Abstract
This research investigates building energy consumption in the Fujian region of China, characterized by warm winters and hot summers. The study focuses on window configurations and their impact on heat exchange and solar gain management. Initially examining three aluminum alloy window frames, the study utilizes the Multi-Quality Metric Calculator (MQMC) software V1 to assess the benefits of filled insulating glass. The reference values for the heat transfer coefficient, visible transmittance, and sun shading coefficient are established. Subsequently, Ecotect software V5.6 is employed to conduct a comprehensive year-round energy consumption simulation analysis, identifying an optimal window layout tailored to Fujian’s climate. In the Fuzhou simulation, aluminum–plastic co-extruded windows exhibit the lowest cooling energy consumption, while aluminum alloy windows have the highest. Summer cooling energy consumption, comprising about 75% of the total annual energy usage in hot summer and warm winter regions, significantly influences overall energy consumption. Windows made of aluminum–plastic co-extruded material with superior thermal insulation qualities can greatly reduce building energy consumption. The results contribute valuable insights to sustainable building practices and energy-conscious designs in regions characterized by warm winters and hot summers.
1. Introduction
Construction accounts for around 40% or more of all energy consumption in China from 1990 to 2009, making it the sector with the highest energy use after the USA [1]. An average home may lose 30% of its heat or air-conditioning energy through its windows [2]. As a result, buildings’ ability to conserve energy is crucial in combating global warming. Building energy efficiency refers to constructing a more energy-efficient building through a practical design and selecting materials for the walls, roof insulation, air-conditioning doors, and windows, among other energy-saving methods. When compared to buildings created without energy-saving features and provided that the same level of indoor thermal comfort is maintained, choosing energy-efficient buildings can increase the effectiveness of electric energy usage and lower building energy consumption. The energy crisis is comparable to the oil crisis of the 1970s, when it contributed to significant advances in energy efficiency [3]. Economic efficiency throughout the life cycle should be addressed as well when designing highly energy-efficient buildings. Buildings are long-term investments, which assume that the initial decision on the quality of the investment has long-term consequences [4]. Buildings are responsible for 40% of energy consumption within the EU, and consequently contribute to approximately 36% of overall carbon emissions [5]. The UK government updated Building Regulations in 2002, 2006, and 2010 to achieve more strict energy efficiency criteria and, eventually, the goal of ‘zero carbon’ new dwellings by 2016 [6]. The notion of Zero Energy Buildings has gained popularity in recent years. Many countries have set ZEBs as their future construction energy objective. ZEBs are a viable strategy for reducing energy consumption in the construction industry and increasing renewable energy contribution [7]. To encourage the use of renewable energy in buildings, China enacted the “Renewable Energy Law of the People’s Republic of China” in 2005 [8].
The Fujian region in southeastern China faces unique climate challenges due to its subtropical monsoon climate, with hot, humid summers, abundant rainfall, typhoons, and mild but damp winters. These conditions strain cooling systems, increase energy consumption, and necessitate robust thermal insulation, shading, and water-resistant materials to handle solar heat gain, strong winds, and heavy rain. High winter humidity can cause condensation and mold, requiring proper ventilation and moisture control, while coastal proximity introduces salt spray and corrosion risks, demanding durable materials and protective coatings for structural integrity. Due to their distance from the construction site and users’ need for awareness, building materials are also thought to have a hidden impact on how much energy a structure consumes. However, they are becoming significant due to promoting building energy efficiency. The effect of producing and transporting building materials from the extraction of raw materials to the construction site is on energy and the environment. The research already conducted minimizes the significance of building materials in favor of reducing the energy consumption of buildings [9]. The window system is part of a structure that connects to the outside that is utilized the most frequently, but it also determines how well the building performs. Much emphasis has been dedicated to increasing energy consumption, and some success has been made. Moreover, China’s energy strategy prioritizes building energy efficiency and has established a legal framework to promote it. Design standards for different building types and climate regions have been established, and cost-effective technologies have been adopted to achieve energy savings. Reward funds for energy-saving retrofitting are also available [10].
If there is a higher U-factor in windows compared to walls and depending on the climate, the thermal transmittance of walls and roofs should be between 0.15 W/(m2·K) and 0.30 W/(m2·K) [11]. The thermal transmittance (U-value) for typical windows ranges from 2 W/(m2·K) to 4.5 W/(m2·K). The U-value of windows, even in high-performance ones, is often much higher than the U-value of walls, ranging from 0.8 W/(m2·K) to 1.5 W/(m2·K) [11]. The dynamic prismatic optical element dPOE coatings, combined with conventional vertical daylight strategies, can significantly reduce U.S. commercial electric lighting demand by 930 TBtu, achieving up to an 85% increase in energy savings over traditional static strategies. The simulations show that dPOE coatings effectively redirect light to avoid glare and provide deeper daylight penetration, particularly benefiting south-facing windows. The market success of dPOE technology hinges on its cost and performance compared to existing technologies [12]. Highly insulated windows have many advantages, including a reduction in the energy needed for heating and cooling, a more stable interior thermal environment, a reduction in the size of heating and cooling systems, and an improvement in occupant health and well-being [13]. The certification of new buildings and the energy-efficient rehabilitation of older structures greatly reap huge fruits from the study on the thermal performance evaluation techniques of building windows.
This paper compared the reference values of the heat transfer coefficient, visible transmittance, and sun shading coefficient of three window frames based on the MQMC software [14]. It examined the thermal performance of three types of windows to discover several potential window renovation methods. By adjusting the heat transfer coefficient and visible transmittance of windows in Ecotect [15], this research built a straightforward model, defined materials, and tracked changes in building energy usage. A window selection technique based on Ecotect was developed to uncover the problems preventing the advancement of building energy efficiency. In addition, it offers a positive way of assessing the thermal performance of building windows. From the perspective of heat transfer and energy consumption, it can help designers or owners choose window types with more energy-saving applicability.
2. Study Background
Much research on window design conducted in recent years has demonstrated that windows can perform significantly better in energy consumption when designed optimally. Professional simulation software can swiftly generate corresponding experimental data to direct the research by simulating realistic observed locations and situations.
2.1. Simulation Technology for Thermal Performance and Energy Consumption
The conventional method involves creating standard samples and testing them to evaluate the energy-saving capabilities of windows. Subsequent research focuses on modifying and improving the design to enhance test outcomes. This approach could be more laborious and efficient. The design efficiency can be considerably increased, and the test period cut down using computer software to model and evaluate each window component. Geographical limitations can be lifted, and the growth of the door and window sector is facilitated by imitating various climates, including indoor and outdoor environments. Ref. [16] used two analytical tools (THERM and HEAT3) for thermal assessment numerical analysis in the 2D and 3D domains, derived a method to support windows in a layer of asbestos directly, and investigated three alternative energy sources for the support structure performance. Ref. [17] used the ASHRAE area method to measure area-weighted overall U-values for LSF walls. In addition, 3D FEM-based simulations were performed using ANSYS CFX® and 2D FEM-based simulations using THERM software to estimate the U-values for different LSF wall configurations. The analysis estimates were based on the ISO 6946 [18] method (combinatorial method) for building components with inhomogeneous layers. Ref. [19] conducted a performance study on an integrated vacuum glazing with a CdTe PV ventilation window (VPV-DSV) system. It was compared with VPV-IGU through experiments and simulations. A corresponding mathematical model was developed, and a test bench was constructed.
Building models can now be easily created through computer simulation technologies that calculate hourly data and effectively imitate scenarios that can occur in actual surroundings. This has made it possible to estimate building energy use. Tools for energy simulation that include solar functionality include Energy Plus, IES, Ecotect, Design Builder, and DIVA-for-Rhino. Users can gain from coupled solar analysis in energy modeling programs by receiving multiple building performance forecasts using only one model, saving time from developing numerous models using various tools [20]. Ref. [21] investigated the energy performance of buildings using the IESVE building simulation software, considering the impact and relationships of the building’s monthly heating demand, various ventilation rates, the rate at which the demand for space heating was reduced, and the fan power on the window heat recovery system. Ref. [22] used Energy Plus and Daysim to examine how a building-integrated solar thermal shading (BISTS) system affected building energy use and daylight exposure in the climate of Los Angeles. A single adjacent room’s useful daylight level may be raised using BISTS. The advancement of energy-efficient doors, windows, and buildings will be facilitated in large part by computer simulation technologies. One issue that simulation technologies must constantly address is how to increase the consistency between simulated outputs and measured findings. Computer simulation technology will become even more accurate with the help of more precise algorithm optimization, realistic parameter settings, and thorough analysis of increasingly intricate environmental elements.
2.2. Window Frame Performance Characteristics
The National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) is a nonprofit organization whose mission is to promote the ongoing innovation of windows, doors, and skylights to increase buildings’ comfort and energy efficiency. The NFRC compares energy-efficient products by the U-factor, Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC), visible transmittance (Tvis), Air Leakage (AL), and condensation resistance (CR).
The U-factor measures the ability of a product to prevent heat from escaping from the interior of a room. The lower the value, the better. The thermal transmittance of a window frame depends on many factors that affect its performance, including geometry, cavity spacing, and surface emissivity [23]. The fact that windows’ thermal transmittance greatly differs from opaque building envelope components raises concerns for individuals. A large improvement in window thermal resistance is essential for high-performance buildings due to the increased area of glazing elements in current structures [24]. It is possible to reduce the thermal transmittance of the window frame by adding thermal cracks, inserting gaskets or air gaps, and making small frame geometry adjustments [25,26]. The U-value reduction is mainly constrained by frame performance. The Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) is a parameter that measures the increase in indoor temperature due to sunlight. The smaller the SHGC value, the stronger the product can block excessive solar radiation. It is the ratio of the solar energy that enters the building to that that passes through the windows [27,28]. The projected sunshine has an impact on the occupants’ comfort and mood. Insufficient daylight necessitates artificial lighting, which raises energy usage. Sun for inhabitants is complex because each person’s preference for lighting and work type differs. Visible transmittance (Tvis) refers to the ratio of the fraction of incident radiation that penetrates an object. The larger the Tvis value, the better the light transmittance of the glass and the higher the indoor brightness. The ratio typically ranges from 0 to 1. The window frame and edge impact the shading [29]. Air Leakage refers to the ability to prevent air penetration when external doors and windows are normally closed. It is a measure of the air entering the room. The smaller the AL value, the better the air tightness of the product [30]. Condensation resistance (CR), measured on a scale of 1–100, is a window’s capacity to fend off condensation on inside surfaces. Condensation can happen with any building material in specific environmental situations. CR is a means to compare the chance of condensation in various products rather than make a forecast about whether condensation will happen. A window with a higher CR will resist condensation more effectively [31]. Manufacturers use two fundamental techniques to enhance the performance of window frames. One way is to reduce the U-factor using new materials and structures as much as possible. Another way is to reduce the frame’s total size. This creates a slender frame with a high net energy gain. The summary of the related literature review is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of the research articles.
Research Work’s Novelties
- Thermal Insulation and Moisture ManagementThis research introduces advanced methodologies for thermal insulation and moisture management tailored specifically to the Fujian region’s climate. By leveraging cutting-edge materials and design techniques, the study addresses the critical need for energy-efficient and durable building solutions in hot, humid environments.
