Abstract
The fight against climate change is one of the main global challenges of our time, and the European Union (EU) seeks to achieve climate neutrality and energy transition for the continent by 2050 through various policies. This research studies the economic implications of the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) on European ports. By analysing various maritime scenarios, the study assesses how the ETS influences shipping routes, port competitiveness, and overall economic activity. A key finding is that the ETS imposes significant additional costs on shipping companies, which could lead to adjustments in routes and a shift in cargo volumes to ports in regions with less stringent environmental regulations. This could result in job losses in European port communities and reduce the competitiveness of European ports. In addition, the potential for carbon leakage, where shipping activities are simply relocated to regions with fewer emission controls, is explored.
Keywords:
ETS; competitiveness; green ports; European ports; route analysis; emissions; sustainability 1. Introduction
The fight against climate change is one of the major global challenges of our time, and the European Union (EU) has been a pioneer in implementing policies to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions [1]. Taking a firm stance on reducing emissions, not only as an environmental commitment, but also as an opportunity to lead the transition to a more sustainable and resilient economy.
With the aim of achieving climate neutrality by 2050, the EU launched the European Green Deal, an ambitious strategy covering various sectors of the economy, from energy and transport to agriculture and industry. This roadmap not only aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but also to transform the European economy, making it more resource-efficient and less dependent on fossil fuels [2]. In this sense, it also seeks to encourage technological innovation and the creation of new green jobs.
One of the key pillars of the Green Deal is the Fit for 55 legislative package, presented in 2021. This package, which covers multiple regulatory areas, has as its main objective to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030, taking 1990 levels as a reference [3]. To achieve this goal, a number of measures have been proposed that affect different sectors, including maritime transport, as well as energy production and the use of natural resources.
Within the framework of the Blue Economy, which is all those economic sectors related to the ocean [4], one of the most notable developments is the inclusion of maritime transport in the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS). Until recently, shipping, responsible for about 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions, was not subject to the same strict regulations as other industrial sectors. However, with the expansion of the EU ETS, the maritime sector will now be forced to reduce its carbon emissions, a crucial step towards achieving the EU’s climate goals. This system requires shipping companies to purchase permits for every ton of CO2 they emit, creating a financial incentive to reduce their carbon footprint and adopt cleaner technologies [5].
The inclusion of maritime transport in the EU ETS poses a number of important challenges for the European shipping industry and ports. In terms of competitiveness, EU ports could face increased costs, as shipping companies will have to pay for their emissions, which could lead some operators to look for ports in third countries that are not subject to these regulations [6]. This could lead to carbon leakage, i.e., the transfer of polluting activities to areas where regulations are less stringent [7]. On the other hand, ports and shipping companies will have to adapt quickly to new environmental regulations, which means investments in cleaner technologies, such as alternative fuels like hydrogen or ammonia, or improvements in the energy efficiency of ships [6].
The main objective of this research is to analyse the economic impacts of the implementation of the EU ETS on EU ports, with special emphasis on the implications that this may have on the restructuring of trade routes and on the competitiveness of European ports vis-à-vis their counterparts outside the European Economic Area.
To meet this objective, a methodology structured in several phases will be used. First, an Ishikawa diagram will be carried out [8], also known as a cause–effect diagram, to identify and categorise factors that may influence the success or failure of the implementation of the EU ETS in shipping. This analysis will allow the problems to be broken down into key categories, such as technological, economic, regulatory, and social factors, in order to take a comprehensive view of the challenges faced by the actors involved.
Second, simulations of different maritime scenarios will be carried out to predict how shipping companies and ports might react to the new regulations. These simulations will consider variables such as the cost of emission allowances and the competitiveness of ports. Through these models, we will seek to better understand the implications of the expansion of the EU ETS and how different actors could adapt to these changes.
Finally, this work will offer conclusions based on the results obtained, with the aim of mitigating the negative effects of the ETS, protecting the competitiveness of European ports and ensuring that climate objectives are effectively met.
2. State of the Art
2.1. Fit for 55 Legislative Framework
For some years now, the European Commission has set out to achieve climate neutrality on the continent by 2050 [1]. To this end, the European Green Deal was developed, which is carried out through different packages of measures such as RefuelEU, RepowerEU, or Fitfor55.
On 14 July 2021, the European Commission presented the “Fit for 55” package to achieve the targets of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 by at least 55% compared to 1990 levels [3]. This package proposes a series of 14 measures, of which four are closely linked to maritime transport and therefore to port activities:
ETD Maritime: With the new Directive 2003/96/EC on energy taxation, tax exemptions for marine fuels are partially ended. Fuels sold in the European Economic Area (EEA), for travel within the EEA, will no longer be exempt from tax [9]. This directive was still under review in June 2024.
Alternative fuels infrastructure (AFIR): Boosting the expansion of LNG and shore-based power supply facilities in the EU’s main ports [10]. The old Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Directive becomes a regulation.
EU Emission Trade System (EU ETS): Maritime transport is incorporated into the Community Emissions Trading System. Ships are responsible for 100% of their CO2 emissions in and between EU ports, and for 50% when entering or leaving the EU. They must pay according to the current carbon market price (€/tonne of CO2) [5].
Fuel EU: This measure seeks to encourage the adoption of low-emission fuels by imposing limits on the carbon intensity of fuels on board ships. Carbon intensity reduction levels of fuels will progressively increase along different lines (2% in 2025, −6% in 2030, 75% in 2050) [11].
2.2. EU Emission Trade System
The European Union’s Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is a market-based mechanism designed to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the most CO2-intensive sectors [12]. It has been extended to the maritime sector to address rising greenhouse gas emissions from merchant ships. This market mechanism forces shipping companies to acquire emission allowances for each tonne of CO2 emitted, thus incentivising the adoption of cleaner technologies and fuels [13]. The inclusion of maritime transport in the EU ETS, from 2024, represents a significant step towards the decarbonisation of the sector and the achievement of the EU’s climate objectives. The main application features of this system are as follows:
- The Maritime Emissions Trading System (ETS) will apply to all cargo ships and passenger ships over 5000 GT.
- 100% of the emissions of the intra-European routes, 100% of those made while in port, and 50% of the extra-European routes will be covered.
- Gradual application between 2024 and 2026. It will be paid for 40% of emissions in 2024, 70% in 2025, and 100% in 2026.
- Control is extended to methane (CH4) and nitrous oxides (NOx) from 2026.
- In 2026, the inclusion of vessels from 400 GT will be reviewed. Offshore Service Vessels of more than 5000 GT will be included from 2027.
- It includes the measure to redefine the “port of call” to avoid carbon leakage, considering “transparent” non-European ports with more than 65% transshipment activity, located less than 300 nautical miles away.
- If the IMO does not implement measures by 2028, an assessment of the impact of the directive will be carried out.
2.3. Impacts on the Application of Emission Control Regulations
In recent decades, maritime governance has been undergoing regionalisation that contributes to a more complex and distributed system, where different actors share the responsibility for ensuring the sustainability of maritime transport. Traditionally, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has been the main regulatory body for global shipping; however, due to growing environmental concerns and the perceived ineffectiveness of the IMO in certain areas, regional initiatives have emerged in the EU [14].
For years, certain maritime areas of the world have been declared Emission Control Areas (ECAs), which have stricter environmental regulations to reduce emissions of sulphur and nitrogen oxides from ships [15]. Some studies indicate that ECAs can have a negative impact on port efficiency. An average efficiency reduction of 15–18% is estimated in ports within the ECAs. This suggests that measures to comply with environmental regulations may lead to additional costs that affect the operational efficiency of ports [16].
On the other hand, ECAs impose stricter restrictions on sulphur and nitrogen oxide emissions, which can affect ship routes and speeds. Mathematical models currently exist to optimize the speed of a ship considering fuel costs, travel time, and compliance with emissions regulations [17].
