Abstract
The semiconductor industry is a pivotal hub in the global information sector, in which superpowers compete for technological dominance. As a strategic, leading, and foundational sector, it is vital for advancing China’s manufacturing ambitions through new waves of transformation and upgrades. Therefore, of particular concern is the crisis surrounding China’s semiconductor supply chain insecurity and the intensifying U.S. sanctions on China’s high-tech companies. As such, in this study, we utilize data from China’s semiconductor enterprises, investments, and related statistics from 2002 to 2020; industrial agglomeration indicators; and a social network analysis to examine the spatiotemporal pattern, industrial agglomeration, and investment networks of six key value chain segments: wafer materials, packaging materials, semiconductor equipment, integrated circuit (IC) design, manufacturing, and testing/packaging. The research focuses on how these sectors can contribute to sustainable growth and economic responsibility within China’s semiconductor industry. Accordingly, the core questions explored were as follows: what are the provincial-level spatial production dynamics and evolutionary characteristics within China’s semiconductor industry, and how do the inter-provincial investment patterns manifest? The findings reveal the following: (1) The findings reveal a strong concentration of firms in the Eastern Coastal region, particularly in Jiangsu, Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Guangdong. Additionally, IC design exhibits the highest clustering, and other segments such as wafer materials, manufacturing, and packaging/testing are relatively concentrated, whereas equipment distribution is more dispersed. (2) The industry expanded steadily from 2002 to 2013, with a rapid expansion from 2014 to 2020, particularly in Guangdong. (3) Investment patterns are characterized by local and regional focus, strongly influenced by geographical proximity. This study aims to reveal the geographic concentration patterns of China’s semiconductor industry and to explore its investment networks. The findings are intended to provide theoretical support for optimizing sustainable industrial layouts, promoting sustainable industrial practices, and guiding policy formulation. Furthermore, in the broader context of de-globalization, this study offers insights and recommendations for strengthening industrial autonomy and sustainability in response to external challenges, thereby contributing to the sustainable development of a more robust domestic semiconductor supply chain. These insights are particularly significant in safeguarding China’s technological independence and future economic stability amid global tensions. Furthermore, by integrating sustainability into its semiconductor industry, China can create a more resilient, self-sufficient, and environmentally responsible industrial sector, capable of meeting both domestic and global demands. As China continues to expand its semiconductor industry, incorporating sustainable development principles will be essential for long-term success. The sustainable practices not only ensures compliance with environmental regulations but also enhances industrial competitiveness, promotes green techniques and contributes to broader societal goals. This aligns with China’s broader ambitions for sustainable development and positions the country as a key player in the global green technology revolution.
1. Introduction
China’s economy has shifted from high-speed growth to high-quality development, evolving from a large manufacturing base to a manufacturing powerhouse [1,2]. During this transformation, the domestic semiconductor industry has received significant attention from state and local authorities. It is recognized as a strategic, foundational and leading industry that is critical for upgrading China’s manufacturing capabilities [3,4,5]. This focus is reflected in various policy initiatives and substantial investments, including placing IC at a priority position in the “Made in China 2025 (MIC 2025)” [6,7]. Moreover, government initiatives, such as the 2014 “National IC Industry Development Promotion Outline”, aim to elevate the semiconductor industry to a global level by 2030 [8]. The creation of the “National IC Fund” and regional IC funds shows China’s commitment to fostering self-innovation and strengthening semiconductor self-reliance [9,10].
Despite recent progress, China’s semiconductor industry still faces significant challenges. These include being stuck in low value-added segments of the global value chain (GVC) and a persistent gap between high demand and limited domestic supply [11,12]. Figure 1 illustrates this supply–demand mismatch. Figure 1a shows that especially before 2016, most of China’s semiconductor revenue came from lower-value activities like assembly, packaging, and testing. In contrast, there was limited progress in higher-value areas such as IC design and manufacturing. This suggests that despite efforts to develop a strong semiconductor ecosystem, China’s role remains focused on less advanced stages of production. However, since 2016, the revenue from IC design has grown rapidly, surpassing that of packaging and testing. Nevertheless, a growing gap persists in the design and fabrication segments [7,13]. This is especially true in wafer fabrication, where China’s capabilities still lag behind global leaders [14,15,16]. Subsequently, Figure 1b highlights the growing disparity between China’s semiconductor imports and exports from 2002 to 2020. The data shows that import volumes and values have consistently exceeded those of exports, reflecting China’s serious dependence on foreign sources for semiconductors. This mismatch has become more pronounced since 2013, peaking in 2020. This underscores the urgent need for China to strengthen its domestic production capabilities [17]. Table 1 illustrates that China’s nationalization rate for key semiconductor components remains low. This shortfall is exacerbated by reliance on imports for critical components, with domestic production meeting only about 10% of demand. These challenges are particularly concerning given that China is the largest global consumer of semiconductors [15,18,19,20].
More severely, the ongoing China–U.S. tensions since 2018 have intensified the global semiconductor supply chain crisis, and impacted China’s semiconductor sector. The technological conflict and trade war have disrupted China’s semiconductor ecosystem in the global value chain (GVC) [21]. The U.S. has imposed stricter export polices on advanced chip technologies and intended to undermine China’s international competitiveness and hinder knowledge sharing [4]. This has led to two major consequences: first, a weakening high-end semiconductor supply chain, leaving China vulnerable to supply chain disruptions [22], and second, escalating U.S. sanctions on Chinese technological companies like Huawei, destabilizing China’s global business environment [23,24,25,26]. To address these issues, the Chinese government has prioritized achieving semiconductor self-sufficiency as a major strategic goal in the “MIC 2025” plan and launched a dual-cycle economic strategy, aiming to reduce import dependence and foster greater autonomy in this critical sector [27,28].
Figure 1.
Foreign trade, supply and demand structure, and market size of China’s semi capacity, 2002–2020. Source: data is collected from the literature [2,29,30,31].
Figure 1.
Foreign trade, supply and demand structure, and market size of China’s semi capacity, 2002–2020. Source: data is collected from the literature [2,29,30,31].
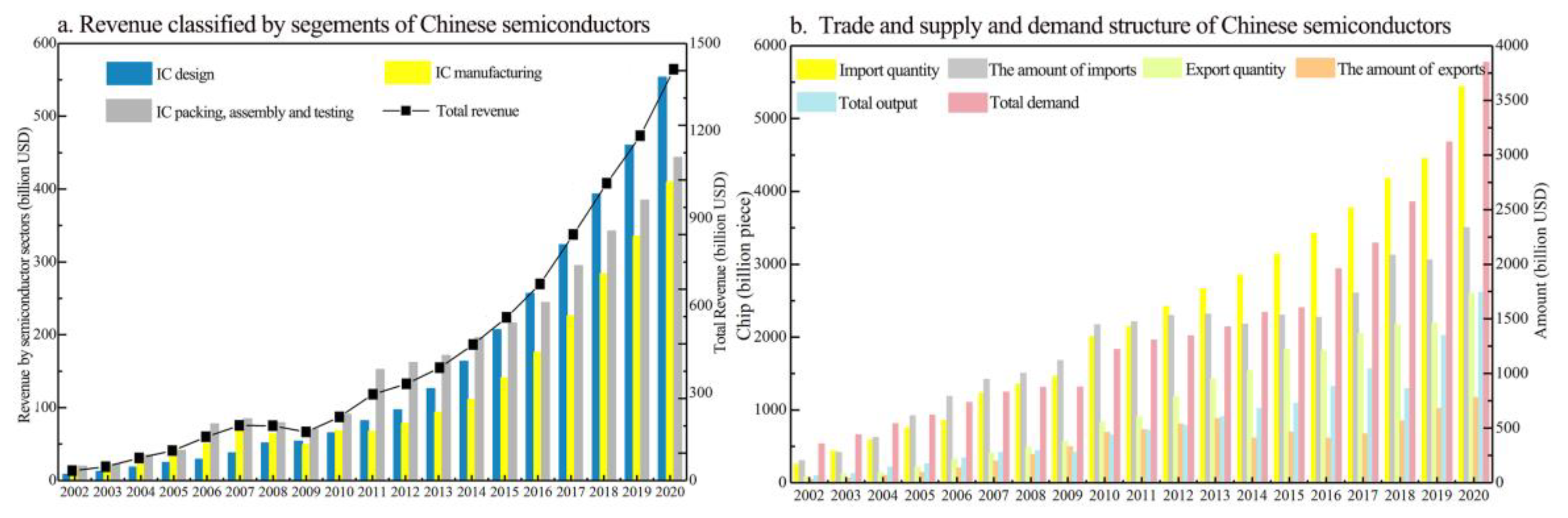

Table 1.
Nationalization rate of materials and equipment in the upstream segmentation of China’s semiconductor industry.
Table 1.
Nationalization rate of materials and equipment in the upstream segmentation of China’s semiconductor industry.
| Segmentation | Nationalization Rate | Segmentation (Continued Left) | Nationalization Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Lithography | <10% | |
| Silicon wafer | 10% | Etching machine | <10% |
| Photoresist | <20% | Ion implantation equipment | <10% |
| Electrical specific gas | <20% | CVD/PVD equipment | 10~15% |
| Polishing liquid in CMP | <10% | Oxidation diffusion equipment | <10% |
| Polishing pad in CMP | <5% | Photoresist developing machine | <10% |
| Pure chemicals | <30% | Wire bonder | <10% |
| Sputtering targets | <5% | Dicing saw | <20% |
| Equipment | Thinning machine | <20% | |
| Single crystal furnace | <20% | Testing and probing machine | <20% |
Note: (1) in China, silicon wafers of below six inches take up a dominant proportion in the domestic market, whereas ones of twelve inches mainly depend on imports; (2) photoresist is heavily imported from the Netherlands; (3) as for the above abbreviations, CMP represents chemical mechanical polishing, and CVD/PVD represent chemical vapor deposition and physical vapor deposition, respectively. Data source from the literature [2,31].