- Structural Resilience to TyphoonsAnother novelty of this work is the development of robust building designs capable of withstanding the frequent typhoons in the region. This includes the use of water-resistant materials and reinforced structures to prevent damage from strong winds and heavy rain.
3. Materials and Methods
The paper utilizes the MQMC and Ecotect software to analyze window frame selection, considering the design factors of glass type, thickness, and frame design. This methodology provides a practical and effective approach for evaluating and improving building energy efficiency.
3.1. Research Object
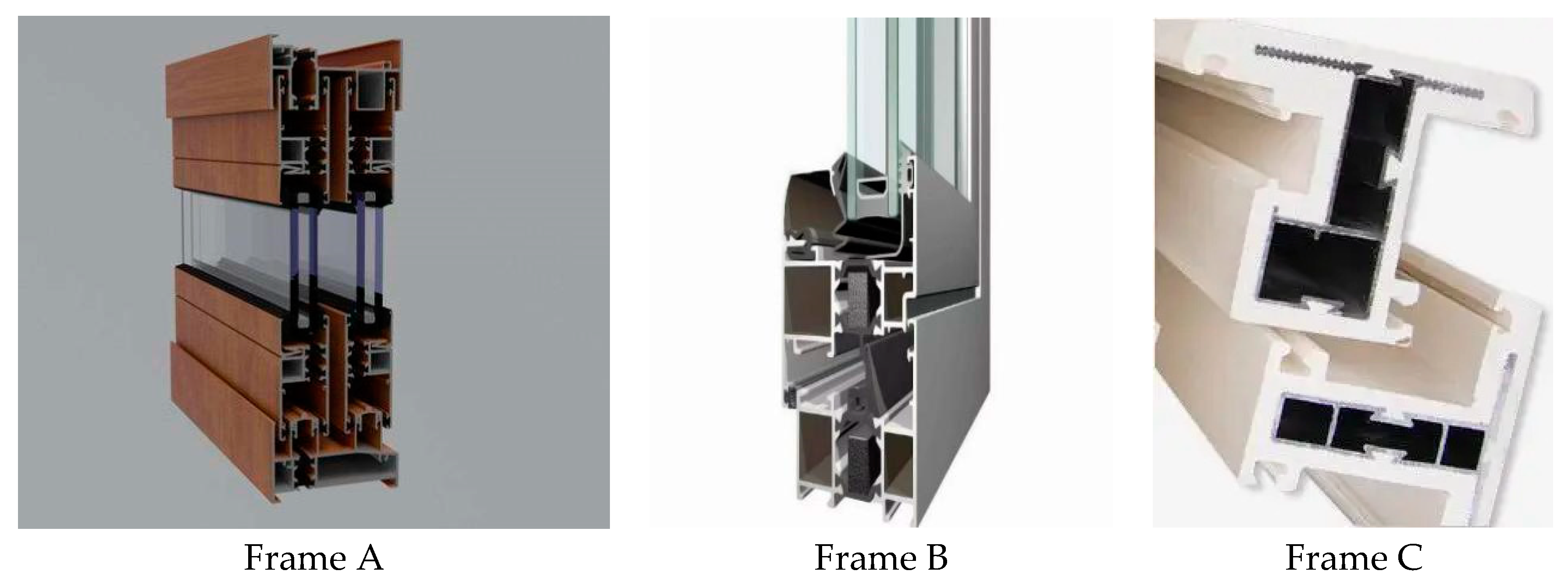
This essay used Fuzhou City in the Fujian Province as the primary example. With an average elevation of 84.00 m, the region is on China’s southeast coast. This region typically has subtropical marine monsoon weather with average outdoor temperatures of 30.9 °C in the summer and 0.0 °C in the winter and average wind speeds of 2.90 m/s and 2.60 m/s, respectively. The average solar irradiance is 630.40 W/m2. The energy-saving design of buildings in hot summer and warm winter areas may consider air conditioning in summer but not heating in winter. We performed thermal performance simulations for three distinct window frames (broken bridge aluminum alloy window A, aluminum alloy frame B, and aluminum–plastic co-extruded window frame C). Window frame A has nylon PA66 and 25% glass fiber in the middle of the aluminum alloy; frame B is an ordinary aluminum alloy material; and frame C is an aluminum alloy coated in a layer of micro-foamed PVC that is thicker than 3.5 mm, as shown in Figure 1.
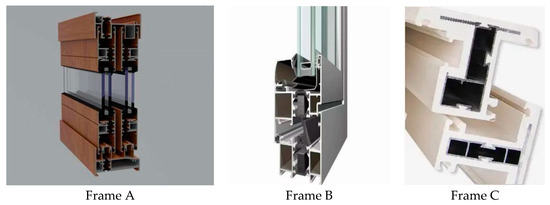
Figure 1.
Pictures of some of the frames investigated in this paper.
The frames are made of double-layer insulating glass with a thickness of 6 mm, filled with helium gas, and coated with Low-E and EPDM as the glass seal. After applying the Low-E coating, the glass heat transfer coefficient U was 1.478 W/(m2·K), the sun shading coefficient SC was 0.484, and the visible transmittance was 0.651. Without a Low-E coating, the heat transfer coefficient U of the glass was 2.611 W/(m2·K), the sun shading coefficient SC was 0.846, and the visible transmittance was 0.802. The Low-E glass has a layer of silver film coating, which improves performance. From the standpoint of optical performance, the silver coating can reduce the sun shading coefficient and heat transfer coefficient of the glass, increase the overall thermal conductivity of the glass, and block solar radiation from entering the room.
3.2. Windows’ Performance Calculation
The MQMC is a computation methodology that is essentially the same as Therm and Windows, but the MQMC’s integration of Optics, Therm, and Windows makes it a highly integrated software. As the first thermal calculation software for doors, windows, and curtain walls in China, the MQMC has optimized some functions in Therm software, such as the following: inserting spacers, defining boundary conditions, and dealing with dead pixels. On the whole, the operation of the MQMC is more concise and practical, and it is more suitable for the application habits of Chinese door, window, and curtain wall enterprises as well as glass enterprises. Therefore, this paper used the MQMC software to calculate the thermal performance of windows in Fujian, China, and analyzed the energy consumption in Fujian. The Fuzhou region of Fujian served as the calculation environment, and Table 2 shows the boundary criteria for calculating the thermal performance and climatic data for Fuzhou.

Table 2.
Thermal performance calculation boundary conditions.
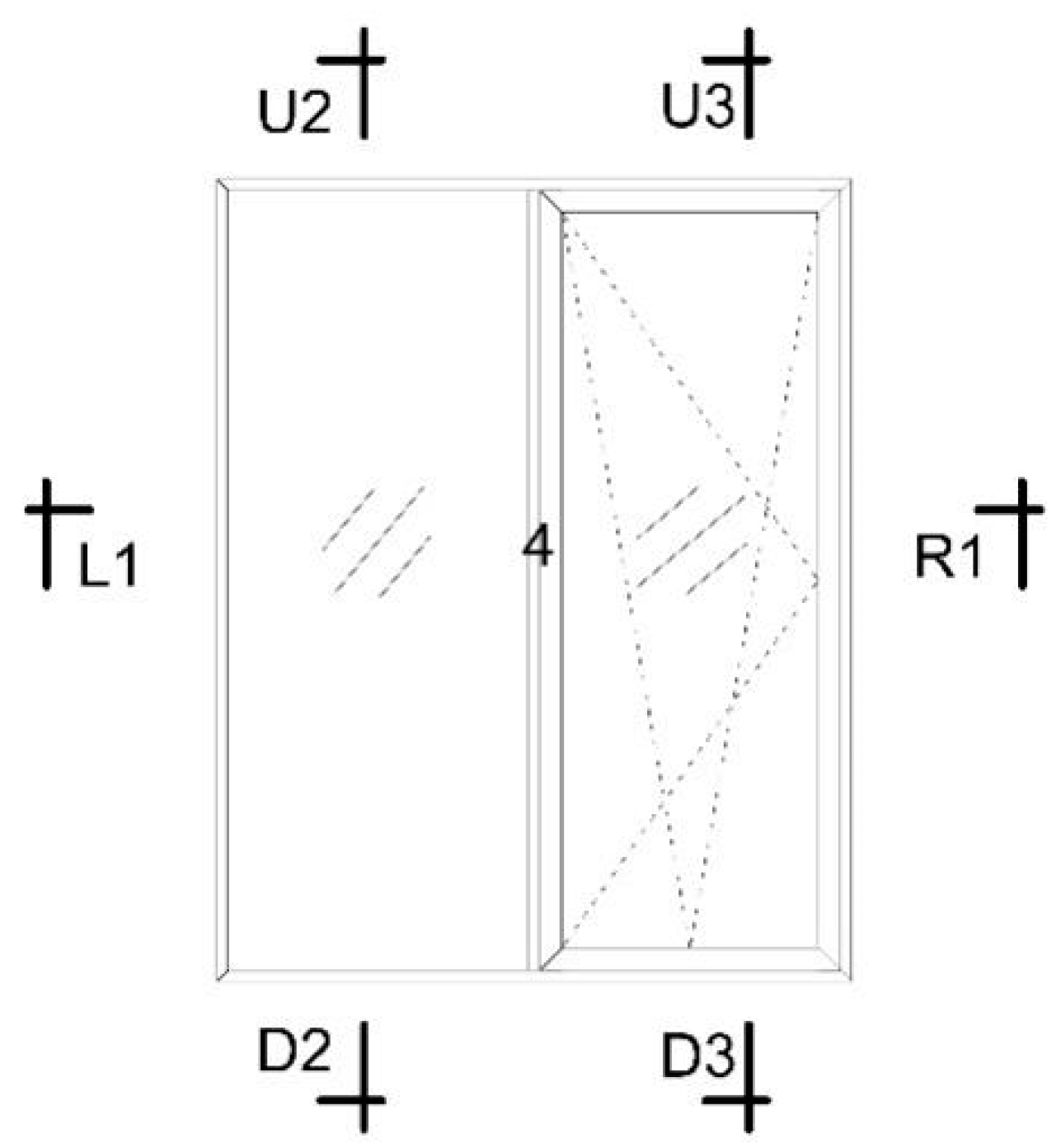
Figure 2 illustrates the establishment of 7 nodes for L1, R1, U2, D2, U3, and 4. An automated conversion process was selected, and the processed DXF window frame file, converted from CAD, was imported. The minimum control length and number of segments for the curve conversion line were then set. The CAD-to-DXF file with glass was imported after specifying the material for each section. This time, there was no need to select automatic conversion, as it served solely as a basic map for positioning. The glass system was incorporated into the node, and its thermal performance was analyzed based on the calculation results.
