Abstract
The materials traditionally used in the construction of flexible and rigid pavements in modern road infrastructure present challenges in achieving sustainable development goals. Advances in technology have introduced the use of different pavement material mixes, leading to the introduction of earth-based alternatives. These materials are environmentally friendly, cost-effective, recyclable, and offer excellent insulation properties. Stabilization of earth-based materials improves their mechanical properties, reducing road construction costs and increasing durability. The present study investigates the mechanical and durability properties of earth-based materials stabilized with various additives, including cement, lime, polymer, and biopolymer, over 28 and 56 days. Fresh properties are assessed using unit volume weight, flow table, air content, and fall cone tests, while hardened properties are assessed using flexural strength, compressive strength, and water absorption. Microstructural analysis is carried out using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The cement-stabilized samples show improved strength and durability, with the 5% cement group showing a 67% increase in compressive strength over the control group and the 10% cement group showing over 200% higher compressive strength. These results suggest that stabilized earth-based materials could provide a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to conventional pavements for low-traffic roads.
1. Introduction
Road construction and maintenance represent foundational infrastructure investments in modern societies. Roads drive economic and social development by facilitating trade, connectivity, and mobility. Significant funds are allocated annually to road projects, which demand meticulous planning, cost-effective materials, and sustainable approaches to meet escalating global demands [1]. Traditionally, concrete and asphalt have served as primary materials for road construction, each with distinct advantages but also notable environmental and structural challenges. Concrete pavements, known for their rigidity, are prone to cracking and require regular maintenance, resulting in high costs and increased carbon emissions due to the energy-intensive cement production process [2,3,4,5]. Asphalt, while more flexible, faces durability issues, particularly in high-temperature climates, leading to deformation, cracking, and reliance on petroleum-based resources [6,7]. Both materials thus contribute to environmental concerns like resource depletion, habitat loss, and significant carbon emissions, underscoring the pressing need for sustainable alternatives [8].
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in earth-based materials as a sustainable alternative in construction, particularly for low-traffic applications. These materials, used in various forms for centuries, offer a cost-effective and eco-friendly solution. Rammed earth and compressed earth blocks, for example, are abundant, require minimal energy for processing, and are fully recyclable [9]. Despite these benefits, challenges such as limited strength and susceptibility to water damage restrict their widespread use, especially in high-traffic and wet environments [10]. Previous studies have shown that incorporating different stabilizers, such as cement, lime, and pozzolanic materials, can improve the strength and durability of earth mixtures [11,12]. The addition of these stabilizers has been shown to increase the strength, durability, and workability of soil while also improving its compressibility [13]. Bio-based stabilizers are also emerging as promising alternatives to conventional stabilizers in earth-based construction, offering potential environmental and performance benefits. However, the literature indicates that comprehensive evaluations comparing these newer options to traditional stabilizers are still limited [14].
This study explores the potential of earth stabilization for pavement applications by evaluating traditional stabilizers, such as cement and lime, alongside innovative bio-based polymers. Stabilization, through mechanical, physical, and chemical methods, improves soil resilience and sustainability, presenting a viable alternative to asphalt and concrete with lower environmental and economic impacts [15]. Various stabilizers, including asphalt emulsions, hydrated lime, calcined gypsum, supplementary cementitious materials, and novel biopolymers, have shown promise in enhancing soil stability and durability [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27].
Specific processes, such as hydraulic reactions in cement stabilization or pozzolanic reactions in lime stabilization, are essential to achieving optimal strength in these materials. [27,28]. The innovative use of alkaline activation and geopolymerization techniques, as seen with fly ash-enriched soils, further expands stabilization options for soil-based materials [29], acetate (PVA), acrylics, and sodium silicate [30]. Biopolymers, also known as polymers, generated from microorganisms, have been introduced as a novel type of earth stabilizer. Additionally, novel biopolymers derived from sources like lignin and polysaccharides, including xanthan gum, guar gum, and sodium alginate, are under investigation for their stabilization capabilities, although their effects on earth-based pavements are not yet fully understood [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. However, the effects of bio-based stabilizers on earth-based road pavements—such as those derived from lignin, polysaccharides, and other naturally sourced polymers—are not yet fully understood. This study intends to bridge this gap by conducting a comparative analysis of bio-based and traditional stabilizers.
This investigation addresses the aforementioned knowledge gap by conducting a comparative analysis of bio-based and conventional stabilizers for earth-stabilized road pavements. It examines the physical and mechanical properties of stabilized earth materials, assessing their feasibility as sustainable pavement options. Through a combination of concrete testing and soil mechanics methods, this study evaluates parameters such as strength, flexibility, and water absorption in stabilized earth mixtures. These findings are particularly relevant for low-traffic, rural roads where eco-friendly, cost-effective solutions are essential. This study aims to guide local authorities toward adopting stabilized earth pavements, contributing to sustainable development by reducing dependence on petroleum-based and high-emission materials. The research presented in this manuscript makes meaningful contributions to the existing body of knowledge in several important areas: i: Empirical evaluation of stabilized earth-based mixtures as a pavement alternative; ii: Comparative analysis of traditional and bio-based stabilizers, offering insights into the most effective solutions for earth-stabilized pavements; iii: Application of concrete testing methods to earth-based materials, contributing to the development of industry standards and advocacy for the integration of earth-based pavements in rural and low-traffic infrastructure projects. In essence, this study offers fresh perspectives on the feasibility of using stabilized earth as an eco-friendly and durable road surface material. This approach is particularly well suited for projects where environmental conservation and reduced costs are key priorities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
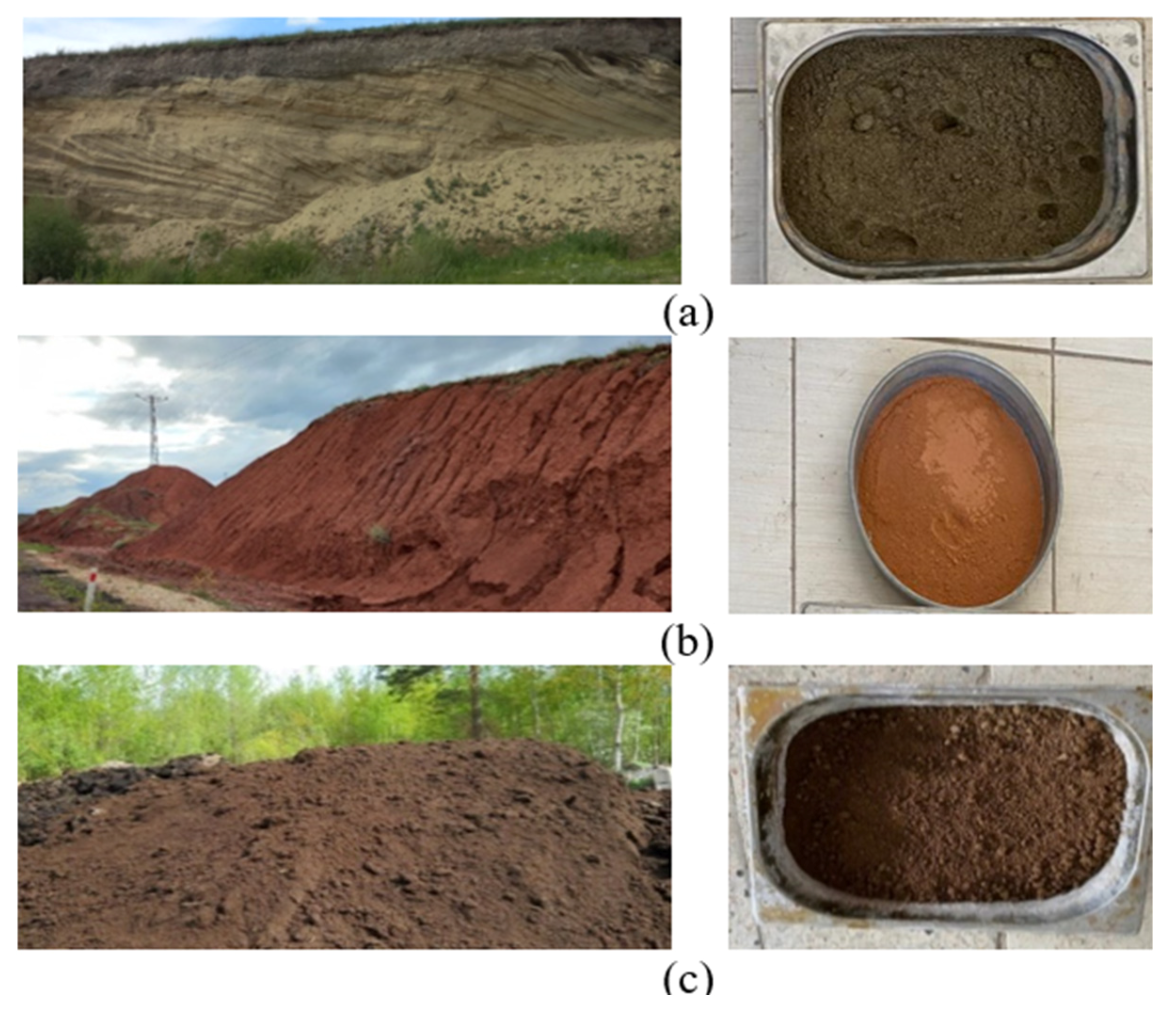
The study focused on developing an earth-based mixture stabilized with various binders to investigate its usability as a new-generation pavement material for low-traffic volume roads. Various earth varieties were assessed for their composition in the earth-based mixture. Initial investigations were performed to create a combination with rheological qualities suitable for workability. Follow-up studies were conducted to assess the characteristics of the combination in both its fresh and hardened forms. Figure 1 illustrates the different types of earth materials and their respective locations for the mixtures.
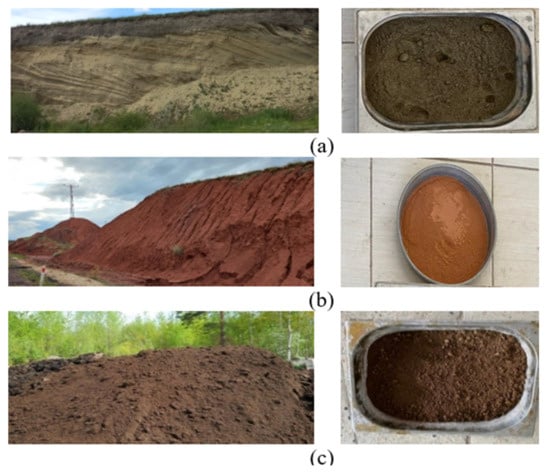
Figure 1.
Raw-earth types used for earth-based mixtures. (a) Erzurum province Aziziye district roadside soil (fine-grained soil. (b) Erzurum province Oltu district soil (Red Mud). (c) Earth with organic content used in agricultural areas.
The physical characteristics of the raw materials that were used in the earth-based combination, which was formed of the different types of earth, are shown in Figure 1: The organic earth used in agricultural areas (Figure 1c) has a unit volume weight of 0.9 g/cm3 and was used in the grain diameter range of 0–2 mm. The sand used (Figure 1a) was obtained from the Aziziye district of Erzurum province, approximately 1~3 m below the roadside ground. It has a unit volume weight of 2.47 g/cm3 and a grain size of 0–2 mm. The red-colored clay-containing soil, which serves as a binder in the earth-based combination, was collected from the roadside in the Oltu district of Erzurum province (Figure 1b) and then sieved through a screen with a 0.074 mm opening. The liquid limit of this clay was found to be 80%, the plastic limit was found to be 31%, and the plasticity index was found to be 49%. These are the Atterberg limits. In accordance with the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS), the clay is categorized as CH, which indicates that the soil is classified as clay of high plasticity. A moisture content is 24%, and the unit volume weight that may be achieved in a dry state is 14.7 kN/m3. The unit volume weights of the earth materials were measured according to TS EN 1097-7/2022 [40], the Atterberg limits were determined using ASTM D4318 [41], and the grain size distribution was obtained using the sieving method per ASTM D422-63 [42].
To stabilize the combination consisting of organic earth, sand, and clay mixtures was created by substituting the stabilizers with clay in a ratio corresponding to the clay content in the mixture. The stabilizers utilized included CEM I 42.5 R type Cement, Hydraulic Lime, a polymer based on Polyester and Cobalt, and Guar Gum (GG) biopolymer.
