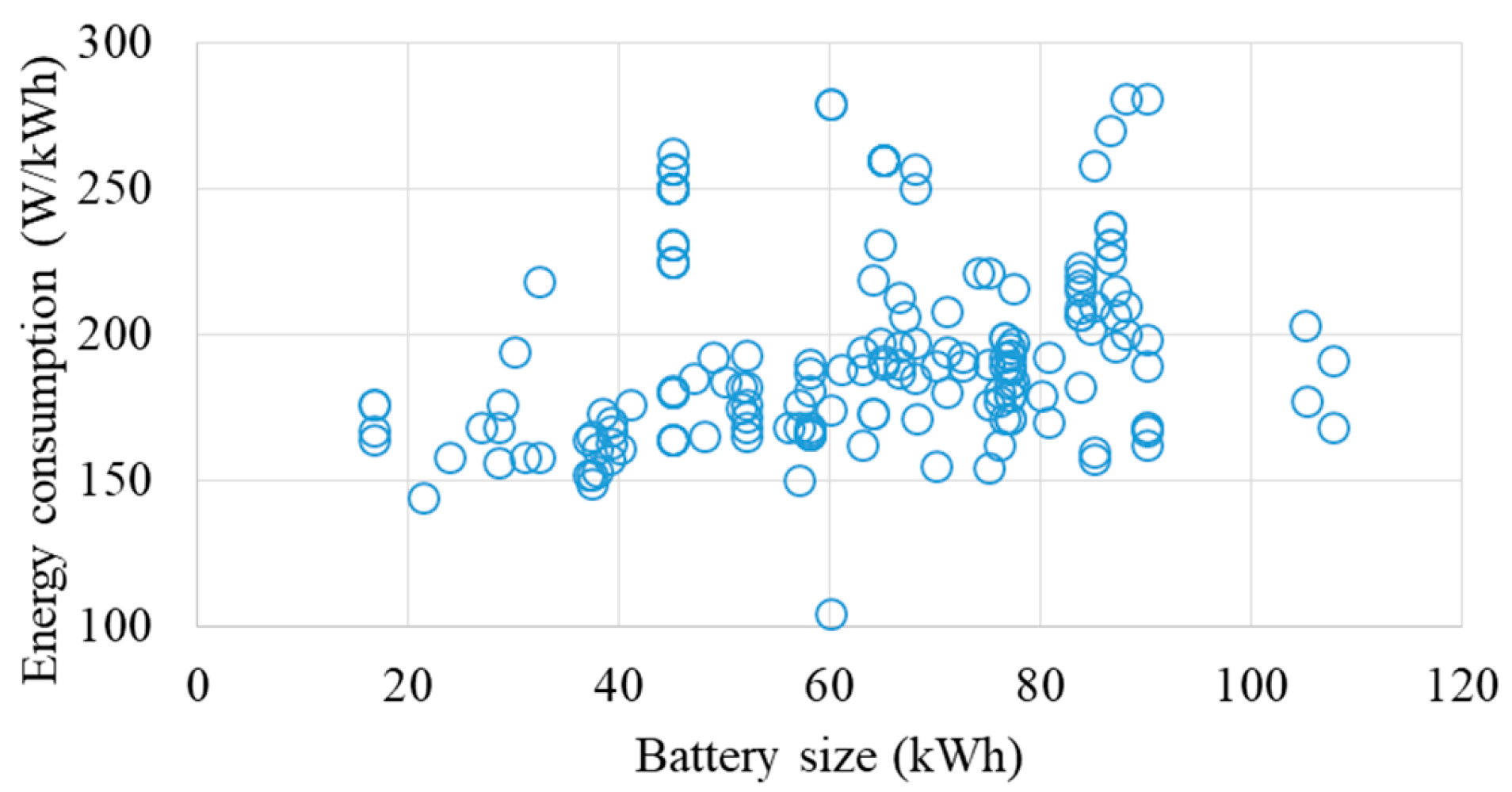
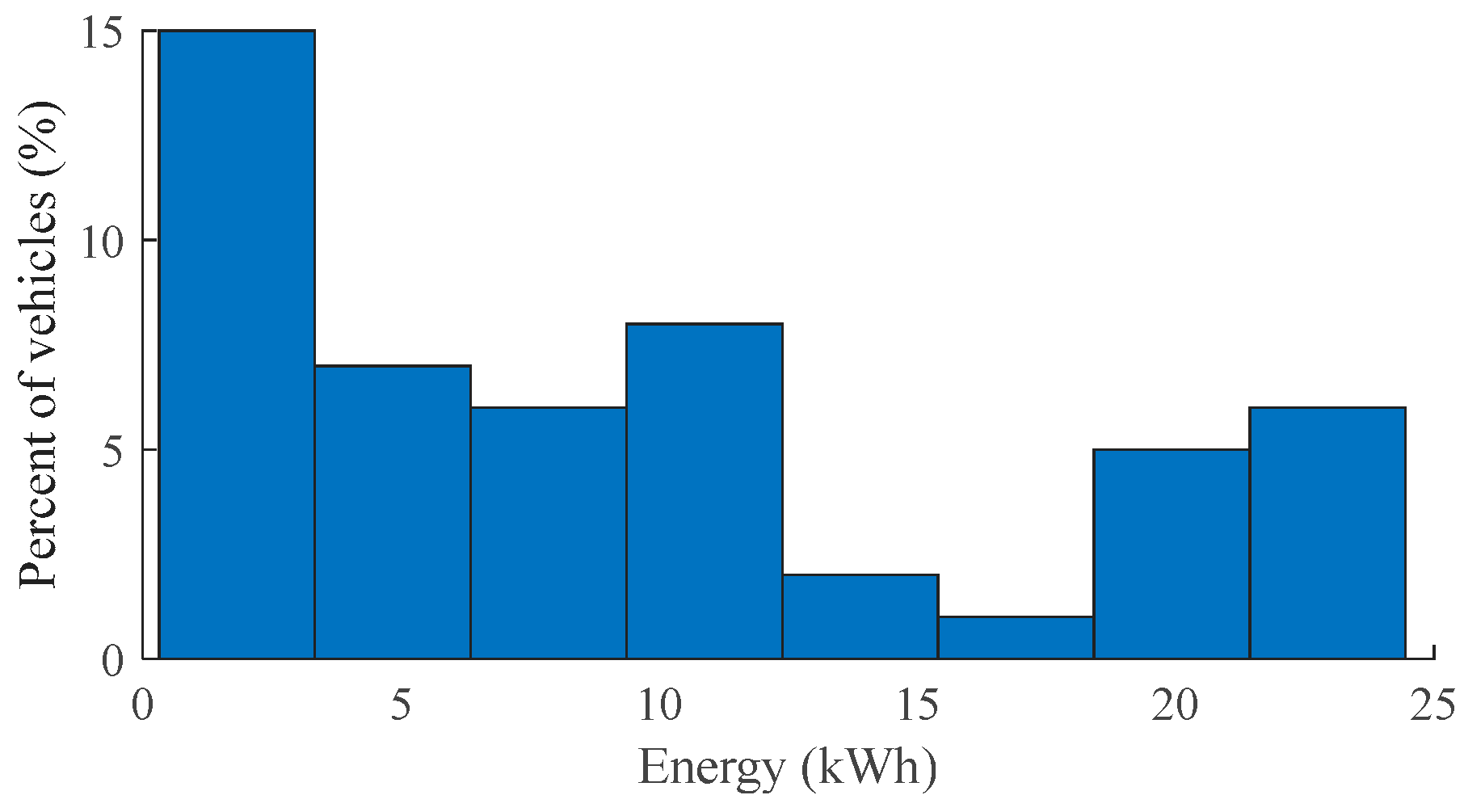
After estimating the daily mileage for vehicles, the study incorporates technical parameters specific to EVs. The dataset, referenced in [35], provides information on the mileage efficiency and usable battery size of all commercially available EVs. As of March 2024, the average energy efficiency for EVs is 195 Wh/km, and the average usable battery size is 68.9 kWh. An overview of different EV models is presented in Figure 2. These data serve as the foundation for computing the daily energy consumption of EVs. Figure 3 illustrates the daily energy consumption of EVs, showing that most EVs consume under 25 kWh of energy per day. This observation aligns well with the average vehicle mileage of under 100 km per day and an average energy efficiency of 195 Wh/km.
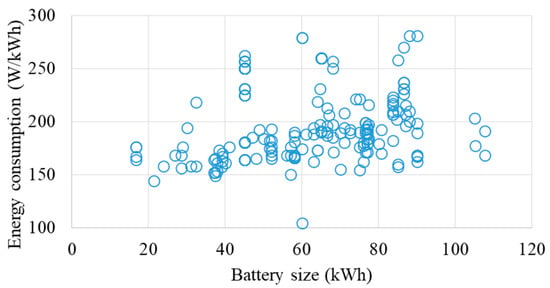
Figure 2.
Energy consumption and battery size of EVs.