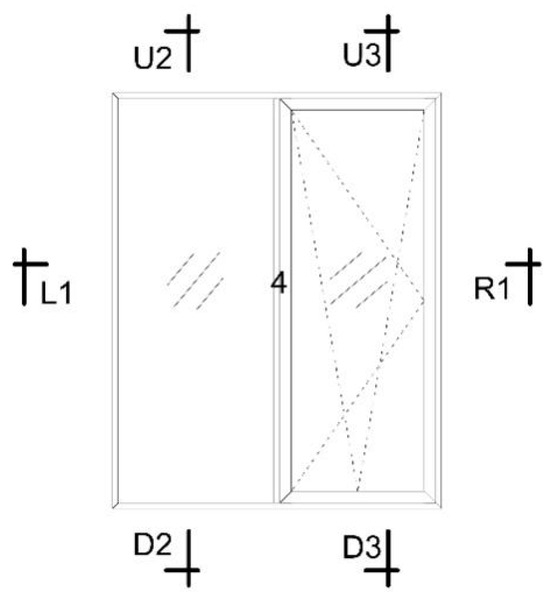
Figure 2.
Window layout (1140 mm × 1440 mm).
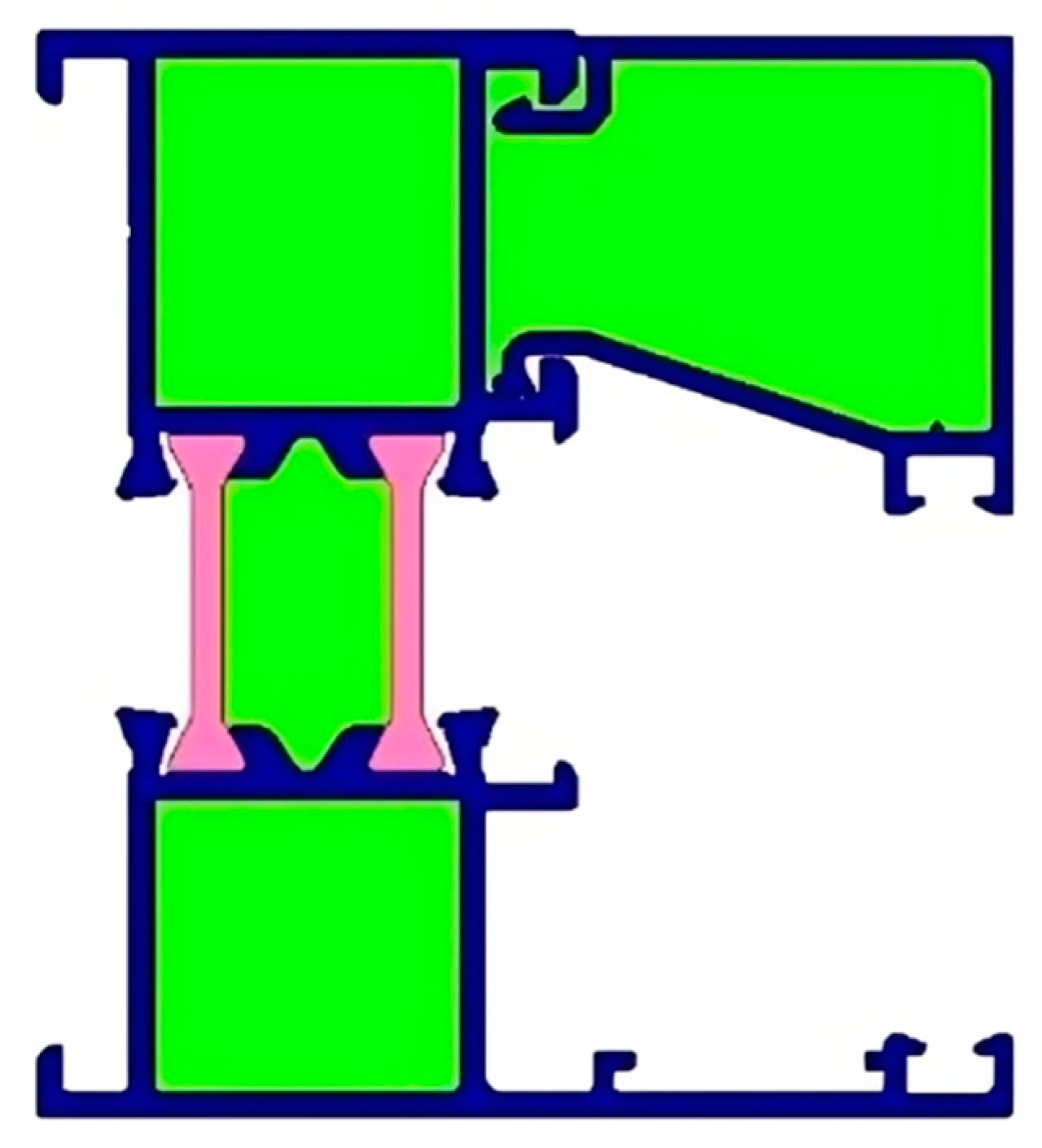
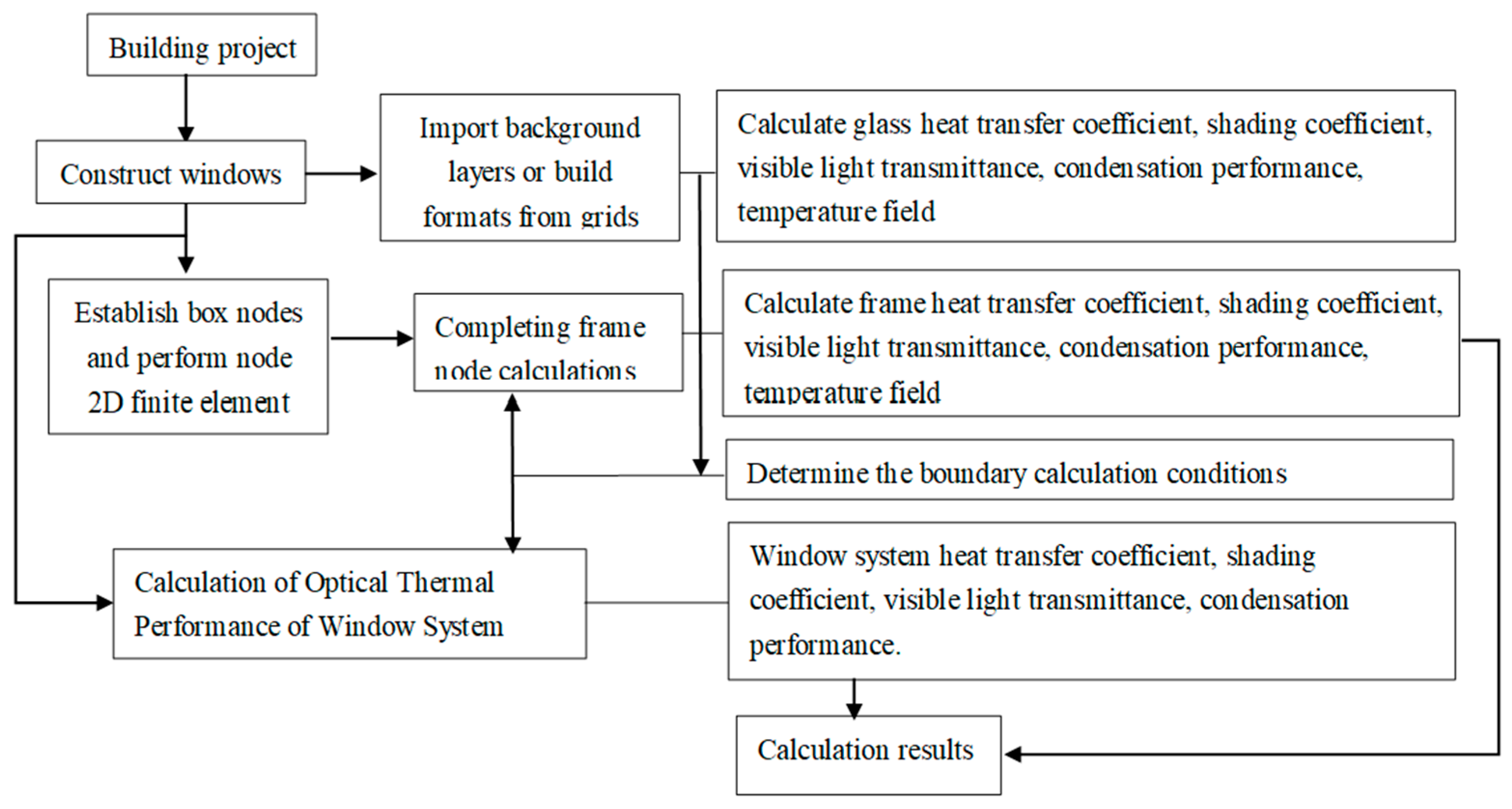
Figure 3 displays a portion of the material definition diagram for window frames, while Figure 4 shows the calculation flow chart for the MQMC software.
Figure 3.
Definition of window frame material.
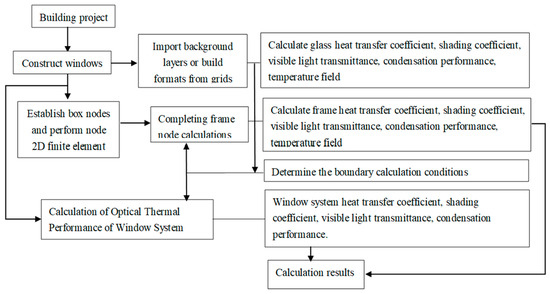
Figure 4.
MQMC software calculation process.
3.3. Energy Simulation and Analysis
This paper modeled a building simply with Autodesk Ecotect Analysis before analyzing the impact of different windows on the structure’s energy consumption [32]. An extensive preliminary analysis of the building’s energy performance was conducted using Autodesk Ecotect Analysis [33]. The application combines an easy-to-use 3D design interface, in-depth performance analysis tools, and interactive information displays. Ecotect is used to simulate the heating and cooling loads of the operational phase under the defined geometry of the building, material properties, and local weather conditions to ensure the accuracy of the results because the active phase is frequently significant in terms of energy consumption and CO2 emissions.