Normal Portland cement (CEM I 42.5R), produced by Aşkale Cement Factory (Erzurum), was used in the combinations, and its properties are shown in Table 1. The hydraulic lime used in the combinations was purchased from Tekno Building Chemicals [43]. The chemical and physical properties provided by the lime and cement manufacturers are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical and physical properties of cement and hydraulic lime.
Guar gum was used as a biopolymer stabilizer in this study to preserve the natural properties of the earth-based mixture. The gum is a polymer extracted from the seeds of the guar bean, formally named Cyamopsis tetragonoloba. The composition comprises polymers of D-galactose and D-mannose in a 1:2 ratio [44]. The GG composition includes moisture (8–14%), galactomannan (75–85%), protein, fiber, and ash [45]. An important advantage is its ability to dissolve in both hot and cold water. Its increased amount of galactose branching sites gives it better stabilizing characteristics than other biopolymers. The molecular structure of the gum increases the viscosity of liquids [46]. Guar gum is used as a gel or glue in various industries, including cosmetics, food, oil and gas drilling, and civil engineering. Guar gum was selected for its cost-effectiveness in comparison to other biopolymers. Table 2 outlines the precise physical and chemical properties of guar gum.

Table 2.
Physical and chemical properties of biopolymer.
Despite its incompatibility with the earth-based combination’s natural composition, polymer material was employed for stabilization purposes in order to evaluate its advantages and disadvantages in comparison to alternative stabilizers. Polyester resin has found extensive application in the production of polymer concrete due to its inherent advantages, which include superior mechanical and chemical properties, cost-effectiveness in comparison to epoxy resin, and broad availability [47]. As a result, polyester resin was chosen as the preferred material for stabilizing the earth-based mixture. The selected polyester resin is an unsaturated polyester resin that has been formulated specifically for use in polyester polymer concrete containing orthophthalics. The technical specifications of the polyester resin procured from the manufacturer are presented in Table 3. GG and polyethylene terephthalate used in this study were supplied by Şahika Group Company, Ümraniye, Turkey [48].

Table 3.
Technical information on polyester resin (Polyethylene terephthalate).
2.2. Production of Mixtures
In order to achieve the desired workability characteristics, the control mix (C) was made up of a combination of 40% organic earth, 30% sand, and 30% red mud by weight, with an additional 14% tap water. The binders (cement, hydraulic lime, and polymer) replaced the percentage of red mud at 5 and 10 percent. Two ratios of each stabilizer were taken into account as factors in order to ascertain the most favorable ratio and stabilizer. In the biopolymer (Guar Gum) mixture, initial tests were conducted using 5% and 1% concentrations of Guar Gum as the biopolymer. However, these mixtures did not harden sufficiently by the end of the molding period and disintegrated when removed from the mold due to excessive gel formation. To address this, the biopolymer concentration was progressively reduced, and a 0.1% concentration was found to successfully mold and harden without any issues. The water quantity in each mixture was adjusted to achieve the desired viscosity with various stabilizers. As a result, eight distinct mortar combinations were prepared, as detailed in Table 4.

Table 4.
Earth-based mixture designs.
The classification of the samples is determined by the specific stabilizer used and the corresponding rate of use. For example, the Ce10 group refers to the earth-based mix stabilized with 10% cement, while Ce5 refers to the mix stabilized with 5% cement. The L10 and L5 groups represent the mixes stabilized with 10% and 5% lime, respectively. The P10 and P5 groups indicate the mixes stabilized with 10% and 5% polymer, respectively. Lastly, the Bio 0.1 group refers to the mix stabilized with 0.1% biopolymer.
The mixtures were produced using a laboratory scale Ele branded counterflow mixer with a capacity of 5 dm3 and a mixing speed of 280 rpm, located in the Civil Engineering Laboratory of Atatürk University, to ensure homogeneous mixing of the mortar mixtures. The control, lime, and cementitious earth-based mixtures were mixed for an initial duration of one minute in the absence of water. Water was then added and mixed at a reduced speed for 1 min. After a 1 min period of rest, the mixture was stirred at a rate of 200 cycles per minute for a further 2 min. Regarding the mixtures of biopolymers and polymers, the earth-based mixture was found to be devoid of moisture, while the mixtures of biopolymers and polymers were mixed with water using a mechanical mixer for a period of 2 min. The mechanical mixer used for mixing polymer and biopolymer was the HeidolpH MR Hei-Standard Heated Magnetic Stirrer. It is manufactured in Germany. Following this, the mixture that was obtained was combined with the dried earth mixture and vigorously stirred for an additional 2 min, thereby concluding the mixing process. In order to evaluate the flexural strength of the mortar samples, rectangular prism specimens with a dimension of 4 × 4 × 16 cm were produced. Also, cube specimens with a size of 5 × 5 × 5 cm were utilized to assess the compressive strength. The prepared earth-based mixtures were placed into lubricated steel molds in three layers. Each layer was compacted by skewering 25 times using a steel rod and further settled using a shaking table to ensure proper consolidation. The earth-based mixtures were poured into a mold and left for one day at a temperature of 21 ± 2 °C and with 50% relative humidity in a laboratory setting. They were then desiccated for one day at 60 ℃ in an oven. Following that, the composites were extracted from the mold and allowed to cure for a duration of 28 days in an indoor setting, maintaining a temperature of 23 ± 2 °C and with 65% moisture content. Following a period of 28 days, evaluations of water absorption, flexural strength, and compressive strength were conducted.
2.3. Experimental Program
Unit volume weight, air content, flow table spread diameter, and penetration depth were measured to assess the rheological and physical properties of the earth-based mixes in their original condition. The hardened samples were evaluated for flexural and compressive strength, as well as the capillary water absorption coefficient. The microstructural characteristics of the samples were analyzed using SEM and XRD techniques.
Geotechnical engineering traditionally used earth-based materials, but recent research is exploring their usage as binding agents in infrastructure projects, in addition to cement and lime. The testing methods commonly used for cementitious materials have been used for earth-based mortars in this study. This allowed for the evaluation of the effectiveness of these items using standardized testing methodologies
2.3.1. Unit Volume Weight
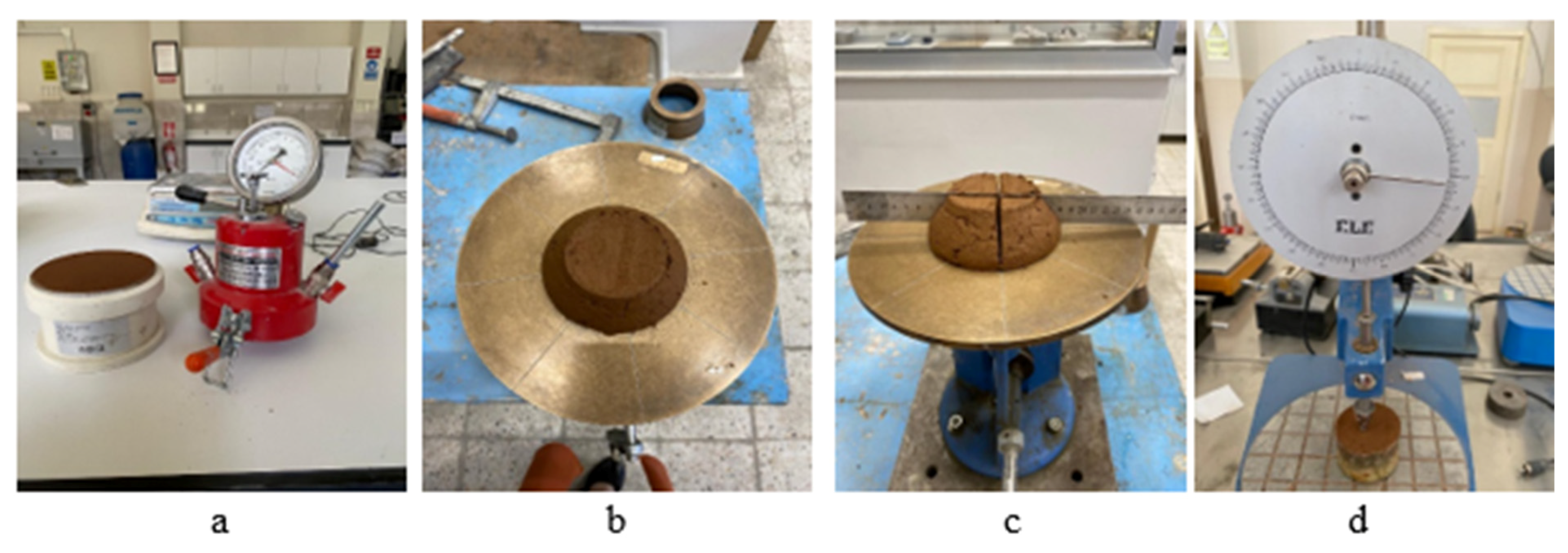
To determine the unit volume weight of fresh mortar, an aluminum pressure-resistant container with a capacity of 1 L, manufactured by Yüksel Kaya Machine, Yenimahalle, Turkey, was used in accordance with the TS EN 12350-7 [49] standard for measuring air content. The mortar was carefully placed in the container, compacted using the graduated tamping rod of the air content meter, and subjected to vibration for 20 s on a Besmak branded vibrating table, which has a capacity of two molds and operates in accordance with the TS EN 12390-2 [50] standard to ensure proper compaction. After compaction, the mortar was weighed, and its unit volume weight was calculated by relating the mass to the volume of the 1 L container. Figure 2a shows the air meter used to determine the air content and the mortar placed in the container to measure the unit volume weight.
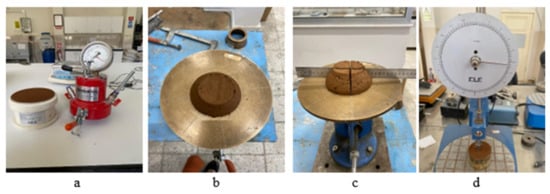
Figure 2.
Fresh state experiments. (a): Using an air content measuring cup for unit volume weight determination and air content determination experiment, (b,c): determination of the spreading diameter with the flow table test, (d): determination of the penetration depth in the fall cone test.
2.3.2. Air Content
The air content determination test was carried out in accordance with the TS EN 12350-7/AC [51] standard. The mixture was placed into a Yüksel Kaya Machine-branded lightweight aluminum air meter container with a 1 L capacity featuring a shock-proof mounted pressure gauge. The mortar was compacted in three stages using a graduated tamping rod, ensuring uniform thickness, and then subjected to vibration on a Besmak-branded vibration table. The flanged, robust, conical structure of the lid, which features a vertical observation pipe, is effectively sealed by means of a clamp mechanism and the inclusion of an internal tire. This configuration effectively impedes the ingress of external air. Following the closure of the primary air valve, water was introduced into the apparatus through one of the two water valves situated on the lid. The filling procedure persisted until water began to flow through the alternate valve. To ensure that no air bubbles remained in the water, a gentle tap was applied to the apparatus using a hammer. By closing the air release valve connected to the sealed air chamber, the air was injected into the chamber until the starting pressure (zero) mark was displayed on the pressure gauge. Both water valves were closed, the main air valve was opened, and the value shown by the pressure gauge needle was read as the percentage of visible air after the needle stabilized. A diagram of the experiment is illustrated in Figure 2a.
2.3.3. Flow Table
The flow table test is conducted to assess the viscosity and workability of fresh concrete [52,53]. The spreading diameters of fresh mortar mixtures were tested in accordance with the TS EN 12350-5 [54] standard, and the influence of both stabilizer type and stabilizer ratio on the spreading diameter was analyzed. The fresh mortar was poured into the spreading tray mold in two identical levels. While filling, every layer was densely compressed by gently tamping it 10 times using a tamping bar. The top plate was placed onto the bottom stops 15 times after the mold was removed. Following the completion of the dropping operations, the ruler was used to measure the maximum dimensions of the mixture layer spread on the top plate in two directions that run parallel to the plate borders. These measurements were then averaged. The experiment’s images are displayed in Figure 2b,c.
