Application of Novel Biochar Derived from Experimental Sewage Sludge Gasification as an Adsorbent for Heavy Metals Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origin and Process of Biochar Production
2.2. Biochar Characterization
2.3. Procedure for Conducting Adsorption Batch Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Properties of the Produced Biochar
3.2. Experimental Design
3.3. Results of Adsorption Experiments
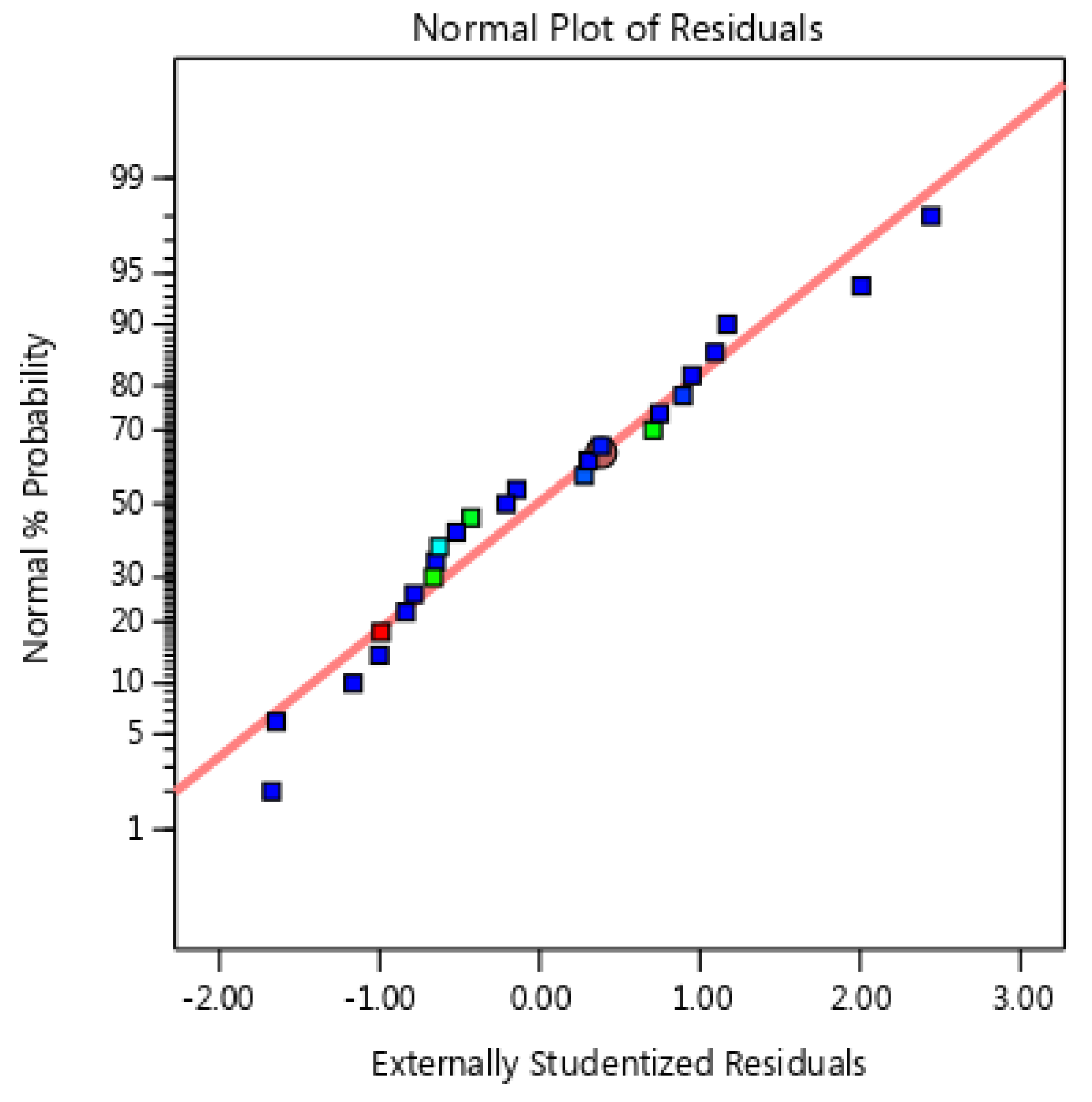
3.3.1. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
3.3.2. Cadmium Removal Efficiency
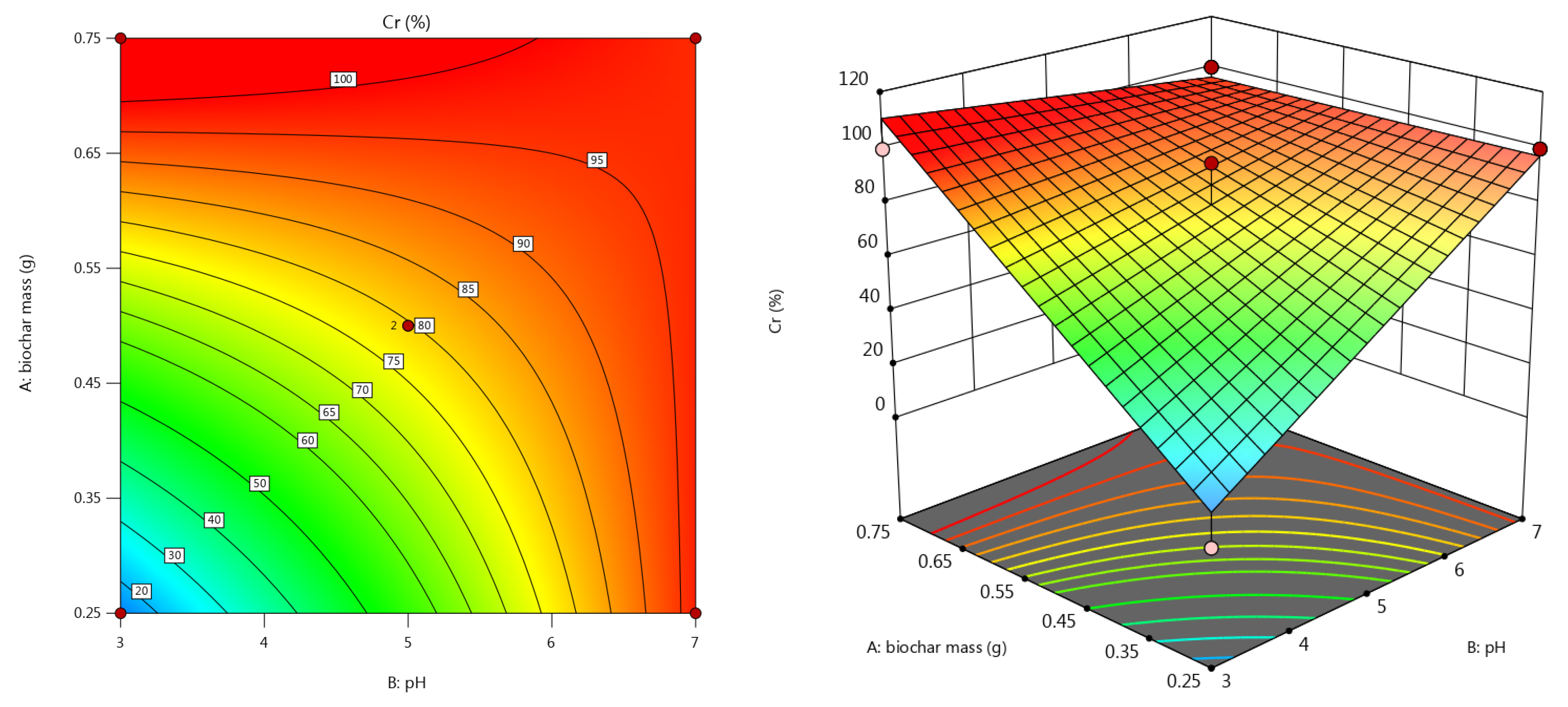
3.3.3. Chromium Removal Efficiency
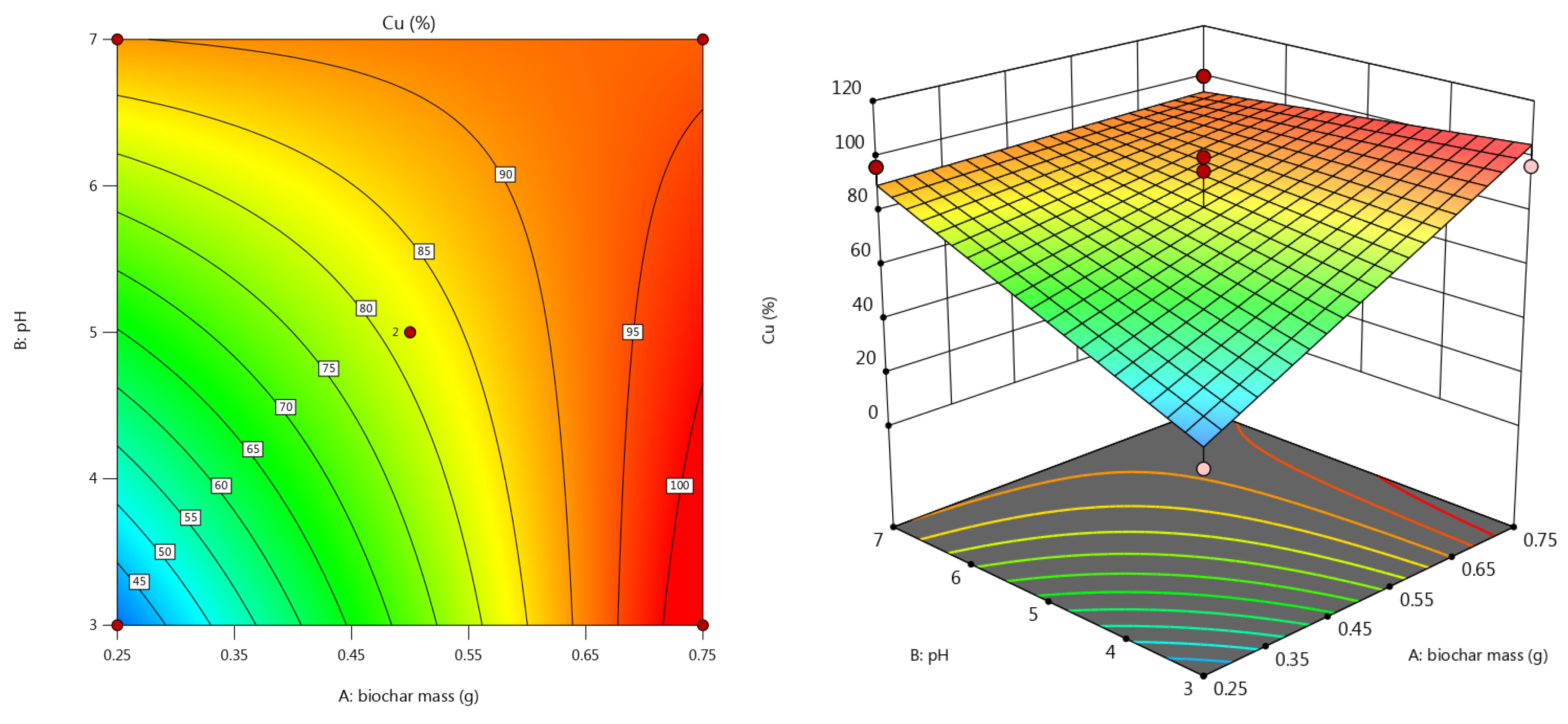
3.3.4. Copper Removal Efficiency
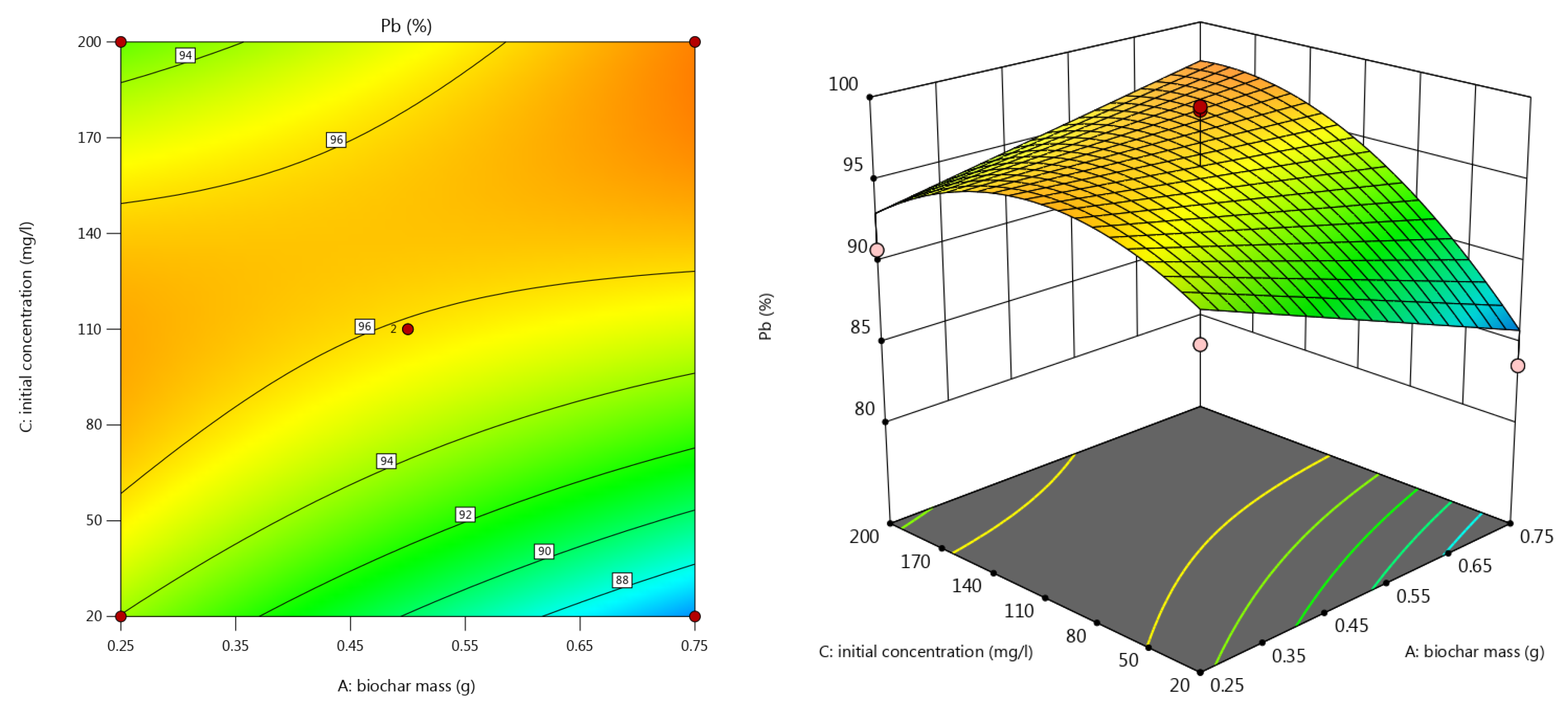
3.3.5. Lead Removal Efficiency
3.3.6. Optimization and Validation of the Model
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Giacomo, G.; Romano, P. Evolution and Prospects in Managing Sewage Sludge Resulting from Municipal Wastewater Purification. Energies 2022, 15, 5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Burke, I.T.; Chen, X. Assessing metal contamination and speciation in sewage sludge: Implications for soil application and environmental risk. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 22, 1037–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, Z.-F.; Pan, X.-W.; Tan, J.-Y.; Yang, S.-S.; Wu, J.-T.; Chen, C.; Yuan, Y.; Ren, N.-Q. Sewage sludge derived biochar for environmental improvement: Advances, challenges, and solutions. Water Res. X 2023, 18, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrafioti, E.; Bouras, G.; Kalderis, D.; Diamadopoulos, E. Biochar production by sewage sludge pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 101, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangabhashiyam, S.; dos Santos Lins, P.V.; de Magalhães Oliveira, L.M.T.; Sepulveda, P.; Ighalo, J.O.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Meili, L. Sewage sludge-derived biochar for the adsorptive removal of wastewater pollutants: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chang, V.W.-C.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and organic fractions of municipal solid waste: Synergistic effects on biochar properties and the environmental risk of heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, D.; Gao, F.; Li, M.; Luo, X. Effects of Biochar-Derived Sewage Sludge on Heavy Metal Adsorption and Immobilization in Soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 4, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Yao, Z.; You, S.; Massier, T.; Stimming, U.; Wang, C.-H. Life cycle assessment of a sewage sludge and woody biomass co-gasification system. Energy 2017, 137, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.S.; Farooq, A.; Valizadeh, B.; Lee, D.; Seo, M.W.; Jung, S.