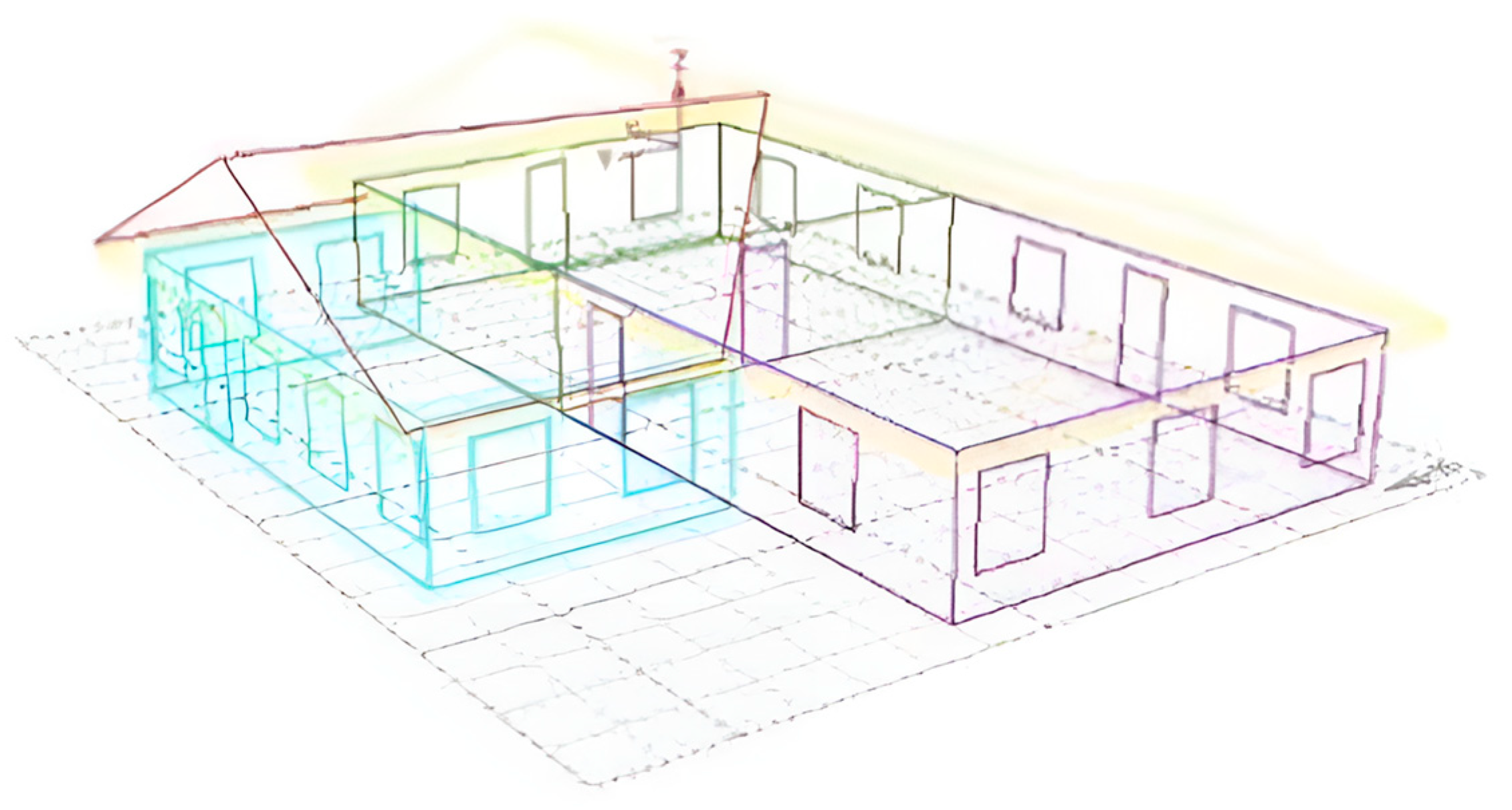
The impact of various windows on the building’s energy consumption was calculated in this research using a straightforward one-layer model. The structure was split into two offices and a restaurant. The two offices were not equally compact, and the roofs sloped downward. The door and window sub-objects were added after the three regions had been established. Figure 5 shows a brief model for modeling. The heat transfer coefficient, visible transmittance, and sun shading coefficient of each window were defined separately without changing the characteristic characteristics of the glass to compare how three different types of windows affected the building’s energy usage. The area properties, which mostly comprised the system type, the individual count, the timetable, and the heat produced by the machinery, were then set. This simulation calculation was based on the “Design Standard for Building Energy Efficiency in Hot Summer and Warm Winter Areas”. The annual energy consumption of buildings with various window frames was examined in light of the calculation’s findings after the meteorological database for Fujian was imported and calculated.
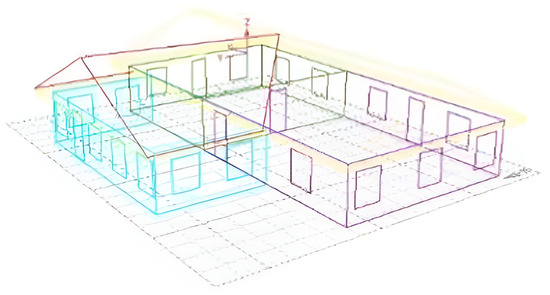
Figure 5.
A brief model for modeling.
4. Results and Discussion
This paper’s Results and Discussion section presents the findings and in-depth analysis of the study on energy consumption and window frame configurations in buildings in Fujian’s, China, warm winter and hot summer regions. This section explores the outcomes of the energy consumption simulation analysis, including the evaluation of different window types and their impact on building energy efficiency and economy. It also discusses the implications of the findings and offers insights into selecting optimal window frame configurations based on the study’s methodology.
4.1. Modeling of Three Window Frames
4.1.1. Frame A
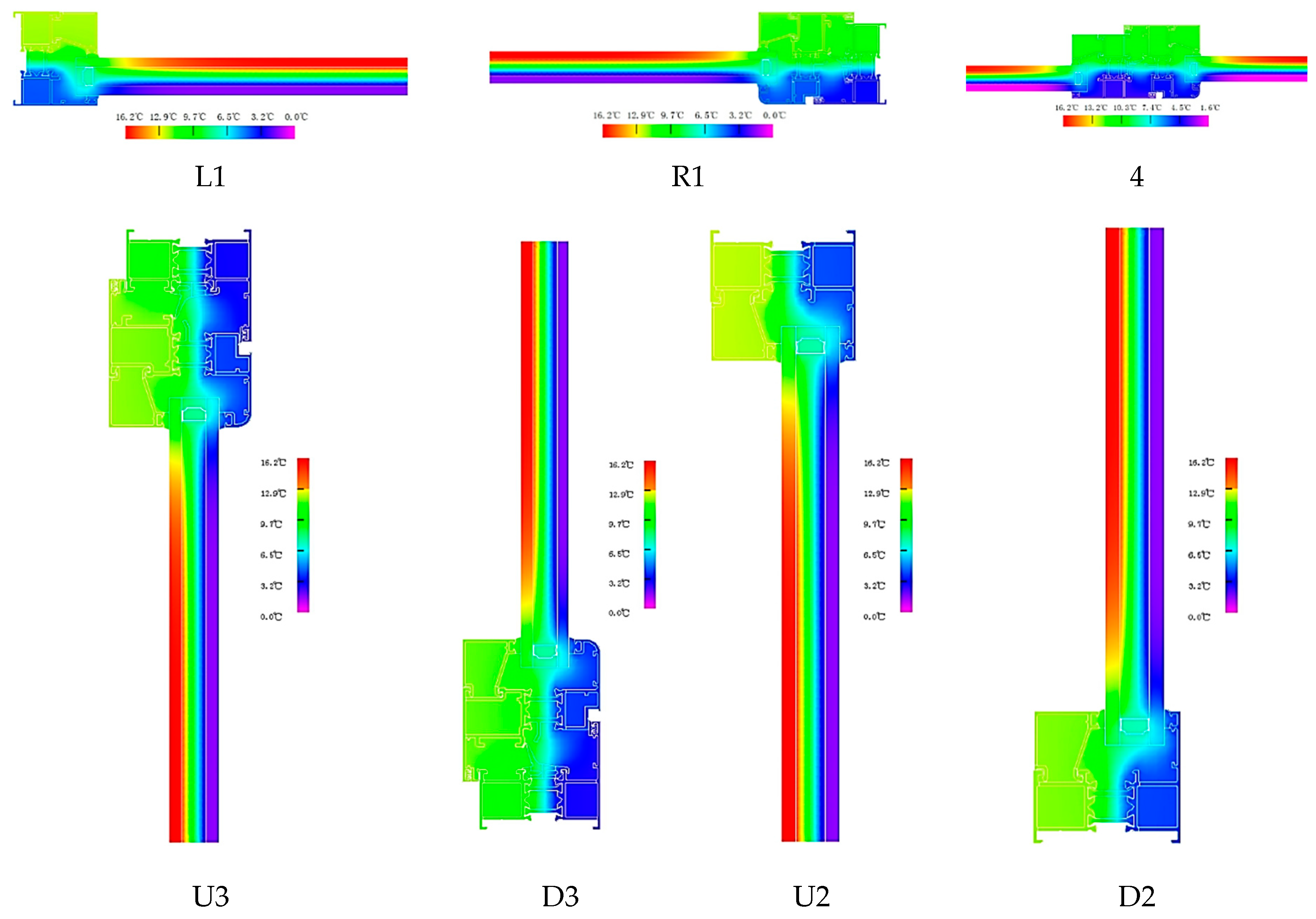
As shown in Figure 2, each window frame has seven nodes labeled L1, R1, U2, D2, U3, D3, and 4. These nodes represent specific points on the window frame where thermal performance is evaluated. The seven nodes of the broken bridge’s aluminum alloy window frame A are calculated using the MQMC software, which allows for the detailed analysis of two-dimensional heat transfer at each of these nodes. The two-dimensional heat transfer values at these seven nodes are presented in Table 3, providing insight into the thermal efficiency and insulation performance at critical points of the window frame, essential for assessing the overall energy efficiency of the window system. Figure 6 provides a schematic diagram of the heat transfer simulation for the node of window frame A, visually representing how heat flows through the material at each node and highlighting areas of potential heat loss or thermal bridging. The simulation helps identify the thermal performance at specific locations, which can then be used to optimize the design for better insulation and energy efficiency.

Table 3.
Two-dimensional heat transfer of window frame A.
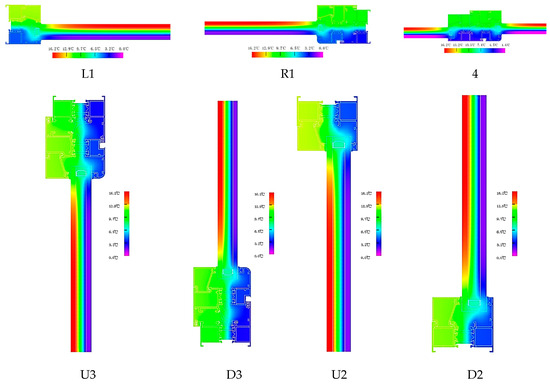
Figure 6.
Frame thermal field in frame A.
The temperature field diagram for window frame A is presented in Figure 6, along with the results indicating how the insulation strip reduces heat transmission within the center cavity. The isotherms demonstrated that even though the overall U-value of the window frame may not have been significantly reduced, installing insulation inside the window frame improved the linear heat transfer with neighboring building components. It can be seen from the thermal field diagram in the simulation results of the window frame in the figure that the thermal insulation strip was of great significance to the thermal insulation effect of aluminum alloy doors and windows. However, due to the gap between the thermal insulation strip and the aluminum alloy profile, it was easy to give rise to air convection and affect its energy-saving effect. In response to this problem, the foam material can be filled in the cavity of the thermal insulation strip further to improve the thermal insulation performance of the window.
After creating the window’s model, the paper imported the nodes determined through modeling, calculated the window’s overall thermal performance, and set the orientation to the northwest. The calculation formula for the window U-value is the following: the calculation formula for the window sun shading coefficient is the following: the formula for calculating the visible transmittance of the window is the following: the thermal performance of frame A was calculated according to the formula, and the values of the heat transfer coefficient, visible transmittance, and sun shading coefficient were obtained, as shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Frame A thermal performance calculation.
Inserted the insulating glass system without Low-E coating into the node, imported all the established nodes into the window panel, and compared the window performance with the above Low-E coating, as shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Thermal performance comparison between Low-E windows and no Low-E windows.