2.3.4. Fall Cone Test
The Fall cone test, outlined in the CEN ISO 17892-6 [55] standard, was employed to evaluate the thixotropic characteristics, particularly the shear strength and yield stress, of earth-based mixtures. This test measures the depth to which a cone may penetrate a surface under a force. From a rheological perspective, the interaction between the cone’s surface and the mortar will increase as it goes further in. The shear stress resistance will increase gradually until it reaches equilibrium with the applied mass. The cone is positioned so that its apex touches the surface of the mixture. The cone was then released for around 5 s to allow sufficient time for it to penetrate the material, and the depth of penetration was recorded. Figure 2d shows the visual representation of the experiment. The yield stress of the mixtures was obtained by estimating the penetration depths using Equation (1) [56].
In the equation, τ is the yield stress (Pa); F is the force generated by the mass (N) of the cone (80 g = 0.78 N); θ is the angle of the cone used (30°), and h is the penetration depth (mm).
2.3.5. Flexural Strength
The flexural strength test was conducted in accordance with the TS EN 12390-5 [57] standard. Following the flexural test, assuming appropriately sized samples were obtained, the separated sections underwent a compressive strength test in accordance with the TS EN 12390-3 [58] standard. The assumption that appropriately sized samples were obtained is based on the guidelines provided in the TS EN 12390-5 [57] standard, which ensures that samples meet the necessary dimensions and quality for subsequent testing. Similar procedures have been followed in previous studies [59,60] where samples from flexural strength tests were subsequently used for compressive strength testing, provided they conformed to the specified size and integrity requirements.
2.3.6. Compressive Strength
The study involved compressive strength testing of hardened mortars at 7 and 28 days. The samples were tested at a constant loading rate of 0.04 MPa/s. When the specimen failed, the maximum load and compressive strength values were recorded from the digital display of the press. The results were evaluated by calculating the average of three samples for each group.
2.3.7. Capillary Water Absorption
Capillarity is crucial to the durability of concrete because it reflects the material’s ability to regulate the flow of water and harmful substances, such as chloride salts, through its capillary pores. This regulation of fluid movement is the key to long-term durability. The Capillary Coefficient (S) provides a useful measure of this capillary action, which directly influences the durability of the concrete. The experiment was carried out in accordance with the TS EN 13057 [61] standard. The samples were dried in an oven at a temperature of 40 ± 2 °C for seven days to ensure a consistent moisture content until a stable mass was achieved. After drying, the sides of the samples were sealed with adhesive tape, and the capillary water absorption test was carried out by placing the samples on steel rods in a tray, ensuring that the bottom surface (to a height of 5 mm) was in contact with tap water. The samples were removed and reweighed after 12 min, 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, and 24 h to assess the increase in mass. The volume of water absorbed was calculated by dividing the mass gained by the nominal surface area of the sample and the density of water. The capillary water absorption rate (i) was calculated by dividing the mass of absorbed water (kg) at each time interval by the surface area (m2) of the sample being examined. The graph was created by plotting the values (i) that represent the square root of the immersion time (h).
2.3.8. Microstructural Analyses
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Following the smoothing of the sample surfaces in the stone-cutting machine, the surface intended for examination was prepared by the process of gold plating under vacuum. The images were captured using the Zeiss Sigma 300 scanning electron microscope headquartered in Oberkochen, Germany, which is located at Atatürk University DAYTAM (Eastern Anatolia High Technology Application and Research Center). The instrument is equipped with a System Schottky field emission electron gun and a 4-segment backscatter electron detector (BSD). The instrument has a resolution of 2.3 nm at 1 kV and a resolution of 1.5 nm at 15 kV. Point analysis was also carried out using the EDX detector within the instrument. The research results section presents the photographs taken and the corresponding comments.
X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
Analyses were performed using a Malvern PANalytical EMPYREAN X-ray diffractometer (manufactured in Almelo, The Netherlands), utilizing Cu-Kα radiation at a wavelength of 1.54 Å, at Atatürk University DAYTAM. The investigation utilized a scanning range (2θ) of 10–900, a scanning speed of 4 degrees/minute, an operating voltage of 5 kV, and an operating current of 40 mA.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fresh State Results
In this study, which investigated the development of an innovative earth-based pavement material for low-traffic volume roads, Table 5 presents the results of tests carried out on fresh mixtures, including fresh unit volume weight, air content, flow table, and cone penetration depth. Each group was replicated at least twice, and the fresh properties were measured separately for each mix, with the averages used to produce Table 5.

Table 5.
Fresh state experimental results.
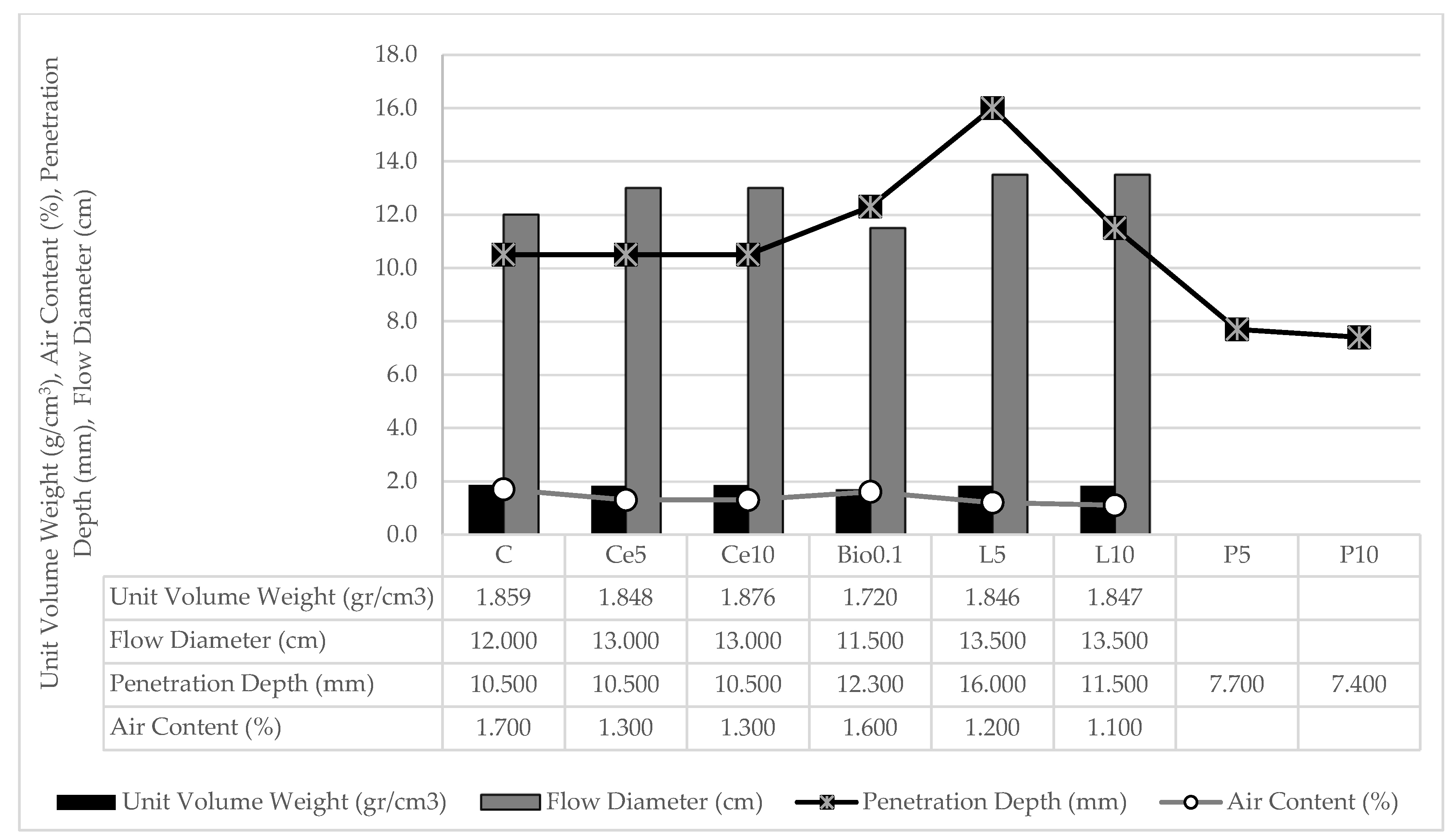
The fresh state outcomes presented in Table 5 are visually represented in Figure 3 below. Figure 3 presents the fresh state test results, allowing for a comprehensive comparison of all samples. As a result of the polymer in the mixture undergoing quick solidification, only the extent to which it penetrated could be assessed, and other tests that need the combination to be in its initial state could not be conducted.
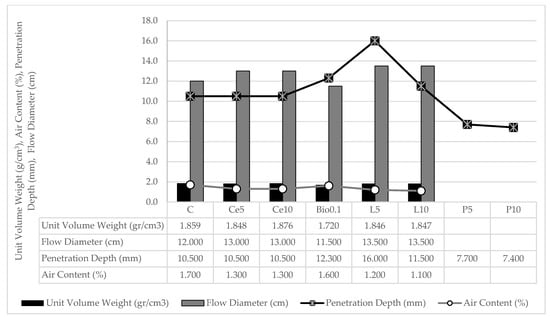
Figure 3.
Fresh state test results graphic presentation of mixtures.
An analysis of Table 5 and Figure 3 shows that the results of the studies on unit volume weight and air content show an inverse relationship. As expected, the density per unit volume weight decreased in proportion to the increase in air content. As the quantities of water in the mixtures formed with different percentages within the same group were identical, it was observed that the unit volume weights and air contents were similar. Consequently, the inclusion of 5% and 10% of the stabilizers used in the mixes did not give different results in the experimental analysis. The combination containing 10% cement gave the highest unit volume weight. The increased air content in biopolymer substitution mixtures can be attributed to the unique interaction between the fine particles of the biopolymer and the water content of the mixture. While smaller particles typically form denser matrices, biopolymers have hydrophilic properties that facilitate water absorption and expansion within the matrix. This expansion can trap more air, leading to greater air entrainment and the gel-like consistency observed in the mix. The biopolymer’s ability to swell in the presence of moisture plays a significant role in this phenomenon, creating air voids throughout the matrix despite its finer particle size. This differs from materials such as lime and cement, which do not exhibit similar moisture absorption and expansion characteristics. According to Raj et al. [62], the hydrophilic properties of biopolymers such as guar gum facilitate the formation of hydrogen bonds between fine soil particles and water molecules, leading to the formation of a network of hydrogels. The inclusion of cement and lime stabilizer resulted in a reduction in air content compared to the control group (C). The densities of the lime and cement mixtures were similar to those of the C, whereas the density of the biopolymer groups was comparatively lower.
The workability (rheological properties) of the mixes was determined using cone penetration depth and flow table tests. The incorporation of cement and lime into the mixture resulted in an increase in the flow diameter, whereas the incorporation of biopolymer and subsequent increase in the ratio resulted in a decrease in the flow diameter of the mix. Incorporation of the biopolymer into the soil mix increased its viscosity, resulting in a reduction in the depth of penetration. The increase in viscosity of the combination can be attributed to the interaction of the biopolymer with water, causing it to change to a gel-like consistency and acquire a more rigid structure.
The yield stress values derived from the falling cone test results, which were used to assess the thixotropic behavior of the mixes, were calculated using Equation (1). The yield strengths of groups C, Ce5, Ce10, Bio0.1, L5, L10, P5, and P10 are as follows: 2910, 2910, 2910, 2131, 6397, 1260, 2439, 5439 Pa. Although the rheological parameters remained unchanged with cement substitution, the presence of other stabilizers had a significant effect on these properties. Although lime and cement stabilizers exhibited similar characteristics in terms of unit volume weight, air content and flow table results of the mixes, they gave different rheological results. The inclusion of 5% hydraulic lime in the mix resulted in a reduction in yield strength of over 50% compared to the C. However, the reduction in yield strength was not as significant when the ratio was increased to 10%. The increased amount of biopolymer and both amounts of polymer resulted in a more than twice increase in yield strength, probably due to polymerization, which increases particle adhesion.