In terms of governance and decision-making model, when implementing emission regulation measures, there are two main types of regulations: a unilateral one, implemented by a single region; and a uniform one, applied to all regions [18]. Considering the competition between shipping companies and ports, as well as operational factors, such as inventory costs and the balance between fleet size and sailing speed, the results indicate that unilateral regulation can even increase total emissions, while uniform regulation always reduces them. In addition, both regulations can have asymmetric effects on shipping companies and ports [19].
In addition, on the one hand, there is a large concentration of fleet, since the five largest shipping companies own 65% of the container transport [20]; however, this is not the case with ports. In Spain alone, for example, there are 46 state ports. Competition between ports can affect the effectiveness of emissions regulations. In addition, the type of regulation (unilateral or bilateral) also influences the results. A port subject to strict regulation may lose competitiveness compared to ports in regions with less stringent standards and, in addition, different regulations may incentivize or discourage investment in clean technologies [6].
On the other hand, it should be noted that carbon leakage in shipping emission control occurs when efforts to reduce emissions in one region or sector lead to an increase in other areas, undermining global goals, given that air emissions are not a local phenomenon but a global one [7]. This can happen by shifting trade routes, relocating fleets to countries with laxer regulations, or evading regulations by changing flags to states with fewer restrictions. Consequences include a global increase in emissions, competitive inequality, and challenges to the effectiveness of emission reduction policies [21]. To mitigate carbon leakage, robust international coordination, which establishes homogeneous regulations and avoids imbalances, is crucial. Organizations such as the IMO are key in the implementation of global standards [22]. In addition, monitoring and verification mechanisms must be improved to ensure compliance with regulations, implementation of economic incentives for companies that adopt sustainable practices, and encouragement of research into and the development of cleaner and more efficient technologies. Addressing carbon leakage in shipping requires a comprehensive approach that combines international cooperation, implementation of homogeneous regulations, and promotion of sustainable technologies [23].
The following are some potential indicators for detecting these carbon leaks:
- Evolution of the number of calls of ships under 5000 GT. This size of ships is exempt during these first years from the ETS levy in EU ports; therefore, a significant increase in the number of calls of this type of ship from other non-European ports could mean a clear carbon leakage [24]. The mother ships would carry out the unloading operation at these transit ports and, by means of smaller vessels exempt from the ETS, they would transport the goods to European ports.
- Trend in the volume of goods in transit in European ports. If European ports that, due to their geographical position, capacity, maritime connectivity index, etc., currently have a high percentage of goods in transit and begin to lose a volume of goods similar to that gained by their non-European competitors, it would be a clear example of this migration of routes to ports exempt from ETS [25].
- Evolution of the distances that the mother ships travel on the last leg of their journey before the European port. If the distance travelled from the last non-European port is significantly reduced, it could be a clear indicator for detecting an unusual previous stopover before the implementation of the ETS in order to pay a lower amount for the journey made [26].
- Investments that are being undertaken in both European and non-European ports in terms of increasing the capacity and efficiency of their terminals. If competing ports are identified as investing to increase their container transshipment capacity, for example, large amounts of traffic may be diverted to these ports [27].
- As for the Short Sea Shipping lines, study the evolution of the volume of trucks that are transported. By applying the ETS package to ships without applying the ETS2 to the road, intra-EU traffic that occurs via SSS pays 100% of the emissions and reduces profitability for trucks to go by boat [28].
On the purely economic side, the application of the ETS to European ports will have a significant negative economic impact due to the increased costs associated with calling at these ports [29]. Shipping companies will face higher operating expenses for having to acquire emission permits for their vessels, which could result in an increase in port fees and prices for related services [30]. This increased cost may discourage shipping companies from using European ports, causing them to opt for alternative routes or ports in regions with less stringent regulations which, in turn, could reduce maritime traffic and negatively affect local economies that depend on trade and port activity [27]. In addition, the competitiveness of European ports could be compromised, affecting related industries such as land transport, logistics, and warehousing, and potentially leading to job losses in these sectors [31].
3. Methodology
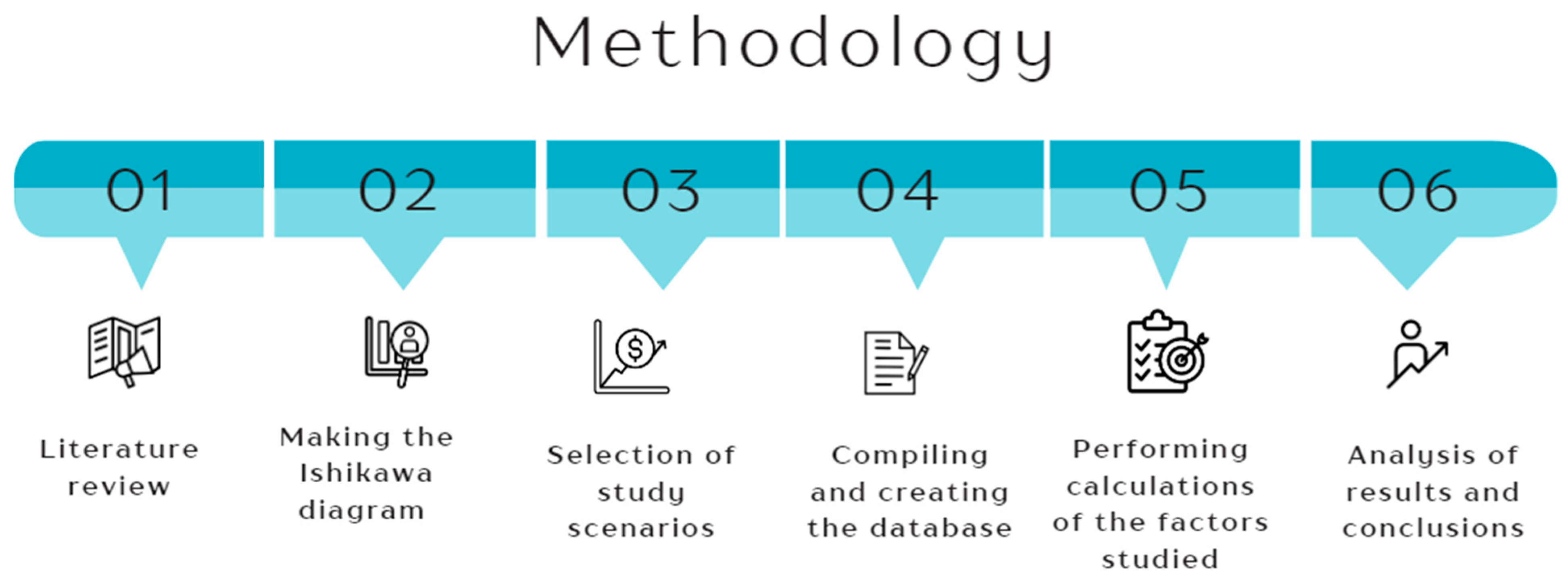
The methodology proposed in this research is framed according to the following phases:
The general steps of the methodology are (Figure 1):
Figure 1.
Work flow. Source: own elaboration.
Phase 1: Bibliographic review. A comprehensive study was conducted to analyse the modes of application of the ETS, its legislative framework, and the expected impacts of its implementation. The literature review covered academic articles, official reports, and EU policy documents. Key sources included the European Green Deal, the Fit for 55 legislative package, and studies on the inclusion of maritime transport in the EU ETS. Databases such as Scopus, Web of Science, and MRV EU repositories were consulted to ensure reliable and relevant data.
Phase 2: An Ishikawa analysis was carried out to detect the main effects of the implementation of the ETS in the maritime domain. The Ishikawa diagram was applied as a structured tool to identify and classify the effects [8] in order to better understand the critical factors affecting the ports of the EEA due to the implementation of the ETS. Once this was done, the dimension with the most significant effects when applying the ETS was quantified according to a panel of experts from shipping companies, ports, consultancies, and universities.
