Evaluating the Applicability of PERSIANN-CDR Products in Drought Monitoring: A Case Study of Long-Term Droughts over Huaihe River Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
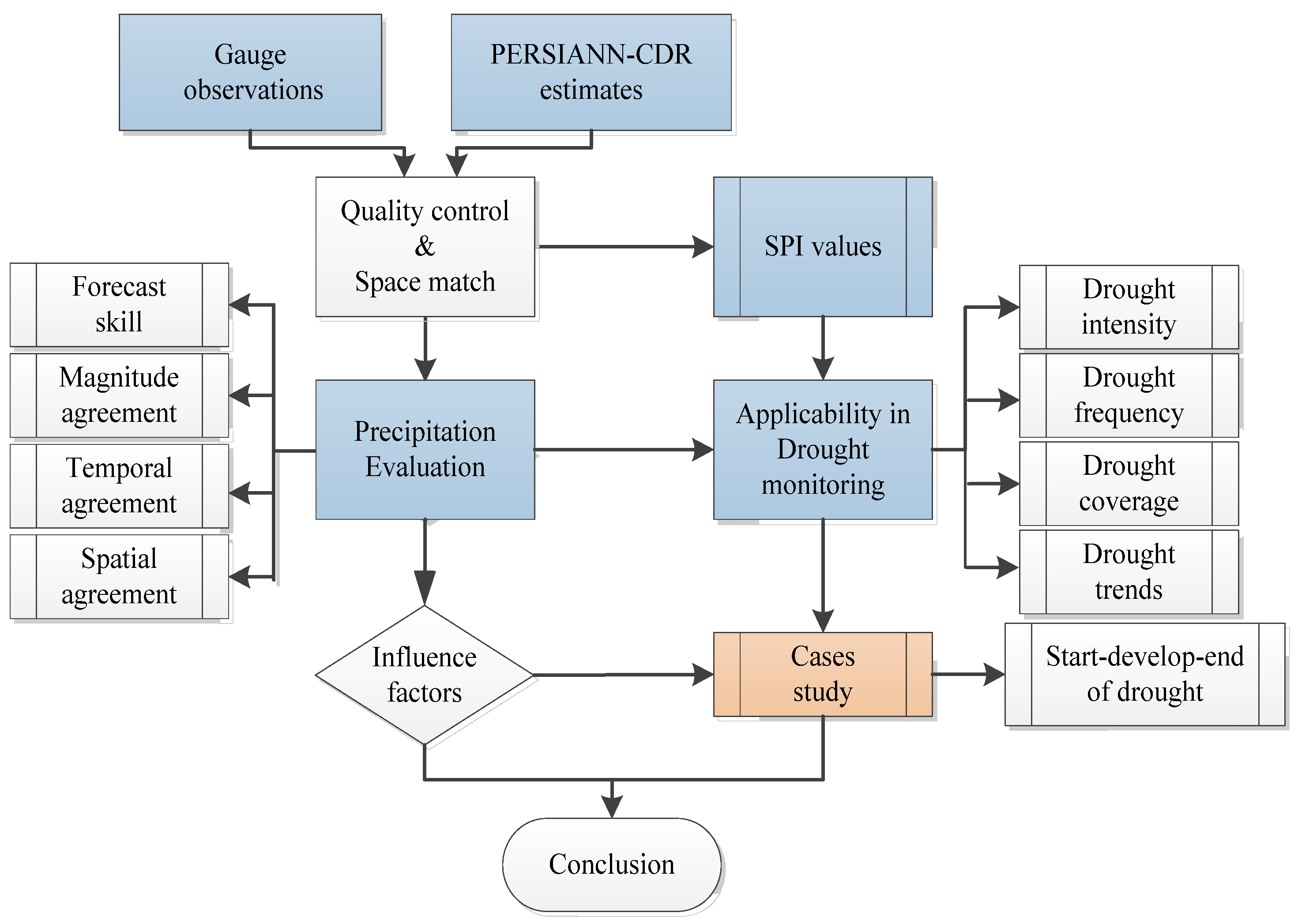
2. Materials and Methods
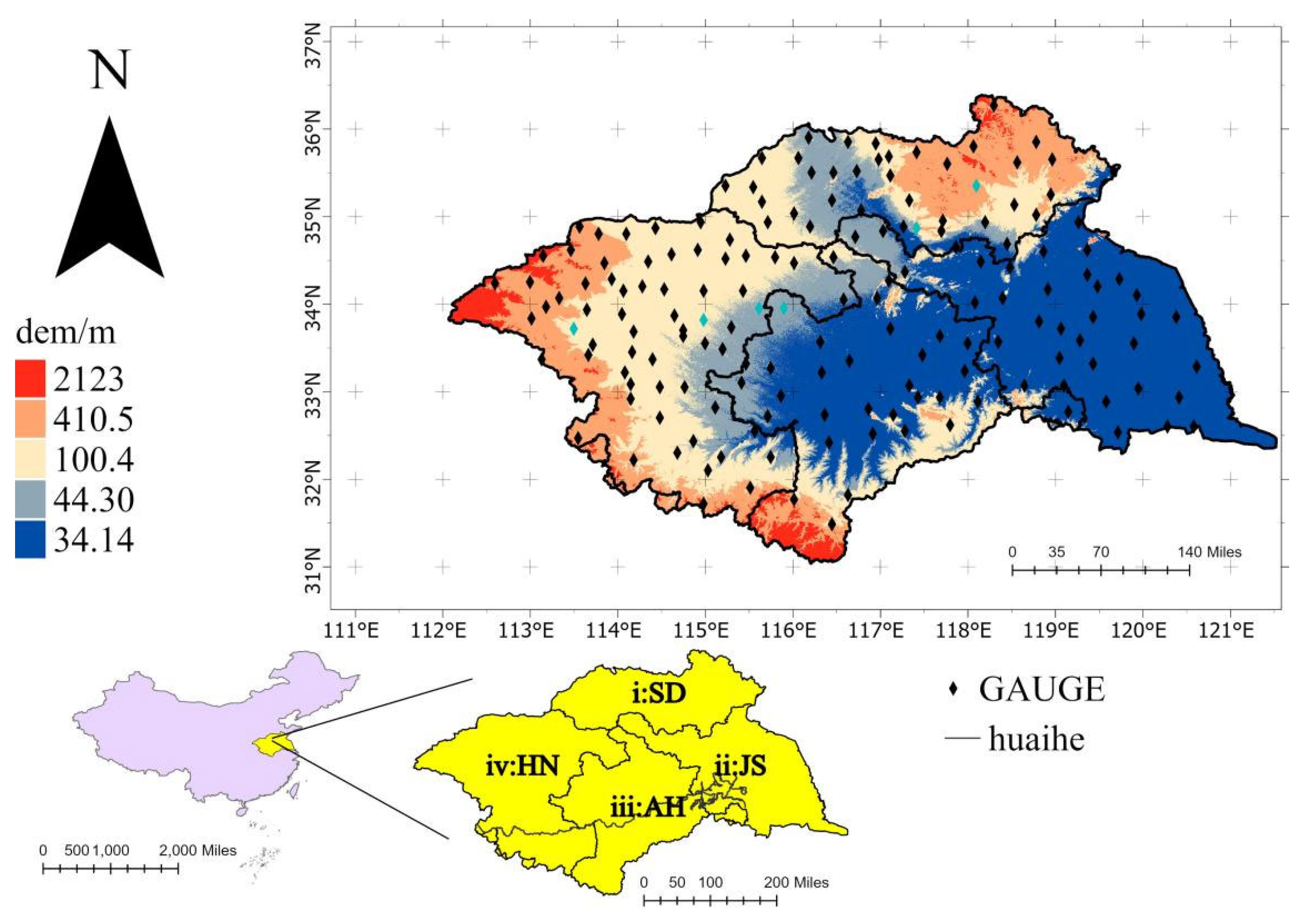
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Statistical Evaluation and Metrics
2.4. Mann–Kendall Test (M–K)
2.5. The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI)
2.6. Drought Station Ratio Pj
3. Results
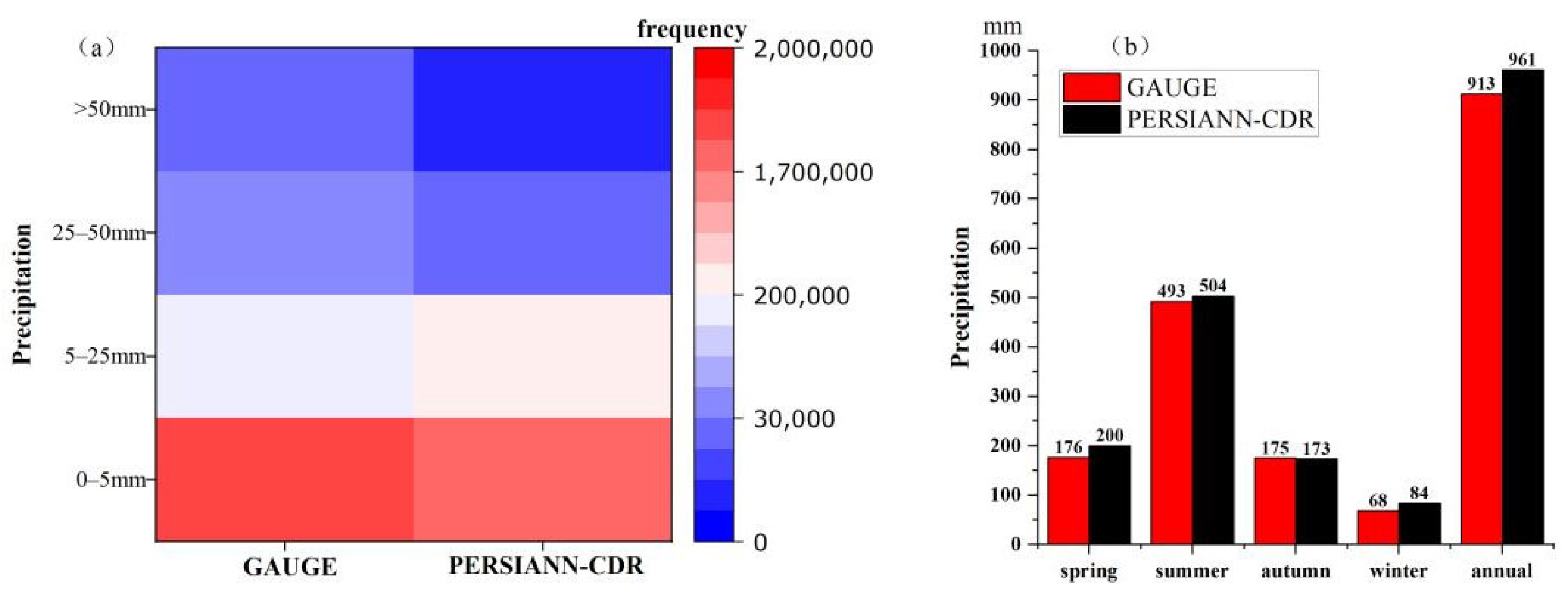
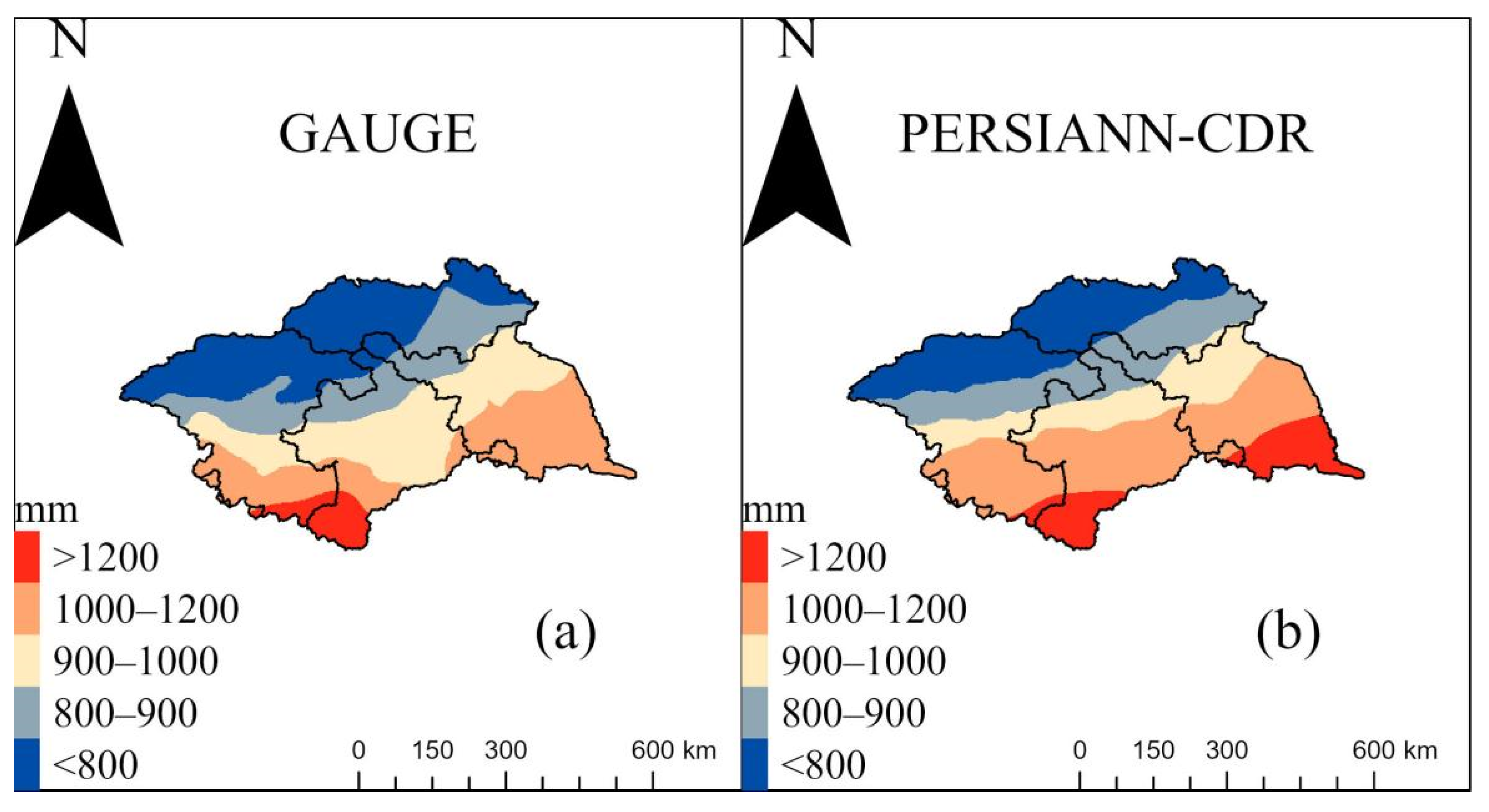
3.1. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CDR Precipitation
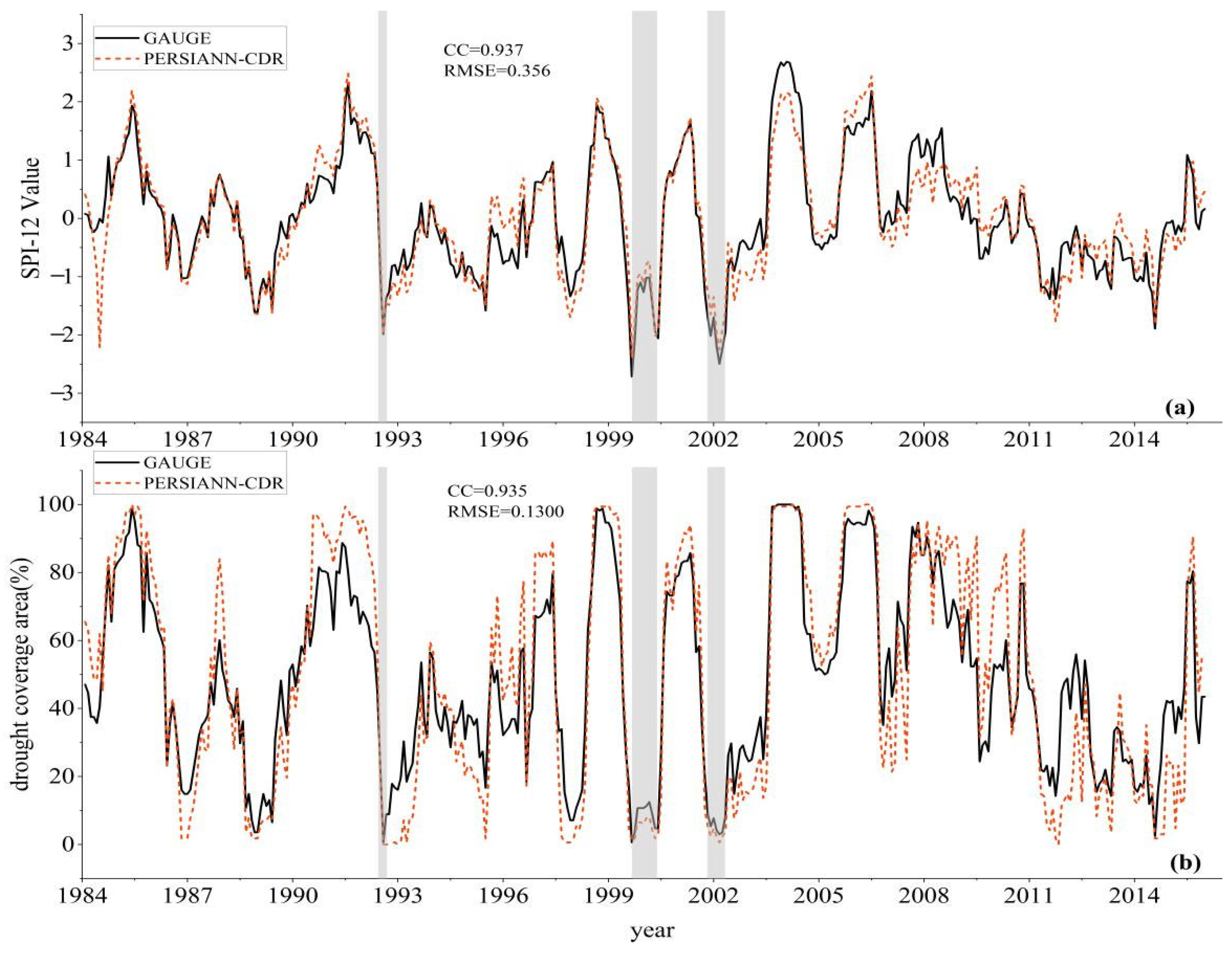
3.2. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CDR in Drought Monitoring
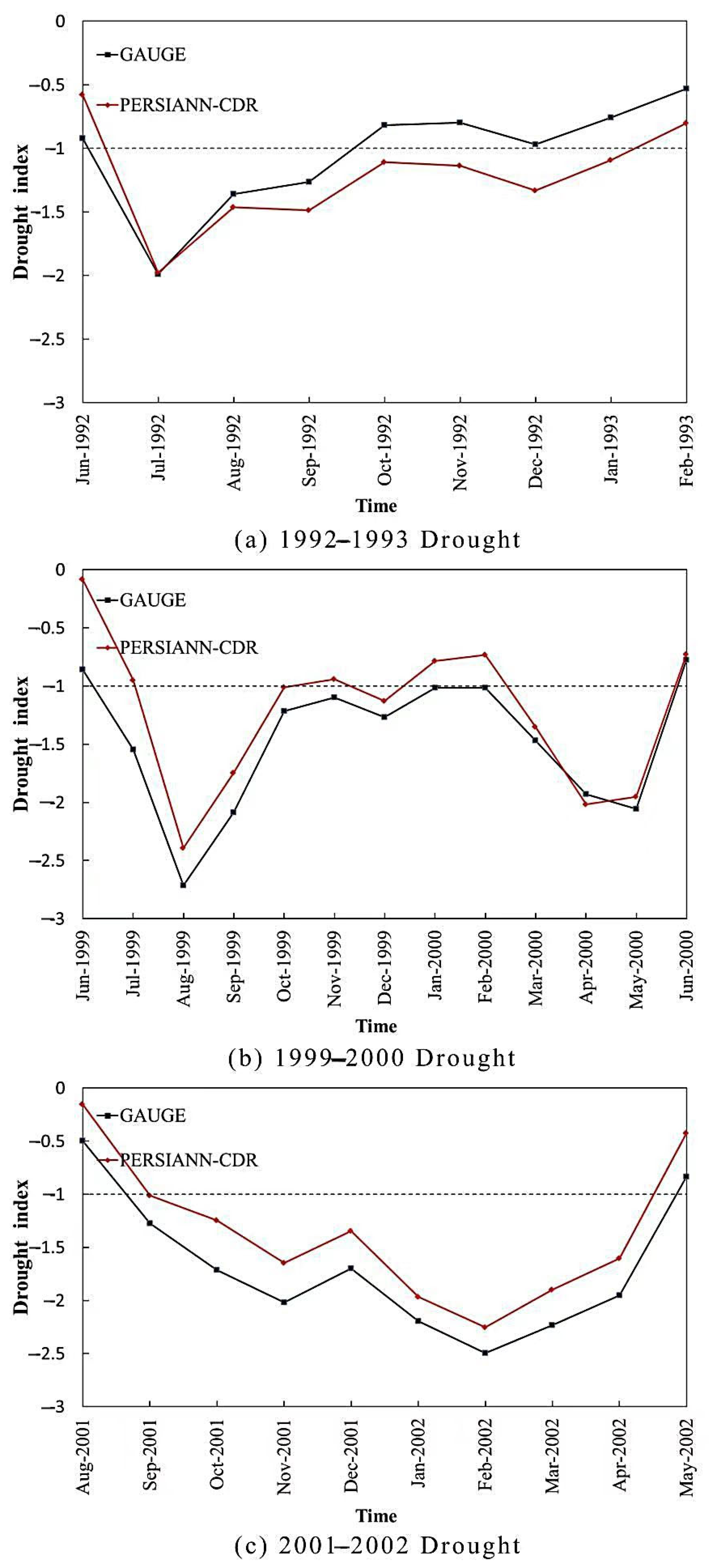
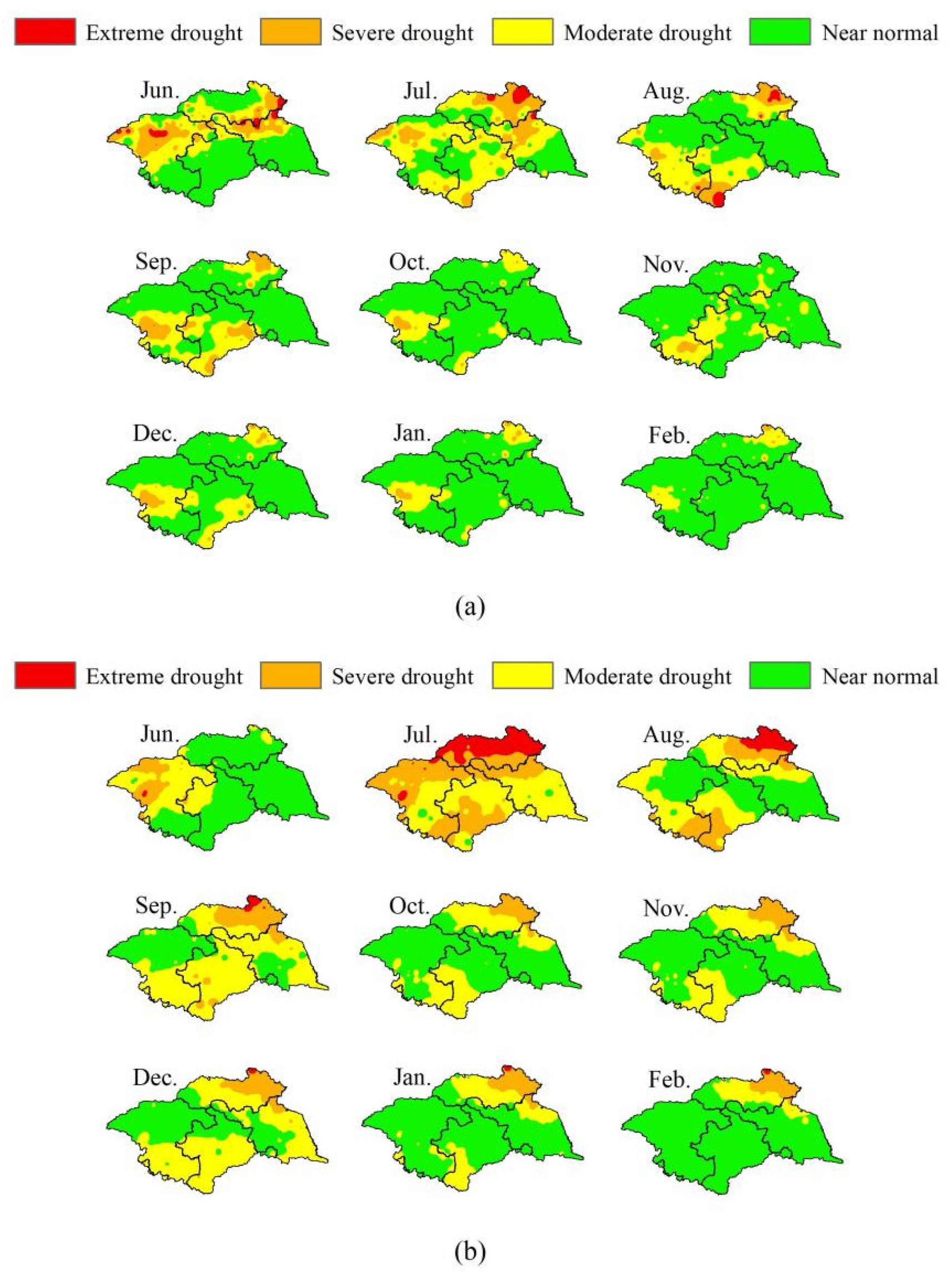
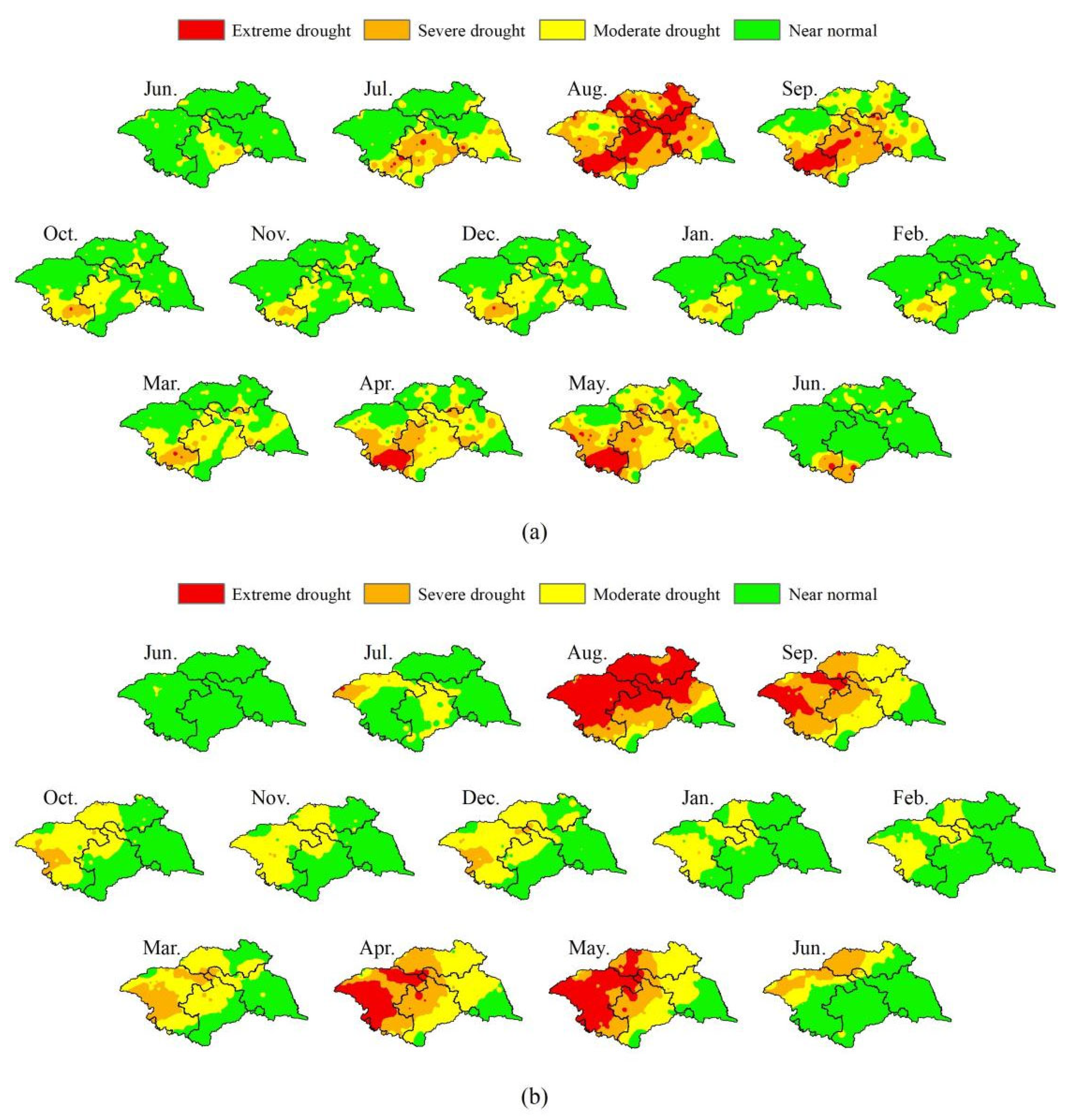
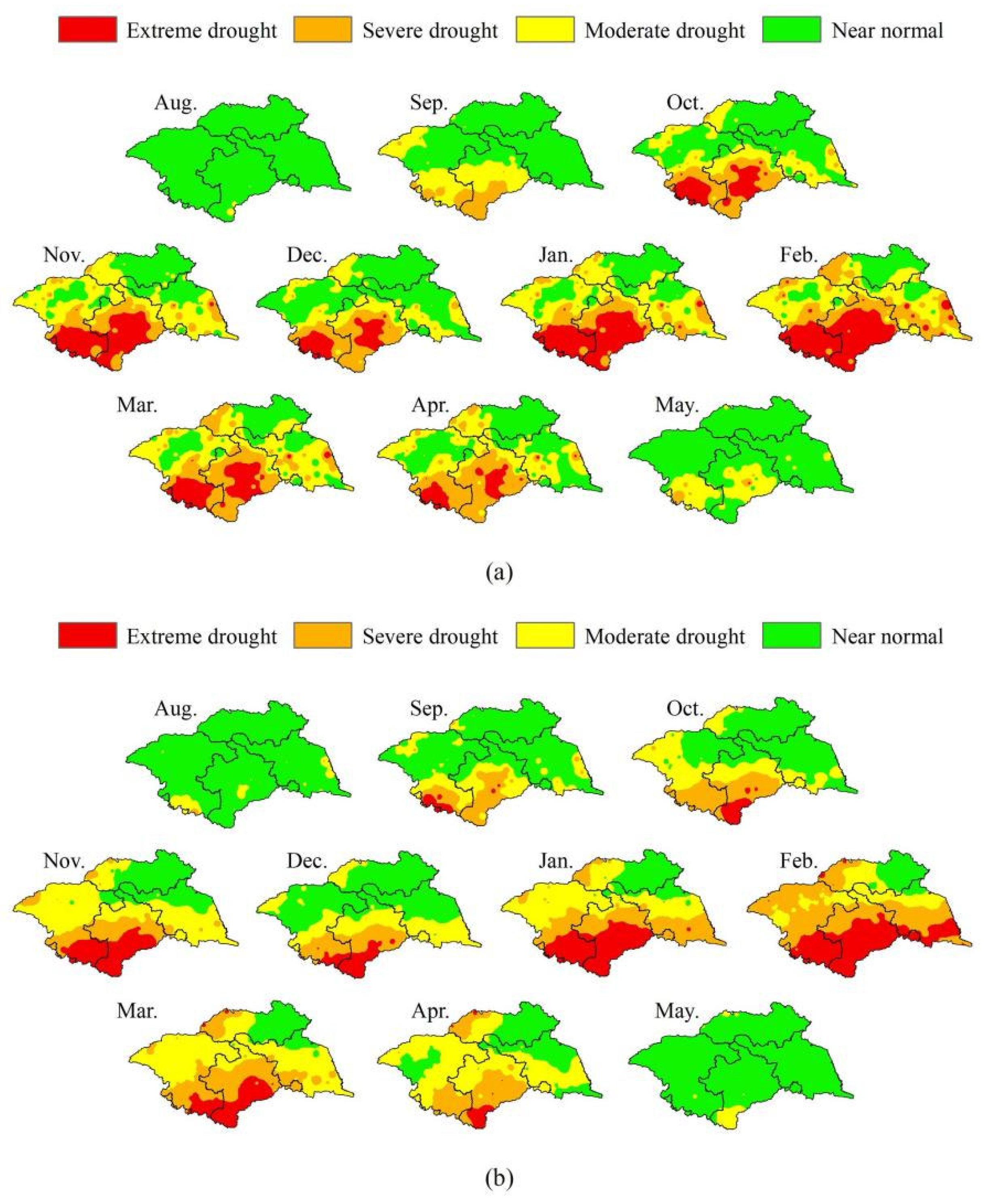
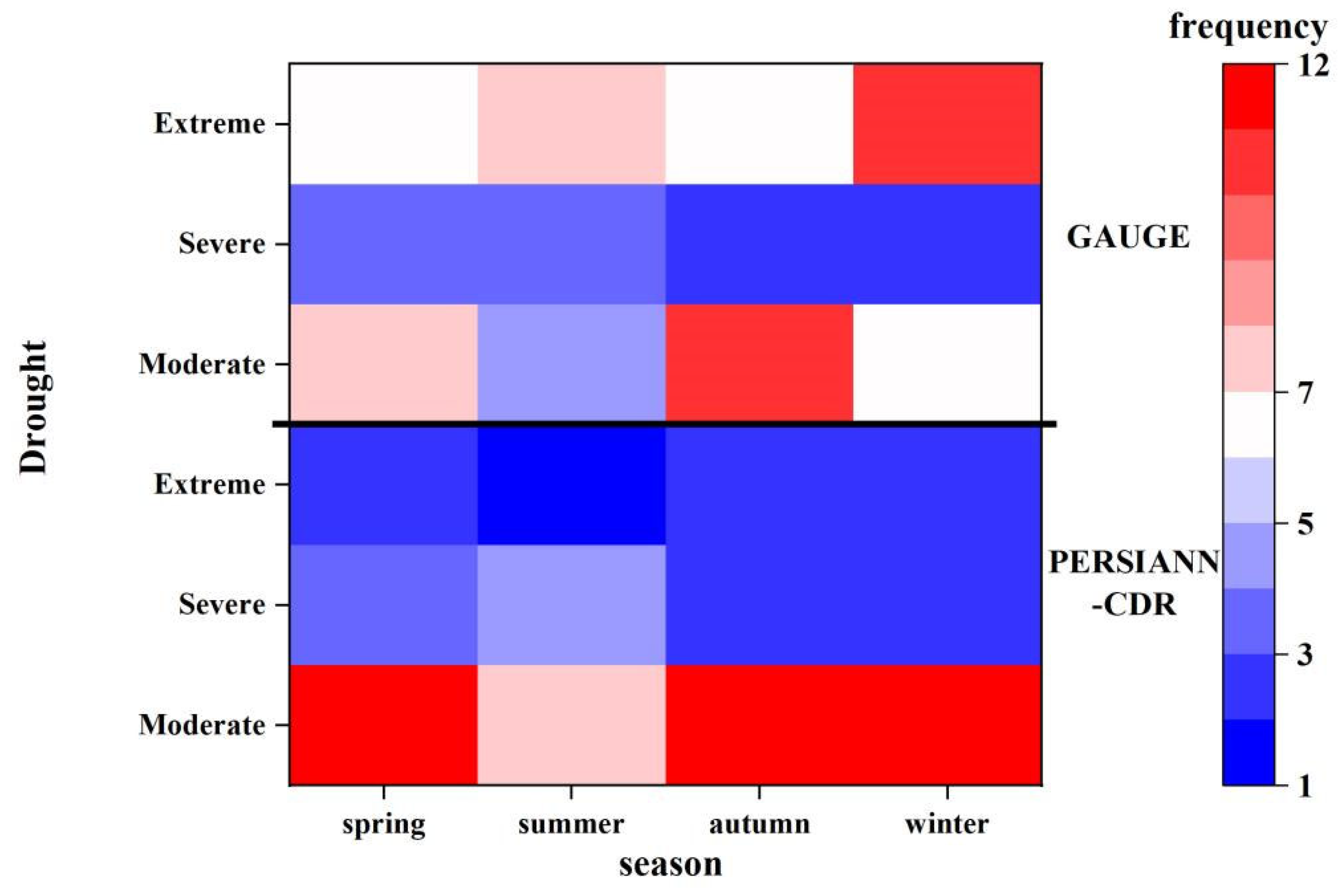
3.3. Performance of PERSIANN-CDR in Specific Drought Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The spatial performances of POD and FAR show that the precipitation forecasting skill of PERSIANN-CDR decreased as the precipitation magnitude increased. The performance of daily PERSIANN-CDR estimates is highly dependent on the spatial distribution of precipitation and performs relatively better in areas with abundant precipitation. In contrast, the monthly and yearly PERSIANN-CD estimates are highly consistent with gauge observations both in magnitude and space. However, PERSIANN-CDR tends to overestimate small precipitation frequency and underestimate big precipitation frequency, which should be addressed in future algorithm development.
- (2)
- These two indices (POD and FAR) were also calculated from the SPI values at various time scales (3, 6, and 12 months). The results show that the POD values are within 0.51–0.73 and the FAR values are within 0.32–0.58 in space, indicating the reliability of PERSIANN-CDR as precipitation input data for drought evaluation in the Huaihe River basin. Although its spatial-temporal performance decreases as the time scale of drought increases, the SPI-12 values estimated from PERSIANN-CDR are still satisfactory, as indicated by the high POD and the low FAR, as well as the high CC values (0.93) and low RMSE (0.356). However, when participating in drought trends analysis, the basin-based results from PERSIANN-CDR do not match that of gauge observations. Caution should be applied when using PERSIANN-CDR for drought trend analysis over the whole basin.
