Abstract
Expanding urbanization in highly fragile desert environments requires a thorough understanding of the current state and trends of land uses to achieve an optimal balance between development and the integrity of vital ecosystems. The objectives of this study are to quantify land use change over the 25-year period 1990–2015 and analyze temporal and spatial urbanization trends in the Middle Rio Grande Basin. We conclude by indicating how the results can inform on-going water resource research and public policy discussion in an arid region. Results show that the predominant upland mixed vegetation land cover category has been steadily declining, giving up land to urban and agricultural development. Urban development across the region of interest increased from just under three percent in 1990 to more than 11 percent in 2015, mainly around the major urban areas of El Paso, Ciudad Juárez, and Las Cruces. Public policy aspects related to results from this study include transfer of water rights from agriculture to land developers in cities, higher risk of flooding, loss of natural ecosystems, and increased water pollution from point and non-point sources. Various stakeholders can find the study useful for a better understanding of historical spatial and temporal aspects of urban development and environmental change in arid regions. Such insights can help municipal authorities, farmers, and other stakeholders to strike a balance between development needs and protecting vital ecosystems that support the much needed development, especially in regions that are endowed with transboundary natural resources that often are incompletely represented in single nation data.
Keywords:
transboundary; arid; water resources; urbanization; agriculture; land use; land cover; environmental impacts 1. Introduction
Concerns on the impact of rapid urbanization on natural resources are increasing with growing population in many parts of the world [1,2,3,4]. Global urban population increased from 746 million in 1950 (30 percent of global population) to 3.9 billion in 2014 (54 percent), and this urban population proportion is expected to grow to 66 percent by 2050 [5]. Urbanization is indeed a pertinent issue in the Middle Rio Grande Basin, where, like many arid and semi-arid urbanized regions of the world, scarce natural resources, such as surface and groundwater, are part of fragile and highly managed ecosystems. One of the most important pressures on resources is competition between user sectors that include agriculture, industry, domestic and public water supply, wildlife habitats, and recreation [6,7]. The basin has supported irrigated agriculture in the area spanning from southern New Mexico to Far West Texas and northern Chihuahua in Mexico for more than a century [8,9]. Three economically important urban centers, El Paso, Texas, Las Cruces, New Mexico, and Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, Mexico are now home to a combined population of more than 2.4 million people [10], and the appetite for more land to accommodate both outward expansion and intense redevelopment is still high [11]. Urban expansion involves increased water use through land use/land cover change—the use of water in urban landscaping and gardening—as well as growing populations consuming residential, commercial, and industrial supplies. Recent studies [12,13,14] remind us that knowledge of the extent and rate of urbanization is of immense interest to growing urban settlements and watersheds for a wide range of purposes that include urban planning, water and land resource management, marketing analysis, tourism, and forestry analysis, among others.
Change detection technologies, such as remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS), are often not constrained by administrative boundaries, making the tools ideal vehicles to promote cross-border studies and to explore transboundary data harmonization opportunities. Remote sensing-based approaches provide cities with specific alternative techniques to monitor urban sprawl [15,16]. It follows that urban sprawl can be monitored across administrative boundaries at various levels using change detection tools. Remote sensing and GIS can help stakeholders to map where changes are happening, get a better understanding of how development patterns influenced by human actions and natural climatic and seasonal landscape changes may trend over time, and therefore evaluate current actions and policies, and anticipate and plan for future changes accordingly. However, there are widely acknowledged constraints or barriers to the use of remote sensing and GIS technologies. These include: (1) hardware and expertise costs, (2) data costs from certain remote sensing platforms that are not free, (3) perceived lack of remote sensing product accuracy, including spatial, spectral, and radiometric accuracy in comparison to in situ measurements, and (4) concerns over data continuity and programmatic support [17,18,19].
A number of investigations have applied remote sensing technology to study land use along different sections of the Rio Grande Basin. For example, a comparative study involving Landsat Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) and IKONOS images was conducted to map active crop lands in the Upper Valley and Lower Valley of El Paso County, Texas [20]. In [21], a supervised maximum likelihood classification system was applied on Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) imagery during a feasibility study on the construction of a binational wetland along the U.S.–Mexico border. The study by [19] mapped riparian vegetation using high resolution airborne multi-spectral imagery, while [22] used aerial photography and a maximum likelihood classifier to map invasive weed infestations in the basin. In another example, an evaluation of airborne hyperspectral imagery was conducted using four different classifiers: maximum likelihood, spectral angle mapper, mixture tuned matched filtering, and support vector machine in mapping saltcedar infestations along the Rio Grande in West Texas [23].
However, comprehensive urbanization studies that integrate the whole Middle Rio Grande Basin to help understand the combined impacts of urban growth and other human impacts on either side of the U.S.–Mexico border in this shared but vulnerable ecosystem that straddles the two countries are scarce. For example, a systems dynamic model was developed to simulate future land use changes for a 10 to 20 year time horizon for commercial, industrial, and residential sectors based on Stella software, but the focus of the case study was the City of Ciudad Juárez in Mexico [11]. Similarly, a rule-based object oriented classification approach was applied to classify QuickBird imagery in a small area of interest in the City of Ciudad Juárez [24]. A significant finding from this study was that rapid urbanization is contributing to significant landscape fragmentation and compromising natural ecological functions in the desert environment. At the national level, the National Land Cover Database (NLCD) that was produced by the Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics (MRLC) consortium [25] is the main source of comprehensive and consistent land-cover data in the United States. The most recent publicly available national land-cover product is the National Land Cover Database 2011 (NLCD 2011) [26].
Municipal authorities and other competing users of natural resources in such a water-scarce a region are well served by a thorough understanding of some fundamental questions associated with the rapid growth of urban areas. Key questions include: (1) what is the extent, and how fast is urbanization and other land use changes happening in the Middle Rio Grande Basin region? (2) where is the land for urbanization coming from?, and (3) what are the impacts of urbanization on agricultural and other land uses in the region? The objectives of this study are: (1) to quantify land use change over the 25-year time period and analyze temporal and spatial urbanization trends, including other broadly defined land use categories (Table 1) and (2) to present how the results can inform on-going water resource research and public policy discussion in an arid region.

Table 1.
Definition of land use categories used in the study.
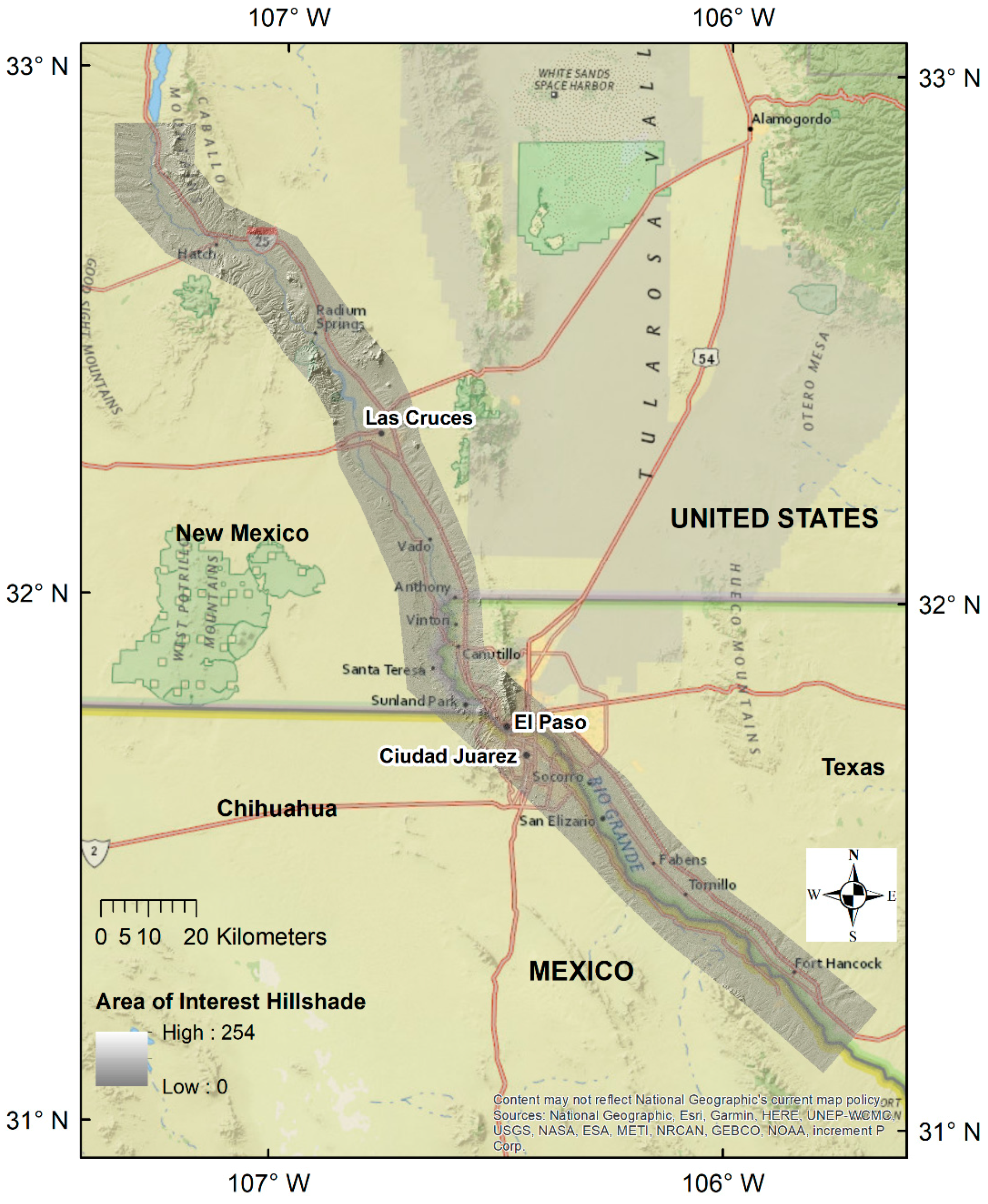
Our selected region of interest for this study is a 16 km (10 mile) wide swath either side of the Rio Grande from below the Caballo Reservoir in south central New Mexico to downstream of Fort Hancock (Figure 1). The total study area was 4288 km2 (1655 sq miles). This area includes the urban development in the major population centers of Las Cruces, El Paso, and Ciudad Juárez, as they expand into the irrigated agricultural zone located along the Rio Grande valley. It begins where river water is released for irrigation and urban use and ends with the end of the irrigation zone. The uplands are occupied by mountains and the Chihuahuan desert ecosystem.