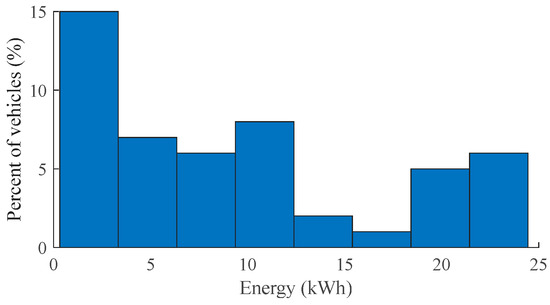
Figure 3.
Daily energy consumption of EVs.
3. Energy Allocation to EVs
The increasing adoption of EVs poses a challenge to the power grid, particularly in urban areas, where transformer overloading can occur due to high concentrations of EVs charging simultaneously [36]. To mitigate this issue, it is essential to allocate the available capacity among EVs effectively. This requires intelligent management systems that can dynamically adjust charging rates based on grid capacity and prioritize EVs based on factors such as battery state of charge and urgency of recharge.
Efficient allocation of available capacity among EVs can help defer equipment upgrades in the power grid. By intelligently managing the charging schedules of EVs, grid operators can reduce peak loads and avoid overloading transformers [37], which are common triggers for equipment upgrades. This optimization allows the existing infrastructure to handle the increased demand from EVs without the immediate need for costly upgrades, thereby deferring these expenses and improving the overall efficiency of the grid.
The proposed model in this study adopts a prioritization strategy for EV charging based on remaining time to deadline and energy demand to prevent transformer overloading. It assumes a static transformer capacity throughout the day and accurate and predictable daily load estimations for buildings and EVs. In addition, it considers prioritization focused solely on time and energy demand, fixed charging rates within defined limits, and exclusive management of EV charging without flexibility in building load handling. Potential scenarios where these assumptions may not hold true include fluctuating transformer capacities due to environmental factors or maintenance, unpredictable variations in load profiles, the need for more nuanced prioritization criteria beyond time and energy, evolving charging infrastructure capabilities such as vehicle-to-grid technologies, and dynamic adjustments in charging strategies based on real-time grid conditions.
3.1. Demand Management of Charging Stations
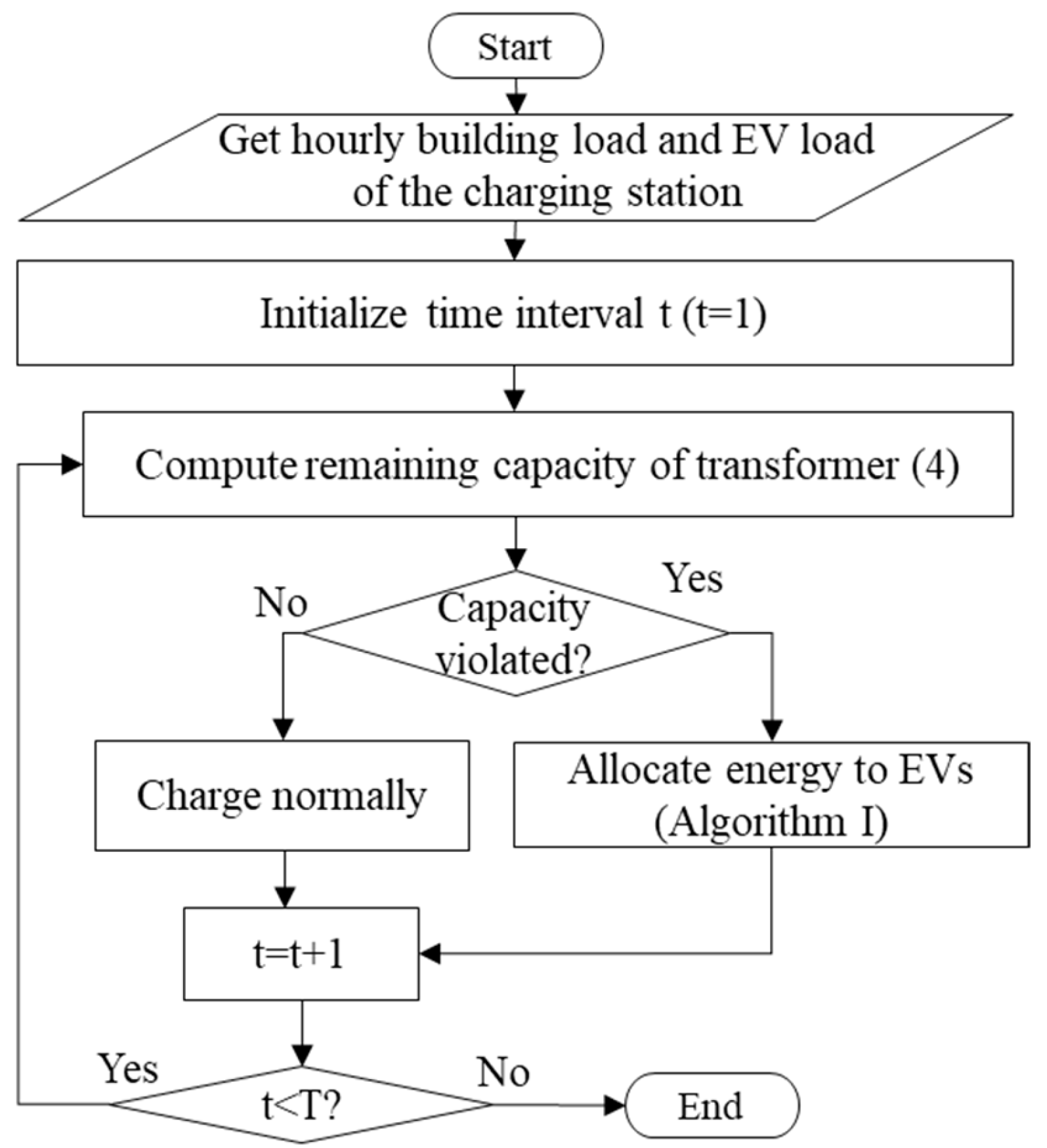
An overview of the proposed demand management process is shown in Figure 4. First, the hourly load of the apartment (building) and the EVs in the parking station (estimated in the previous section) is obtained. Then, the remaining capacity of the transformer for interval t () is determined as
where is the rated capacity of the transformer and is the electric load of the building. If the reaming capacity is positive (capacity not violated), all EVs are charged normally. However, if the remaining capacity is negative (capacity violated), then Algorithm 1 (discussed in the next section) is used to rank and allocate energy to EVs. This process is repeated for all intervals of the day.
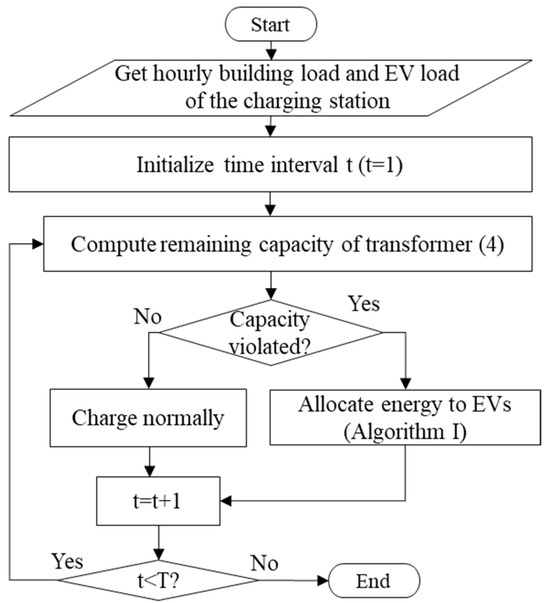
Figure 4.
Flowchart for energy allocation to EVs.
| Algorithm 1 Energy allocation during peak load intervals. |
 |
3.2. Energy Allocation during Peak Load Intervals
In case of capacity violation, EVs are ranked based on the time to deadline and required energy by each EV. For each interval t, the number of EVs in the parking station, the energy demand of each EV, and the deadline for charging each EV are obtained. Then, the remaining capacity of the transformer is obtained using (4). Then, the normalized energy for each EV () is computed as
where is the original energy demand of EV n. Similarly, the normalized time to deadline () is computed as
where is the original time to the deadline of EV n (in minutes). Based on the normalized energy and time-to-deadline factors, the rank of EV n () is computed as
where are weight factors signifying the importance of each portion (required energy and time to deadline). It can be observed that EVs having the lowest time to deadline and lowest required energy will be ranked higher. This is to maximize the number of EVs that have urgent needs to fulfill their energy demand while respecting equipment constraints.
After determining the rank of each EV, EVs are sorted (EVs with the highest rank are placed on the top of the queue). Energy is allocated to EVs starting from the top of the queue using
where is the energy allocated to EV n at time t and is time in hours. After each allocation, the remaining capacity of the transformer is updated as
This process is repeated until the transformer is near overload. EVs ranked below this point do not receive power for the current interval, but they are considered for the next interval.