3.2. Hardened State Results
3.2.1. Mechanical Properties
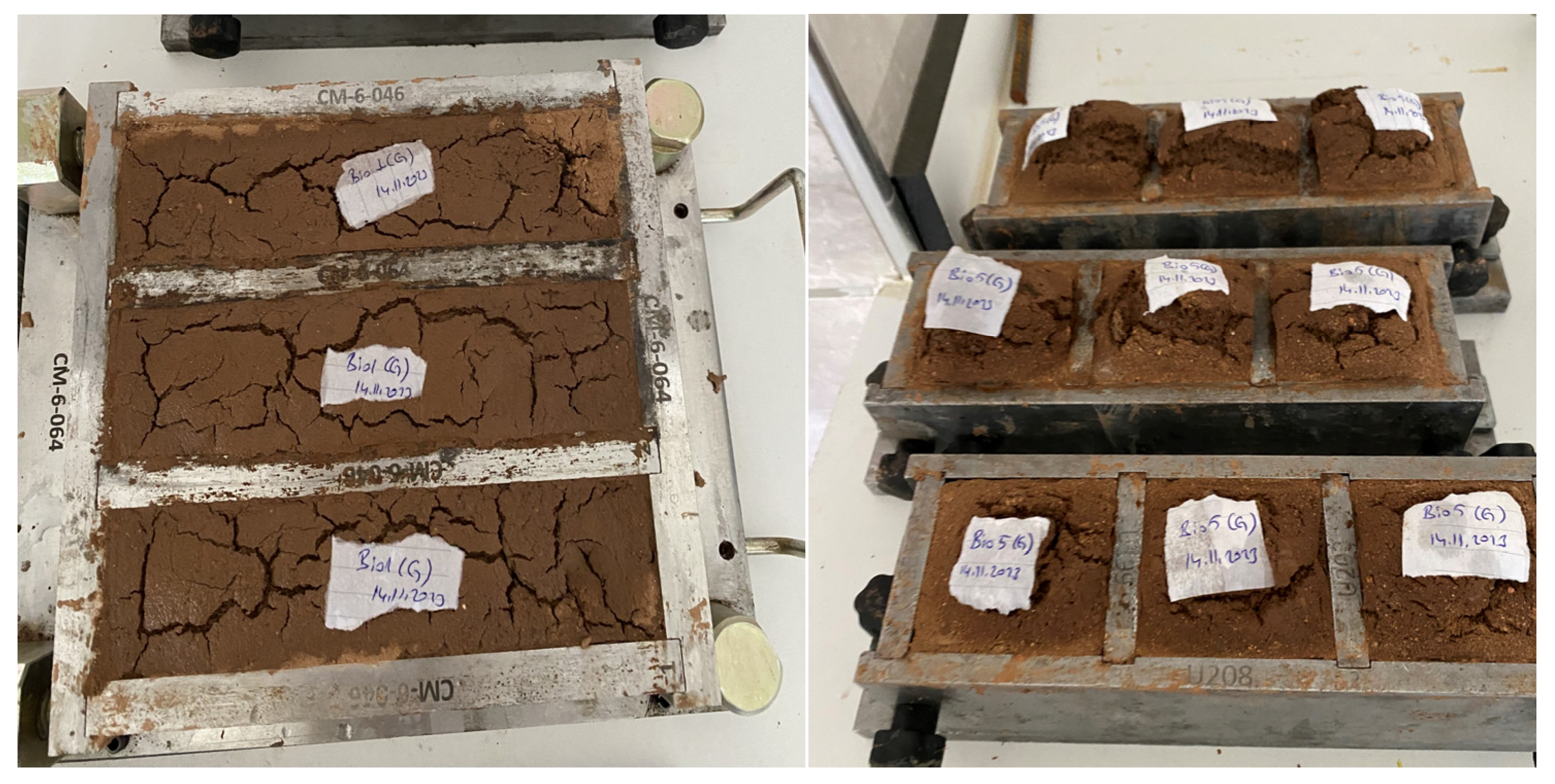
Initially, a 5% concentration of biopolymer was used with additional stabilizers. However, as shown in Figure 4, the samples expanded while waiting to be removed from the molds and eventually disintegrated. A 1% biopolymer stabilizer was then added to the mix, but like the 5% case, the samples could not be extracted from the mold. At a 0.5% concentration, the biopolymer dissolved in water, forming a thick gel-like substance. To prevent this, the concentration was reduced to 0.1%. This mixture was successfully molded and hardened without any issues, leading to the decision to use a 0.1% biopolymer rate for producing biopolymer-stabilized earth-based mixtures.

Figure 4.
Degradation of mixtures containing 1% and 5% biopolymer in the mold due to volume increase.
Table 6 provides the test findings for the 28-day flexural strength and the 28 and 56-day compressive strength of both the control group and the groups that received the addition of a stabilizer.

Table 6.
Hardened state test results.
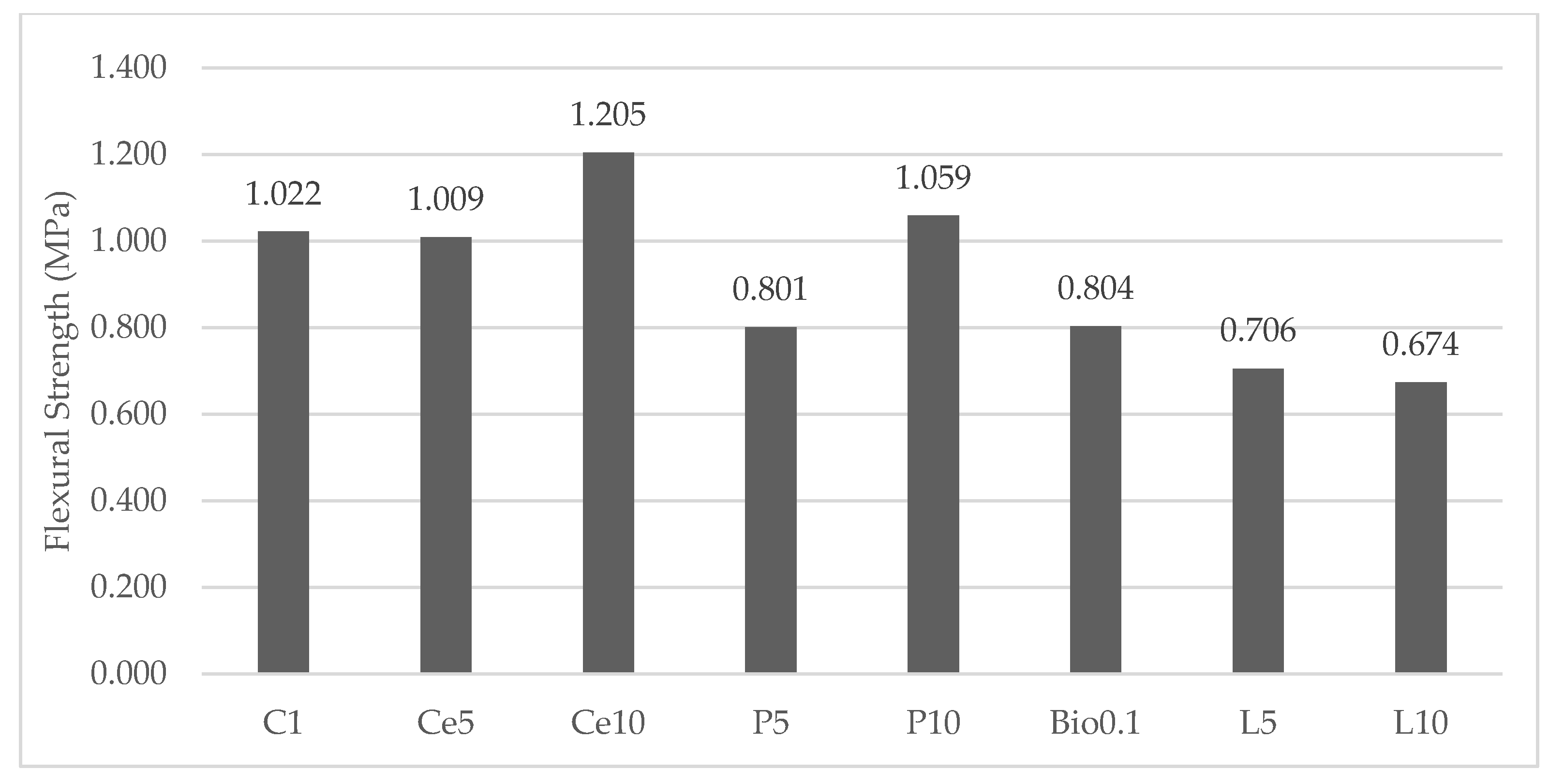
Table 6 shows the mechanical robustness of the hardened mixtures of earthen materials. Within each group, three cube samples measuring 5 × 5 × 5 cm and three rectangular prism samples measuring 4 × 4 × 16 cm were fractured and the results averaged. The results for flexural strength is shown in Figure 5.
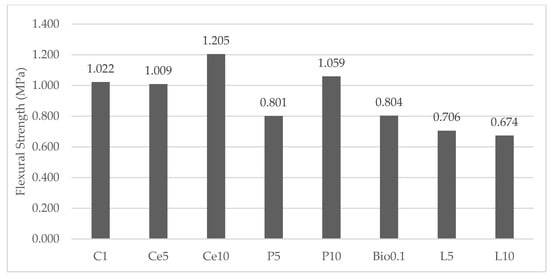
Figure 5.
Flexural strength of earth-based samples.
From the flexural strength data shown in Figure 5, it can be concluded that the Ce10 group achieved the highest possible flexural strength of 1.205 MPa. The addition of cement and polymer stabilizers at a concentration of 10% resulted in an increase in the flexural strength of the material compared to the C. The flexural strength of the groups decreased when both lime stabilizer and polymer were used at a ratio of 5%. This was the case when the groups were compared. When a biopolymer was applied to the specimens at a concentration of 0.1%, the flexural strength of the specimens showed higher values compared to the groups treated with lime and a polymer concentration of 5%. When compared to the C, it was found that the use of stabilizers other than cement was predicted to increase the flexural strength of the earth-based mixes. However, the flexural strength was actually reduced by these stabilizers, contrary to what was expected. This led to the conclusion that the bonds between the earth elements and the stabilizers were not as strong as they could have been.
Several studies in the literature confirm that biopolymers, even in low concentrations, can significantly influence the mechanical properties of earth-based mixes. For instance, Mendonça et al. [63] demonstrated that xanthan gum, when applied as a soil treatment, partially fills the voids in the soil matrix and establishes additional bonds between soil particles. This leads to a reduction in permeability and an enhancement of the soil’s mechanical properties. Similarly, Chang et al. [64] indicated that biopolymers show great promise as sustainable alternatives to cement in soil treatment applications. Their research highlights that biopolymers, with their large specific surface areas and electrical charges, directly interact with fine soil particles, forming strong biopolymer-soil matrices. SEM images from their study illustrate the formation of direct bonds between biopolymers and kaolinite particles.
Furthermore, Laird [65] found that anionic polyacrylamide effectively reduces soil erosion and runoff by forming electrostatic bonds with clay particles. In another example, Whiffin et al. [66] explored microbial-induced calcite precipitation (MICP), wherein calcium carbonate crystals precipitated in soil voids through microbial activity, promoting inter-particle bonding. Chang et al. [67] also examined xanthan gum’s capacity as a soil stabilizer, revealing that it creates robust xanthan gum-clay matrices via hydrogen bonding.
In terms of lime-based stabilizers, multiple studies corroborate the findings in this paper. For example, Jha et al. [68] found that lime stabilization does not always yield optimal results, particularly in expansive or highly clayey soils. Eisazadeh et al. [69] observed similar trends, indicating that lime, when used in tropical lateritic clay, may result in weaker bonding or even adverse effects, such as increased porosity and reduced compressive strength. The effectiveness of lime as a stabilizer is often dependent on soil type, curing conditions, and lime concentration. Improper curing or delayed compaction in lime-treated soils can further impair strength development [68].