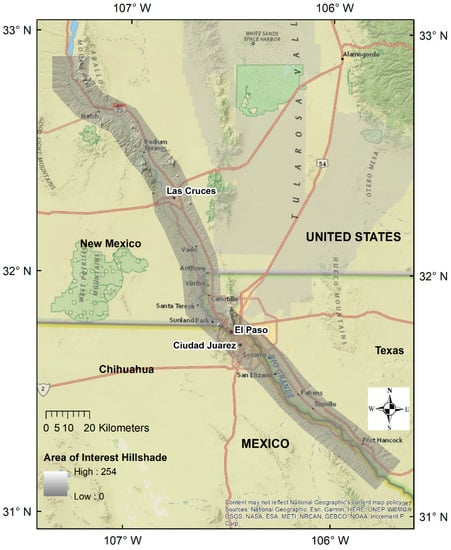
Figure 1.
The study area showing the region of interest delineated by a hillshade.
In addition to alternative methods for comparing change (Table 2), the following two major types of change have been suggested: (1) a change in the location of features and (2) a change in character or magnitude of features [27]. Our study integrates remote sensing and GIS techniques and it focuses on the “measuring change” and “time series” methods to assess urbanization trends for a 25-year temporal window from 1990 to 2015 in the transboundary Middle Rio Grande Basin (Figure 1).

Table 2.
Methods of comparing change.
2. Materials and Methods
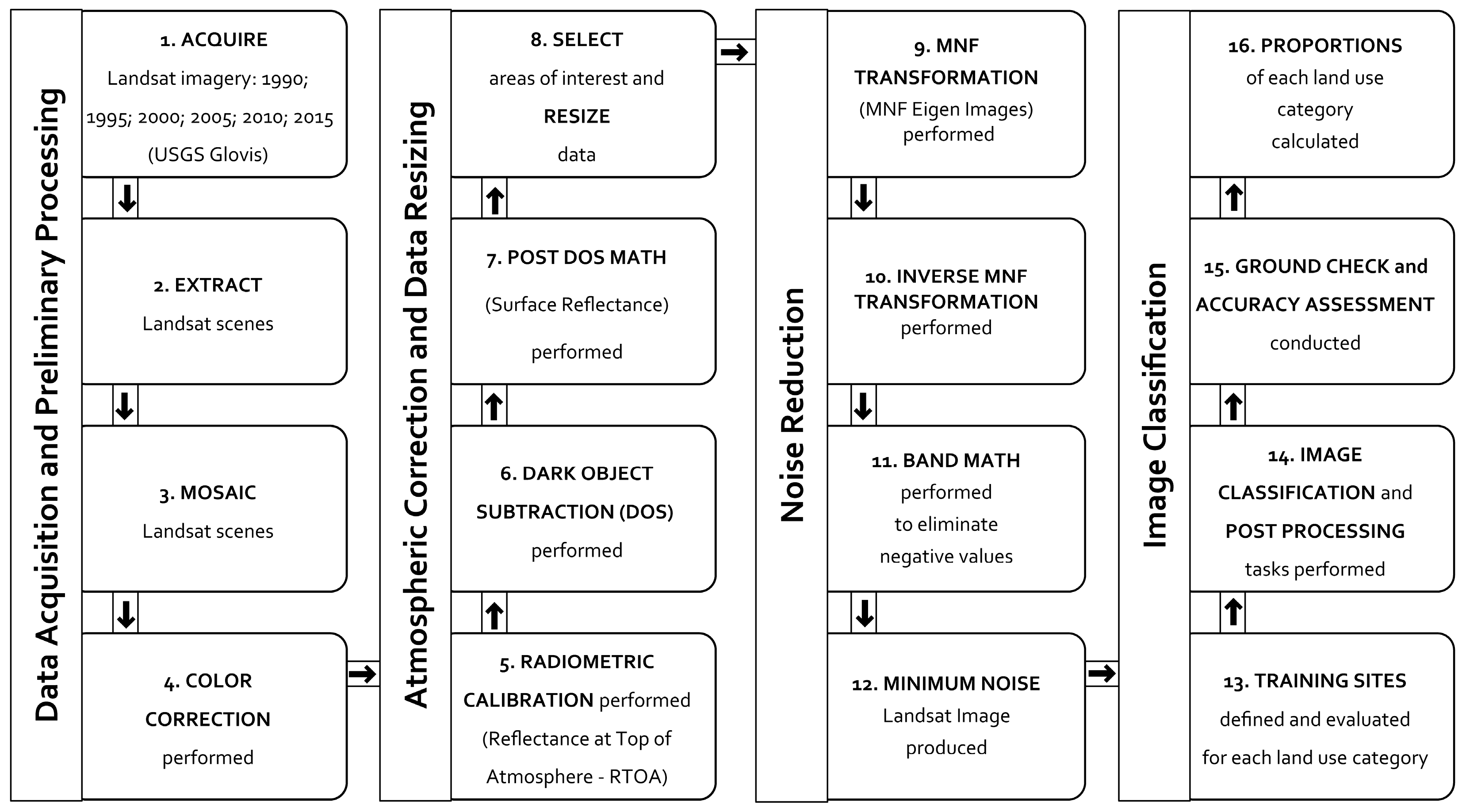
The methodology workflow integrating remote sensing and GIS methods that was applied in this study is shown in Figure 2. Major steps included imagery data acquisition and preliminary processing, atmospheric correction and data resizing, noise reduction, and image classification. Selected aspects of these four major steps are described below. The analysis was performed using a suite of standard software applications that included ArcGIS Desktop, ArcGIS Online, ENVI, Microsoft Excel, and Google Earth Pro.
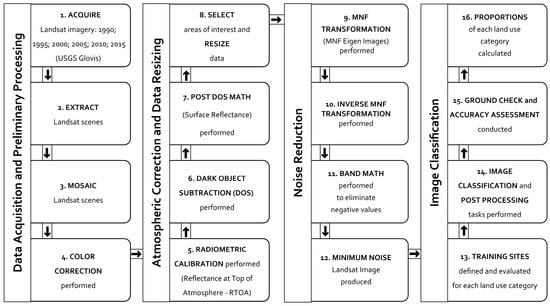
Figure 2.
Workflow diagram showing integrated remote sensing—GIS methods used for the study.
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preliminary Processing
Landsat images were acquired [28] for the years 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, and 2015. The region of interest shown in Figure 1 is covered by the following seven multispectral Landsat scenes (Path/Row): 031/039, 032/038, 032/039, 033/037, 033/038, 034/037, and 034/038.
Each scene had 10 percent or less cloud cover. Landsat missions that provided the images for the chosen region of interest include Landsat 5 Thematic Mapper (TM), Landsat 7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+), Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI), and Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS). Acquisition dates for the Landsat images ranged between the months of June and August, and so were considered “leaf on”. Preliminary processing steps on the imagery included extracting the imagery to the study area boundaries, creating mosaics, and color correction.
2.2. Atmospheric Correction and Data Resizing
Atmospheric correction was carried out using the widely cited procedure in [29]. Specific steps included radiometric calibration to determine reflectance at the top of the atmosphere, dark object subtraction (DOS) for haze and moisture correction, and post-DOS computations to determine surface reflectance. All atmospheric correction procedures were performed while using the module implemented in ENVI software, and the steps repeated to cover scenes for all the years analyzed. The images were then resized to selected regions of interest across the study area.