Low-E glass has the potential to enhance the thermal performance of windows significantly. The heat transfer coefficient is lowered by about 23%, the sun shading coefficient is reduced by about 25%, and the visible transmittance is reduced by about 28% compared to regular insulating glass.
4.1.2. Frame B
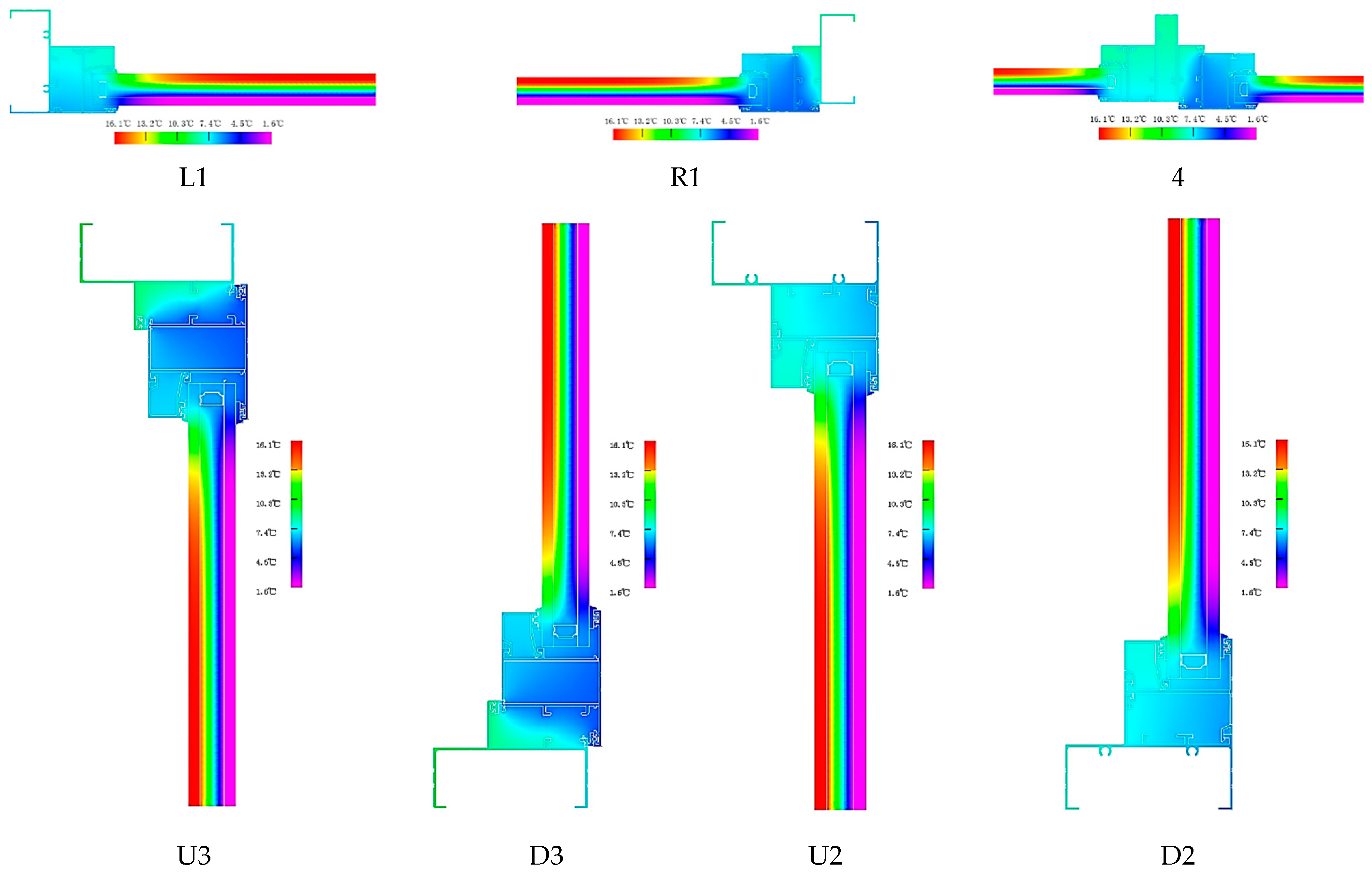
The two-dimensional heat transfer values of the seven nodes can be obtained, as shown in Table 6. The schematic diagram of the heat transfer simulation of the node of window frame B is shown in Figure 7.

Table 6.
Calculation table of two-dimensional heat transfer of window frame B.
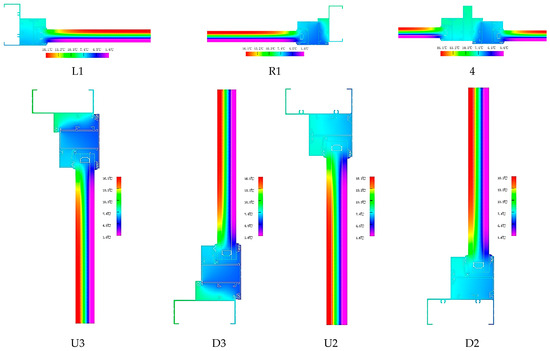
Figure 7.
Frame thermal field in frame B.
Figure 7 displayed the results of the temperature field diagram for window frame B, and the isotherm results showed that linear heat transfer within the frame with nearby building components was more than it was for window frame A. The thermal performance of frame B was calculated according to the formula, and the heat transfer coefficient, visible transmittance, and sun shading coefficient values were obtained, as shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Frame B thermal performance calculation.
4.1.3. Frame C
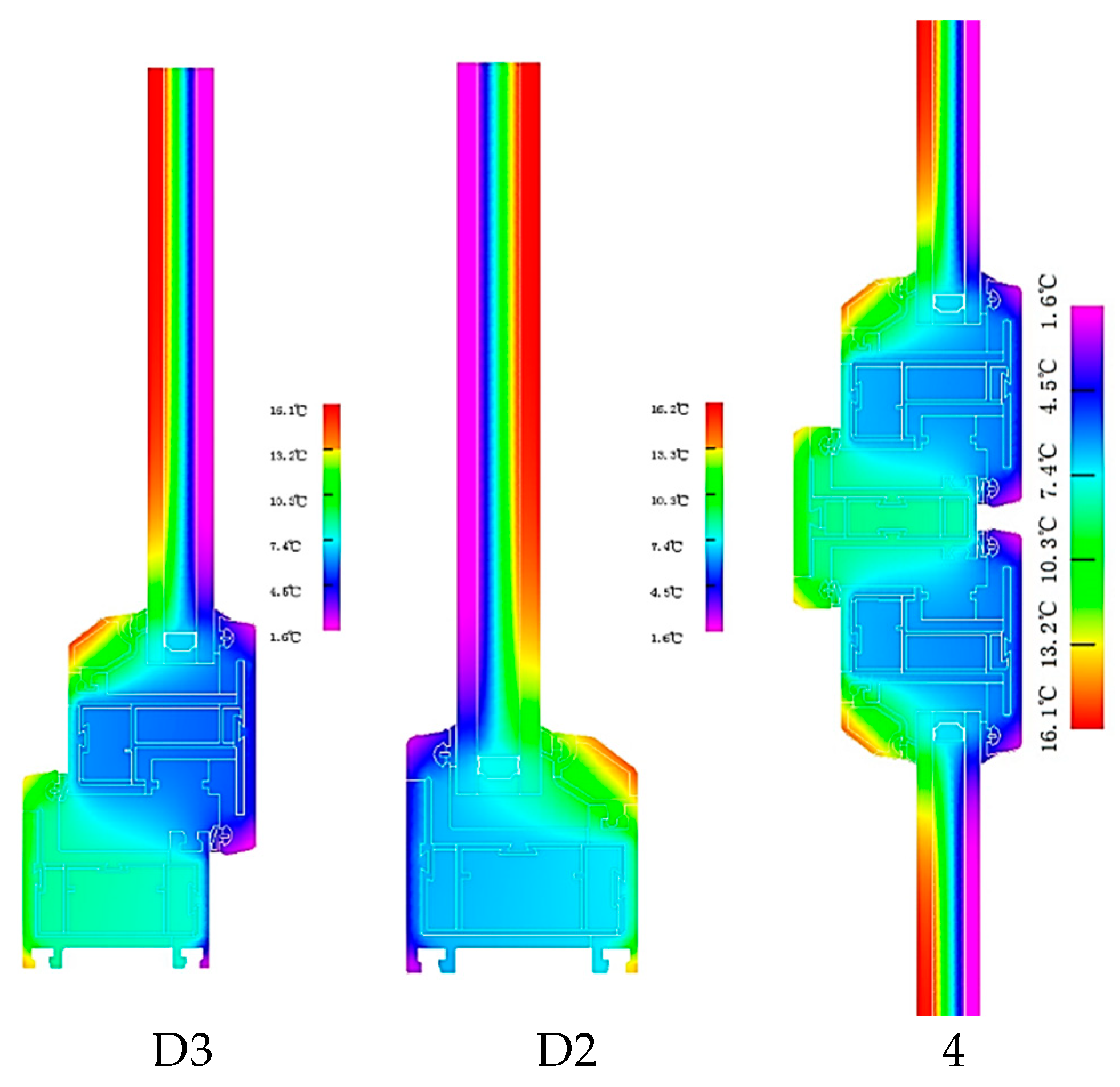
The two-dimensional heat transfer values of the seven nodes can be obtained, as shown in Table 8. The schematic diagram of the heat transfer simulation of the node of window frame B is shown in Figure 8.

Table 8.
Calculation table of two-dimensional heat transfer of window frame C.
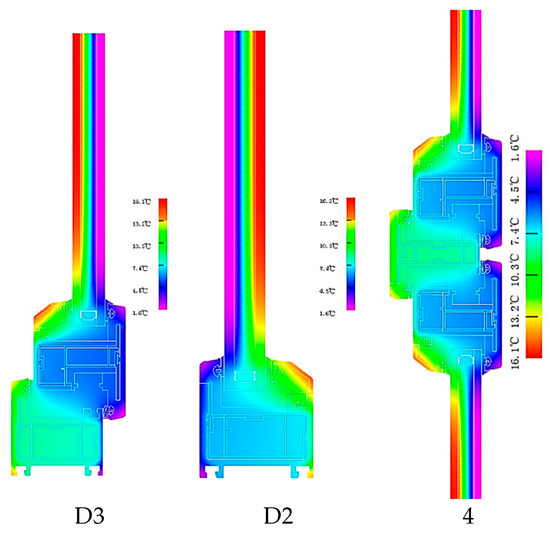
Figure 8.
Frame thermal field in frame C.
The results of the temperature field diagram for window frame C are given in Figure 8, where a layer of micro foam PVC wrapped around the aluminum alloy reduces the heat flow in the central cavity. The isotherm results showed that the window frame effectively reduced the linear heat transfer with the adjacent building components. The thermal performance of frame C was calculated according to the formula, and the heat transfer coefficient, visible transmittance, and sun shading coefficient values were obtained, as shown in Table 9.

Table 9.
Frame C thermal performance calculation.