The process can be summarised as follows. First, EVs are prioritized based on their time to deadline and energy demand. For each time interval, the model computes normalized energy and time factors for EVs, ranks them using weighted criteria, and allocates energy starting from the highest-ranked EVs. Energy allocation continues until the transformer’s capacity nears overload, updating the capacity after each allocation. EVs ranked lower in priority for a given interval are considered in subsequent intervals. This approach aims to optimize grid resource utilization while ensuring critical energy needs are met efficiently during high-demand periods.
3.3. Performance Evaluation Indices
To evaluate and compare the performance of different methods for managing EV loads, common indices are essential. These indices provide a standardized way to measure key metrics such as the number of EVs served under different methods. By using indices, researchers and policymakers can objectively assess the effectiveness of various strategies and make informed decisions about which methods are most suitable for their specific needs and goals.
Therefore, to evaluate the performance of the proposed method and compare it with other existing methods, an index is proposed in this study. It is named an unserved index, and it measures the percentage of EVs not served during different intervals of the day. It can be mathematically modeled as
where is the number of EVs present in the charging station during interval t and is the number of EVs served during interval t under method m. This index gives a quantitative measure of the percentage of unserved EVs under different methods.
The unserved index proposed in this study offers a valuable quantitative measure of the effectiveness of EV load management methods. Calculated as the percentage of EVs not served during charging intervals, it directly reflects how well a method meets EV charging demand. A lower unserved index indicates higher efficiency in serving EVs, minimizing unmet demand and potential waiting times. Conversely, a higher index suggests inefficiencies in allocation or capacity, highlighting areas for improvement in charging infrastructure or management strategies. Policymakers and researchers can utilize this index to compare and optimize different methods, ensuring more reliable and responsive EV charging systems that better meet the needs of users and contribute to sustainable transportation goals.
4. Simulation Results