2.3. Noise Reduction
The minimum noise fraction (MNF) linear transformation procedure was used to transform the resized images for all analysis years. This noise reduction technique that was widely applied in remote sensing is implemented in ENVI software (see [30,31] for details), and it reduces inherent spectral dimensionality and data noise. We approved the final minimum noise Landsat images that were used for classification based on both eigenvalue plots and visual inspection of the images.
2.4. Supervised Classification
Supervised classification is among one of the most extensively applied land use classification techniques, for example, [32,33,34,35,36,37]. The technique involves collecting training samples that are then used to derive spectral signatures of pixels in an image, and therefore it requires prior knowledge of land use types in the study area. Pixel signatures are generated and stored in signature files, and digital numbers (DN) of each pixel are then converted to radiance values [38,39]. The interactive supervised classification module that was used to classify the minimum noise images is found in ArcMap software [40]. The module was applied for the six analysis years of 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, and 2015 using the four broad land use categories, as defined in Table 2. Spectral signatures of the training samples were first analyzed using statistical methods. A satisfactory spectral signature is one that minimizes confusion between different land use categories to be mapped [41]. The whole region of interest was classified by assigning each image cell to the training sample category of the highest probability of match. On average, 150 training samples were created for each land use category using the 1990 Landsat TM imagery, since this was the year with the least amount of developed land. A minimum of 500 pixels for each training sample category were used.
2.5. Post Processing Tasks
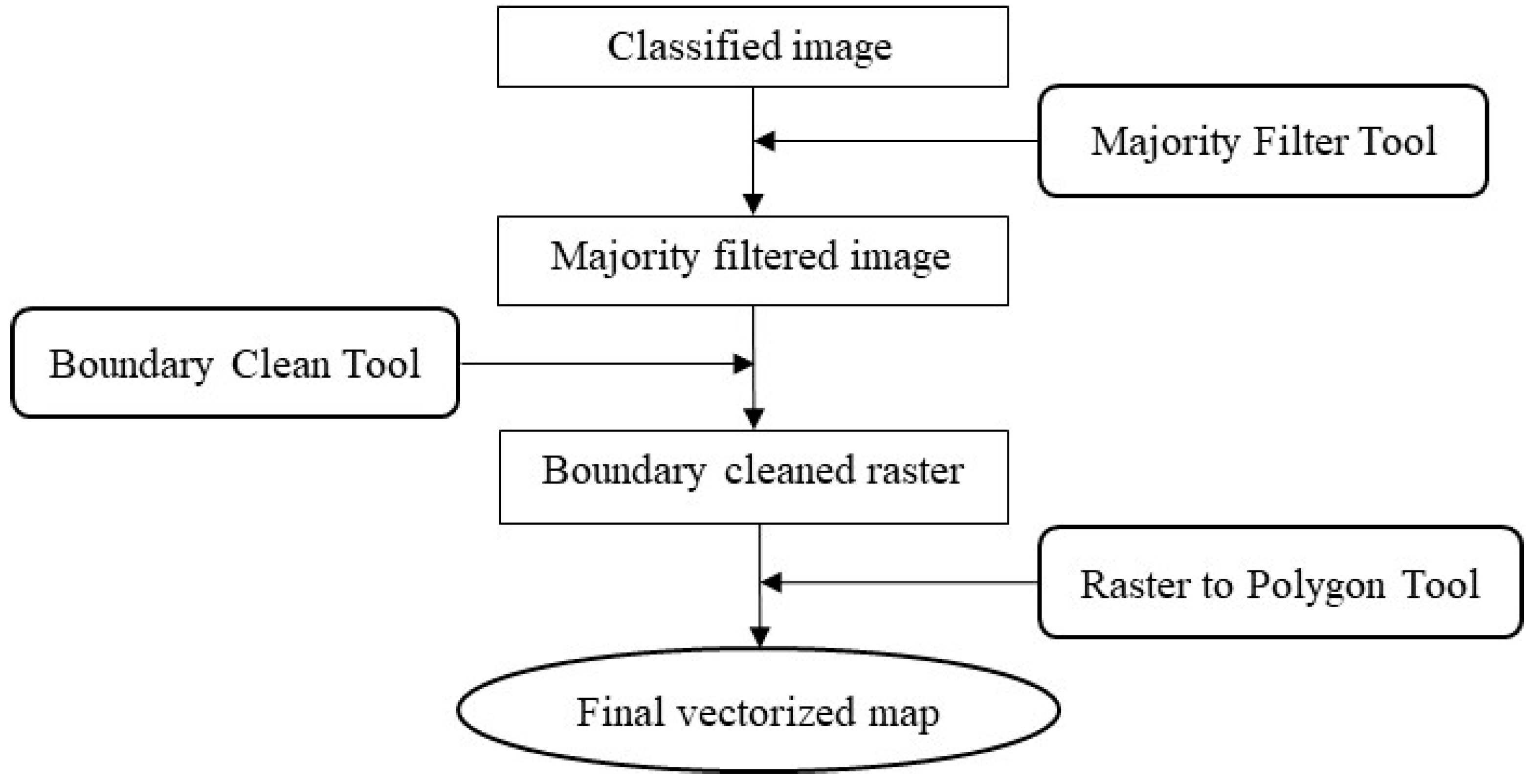
Post classification processing was done to remove noise generated from misclassified isolated pixels or small regions in the classified output, and to smooth out boundaries between classified categories. Conducting post classification processing tasks involves a fine balance between achieving a good quality classified final output and the potential loss of important map details through the excessive use of generalization tools [16]. The workflow chart in Figure 3 summarizes the post processing procedure that was followed in this study. These steps were accomplished through a series of geoprocessing tools in the Spatial Analyst Extension of ArcGIS.
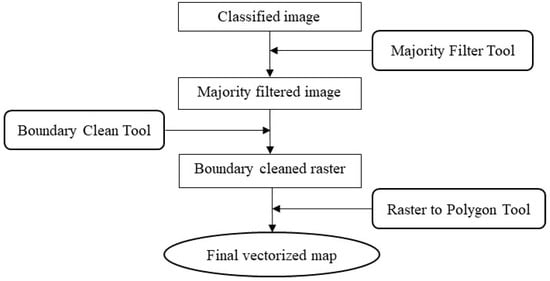
Figure 3.
Flowchart of post processing tasks performed in this study.
2.6. Ground Checking
Field visits were made to selected familiar features in the study region to check for correspondence between the classified features and their actual location on the ground using portable Global Positioning System (GPS) units. Because it was not practical to collect GPS points across the whole study area, some of the land use categories assigned to places that were familiar to our team were checked through image visualization in Google Earth.
2.7. Accuracy Assessment
The reliability of classification was determined by calculating the overall accuracy as well as the classification accuracy of individual land use categories. This was accomplished through the construction of a confusion matrix, or an error matrix of omission and commission [42] for each region of interest. The following five statistics were calculated: (1) overall accuracy, (2) Kappa coefficient, (3) user accuracy, (4) producer accuracy, (5) omission error, and (6) commission error. Overall accuracy represents the proportion of all correct classifications; the Kappa coefficient is a measure of agreement of accuracy in classification assessment [43]; user accuracy is a calculation of the probability that a pixel classification is correct on the ground, and producer accuracy is the probability that a pixel of a particular land use type is assigned the correct land use category. Omission errors represent certain categories that were omitted when they exist on the ground, while the commission errors represent categories that were identified as existing on the ground when in fact they do not.
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Assessment
We classified 18 maps for each of the years 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, and 2015:6 for the larger region of interest, and six each for the extracted subregions focusing on major urban areas of El Paso-Ciudad Juárez and Las Cruces. For simplicity, we only detail accuracy assessment results for the larger region of interest, focusing on analysis year 2015. The quality of our classification is provided in the form of an error matrix, a widely used tool to present accuracy assessment information in remote sensing [38,39]. An average of 122 sampling points were used for each analysis year, and the overall accuracy ranged from 85 percent in 2005 to 93 percent for the year 2015. The overall Kappa coefficient of 89 percent statistically supported the overall accuracy of the classification scheme used. Producer accuracy for all land use categories ranged from 80 percent to 95 percent for the year 2015, and user accuracy from 80 to 97 percent (Table 3). A typical reasonable number of sampling points is around 25–30 points, and the overall classification accuracy and accuracy for all classes greater than the 75–85 percent is acceptable, given that accuracy assessment is a compromise between the ideal and the affordable [3,16,44]. In an evaluation of the national standard U.S. National Land Cover Database (NLCD) classification system [45], an acceptable overall classification accuracy in the range of 84–85 percent for most satellite data classification studies is recommended. We generated an average of 122 points for each analysis year, and the reliability of our classified results is generally acceptable, since the ranges of our accuracy assessment results are within these minimum recommended ranges (Table 3).