4.2. Thermal Performance Comparison
The thermal characteristics of the three window frames were compared in light of the calculation mentioned above results. The comparison of the three windows’ calculated thermal and optical performance is shown in Table 10.

Table 10.
Comparison of thermal performance results.
The thermal insulation performance of frames A and C is significantly superior to that of frame B for the heat transfer coefficient U. They are about 75% of frame B. And there is little difference between the heat transfer coefficients of frames A and C. In terms of cost, the amount of aluminum alloy in frame C with the same width is significantly less than that in frame A of the same series, resulting in cheaper engineering expenses even though frame A’s heat transfer coefficient is slightly lower than that of frame C. Although the aluminum–plastic co-extrusion window has a low total energy consumption and low cost, the surface hardness of the foamed PVC wrapped on the aluminum alloy surface is still insufficient. After prolonged usage, it will get damaged, aged, and deformed. The window frame and glass materials significantly influence the heat transmission coefficient of doors and windows. The thermal insulation performance of doors and windows can be considerably enhanced by using Low-E insulating glass, PVC, and other materials with low thermal conductivity when making doors and windows.
For the sun shading coefficient SC, the factors that affect the larger value change are mainly related to the setting of the glass system. The smaller sun shading coefficient of frame C is because the window frame profiles used in the calculation are wider and thicker than those of frame A and frame B. The visible transmittance of the three windows is greater than 0.350, which meets the normal indoor lighting needs.
4.3. Condensation Performance Analysis
Analyzed the temperature field diagram, the heat transfer simulation schematic diagram for each frame node, and the accompanying calculation table. The condensation performance of these three window frames was determined, with the dew condensation temperature of the air being 1.9 °C, as shown in Table 11 and Table 12.

Table 11.
Condensing temperature calculation.

Table 12.
Dew condensation calculation results.
According to the dew condensation calculation results, the three window frames will not condense in Fujian Province under the simulated calculation environment’s exterior and internal boundary conditions. It demonstrates that these three types of windows will not have dew condensation in most regions with hot summers and warm winters.
4.4. Ecotect Modeling Analysis
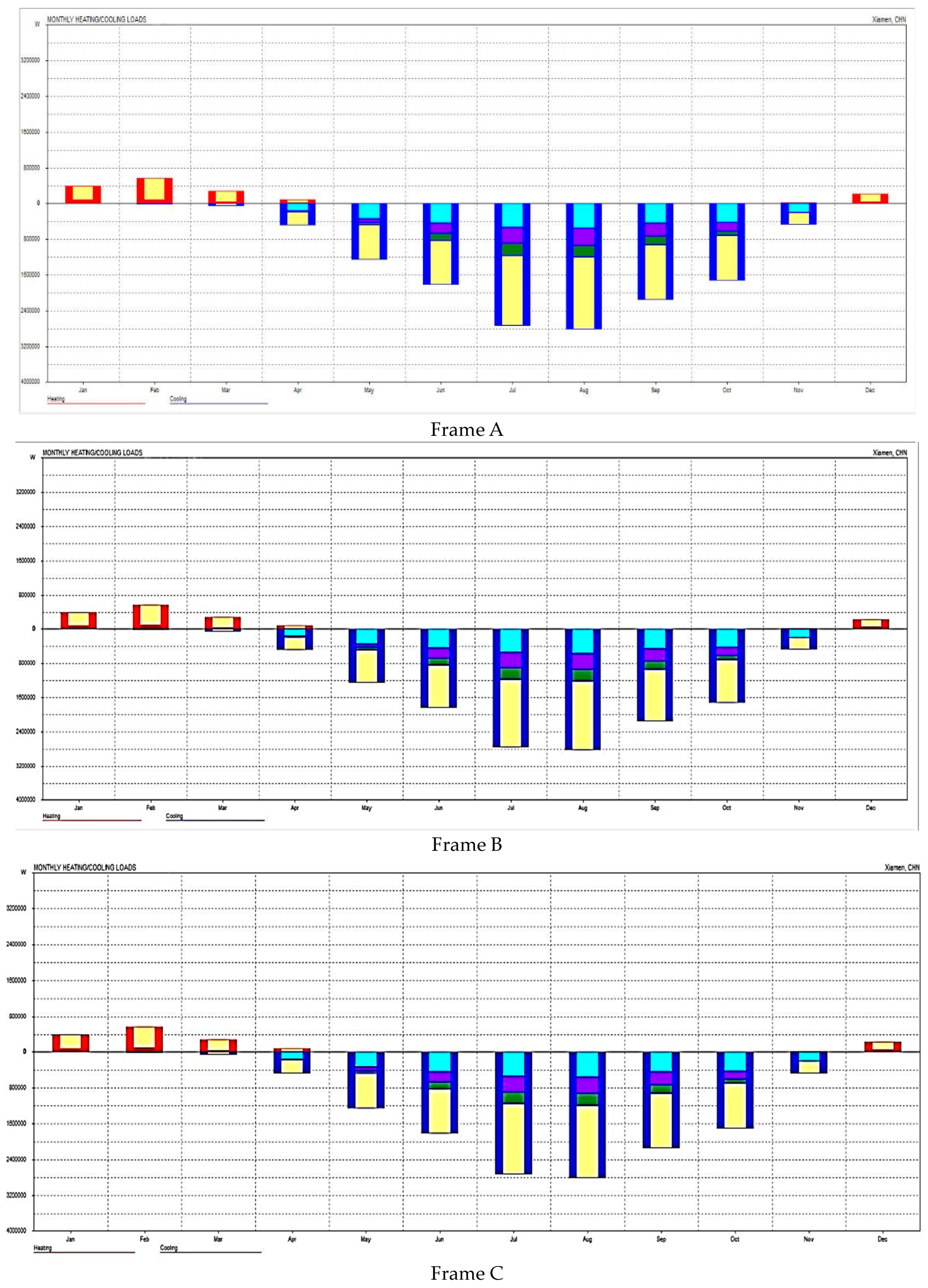
The annual maximum load and monthly energy consumption of the entire building and each area were calculated and analyzed using Autodesk Ecotect Analysis. Bar charts and data tables were used to show the simulation findings. The three window frames are offered in Figure 9, along with their monthly building energy consumption, with the red portion representing heating energy use and the blue portion representing cooling energy use. Due to the mild winter conditions in the area, heating energy usage was significantly lower than cooling energy usage. As can be observed from the image, there was not much of a difference in energy consumption between frames A and C, whereas frame B used more energy.
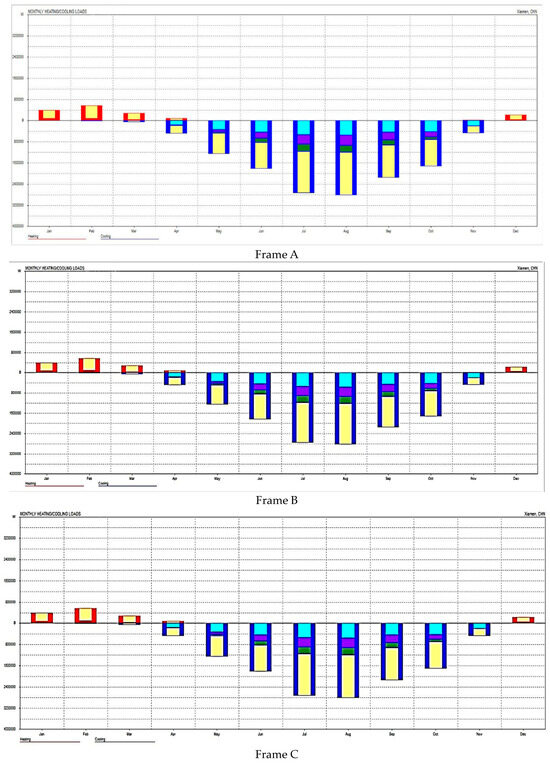
Figure 9.
Building energy consumption of windows (unit: Wh).
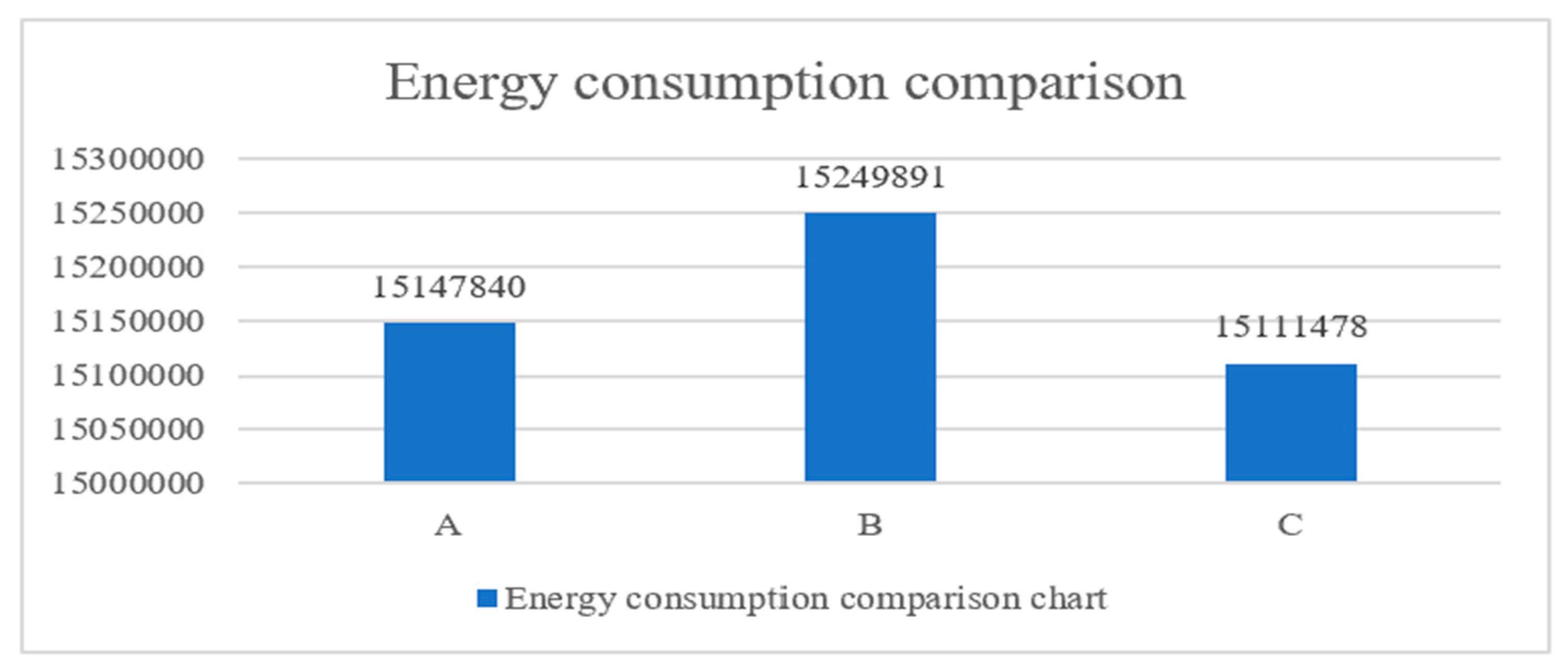
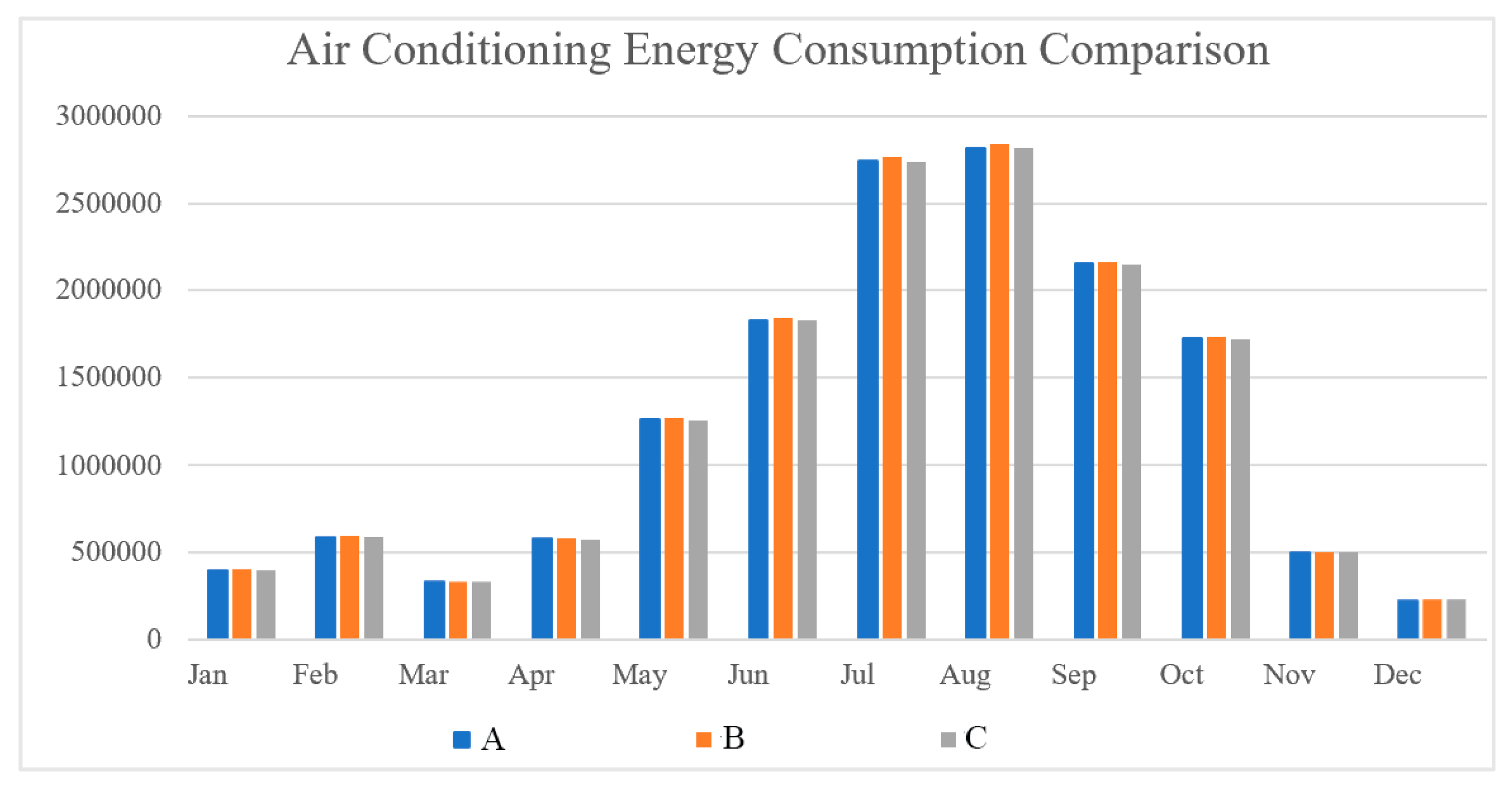
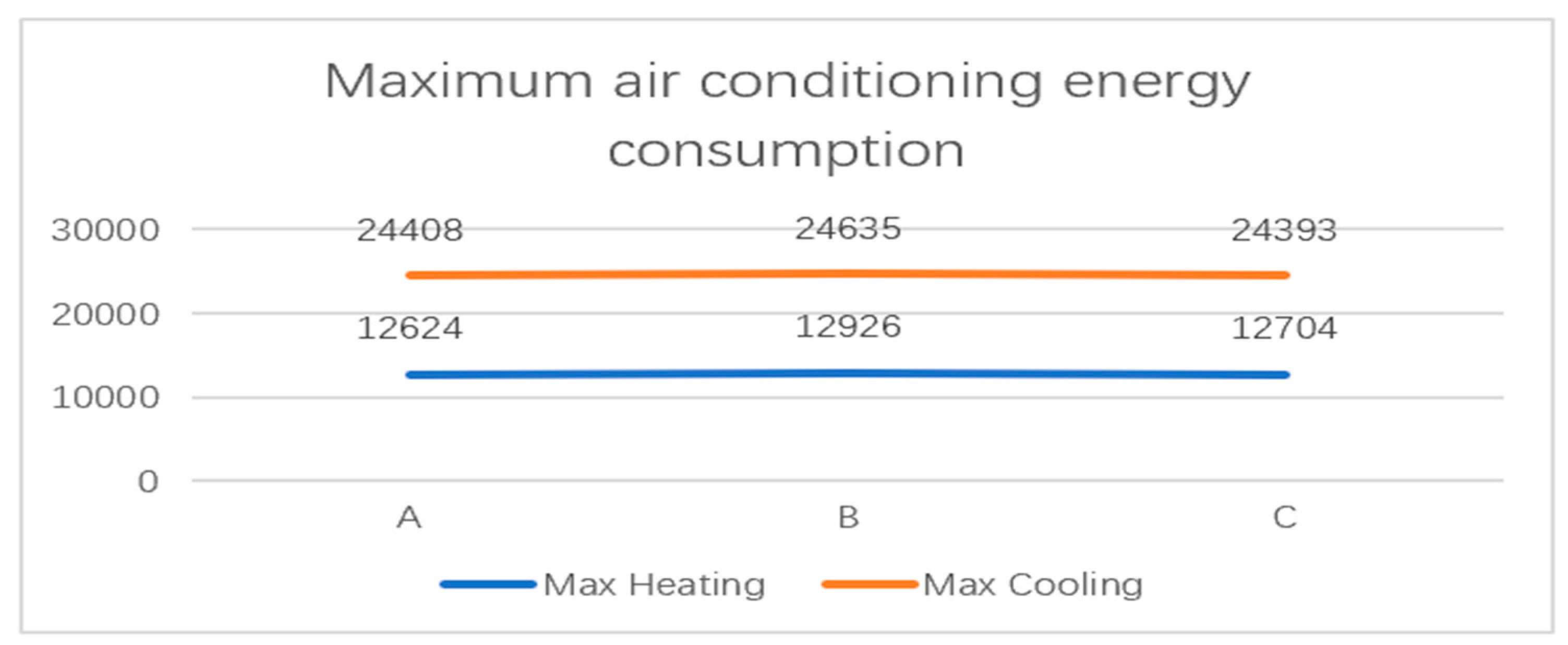