To evaluate the performance of the proposed method in allocating power to EVs during peak load intervals, daily energy consumption profiles from a dataset representing an actual distribution system are utilized. The dataset used in this study pertains to a bus of an actual distribution system owned by a municipal utility situated in the Midwest region of the United States. This system constitutes a fully observable network equipped with smart meters installed across all customer sites [16]. Specifically, a bus from feeder 3 is selected, encompassing 135 secondary distribution transformers and fed by a 69-kV substation. This section of the distribution grid predominantly serves residential areas and accommodates both single and three-phase loads.
4.1. Input Data
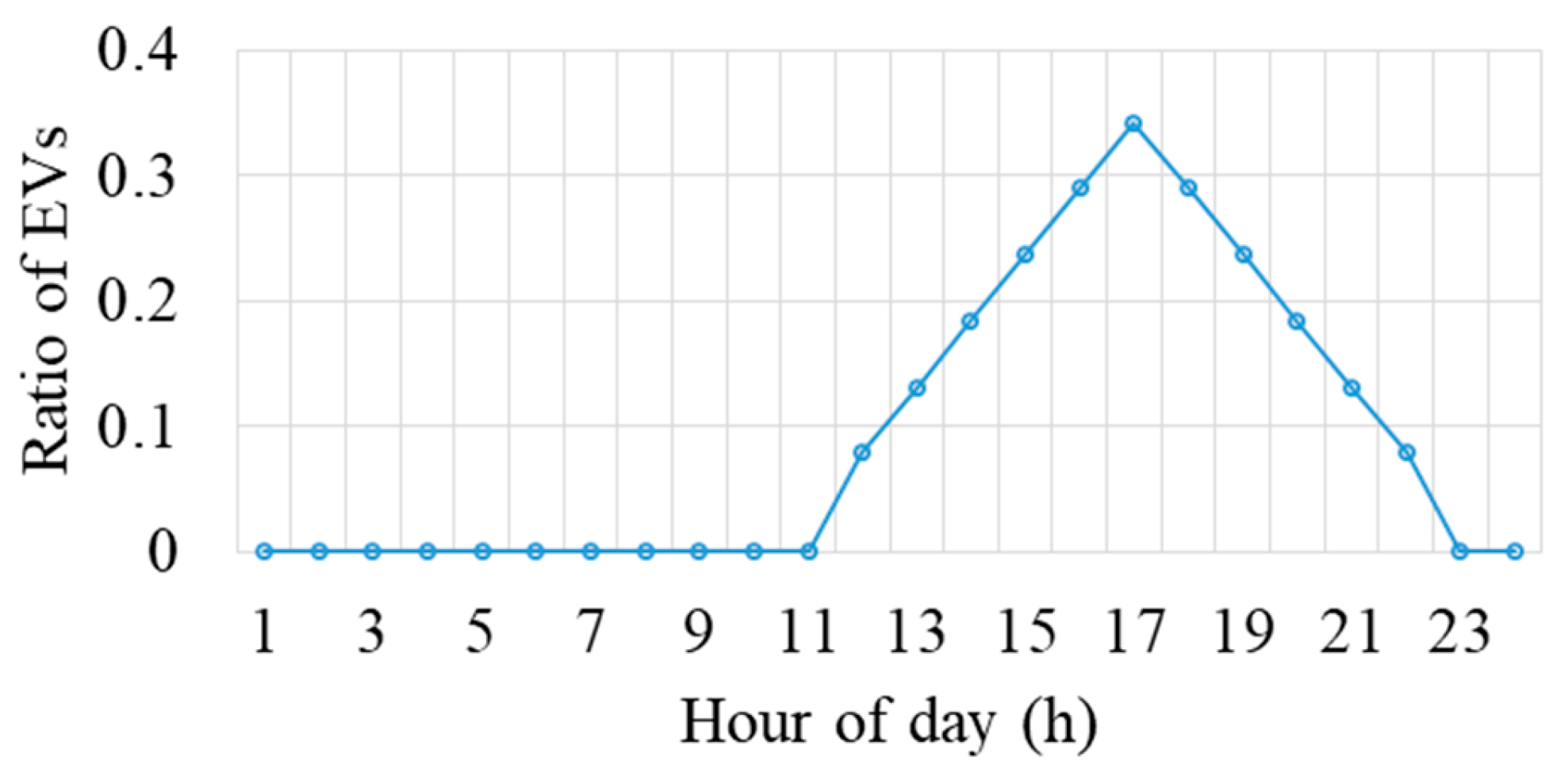
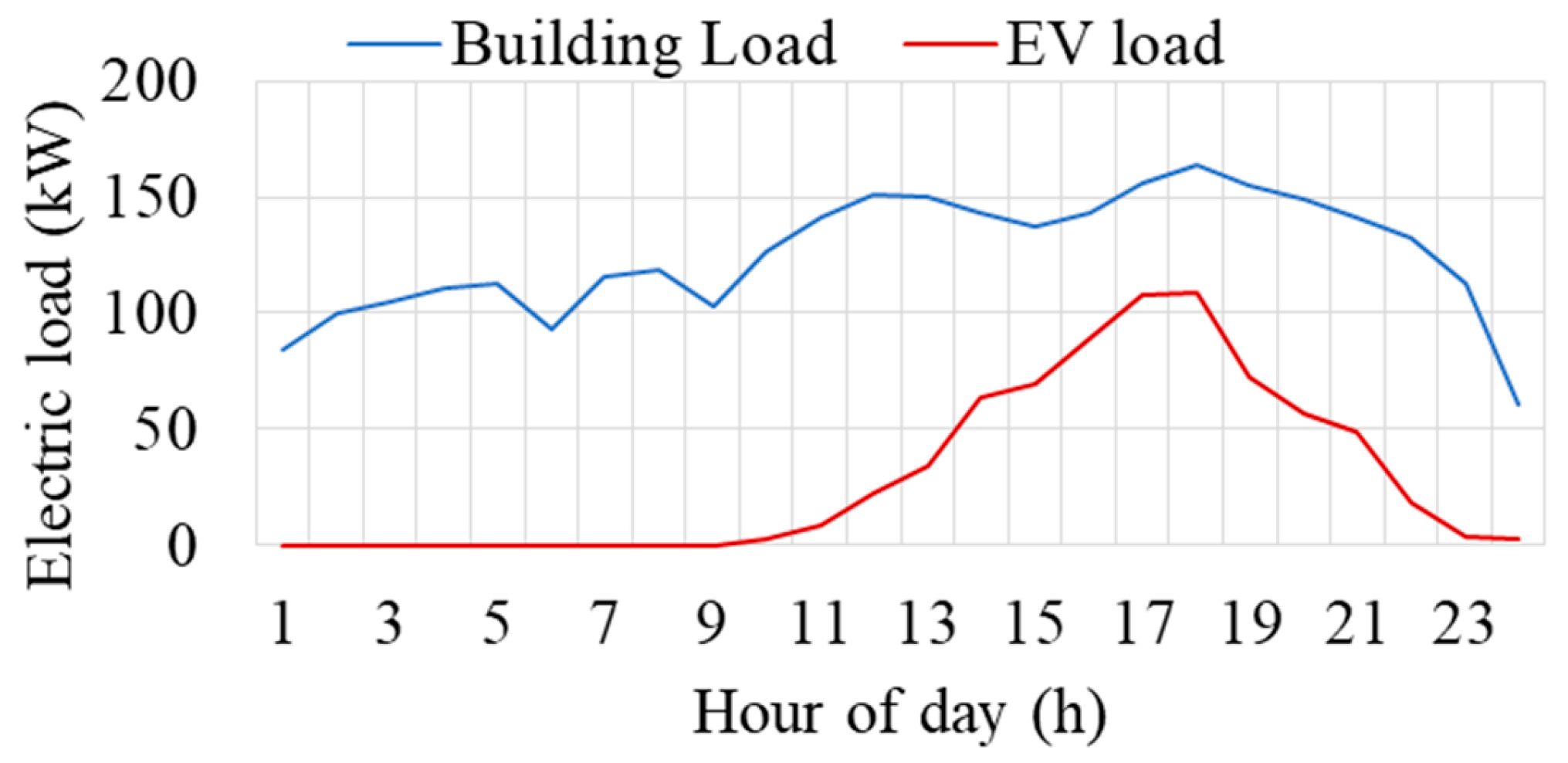
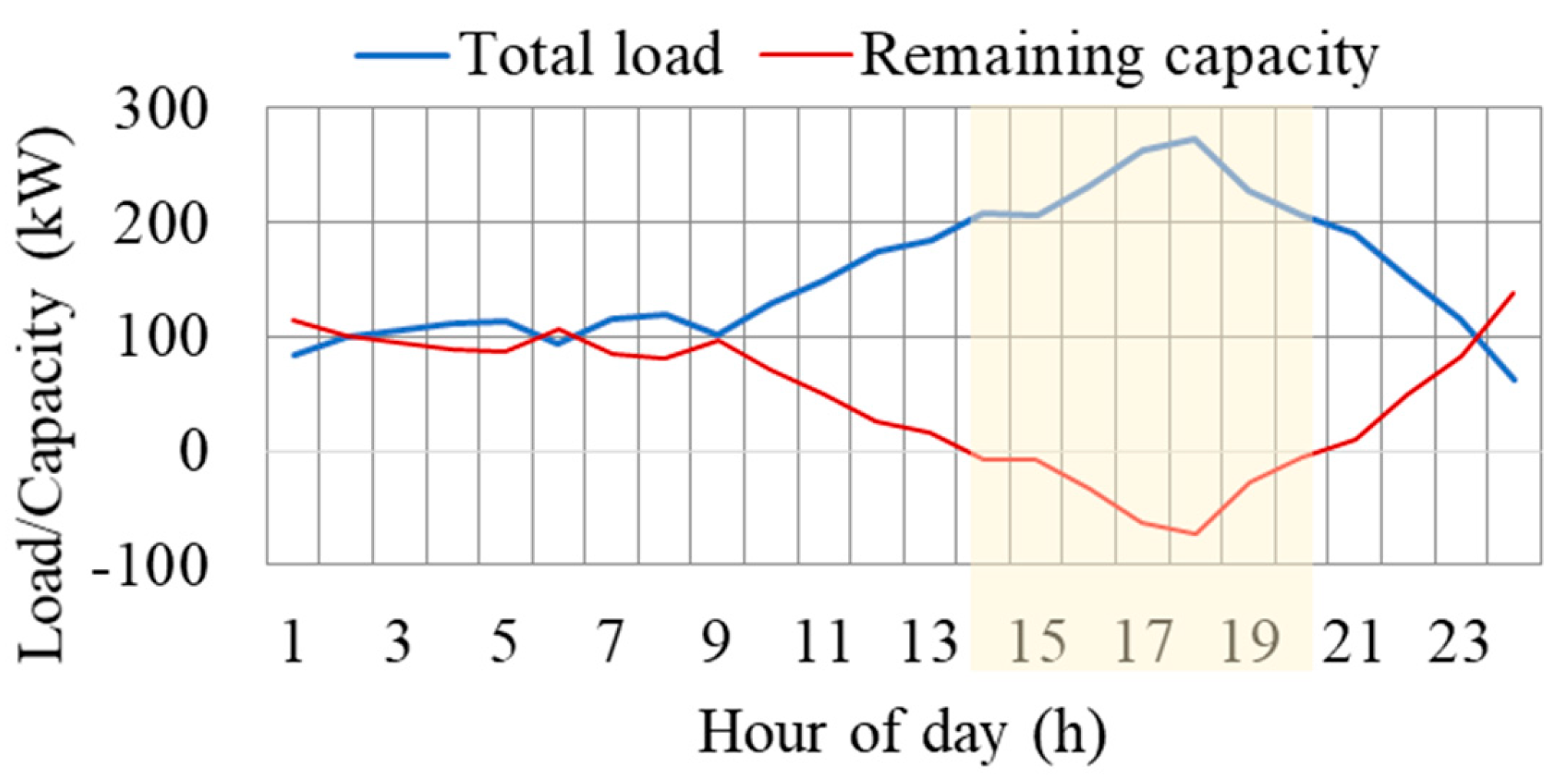
In this study, a residential apartment with a shared parking station is used, as shown in Figure 1. An EV fleet of 50 EVs is considered [35], and the distribution of EVs at the charging station during different hours of the day is depicted in Figure 5. Level 1 and level 2 chargers are considered, which are most commonly used in the residential sector. Notably, as a residential community, the majority of EVs arrive during evening hours, as expected. Figure 6 shows the hourly load profile of the building (apartment) sourced from the US distribution network, coupled with the EV load estimated as discussed in Section 2.2. This figure highlights the simultaneous occurrence of the EV peak load with the residential peak load, as previously mentioned in the introduction [5]. Finally, Figure 7 presents the total load, comprising both the combined EV and building load, shown with the remaining capacity of the transformer. The remaining capacity denotes the transformer capacity available after catering to the building and EV load. Notably, during intervals 14–20, the transformer’s remaining capacity becomes negative, indicating overload situations. This signifies the necessity for load adjustments to avert transformer overloading during these intervals.
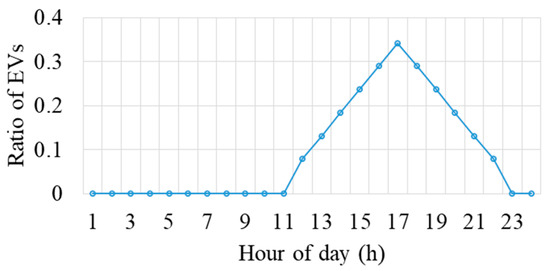
Figure 5.
Ratio of EVs arriving at the charging station.
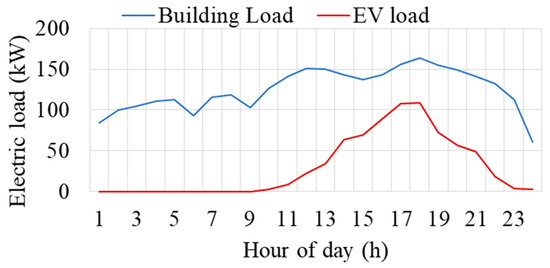
Figure 6.
Hourly load of apartment and EVs.
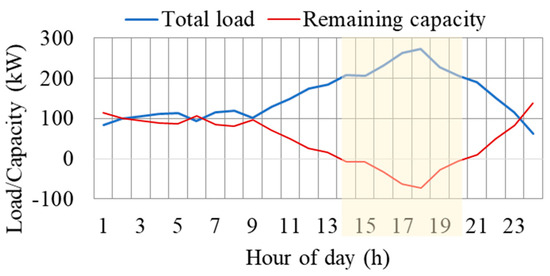
Figure 7.
Total (apartment and EVs) electric load and remaining capacity of the transformer.
A scheduling horizon of 24 h (1 day) with a time interval of 1 h is considered in this study. The model is developed and coded in MATLAB and tested on a computer with core i7 and 8 GB RAM.