- (3)
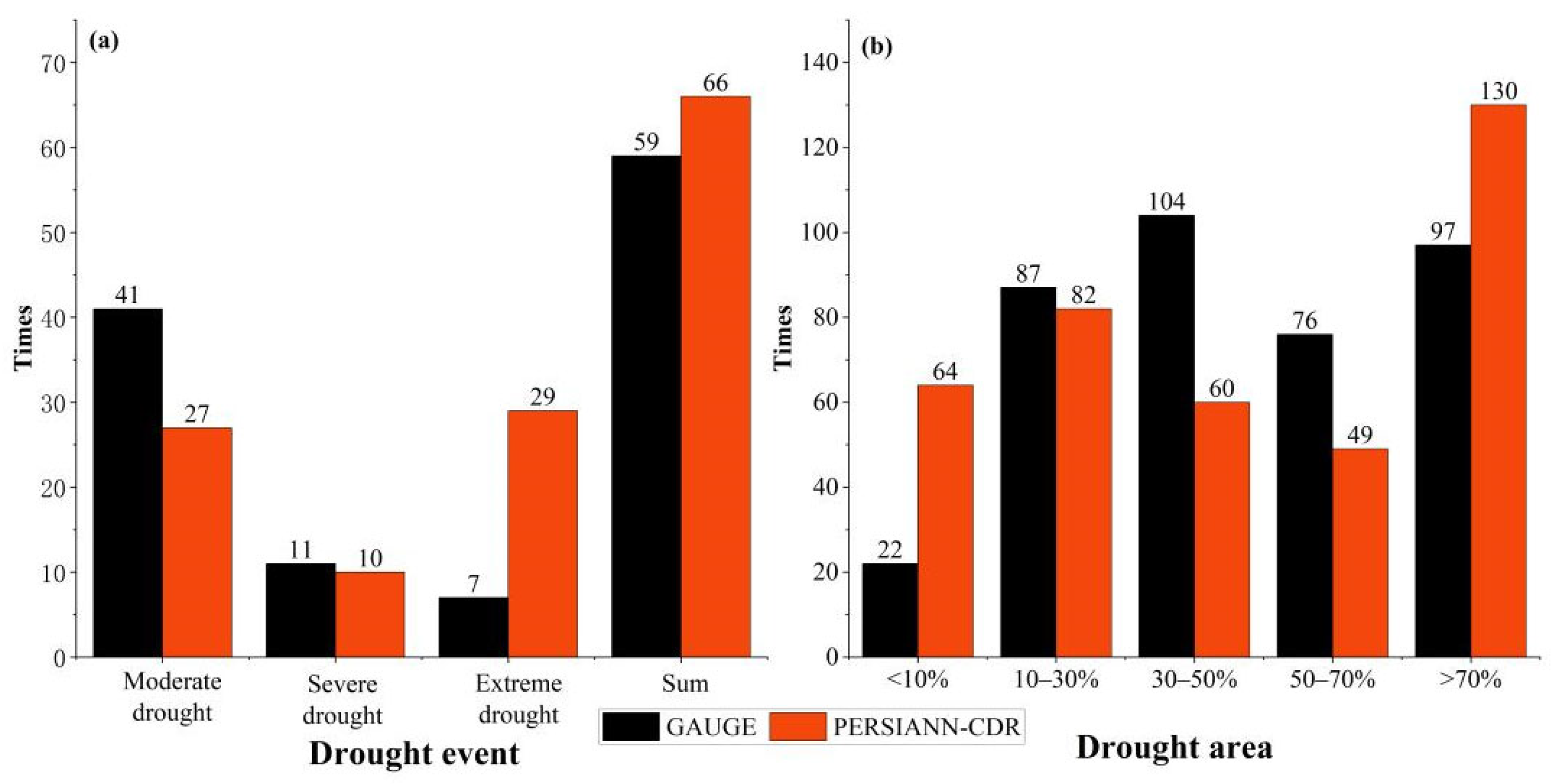
- Three specific drought events are selected further evaluate the ability of PERSIANN-CDR in drought monitoring. Basically, PERSIANN-CDR captures the spatial development of long-term drought events, such as the start–end time, the outbreak periods, and the spread range. The reliability of PERSIANN-CDR application for drought monitoring in the study basin is thus well verified. The case study also shows that the SPI values of PERSIANN-CDR perform relatively better in autumn than in other seasons. This is probably related to the strong ability of PERSIANN-CDR to estimate autumn precipitation. However, due to the overestimation of low precipitation events, PERSIANN-CDR tends to overestimate the number of extreme droughts and their coverage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, B.; Guo, H.; De Maeyer, P. Monitoring and Predicting Drought Based on Multiple Indicators in an Arid Area, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, X.; Gun, Z.; Lin, J.; Zhao, J.; Yao, L.; Zhou, C. Drought assessment of China in 2002–2017 based on a comprehensive drought index. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 319, 108922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, R.; Liu, J. Drought severity change in China during 1961–2012 indicated by SPI and SPEI. Nat. Hazards 2014, 75, 2437–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Chen, S.; Tan, X.; Gu, W. Drought characteristics over China during 1980–2015. Int. J. Clim. 2018, 38, 3532–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Duan, Y.; Duan, J.; Chen, L.; Jian, D.; Lv, M.; Yang, Q.; Ma, Z. A daily drought index-based regional drought forecasting using the Global Forecast System model outputs over China. Atmos. Res. 2022, 273, 106166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Gong, X.; Xing, Z.; Cai, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, D.; Sun, P.; Shi, H. Attribution of meteorological, hydrological and agricultural drought propagation in different climatic regions of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 106996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, K.; Wei, S.; Guga, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and hazard assessment of millet drought disaster in Northern China under climate change. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 272, 107849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Ibrahim, A.L.; Duan, Z.; Cracknell, A.P.; Chaplot, V. Evaluation of Six High-Resolution Satellite and Ground-Based Precipitation Products over Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1504–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Hong, Y.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) and Its Utility in Hydrologic Prediction in the La Plata Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-A.; Huang, W.-R.; Chang, Y.-H.; Huang, S.-M. Impact of multiple-scale circulation interactions on the spring diurnal precipitation over Luzon. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P. Performance of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over China. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salio, P.; Hobouchian, M.P.; Skabar, Y.G.; Vila, D. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates over southern South America using a dense rain gauge network. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chiu, L.S.; Hao, X.; Yang, C. Spatiotemporal Trends and Variations of the Rainfall Amount, Intensity, and Frequency in TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Peng, T.; Wu, Z.; Guo, J.; Chang, W.; Xu, Z. Performance evaluation, error decom-position and Tree-based Machine Learning error correction of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42 products in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Atmos. Res. 2022, 268, 105988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Hsu, K.; Liu, C.; Sorooshian, S. Evaluating the streamflow simulation capability of PERSIANN-CDR daily rainfall products in two river basins on the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017, 21, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Ji, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, W. Spatial Downscaling Model Combined with the Geographically Weighted Regression and Multifractal Models for Monthly GPM/IMERG Precipitation in Hubei Province, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Fang, G.; Ye, J.; Huang, X. Accuracy assessment of IMERG and TRMM remote sensing precipitation data under the influence of monsoon over the upper and middle Lancang River basin, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; Hong, Y. Near real-time hurricane rainfall forecasting using convolutional neural network models with Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) product. Atmos. Res. 2022, 270, 106037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, K.