To compare the annual total energy consumption of the three types of windows, the paper summarized the table above showing building energy usage, as shown in Figure 10. (Unit: Wh) Figure 11 compares the three windows’ monthly air conditioning energy use. Figure 12 displays the annual maximum energy use for air conditioning for three different types of windows.
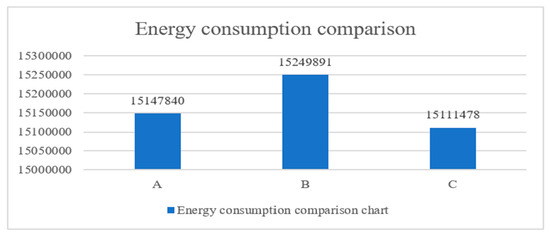
Figure 10.
Energy consumption comparison (unit: Wh).
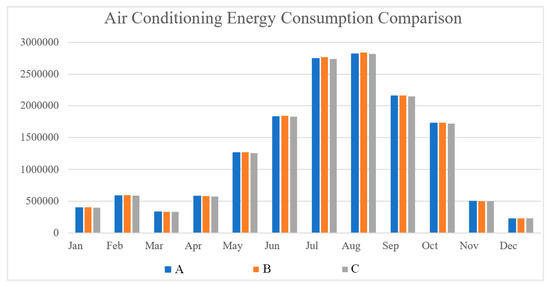
Figure 11.
Air conditioning energy consumption comparison (unit: Wh).
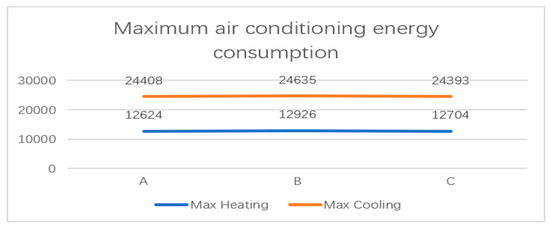
Figure 12.
Maximum air conditioning energy consumption (unit: Wh).
The aluminum alloy window frame has the highest cooling energy consumption in Fuzhou’s simulation of cooling energy consumption. In contrast, the aluminum–plastic co-extruded window has the lowest cooling energy consumption. The energy consumption for cooling in the summer, which is significantly higher than the energy consumption for heating in the winter, accounts for around 75% of the overall energy consumption for the year for the hot summer and warm winter regions represented by Fuzhou. As a result, the total energy consumption throughout the year is significantly influenced by cooling energy usage. Building energy consumption can be greatly decreased using windows made of aluminum–plastic co-extruded material with superior thermal insulation qualities. Although it is not immediately apparent, using glass systems can further reduce the energy required for building cooling.
Based on the cooling, heating, and annual total building energy consumption of different energy-saving doors and windows in Fuzhou, it can be seen that the energy consumption of cooling in the summer is relatively high. This is especially true in locations with hot summers and warm winters. Therefore, cutting back on summer cooling energy use is the key to building energy savings in regions with hot summers and warm winters. Reduced solar transmittance from Low-E glass and aluminum–plastic co-extruded window frames significantly lowers summer cooling energy demand. The thermal insulation performance of the structure has a certain influence on the warming in winter. Still, the effect of reducing annual energy consumption is not obvious based on the yearly energy consumption.
5. Conclusions
Due to global warming, energy consumption is on the rise. This study utilized the MQMC and Ecotect to offer an easy and effective technique for examining window frame selection. Design criteria such as glass type, glass thickness, window frame type, and configuration were employed in this method to analyze the optimal window frame configuration in various cities, as mentioned in the literature review earlier. Ecotect and the MQMC are specialized software tools used in the building industry for enhancing the design and performance of building components, but they serve different purposes. Ecotect, developed by Autodesk, is a comprehensive building design and analysis tool that includes thermal performance, energy consumption, lighting, and acoustic analysis. It helps architects and engineers simulate and optimize the overall performance of a building, addressing broad environmental factors such as solar gain, daylighting, and energy usage. On the other hand, the MQMC (Multi-Quality Metric Calculator) focuses specifically on the thermal efficiency of doors, windows, and curtain walls. The MQMC integrates methodologies from Optics, Therm, and Windows software, providing detailed thermal performance analysis at critical nodes in window frames. It is tailored to the standards and application habits of Chinese door, window, and curtain wall enterprises, optimizing functions like inserting spacers, defining boundary conditions, and dealing with dead pixels.