Despite prior studies on this topic, several gaps in the literature still need to be filled. ① The focus on emerging countries/regions has been insufficient. Most studies have largely concentrated on established semiconductor hubs such as the U.S., East Asia (Taiwan, Republic of Korea, and Japan), and Western Europe. However, research on the role of emerging countries and latecomers (i.e., China, Vietnam, Malaysia, and India) to the global semiconductor landscape is still limited. In particularly, China’s semiconductor industry has seen remarkable growth recently, with its design sector now ranking the second largest worldwide. Furthermore, China has become a crucial “world factory” in the assembly and testing segments. The country has become deeply integrated into the international division of labor in various niche semiconductor markets, gradually becoming a critical force in the global semiconductor network [11,32,33]. However, the existing literature has paid little attention to the geographical production patterns of China’s semiconductor industry. ② More specific production segments of the semiconductor industry have been under-explored. Prior studies have primarily focused on semiconductor design, manufacturing, and packaging/testing processes, lacking exploration into the finer segments across the entire semiconductor value chain and related production [32]. In particular, studies have not been fully extended to the upstream and front-end segments of the semiconductor industry [5]. For instance, the semiconductor materials and equipment segments have not yet been fully taken into account. Given the above research gaps, the aim of this study is to explore the geographical distribution and clustering networks of the entire value chain segments related to China’s semiconductor industry, especially with broad extension to the front-end segments like semiconductor materials and equipment segments. This research has the following significance: for one, the industrial layout can be refined and high-quality development will be allowed to flourish; for another, amidst the wave of anti-globalization discourse, it aids in building a relatively independent domestic industrial chain and supports the globalized operations of local enterprises in China’s still-developing semiconductor industry. Given the aforementioned practical implications, this study aims to answer the following questions: how are China’s semiconductor production space and inter-provincial investment network distributed, and how do they critically reflect the industrial dynamic characteristic underpinned by the six value segments of semiconductor production. The study proceeds as follows: First, the related literature and theoretical contributions are revisited. Next, the empirical section interprets the semiconductor value chain production process, identifying and generalizing six major value segments as the basis for empirical analysis. The empirical results are then presented, focusing on the spatial and dynamic characteristics of semiconductors and the investment network across the six value segments. Finally, the paper conclusions are provided.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Initial Geographical Pattern of Semiconductor Global Production (1950s–2000s)
The semiconductor industry, which began its commercial production in the U.S. during the 1950s, was one of the first sectors to be labeled as a global factory. However, its global production did not expand significantly until the late 1980s and 1990s [1,34]. During this period, scholars started to explore the geographic distribution and global transfer of semiconductor production. A J Scott provided key insights into the global landscape, identifying the U.S. and East Asia as dominant regions, with Europe playing a secondary but still important role [35,36,37,38]. Scott also emphasized the global assembly operations and offshore transfers of U.S. semiconductor firms [32]. For nearly 20 years, the U.S. maintained dominance in the global semiconductor map, but Japan eventually emerged as a key player, particularly in commercial memory chips. Scholars extensively analyzed the competition between the U.S. and Japan, outlining the Japanese rise in the global market [39,40,41,42]. Later on, the rise of semiconductor industries in Republic of Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore, driven by the technological catch-up of newly industrialized Asian economies, also became a significant focus of academic study [43,44,45,46]. By the mid-to-late 1990s, the U.S. semiconductor industry experienced a resurgence. It regained its dominance through Wintelism and the refinement of East Asian production networks, which attracted considerable scholarly attention [44]. Borrus explored the concept of Wintelism, which combined leading-edge software ecosystems with microprocessor manufacturing. This shift moved the focus from previous memory chips to advanced semiconductor equipment and multi-core processors [45,46]. The restructuring of East Asian production networks was also essential. It helped the U.S. semiconductor industry redevelop by leveraging growing Asian technological expertise [1,47,48].
2.2. Restructuring of Spatial Distribution and Agglomeration of Semiconductors (Post-2000s)
Since the 2000s, the global semiconductor industry has undergone significant spatial redistribution [1,33,49]. Globalization and rapid technological innovation have driven the industry to shift from a single-region concentration to a more diversified, multipolar structure [50]. This transformation is visible not only in the geographical spread of semiconductor firms but also in the development and evolution of industrial clusters [32]. Recent studies highlight the increasing complexity of geographic clustering patterns and investment networks within the semiconductor industry. The core research themes focus on the following areas:
(1) Spatial distribution and clustering patterns in the semiconductor industry. Since the 21st century, the global semiconductor industry has expanded significantly. East Asia, in particular, has become a core region for global semiconductor production [1,22,51]. Recent studies indicate that semiconductor firms are increasingly clustered in specific regions, with new centers emerging [52,53]. For example, Rajah et al. analyzed data from major semiconductor-producing countries and found that the clustering effect in East Asia has intensified. Research also suggests that the coexistence of upstream and downstream enterprises in the supply chain and local collaborative effects are crucial factors in determining firm locations [54,55]. Additionally, studies show that semiconductor clusters are formed in specific regions with a strong technological foundation and abundant R&D resources [56]. Chou et al. identified the YRD as the key semiconductor clusters in mainland China [57]. While East Asia plays a critical role in global semiconductor production, the U.S. and Europe maintain their competitiveness in high-end design and R&D [58,59]. Kenny noted htat the U.S. remains the world’s most leading center for semiconductor design and innovation, particularly in IC design [60]. Europe, meanwhile, aims to maintain its edge in advanced semiconductor technologies, especially in automotive and industrial electronics, through collaborative international R&D initiatives [59,61]. (2) Investment networks and capital flows in the semiconductor industry. Recent literature shows that under globalization, semiconductor industry investment networks have become more complex and transnational [62]. Park observed a significant rise in strategic alliances, mergers and acquisitions among multinational firms, leading to a highly interconnected investment network. Moreover, with the changing global geopolitical landscape, government policies are playing a growing role in shaping these investment networks [63]. Miller highlighted that national security and technological competition are increasingly influencing cross-border investment decisions and layouts in the semiconductor industry [22,64]. Chang et al. found that in China, government policy interventions and financial support were key drivers of rapid local industry growth. This support not only attracted substantial foreign investment but also spurred reinvestment of local capital [65]. Xiong et al. noted that supply chain disruptions, technological protectionism, and uncertainties in international regulations pose significant threats to the capital flows of semiconductor sector [66].
Two gaps still exist in the existing research: (1) Previous research primarily focused on specific leading regions such as the U.S. and Western Europe, with relatively little analyses of emerging markets and other potential semiconductor clusters. Although some studies have highlighted the importance of studies in East Asia, their focus has mainly been on Japan, Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore. Less attention has been paid to other emerging regions, like China. China has been deeply integrated into the international division of labor in various niche semiconductor markets, gradually becoming a critical force in the global semiconductor network. However, the existing literature has paid little attention to the geographical production patterns of China’s semiconductor industry. (2) Lack of focus on dynamic evolution. Many studies tend to analyze the spatial distribution of semiconductor industry from a static perspective, overlooking the dynamic evolution of semiconductor clustering in response to changes in the global economy. The geographical distribution and long-term impacts of these dynamic changes of semiconductors require further investigation. (3) Classifications of the value chain segments of the semiconductor industry have been insufficient. Current studies pay close attention to semiconductor design, fabrication, and assembly but rarely extend to the whole semiconductor production chain, especially to front-end segments such as the semiconductor materials and equipment segment. By contrast, this study makes the following theoretical contributions to the existing literature and highlights clear innovative objectives: Firstly, in this study, we mainly focus on typical emerging regions like China to pay the necessary attention to this previous latecomer but current player. Secondly, this study employs dynamic analysis methods to explore the evolution of semiconductor distribution and investment networks. In this study, we aim to classify the value chain segments of the semiconductor industry in more detail by including more front-side segments like semiconductor materials and equipment. Then, we attempt to bridge the gap in the literature by conducting more specific research and analyses on this distinct industry.
3. Empirical Setting, Data and Methods
3.1. Production Process of Semiconductor Industry and Empirical Classification Basis
This section provides the empirical classification and the basic analysis unit of the semiconductor industry used throughout the paper. It begins with a brief overview of semiconductor production. Six key value segments are subsequently identified as follows: wafer manufacturing materials, packaging materials, semiconductor equipment, IC design, semiconductor manufacturing, and packaging/testing. These segments are used to analyze geographic and investment patterns of China’s semiconductor industry.
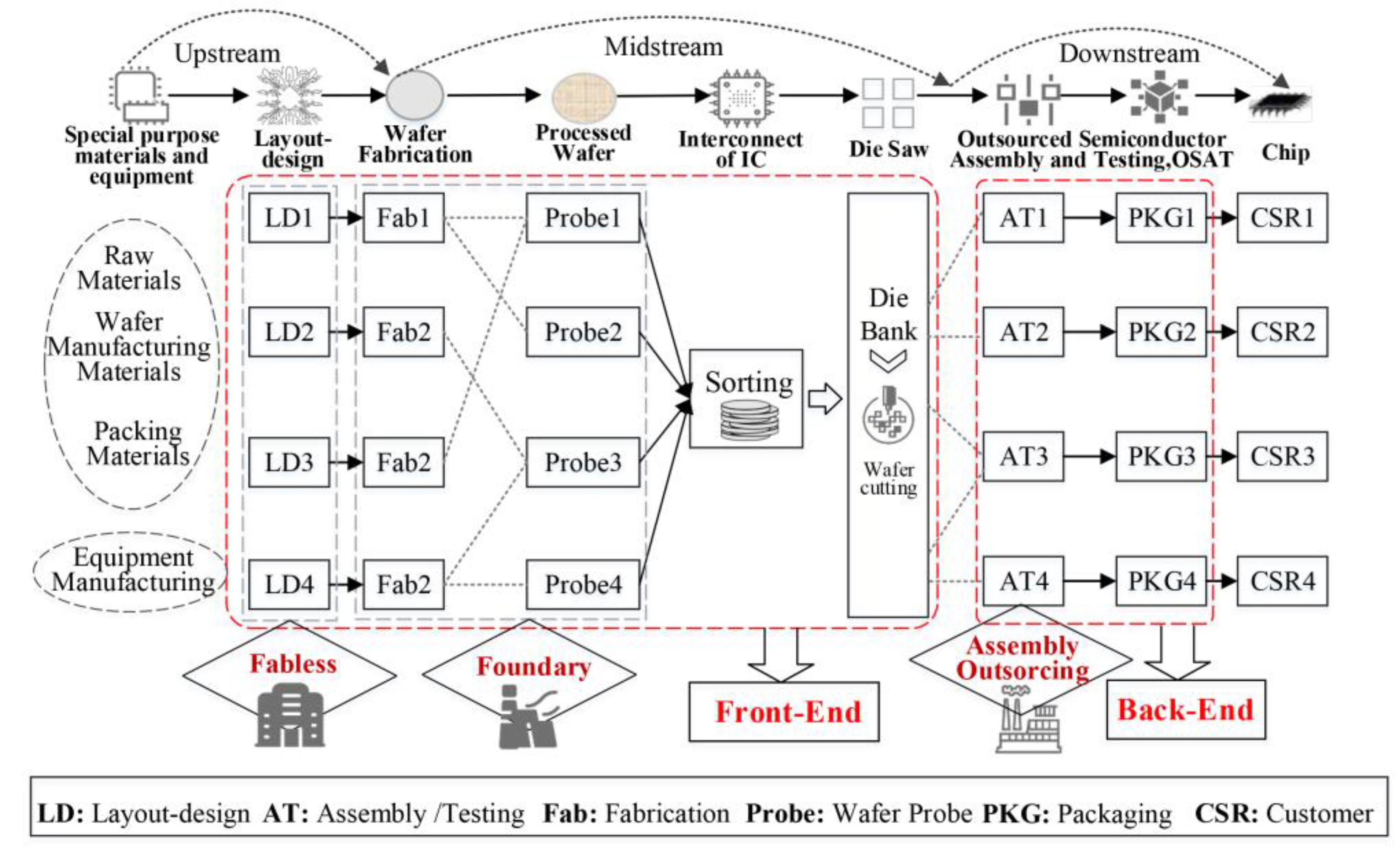
The semiconductor production process, as depicted in Figure 2, involves several discrete steps, primarily based on the mainstream “Fabless + Foundry + OSAT” model (in this model, Fabless companies focus on design without manufacturing, Foundries handle semiconductor fabrication using standardized wafer technology, and OSAT companies specialize in IC packaging and testing, forming a closely integrated industrial chain). Specifically, the upstream semiconductor industry chain includes equipment and special material suppliers, which are further divided into wafer fabrication and packaging/testing processes. The entire semiconductor manufacturing process is technically interdependent with IC design and manufacturing as front-end techniques and packaging and testing as back-end processes. IC design, the first stage of production, involves creating detailed and complex IC layouts. Semiconductor fabrication follows, where stenciled circuit diagrams are transferred onto wafers by foundries. Wafer fabrication involves interconnected steps like diffusion, oxidation, lithography, etching, deposition, and passivation in traditional fabs. The processed wafer is then tested for imperfections, where each chip undergoes detailed probing. The wafers are then sent for final inspection, assembly, packaging, and testing. Then, they are scribed and broken into individual chips. After slicing and testing, the chips are mounted on a substrate, wired, encapsulated if necessary, and finally shipped to customers.