-C.; Hussain, M.; Kim, Y.M.; Khan, M.A.; Jeon, B.-H.; et al. Valorization of sewage sludge via air/steam gasification using activated carbon and biochar as catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 54, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Lehmann, J.; McBride, M.B.; Hay, A.G. Adsorption of copper and zinc by biochars produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.R.; Patel, A.K.; Jaisi, D.P.; Adhikari, S.; Lu, H.; Khanal, S.K. Environmental application of biochar: Current status and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Zou, W.; He, F.; Hu, X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Gao, B. Biochar technology in wastewater treatment: A critical review. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Zakharova, J.; Batool, M.; Coley, M.P.; Arjunan, A.; Hawkins, A.J.; Bolarinwa, T.; Devi, S.; Thumma, A.; Williams, C. Removal of cadmium and zinc from water using sewage sludge-derived biochar. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2024, 6, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, X.; Li, L.; Cao, S.; Dou, J.; Chen, R.; Hu, X.; Qiu, Z.; Li, M.; et al. Sludge-based biochar preparation: Pyrolysis and co-pyrolysis methods, improvements, and environmental applications. Fuel 2024, 373, 132265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh Dhanjal, D.; Datta, S.; Bhatia, D.; Dhiman, J.; Samuel, J.; Prasad, R.; Singh, J. A sustainable paradigm of sewage sludge biochar: Valorization, opportunities, challenges and future prospects. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozada, F.; Otero, M.; Moran, A.; Garcia, A.I. Adsorption of heavy metals onto sewage sludge-derived materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6322–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Liu, M.; Ren, H. Biochar produced from the co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and walnut shell for ammonium and phosphate adsorption from water. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.O.; Aturagaba, G.; Ntale, M.; Nyakairu, G.W. A review of adsorption techniques for removal of phosphates from wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 3113–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Quan, W.; Chen, Q.; Gong, W.; Wang, A. Efficient Adsorption of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Wastewater by Biochar. Molecules 2024, 29, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.H.; Cheng, H.; Chen, G.Y. Preparation and characterization of carbonaceous adsorbents from sewage sludge using a pilot-scale microwave heating equipment. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2012, 93, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Xiao, F.