Phase 3: Selection of study scenarios. Once the Ishikawa analysis was completed, the study focused on analysing the derived economic aspects in more detail. Different scenarios of maritime routes that could be affected by the application of the ETS, on both the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts, were proposed.
Phase 4: Database collection and creation. Once the routes to be studied were selected, data were collected from different sources (MRV emissions, SBC, European Commission, Algeciras Port, etc.) and the database was created.
Phase 5: Realisation of the factors studied. Once the database was created, the economic effects of a ship’s scale were calculated based on the scenarios outlined in Phase 3.
Phase 6: Analysis of results and conclusions. Once the results were obtained, these were analysed and the conclusions drawn from the study were compiled.
4. Results and Analysis of Results
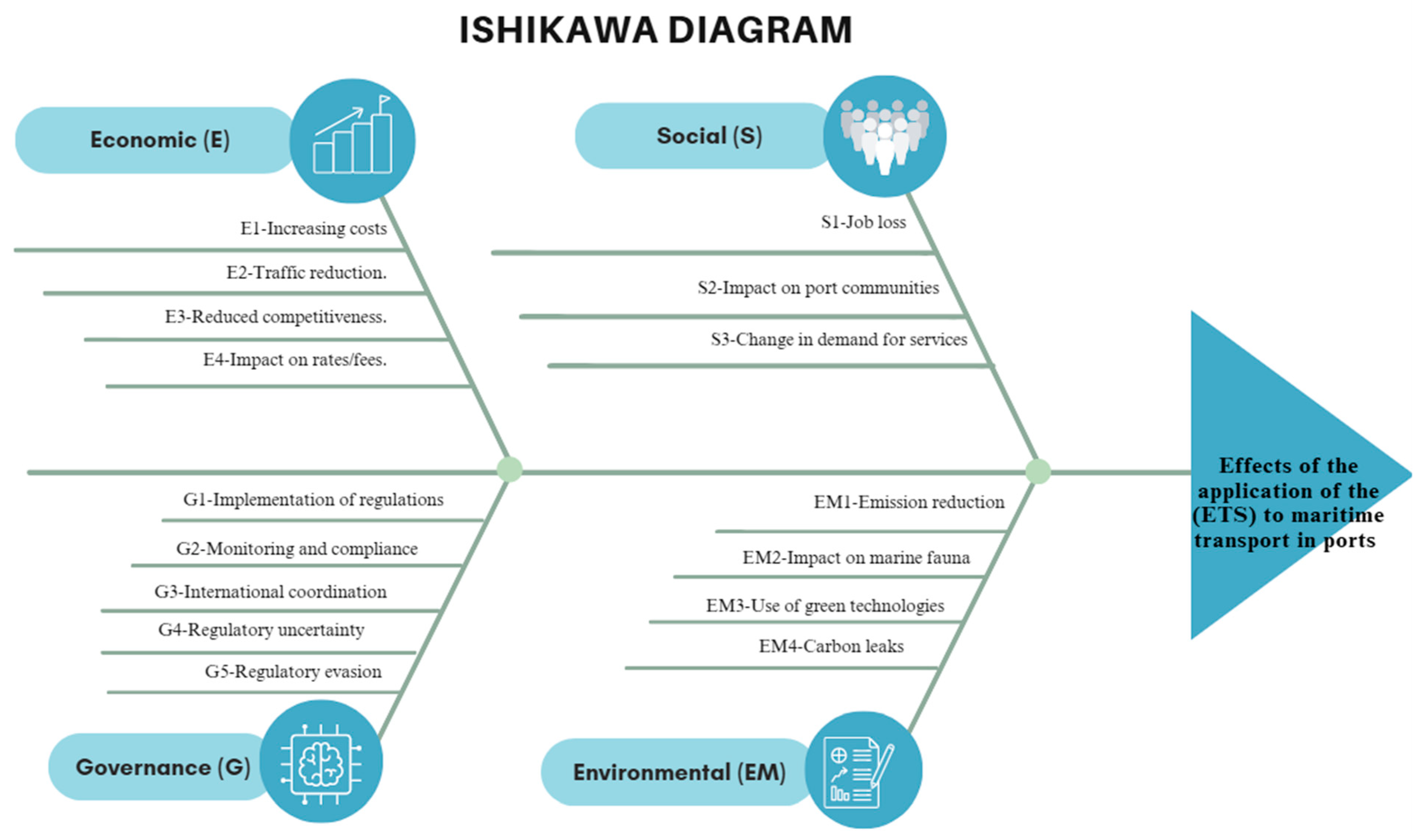
The Ishikawa diagram (fishbone) showing the effects of the application of the ETS to maritime transport in EU ports, categorized into four main areas: Economic, Social, Governance, and Environmental (Figure 2).
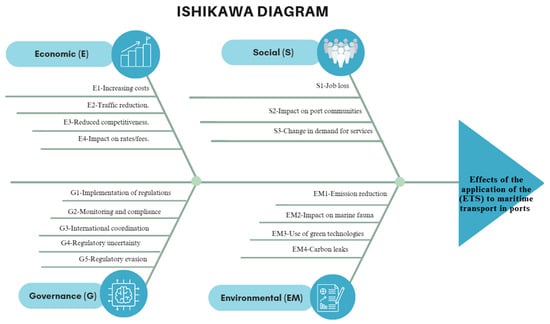
Figure 2.
Ishikawa diagram. Source: own elaboration.
Economy (E):
- E1-Increased costs: shipping companies face higher operating expenses by having to acquire emission permits.
- E2-Traffic reduction: the increase in costs can dissuade shipping companies from using European ports, reducing the volume of traffic.
- E3-Reduced competitiveness: European ports may lose competitiveness to ports in regions with more lax regulations.
- E4-Impact on tariffs/fees: loss of the business volume of a port can translate into an increase in port tariffs for users who have been maintained to be able to resist the structure of port expenses.
Social (S):
- S1-Loss of jobs: reduced traffic and competitiveness can lead to job losses in the port sector and related areas.
- S2-Impact on port communities: local economies that depend on port trade may suffer due to decreased activity.
- S3-Change in the demand for services: the dynamics in the demand for logistics and support services may change, affecting local suppliers.
Governance (G):
- G1-Implementation of regulations: the development and application of new regulations is required to control emissions.
- G2-Supervision and compliance: it is necessary to establish effective mechanisms to monitor and ensure compliance with regulations.
- G3-International coordination: cooperation between countries is crucial in harmonising regulations and avoiding competitive inequalities.
- G4-Evasion of regulations: companies may attempt to circumvent regulations by changing flags or alternative routes.
- G5-Regulatory uncertainty: shipping companies face uncertainty due to possible changes in policies and regulations.
Environmental (EM):
- EM1-Emission reduction: the main objective of the ETS is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from maritime transport.
- EM2-Impact on marine wildlife: the implementation of the ETS can have both positive and negative effects on marine fauna, depending on changes in the routes and technology used.
- EM3-Use of green technologies: the need to reduce emissions will encourage the development and adoption of cleaner and more efficient technologies.
- EM4-Carbon leakage: moving operations to regions with less stringent regulations can increase global emissions.
This diagram helps to visualize the different areas of impact and the possible consequences that the implementation of the ETS may have on EU shipping and ports.
Once the Ishikawa diagram was developed, a focus group was conducted with a panel of eight experts, whose affiliations are listed here: three university professors specializing in Port Operations, one consultant from a maritime traffic consultancy, two representatives from shipping companies, and two professionals from the operations department of the public organisation Puertos del Estado.