Table 3.
Error matrix for 2015 image showing classification errors of omission and commission.
3.2. Quantification of Regional Land Use Change and Trends
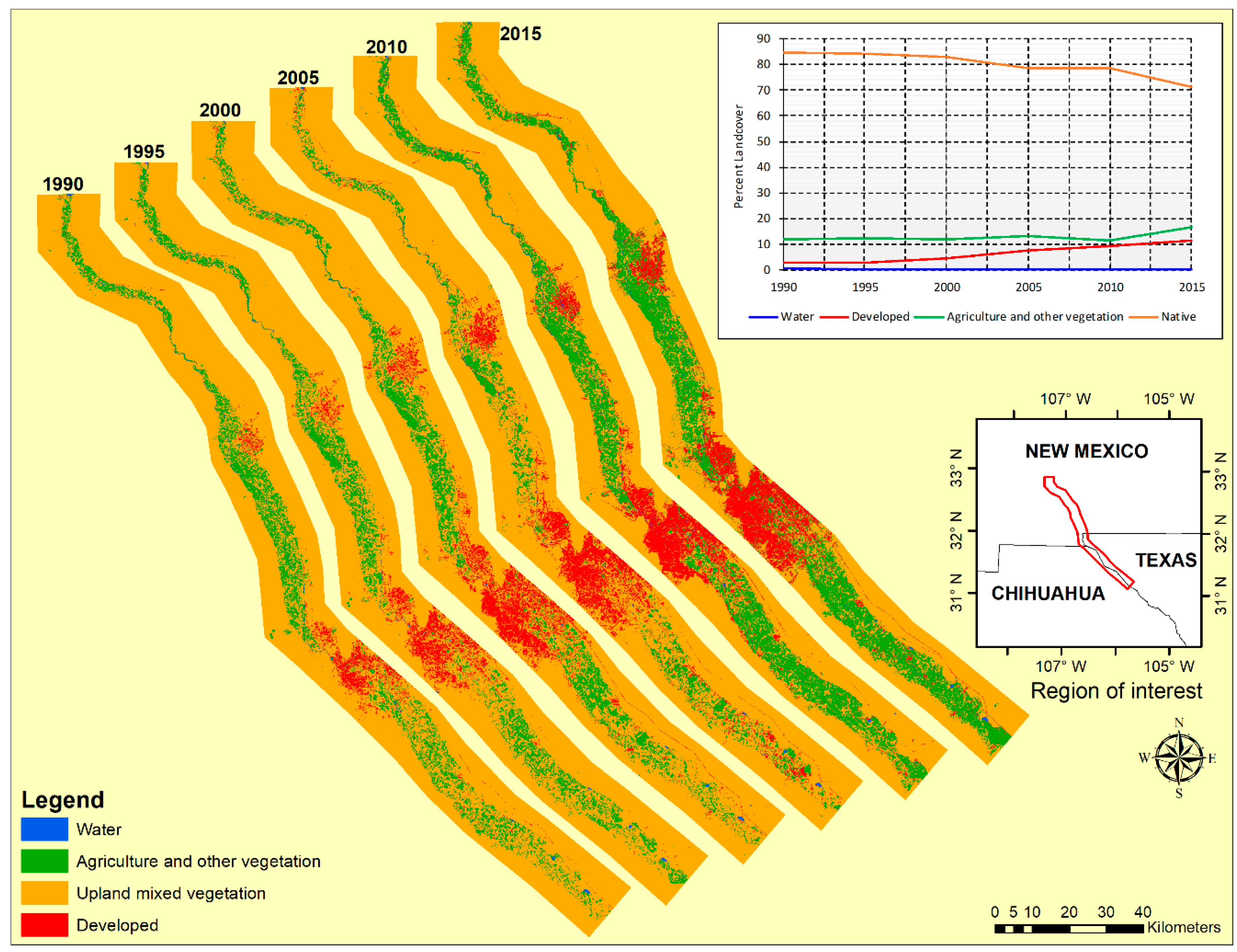
A post-classification comparison technique of the time series images was applied in ArcGIS to determine the nature, size, and spatial location of changes. Upland mixed vegetation was the most dominant category based on our broadly defined classes in the delineated areas of interest, followed by the agriculture and other vegetation category (Table 4 and Figure 4). Our results revealed an increasing urbanization trend from 2.92 percent (125.2 km2) in 1990 to 11.31 percent (485.1 km2) in 2015 for the whole region of interest, and this is also reflected in the land use change mapping results for the 25-year period 1990–2015. The main urban centers of El Paso, Ciudad Juárez, and Las Cruces are unsurprisingly responsible for this increase in urban growth. Close examination of the land use trend lines in Figure 4 shows that the upland mixed vegetation category is the main contributor of land for urban development, declining from 84.6 percent (3627.2 km2) in 1990 to 71.4 percent (3060.4 km2) in 2015. In our category definition table, upland mixed vegetation land use includes fallow agricultural land, so it is reasonable to expect its proportion to fluctuate with variations in the area under crop cultivation as well. The trendline for agriculture and other vegetation category was fairly stable, at just over 10 percent between 1990 and 2010, and it then increased to nearly 19 percent in 2015 (Figure 4). This can be attributed mainly to the intensification of agricultural activities for the 2015 analysis year. The water category trendline is less than 0.5 percent over the whole analysis period, consistent with a dry region that is not typically endowed with significant open natural surface water bodies. The nearest large dams of Caballo and Elephant Butte are located just outside the region of interest that was delineated for this study.

Table 4.
Land use quantification results for region of interest and urban areas.
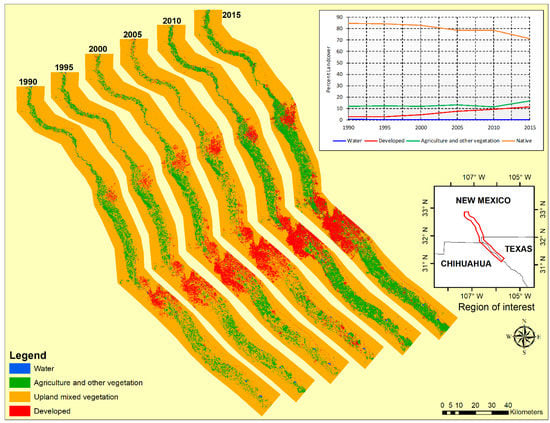
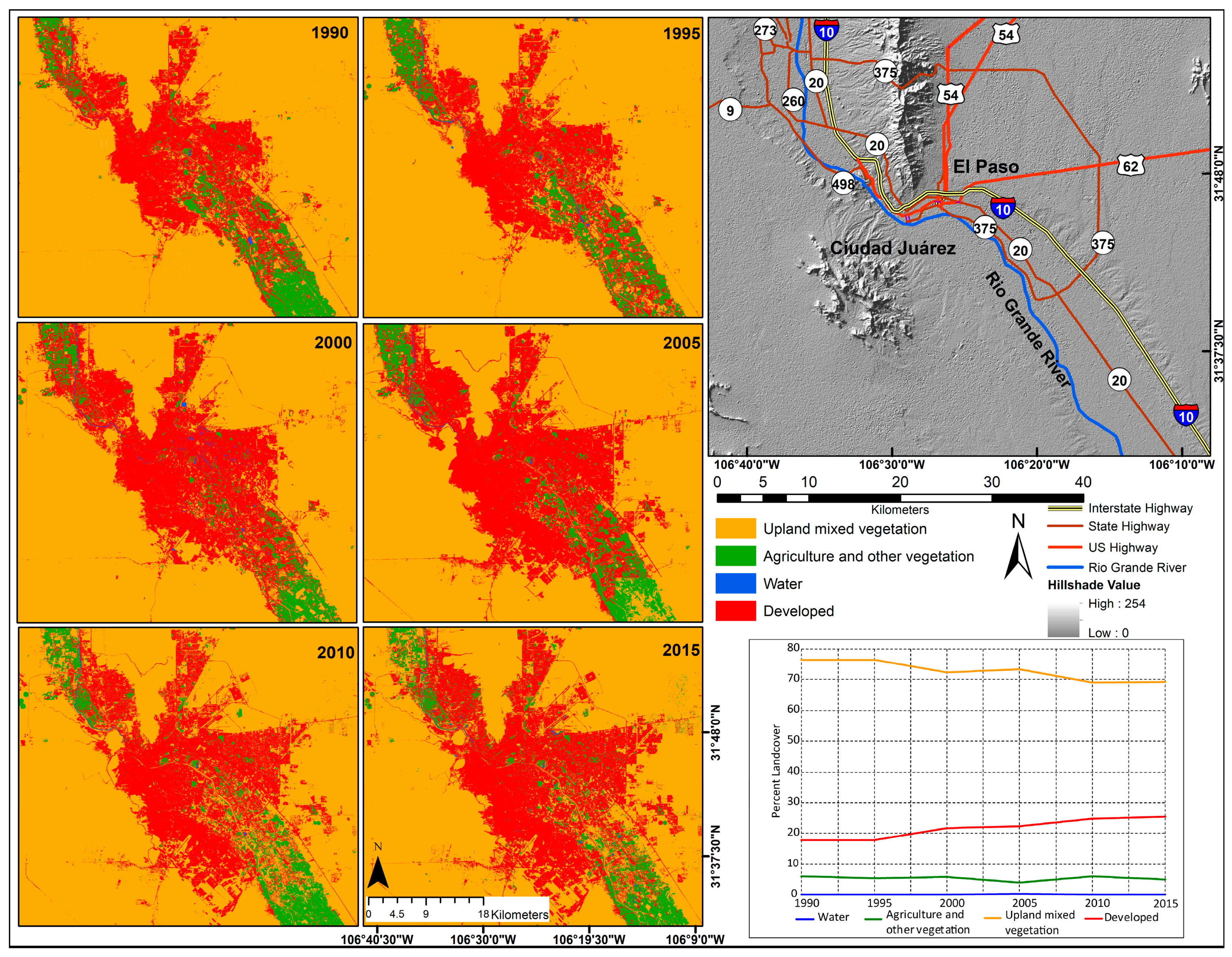
Figure 4.