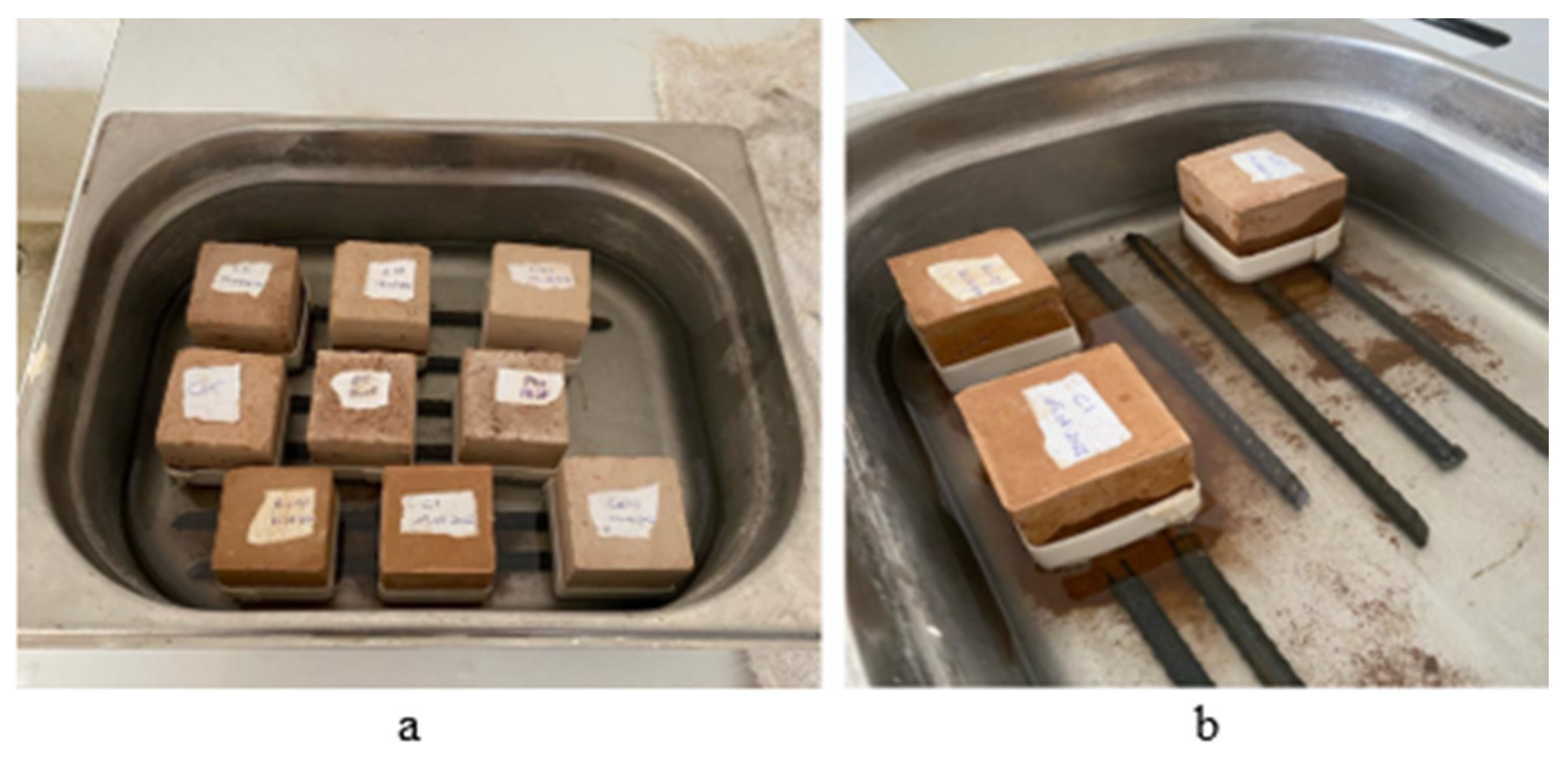
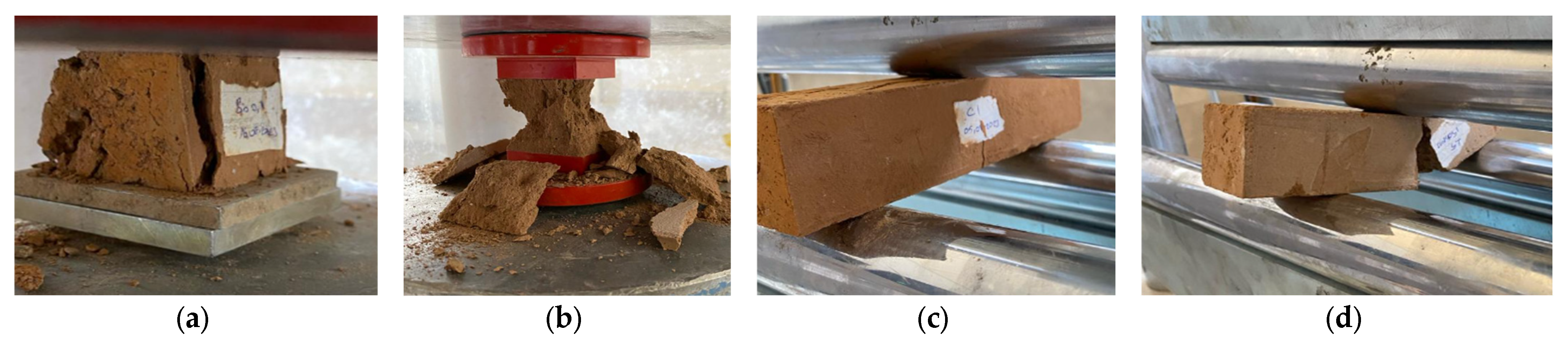
Figure 6 presents photographs of selected specimens from the compressive and flexural tests. In Figure 6a, the fracture pattern of the Bio0.1 specimen is shown following the compressive test, while Figure 6b illustrates the fracture of the cement-stabilized earth-based sample, displaying a characteristic cone prism failure. Figure 6c highlights the fracture pattern of the control group specimen, and Figure 6d captures the fracture of the lime-stabilized earth-based sample after the flexural test.

Figure 6.
Photographs of compressive strength tests (a,b) and flexural strength tests (c,d) on various samples.
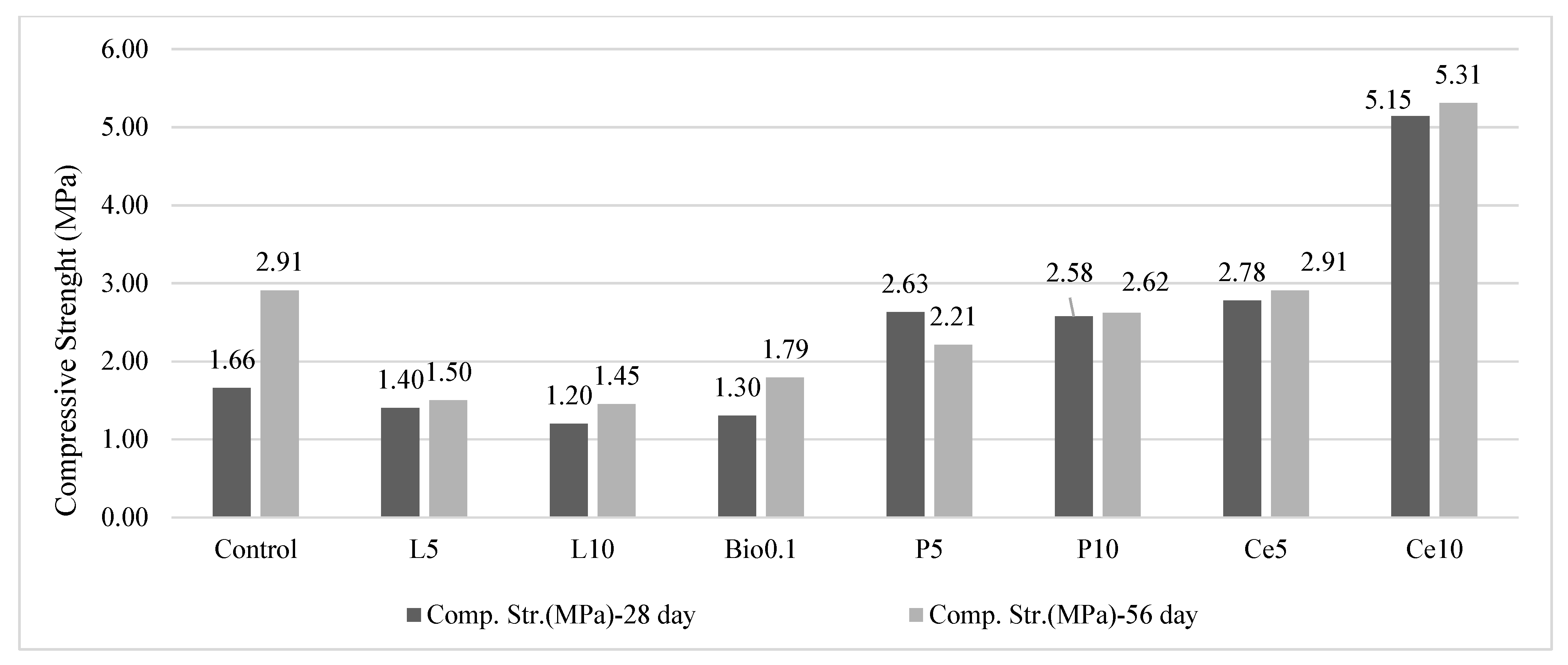
Figure 7 shows the compressive strength values of the soil samples at 28- and 56-day intervals.
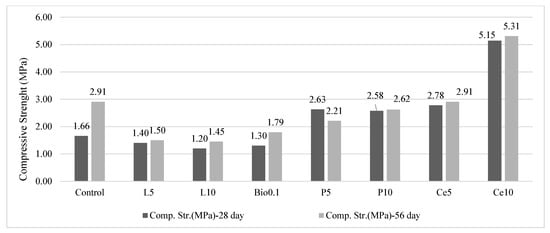
Figure 7.
Compressive strength results of the earth-based samples.
Analysis of the flexural and compressive strength data presented in Figure 5 and Figure 7 shows that while flexural strength showed no significant differences between groups, compressive strength showed significant differences both between and within groups. The cement-stabilized specimens showed the highest compressive strength, with the 28-day compressive strength doubling when the cement content was increased from 5% to 10%. Specifically, the use of 5% cement resulted in a 67% increase in compressive strength compared to the C, while 10% cement resulted in an increase of almost 200%.
In the control group with no stabilizing binder, the compressive strength increased by 75% between 28 and 56 days. This indicates that the clayey red mud used in the mixes had pozzolanic properties and contributed to a reaction similar to cement hydration. The compressive strength of the cement-stabilized group did not increase much in the 56-day tests because cement hydration was almost complete (over 90%) at 28 days, but the C continued to gain strength for 56 days. This continued strength development in the C was attributed to the interaction between the clayey red mud and the organic content of the soil, resulting in a more gradual but consistent response over time.
Both polymer ratios in the mix significantly improved compressive strength after 28 days compared to the C group, with an average increase of 62%. However, doubling the polymer ratio from 5% (P5) to 10% (P10) did not result in a notable additional strength gain. By 56 days, the C group continued to show strength improvement, as did the cement-stabilized groups (Ce5 and Ce10), which exhibited slight increases in compressive strength from 28 to 56 days. In contrast, the P5 group experienced a 16% reduction in strength, while the P10 group maintained its 28-day strength. These results indicate that the polymer-stabilized groups achieved their peak strength at 28 days, with the subsequent decline attributed to the replacement of clay with polymer, which limited further strength development. By 56 days, the C group, composed entirely of clay materials, outperformed the polymer-stabilized groups, suggesting that the polymer provided no long-term strength advantages in this study.
Compared to the C group at 28 days, the mixtures containing 0.1% biopolymer showed even lower strength at both 28 and 56 days. The application of the biopolymer (guar gum) resulted in a reduction in strength at 56 days, suggesting a weak bond between the soil components and the biopolymer. Consequently, Guar Gum was considered to be an ineffective stabilizer for these materials.
Lime-stabilized samples showed the lowest strength at both 28 and 56 days. Strength decreased as lime content increased from 5% to 10%, although a slight increase in strength was observed between 28 and 56 days, consistent with the slower strength development of lime compared to other stabilizers. Overall, lime was found to be an unsuitable stabilizer for these earth-based materials.
Analysis of the 28-day compressive strength data, as shown in Figure 7, indicated a positive correlation between strength and cement content, with an R-squared value of 0.67. However, at 56 days, the R-squared value dropped to 0.42, indicating a weaker correlation and highlighting the significant variability in the data over time.