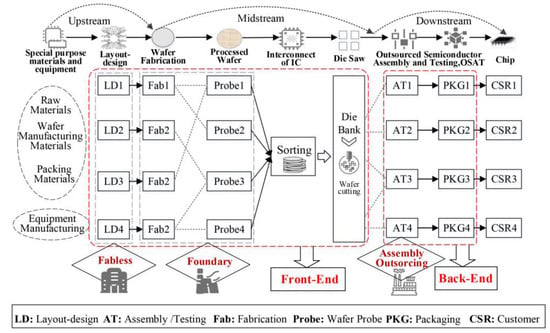
Figure 2.
Principal stages in the process of semiconductor production (based on Fabless + Foundary + OSAT model). Source: drawn by author, partly referring to the literature [67].
After outlining the semiconductor production process (see Table 2), it is categorized into six broad value segments, each with multiple subcategories. Wafer manufacturing materials include front-end components like silicon crystals, photoresists, and high-purity chemicals. Packaging materials involve back-end items such as lead frames, polyimide, and packaging substrates. Semiconductor equipment is split into complex front-end fabrication equipment (e.g., lithography and etching machines) and simpler back-end packaging equipment (e.g., dicing and wire bonding machines). The IC design segment involves layout design and supporting IP/EDA tools. Wafer manufacturing covers processes like diffusion and etching, while packaging and testing involve techniques like flip-chip and 3D stacked packaging.

Table 2.
Segment classification and component composition in the semiconductor industry.
3.2. Data Sources
The data sources consist of two parts. First, our primary was derived from China’s total of 1491 semiconductor companies in the six value chain segments, further consisting of 418 wafer material companies, 196 packaging material companies, 113 equipment companies, 114 Fabless companies, 375 Foundry companies, and 275 packaging and testing companies, respectively. The data mainly came from China Integrated Circuit Yearbook and some semi market research reports published in the PriceWaterHouseCoopers (pwc) and IC insights. This study focuses on 2020 to capture the latest developments with maximized data accessibility. The data was processed at the provincial/municipal level to measure the geographical spatial distribution of China’s six segments of semiconductors. In addition to the primary data, some statistics on China’s semiconductors (2002–2020) as an important supplement to strengthen the elaboration were utilized. The quantitative data was extracted from various secondary sources, including IC insight, Gartner Dataquest, China Electronics Industrial Yearbook, China’s Electronics Industry, China’s Integrated Circuit Yearbook, Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA), and China Statistical Yearbook On Science and Technology [29,30,31,68,69,70,71]. The data periods were selected based on the following considerations: ① Accessibility of data. The availability of data in many Chinese semiconductor-related statistical yearbooks begins in 2002 and extends until 2020. This is the longest data span we can access, up until the time we conducted this study. ② Suitability of data. The data from 2002 to 2020 is comprehensive enough to capture the long-term semiconductor development trends. This is due to significant developments in the Chinese semiconductor industry during this time-frame, such as representative policy changes, technological advancements, or major investments in the industry. Specifically, starting in 2000, the Chinese government introduced several incentive policies for the development of Chinese semiconductors, especially Several Policies to Encourage the Development of Software Industry and Integrated Circuit Industry, collectively known as “Document No. 18” [8]. These initiatives spurred a period of rapid growth in China’s semiconductor industry, often referred to in the industry as the “Golden Period” from 2000 to 2020 [72]. Additionally, post-2018 changes, including the global semiconductor shortage and geopolitical tensions, such as the U.S.–China trade rivalry, significantly impacted supply chains and technological progress of China’s semiconductor industry. This helps contextualize the findings within the broader ongoing trends. Therefore, it is very typical research period.
3.3. Hypothesis and Methodology
At first, we propose the following:
Hypothesis (H1).
China’s semiconductor industry exhibits a spatially clustered distribution overall.
Hypothesis (H2).
Knowledge- and capital-intensive segments of the semiconductor industry are geographically concentrated in specific regions due to the availability of specialized resources, infrastructure, and technological capabilities.
Hypothesis (H3).
Labor- and resource-intensive segments of the semiconductor industry are more geographically dispersed in more cost-effective regions with a higher demand for low-cost labor and raw materials.
Four key analytical approaches were selected to assess the hypothesis. The methodology of the study involves statistical analysis (including three agglomeration indexes) and social network analysis. Together, these two approaches offer a comprehensive analytical framework that examines both market dynamics and geographic factors, evaluating the distribution, concentration, and investment patterns in China’s semiconductor industry.
3.3.1. Locational Gini Index (L_Gi)
L_Gi is commonly used in measuring income or market equality [73,74]. The L_Gi was chosen because it is a widely recognized measure of inequality, which is crucial for understanding the distribution of market share or resources within the semiconductor industry. The metric helps to understand whether market power and resources are concentrated among a few Chinese semiconductor companies or more evenly distributed, indicating potential vulnerabilities. Its value ranges from 0 to 1. If the value reaches 0, it means that the regional distribution pattern of the industry is completely equal; conversely, if the value reaches 1, it signals that all the production activities of the industry are considerably concentrated in the area. Then, the calculation formula of L_Gi is as follows:
Xi represents the national gross output value of a value segment i of semiconductor industry; xij and xik represent the output value of a semiconductor value segment i in j province/municipality or k province/municipality, respectively; μ means the average proportion of the value segment i of the semiconductor industry in each province/municipality, where μ is equal to 1/N, and N represents the sum of province/municipality distributed in the value segment i of semiconductors.
3.3.2. Regional Geographic Concentration (CRn)
CRn is widely used in measuring the degree of industrial concentration within specific geographic regions [75]. It reflects the ratio to which a certain industry index of the top n provinces/municipalities with the largest industrial share accounts for share proportion of the same industry nationwide. CRn was chosen to evaluate the spatial distribution of the semiconductor industry across different regions [76]. It helps identify whether the industry is overly concentrated in specific regions. Notably, it offers a spatial perspective on the development of semiconductors, complementing the market-based insights provided by the L_Gi and HHI indexes. The formula for CRn is as follows:
Xi represents the ratio that the share of an industry index takes up that in the same national industry; n and N represent the sum of the top n provinces/cities with the largest industrial share and the total number of provinces/municipalities nationwide, respectively. The number of semiconductor companies based on six value segments in each province/municipality were seized as a metric dimension in this work for calculating the CRn under the conditions of n = 1, 4, and 8 (first province/municipality, top four, and top eight provinces/municipalities, respectively).
3.3.3. Herfindahl–Hirschman Index (HHI)
The HHI is an internationally accepted comprehensive index reflecting the effect of industrial or market agglomeration [77,78]. The HHI was selected for this study as it is a standard tool for measuring market concentration, which helps to assess the level of competition within a particular industry. In the context of China’s semiconductor industry, it reveals how much the semiconductor is dominated by a few companies, especially in critical segments like wafer fabrication and equipment [79]. It allows the study to identify the extent to which the domestic semiconductor market is monopolized or competitive, impacting innovation and market resilience. A higher HHI value signifies greater geographic concentration of the industry, whereas a lower value reflects a more scattered industrial distribution. The formula for HHI is as follows:
Sij represents the percentage of the number of companies in a semiconductor value segment i in j province/municipality accounting for nationwide enterprises in the same semiconductor value segment i; correspondingly, xij represents the number of companies of semiconductor value segment i in j province/municipality, while T represents the sum of companies of semiconductor value chain i in China.
These three indexes each provide a distinct and complementary perspective on China’s semiconductors. Specifically, as for differences, L_Gi Index highlights inequality among semiconductor participants, CRn examines the spatial distribution of the industry, and HHI assesses the level of market concentration and competition. With regard to connections, together, they offer a comprehensive analytical framework that addresses both market dynamics and geographic factors. When combined, these indexes can offer insights into which regions navigate the industry and how evenly the benefits of the industry are distributed. This can be crucial for policymakers or business leaders trying to address disparities or enhance competitiveness in China’s semiconductor industry.
3.3.4. Social Network Analysis
(1) The network construction process involves creating a directed weighted network model to analyze the investment patterns in China’s semiconductor industry across different provinces/municipalities. The model is defined as follows: Vector Vi represents the province/municipality where a semiconductor company invests in other semiconductor companies, expressed as Vi = [vi] (i = 1, 2, …, n). Correspondingly, vector Vj represents the province/municipality where a semiconductor company receives investments from other semiconductor companies, expressed as Vj = [vj] (j = 1, 2, …, n). The weight matrix W represents the number of investments from Vi to Vj, forming an N × N adjacency matrix A = [ai, j] (i = 1, 2, …, n; j = 1, 2, …, n). Finally, the vector equation C = (Vi, Vj, W, A) represents the provincial/municipal investment network model of China’s semiconductor companies.
(2) Core–Periphery Analysis (CPA).
CPA (Core–Periphery Analysis) is suitable for analyzing a network structure consisting of interconnected elements, where the central elements are closely connected to each other while the peripheral elements are sparsely scattered. In this study, we adopt a continuous core–periphery model to calculate the core degree of each member in the investment network. Specifically, we predict the coreness based on investment flows between provinces/municipalities and visualize it to analyze the structure and characteristics of investment networks in the six value segments. The detailed calculation formula can be set as follows:
ci and cj represent the core degrees of node i and node j, respectively. δij represents the element in the pattern matrix δ compared to the ideal CPA model; aij represents the element in the practical adjacency weight matrix A; ρ is the correlation index between A and δ. Different pattern matrices δ are iteratively, repetitively tested until ρ reaches the peak, and δ represents the CPA matrix corresponding to the closest approximation to the ideal model.