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, L.; Wang, L. Study on the performance of sewage sludge biochar modified by nZVI to remove Cu(II) and Cr(VI) in water. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 1821–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Lin, H.; Huang, L. Removal and reduction of Cr(VI) in simulated wastewater using magnetic biochar prepared by co-pyrolysis of nano-zerovalent iron and sewage sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, R.; Ji, S.; Xie, L.; Zhang, H. Effects of biochar derived from sewage sludge and sewage sludge/cotton stalks on the immobilization and phytoavailability of Pb, Cu, and Zn in sandy loam soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on biochar’s characteristics and speciation and environmental risks of heavy metals in sewage sludge biochars. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, J. Decontamination of Cr(VI) from water using sewage sludge derived biochar: Role of environmentally persistent free radicals. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 56, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, L.; Li, B.; Huang, H.; Yu, W.; Sun, C.; Long, K.; Young, B. Utilization of activated sludge and shell wastes for the preparation of Ca-loaded biochar for phosphate removal and recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakić, D.; Vouk, D.; Štirmer, N.; Serdar, M. Management of sewage sludge—New possibilities involving partial cement replacement. Civ. Eng. 2018, 70, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubalo, A.; Vouk, D.; Ćurković, L.; Rogošić, M.; Nakić, D.; Cheeseman, C. Influence of combustion temperature on the performance of sewage sludge ash as a supplementary material in manufacturing bricks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; Antelo, J.; Fiol, S.; Macías-García, F. Phosphate adsorption on an industrial residue and subsequent use as an amendment for phosphorous deficient soils. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardis, B.O.; Santana Da Silva Carneiro, J.; Souza, I.M.G.D.; Barros, R.G.D.; Azevedo Melo, L.C. Phosphorus recovery using magnesium-enriched biochar and its potential use as fertilizer. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 67, 1017–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Chen, J.J.; Zhang, M.; Inyang, M.; Li, Y.C.; Alva, A.; Yang, L.Y. Engineered carbon (biochar) prepared by direct pyrolysis of Mg-accumulated tomato tissues: Characterization and phosphate removal potential. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 138, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubalo, A.; Vouk, D.; Maljković, D.; Bolanča, T. Gasification of Sewage Sludge in a Rotary Kiln Reactor—A Case Study with Incorporation of Sewage Sludge Ash in Brick Production. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2022, 36, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakić, D.; Vouk, D.; Donatello, S.; Anić Vučinić, A. Environmental impact of sewage sludge ash assessed through leaching. Eng. Rev. 2017, 37, 222–234. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.Y.; Liu, H.; Shen, W.Q.; Luo, G.Q.; Li, A.J.; Lu, Z.L.; Yao, H. Comparison of CaO’s effect on the fate of heavy metals during thermal treatment of two typical types of MSWI fly ashes in China. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, L. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics and heavy metal adsorptive performance of biochar derived from municipal sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, A.; Oleszczuk, P.; Charmas, B.; Skubiszewska-Zieba, J.; Pasieczna-Patkowska, S. Effect of sewage sludge properties on the biochar characteristic. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 112, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kończak, M.; Oleszczuk, P. Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and biomass in carbon dioxide as a carrier gas affects the total and leachable metals in biochars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Suvarna, M.; Pan, L.; Tabatabaei, M.; Sik Ok, Y.; Wang, X. Wet wastes to bioenergy and biochar: A critical review with future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Whitcomb, P.J. DOE Simplified: Practical Tools for Effective Experimentation; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; 268p. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Zhou, Z.; Han, R.; Meng, R.; Wang, H.; Lu, W. Adsorption of cadmium by biochar derived from municipal sewage sludge: Impact factors and adsorption mechanism. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.Q.; Chen, C.; Cui, H.J.; Fu, M.L. Enhanced removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solution using CaCO3 nanoparticle modified sewage sludge biochar. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16238–16243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Shao, N.; Zheng, C.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Z. Amino-functionalized sewage sludge-derived biochar as sustainable efficient adsorbent for Cu(II) removal. Waste Manag. 2019, 90, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Chen, H.; Xi, J.; Yao, D.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, Y.; Lu, X. Biochars with Excellent Pb(II) Adsorption Property Produced from Fresh and Dehydrated Banana Peels via hydrothermal Carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, J.; Jin, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H. Sludge-based biochar activation to enhance Pb(II) adsorption. Fuel 2019, 252, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jia, H.; Jiang, L.; Mou, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. Biochar Prepared from Steam-Exploded Bitter Melon Vine for the Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution: Kinetics, Isotherm, Thermodynamics and Mechanism. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, O.P.; Vashishtha, M.; Palanisamy, P.; Kumar, K.V. A Review on the Adsorption Isotherms and Design Calculations for the Optimization of Adsorbent Mass and Contact Time. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 17407–17430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Alazba, A.A.; Amin, M.T. Kinetic and Isotherm Studies of Ni2+ and Pb2+ Adsorption from Synthetic Wastewater Using Eucalyptus camdulensis—Derived Biochar. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood-ul-Hassan, M.; Yasin, M.; Yousra, M. Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic studies of lead, chromium, and cadmium bio-adsorption from aqueous solution onto Picea smithiana sawdust. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12570–12578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhang, M.; Shao, S. Optimization of target biochar for the adsorption of target heavy metal ion. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.; Shim, J.; Deka, S.; Kumari, D.; Kataki, R.; Kumar, M. Characterization of cadmium removal from aqueous solution by biochar produced from Ipomoea fistulosa at different pyrolytic temperatures. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; Yao, Z. The Application of Biochar as Heavy Metals Adsorbent: The Preparation, Mechanism, and Perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2024, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doczekalska, B.; Ziemińska, N.; Kuśmierek, K.; Świątkowski, A. Activated Carbons Derived from Different Parts of Corn Plant and Their Ability to Remove Phenoxyacetic Herbicides from Polluted Water. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, X. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using biochars: Adsorption and mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2022, 34, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudair, D.S.; Abdulaziz, Y.I. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Biochar Developed from Peganum Harmala Seeds to Adsorb Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solution. J. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 25, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.H.K.; Seshaiah, K.; Reddy, A.; Rao, M.M.; Wang, M. Biosorption of Pb2+ from aqueous solutions by Moringa oleifera bark: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, L. Adsorption Behaviors and Removal Efficiencies of Inorganic, Polymeric and Organic Phosphates from Aqueous Solution on Biochar Derived from Sewage Sludge of Chemically Enhanced Primary Treatment Process. Water 2018, 10, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, X.; Miao, J.; Liu, Q.; Cai, J.; An, X.; Chen, F.; Cheng, L.; Chen, W.; Luo, H.; et al. Na4P2O7-Modified Biochar Derived from Sewage Sludge: Effective Cu(II)-Adsorption Removal from Aqueous Solution. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2023, 2023, 8217910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regkouzas, P.; Diamadopoulos, E. Adsorption of selected organic micro-pollutants on sewage sludge biochar. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Dong, F.-X.; Lin, X.; Zhou, X.-H.; Kong, L.-J.; Chu, W.; Diao, Z.-H. Insights into the removal of Cr(VI) by a biochar–iron composite from aqueous solution: Reactivity, kinetics and mechanism. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
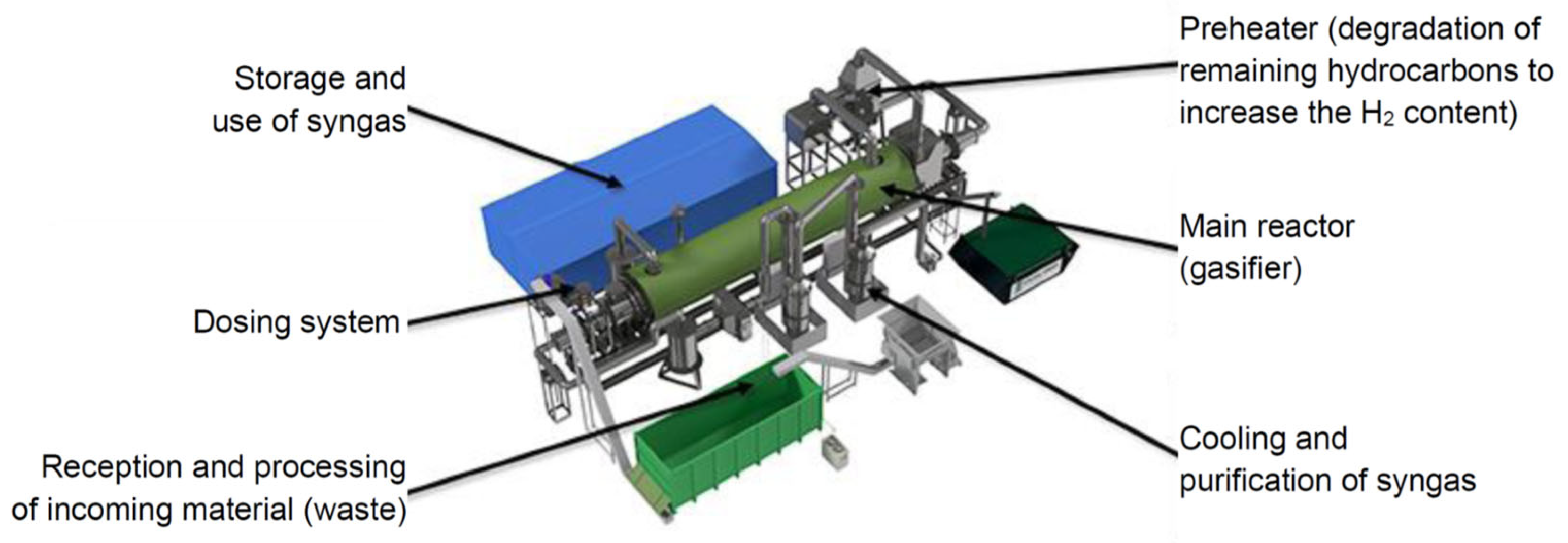
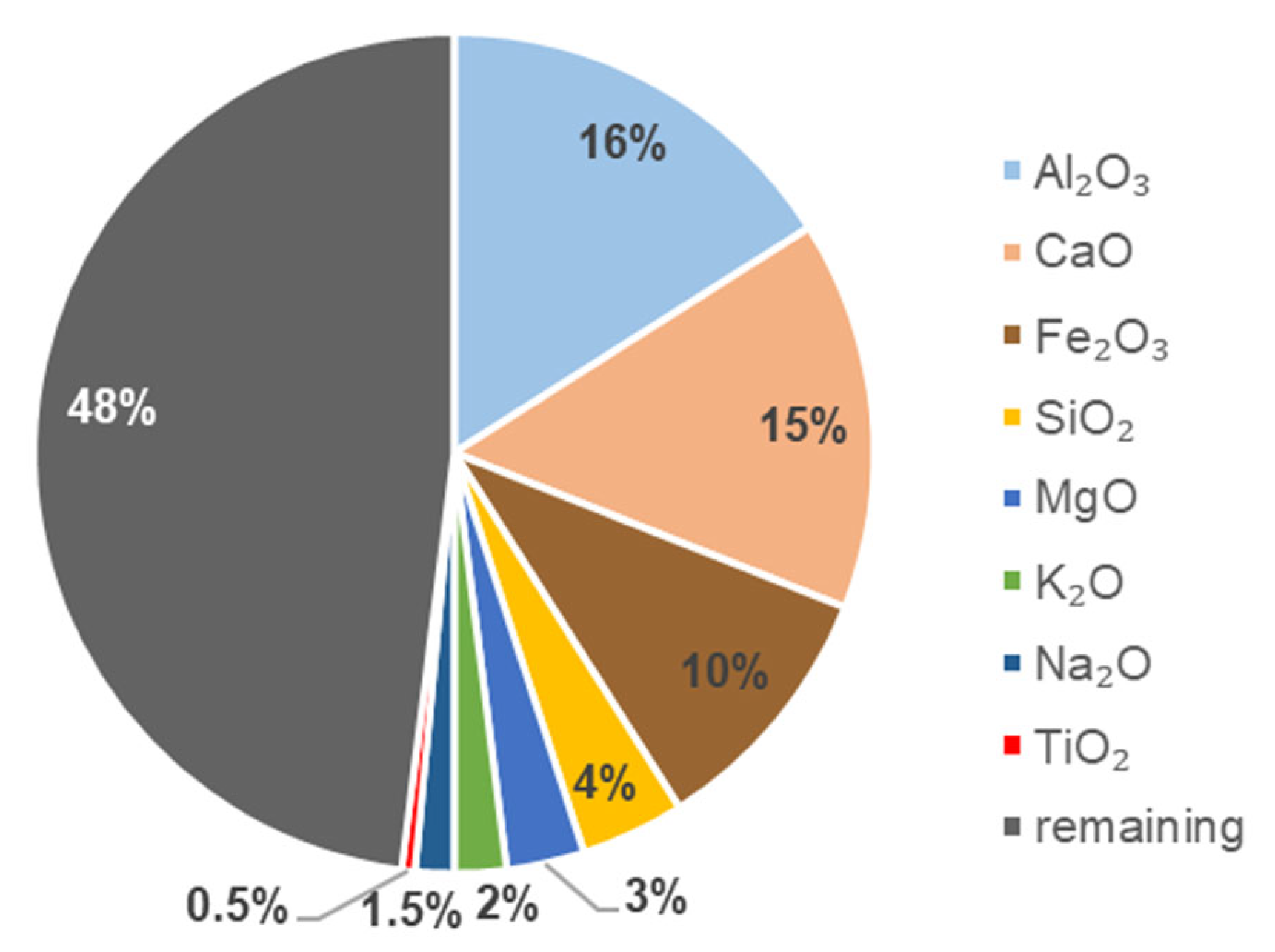
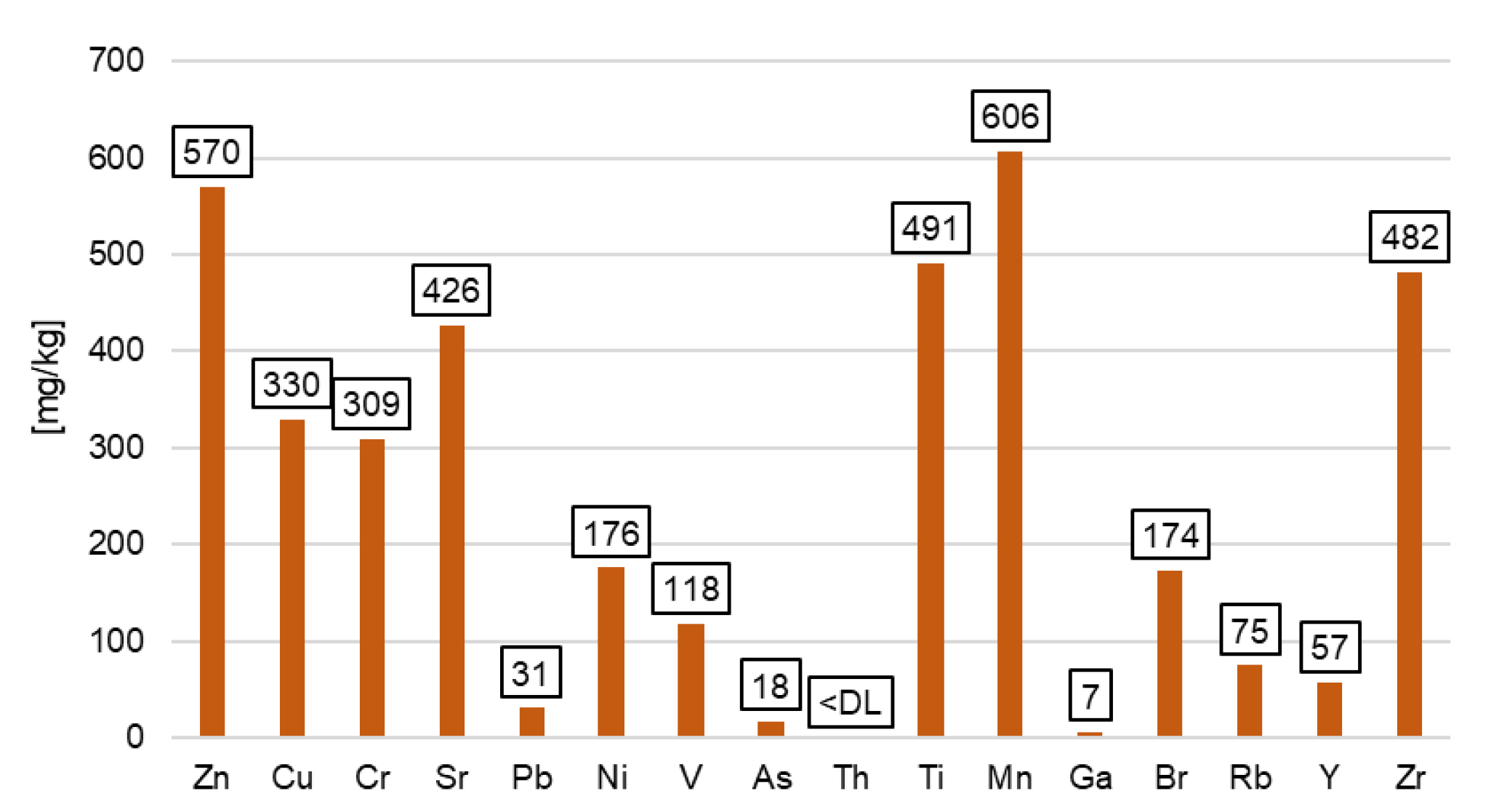

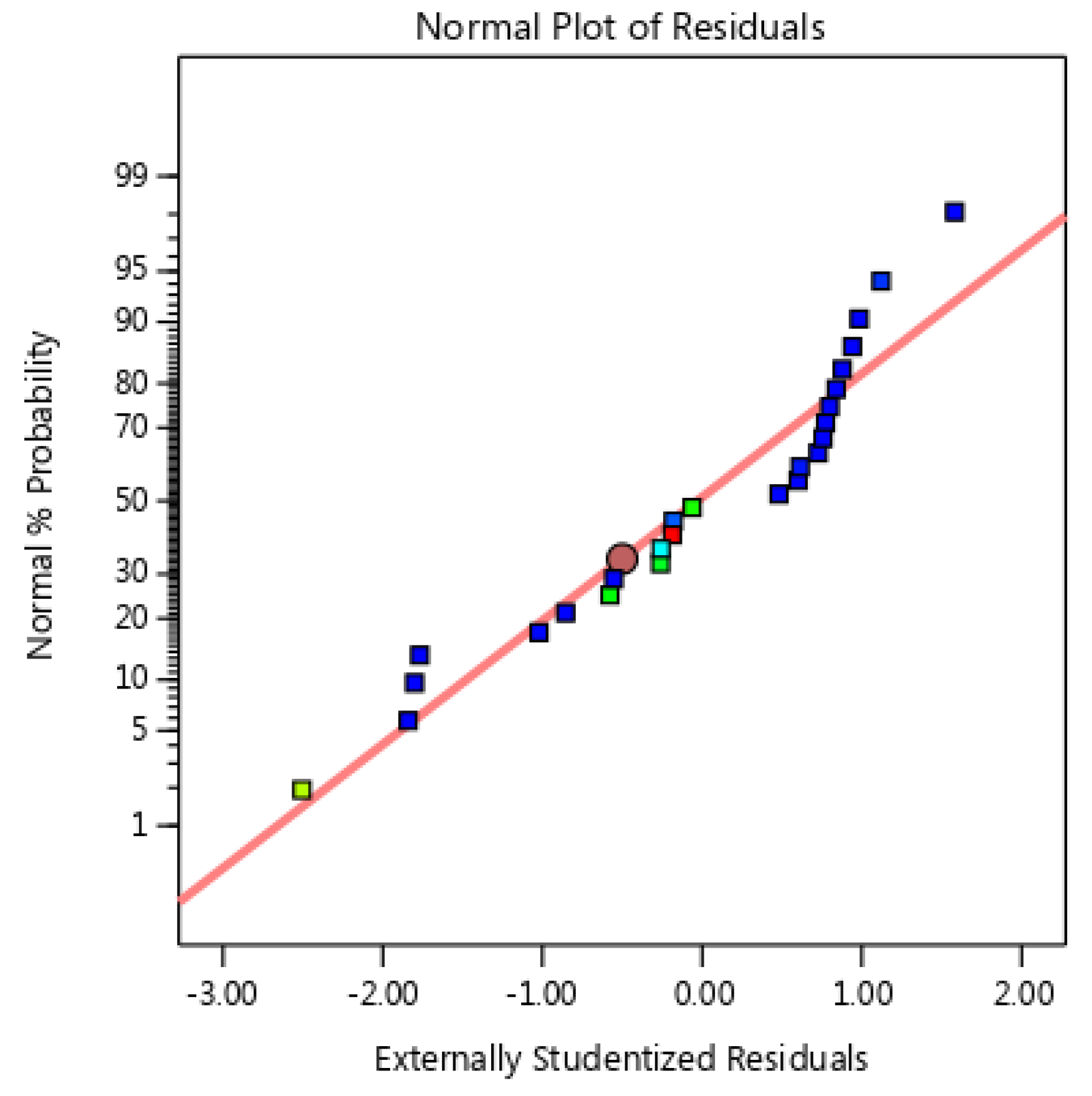









| Heavy Metal | Biochar Sample |
|---|---|
| As | <DL |
| Ba | 10.600 |
| Cd | <DL |
| Co | 0.005 |
| Cr | 0.350 |
| Cu | <DL |
| Mo | 0.800 |
| Ni | <DL |
| Pb | 0.008 |
| Se | 0.006 |
| Zn | <DL |
| Factor (Unit) | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| (A) Biochar mass (g) | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
| (B) pH | 3 | 5 | 7 |
| (C) Initial heavy metal concentration, cin (mg/L) | 20 | 110 | 200 |
| (D) time (h) | 6 | 12 | 24 |
| Run | A: Biochar Mass (g) | B: pH | C: cin (mg/L) | D: Time (h) | Cd yexp. (%) | Cd ypred. (%) | qt (Cd) (mg/g) | Cr yexp. (%) | Cr ypred. (%) | qt (Cr) (mg/g) | Cu yexp. (%) | Cu ypred. (%) | qt (Cu) (mg/g) | Pb yexp. (%) | Pb ypred. (%) | qt (Pb) (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.25 | 5 | 110 | 6 | 60.34 | 60.62 | 26.55 | 9.25 | 43.40 | 4.07 | 40.48 | 64.71 | 17.81 | 94.89 | 96.83 | 41.75 |
| 2 | 0.75 | 5 | 110 | 6 | 99.89 | 102.3 | 14.65 | 97.34 | 90.78 | 14.28 | 99.51 | 99.07 | 14.59 | 95.87 | 94.96 | 14.06 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 3 | 20 | 15 | 99.30 | 95.03 | 3.97 | 99.90 | 76.13 | 4.00 | 99.95 | 93.49 | 4.00 | 98.95 | 94.03 | 3.96 |
| 4 | 0.5 | 7 | 20 | 15 | 99.80 | 108.9 | 3.99 | 99.80 | 110.04 | 3.99 | 99.90 | 113.22 | 4.00 | 97.35 | 91.53 | 3.89 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 7 | 200 | 15 | 99.13 | 95.82 | 39.65 | 99.99 | 83.06 | 40.00 | 66.75 | 70.30 | 26.70 | 97.94 | 96.89 | 39.18 |
| 6 | 0.75 | 5 | 20 | 15 | 99.60 | 95.98 | 2.66 | 99.80 | 116.78 | 2.66 | 99.90 | 120.53 | 2.66 | 83.60 | 85.84 | 2.23 |
| 7 | 0.5 | 3 | 110 | 24 | 99.90 | 94.91 | 21.98 | 93.82 | 75.13 | 20.64 | 99.92 | 72.03 | 21.98 | 98.51 | 100.03 | 21.67 |
| 8 | 0.75 | 7 | 110 | 15 | 99.93 | 95.72 | 14.66 | 99.97 | 95.98 | 14.66 | 99.99 | 93.73 | 14.67 | 96.00 | 96.60 | 14.08 |