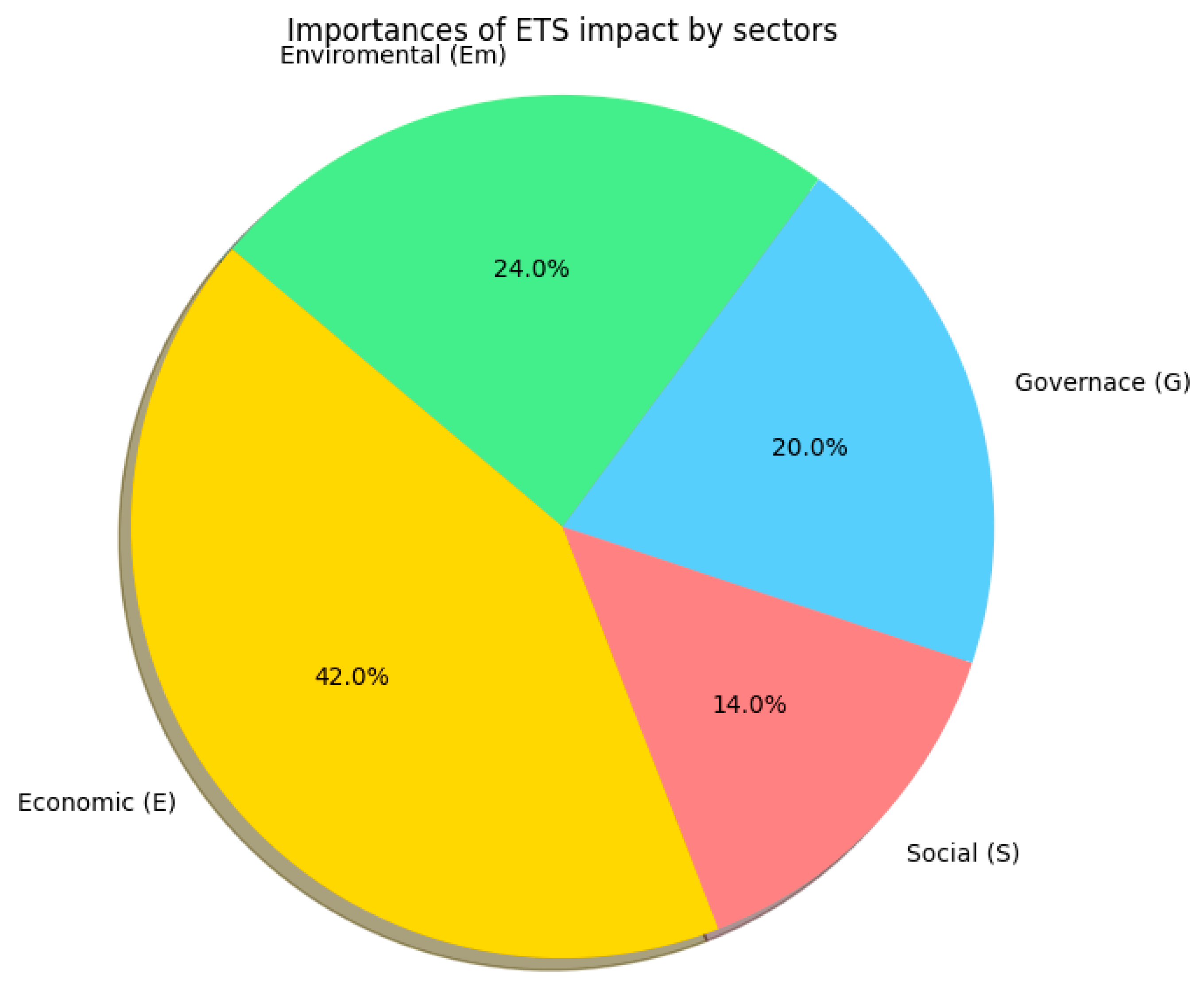
During the session, the experts were asked to rank the four dimensions where the effects of ETS application occur in order of importance, from highest to lowest. This process was carried out in a structured manner, first by collecting individual evaluations and subsequently by analysing the combined results. The data obtained were processed to convert them into representative percentages, which allowed the relative impact of each dimension to be quantified.
Based on this analysis, it was concluded that, of the four dimensions considered, the economic dimension has the greatest effect on the development of the competitiveness of European ports (Figure 3). Consequently, in the subsequent phases of the study, these economic factors were analysed in greater detail.
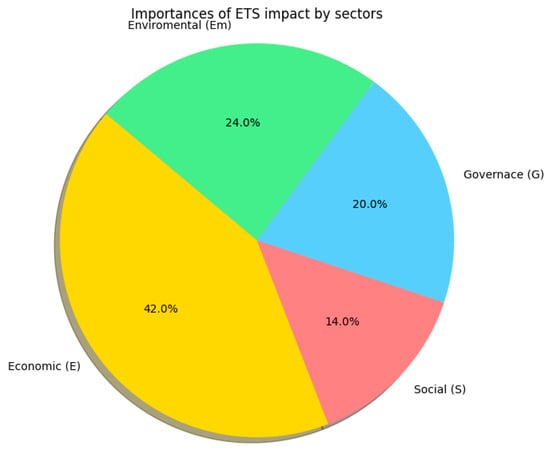
Figure 3.
Impact of ETS application by dimension. Source: own elaboration.
The work scenarios on which the analysis of the study will be carried out are set out below (Table 1):

Table 1.
Scenarios proposed in the study. Source: own elaboration.
- Scenario 1: North America–Europe–East sea route. This maritime route has been chosen because of its importance in connecting the three main continents and the conjunction of areas that produce and consume goods. Some of the legs of this route are Huston (non-EEA), Algeciras (EEA), and Dubai (non-EEA).
- Scenario 2: North America–Northern Europe sea route. The selection of this route aims to demonstrate how to reduce the payment of allowances when interspersing a port in the United Kingdom (non-EEA). The selected example is Montreal (non-EEA), Liverpool (non-EEA), and Le Havre (EEA).
- Scenario 3: Asia–Mediterranean–Northern Europe sea route. This last scenario seeks to show the effects of applying ETS in ports where, as on the EU’s southern border, in this case, there are third-country ports with the potential to attract this traffic, as the ETS would not apply. The example studied is Singapore (non-EEA), Algeciras (EEA), Singapore (non-EEA), Tangier Med (non-EEA), and Rotterdam (EEA).