Land use land/cover maps in region of interest.
3.3. Land Use Change by Urban Area
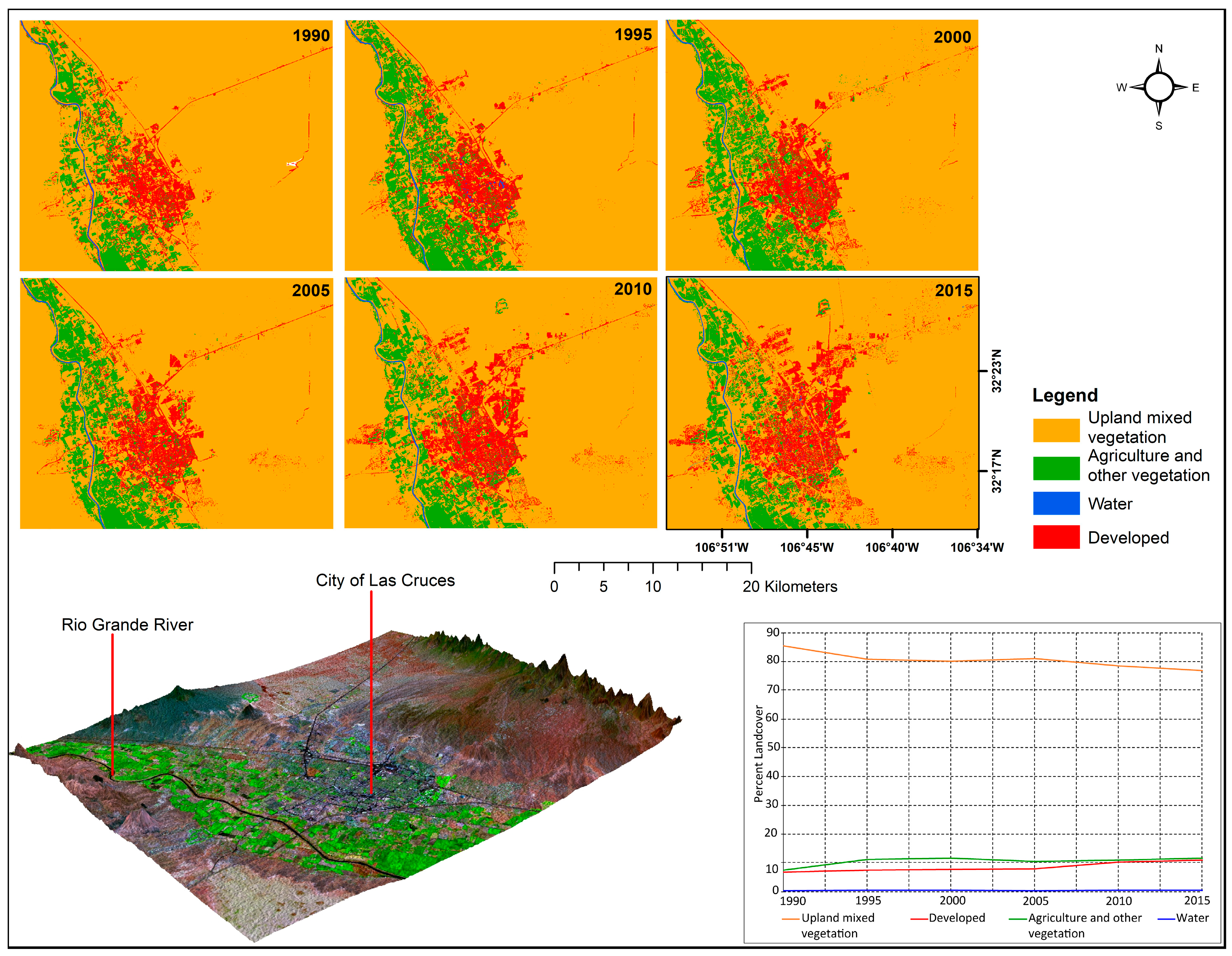
To better understand the rate of change around urban areas, we zoomed in and focused on the three major urban settlements—the neighboring cities of El Paso and Ciudad Juárez combined into one sub region of interest, and Las Cruces. Similar to the whole region of interest results that are shown in Figure 4, these two regions of interest were classified using the interactive supervised classification module in ArcGIS, and the changes quantified using the same four broad categories of land use for the period 1990–2015. The classification results for the two urban regions of interest are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
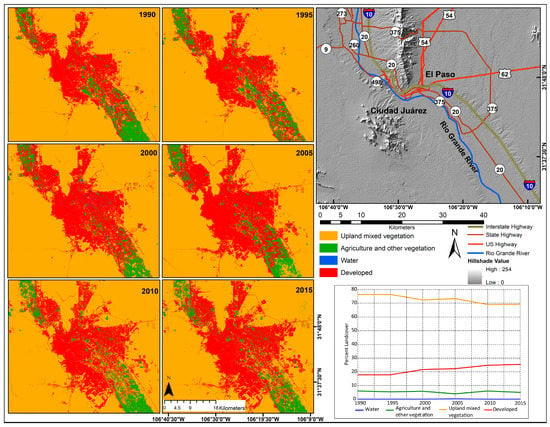
Figure 5.
Land use change around the El Paso-Ciudad Juárez metropolitan area, 1990–2015.
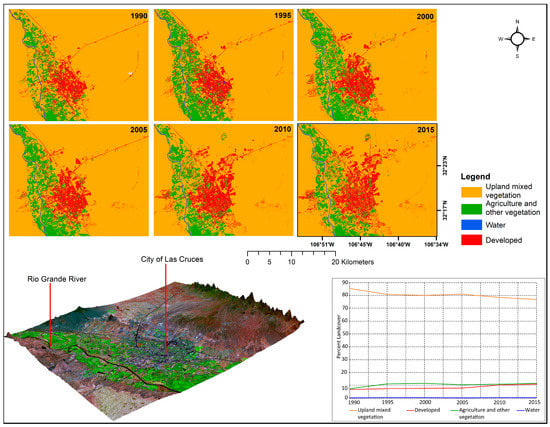
Figure 6.
Land use change around the City of Las Cruces, 1990–2015.
3.3.1. El Paso-Ciudad Juárez Metropolitan Area
The period 1990 to 2015 experienced an increase built up area (Figure 5). Urban sprawl can be visualized on the time series maps, especially towards east El Paso and southern Ciudad Juárez. The developed category proportion was about 17.7 percent (482.2 km2) in 1990 and it grew to 25.4 percent (692 km2) of this sub region of interest, or an increase of 43.5 percent, taking the 1990 level of urbanization as the base year (Table 4). The agriculture and other vegetation category was nearly constant at around 5 percent for the analysis period. Any slight fluctuations in this largely urban region of interest can be attributed to changes in the amount of land that was in and out of cropland. The results also show an overall regression of the upland mixed vegetation category in this metro region, from 76.2 percent (2072.6 km2) in 1990 to 69.3 percent (1883.9 km2) in 2015. Reduction of upland mixed vegetation land can be attributed to the clearing of scrub land for urban development and the cropping of previously bare agricultural land that was classified under upland mixed vegetation. Change for the water category was insignificant as expected, less than 0.5 percent throughout the study period for area of interest that has no significant surface water bodies.