4. Geographical Distribution of China’s Semiconductor Industry
4.1. Geospatial Distribution of China’s Semiconductor Industry at Provincial and Municipal Scales
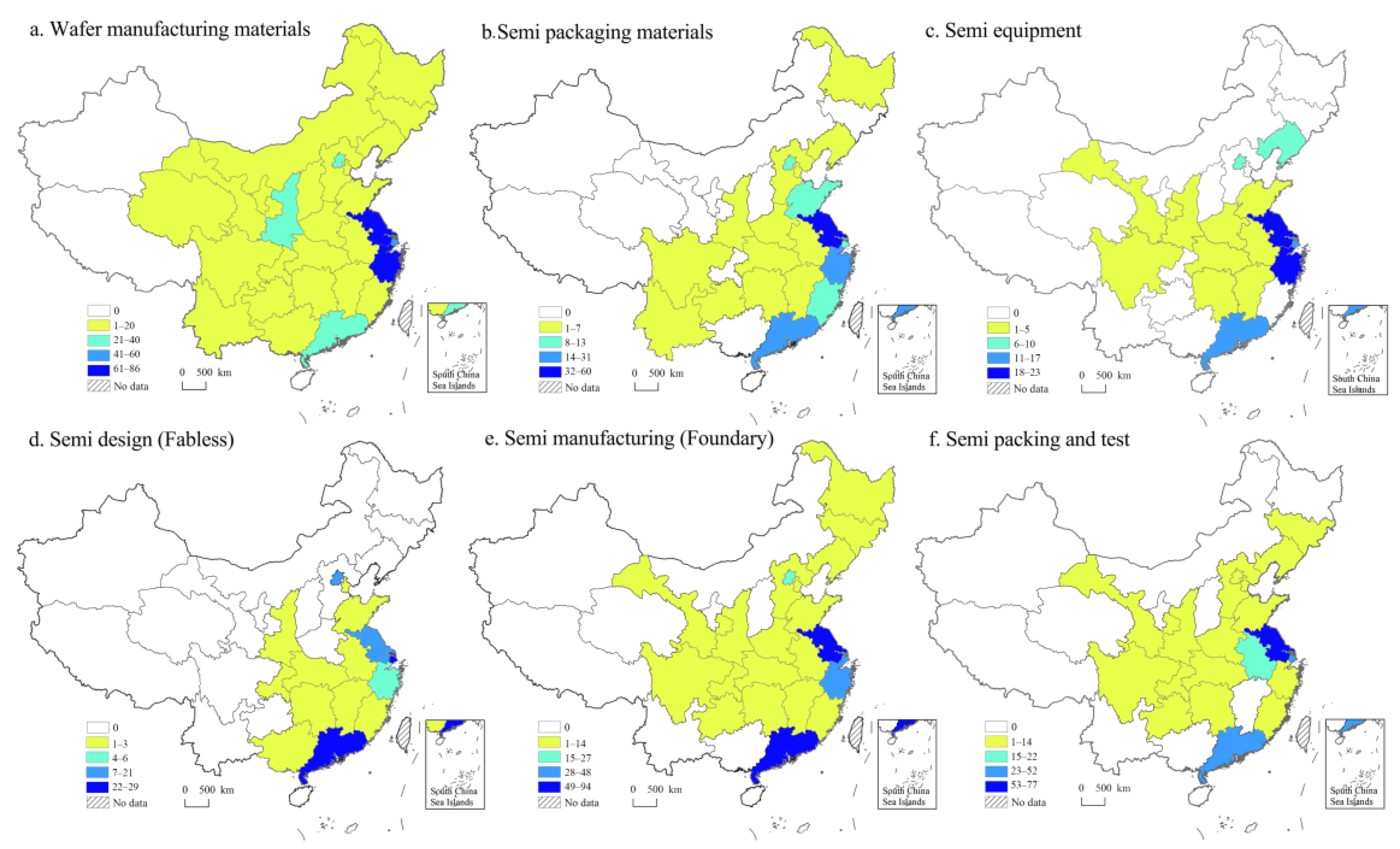
First, the number of semiconductor firms in each province or municipality illustrates the spatial distribution of the semiconductor industry. Figure 3a shows that wafer manufacturing firms are highly concentrated in the urban areas of the YRD, with Jiangsu and Zhejiang having the most firms, followed by Shanghai. Additionally, secondary cores have formed in Guangdong, Beijing, and Shaanxi, whereas other regions have smaller production volumes. Regarding packaging materials, as shown in Figure 3b, firms are predominantly clustered in the Eastern Coastal areas, with the highest concentration in Jiangsu, followed by secondary clusters in Guangdong and Zhejiang, and smaller clusters in Beijing, Shandong, and Fujian. Additionally, there is a low-density distribution in a few Mid-Western regions. Figure 3c shows that equipment firms are mainly located in the Eastern Coastal areas of Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Guangdong, and Liaoning, with discontinuous clusters, whereas inland provinces have sparse distributions. Figure 3d illustrates that firms in the IC design segment have the smallest distribution and size owing to the high entry threshold and focus on R&D as well as innovation by leading companies. The largest firms are in Guangdong, with smaller clusters in Shanghai, Jiangsu, and Beijing. Figure 3e shows that wafer manufacturing firms dominate in Guangdong and Jiangsu, with additional concentrations in Zhejiang and Beijing, whereas other firms are dispersed in Mid-Western and Northeastern regions. Figure 3f shows that testing and packaging firms are highly concentrated in Jiangsu, followed by secondary clusters in Shanghai and Guangdong, with significant production in Anhui and scattered bases in the Middle and Western regions.
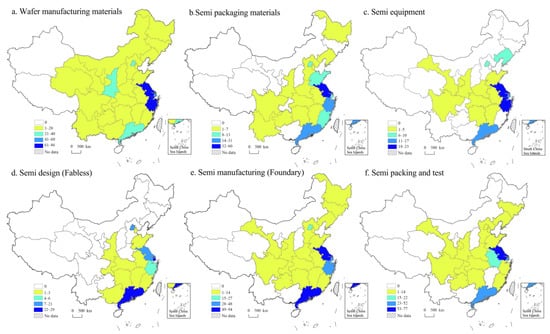
Figure 3.
The provincial/city distribution pattern of the number of firms in six value segments (unit: item).
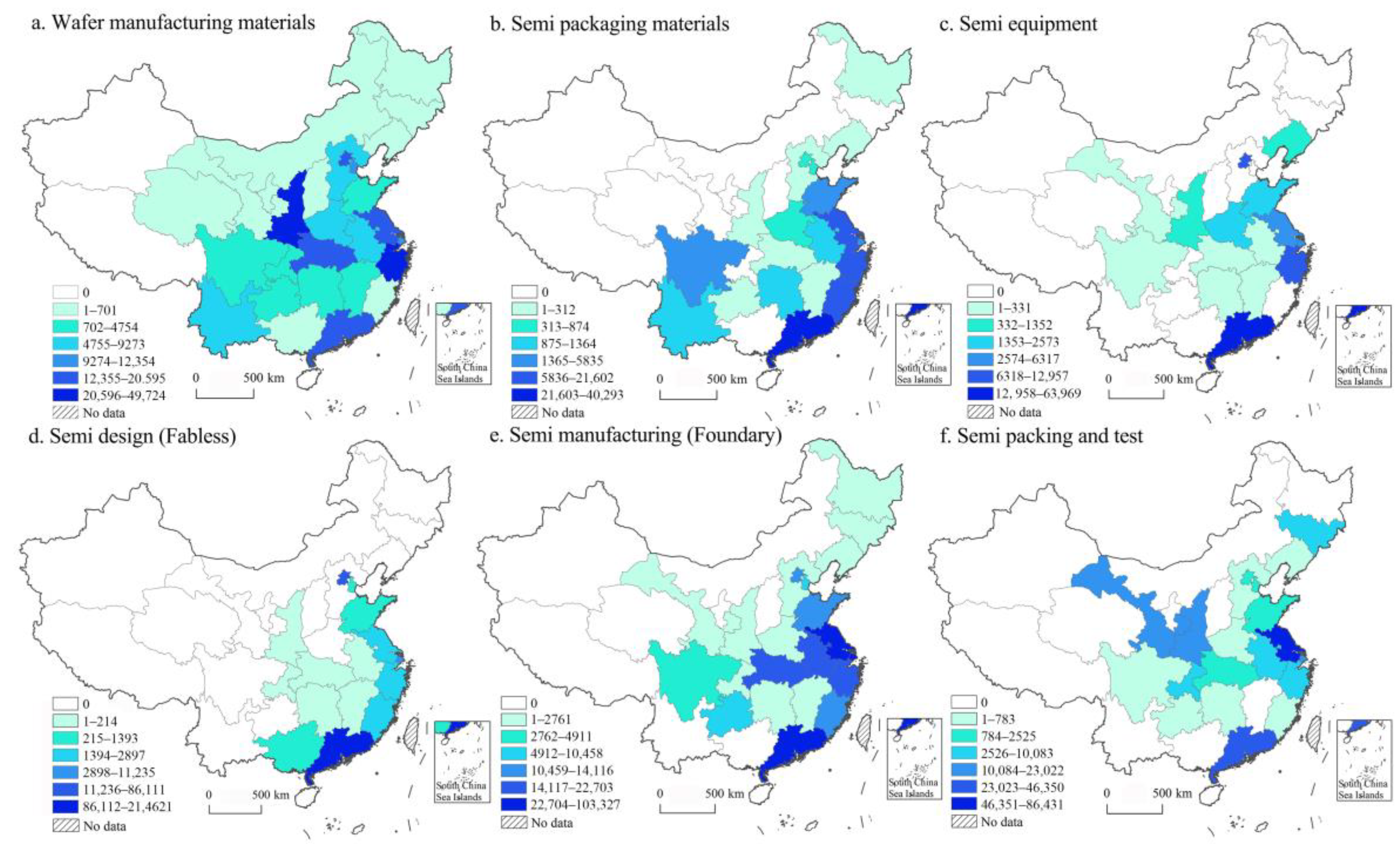
The number of employees in China’s semiconductor firms is used to illustrate spatial distribution at the provincial/municipal levels (Figure 4). Generally, regions with a large number of firms also have a correspondingly large number of employees. This is especially evident in areas involved in wafer manufacturing materials, packaging materials, and IC design, as shown in Figure 4a,b,d. However, the other three segments show varying distributions. Guangdong has the most employees, followed by Zhejiang and Beijing in the equipment segment (Figure 4c). Although Jiangsu has the highest number of equipment firms, it ranks fourth in number of employees. Figure 4e shows that semiconductor manufacturing firms and their employees are concentrated in Guangdong and Jiangsu. A high number of employees are in Shanghai, Anhui, Zhejiang, Hubei, Beijing, and Shandong. The number of firms in Jiangsu and Guangdong matches the scale of employees in the testing and packaging segment, as shown in Figure 4f. Conversely, although Gansu and Shaanxi have few firms, they have a high number of employees. This is likely owing to major firms, such as Tianshui Alex Hua Tian Polytron Technologies, contributing a large workforce to these provinces.