4.2. Load Adjustment Analysis
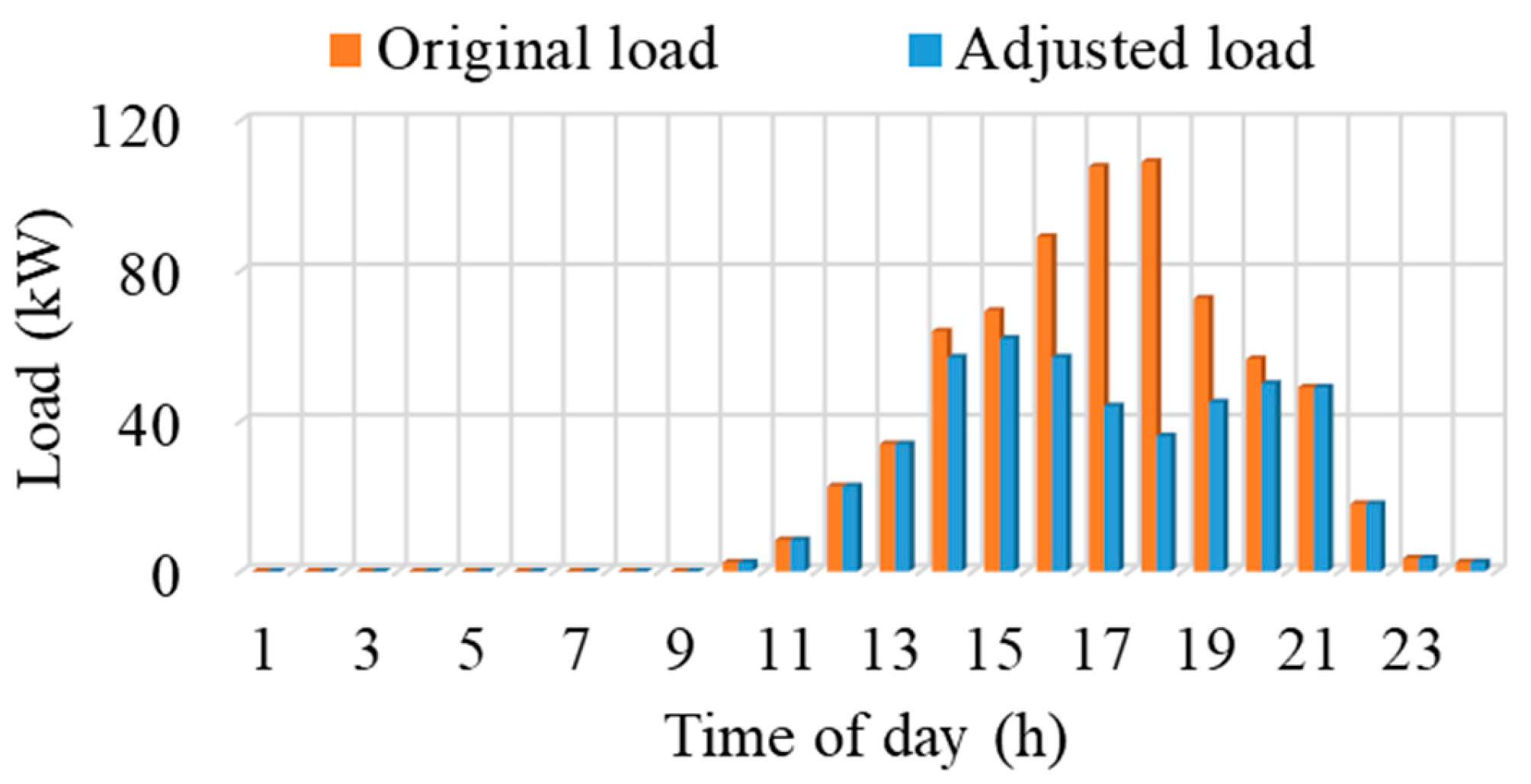
This section analyzes the load adjustment achieved through the proposed method by comparing it with the original EV load. Figure 8 provides an overview of the results, while a more in-depth analysis is presented in the subsequent section. The original EV load directly corresponds to the count of EVs at the charging station during different hours of the day (highlighted in figure). Notably, the proposed method reduces the load solely during the 14–20 h intervals, a response to identified transformer overloading occurrences within these time frames, as evidenced in Figure 7. The adjusted load correlates directly with the extent of transformer overload. For instance, the most substantial load reduction is evident in intervals 17 and 18, coinciding with severe transformer overloading. Conversely, minor load adjustments are visible in intervals 14 and 20 due to marginal overloading. No load adjustment during 10–13 h and 21–24 h, as the load remains lower compared to the transformer capacity.
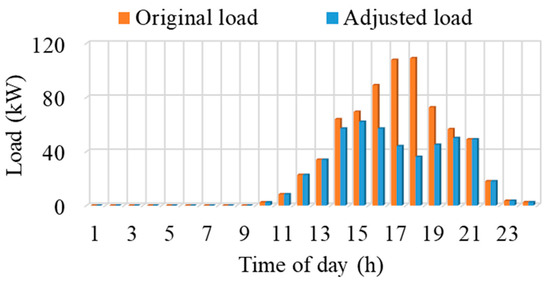
Figure 8.
Load adjustment to avoid transformer overload.
4.3. Energy Allocation to EVs
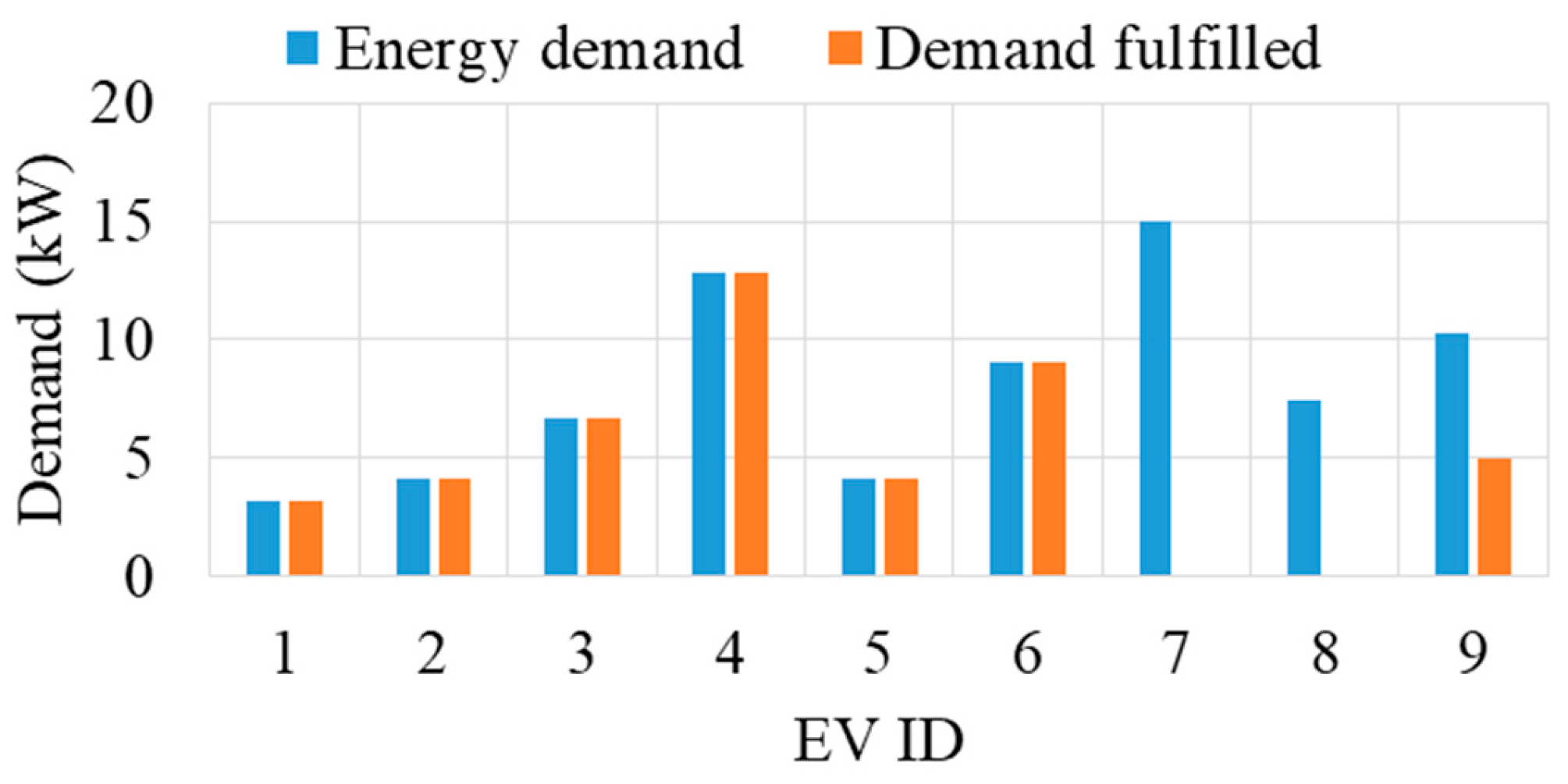
This section provides a detailed analysis of a specific interval (interval 19) to elaborate on the operational principles of the proposed method. During interval 19, the charging station has 9 EVs. At this time, the transformer had a remaining capacity of 45 kW, while the cumulative energy demand of the EVs amounted to 72.2 kW, necessitating a load adjustment of at least 27.7 kW. Table 1 presents the individual energy demands of the EVs in kW and their corresponding time to deadline in minutes. To facilitate the analysis, we computed the normalized energy demand (energy ratio) and time to deadline (time ratio) using Equations (5) and (6), respectively, with the results detailed in Table 1. These ratios were then employed to determine the rank (final rank) of each EV, also depicted in Table 1.

Table 1.
Ranking and allocation of energy to EVs.
Utilizing the final rank, energy is allocated to the EVs, and the outcomes for interval 19 are depicted in Figure 9. Notably, full energy allocation is made to EVs 1–6, while partial energy fulfillment for EV 9. This allocation sequence is determined by the ranking based on the time-to-deadline and required energy ratios of the EVs. For instance, EV2 secures the top rank, and its entire energy demand is met first, followed by EV1, EV6, EV5, EV3, and EV4, in that order. Subsequently, the remaining capacity is updated after each allocation. However, despite allocating energy to EV4, the remaining capacity was insufficient to fulfill the entirety of EV9’s energy demand. Therefore, partial energy is allocated to EV9. Ultimately, no energy allocation is made for EVs 7 and 8 due to their lowest rank, as outlined in Table 1, indicating higher deadlines and comparatively greater energy demands for both EVs.