3.3.2. City of Las Cruces
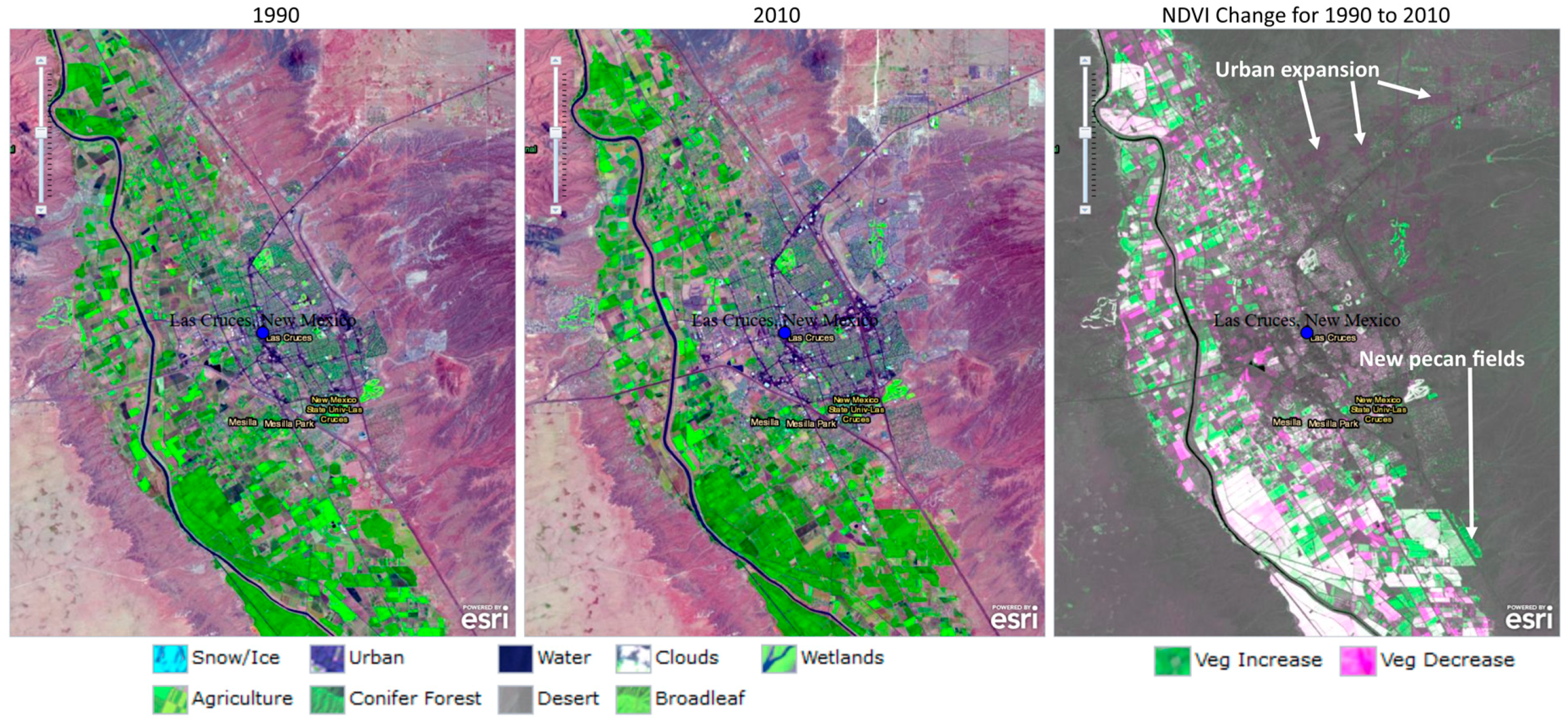
Visual and quantitative results of urbanization trends around the City of Las Cruces are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7, and Table 4. An increase in urban developments was mainly to the eastern side of the city, although there was urban encroachment into the agricultural areas around the southwestern part of the city (Figure 7). Urban development increased from about 7 percent of the sub region area of interest in 1990 (44.51 km2) to about 11 (72.83 km2) percent, or a growth of around 63.6 percent using the 1990 urbanization level as the base year (Table 4). Overall, the upland mixed vegetation land use category decreased continuously from 1990 to 2015, and this downward trend is mainly attributable to the intensification of urbanization, as demonstrated, for example, by the eastward expansion of the city (Figure 7). The fraction that is covered by the agriculture and other vegetation category fluctuated between 7.6 percent (50.4 km2) in 1990 and 11.7 percent (77.9 km2) in 2015. A substantial portion of agricultural land in this sub region of interest is permanently under pecan trees. The pecan tree cover appears as dark fields in the natural color, 1990 and 2010 change comparison image in Figure 7. The pecan fields are also shown among the no change white zones calculated in the Normalized Difference Vegetative Index (NDVI) [46] portion visualized on the right side of Figure 7. Changes in vegetation cover can be clearly visualized in Figure 7 as increased or decreased areas due to intense agricultural and urban development, respectively. NDVI change visualization in Figure 7 corroborates our finding showing a downward trend in the upland mixed vegetation land use category, as shown by a vegetation decrease as land was cleared for urban development, and an increase in vegetation cover as upland mixed vegetation or previously fallow fields were now under crops. Similar to other dry regions of interest in this study, the proportion of open water is an average of less than 0.5 percent over the analysis period.
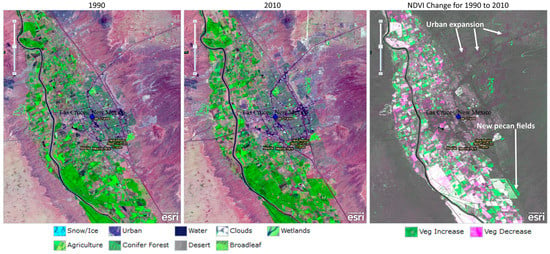
Figure 7.
Visualizing land use and Normalized Difference Vegetative Index (NDVI) change around the City of Las Cruces for the years 1990 and 2010 (Source: Esri Change Matters Viewer).
4. Discussion
4.1. Accuracy, Uncertainty and Errors
While our user and producer accuracy results were reasonable, difficulties were encountered in separating pixels for some classes. Accurate reference data is important for testing classification accuracy [47], and therefore classification errors in our results are partly due to impure training samples that captured mixed land use categories. For example, spectral mixing for water and agriculture and other vegetation categories was encountered for some locations where wetlands are known to exist, although these were isolated cases for this generally dry study region. Bare agricultural land was classified under the upland mixed vegetation category in our definition of land use categories (Table 2), and spectral confusion was also problematic between the upland mixed vegetation and developed categories. This was not a surprise for this study region, where abundant and naturally occurring stones are extracted from the natural environment and are used in construction projects. Classification errors are also attributable to the coarse 30 m spatial resolution of the Landsat images that were used for the study. Two or even more spectral classes were often observed within one pixel using this course resolution data, and this obviously affected the accuracy of classification. Other possible sources of intrinsic uncertainty and error that may have been propagated in this type of study includes subjectivity in interpreting the classification results, fuzzy boundaries between land use categories, and uncertainty in the supervised classification algorithm in assigning land use categories to mixed pixels. An alternative method of estimating classification accuracy is calculating the Kappa statistics to account for classification agreements due to chance. The overall Kappa coefficient of 89 percent calculated from Table 3 supported the overall accuracy of the classification scheme that was used in this study, despite the fact others argue that Kappa normally underestimates overall accuracy and it is therefore recommended for vegetation mapping [19,44].