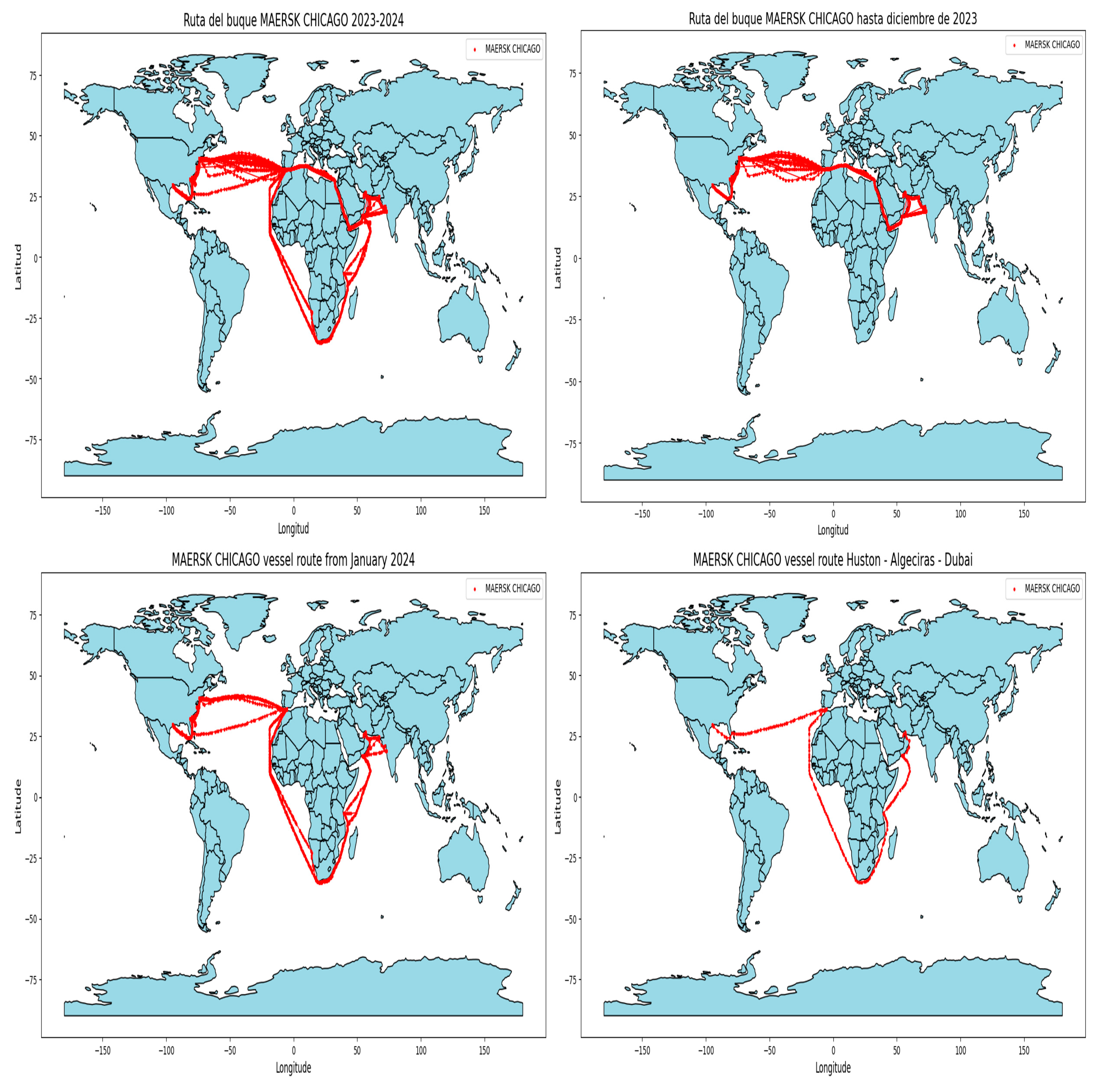
Finally, it should be noted that, in both scenarios 1 and 3, due to geopolitical instabilities in the Bad-al-Mandeb Strait, the calculations made include the casuistry of making the Europe–East route through the Suez Canal or circumnavigating the Cape of Good Hope. A clear example of this is the route of the Maersk Chicago ship that covers the route of scenario 1: Huston–Algeciras–Dubai (Figure 4). It shows how, until December 2023, the logical passage of connection between Asia and Europe took place through the tandem of choke points between the Suez Canal and the Bab-al-Mandeb Strait. From that date on, instabilities with the Yemeni Houthis in the area began and it can be observed that, from January 2024, the route changes to circumnavigate Africa through the Cape of Good Hope.
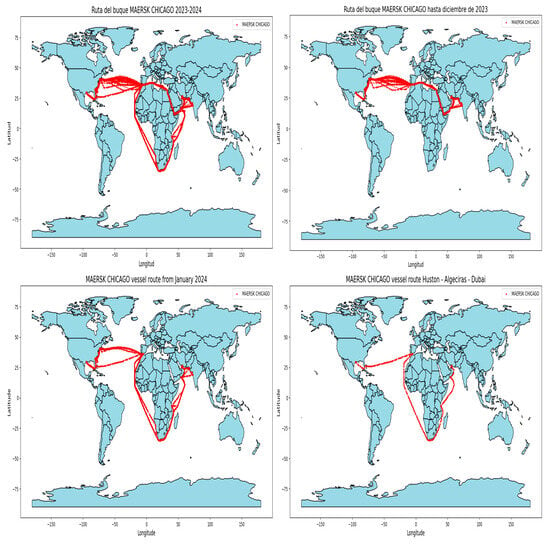
Figure 4.
Maersk Chicago vessel GPS position. Source: own elaboration, data: SBC.
Following the indications of the European directive [32], the ETS calculation is made following Formula (1):
Being:
- : number of annual stopovers subject to ETS.
- : distance in nautical miles travelled between ports.
- : situation factor of the ports. If the port of departure is a non-European port, the factor is 0; if it is a transparent port, it is 0.5 and, if it is European, 1.
- : emissions reported by the ship in MRV ().
- : cost of the allowance (.

Table 2.
Results of the application of the ETS in scenario 1. Source: Own elaboration.

Table 3.
Results of the application of the ETS in scenario 2. Source: Own elaboration.

Table 4.
Results of the application of the ETS in scenario 2. Source: Own elaboration.
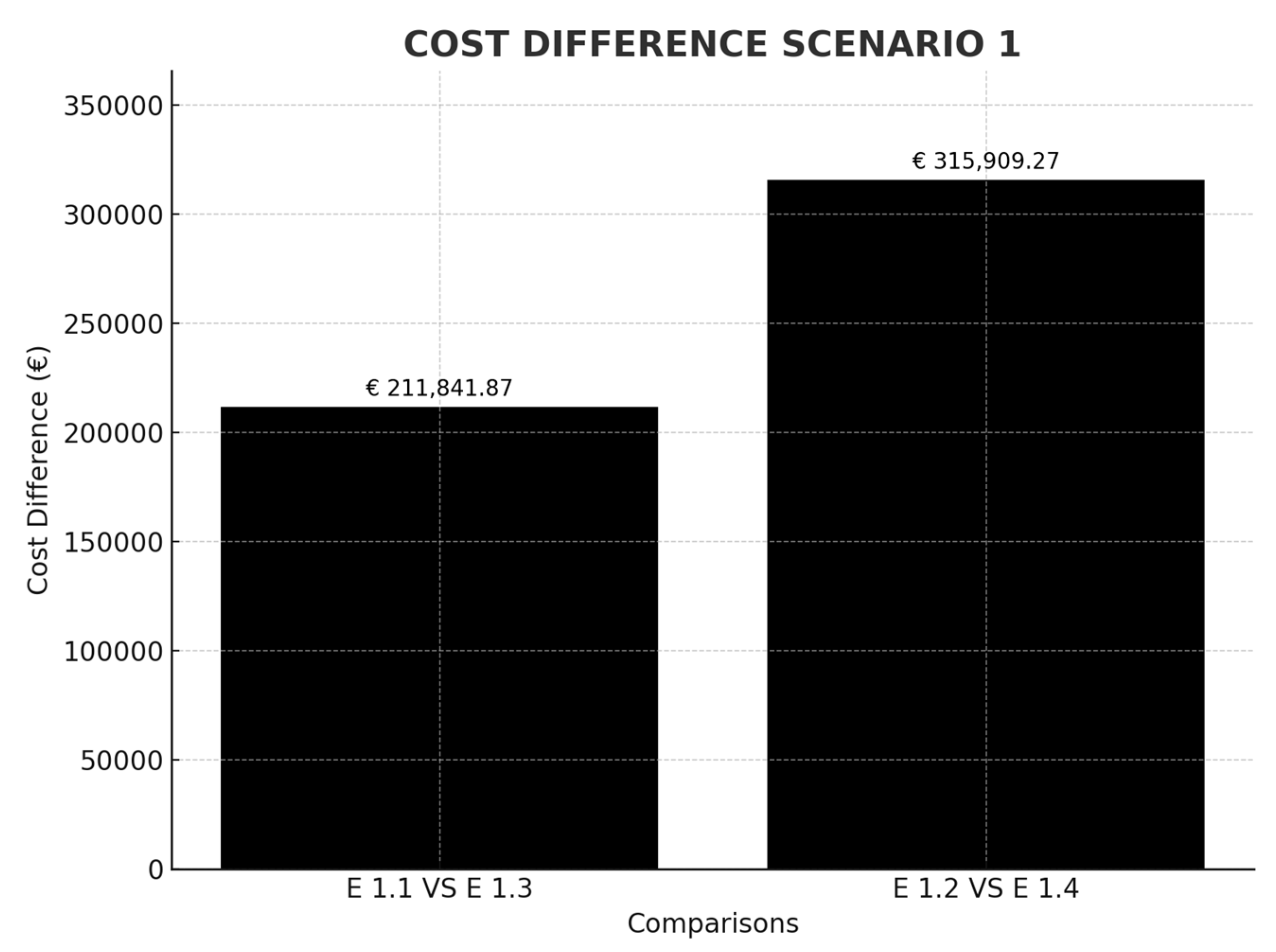
Table 2 shows the calculations made for Scenario 1. In this case, the ship that makes the European Huston–Algeciras–Dubai route between legs, and whose emission factor has been obtained from the emissions declared by the ship in the year 2023 in the MRV, is studied [33]. The ETS price (€/ton CO2) for all scenarios has been obtained from trading economics in July 2024. The circumnavigation casuistry of the African continent is taken into account, which implies an increase in crossing distance by 49.1%. The cost of making a stopover in a European port on the route on which the ship circumnavigates Africa is €104,067.40, higher than the passage of the Suez Canal. On the other hand, in the event that, due to the cost of ETS, the ship decides to make an intermediate call in Tangier, a non-European port, 100% of the costs would be saved since none of the legs of the crossing would call at a port subject to ETS. This represents a saving of €211,841.87 if circumnavigation is not carried out and €315,909.27 if it is carried out (Figure 5).