| 9 | 0.25 | 5 | 20 | 15 | 99.35 | 92.86 | 7.95 | 99.75 | 69.39 | 7.98 | 98.40 | 86.17 | 7.87 | 92.05 | 93.95 | 7.36 |
| 10 | 0.5 | 5 | 110 | 15 | 99.90 | 95.43 | 21.98 | 94.65 | 79.59 | 20.82 | 94.97 | 81.89 | 20.89 | 99.45 | 95.90 | 21.88 |
| 11 | 0.5 | 3 | 200 | 15 | 80.54 | 81.95 | 32.22 | 46.20 | 49.14 | 18.48 | 39.43 | 50.57 | 15.77 | 98.23 | 99.39 | 39.29 |
| 12 | 0.75 | 5 | 200 | 15 | 99.88 | 103.57 | 26.63 | 97.85 | 89.79 | 26.09 | 83.55 | 77.61 | 22.28 | 94.87 | 97.44 | 25.30 |
| 13 | 0.25 | 5 | 110 | 24 | 96.13 | 91.36 | 42.30 | 54.58 | 68.40 | 24.02 | 64.06 | 64.71 | 28.19 | 99.42 | 96.83 | 43.74 |
| 14 | 0.5 | 7 | 110 | 6 | 99.84 | 95.94 | 21.96 | 94.04 | 84.05 | 20.69 | 99.86 | 91.76 | 21.97 | 92.82 | 97.53 | 20.42 |
| 15 | 0.5 | 7 | 110 | 24 | 99.98 | 108.78 | 22.00 | 99.26 | 109.05 | 21.84 | 99.86 | 91.76 | 21.97 | 95.19 | 97.53 | 20.94 |
| 16 | 0.75 | 5 | 110 | 24 | 99.86 | 97.24 | 14.65 | 99.97 | 115.78 | 14.66 | 99.50 | 99.07 | 14.59 | 97.16 | 94.96 | 14.25 |
| 17 | 0.5 | 5 | 20 | 6 | 98.15 | 95.55 | 3.93 | 99.95 | 80.59 | 4.00 | 99.45 | 103.35 | 3.98 | 87.95 | 89.90 | 3.52 |
| 18 | 0.25 | 7 | 110 | 15 | 93.13 | 93.92 | 40.98 | 99.75 | 97.12 | 43.89 | 96.40 | 89.79 | 42.42 | 99.25 | 98.47 | 43.67 |
| 19 | 0.5 | 5 | 110 | 15 | 99.99 | 95.43 | 22.00 | 46.76 | 79.59 | 10.29 | 99.97 | 81.89 | 21.99 | 99.23 | 95.90 | 21.83 |
| 20 | 0.25 | 5 | 200 | 15 | 58.30 | 59.12 | 46.64 | 44.55 | 42.41 | 35.64 | 41.39 | 43.25 | 33.11 | 90.82 | 93.06 | 72.66 |
| 21 | 0.25 | 3 | 110 | 15 | 48.70 | 58.06 | 21.43 | 2.34 | 14.68 | 1.03 | 32.25 | 39.64 | 14.19 | 79.85 | 82.03 | 35.13 |
| 22 | 0.5 | 5 | 200 | 24 | 99.98 | 95.31 | 39.99 | 99.55 | 78.60 | 39.82 | 62.29 | 60.43 | 24.91 | 98.07 | 95.25 | 39.23 |
| 23 | 0.5 | 5 | 20 | 24 | 99.45 | 108.39 | 3.98 | 97.05 | 105.58 | 3.88 | 95.95 | 103.35 | 3.84 | 85.25 | 89.90 | 3.41 |
| 24 | 0.5 | 3 | 110 | 6 | 80.67 | 82.07 | 17.75 | 47.47 | 50.13 | 10.44 | 76.17 | 72.03 | 16.76 | 98.20 | 100.03 | 21.60 |
| 25 | 0.5 | 5 | 200 | 6 | 79.36 | 82.47 | 31.74 | 46.19 | 53.60 | 18.48 | 42.63 | 60.43 | 17.05 | 97.37 | 95.25 | 38.95 |
| 26 | 0.75 | 3 | 110 | 15 | 99.46 | 103.83 | 14.59 | 99.58 | 110.58 | 14.61 | 96.67 | 104.41 | 14.18 | 98.69 | 99.10 | 14.47 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd removal | |||||
| Model | 4880.45 | 8 | 610.06 | 16.66 | <0.0001 |
| A—biochar mass | 1696.55 | 1 | 1696.55 | 46.34 | <0.0001 |
| B—pH | 577.15 | 1 | 577.15 | 15.76 | 0.001 |
| C—cin | 513.13 | 1 | 513.13 | 14.02 | 0.0016 |
| D—time | 494.69 | 1 | 494.69 | 13.51 | 0.0019 |
| AB | 483.2 | 1 | 483.2 | 13.2 | 0.0021 |
| AC | 427.15 | 1 | 427.15 | 11.67 | 0.0033 |
| AD | 320.57 | 1 | 320.57 | 8.76 | 0.0088 |
| A2 | 368.03 | 1 | 368.03 | 10.05 | 0.0056 |
| Cr removal | |||||
| Model | 16,600.2 | 5 | 3320.04 | 9.5 | <0.0001 |