4.2. Comparison Classification Results with other Published Work
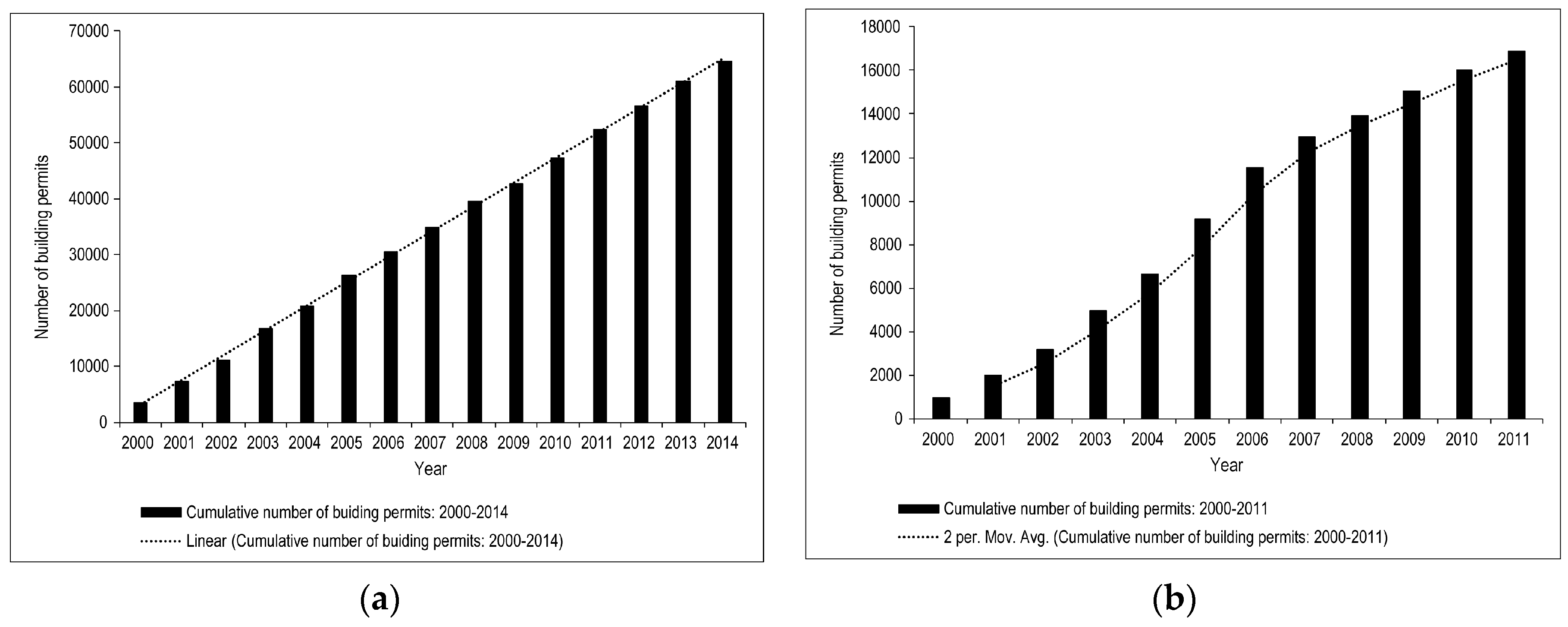
There is a paucity of comprehensive land use change studies covering both the U.S. side and the Mexican side of this transboundary metropolitan region to adequately compare our results with. A case study that was conducted on the Mexican side of the border showed an increase in urban related land cover between 2002 and 2007 in a third of the area of interest studied [24]. On the U.S. side of the border, we use the cumulative number of building permits for single-family and multifamily residential units compiled from U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) data for the City of El Paso as a proxy for urban development. Figure 8a shows a linear increase for the period 2000 to 2014. Although building permits do not necessarily reflect all construction activity that happened in this city, the trend that is reflected in Figure 8a is actually an underestimate because commercial units are not included in this data, in addition to structures that were constructed without a building permit, or under a different type of building permit [48]. Both examples on either side of the U.S.-Mexico border corroborate our findings on increasing urbanization trends in the El Paso-Ciudad Juárez metropolitan area. In Figure 8b, building permits for single-family and multifamily residential units for the City of Las Cruces increased exponentially from 2000 to 2005, but slowed down between 2006 and 2011 [49], reflecting a slowing down in permitting activity for the latter period. The overall trend supports our finding on increasing the development trends for the analysis period 1990–2015. We verified our classification results by comparing with reclassified results from the the U.S. NLCD [25]. For the most recent 2015 analysis year, we used the Data Enrichment algorithm in ArcGIS Online to calculate land use variables for our three regions of interest and then aggregated the results to the four broad land use categories in our classification scheme for this study. The results from the land use module in ArcGIS Online are based on the NLCD dataset for 2011, the latest land cover year that is available from the USGS that also falls within our analysis time frame for this study. We did not have an exact match of analysis years between the two classification systems, but we considered the two years close enough to provide a good sense of the comparison order of magnitudes. The comparison results after analysis in AGIS Online and aggregating the NLCD system land cover classes are shown in Table 5. Our results for the four defined land use categories are comparable to those that were derived from the NLCD classification system in the subregion of interest around the City of Las Cruces—the only area of interest that is wholly within the U.S. and covered by the NLCD (Table 5). Similarly, comparisons for years prior to 2015 produced comparable results through the application of geoprocessing tools in ArcGIS Desktop software to extract and reclassify historical NLCD data according to our customized land class aggregation scheme that is presented in Table 2. Slight differences between the NLCD and this study are attributed to possible sources of intrinsic uncertainty and error results discussed under the classification accuracy section, and the fact that we are not comparing data from exactly the same time snapshot. Table 5 also highlights the need to conduct a more comprehensive land use study that covers the transboundary Rio Grande basin on both the Mexico and U.S. sides of the border. Essentially, we are arguing that, in this transboundary basin, urbanization and other land use practices on either side of the border will impact shared resources that include both surface and groundwater.
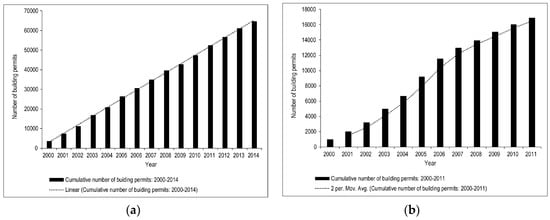
Figure 8.
(a) Cumulative total number of building permits in for the City of El Paso, 2000–2014; (b) Cumulative total number of building permits in the City of Las Cruces, 2000–2011.

Table 5.
Summary of land cover results calculated from National Land Cover Database (NLCD) in ArcGIS Online compared to results from this study.
5. Conclusions
This study utilized remote sensing and GIS technologies to assess and visualize trends in urban and other land uses in a rapidly growing but highly fragile arid environment. The results showed that urban development across the region of interest increased from just under three percent in 1990 to more than 11 percent in 2015, with most of the urban growth occurring around the major urban settlements of El Paso, Ciudad Juárez, and Las Cruces. The predominantly upland mixed vegetation land cover category has been steadily declining, giving up land to urban and agricultural development. There are significant natural capital implications that are associated with the conversion of land use from one category to another, especially in relation to the sustainable management of natural resources in desert environments.
Ultimately, what is at stake as cities in this dry region and other similar locations continue to urbanize or expand agricultural activities to produce more food for growing populations is the sustainability of natural areas that are taken over for such developments. Natural areas surrounding urban areas often provide valuable ecosystem services [50], among them water provision and purification, erosion control, and recreation, among others. Insights from this study will help to improve our understanding of historical spatial and temporal aspects of urban development and environmental change in this region, and help municipal authorities, farmers, and other stakeholders to strike a balance between development needs and protecting vital ecosystems that support the much needed development. The findings also provide crucial baseline data for resource managers, policymakers, and other stakeholders that are interested in estimating future demand for land and other shared resources in the basin. Our findings also have important consequences for the broader domain of transboundary natural resources utilization in economic development. Geospatial technologies, like remote sensing and GIS, can be applied across administrative boundaries and they are therefore vehicles that can promote cross-border cooperation through data harmonization and sharing arrangements at various levels. Groundwater is a key source of water in the Middle Rio Grande Basin, and there is need for better understanding of the interaction between this key resource and riparian vegetation along the Rio Grande through more detailed vegetation mapping and salinity studies using high resolution multi-spectral and hyperspectral imagery. Additional land use studies that are based on more detailed land use categories covering the whole Middle Rio Grande Basin are required, taking into account the need to manage shared water resources in this important transboundary basin in a holistic and coordinated manner. We also recommend a detailed examination of the driving forces behind the trends and the patterns of land use change revealed in this study as an area of future studies.
We end by highlighting some potential future research and public policy aspects of this study. We found that most of the land for urban development in the study region comes from the upland mixed vegetation category. The loss of grasslands, shrubs, and forests to urban development can lead to loss of natural habitats and ecological diversity, higher risk of flooding due to increased surface runoff in paved urban areas, and increased water pollution from point and non-point sources, such as new industries waste facilities. When considering outdoor recreation, loss of natural landscapes may decrease income from tourism that is associated with water-dependent natural ecosystems. Urban landscapes use significantly more water than upland mixed vegetation desert landscapes, an important factor in understanding regional water demand trends. Impacts of converting natural land to agriculture include soil erosion, siltation of dams and rivers, non-point source water pollution from agricultural lands, and fluctuations in groundwater levels, depending on whether there is depletion or recharge in the process of agricultural irrigation. The conversion of agricultural land to urban development in this region has resulted in the transfer of existing agricultural water rights to cities and developers, although the number of transferred water rights is not publicly available. The quantity of water used per area unit in urban areas versus irrigated agriculture is an important direction for research, as are policy changes to reallocate possible water savings. Likewise, land use change implies the alteration of percolation to groundwater. Other impacts include increased point source pollution from industrial developments, increased unit cost of water in the urban sector when compared to agriculture, and increased water treatment costs to meet the higher quality water levels that are required by urban and industrial consumers. The change in water use in the urbanization of agricultural land is an important topic, and knowledge of land use change thus provides an important background to this area of future study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M., W.H. and J.H.; Formal analysis, S.M. and O.B.; Investigation, S.M., O.B., W.H. and J.H.; Methodology, S.M., O.B. and C.R.; Software, O.B. and C.R.; Writing—original draft, S.M.; Writing—review & editing, S.M., W.H. and J.H.