3.2.2. Durability Properties
Table 7 shows the test results for capillary water absorption. In the table, two samples were selected from each group, and the capillary water absorption was measured as the average of the two samples. The first row (beginning) represents the average weight of the samples just before they were immersed in water. The ‘2 min’ row shows the average weight of the samples after immersion and weighed 2 min later. This process was repeated for each subsequent time interval (2 min, 6 min, 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h), with the average values for each time point recorded in the table.

Table 7.
Capillary water absorption coefficient test results.
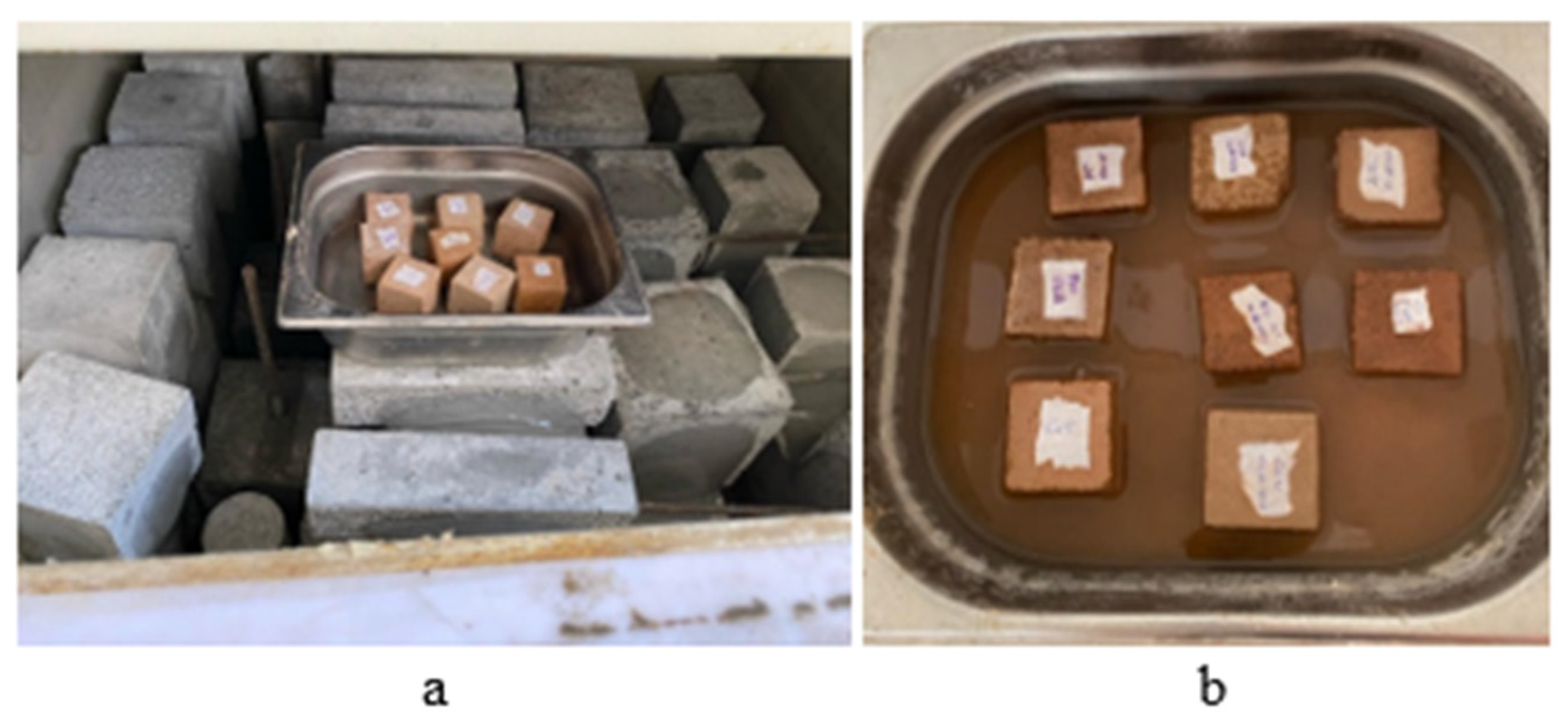
It was understood from Table 7 that the Capillary Water Absorption Coefficient test, according to TS EN 13057 [61], is typically used to assess the capillary water absorption resistance of concrete specimens. However, it was hypothesized that the stabilization of earth-based samples with binders such as cement, lime and polymers would result in higher impermeability compared to non-stabilized earth samples, although not as impermeable as concrete. Therefore, this method was used to gain an initial understanding of the capillary water absorption and water permeability of these earth-based specimens, although the method was designed for concrete.
The L5 group showed the lowest water resistance, dissolving and disintegrating in water within six minutes. The L10 group started to disintegrate after one hour. Both the Bio0.1 group and the C group disintegrated within 30 min, and the experiment was terminated for these samples. For the cement-stabilized groups, the test was stopped after one hour as the water reached the top of the sample.
Notably, the polymer-stabilized groups exhibited the highest water resistance among all samples; however, they began to disintegrate after four hours, leading to the termination of the test. These findings suggest that the current capillary water absorption coefficient test may not be suitable for evaluating the durability of earth-based materials when exposed to water, as illustrated in Figure 8.

Figure 8.
Images of the capillary water absorption coefficient test. (a): At the beginning of the experiment, (b): deterioration of the samples a few minutes after the start of the experiment.
The freeze–thaw test was employed as another method to assess the durability characteristics of the earth-based specimens fabricated for this investigation. During the freeze–thaw test conducted following the ASTM C 666- [70] technique, the samples, which were frozen in the air and then thawed in water, immediately disintegrated upon contact with water, as depicted in Figure 9.

Figure 9.
Freeze–thaw test. (a): Image during freezing, (b): damage to samples placed in water for thawing.
Figure 9 illustrates that the samples subjected to freeze–thaw cycles were unable to withstand even the initial cycle, which resulted in the experiment being terminated.
3.2.3. Microstructural Analysis
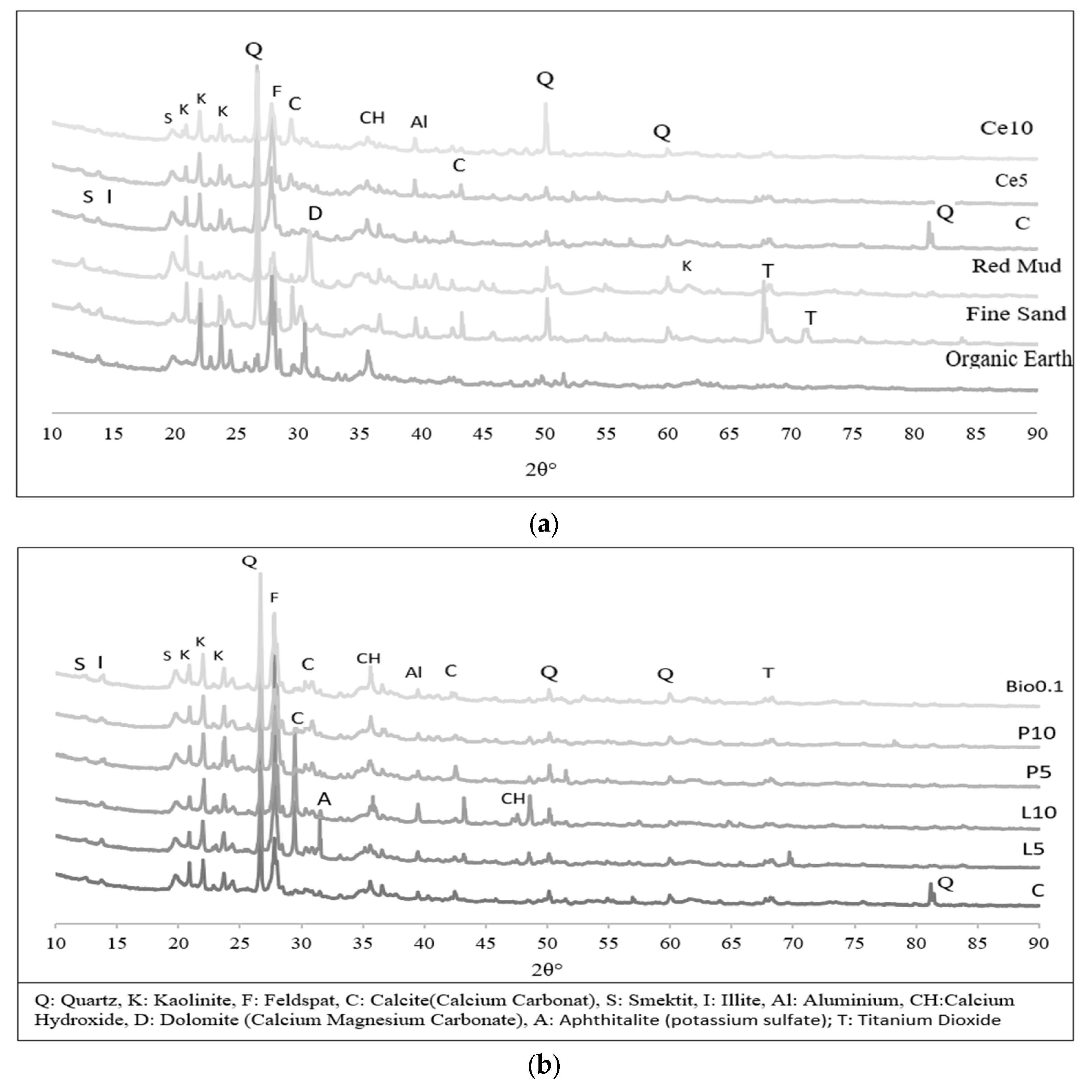
Figure 10 displays the XRD analysis graphs of the groups formed by stabilizing the organic earth, clayey red mud, fine sand, and earth-based composites with cement, lime, polymer, and biopolymer materials.
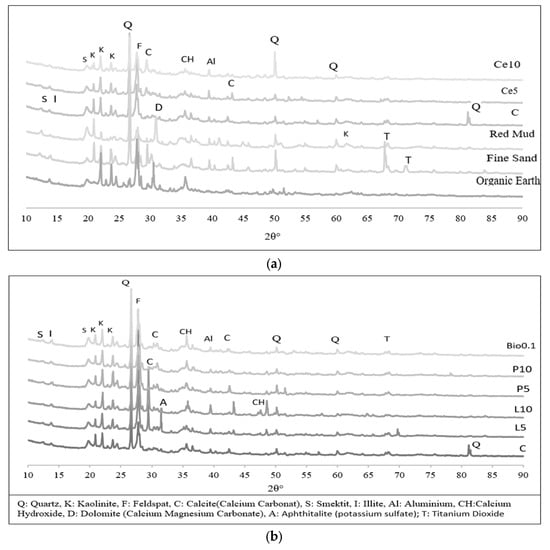
Figure 10.
(a): XRD graph of organic soil, fine sand, red mud, C, Ce5, Ce10 mixtures, (b): XRD graphs of C, L5, L10, P5, P10 and Bio0.1 mixtures.
The XRD analysis in Figure 10 identifies the presence of several ceramic-based minerals, including Quartz, Kaolinite, Feldspar, Calcite (Calcium Carbonate), Smectite, Illite, Aluminium, Calcium Hydroxide, Dolomite (Calcium Magnesium Carbonate), Aphthitalite (potassium sulfate), and Titanium Dioxide. Notably, Aphthitalite was detected only in the lime-stabilized mixes (L5 and L10), while similar mineral peaks were observed across most other mixtures.
The findings on Aphthitalite align with research conducted by Huang et al. [71], which examined its impact on the sintering and hydration processes of clinker, particularly in the context of sulfate-containing wastes in cement production. Their study demonstrated that Aphthitalite negatively affects the formation of critical cement hydration products, specifically C3S, and accelerates the appearance of Portlandite (calcium hydroxide). This leads to variations in clinker hydration and surface imperfections due to heterogeneous concentrations of Aphthitalite. Similarly, Ma et al. [72] research showed that alkali sulfates such as Aphthitalite significantly reduce the compressive strength of Portland cement after 28 days by influencing hydration and solidification.
In this study, the reduced strength and durability of the lime-stabilized specimens are associated with the presence of aphitalite, which promotes Portlandite formation. This, in turn, interferes with the hydration process, resulting in diminished performance. The formation of Portlandite during hydration in lime-based systems can lead to weaker bonds and reduced durability, as supported by the literature [68,69].