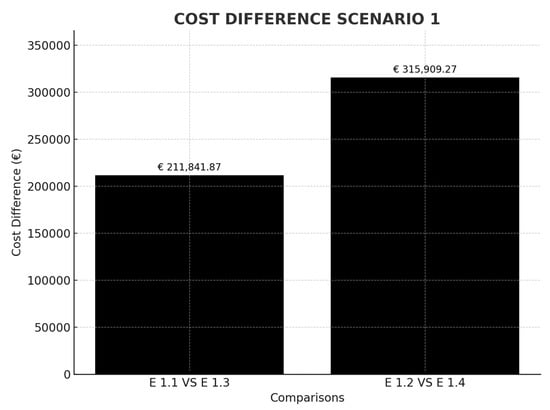
Figure 5.
Cost difference in scenario comparison 1. Source: own elaboration.
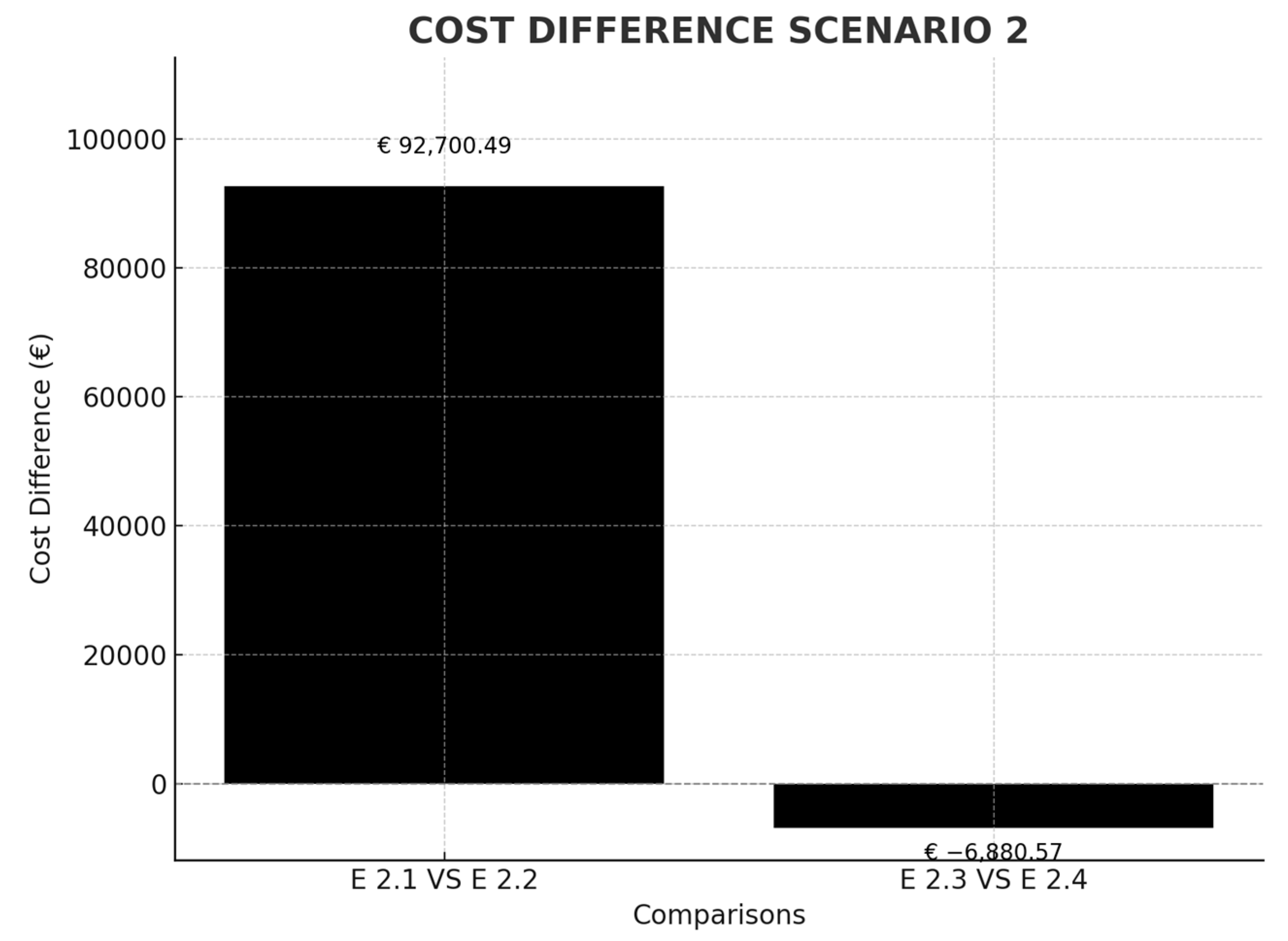
Table 3, belonging to Scenario 2, studies a ship that makes the Montreal–Liverpool–Le Havre route. In this scenario, the aim is to analyse the effect of including a call at a port in the United Kingdom for routes between North America and northern Europe. It can be seen that a ship between Montreal and Le Havre would pay 50% of the emissions produced on that route but, if Liverpool, a non-European port, is included, the emissions subject to ETS would become only 50% of those produced in the approximately 500 nautical miles between Liverpool and the French coast, which represents a saving per stopover of €92,700.49. In the future event that the EU includes this British port (as it already has others), modifying the criteria, in the transparent list of ports, it is observed that, in a stopover in Liverpool, travelling more miles, carbon leakage could not occur because it would not be economically profitable for the shipping company (Figure 6) (currently the criteria are that ships are located less than 300 nautical miles from the European port and that they carry out transshipment activity equal to or greater than 65%).