| A—biochar mass | 6735.13 | 1 | 6735.13 | 19.27 | 0.0003 |
| B—pH | 3451.47 | 1 | 3451.47 | 9.88 | 0.0051 |
| C—c, in | 2185.25 | 1 | 2185.25 | 6.25 | 0.0212 |
| D—time | 1874.78 | 1 | 1874.78 | 5.37 | 0.0313 |
| AB | 2353.57 | 1 | 2353.57 | 6.74 | 0.0173 |
| Cu removal | |||||
| Model | 11,160.81 | 4 | 2790.202 | 16.41202 | <0.0001 |
| A—biochar mass | 3541.032 | 1 | 3541.032 | 20.82842 | 0.000169 |
| B—pH | 1167.702 | 1 | 1167.702 | 6.868446 | 0.015972 |
| C—cin | 5526.808 | 1 | 5526.808 | 32.50879 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 925.2658 | 1 | 925.2658 | 5.442431 | 0.029679 |
| Pb removal | |||||
| Model | 279.99 | 6 | 46.66 | 4.35 | 0.0069 |
| A—biochar mass | 9.4 | 1 | 9.4 | 0.8766 | 0.3615 |
| B—pH | 16.8 | 1 | 16.8 | 1.57 | 0.2266 |
| C—cin | 86.05 | 1 | 86.05 | 8.03 | 0.011 |
| AC | 39.03 | 1 | 39.03 | 3.64 | 0.0724 |
| B2 | 48.69 | 1 | 48.69 | 4.54 | 0.0471 |
| C2 | 65.68 | 1 | 65.68 | 6.13 | 0.0235 |
| PSO | PFO | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cd | Cr | Cu | Pb | Cd | Cr | Cu | ||
| qe (mg/g) | 3.008 | 3.019 | 3.018 | 3.028 | qe (mg/g) | 1.573 | 1.973 | 2.273 | 2.461 |
| k2 (g/mg·h) | 5.212 | 2.533 | 0.681 | 1.077 | k1 (h−1) | 1.689 | 1.732 | 0.604 | 0.989 |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.981 | 0.993 | R2 | 0.922 | 0.918 | 0.916 | 0.984 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cd | Cr | Cu | Pb | Cd | Cr | Cu | ||
| qm | 39.996 | 26.042 | 18.018 | 17.986 | n | 1.570 | 2.285 | 2.861 | 2.766 |
| kl | 0.594 | 0.492 | 0.074 | 0.146 | kf | 12.622 | 6.448 | 3.195 | 3.542 |
| R2 | 0.773 | 0.997 | 0.864 | 0.988 | R2 | 0.990 | 0.865 | 0.975 | 0.997 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakić, D.; Posavčić, H.; Licht, K.; Vouk, D. Application of Novel Biochar Derived from Experimental Sewage Sludge Gasification as an Adsorbent for Heavy Metals Removal. Sustainability 2025, 17, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030997
Nakić D, Posavčić H, Licht K, Vouk D. Application of Novel Biochar Derived from Experimental Sewage Sludge Gasification as an Adsorbent for Heavy Metals Removal. Sustainability. 2025; 17(3):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030997
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakić, Domagoj, Hana Posavčić, Katarina Licht, and Dražen Vouk. 2025. "Application of Novel Biochar Derived from Experimental Sewage Sludge Gasification as an Adsorbent for Heavy Metals Removal" Sustainability 17, no. 3: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030997
APA StyleNakić, D., Posavčić, H., Licht, K., & Vouk, D. (2025). Application of Novel Biochar Derived from Experimental Sewage Sludge Gasification as an Adsorbent for Heavy Metals Removal. Sustainability, 17(3), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030997