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xue, X.; Chen, S. Evaluation of the TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis and its applicability in supporting reservoir operation and water resources management in Hanjiang basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Bolvin, D.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.; Sorooshian, S.; Tan, J.; Xie, P. NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG). Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) Version 06, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, 3 January 2020, Greenbelt, MD, USA. Available online: https://gpm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/2020-05/IMERG_ATBD_V06.3.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Sodunke, M.; Ojo, J.; Adedayo, K.; De, A. Performance evaluation of metric measures for converting 30-min GPM rain data to 1-min for microwave applications in Tropical region of Nigeria: A multivariate approach. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 3117–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from pas-sive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. Hydrometeor 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshuma, A.E.; Debebe, Y.E.; Dasho, D.K.; Lohani, T.K. Application of Different Modelling Methods to Arbitrate Various Hydrological Attributes Using CMORPH and TRMM Satellite Data in Upper Omo-Gibe Basin of Ethiopia. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Sasashige, K.; Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Okamoto, K.; Aonashi, K.; Inoue, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iguchi, T.; Kachi, M.; et al. A Kalman Filter Approach to the Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) from Combined Passive Microwave and Infrared Radiometric Data. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2009, 87, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.M.; Bufon, V.B.; Maia, F.C.O. Improving GSMaP V06 precipitation products over the Upper Tocantins River basin in the Brazilian Cerrado, based on local rain-gauge network. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 2022, 148, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.K.; Knapp, K.R.; Cecil, L.D.; Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P. PERSIANN-CDR: Daily precipitation climate data record from multi-satellite observations for hydrological and climate studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijanian, M.; Rakhshandehroo, G.R.; Mishra, A.K.; Dehghani, M. Evaluation of satellite rainfall climatology using CMORPH, PERSIANN-CDR, PERSIANN, TRMM, MSWEP over Iran. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4896–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-L.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN System Satellite–Based Estimates of Tropical Rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Gao, B.; Jiao, Y.; Hong, Y.; Xu, T. Multiscale Hydrologic Applications of the Latest Satellite Precipitation Products in the Yangtze River Basin using a Distributed Hydrologic Model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazami, S.; Golian, S.; Hong, Y.; Sheng, C.; Kavianpour, M.R. Comprehensive evaluation of four high-resolution satellite precipitation products under diverse climate conditions in Iran. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 61, 420–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Ombadi, M.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; AghaKouchak, A.; Braithwaite, D.; Ashouri, H.; Thorstensen, A.R. The PERSIANN family of global satellite precipitation data: A review and evaluation of products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5801–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmani-Dehaghi, N.; Samani, N. Spatiotemporal assessment of the PERSIANN family of satellite precipitation data over Fars Province, Iran. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 2019, 138, 1333–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, M.C.C.; Uliana, E.M.; Da Silva, D.D.; Aires, U.R.V.; Martins, C.A.D.S.; Junior, M.F.D.S.; Da Cruz, I.F.; Mendes, M.A.D.S.A. Drought Monitoring Based on Remote Sensing in a Grain-Producing Region in the Cerrado–Amazon Transition, Brazil. Water 2020, 12, 3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-R.; Liu, P.-Y.; Hsu, J. Multiple timescale assessment of wet season precipitation estimation over Taiwan using the PERSIANN family products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. ITC J. 2021, 103, 102521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Shi, W.; Chai, R.; Wang, G. Capacity of the PERSIANN-CDR Product in Detecting Extreme Precipitation over Huai River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eini, M.R.; Rahmati, A.; Piniewski, M. Hydrological application and accuracy evaluation of PERSIANN satellite-based precipitation estimates over a humid continental climate catchment. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Liu, J.; Tuo, Y.; Chiogna, G.; Disse, M. Evaluation of eight high spatial resolution gridded precipitation products in Adige Basin (Italy) at multiple temporal and spatial scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1536–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Coz, C.; van de Giesen, N. Comparison of Rainfall Products over Sub-Saharan Africa. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 553–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, M.A.; Bewket, W.; Amha, Y. Evaluating performance of 20 global and quasi-global precipitation products in representing drought events in Ethiopia I: Visual and correlation analysis. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2022, 35, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Bao, A.; Liu, T.; Chen, S.; Ndayisaba, F. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CDR for Meteorological Drought Monitoring over China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazemzadeh, M.; Noori, Z.; Alipour, H.; Jamali, S.; Akbari, J.; Ghorbanian, A.; Duan, Z. Detecting drought events over Iran during 1983–2017 using satellite and ground-based precipitation observations. Atmos. Res. 2022, 269, 106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, F.; Wardlow, B.; Tadesse, T.; Lillo-Saavedra, M.; Lagos, O. Evaluating satellite-derived long-term historical precipitation datasets for drought monitoring in Chile. Atmos. Res. 2017, 186, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Duan, Z. Preliminary Utility of the Retrospective IMERG Precipitation Product for Large-Scale Drought Monitoring over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the Eighth Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.R.; Wilhite, D.A. Objective quantification of drought severity and duration. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2747–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Moon, J.; Ahn, J. Development of Water Supply Capacity Index to Monitor Droughts in a Reservoir. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 39, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadr, M.; Morgenschweis, G.; Schlenkhoff, A. Analysis of meteorological drought in the ruhr basin by using the standardized precipitation index. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2009, 57, 607–616. [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia, P.; Das, P.; Maiti, R. Meteorological Drought Study Through SPI in Three Drought Prone Districts of West Bengal, India. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 4, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Chen, X.; Lai, C.; Wang, Z.; Lian, Y.; Yu, H.; Wu, X. Drought monitoring utility of satellite-based precipitation products across mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 568, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukat, P.; Bednorz, E.; Ziemblińska, K.; Urbaniak, M. Trends in drought occurrence and severity at mid-latitude European stations (1951–2015) estimated using standardized precipitation (SPI) and precipitation and evapotranspiration (SPEI) indices. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 2022, 134, 20–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; AghaKouchak, A. A Nonparametric Multivariate Multi-Index Drought Monitoring Framework. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, W.; van Oel, P.R.; Lu, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, H. Impacts of different human activities on hydrological drought in the Huaihe River Basin based on scenario comparison. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 37, 100909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C. The proof and measurement of correlation between two things. Am. J. Psychol. 1904, 15, 72–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoulaud-Gouin, V.; Mourlon, C.; Tanaka, T.; Le Dizes-Maurel, S.; Garcia-Sanchez, L.; Attard, J.; Zorko, B.; Mora, J.; Simon-Cornu, M. Sensitivity analysis in a radiological impact assessment of a nuclear power plant discharge. A comparison of the Morris, Spearman and Sobol’ approaches. J. Environ. Radioact. 2021, 242, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Stephenson, D.B. Forecast Verification: A Practitioner’s Guide in Atmospheric Science, 2nd ed.; Wiley and Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 274. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Walker, G.R. Response of mean annual evapotranspiration to vegetation changes at catchment scale. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shao, Q.; Yang, T.; Peng, S.; Xing, W.; Sun, F.; Luo, Y. Quantitative assessment of the impact of climate variability and human activities on runoff changes: A case study in four catchments of the Haihe River basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 27, 1158–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CD performance for drought charac-teristics identification in the Huaihe River Basin. Water Resour. Power 2020, 38, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]





| Category | SPI Value |
|---|---|