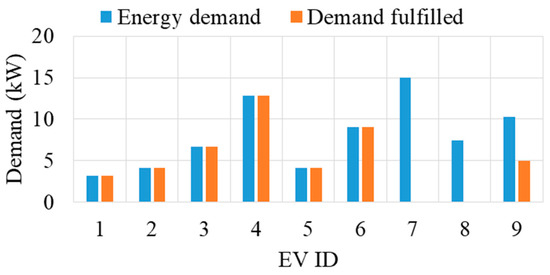
Figure 9.
Energy allocation to EVs under the proposed allocation method.
4.4. Comparative Analysis
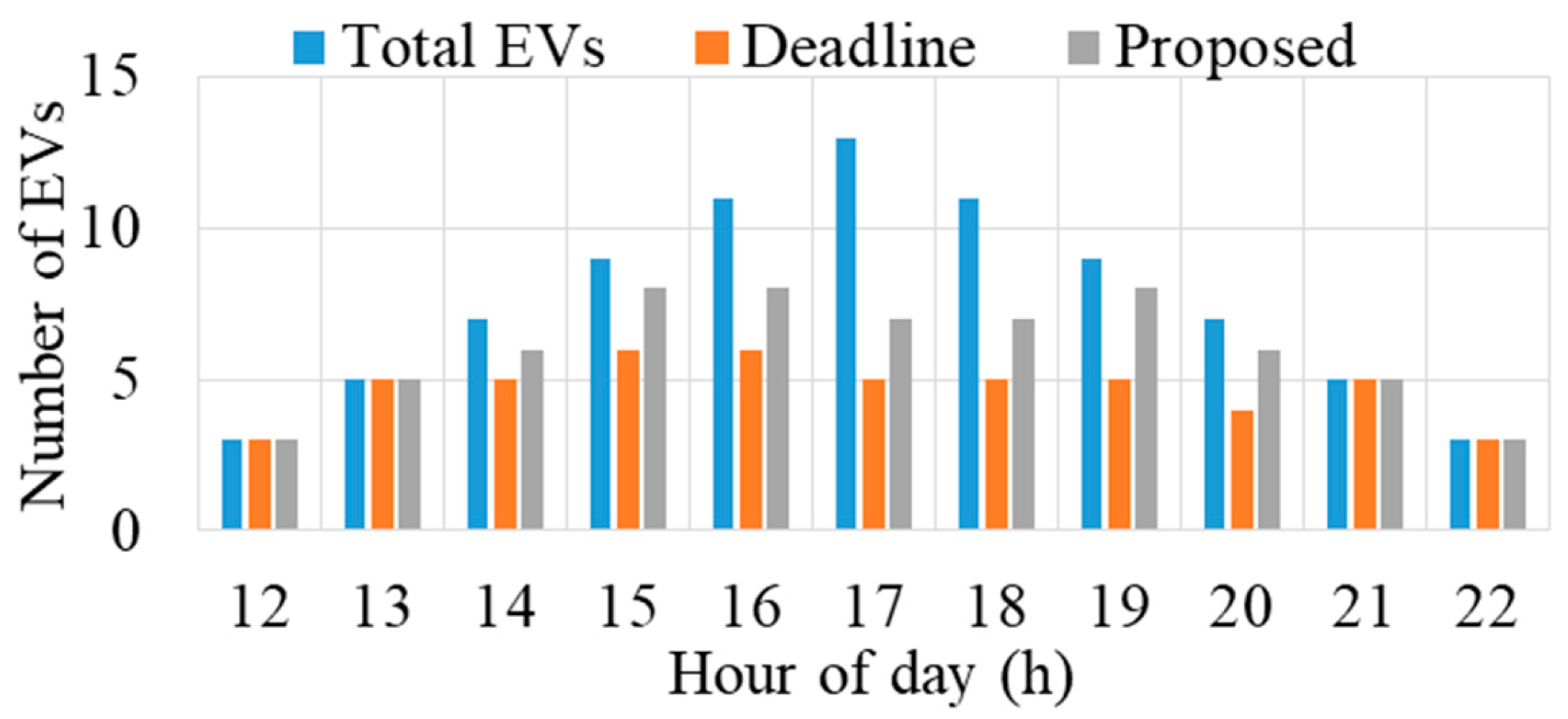
In this section, the performance of the proposed method is evaluated against the earliest deadline first method in terms of served and unserved EVs within intervals 12–22. The results presented in Figure 10 indicate that during Intervals 12, 13, 21, and 22, all EVs are served due to the absence of capacity constraints. However, from Intervals 14 to 20, only a portion of EVs is served due to the transformer’s capacity limitations. Notably, the proposed method consistently serves more EVs than the earliest deadline method throughout these intervals. This advantage is attributed to the proposed method considering both energy demand and time deadline for allocation decisions.
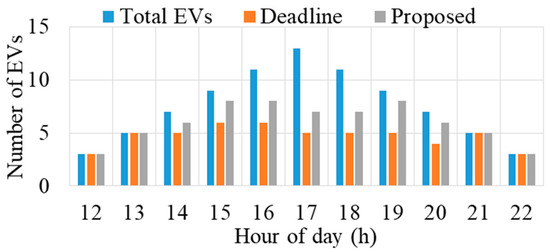
Figure 10.
Number of EVs served under different methods.
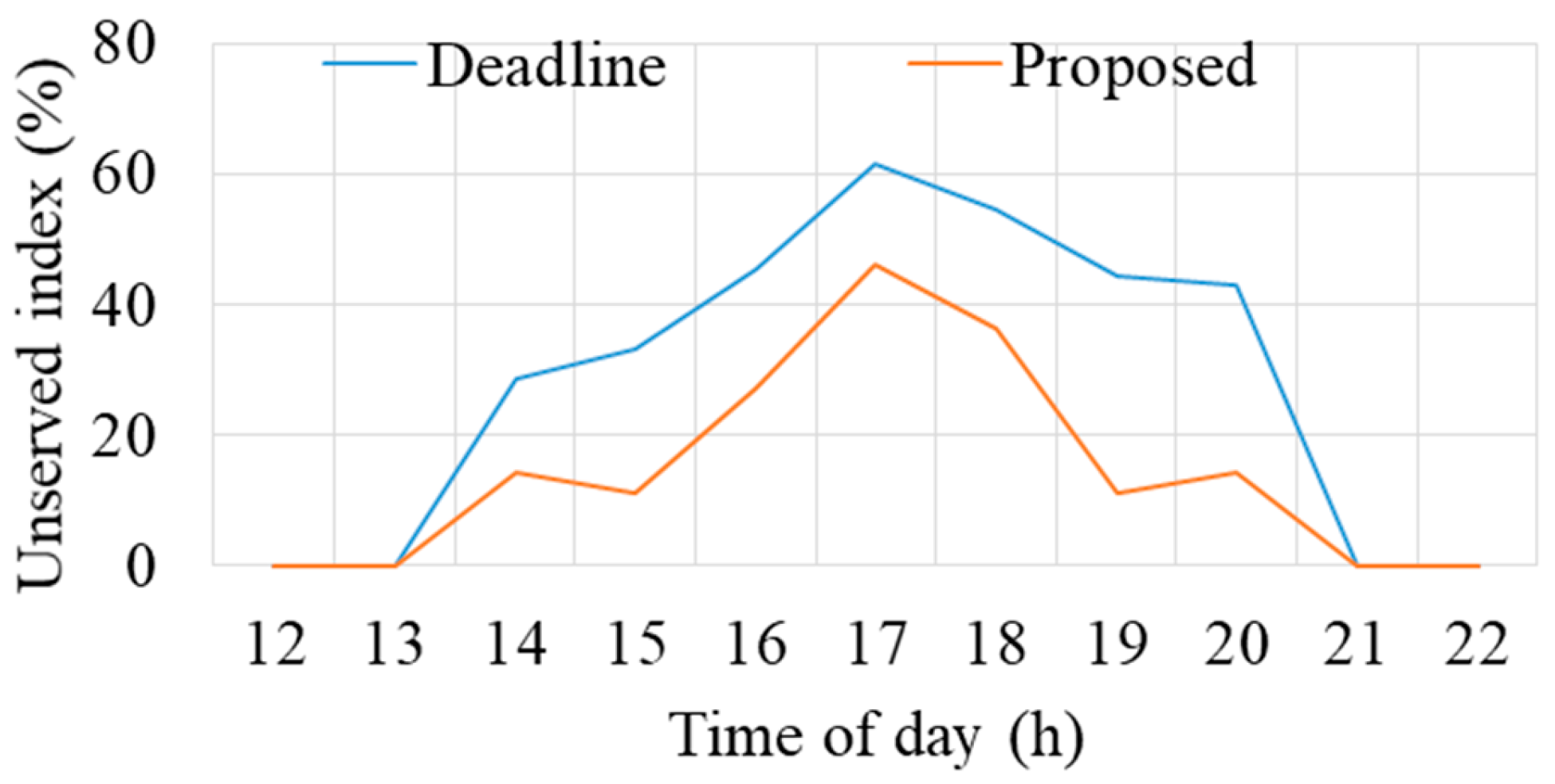
Additionally, both methods are also compared using the proposed unserved index, as shown in Figure 11. Similarly, the unserved index values consistently favor the proposed method over the earliest deadline method, showcasing lower values. During load adjustment intervals, this difference ranges from 14% to 33%, signifying the superiority of the proposed method in efficiently managing EV demand.