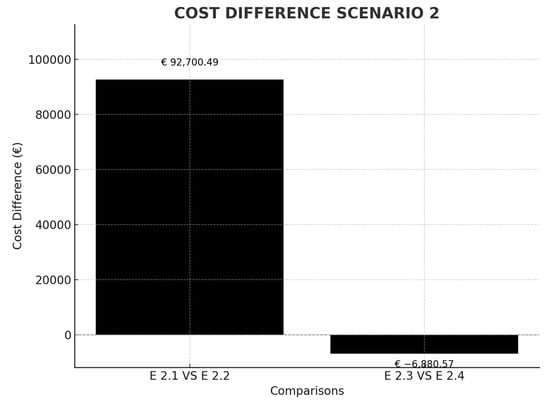
Figure 6.
Cost difference in scenario comparison 2. Source: own elaboration.
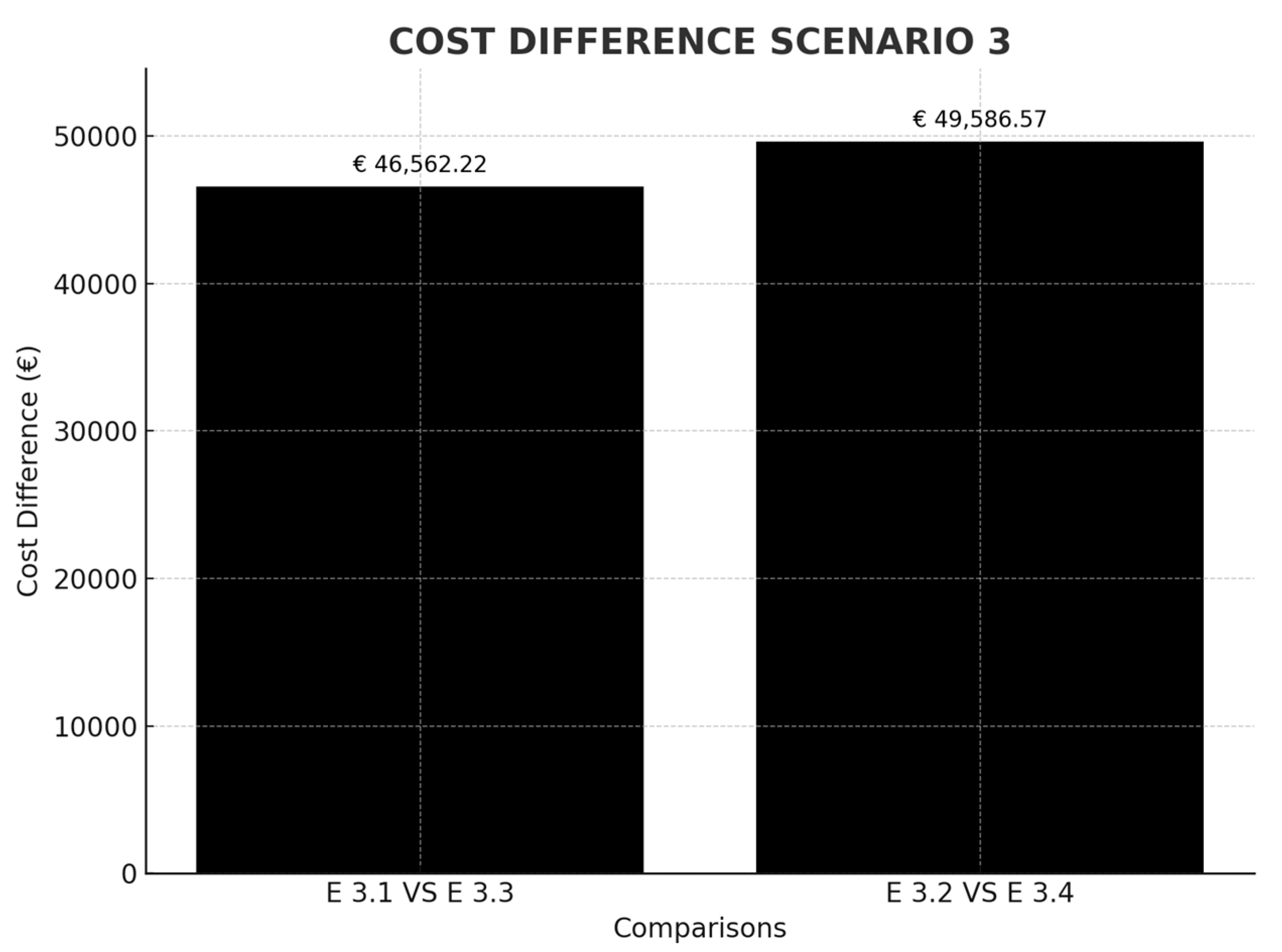
Finally, Table 4 shows the results of Scenario 3, the Maersk A2 route between Singapore and Algeciras and Rotterdam (Asia–Mediterranean–Northern Europe). Two main cases are shown. The first shows an increase in crossings to circumnavigate Africa, which means an increase in emission rights costs of €135,549.00 per stopover. A second possibility is being studied; that the shipping company in question decides, due to the cost of calling at a European port such as Algeciras, to change and start calling in at Tangier (a port located on the same route with zero deviation). As Tangier is a port classified as transparent by the EU, the ship would pay 50% of the emissions for the Singapore–Tangier route and 50% for the emissions of Tangier–Rotterdam. This change would mean the shipping company now pays approximately €46,562.22 per stopover and vessel (Figure 7).
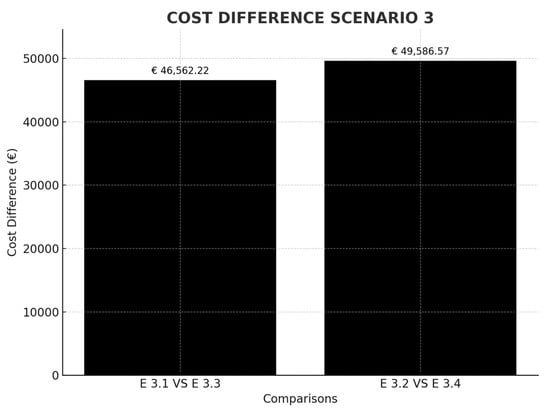
Figure 7.
Cost difference in scenario comparison 3. Source: own elaboration.
5. Conclusions
It is clear that the Emissions Trading System (ETS) represents one of the main tools that the European Union (EU) has implemented to move towards the continent’s energy transition. However, it is critical to develop a clear proposal for how the funds raised through this system will be allocated. These resources could be channelled towards the promotion of green technologies and the energy transition of shipping companies, ports, and other key agents in the logistics chain, thus ensuring a positive and equitable impact. Additionally, specific legislative measures could be considered, such as fiscal incentives or direct subsidies for the ports most affected by the loss of competitiveness due to the ETS. A portion of the funds raised could also be allocated to modernizing port infrastructures and fostering the transition to sustainable fuels.
The results obtained meet the objective of the research and show that the maritime trade of European ports will be affected, especially those that have close competitors in regions outside the EU, which could erode their competitiveness. In this context, the concept of “transparent ports” could require a revision, adjusting the inclusion criteria to incorporate ports that, while not currently meeting the threshold of 65% transshipment or located more than 300 nautical miles from a European port, represent direct competitors in terms of carbon leakage (such as certain African or British ports). Legislative adjustments to redefine these criteria could include relevant ports based on their competitive relevance rather than geographical proximity or current transshipment percentages.
Although a readjustment of routes and a possible loss of traffic in the coming years is foreseeable, this change will not be immediate. In 2024, only 40% of emissions will be paid, rising to 70% in 2025 and reaching 100% in 2026. Therefore, the real impact on shipping routes and traffic is not likely to be fully reflected for two to three years, as shipping companies consider multiple factors when designing their logistics chains.
One of the main challenges encountered during this research was limited access to up-to-date, real-time data on ship emissions. The large amount of data required underscores the need for big data analysis, which would allow for a more comprehensive and detailed study of a larger part of the global fleet.