| Extremely wet | 2.0 or above |
| Severely wet | 1.5 to 1.99 |
| Moderately wet | 1.0 to 1.49 |
| Near normal | −0.99 to 0.99 |
| Moderately dry | −1.0 to −1.49 |
| Severely dry | −1.5 to −1.99 |
| Extremely dry | −2.0 or below |
| Category | SD | HN | AH | JS | Basin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gauge | Satellite | Gauge | Satellite | Gauge | Satellite | Gauge | Satellite | Gauge | Satellite | |
| Moderate drought | −2.68 * | −1.09 | −0.54 | −0.81 | 0.37 | −0.42 | −0.53 | 0.16 | 0.14 | −0.61 |
| Severe drought | −0.95 | −1.16 | −0.18 | −0.23 | 0.26 | 0.04 | −0.42 | −0.04 | −0.60 | −0.18 |
| Extreme drought | −0.11 | −0.02 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.51 | 0.21 | −0.33 | −0.67 | 0.14 | −0.44 |
| All droughts | −2.46 * | −0.81 | −0.16 | −0.21 | 0.53 | 0.11 | −0.53 | −0.19 | 0.35 | −0.68 |
| Time | Product | Start–End | Duration (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | Gauge | June 1992–October 1992 | 5 |
| PERSIANN-CDR | June 1992–February 1993 | 8 | |
| 1999–2000 | Gauge | June 1999–June 2000 | 13 |
| PERSIANN-CDR | July 1999–June 2000 | 13 | |
| 2001–2002 | Gauge | August 2001–May 2002 | 10 |
| PERSIANN-CDR | August 2001–May 2002 | 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, N.; Yu, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y. Evaluating the Applicability of PERSIANN-CDR Products in Drought Monitoring: A Case Study of Long-Term Droughts over Huaihe River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184460
Yang N, Yu H, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Zheng Y. Evaluating the Applicability of PERSIANN-CDR Products in Drought Monitoring: A Case Study of Long-Term Droughts over Huaihe River Basin, China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(18):4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184460
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Na, Hang Yu, Ying Lu, Yehui Zhang, and Yunchuan Zheng. 2022. "Evaluating the Applicability of PERSIANN-CDR Products in Drought Monitoring: A Case Study of Long-Term Droughts over Huaihe River Basin, China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 18: 4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184460
APA StyleYang, N., Yu, H., Lu, Y., Zhang, Y., & Zheng, Y. (2022). Evaluating the Applicability of PERSIANN-CDR Products in Drought Monitoring: A Case Study of Long-Term Droughts over Huaihe River Basin, China. Remote Sensing, 14(18), 4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184460