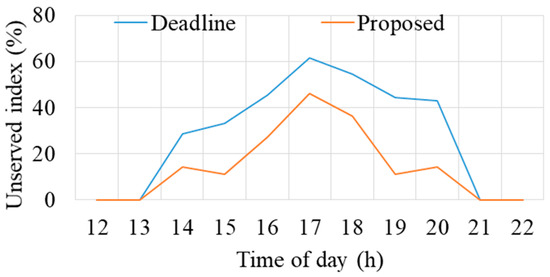
Figure 11.
Unserved index for different methods.
4.5. Weekly Analysis
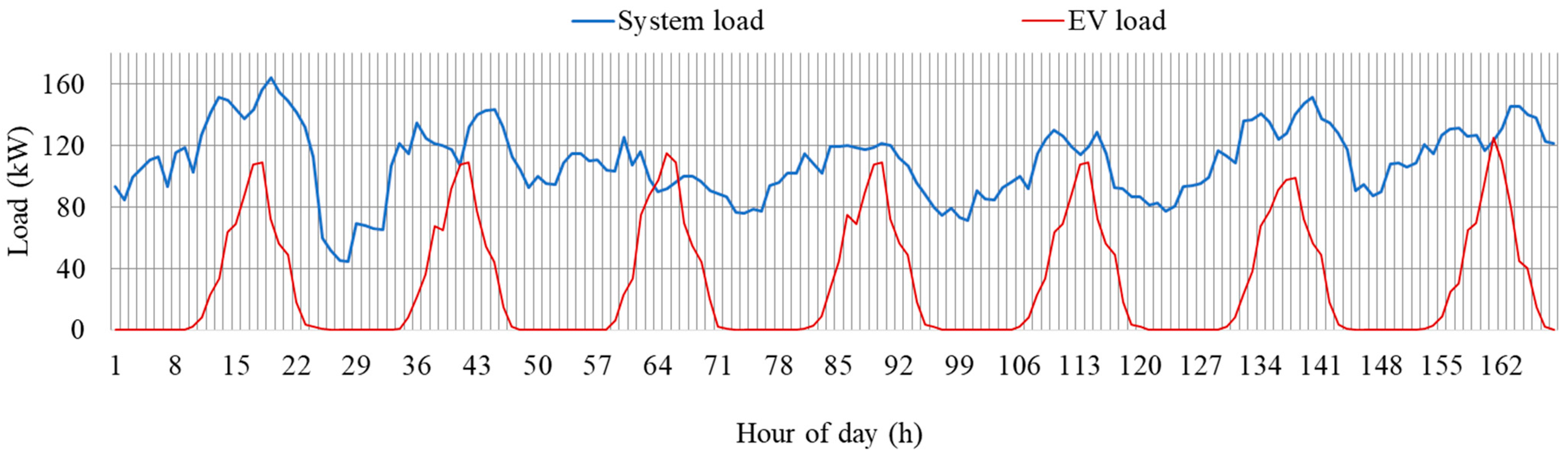
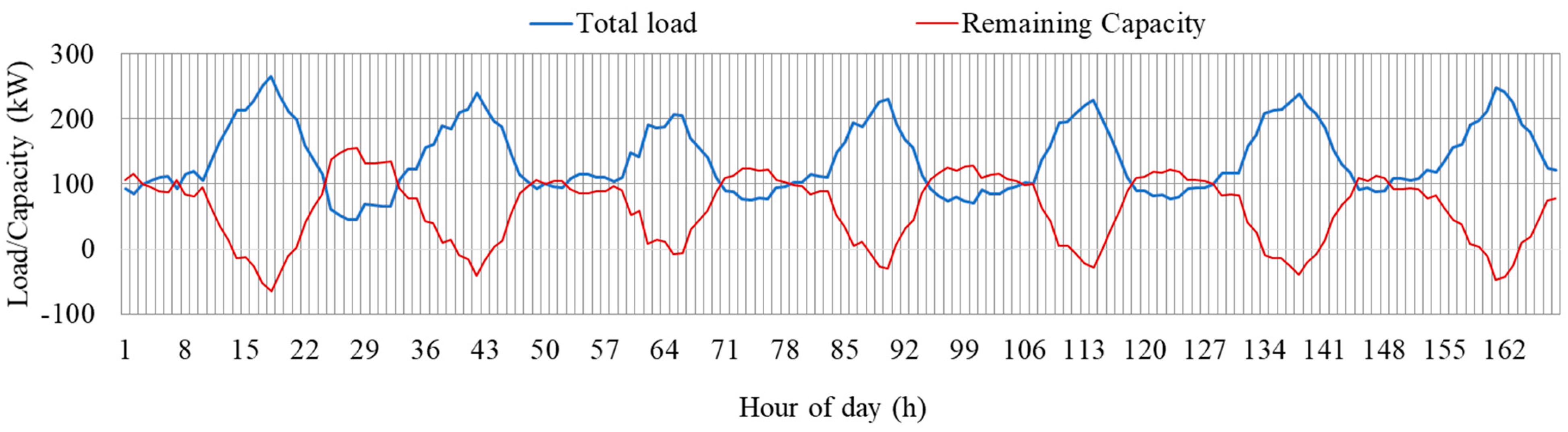
In this section, the performance of the proposed method is evaluated for seven consecutive days (a week). The purpose of this analysis is to determine the capability of the proposed method in managing the load of the network under different day types, such as weekdays and holidays. The hourly load profiles of the system and the EV fleet are shown in Figure 12. System load refers to the electric load of the transformers, excluding the load of EVs. The remaining capacity and total load of the transformer are shown in Figure 13. Total load refers to the system load and EV load. The remaining capacity refers to the capacity of the transformer after fulfilling the total load. It can be observed that the remaining capacity becomes negative during the evening hours of the day. This is due to the higher EV load coupled with higher residential load during evening hours, as shown in Figure 12.
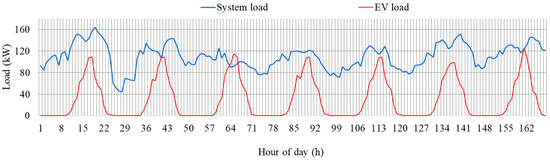
Figure 12.
Hourly profiles of the system and EV loads for one week.
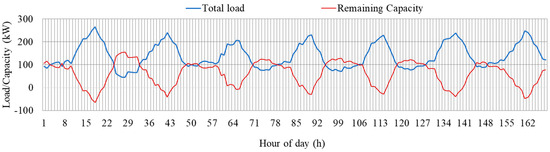
Figure 13.
Hourly total load and transformer remaining capacity.
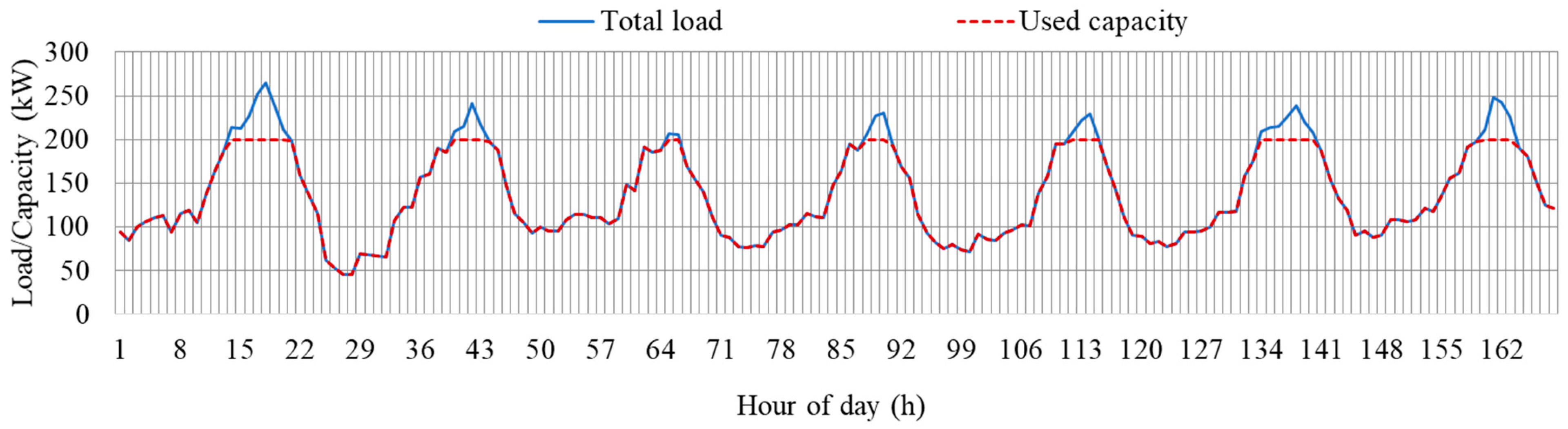
Figure 14 shows the performance of the proposed method in respecting the limits of the transformer. It can be observed that during normal hours, all the load is served, but during evening hours, some of the load is clipped to keep it below the ratings of the transformer. It should be noted that the system load is served first, and the clipped load is the EV load, as discussed in the previous section. The EVs to be served during these higher load intervals are based on the proposed method of ranking EVs.