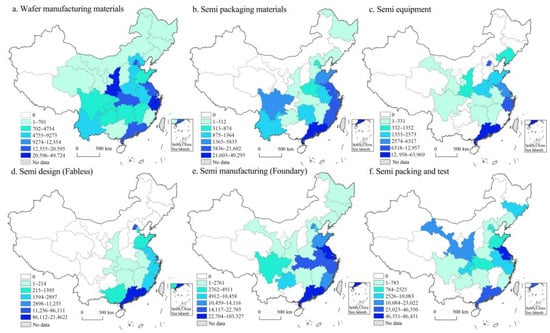
Figure 4.
The provincial/city distribution pattern the number of employees in six value segments (unit: person).
4.2. Agglomeration of China’s Semiconductor Industry
At first, we investigate aggregated distribution of semiconductor industry using L_Gi, (Table 3), which shows a appreciably high value upwards of 0.55 in most of the value segments, indicating that spatial agglomeration gained ascendancy. Distinctive value segments whose degree of concentration varies significantly have been considered. Evidently, both IC design and wafer fabrication belong to markedly concentrated sectors, with their own L_Gi, being just over 0.70. Notably, IC design gains particular attention due to its overwhelmingly high L_Gi. It is evident that the relatively concentrated phenomena occur in the segments of wafer manufacturing materials, packaging materials, and packaging and testing segments, accompanied by L_Gi ranging between 0.55 and 0.70. Comparably, there appears to be a marginally dispersed distribution whose L_Gi is even lower than 0.50. Such sectoral agglomeration discrepancies as the aforementioned can be further consolidated by the results from HHI measurement. The HHI value of IC design is the highest, at 0.18, whereas that of semiconductor equipment is at the lowest level, at 0.11; the other figures pertaining to this category range from 0.13 to 0.16. In addition to HHI, the industrial agglomeration needs further verification via CRn as another alternative, as it can reasonably reflect the nature of industrial monopoly and agglomeration in certain provinces/municipalities. Concretely, the figures of CR1 (concentration section of ranked-first province/municipality in each segment) in the six value segments all exceed 20%, among of which the packaging materials and packaging test are even higher at 28% and are both dominantly clustered in Jiangsu and Guangdong. There are five value segments in which the concentration of the top four provinces/municipalities (CR4) exceeds 60%. Notably, there occurs a substantial peak in IC design overwhelmingly distributed in Guangdong, Shanghai, Jiangsu, and Beijing, in which the top four regions account for 81.7% of the geographic distribution of China’s entire semiconductor design sector. Furthermore, the CR8 of IC design is at 92.98%. It is reasonable to assume that IC design is the most agglomerated value segment at the provincial/municipal level compared to the other five and is characterized by the monopoly of technological giants. By contrast, the CR4 and CR8 of wafer manufacturing materials are the lower than the figures for the other five segments, indicating that the segment is more inclined to geographical dispersion, with most provinces/municipalities having undertaken division of labor. According to common features of CR4 in six value segments, the semiconductor industry is generally intensively centralized in Jiangsu, Shanghai, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Fujian, and Beijing.

Table 3.
Spatial agglomeration of China’s six semi segments, 2020.
4.3. Evolution of the Semiconductor Industry on the Provincial/Municipal Scale
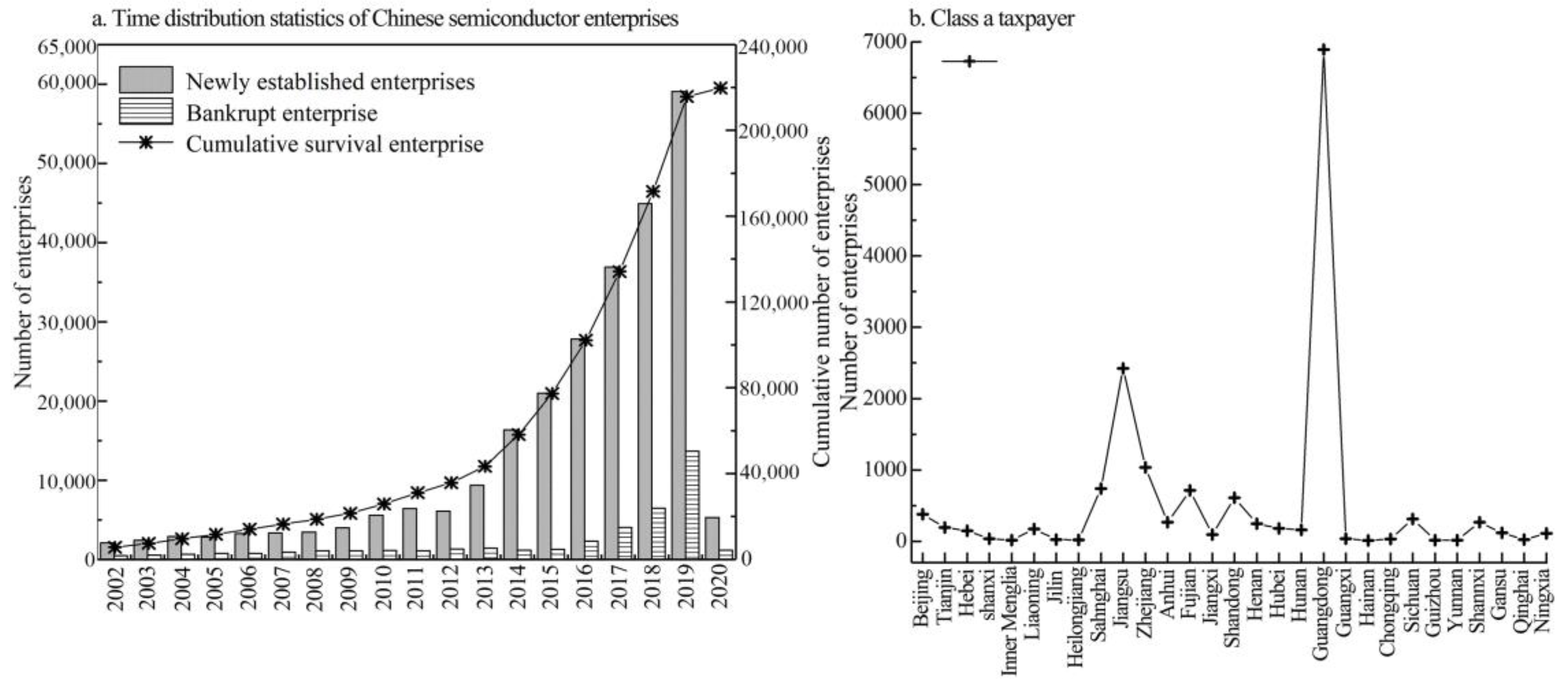
Data on the number of establishments, deaths, survivals and first-ranked prominent taxpayers (Class A taxpayer firms in China refers to a firm that has been in business for more than two years at least with a trustworthy tax credit performance, where tax authorities have levied tax on the taxpayer for two consecutive years or more. The indicator mirrors the conditions of productivity, vitality, resilience, resistance against risk environment, and survival of a firm.) of China’s semiconductor firms from 2002 to 2020 are employed in this section to trace out evolutionary trends, survival, and growth. First, Figure 5a shows a steady increase in the number of surviving semiconductor firms. The rise in new and bankrupt firms also correlates with the survivors, indicating different growth stages. Initially, from 2002 to 2013, most firms were foreign-owned or joint ventures. From 2014 to 2020, the number of firms surged due to government support and investment, leading to an expansion in China’s semiconductor industry. Second, from the perspective of first-ranked prominent firms’, taxpayers should observe firms’ resilience and vitality against the risk environment. Notably, there were 6498 firms pertaining to first-ranked prominent taxpayers in Guangdong in 2020, which was the largest and drastically outnumbered the figures for other regions, approximately three times that of second-ranked Jiangsu (2435 items). This phenomenon shows that the overall productivity resistances and operating conditions of firms in Guangdong are the most prominent. A total of 1037 firms in Zhejiang ranked third, with the figures of the Eastern and Mid-Western regions retaining dispersal ranging between 93 and 738, with some dramatically low values partly located in the Southern, Northwest, and Northeast provinces (Figure 5b).
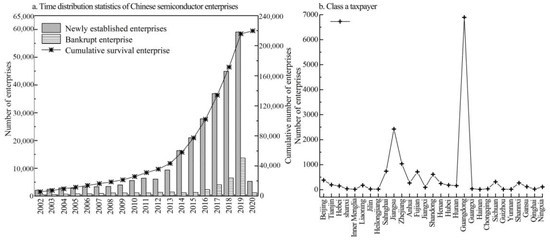
Figure 5.
Statistics on the growth and survival conditions of China’s semiconductor firms (unit: item). Data source: China Statistical Yearbook On Science and Technology (2002–2020); China’s integrated circuit Yearbook (2002–2020).