Future lines of research could focus on expanding the scope of the study, including a greater number of routes and vessels. In addition, the impact of the United Kingdom not being part of the EU and not applying the ETS, which could influence northern European ports, must be considered. It would also be relevant to analyse the evolution of stopovers and route changes using satellite information to gain a more detailed understanding of how ETS affects maritime operations.
Finally, from an environmental perspective, it would be interesting to explore how ETS could influence Short Sea Shipping (SSS) routes. As these routes are fully subject to 100% emissions from 2026, it could be economically unfeasible for some shipping companies to maintain such operations, which could reverse some progress made in terms of decarbonising land transport and increase emissions again due to greater road traffic.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.G.-C. and M.M.E.-I.C.; Methodology, J.V.-C., N.G.-C., A.C.-O., M.M.E.-I.C. and S.R.; Validation, J.V.-C. and M.M.E.-I.C.; Formal analysis, J.V.-C., N.G.-C. and A.C.-O.; Investigation, J.V.-C., A.C.-O. and S.R.; Resources, J.V.-C.; Data curation, J.V.-C.; Writing – original draft, J.V.-C.; Writing – review & editing, J.V.-C.; Visualization, J.V.-C.; Supervision, N.G.-C., A.C.-O. and S.R. All the authors have contributed on each of the themes. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank the Polytechnic University of Madrid in general and, in particular, the support received from the Department of Transport, Territory and Urban Planning Engineering of the Polytechnic University of Madrid.
Conflicts of Interest
Author María Magdalena Esteban-Infantes Corral was employed by the company Ingeniería y Economía del Transporte S.M.E. M.P., S.A. (INECO). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| ETS | Emissions Trading System |
| EU | European Union |
| EEA | European Economic Area |
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| MRV | Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification |
| IMO | International Maritime Organization |
| ECA | Emission Control Area |
| GT | Gross Tonnage |
| LNG | Liquefied Natural Gas |
| AFIR | Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation |
| SSS | Short Sea Shipping |
| CH4 | Methane |
| NOx | Nitrogen Oxides |
| n.m. | Nautical Miles |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
References
- Cifuentes-Faura, J. European Union policies and their role in combating climate change over the years. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipović, S.; Lior, N.; Radovanović, M. The green deal–just transition and sustainable development goals Nexus. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbach, G.; Jensen, L.; Chahri, S.; Claros, E. EPRS|European Parliamentary Research Service. Available online: https://data.consilium.europa.eu/doc/document/PE-25-2023-INIT/en/pdf (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Vaca Cabrero, J.; Gómez Garach, C.P.; Camarero Orive, A.; González-Cancelas, N. Evaluation of the Implementation of the Dimensions of the Blue Economy in Spanish Ports. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Managing Compliance Under the EU’s New Regime|LR. Available online: https://www.lr.org/en/knowledge/research-reports/optimising-compliance-under-the-eus-new-regime/ (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- Park, H.K.; Chang, Y.-T.; Zou, B. Emission control under private port operator duopoly. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2018, 114, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, K.X.; Xiao, Y.; Yuen, K.F. Carbon Emission Trading Scheme in the shipping sector: Drivers, challenges, and impacts. Mar. Policy 2022, 138, 104989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cancelas, N.; Cabrero, J.V.; Orive, A.C.; Párraga, M.J.M.; Gutierrez, D.D.; Santiago, J.I.P. Assessing Port Sustainability in Ecuador Using an Ishikawa Diagram. World Sci. News 2023, 186, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- Revision of the Energy Taxation Directive: Fit for 55 package. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/BRIE/2022/698883/EPRS_BRI(2022)698883_EN.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Alternative Fuels Infrastructure: Council Adopts New Law for More Recharging and Refuelling Stations Across Europe. Available online: https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/press/press-releases/2023/07/25/alternative-fuels-infrastructure-council-adopts-new-law-for-more-recharging-and-refuelling-stations-across-europe/ (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- Use of Renewable and Low-Carbon Fuels in Maritime Transport, and Amending Directive 2009/16/EC, 2nd ed.; Radley-Gardner, O., Beale, H., Zimmermann, R., Eds.; Hart Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-1-78225-867-4. [Google Scholar]
- Muûls, M.; Martin, R.; Colmer, J.; Wagner, U. Does Pricing Carbon Mitigate Climate Change? Firm-Level Evidence from the European Union Emissions Trading Scheme. CEPR Discussion Paper No. DP16982. 2022. Available online: https://repec.cepr.org/repec/cpr/ceprdp/DP16982.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Christodoulou, A.; Cullinane, K. The prospects for, and implications of, emissions trading in shipping. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2024, 26, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, J. The regionalization of maritime governance: Towards a polycentric governance system for sustainable shipping in the European Union. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 117, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, A. The Influence of MARPOL Annex VI on Global Ship Emission: A Study Based on the Impact in the ECAs. Master’s Thesis, University of South-Eastern Norway, Notodden, Norway, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.-T.; Park, H.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, E. Have emission control areas (ECAs) harmed port efficiency in Europe? Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 58, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerholt, K.; Psaraftis, H.N. On two speed optimization problems for ships that sail in and out of emission control areas. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2015, 39, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knill, C.; Liefferink, D. Environmental politics in the European Union: Policy-making, implementation and patterns of multi-level governance. In Environmental Politics in the European Union; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, D.; Li, Z.-C.; Fu, X.; Gillen, D. Modeling the effects of unilateral and uniform emission regulations under shipping company and port competition. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2017, 101, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Hirata, E.; Kawasaki, T. Monopoly in the container shipping market: An econometric approach. Marit. Bus. Rev. 2021, 7, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, E. Implications of Application of the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) to International Shipping, and Potential Benefits of Alternative Market-Based Measures (MBMs); ECSA: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; An, C.; Chen, Z.; Tian, X.; Sun, Y. Promoting Cross-Regional Integration of Maritime Emission Management: A Euro-American Linkage of Carbon Markets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 12180–12190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamoush, A.S.; Ballini, F.; Ölçer, A.I. Revisiting port sustainability as a foundation for the implementation of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs). J. Shipp. Trd. 2021, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinas, O. Sustainable Maritime Transport: European Policy Perspective and Potential Impact. In SDGs in the European Region; Leal Filho, W., Dinis, M.A.P., Moggi, S., Price, E., Hope, A., Eds.; Implementing the UN Sustainable Development Goals—Regional Perspectives; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1061–1086. ISBN 978-3-031-17460-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ricardo. Supporting Study for the Implementation of the ETS Directive and MRV Requirements For Maritime Transport CCEG Maritime; Ricardo: Shoreham-by-Sea, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lagouvardou, S.; Psaraftis, H.N. Implications of the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) on European container routes: A carbon leakage case study. Marit. Transp. Res. 2022, 3, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Faria, D.L. Crossing the “European Green Deal” Maritime Measures and the Unfair Competition on the ETS Tax Regime—The Deviation Traffic Danger Between EU and Non-EU Hub Ports. 2024. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202407.1037 (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- Vierth, I.; Ek, K.; From, E.; Lind, J. The cost impacts of Fit for 55 on shipping and their implications for Swedish freight transport. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2024, 179, 103894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, M.; De Domenico, M.; Murgia, T.; Stimilli, A. The Port Sector in Italy: Its Keystones for Energy-Efficient Growth. Energies 2024, 17, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinane, K.; Yang, J. Evaluating the costs of decarbonizing the shipping industry: A review of the literature. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, İ.S.; Bucak, U.; Esmer, S. How to integrate ports into the EU ETS: The CAS approach perspective. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2024, 35, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIRECTIVE (EU) 2023/959 Establishment and Operation of a Market Stability Reserve for the Union greenhouse Gas Emission Trading System. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32023L0959 (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- THETIS-MRV. Available online: https://mrv.emsa.europa.eu/#private/myfleet (accessed on 9 September 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).