When used together, Ecotect and the MQMC offer a thorough understanding of both macro and micro aspects of building performance. Ecotect is used for the initial building design and overall performance analysis, while the MQMC provides detailed thermal efficiency analysis for specific components. The data from the MQMC can be integrated back into Ecotect to refine the overall building model, creating an iterative optimization loop that enhances both the building’s energy efficiency and the performance of individual components. This combined approach ensures the comprehensive optimization of both the overall design and specific building elements. The results of the study can be summarized as follows:
This study identified the best window type selection for regions in Fujian with mild winters and hot summers. From the perspective of building energy efficiency and economy, the simulated aluminum–plastic co-extruded window frame is recommended for future use, with Low-E coatings on PVC and aluminum window frames to reduce radiative heat transmission. In conclusion, the case study findings on window frame selection, utilizing the MQMC and Ecotect, serve as a valuable guide for buildings facing similar climatic and economic conditions in Fujian and other emerging regions. These findings contribute to constructing energy-saving window systems that consider heat transmission and energy consumption, reducing the air-conditioning load in buildings. Moreover, the results provide rewarding insights for upgrading facilities with energy-efficient features. While this study primarily focuses on thermal comfort and energy consumption in window frames, future optimization considerations may include building maintenance structure, HVAC set temperatures, and other relevant characteristics.
5.1. Study Limitations
- Regional specificity: The findings and recommendations of this study are limited to the warm winter and hot summer regions of Fujian, China. The applicability of the results may vary in different climatic areas, and caution should be exercised when extrapolating the findings to other locations.
- Simplified modeling: The study utilizes software simulations to analyze window configurations and energy consumption. While these simulations provide valuable insights, they are based on assumptions and simplifications that may not capture the full complexity of real-world conditions. Real-world measurements and field studies would complement the findings.
- Lack of cost analysis: The paper focuses on building energy efficiency and economy but needs to provide a detailed cost analysis of implementing the recommended window configurations. Considering the financial constraints mentioned in the abstract, a comprehensive economic evaluation would enhance the practicality of the recommendations.
5.2. Implementation Recommendations
- Field validation: It is recommended to conduct field studies and monitor the performance of buildings with the recommended window configurations in Fujian or similar regions. Real-world data collection would provide more accurate insights into energy savings, occupant comfort, and long-term performance.
- Cost-benefit analysis: A detailed economic analysis should be carried out to assess the cost-effectiveness and payback period of implementing the recommended window configurations. This would help building owners and policymakers make informed decisions regarding retrofitting or new construction projects.
- Collaboration with industry: Collaborating with window manufacturers and suppliers would facilitate the implementation of the recommended window frames in the market. Encouraging the production and availability of aluminum–plastic co-extruded window frames and low-e coatings on PVC and aluminum frames would support adopting energy-efficient window systems.
5.3. Future Study Recommendations
- Comprehensive optimization: Future studies can explore additional optimization factors beyond thermal comfort and energy consumption. Factors such as building maintenance structure, HVAC set temperatures, natural ventilation strategies, and occupant behavior could be integrated into the analysis to provide a more holistic approach to building energy efficiency.
- Life cycle assessment: Considering the environmental impacts of different window types’ production, use, and disposal would contribute to a more comprehensive evaluation. Life cycle assessments could help identify the most sustainable window options by considering embodied energy, material recyclability, and end-of-life disposal.
- Multi-objective optimization: Incorporating multiple objectives, such as energy efficiency, thermal comfort, daylighting, and views, into the optimization process would enable the identification of window configurations that balance various performance criteria. This approach would produce more customized and adaptable solutions for different building types and occupant preferences.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.M., C.W., D.W. and M.A.K.; Methodology, Y.M., D.W., C.W. and M.A.K.; validation, Y.M., D.W., C.W. and M.A.K.; formal analysis, Y.M., Z.C., C.W. and M.A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.M., D.W., C.W. and M.A.K.; writing—review and editing Z.C., C.W. and M.A.K.; visualization, Y.M., Z.C., C.W. and M.A.K.; supervision, C.W. and M.A.K.; project administration, C.W. and M.A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fujian Provincial Department of Housing and Urban Rural Development (Grant Number: 2023-K-31; 2023-K-63; 2023-K-73), the Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Grant Number: 2021I0014), and the Xiamen Municipal Construction Bureau (Grant Number: XJK2022-1-7).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data sets during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Defa Wang was employed by the China Railway No. 18 Bureau Group No. 1 Engineering Co., Ltd. Author Zhibin Chen was employed by the China Construction Third Engineering Bureau Group South China Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following symbols are used in this paper:
| A | Area of the frame (m2) |
| At | Total area of the window (m2) |
| E | Air’s water vapor pressure (hPa) |
| Es | Air’s saturation water vapor pressure (hPa) |
| f | Relative humidity of air (%) |
| G | Sunlight transmission rate in the frame |
| GD | Gravity’s axis |
| l | Frame wire heat transfer length (m) |
| SC | Sun shading coefficient of the window |
| Td | Dew point temperature of air (°C) |
| t | Ambient temperature (°C) |
| U | Heat transfer coefficient of the frame (W/(m2·K)) |
| Ψ | Frame wire heat transfer coefficient (W/(m·K)) |
| τt | Visible transmittance |
References
- Cao, X.; Dai, X.; Liu, J. Building energy-consumption status worldwide and the state-of-the-art technologies for zero-energy buildings during the past decade. Energy Build. 2016, 128, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisette, P. Windows: Understanding Energy Efficient Performance; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdzik, B.; Wolniak, R.; Nagaj, R.; Žuromskaitė-Nagaj, B.; Grebski, W.W. The Influence of the Global Energy Crisis on Energy Efficiency: A Comprehensive Analysis. Energies 2024, 17, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, D.; Tănasă, C. Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Energy Efficient Buildings: Theory and Study Case. In Environmental and Human Impact of Buildings: An Energetics Perspective; Moga, L., Șoimoșan, T.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 293–311. ISBN 978-3-030-57418-5. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, K.; Connelly, K.; Rutherford, P.; Wu, Y. Smart windows—Dynamic control of building energy performance. Energy Build. 2017, 139, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Garmston, H. Building regulations in energy efficiency: Compliance in England and Wales. Energy Policy 2012, 45, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszal, A.; Heiselberg, P.; Bourrelle, J.; Musall, E.; Voss, K.; Sartori, I.; Napolitano, A. Zero Energy Building—A review of definitions and calculation methodologies. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussault, J.-M.; Sourbron, M.; Gosselin, L. Reduced energy consumption and enhanced comfort with smart windows: Comparison between quasi-optimal, predictive and rule-based control strategies. Energy Build. 2016, 127, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thormark, C. The Effect of Material Choice on the Total Energy Need and Recycling Potential of a Building. Build Env. 2006, 41, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Barriers’ and policies’ analysis of China’s building energy efficiency. Energy Policy 2013, 62, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Santana, J.L.; Velasco-Carrasco, M.; Riffat, S. Thermal Transmittance (U-Value) Evaluation of Innovative Window Technologies. Future Cities Environ. 2020, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabi, A.; DeForest, N.; McNeil, A.; Masanet, E.; Greenblatt, J.; Lee, E.S.; Masson, G.; Helms, B.A.; Milliron, D.J. U.S. energy savings potential from dynamic daylighting control glazings. Energy Build. 2013, 66, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghifam, A.N.; Meynagh, M.M.; Tabatabaee, S.; Mahdiyar, A.; Memari, A.; Ismail, S. Assessment of the building components in the energy efficient design of tropical residential buildings: An application of BIM and statistical Taguchi method. Energy 2019, 188, 116080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, F. Multiphysics Modelling of the LHC Individually Powered Quadrupole Superconducting Circuits. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, L.; Guo, X.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, F.; Chen, L. Analysis Based on Ecotect Software of the Energy Consumption and Economic Viability of Solar Collector Pig Houses with Different Roof Forms and Translucent Materials. Buildings 2024, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuce, E.; Riffat, S.B. A state-of-the-art review on innovative glazing technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 695–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terentjevas, J.; Šadauskaitė, M.; Šadauskienė, J.; Ramanauskas, J.; Buska, A.; Fokaides, P.A. Numerical investigation of buildings point thermal bridges observed on window-thermal insulation interface. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6946:2017; Building Components and Building Elements—Thermal Resistance and Thermal Transmittance—Calculation methods. CEN (European Committee for Standardization): Brussels, Belgium, 2017.
- Santos, P.; Gonçalves, M.; Martins, C.; Soares, N.; Costa, J.J. Thermal transmittance of lightweight steel framed walls: Experimental versus numerical and analytical approaches. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 25, 100776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ji, J.; Wang, C.; Ke, W.; Xie, H.; Yu, B. Experimental and numerical studies on the thermal and electrical performance of a CdTe ventilated window integrated with vacuum glazing. Energy 2022, 244, 123128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, I.L. A review of daylighting design and implementation in buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, G.; Qu, K.; Wang, Y.; Iten, M.; Riffat, S. An innovative window heat recovery (WHR) system with heat pipe technology: Analytical, CFD, experimental analysis and building retrofit performance. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 3289–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qu, M.; Peng, S. Performance evaluation of building integrated solar thermal shading system: Building energy consumption and daylight provision. Energy Build. 2016, 113, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaux, G.; Greffet, R.; Salagnac, P.; Ridoret, J.-B. Modelling of an airflow window and numerical investigation of its thermal performances compared to conventional double and triple-glazed windows. Appl. Energy 2019, 242, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsen, A.; Grynning, S.; Arasteh, D.; Jelle, B.P.; Goudey, H. Key elements of and material performance targets for highly insulating window frames. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 2583–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Bossche, N.; Buffel, L.; Janssens, A. Thermal Optimization of Window Frames. Energy Procedia 2015, 78, 2500–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, N.; Rospi, G.; Cardinale, T. Numerical and experimental thermal analysis for the improvement of various types of windows frames and rolling-shutter boxes. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2015, 6, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Sangireddy, S.A.R.; Garg, V. An approach to calculate the equivalent solar heat gain coefficient of glass windows with fixed and dynamic shading in tropical climates. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 22, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Zadeh, P.A.; Staub-French, S.; Froese, T.; Cavka, B.T. Assessment of the Impact of Window Size, Position and Orientation on Building Energy Load Using BIM. Procedia Eng. 2016, 145, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, P.; Hernández, J.A. Solar heat gain coefficient of water flow glazings. Energy Build. 2017, 139, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuce, E. Role of airtightness in energy loss from windows: Experimental results from in-situ tests. Energy Build. 2017, 139, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Shen, Z.; Barryman, C. A Building LCA Case Study Using Autodesk Ecotect and BIM Model; Papers in Construction Management. 2011. 6. Available online: http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/constructionmgmt/6 (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Trisnawan, D. Ecotect Design Simulation on Existing Building to Enhance Its Energy Efficiency. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 105, 12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).