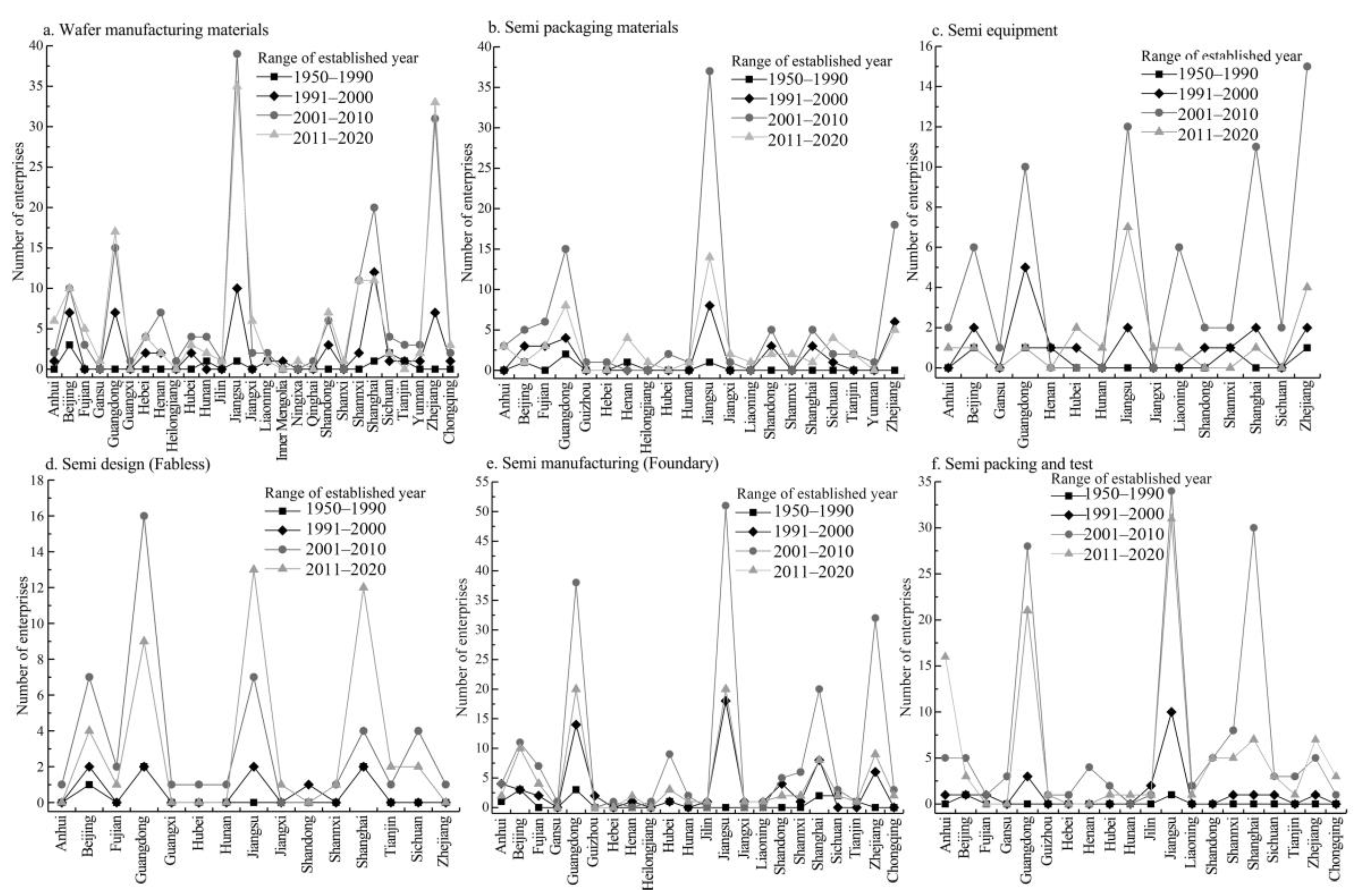
In response to the spatial distribution of entry dynamics of various semiconductor firms, the time of establishment of firms in six value segments are collected and subjected to four broad types of time intervals (Figure 6). (1) The number of currently established firms in all six segments is negligible from 1950 to 2000 and a majority of them are at single digits and are distributed at the provincial/municipal level. The firms in Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Guangdong emerged and formed the initial level. The firms proliferated unexceptionally from 2000 to 2010; in addition to the intensively soaring number of firms in Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Guangdong, a considerable number of start-ups are in Beijing and Zhejiang. From 2011 onwards, the currently established firms continued increasing, but their growth rates marginally reduced compared to those of 2000 to 2010.
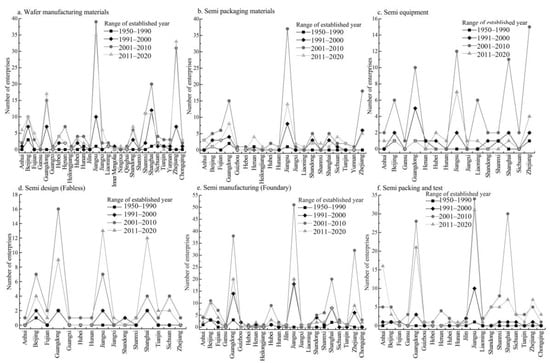
Figure 6.
The provincial/municipal distribution of time of founding of China’s semiconductor firms (unit: item).
(2) Demonstration of the firms’ growth dynamics of spatial distribution by segments: generally, the reactiveness to numbers of IC design or semiconductor equipment firms are low values, whereas the number of wafer materials or semiconductor manufacturing firms is the majority. Specifically, as listed in Figure 6a regarding wafer materials, the YRD, represented by Shanghai, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang, brims with the recently founded enterprises, with those of Guangdong and Beijing ranking second. The following are the subgroups of the number of firms: Henan, Shandong, Jiangxi, Hubei, and Hunan. Figure 6b indicates that Jiangsu has the highest number of packaging materials firms in the country, with the number of newly founded firms reaching overwhelming dominance throughout 2001–2010. There is a considerable number of newly established firms in Guangdong and Zhejiang, closely followed by those with a slight decline in the following decade onward. Regarding semiconductor equipment, the distribution of recently established firms are more prone to geographic dispersal, forming a multi-core growth pattern dominated by Beijing, Guangdong, Jiangsu, Liaoning, Shanghai, and Zhejiang (Figure 6c). Data on IC design in Figure 6d suggests that from 2000 onward, many IC design firms appear in Guangdong, Beijing, Jiangsu, and Shanghai, especially a proliferation of firms in Beijing and Guangdong from 2001 to 2010, with a slight decline in the next decade forward. Comparably, the growth rates of firms in Shanghai and Jiangsu were lower than those of the Beijing and Guangdong from 2001 to 2010; nonetheless, the figures surge in the subsequent decade. Figure 6e shows that Jiangsu’s newly founded start-ups dominate at the first rank, with the largest quantities in the regional dynamics of semiconductor manufacturing, followed by those of Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Guangdong as multi second-ranked cores, while the others are scattered in the other provinces/municipalities in a limited scope. As shown in Figure 6f, regarding the testing and packaging segment, which is generally consistent with the trend of semiconductor manufacturing, large-scale firms are intensively located in Jiangsu, Guangdong, Shanghai, and Beijing, whereas the remaining firms are located geographically in the inland provinces/municipalities.
5. Semiconducting Investment Network Pattern of Six Value Segments
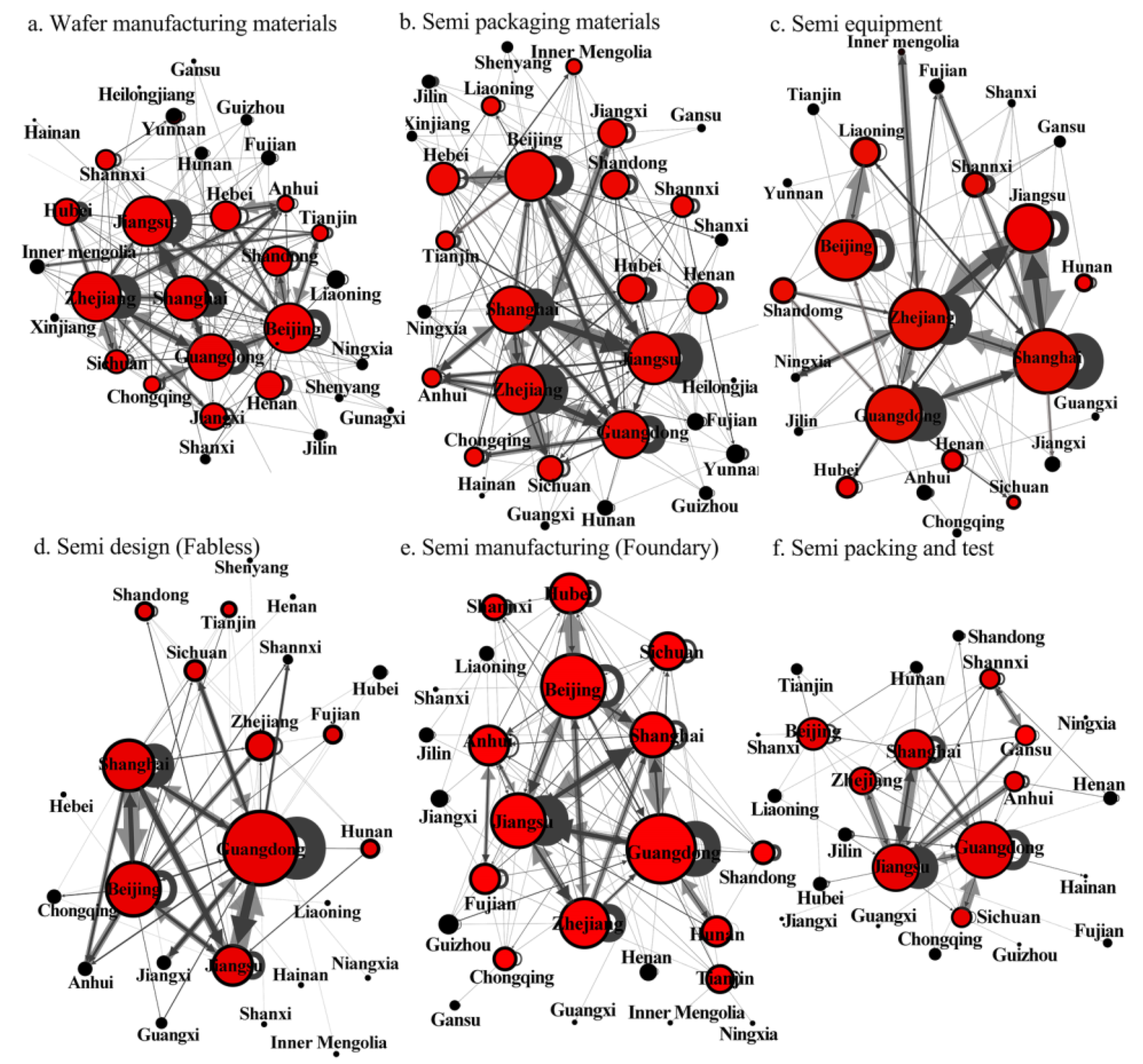
In 2020, semiconductor investment networks across six value segments show clear trends of localization, regionalization, and geographical proximity. Most investments are concentrated in the YRD and the PRD. For wafer materials, key investment hotspots are in Beijing, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Guangdong. These areas heavily emphasized local investments. Shanghai, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang are major centers for outward investments. In contrast, Guangdong and Shanghai attracted more inward investments, highlighting their prestige and strategic importance. Firms in Beijing mainly draw external investments from the Bohai Area. Meanwhile, firms in Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Shanghai focus on attracting investments within the YRD and the Central China Triangle. Investments in Guangdong, Chengdu-Chongqing, and other Midwest provinces are comparatively limited (Figure 7a). In the packaging materials segment, Beijing, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Guangdong are key nodes. Firms in Beijing mainly invested in Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Shanghai. Firms in Shanghai spread their investments across Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, and Guangdong. Guangdong stood out as a major recipient of nationwide external investments. Secondary centers with significant investments were found in Jiangxi, Shandong, Sichuan, Hebei, Henan, and Anhui (Figure 7b). The equipment investment network showed Beijing, Zhejiang, Shanghai, and Jiangsu as primary nodes (Figure 7c). In these areas, local investments in Guangdong, Shanghai, and Zhejiang surpassed external investments. Shanghai and Zhejiang were the top destinations for investments originating from Jiangsu. Peripheral nodes, including Hubei, Jiangxi, Inner Mongolia, and Ningxia, were connected to these central hubs.