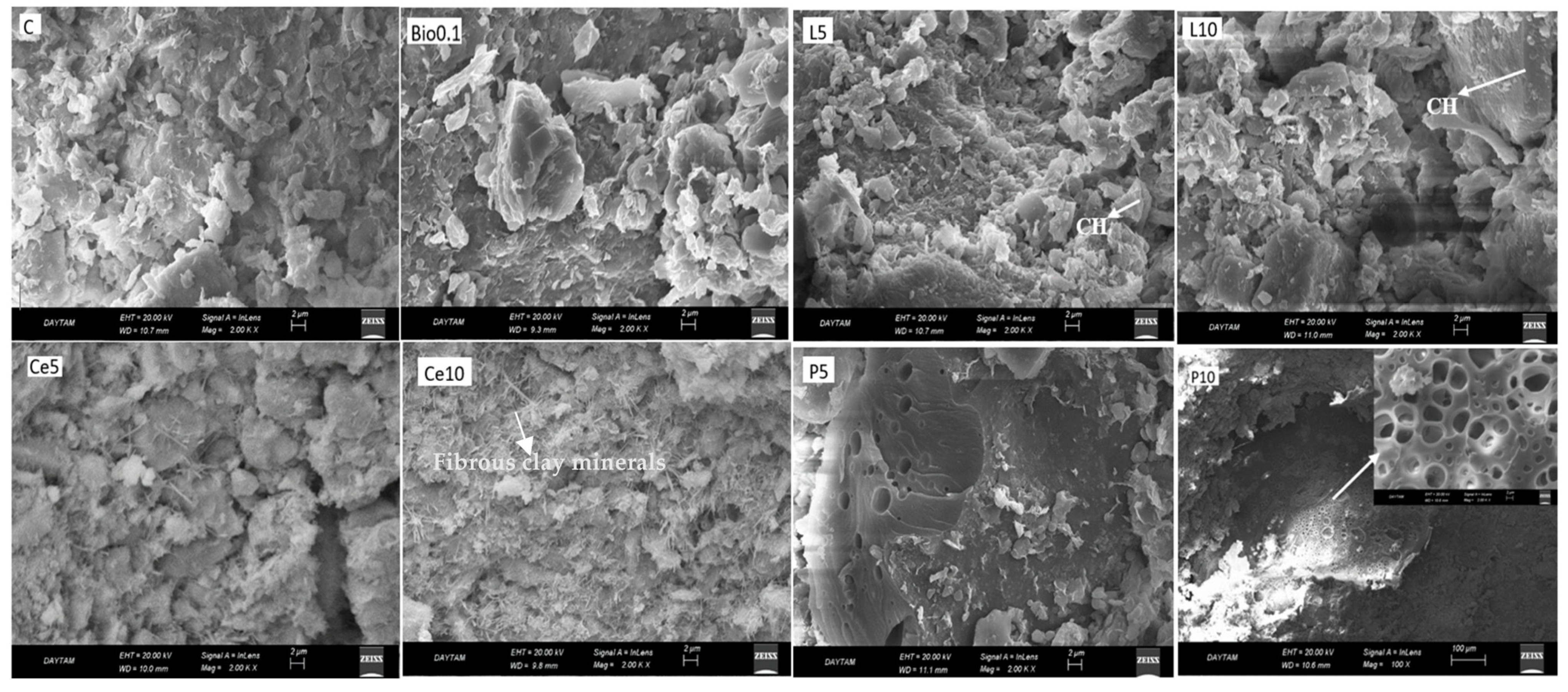
Figure 11 presents SEM analysis pictures depicting the microvoids generated in the C, L5, L10, Bio0.1, P5, P10, Ce5, and Ce10 group samples, as well as the subsequent hydration products.
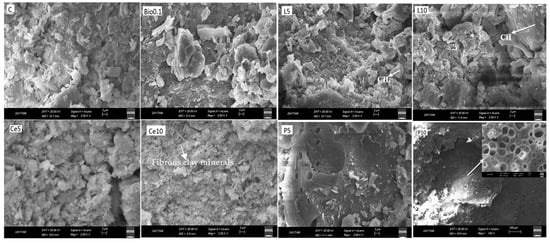
Figure 11.
SEM images of the groups.
The SEM images in Figure 11 reveal the presence of fibrous clay minerals in the C, Ce5, and Ce10 combinations, while this structure was absent in other samples due to the formation of bonds between clay minerals and stabilizers, which rendered the clay minerals less distinct. Portlandite formation was observed in the L5 and L10 mixtures, consistent with lime stabilization. In the P5 and P10 groups, polymerization was evident, with clear chemical bonding between the polymer and earth-derived components. This demonstrates the ability of polymeric materials to effectively stabilize earth-based materials by forming strong, durable links.
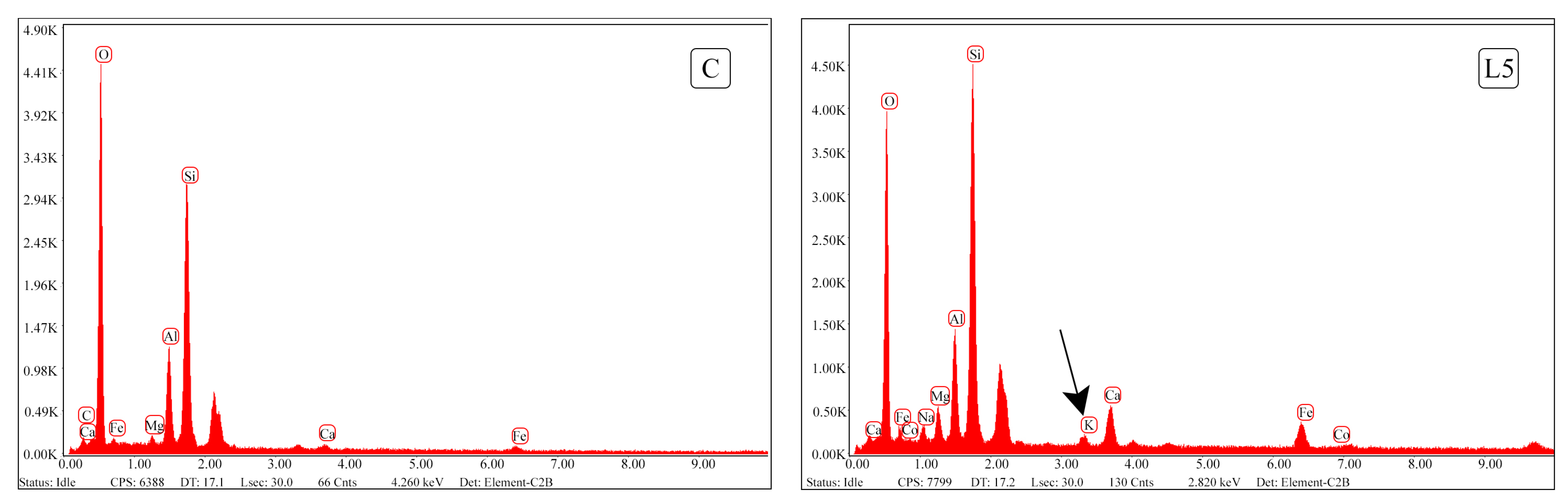
Additionally, the compound Aphthitalite (K₃Na(SO₄)₂—Potassium Sulfate) was detected in both the L5 and L10 mixtures, as confirmed by the XRD graphs and further validated through Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (EDS) analysis. Figure 12 presents the EDS analysis results, showing the presence of potassium in the L5 group, which was absent in the control (C) group. These findings highlight the influence of lime on the chemical composition and structure of the stabilized earth-based materials, particularly through the formation of Aphthitalite and Portlandite, which could affect the mechanical properties of the mixtures.
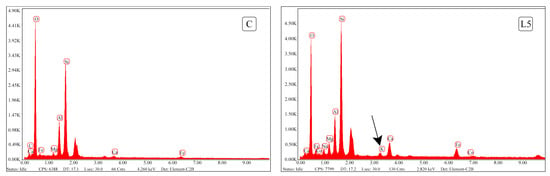
Figure 12.
Potassium minerals observed in the lime mixture as a result of EDS analysis.
4. Conclusions
This study presents a comprehensive investigation of the stabilization of earth-based materials using cement, lime, polymer, and biopolymer stabilizers. Key findings are based on empirical data and provide insights into the mechanical, rheological, and durability characteristics of these stabilized materials.
An inverse relationship was identified between unit volume weight and air content in fresh mixtures, with biopolymer-based combinations showing higher air content, while cement and lime reduced it. The mixture containing 10% cement exhibited the greatest unit volume weight. Cement and lime stabilizers expanded the flow diameter, whereas biopolymer addition reduced it. Biopolymers also increased density and decreased penetration depth, significantly impacting the rheological properties of the mixtures. The fall cone test results indicated that biopolymer substantially increased yield stress, particularly at higher concentrations, demonstrating the need to limit biopolymer content in earth-based mixes.
The flexural strength test showed that the Ce10 group (10% cement) achieved the highest flexural strength (1.205 MPa). In contrast, lime and biopolymer resulted in reduced flexural strength, indicating weak bonding between these stabilizers and the earth materials. Cement-stabilized groups exhibited the highest compressive strength, with a 200% increase observed when the cement ratio was raised from 5% to 10%. Biopolymer reduced compressive strength compared to the C, while polymer groups performed better than the C at 28 days but experienced a decline at 56 days. Lime-stabilized groups exhibited the lowest compressive strength, with slow strength development over time, making lime an unsuitable stabilizer for earth-based materials.
Capillary water absorption and freeze–thaw tests were inconclusive, as most stabilized samples disintegrated upon water exposure, demonstrating the inadequacy of these tests for earth-based materials. XRD analysis identified several ceramic minerals, including Quartz, Kaolinite, and Calcite. The presence of Aphthitalite in lime-stabilized mixtures had a negative impact on strength. SEM analysis revealed fibrous clay minerals in the C, Ce5, and Ce10 mixtures, while Portlandite formation was observed in the L5 and L10 groups. Polymerization was detected in the P5 and P10 samples, confirming strong chemical bonding in polymer-stabilized mixtures.
The suitability of pavement materials for low-traffic roads is generally assessed on the basis of key factors such as durability, load-bearing capacity, and resistance to environmental and wear degradation. To perform well under these conditions, the material must be able to withstand occasional vehicle loads without significant deformation or deterioration over time. In this study, the 10% cement stabilized earth mix shows improved compressive and flexural strength compared to other formulations, suggesting that it meets these criteria. Although these properties are not sufficient for heavily trafficked roads, they provide adequate stability for roads with lower traffic and lighter vehicle loads.