Funding
This research was funded by the NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF FOOD AND AGRICULTURE, U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, grant number 2015-68007-23130. The opinions in this paper are those of the authors, and not necessarily reflect the views of the USDA.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge valuable comments and inputs from various collaborators on the USDA-NIFA project. We thank 3 anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sleeter, B.M.; Sohl, T.L.; Wilson, T.S.; Sleeter, R.R.; Soulard, C.E.; Bouchard, M.A.; Sayler, K.L.; Reker, R.R.; Griffith, G.E. Projected Land-Use and Land-Cover Change in the Western United States. In Baseline and Projected Future Carbon Storage and Greenhouse-Gas Fluxes in Ecosystems of the Western United States; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Vibhute, A.D.; Nagne, A.D.; Gawali, B.W.; Mehrotra, S.C. Comparative Analysis of Different Supervised Classification Techniques for Spatial Land Use/Land Cover Pattern Mapping Using RS and GIS. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2013, 4, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar]
- Wondrade, N.; Dick, O.B.; Tveite, H. GIS Based Mapping of Land Cover Changes Utilizing Multi-Temporal Remotely Sensed Image Data in Lake Hawassa Watershed, Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1765–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoumi, H.E.; Roque, D. Evaluation of Urban Sprawl Speed and Intensity Based on International Urbanization. Example from a Mexican City. J. Settl. Spat. Plan. 2015, 6, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision, Highlights; (ST/ESA/SER.A/352); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, L.; Brown, C.; Demeter, K.; Lasserre, F.; Milanés-Murcia, M.; Mumme, S.; Sandoval-Solis, S. Existing Opportunities to Adapt the Rio Grande Basin Water Resources Allocation Framework. Water 2016, 8, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, S.L.; Thomas, B.F.; Reager, J.T.; Rodell, M.; Swenson, S.C.; Famiglietti, J.S. Groundwater Depletion during Drought Threatens Future Water Security of the Colorado River Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5904–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, F.A.; Booker, J.F.; Michelsen, A.M. Integrated Economic, Hydrologic, and Institutional Analysis of Policy Responses to Mitigate Drought Impacts in Rio Grande Basin. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2006, 132, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, A.M.; Shrestha, M.; Boone, C.G.; Zhang, S.; Harrington, J.A.; Prebyl, T.J.; Swann, A.; Agar, M.; Antolin, M.F.; Nolen, B.; et al. Land Fragmentation under Rapid Urbanization: A Cross-Site Analysis of Southwestern Cities. Urban Ecosyst. 2011, 14, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Ibáñez, C.G.; Heyman, J. The U.S.-Mexico Transborder Region: Cultural Dynamics and Historical Interactions; University of Arizona Press: Tusang, AZ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Peña, S.; Fuentes, C.M. Land Use Changes in Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua: A Systems Dynamic Model. Director 2007, 8, 65–89. [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin, J.; Brabyn, L. Using Remote Sensing and GIS to Investigate the Impacts of Tourism on Forest Cover in the Annapurna Conservation Area, Nepal. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 43, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.; Shabbir, R.; Ahmad, S.S.; Aziz, N. Land Use Change Mapping and Analysis Using Remote Sensing and GIS: A Case Study of Simly Watershed, Islamabad, Pakistan. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, M.A.; Atif, I.; Iqbal, J. Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Assessment of Urban Sprawl in Karachi, Pakistan. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2015, 34, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, T.; Jürgens, C. Remote Sensing of Urban and Suburban Areas; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Keranen, K.; Kolvoord, R. Making Spatial Decisions Using GIS and Remote Sensing: A Workbook; Esri Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer, B.A.; Schaeffer, K.G.; Keith, D.; Lunetta, R.S.; Conmy, R.; Gould, R.W. Barriers to Adopting Satellite Remote Sensing for Water Quality Management. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7534–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote Sensing of Soil Salinity: Potentials and Constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasheh, O.Z.; Neale, C.M.U.; Jayanthi, H. Detailed Mapping of Riparian Vegetation in the Middle Rio Grande River Using High Resolution Multi-Spectral Airborne Remote Sensing. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Tian, Y.Q.; Granillo, J.A.; Keller, G.R. Suitable Remote Sensing Method and Data for Mapping and Measuring Active Crop Fields. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lougheed, V.L.; Rodriguez, R. Creation of a Chihuahuan Desert Bi-National Wetland: A Feasibility Assessment; World Wildlife Fund: Grand, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Everitt, J.H.; Goolsby, J.A. Mapping Giant Reed (Arundo Donax) Infestations along the Texas–Mexico Portion of the Rio Grande with Aerial Photography. Invasive Plant Sci. Manag. 2011, 4, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Everitt, J.H.; Fletcher, R.S. Using Airborne Hyperspectral Imagery for Mapping Saltcedar Infestations in West Texas. In Proceedings of the 2005 American Society for Photgrammetry and Remote Sensing (ASPRS) Annual Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 26–30 April 2010. No. 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, E.S.; Olivas, A.G.; Chávez, J. Land Cover Change and Landscape Dynamics in the Urbanizing Area of a Mexican Border City. In Proceedings of the ASPRS 2008 Annual Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 28 April–2 May 2008; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- The Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics (MRLC) Consortium. Available online: https://www.mrlc.gov/about.php (accessed on 18 November 2018).
- Homer, C.G.; Dewitz, J.A.; Yang, L.; Jin, S.; Danielson, P.; Xian, G.; Coulston, J.; Herold, N.D.; Wickham, J.D.; Megown, K. Completion of the 2011 National Land Cover Database for the Conterminous United States-Representing a Decade of Land Cover Change Information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.; Minami, M. The ESRI Guide to GIS Analysis: Geographic Patterns & Relationships; ESRI, Inc.: Redlands, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. USGS Global Visualization Viewer (GloVis). Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/software/usgs-global-visualization-viewer-glovis (accessed on 25 September 2017).
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of Current Radiometric Calibration Coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI Sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.A.; Berman, M.; Switzer, P.; Craig, M.D. A Transformation for Ordering Multispectral Data in Terms of Image Quality with Implications for Noise Removal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J.W.; Kruse, F.A. Automated Spectral Analysis: A Geologic Example Using AVIRIS Data, North Grapevine Mountains, Nevada. In Proceedings of the Tenth Thematic Conference on Geologic Remote Sensing, Environmental Research Institute of Michigan, San Antonio, TX, USA, 9–12 May 1994; pp. 1407–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, M.; Johnson, E. Temporal Variations of Natural Soil Salinity in an Arid Environment Using Satellite Images. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2010, 30, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, J.S.; Biswas, V.; Kumar, M. Changes in Land Use/Cover Using Geospatial Techniques: A Case Study of Ramnagar Town Area, District Nainital, Uttarakhand, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2013, 16, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallupattu, P.K.; Sreenivasula Reddy, J.R. Analysis of Land Use/Land Cover Changes Using Remote Sensing Data and GIS at an Urban Area, Tirupati, India. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churches, C.E.; Wampler, P.J.; Sun, W.; Smith, A.J. Evaluation of Forest Cover Estimates for Haiti Using Supervised Classification of Landsat Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boori, M.S.; Voženílek, V.; Choudhary, K. Land Use/Cover Disturbance Due to Tourism in Jeseníky Mountain, Czech Republic: A Remote Sensing and GIS Based Approach. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, J.S.; Kumar, M. Monitoring Land Use/Cover Change Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques: A Case Study of Hawalbagh Block, District Almora, Uttarakhand, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R. Remote Sensing of the Environment: An Earth Resource Perspective, 2nd ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.B.; Wynne, R.H. Introduction to Remote Sensing, 5th ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Systems Research Institute. Image Classification Using the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst Extension. Available online: http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/extensions/spatial-analyst/image-classification/image-classification-using-spatial-analyst.htm (accessed on 19 November 2018).
- Gao, J.; Liu, Y. Determination of Land Degradation Causes in Tongyu County, Northeast China via Land Cover Change Detection. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. A Review of Assessing the Accuracy of Classifications of Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikiel, C.; Ustaoglu, B.; Dutucu, A.A.; Kilic, D.E. Remote Sensing and GIS-Based Integrated Analysis of Land Cover Change in Duzce Plain and Its Surroundings (North Western Turkey). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 1699–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, J.D.; Stehman, S.V.; Gass, L.; Dewitz, J.; Fry, J.A.; Wade, T.G. Accuracy Assessment of NLCD 2006 Land Cover and Impervious Surface. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and Photographic Infrared Linear Combinations for Monitoring Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Brabyn, L.; Beard, C. Effects of Class Granularity and Cofactors on the Performance of Unsupervised Classification of Wetlands Using Multi-Spectral Aerial Photography. J. Spat. Sci. 2014, 59, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). Comprehensive Housing Market Analysis-El Paso, Texas; U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD): Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 1–11.
- U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). Comprehensive Housing Market Analysis-Las Cruces, New Mexico; U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD): Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 1–9.
- Thompson, D. Suburban Sprawl: Exposing Hidden Costs, Identifying Innovations; University of Ottawa: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).