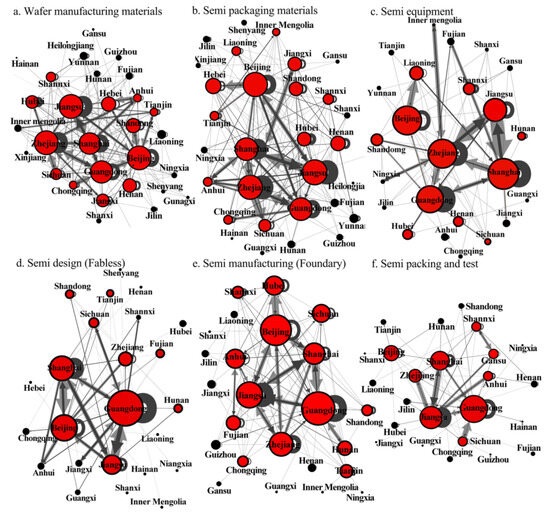
Figure 7.
The investment networks based on the six value segments of semiconductor firms in China.
Figure 7d highlighted key trends in IC design investment. Guangdong led the network, primarily attracting localized and mass investments, particularly from Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Beijing. Furthermore, Jiangsu formed a strong secondary cluster focused on intraregional investment in the YRD. Emerging investment hotspots included Zhejiang, Sichuan, Tianjin, Shandong, and Hunan, which benefit from these core areas. In the manufacturing sector (Figure 7e), Guangdong, Beijing, Jiangsu, and Shanghai stood out as influential nodes. Investment flows were concentrated in Jiangsu and Guangdong, with localized investments being the most prominent. Provinces such as Zhejiang, Hunan, Anhui, Shaanxi, Fujian, Sichuan, and Chongqing are receiving substantial investments from these core nodes. In the packing and testing, Guangdong, Shanghai, and Jiangsu dominated. Investment was largely centralized within the firms in the YRD, creating an intraregional cluster. This cluster is particularly evident among Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Anhui. Some inland regions, previously receiving little investment, are now seeing significant interest. Additionally, bilateral investments were emerging in western provinces like Gansu and Shaanxi (Figure 7f).
6. Discussions and Conclusions
6.1. Discussion
We recall the empirical results and literature review that further generalized three issues for discussion. (1) Observation of three agglomeration indexes. First, the analysis of L_Gi shows that China’s semiconductor design and wafer manufacturing segments, which are capital- and technology-intensive, are highly concentrated in specific regions. This indicates their reliance on local technological resources, capital accumulation, and skilled labor. Conversely, the packaging materials as well as packing and testing segments show moderate concentration. As these sectors require low-cost labor and raw materials, they are located in various cost-effective regions. Second, HHI results show significant differences in market concentration in different segments of the Chinese semiconductor industry. The design segment has the highest HHI value, indicating that a few provinces dominate and create a highly concentrated market structure. The findings are consistent with the L_Gi analysis, further confirming the regional monopoly in the design segment. Third, CRn results show that China’s semiconductor industry is primarily concentrated in the Eastern Coastal provinces/cities, such as Jiangsu, Shanghai, Guangdong, and Zhejiang. Owing to their geographic advantages, industrial chain support, and policy incentives, these regions have emerged as the core of China’s semiconductor industry. (2) Challenges in Chinese wafer fabrication and equipment. This study explores the challenges facing domestic production in wafer manufacturing and equipment. This study shows that while China has made some progress in wafer manufacturing materials, particularly in electronic specialty gases and high-purity chemicals, high-end materials such as photoresist and sputtering targets remain heavily reliant on imports. Additionally, high-end wafer manufacturing equipment, such as lithography machines and etching tools, are monopolized by foreign companies. This heavy reliance on imports underscores the urgent need for China to enhance its self-sufficiency in core semiconductor technologies. (3) The gap between wafer manufacturing capacity and fabless demand in the Chinese semiconductor industry. Following the previous analysis, this study examines the gap between China’s wafer manufacturing capacity and demands for domestic Fabless. The study indicates that owing to insufficient high-end wafer manufacturing capacity in China, major domestic semiconductor companies rely on the advanced process technology of TSMC. This reliance limits the rapid development of China’s design companies and integrated device manufacturers and hinders the development of independent production capacity in critical products such as memory, baseband chips, MEMS, and power devices, etc. Considering the aforementioned developmental dilemma in the Chinese semiconductor industry, a knowledge-sharing environment and open self-innovation are essentials.
The following suggestions can be outlined based on the aforementioned discussion points: first, the results of the aforementioned three agglomeration indices indicate that the spatial distribution of China’s semiconductor industry highly depends on regional resource endowments and industrial policies, which determine the degree of agglomeration and market concentration at different stages. Future industrial policies should focus on promoting balanced development in the regions and improving the efficient allocation of resources and technology to strengthen the overall competitiveness of China’s semiconductor industry. Second, large-scale enterprises should utilize their leadership position and the spillover effects to establish independent and comprehensive regional supply chains and enhance the accessibility of their technology for small-scale firms. Chinese industrial decision-makers should focus more on open-access (OA) communities. Although OA is not widely recognized in Chinese industrial practices, it is crucial to acknowledge its vital role as a fundamental component and upstream foundation in the overall industrial ecosystem. The industrialization of OA contributions and OA software both represent important aspects of domestic substitution. Second, Chinese semiconductor companies must re-balance the relation between globalization and self-innovation. Chinese semiconductor firms have demonstrated proficiency in incremental innovation, and globalization provides a conducive environment for such endeavors. Enterprises should use globalized resources to access technologies for self-innovation. Moreover, innovative outcomes can be used globally, creating a ripple effect using the dividends of self-innovation.
6.2. Conclusions
This study uses data from China’s six major semiconductor value segments to analyse spatial distributions and investment linkages. The main conclusions are as follows: (1) The semiconductor value chain is densely located in the Eastern Coastal areas. Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Zhejiang lead in materials, equipment, manufacturing, and packing and testing, whereas packing and testing as well as manufacturing are sparsely located in Mid-Western regions. The design segment is concentrated in Guangdong, followed by Shanghai and Beijing. (2) The number of semiconductor companies in China has maintained steady growth for 18 years. Moderate expansion was experienced from 2002 to 2013, whereas considerable expansion was experienced from 2014 to 2020. The overall productivity and operational status of enterprises in Guangdong are significantly higher than those in other provinces. (3) Firm investments exhibit regionality and geographical proximity. Local investments in Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Guangdong surpass external investments. Semiconductor materials investments are mainly concentrated in the YRD and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban clusters. Equipment and design investments are located in the YRD and Pearl River Delta (PRD). Manufacturing, packing, and testing investments are exchanged between the YRD and PRD and extend to the Central and Western provinces. More importantly, the empirical analysis in this study verifies the aforementioned three hypotheses. First, the research results confirm the first hypothesis, that China’s semiconductor industry displays overall spatial clustering, primarily concentrated in a few leading regions with advanced technology and industrial development, such as the YRD and PRD. Second, this study supports the second hypothesis, and high concentration of knowledge- and capital-intensive segments are evident. Semiconductor design is mainly concentrated in specific regions with stable technological capabilities and innovation potential. These regions typically have well-developed infrastructure, a highly skilled workforce, and favorable policies, which foster geographical concentration in these segments. Third, the study confirms the third hypothesis, showing geographical dispersion of labor- and resource-intensive segments. This dispersion is owing to the high reliance of these segments on low-cost labor and resources, leading semiconductor companies to establish production bases in cost-effective regions. Overall, the findings of this study support the proposed hypotheses and provide new insights into the spatial layout of China’s semiconductor industry. When formulating relevant policies and strategies, decision-makers should consider the geographical distribution features of different segments to optimize resource allocation and promote synergistic industrial development.
The findings provide valuable insights into the semiconductor industrial development while emphasizing the importance of sustainability in global production and supply chains. It further offers lessons and inspirations for sustainable industrial practices from the Chinese case study as follows: (1) Sustainable supply chain management. The global semiconductor supply chain is complex and highly interconnected, making it vulnerable to geopolitical tensions and environmental challenges. Building a sustainable supply chain in China involves improving the resilience of local semiconductor production by reducing dependency on foreign suppliers, fostering local technological innovation, and ensuring the efficient distribution of resources across the country. Sustainable supply chain management also entails incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment and production decisions, aligning with global sustainability standards. (2) Eco-friendly policies and techniques for sustainable growth. China’s government has increasingly emphasized the importance of sustainable industrial development through various policies and initiatives. For the semiconductor sector, this translates into promoting innovation in green technologies, offering incentives for companies to adopt eco-friendly practices, and supporting research into new materials and energy-efficient manufacturing techniques. More attention has paid to energy efficiency and green manufacturing in this sector, such as the use of solar or wind energy to power manufacturing plants, improving energy efficiency through advanced process technologies, and implementing waste heat recovery systems. These policies not only aim to enhance the industrial global competitiveness but also to ensure that growth does not come at the expense of the environment. (3) Contribution to global sustainability goals. The development of a sustainable semiconductor industry in China also contributes to global efforts to mitigate climate change and achieve sustainable development goals (SDGs). By adopting practices that reduce emissions, conserve resources, and promote responsible production, China’s semiconductor sector can play a pivotal role in meeting global targets for sustainability. This is particularly relevant as semiconductors are essential for the development of renewable energy technologies, electric vehicles, and smart cities, all of which are integral to a sustainable future.
The advantages of this study are as follows: (1) Extensive data coverage. This study uses data from six major segments of China’s semiconductor value chain from 2002 to 2020. The dataset includes information on enterprises, investments, and related statistics, providing strong representativeness and timeliness. (2) Detailed classification and quantitative measurement. This study extends the analysis to upstream segments, including materials and equipment, which have been insufficiently emphasized in previous research that primarily focuses on semiconductor design, manufacturing, and packaging/testing. This provides a more comprehensive and quantified understanding of the entire semiconductor industry chain. (3) Revelation of investment trends. This study reveals the geographical characteristics of semiconductor enterprise investments, particularly highlighting the superior performance of local investments in major nodes. These findings provide crucial insights into the underlying drivers of the industry chain. (4) Identification of industrial clusters. The study identifies Jiangsu, Guangdong, Shanghai, and Zhejiang as major hubs of the semiconductor industry. Moreover, to extend this study, future research should consider the following subjects: (1) Dynamic evolution at the urban scale. Future studies could focus on the long-term and fine-grained evolution of semiconductor clusters and investment patterns at the urban level, providing deeper insights into how these factors develop over time and space. (2) Comparative studies in a global context. Comparative studies between China’s semiconductor industry and those of other typical nations would help clarify their respective roles and competitiveness in the GVC. This type of research would contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the semiconductor industry on a global scale. (3) Impact of emerging technologies on the semiconductor value chain. With advances in some relevant technologies such as AI and 5G, future research should explore how these innovations affect different sections of the semiconductor value chain. Such studies could provide critical insights into how emerging technologies are reshaping the semiconductor landscape and driving shifts in industry structure and location. (4) Involvement of urban communities and complex networks. Future research should incorporate theories and approaches of urban communities and complex networks to conduct in-depth analysis. This approach will help uncover the intrinsic logic and future trends in the development of the semiconductor industry.