In addition, earthen pavements, such as the one proposed here, provide environmental benefits by minimizing energy consumption during construction and reducing environmental impact, primarily through the use of locally sourced, natural materials. This sustainable approach not only improves technical feasibility but also supports local economic growth. These findings provide a basis for future sustainable infrastructure projects that emphasize the use of natural materials and low carbon alternatives, providing an environmentally friendly solution for low-traffic roads.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.T. and N.K.; methodology, Y.T. and N.K.; validation, Y.T. and N.K.; investigation, Y.T. and N.K.; resources, Y.T.; data curation, N.K.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.T. and N.K.; writing—review and editing, Y.T. and N.K.; visualization, Y.T. and N.K.; supervision, Y.T. and N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Coordinatorship of Scientific Research Projects (BAP) of Atatürk University, grant number FKP-2023-13046.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting the reported results of this study are included within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Taher, S.A.; Alyousify, S.; Jalal, H.; Hassan, A. Comparative Study of Using Flexible and Rigid Pavements for Roads: A Review Study. J. Univ. Duhok 2020, 32, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohod, M.V.; Kadam, K.N. A Comparative Study on Rigid and Flexible Pavement: A Review. IOSR J. Mech. Civ. Eng. (IOSR-JMCE) 2016, 13, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, M.I.; Elayat, A.; Reda, M.; Elsamak, G. Influence of Concrete Type on Rigid Pavement Behavior under Static Loads. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2024, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thives, L.P.; Ghisi, E. Asphalt Mixtures Emission and Energy Consumption: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Vaddy, P.; Biligiri, K.P. Quantification of Embodied Energy and Carbon Footprint of Pervious Concrete Pavements through a Methodical Lifecycle Assessment Framework. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maadani, O.; Shafiee, M.; Egorov, I. Climate Change Challenges for Flexible Pavement in Canada: An Overview. J. Cold Reg. Eng. 2021, 35, 03121002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.J.; Król, J.; Radziszewski, P.; Casado, R.; Blanco, V.; Pérez, D.; Viñas, V.M.; Brijsse, Y.; Frosch, M.; Le, M.; et al. ScienceDirect Eco-Friendly Materials for a New Concept of Asphalt Pavement. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 3582–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, D.; Mallick, R.; Fini, E.H. Reducing Susceptibility to Moisture Damage in Asphalt Pavements Using Polyethylene Terephthalate and Sodium Montmorillonite Clay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposito, S.; Scalisi, F. Sustainable Architecture: The Eco-Efficiency Earth Construction. Eur. J. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 6, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fabbri, A.; Morel, J.C.; Gallipoli, D. Assessing the Performance of Earth Building Materials: A Review of Recent Developments. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2018, 3, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.-N.; Oh, E.; Ong, D.E.L. Effects of Binder Types and Other Significant Variables on the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Chemical-Stabilized Clayey Soil Using Gene-Expression Programming. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 9103–9121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xue, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, K. Experimental Study on Material Ratio and Strength Performance of Geopolymer-Improved Soil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 267, 120469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, D.; Dash, S.K. Stabilization of Expansive Soils Using Chemical Additives: A Review. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 14, 1319–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guihéneuf, S.; Rangeard, D.; Perrot, A.; Cusin, T.; Collet, F.; Prétot, S. Effect of Bio-Stabilizers on Capillary Absorption and Water Vapour Transfer into Raw Earth. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constr. 2020, 53, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubbar, A.A.; Sadique, M.; Kot, P.; Atherton, W. Future of Clay-Based Construction Materials—A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 210, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei Baghini, M.; Ismail, A.; Kheradmand, B.; Hesam Hafezi, M.; Alezzi Almansob, R. The Potentials of Portland Cement and Bitumen Emulsion Mixture on Soil Stabilization in Road Base Construction. J. Teknol. (Sci. Eng.) 2013, 65, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar, M.V.; Pancar, E.B.; Şengül, E.; Aslan, H. Pavement Subgrade Stabilization with Lime and Cellular Confinement System. Balt. J. Road Bridge Eng. 2018, 13, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portelinha, F.H.M.; De Souza Correia, N.; Santos Mendes, I.; Silva, J.W.B. Da Geotechnical Properties and Microstructure of a Diesel Contaminated Lateritic Soil Treated with Lime. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2021, 30, 838–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolvand, Y.; Sadeghiamirshahidi, M. Soil Stabilization with Gypsum: A Review. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fořt, J.; Černý, R. Carbon Footprint Analysis of Calcined Gypsum Production in the Czech Republic. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.L.; Phan, V.T.A.; Tran, H.B. Potential of Fly Ash, Cement, and Enzyme Stabilized Soil for Road Construction. Transp. Infrastruct. Geotechnol. 2023, 10, 1050–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanikumar, B.R.; Raju, M.J.; Raju, E.R. Silica Fume Stabilization of an Expansive Clay Subgrade and the Effect of Silica Fume-Stabilised Soil Cushion on Its CBR. Geomech. Geoengin. 2020, 15, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandial, M.; Gupta, S. Soil Stabilization by Using Fly Ash and Ferric Chloride. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2020, 9, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.R.; Patel, S.; Shahu, J.T. Utilization of Class ‘C’ Fly Ash in Flexible Pavement System—A Review. Lect. Notes Civ. Eng. 2019, 29, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phummiphan, I.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Rachan, R.; Arulrajah, A.; Shen, S.L.; Chindaprasirt, P. High Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer Stabilized Lateritic Soil and Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Blends as a Pavement Base Material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rind, T.A.; Karira, H.; Mirani, S.A.; Mari, A.K. Influence of Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag on the Index, Compaction Parameters and Mechanical Strength of Khairpur Mir’s Natural Soil. J. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2020, 10, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, H.; Houben, H. Earth Concrete. Stabilization Revisited. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Cai, G.; Dong, X.; Pu, S.; Dai, X.; Duan, W. Green Utilization of Modified Biomass By-Product Rice Husk Ash: A Novel Eco-Friendly Binder for Stabilizing Waste Clay as Road Material. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristelo, N.; Glendinning, S.; Miranda, T.; Oliveira, D.; Silva, R. Soil Stabilisation Using Alkaline Activation of Fly Ash for Self Compacting Rammed Earth Construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kogbara, R.B.; Hariharan, N.; Masad, E.A.; Little, D.N. A State-of-the-Art Review of Polymers Used in Soil Stabilization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 305, 124685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.-L.; Liu, S.-Y. Application of Biomass By-Product Lignin Stabilized Soils as Sustainable Geomaterials: A Review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 728, 138830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouazza, A.; Gates, W.P.; Ranjith, P.G. Hydraulic Conductivity of Biopolymer-Treated Silty Sand. Géotechnique 2015, 59, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, H.R.; O’Kelly, B.C. Improving Mechanical Properties of Sand Using Biopolymers. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2013, 139, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Kharis Prasidhi, A.; Im, J.; Cho, G.-C. Soil Strengthening Using Thermo-Gelation Biopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Cho, G.-C. Geotechnical Behavior of a Beta-1,3/1,6-Glucan Biopolymer-Treated Residual Soil. Geomech. Eng. 2014, 7, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, H.S.G.M. High-Speed Railway Embankments Stabilization by Using a Plant Based Biopolymer. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 25, 7626–7633. [Google Scholar]
- Cabalar, A.F.; Awraheem, M.H.; Khalaf, M.M. Geotechnical Properties of a Low-Plasticity Clay with Biopolymer. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, H.; Modiri, F. Application of Novel Persian Gum Hydrocolloid in Soil Stabilization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, 116639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, S.; Ballard, J.; Griggs, C.; Newman, J.K.; Nestler, C. An Innovative Non-Petroleum Rhizobium Tropici Biopolymer Salt for Soil Stabilization. In Volume 5: Energy Systems Analysis, Thermodynamics and Sustainability; NanoEngineering for Energy; Engineering to Address Climate Change, Parts A and B, Proceedings of the ASME 2010 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–18 November 2010; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1279–1284. [Google Scholar]
- TS EN 1097-7; Tests for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates—Part 7: Determination of the Particle Density of Filler—Pyknometer Method. TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2015. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/standard/standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073081072114080047066098043116070117 (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- ASTM-D4318; Standard Test Methods for Liquid Limit, Plastic Limit, and Plasticity Index of Soils. ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d4318-17e01.html (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- ASTM-D422; Standard Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils. ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d0422-63r07.html (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- Webpage of Tekno Building Chemicals Teknorep 500 Doğal Hidrolik Kireç. Available online: https://teknoyapi.com.tr/tr/urunler/yapisal-guclendirme-urunleri/teknorep-500-dogal-hidrolik-kirec (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- Smitha, S.; Sachan, A. Use of Agar Biopolymer to Improve the Shear Strength Behavior of Sabarmati Sand. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 10, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Jung, J.; Song, X.; Bate, B. On the Soil Water Characteristic Curves of Poorly Graded Granular Materials in Aqueous Polymer Solutions. Acta Geotech. 2018, 13, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Pan, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, J. Improving the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Red Clay by Combining Biopolymers with Fibers. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 1503–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artuk, F. Investigation of the Behavior of E-Waste Additive Polymer Based Piles Under Vertical Load on Cohesionless Soil. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of science, Ataturk University, Erzurum, Turkey, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Şahika Group Company. Webpage of Şahika Group Company. Available online: https://sahikagroup.com/ (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- TS EN 12350-7; Testing Fresh Concrete—Part 7: Air Content—Pressure Methods. TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2019. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/standard/standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073088081118112120109113102075111106 (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- TS EN 12390-2; Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 2: Making and Curing Specimens for Strength Tests. TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2019. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/standard/standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073100050117105081076047107088073054 (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- TS EN 12350-7/AC; Beton—Taze Beton Deneyleri—Bölüm 7: Hava Içeriğinin Tayini—Basınç Yöntemleri (Testing Fresh Concrete—Part 7: Air Content—Pressure Methods). TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2022. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/Standard/Standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073086065089087052072056121054068120 (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Lachemi, M.; Hossain, K.M.A.; Lambros, V.; Nkinamubanzi, P.-C.; Bouzoubaâ, N. Performance of New Viscosity Modifying Admixtures in Enhancing the Rheological Properties of Cement Paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Sanjayan, J. Mechanical Anisotropy of Aligned Fiber Reinforced Composite for Extrusion-Based 3D Printing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 202, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TS EN 12350-5; Beton—Taze Beton Deneyleri—Bölüm 5: Yayılma Tablası Deneyi (Testing Fresh Concrete—Part 5: Flow Table Test). TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2010. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/standard/standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073082112065070113087101115117109052 (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- CEN ISO 17892-6:2017; Geotechnical Investigation and Testing—Laboratory Testing of Soil—Part 6: Fall Cone Test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/55248.html (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Baz, B.; Aouad, G.; Leblond, P.; Al-Mansouri, O.; D’hondt, C.M.; Remond, S. Mechanical Assessment of Concrete-Steel Bonding in 3D Printed Elements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TS EN 12390-5; Beton—Sertleşmiş Beton Deneyleri—Bölüm 5: Deney Numunelerinin Eğilme Dayanımının Tayini (Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 5: Flexural Strength of Test Specimens). TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2002. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/standard/standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073087081102083106066101108115069070 (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- TS EN 12390-3; Beton—Sertleşmiş Beton Deneyleri—Bölüm 3: Deney Numunelerinin Basınç Dayanımının Tayini (Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 3: Compressive Strength of Test Specimens). TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2010. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/standard/standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073084068118118070102085087098097087 (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Mohamed, A.M. Influence of Nano Materials on Flexural Behavior and Compressive Strength of Concrete. HBRC J. 2016, 12, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husem, M. The Effects of High Temperature on Compressive and Flexural Strengths of Ordinary and High-Performance Concrete. Fire Saf. J. 2006, 41, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TS EN 13057; Beton Yapılar—Koruma ve Tamir Için Mamul ve Sistemler—Deney Metotları—Kılcal Su Emmeye Direncin Tayini (Products and Systems for the Protection and Repair of Concrete Structures—Test Methods—Determination of Resistance of Capillary Absorption). TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2002. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/standard/standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073081068111056079084053120078107114 (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Raj, N.; Selvakumar, S.; Soundara, B.; Kulanthaivel, P. Sustainable Utilization of Biopolymers as Green Adhesive in Soil Improvement: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 118117–118132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, A.; Morais, P.V.; Pires, A.C.; Chung, A.P.; Oliveira, P.V. A Review on the Importance of Microbial Biopolymers Such as Xanthan Gum to Improve Soil Properties. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Im, J.; Cho, G.C. Introduction of Microbial Biopolymers in Soil Treatment for Future Environmentally-Friendly and Sustainable Geotechnical Engineering. Sustainability 2016, 8, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.A. Bonding Between Polyacrylamide And Clay Mineral Surfaces. Soil Sci. 1997, 162, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiffin, V.S.; van Paassen, L.A.; Harkes, M.P. Microbial Carbonate Precipitation as a Soil Improvement Technique. Geomicrobiol. J. 2007, 24, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Im, J.; Prasidhi, A.K.; Cho, G.C. Effects of Xanthan Gum Biopolymer on Soil Strengthening. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 74, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Sivapullaiah, P.V. Lime Stabilization of Soil: A Physico-Chemical and Micro-Mechanistic Perspective. Indian Geotech. J. 2020, 50, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisazadeh, A.; Kassim, K.A.; Nur, H. Characterization of Phosphoric Acid- and Lime-Stabilized Tropical Lateritic Clay. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C666-97; Standard Test Method for Resistance of Concrete to Rapid Freezing and Thawing. ASTM International: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- Huang, L.; Song, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z. Effects of Aphthitalite on the Formation of Clinker Minerals and Hydration Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qian, J. Influence of Alkali Sulfates in Clinker on the Hydration and Hardening of Portland Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).