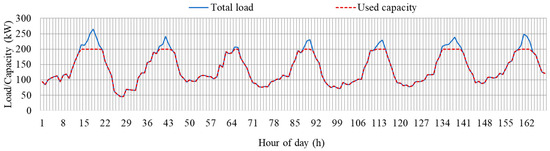
Figure 14.
Hourly profiles of transformer used capacity and total network load.
5. Conclusions
The study evaluates the performance of a method that prioritizes and allocates energy to electric vehicles based on time to deadline and energy demand to prevent transformer overload during peak load intervals. Over a period of seven consecutive days, including weekdays and holidays, the method’s effectiveness in managing network loads is assessed. It successfully alleviates transformer overload during peak periods by adjusting EV loads. The method ensures that system load, excluding electric vehicles, is prioritized, with any excess load being clipped to maintain transformer ratings, particularly evident during evening hours when residential and EV loads peak simultaneously. Comparisons with the earliest deadline method reveal that the proposed approach meets the energy demands of a significantly higher number of EVs, demonstrating a performance improvement of up to 33%. This method, originally tested in a residential complex with a shared parking lot, holds promise for adaptation to commercial and industrial buildings equipped with similar facilities.
Implementing dynamic optimization algorithms that can adjust in real time to changing grid conditions and user behaviors would improve the method’s ability to handle uncertainties and fluctuations in demand effectively. This approach aligns with the need to assess the validity of assumptions underlying the model and consider scenarios where these assumptions may not hold true, as discussed previously.
Funding
The author extends the appreciation to the Deanship of Postgraduate Studies and Scientific Research at Majmaah University for funding this research work through the project number R-2024-1205.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Will be provided on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| DSO | Distribution system operator |
| EM | Energy manager |
| EV | Electric vehicle |
| NHTS | National Household Travel Survey |
| SOC | State of charge |
| V2G | Vehicle to grid |
| V2V | Vehicle to vehicle |
References
- Wei, F.; Walls, W.D.; Zheng, X.; Li, G. Evaluating environmental benefits from driving electric vehicles: The case of Shanghai, China. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 119, 103749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Musilek, P. Resilience Enhancement Strategies for and Through Electric Vehicles. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.; Cezar, G.V.; Min, L.; Azevedo, I.M.L.; Rajagopal, R. Charging infrastructure access and operation to reduce the grid impacts of deep electric vehicle adoption. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, B. Adaptive real power capping method for fair overvoltage regulation of distribution networks with high penetration of PV systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 2729–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FleetCarma. Charge the North—Results from the World’s Largest Electric Vehicle Charging Study. 2018. Available online: https://www.geotab.com/blog/preparing-for-evs/ (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Hussain, A.; Gerasimov, K.; Chapelsky, C.; Musilek, P. Utility-scale energy storage system for managing EV load in connected distribution circuits. In Proceedings of the CIRED Porto Workshop 2022: E-Mobility and Power Distribution Systems, Porto, Portugal, 2–3 June 2022; pp. 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasnim, M.N.; Akter, S.; Shahjalal, M.; Shams, T.; Davari, P.; Iqbal, A. A critical review of the effect of light duty electric vehicle charging on the power grid. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 4126–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoi, M.S.; Zhuang, S.; Munir, H.M.; Haris, M.; Hassan, M.; Usman, M.; Bukhari, S.S.H.; Ro, J.S. An in-depth analysis of electric vehicle charging station infrastructure, policy implications, and future trends. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11504–11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaili, A.; Oshanreh, M.M.; Naderian, S.; MacKenzie, D.; Chen, C. Assessing the spatial distributions of public electric vehicle charging stations with emphasis on equity considerations in King County, Washington. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 107, 105409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasri, R.A.; Alharbi, T.; Alshitawi, M.S.; Alrumayh, O.; Ajib, S. Related Work and Motivation for Electric Vehicle Solar/Wind Charging Stations: A Review. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A.; Aiman, M.H.; Faizal, W.M.; Khor, C.Y. Charging strategy in electric vehicle chargers by utilizing demand side management scheme. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 220, 109240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y. Demand response to improve the shared electric vehicle planning: Managerial insights, sustainable benefits. Appl. Energy 2021, 292, 116823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.; Zamora, R.; Lie, T.T. Transactive Energy Management of PV-Based EV Integrated Parking Lots. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 5674–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, H.; Dong, H. Optimal Public Parking Lot Allocation and Management for Efficient PEV Accommodation in Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 5984–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, A.; Alammari, R.; Iqbal, A. Utilization of EV Charging Station in Demand Side Management Using Deep Learning Method. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 8747–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuvo, S.S.; Yilmaz, Y. Demand-Side and Utility-Side Management Techniques for Increasing EV Charging Load. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 3889–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Haque, A.; Zaman, H.; Morsalin, S.; Islam, S. Domestic Load Management with Coordinated Photovoltaics, Battery Storage and Electric Vehicle Operation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 12075–12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, A.; Aljohani, T.M. Reliability-driven time-of-use tariffs for efficient plug-in electric vehicle integration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 107, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, T.; Mohamed, M.A.; Mohammed, O. Tri-level hierarchical coordinated control of large-scale EVs charging based on multi-layer optimization framework. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 226, 109923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Bui, V.-H.; Musilek, P. Local demand management of charging stations using vehicle-to-vehicle service: A welfare maximization-based soft actor-critic model. eTransportation 2023, 18, 100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeballos, M.; Ferragut, A.; Paganini, F. Proportional Fairness for EV Charging in Overload. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 6792–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Dong, Z.Y.; Wong, K.P.; Huang, T. Noncooperative Game-Based Distributed Charging Control for Plug-In Electric Vehicles in Distribution Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Musilek, P. A Game-Theoretic Approach for Charging Demand Management of Electric Vehicles during System Overload. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference (EPEC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 22–31 October 2021; pp. 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Faria, P.; Barreto, R.; Vale, Z. Fair Management of Vehicle-to-Grid and Demand Response Programs in Local Energy Communities. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 79851–79860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, V.; Ferro, G.; Robba, M. A decentralized optimization approach to the power management of electric vehicles parking lots. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2024, 38, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostado-Véliz, M.; Jin, X.; Bhakar, R.; Jurado, F. Coordinated pricing mechanism for parking clusters considering interval-guided uncertainty-aware strategies. Appl. Energy 2024, 355, 122373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Bui, V.H.; Kim, H.M. A Decentralized Dynamic Pricing Model for Demand Management of Electric Vehicles. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 13191–13201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorokhova, M.; Martinson, Y.; Ballif, C.; Wyrsch, N. Deep reinforcement learning control of electric vehicle charging in the presence of photovoltaic generation. Appl. Energy 2021, 301, 117504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Household Travel Survey. Available online: https://nhts.ornl.gov/downloads (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Lo Franco, F.; Ricco, M.; Cirimele, V.; Apicella, V.; Carambia, B.; Grandi, G. Electric Vehicle Charging Hub Power Forecasting: A Statistical and Machine Learning Based Approach. Energies 2023, 16, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, A.; Alyami, S. Load Profile Modeling of Plug-In Electric Vehicles: Realistic and Ready-to-Use Benchmark Test Data. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 59637–59648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Zhou, C.; Allan, M.; Yuan, Y. Modeling of load demand due to EV battery charging in distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Qian, K.; Zhou, C.; Stewart, B.G.; Hepburn, D.M. A methodology for optimization of power systems demand due to electric vehicle charging load. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dehghanpour, K.; Kimber, A. A Time-Series Distribution Test System Based on Real Utility Data. In Proceedings of the NAPS2019: 51st North American Power Symposium, Wichita, KS, USA, 13–15 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electric Vehicle Database. Energy Consumption of Full Electric Vehicles Cheatsheet—EV Database. 2020. Available online: https://ev-database.org/cheatsheet/energy-consumption-electric-car (accessed on 3 October 2021).
- van den Berg, M.A.; Lampropoulos, I.; AlSkaif, T.A. Impact of electric vehicles charging demand on distribution transformers in an office area and determination of flexibility potential. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2021, 26, 100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strezoski, L.; Stefani, I. Enabling mass integration of electric vehicles through distributed energy resource management systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 157, 109798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).