Author Contributions
Q.L. conceived the presented idea, did field research, wrote the whole manuscript, and revised the content of manuscript based on the comments of the four reviewers and editors; D.X. verified the analytical methods, provided project management and language supervision, and then confirmed the manuscript; W.L. also contributed to the methodology, and participated in the field trip and data collection of the study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is subsidized by the Major Projects of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 41930646, the Program of China Scholarship Council, Grant No. 202306380174.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data analyzed during this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interests with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
References
- Dicken, P. Global Shift: Reshaping the Global Economic Map in the 21st Century; Liu, W., Translator; The Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.B. Annual Report on the Development of Integrated Circuit Industry (2018–2019); Social Sciences Academic Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Capri, A. Semiconductors—Beijing versus the West China’s push runs into trouble amid trade war and US companies’ tech theft fears. Nikkei 2018, 10, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Capri, A. The Geopolitics of Semiconductors in the U.S.-China Trade War; Hinrich Foundation: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, L. The China semiconductor industry: Growth, challenges, and global integration. J. Glob. Econ. 2022, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Duhalde, M.; Liu, Y. ‘Made in China 2025’: How Beijing is boosting its semiconductor industry. SCMP 2018, 9, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. China Manufacturing 2025: Upgrading China’s Role in Global Manufacturing. China Econ. J. 2018, 11, 28–45. [Google Scholar]
- Software and Integrated Circuit Promotion Centre, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. The Golden Decade of China’s IC Industry; Electronic Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J. China’s Impact on the Semiconductor Industry. 2016 Update Section II: IC Design and Manufacturing; PriceWaterHouseCoopers: Melbourne, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, C. Funding Innovation in China’s Semiconductor Industry: The Role of National and Local IC Funds. China Econ. Rev. 2017, 45, 102–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, L. Global Value Chain Analysis of China’s Semiconductor Industry: Opportunities and Constraints. J. Dev. Stud. 2018, 54, 391–407. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, M. China’s semiconductor industry: Addressing the global supply chain mismatch. J. Asian Econ. 2021, 75, 101239. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, J. The Impact of U.S.-China Tensions on the Global Semiconductor Supply Chain. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2020, 52, 1058–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Fulco, M. Betting all the chips: China seeks to build a world-class semiconductor industry. CKGSB Knowl. 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Fulco, M. China’s Semiconductor Market Faces a Test as U.S. Sanctions Bite. Nikkei Asia 2018, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, C.; Gao, J.; Lynn, L.; Verena, J. China Semiconductors Localizing the Next Generation of Long-Term Winners; The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. The Supply Chain Dependency of China’s Semiconductor Industry: Risks and Solutions. Asia-Pac. J. Bus. 2020, 12, 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Li, H. China’s Semiconductor Industry Nationalization and Its Global Implications. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2019, 31, 945–960. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, W.C. Interconnected Worlds: Global Electronics and Production Networks in East Asia; Stanford Univeristy Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, W.C. Explaining Geographic Shifts of Chip Making toward East Asia and Market Dynamics in Semiconductor Global Production Networks. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 98, 272–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, S.; Du, D. China’s emerging role in the global semiconductor value chain. Telecommun. Policy 2022, 46, 101959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Rho, S. The US–China Chip War, Economy–Security Nexus, and Asia. J. Chin. Political Sci. 2024, 29, 433–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, E. U.S. Move to Isolate Huawei Sends Ripples through Global Supply Chain; National Public Radio: Washington, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.S. Great Powers and New Risks: What Businesses and Regulators Should Know about China’s Strategic Ambitions. Orbis 2020, 68, 257–274. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.S. Stuck in the Middle: Taiwan’s Semiconductor Industry, the U.S.-China Tech Fight, and Cross-Strait Stability. Winter 2021, 65, 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Du, J.; Li, Y. Research on the characteristics and influencing factors of Huawei’s mobile phone production network from GPN. Geogr. Res. 2024, 43, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, D. China’s Bold Strategy for Semiconductors—Zero-Sum Game or Catalyst for Cooperation? East-West Center; Honolulu & Centre for International Governance Innovation: Waterloo, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. China’s Dual-Cycle Economic Strategy and Its Implications for Semiconductor Self-Sufficiency. J. Chin. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2020, 18, 247–263. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Yang, K. China Electronic Industry Development Research Report; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. China Statistical Yearbook On Science and Technology (2002~2020); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Moonsup, S.; Peng, R. China Semiconductor White Paper; Bain & Company: Boston, MA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://www.bain.cn/pdfs/202208220536478028.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Liu, Q.; Xue, D.; Huang, G. Spatial organization and network externalities of the cluster networks in China’s semiconductor industry: A view on production segments of semiconductor industrial value chain. Geogr. Res. 2024, 43, 909–930. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Xue, D.; Gao, Q. The progress and prospect of world semiconductor cluster research: From the perspective of organizational pattern of semiconductors. World Reg. Stud. 2024; early access. [Google Scholar]
- Angel, D. Restructuring for Innovation: The Remaking of the US Semiconductor Industry; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, A.J. The global assembly operations of US semiconductor firms: A geographical analysis. Environ. Plan. A 1988, 20, 1047–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.J. The Geographic Foundations of Industrial Performance. Compet. Change 1995, 1, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.J. Regions and the World Economy: The Coming Shape of Global Production, Competition, and Political Order; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, A.J.; Quinn, B. US Investment Bank as Multinationals; Jones, G., Ed.; Bank as Multinationals; Routledge: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, S. Delicate bonds: The global semiconductor industry. Pac. Res. 1980, 11, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, R.M.; Appleyard, L. The Evolving Role of Semiconductor Consortia in the United States and Japan. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1998, 41, 137–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, T.; McCann, P. The spatial and hierarchical organization of Japanese and US multinational semiconductor firms. J. Int. Manag. 2002, 8, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourevitch, P.; Bohn, R.; Mckendrick, D. Globalization of Production: Insights from the Hard Disk Drive Industry. World Dev. 2000, 28, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.A. A Silicon Valley of the East: Creating Taiwan’s Semiconductor Industry. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1997, 39, 26–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.A. A Silicon Island of the East: Creating a Semiconductor Industry in Singapore. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1999, 41, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.A.; Cho, D.-S. Tiger Technology: The Creation of a Semiconductor Industry in East Asia; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Satō, Y. Diverging Development Paths of the Electronics Industry in Korea and Taiwan. Dev. Econ. 1997, 35, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OhUallachain, B. Restructuring the American semiconductor industry. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1997, 87, 213–237. [Google Scholar]
- Borrus, M. The Resurgence of US Electronics: Asia Production Networks and the Rise of Winterlism; Routledge: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Macher, J.T.; Mowery, D.C.; Hodges, D.A. Reversal of Fortune? The Recovery of the U.S. Semiconductor Industry. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1998, 41, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.Q. The Study on the Development Pattern and Spatial Diffusion of IC Industry in Taiwan. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, S.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J. The global production pattern of the semiconductor industry: An empirical research based on trade network. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Dynamics of the global semiconductor trade and its dependencies. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 1141–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W. China-U.S. Tech Rivalry and the Impact on Semiconductor Industry Supply Chains. Pac. Aff. 2020, 93, 609–631. [Google Scholar]
- Rasiah, R.; Wong, S.H. Industrial upgrading in the semiconductor industry in East Asia. Innov. Dev. 2022, 11, 413–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.T.; Grimes, S. China’s increasing participation in ICT’s global value chain: A firm level analysis. Telecommun. Policy 2016, 40, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, D.B. Chip design in China and India: Multinationals, industry structure and development outcomes in the integrated circuit industry. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2014, 81, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.L.; Chang, J.Y.; Li, T.C. Government Support, FDI Clustering and Semiconductor Sustainability in China: Case Studies of Shanghai, Suzhou and Wuxi in the Yangtze Delta. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.P. How the United States marched the semiconductor industry into its trade war with China. CEPR Discussion Papers. Asian Econ. Rev. 2020, 24, 349–388. [Google Scholar]
- Huggins, R.; Johnston, A.; Munday, M.; Xu, C. Competition, open innovation, and growth challenges in the semiconductor industry: The case of Europe’s clusters. Sci. Public Policy 2023, 50, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, M. Explaining the Growth and Globalization of Silicon Valley: The Past and Today; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, L.; Li, N.; Yu, X. Unveiling the influence of global innovation networks on corporate innovation: Evidence from the international semiconductor industry. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamsal, R.R.; Devkota, A.; Bhusal, M.S. Navigating Global Challenges: The Crucial Role of Semiconductors in Advancing Globalization. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 2023, 104, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Semiconductors at the Intersection of Geoeconomics, Technonationalism, and Global Value Chains. Soc. Sci. 2023, 12, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C. Global chip war for strategic semiconductors. Nat. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2024, 1, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.F.; Lin, C.; Shen, C.H.; Wang, S.W.; Chang, K.C.; Chang, R.C.H.; Yeh, W.K. The role of government policy in the building of a global semiconductor industry. Nat. Electron. 2021, 4, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Wu, D.; Yeung, J. Semiconductor supply chain resilience and disruption: Insights, mitigation, and future directions. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahinipati, B.K.; Deshmukh, S.G. Vertical collaboration in the semiconductor industry: A decision framework for supply chain relationships. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2012, 62, 504–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IC Insights. McClean Report—A Complete Analysis and Forecast of the Integrated Circuit Industry. 2019. Available online: http://www.icinsights.com/services/mcclean-report/ (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Gartner Research. Forecast Analysis: Semiconductors and Electronics, Worldwide. 2024. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/5401163/ (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Semiconductor Industry Association. Beyond Borders: The Global Semiconductor Value Chain; Nathan Associates: Arlington, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pecht, M. China’s Electronics Industry: The Definitive Guide for Companies and Policy Makers with Interest in China; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. The Semiconductor Industry: A Strategic Look at China’s Supply Chain. In The New Chinese Dream; Spigarelli, F., McIntyre, J.R., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Font, J.; Cowell, F.A. Measurement and explanation of inequality in health and healthcare in low-income settings. J. Dev. Econ. 2019, 133, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, V.; Gherman, T.; Paliza, J.C. The Gini Index: A Modern Measure of Inequality; Springer Books: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, G.; Glaeser, E.L. Geographic concentration in US manufacturing industries: A dartboard approach. J. Political Econ. 1997, 105, 889–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Industrial agglomeration, technological innovation and carbon productivity: Evidence from China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 166, 105330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, S.A. The Herfindahl-Hirschman Index. Fed. Reserve Bull. 1993, 79, 188–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kvålseth, T. Cautionary Note About the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index of Market (Industry) Concentration (25 March 2020). Contemp. Econ. 2022, 16, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.H.; Chen, C.H. The competition between the US, Europe, and Asia in the semiconductor industry. Technol. Soc. 2012, 34, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).