Abstract
Understanding the phenology of urban trees can help mitigate the heat island effect by strategically planting and managing trees to provide shade, reduce energy consumption, and improve urban microclimates. In this study, we carried out the first evaluation of high spatial resolution satellite images from Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope images to quantify urban street tree phenology in downtown Beijing. The major research goals are to evaluate the consistency in pixel-level spring–summer growth period phenology and to investigate the capacity of high-resolution satellite observations to distinguish phenological transition dates of urban street trees. At the city scale, Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope show similar temporal NDVI trends in general. The pixel-level analysis reveals that green-up date consistency is higher in areas with medium (NDVI > 0.5) to high (NDVI > 0.7) vegetation cover when the impacts of urban surfaces on vegetation reflectance are excluded. Similarly, maturity date consistency significantly increases in densely vegetated pixels with NDVI greater than 0.7. At the street scale, this study emphasizes the efficacy of NDVI time series derived from PlanetScope in quantifying the phenology of common street tree genera, including Poplars (Populus), Ginkgos (Ginkgo), Chinese Scholars (Styphnolobium), and Willows (Salix), in downtown Beijing to improve urban vegetation planning. Based on PlanetScope observations, we found that the four street tree genera have unique phenological patterns. Interestingly, we found that the trees along many major streets, where Chinese Scholars are the major tree genus, have later green-up dates than other areas in downtown Beijing. In conclusion, the three satellite observation datasets prove to be effective in monitoring street tree phenology during the spring–summer growth period in Beijing. PlanetScope is effective in monitoring tree phenology at the street scale; however, Landsat-8 may be affected by the mixture of land covers due to its relatively coarse spatial resolution.
1. Introduction
Studying urban tree phenology, which focuses on the timing of transitions in the life cycles of trees within urban environments, is particularly important due to the unique challenges and opportunities in urban settings [1]. Urban areas often experience higher temperatures compared to surrounding rural areas, creating “urban heat islands”. Understanding the phenology of urban trees can help mitigate this effect by strategically planting and managing trees to provide shade, reduce energy consumption, and improve urban microclimates [2].
Urban trees provide a series of ecosystem services that benefit urban citizens [3]. For example, urban spaces have great potential to regulate urban temperature and cool down cities (e.g., [2]), store and sequester carbon from anthropogenic emissions through photosynthesis (e.g., [4]), improve air quality by absorbing air pollutants (e.g., [5]), reduce urban noise (e.g., [6]), improve urban biodiversity by retaining habitats (e.g., [7]), and provide areas of recreation for urban citizens (e.g., [8]). In particular, urban green is very helpful for improving public health, for example, by promoting physical activities and early warning of pollen allergy (e.g., [9,10]). All of these make urban trees important for sustainable cities in times of climate change.
As cities grow and evolve, proper management of urban trees becomes crucial for sustainable development. Studying tree phenology can guide policies and practices to balance urban growth with ecosystem conservation. To quantify vegetation phenology, observation scales can be approximately categorized into the intercontinental scale [11,12], interstate/interprovincial scale [13,14], state/province scale [14,15,16,17], county/municipality scale [14,18,19], and district scale [20,21]. However, there is a limited understanding of tree phenology modeling at the urban street scale, which detailed urban landscape management plans can refer to. With the increasing popularity of using remote sensing data with high spatial and temporal resolution, more detailed information on vegetation phenology can be observed [20], especially in dense and heterogeneous downtown areas where complex environmental factors interact. At the city scale and the neighborhood scale, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS; 250 m resolution) and Landsat (30 m resolution) show strong consistency in observing time series of mean NDVI, even though MODIS has a much coarser resolution [22]. The MODIS resolution is coarser for observing urban vegetation phenology, and within each MODIS 250 m pixel, complex interactions between vegetation phenology and diverse land cover typologies exist [18,20]. To further advance the spatial resolution for vegetation phenology analysis at the street scale, vegetation data with a high spatial resolution (≤ 10 m) is necessary.
With the availability of the PlanetScope constellation in recent years, researchers have found it easier and more accessible to observe vegetation phenology at a much higher spatial resolution of 3 m in a more continuous time series (with observations almost daily). As of 2023, Planet Labs [23] operates roughly 200 Dove satellites, including PlanetScope, to monitor the Earth. The PlanetScope image collection has been used to study vegetation phenology in natural environments [24,25], crop phenology [26,27], and flowering phenology [28,29]. PlanetScope has been proven to have high consistency with PhenoCam imagery and harmonized Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 in monitoring vegetation phenology in deciduous broadleaf forests, evergreen needleleaf forests, grasslands, and shrublands [24]. PlanetScope can be integrated with drone observations to estimate the autumn phenology of individual trees at the crown scale in a temperate forest [25]. Myers et al. [26] use PlanetScope images to derive time series of mean NDVI in crop sample plots and analyze the impact of temporal resolution on the absolute deviation of estimated phenological transition dates. PlanetScope images can also complement Sentinel-2 in observing crop phenology [27]. PlanetScope NDVI can be independently used or combined with high-quality Landsat and Sentinel images to predict the flowering peak of an alpine meadow with medium-to-high accuracy [28].
Previous urban studies using the NDVI time series from PlanetScope involved the detection of land use/land cover change [30] and phenological metrics of unique tree species and canopy composition [31]. Although MODIS and Landsat have provided observations of urban vegetation phenology, the low spatial resolution has limitations for capturing the trees at the street scale. In this study, we carried out the first evaluation of high spatial resolution satellite images from Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope images to quantify urban street tree phenology in downtown Beijing. The major research goals are to evaluate the consistency of pixel-level phenology and to investigate the capacity of high-resolution satellite observations to distinguish phenological transition dates for urban street trees.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
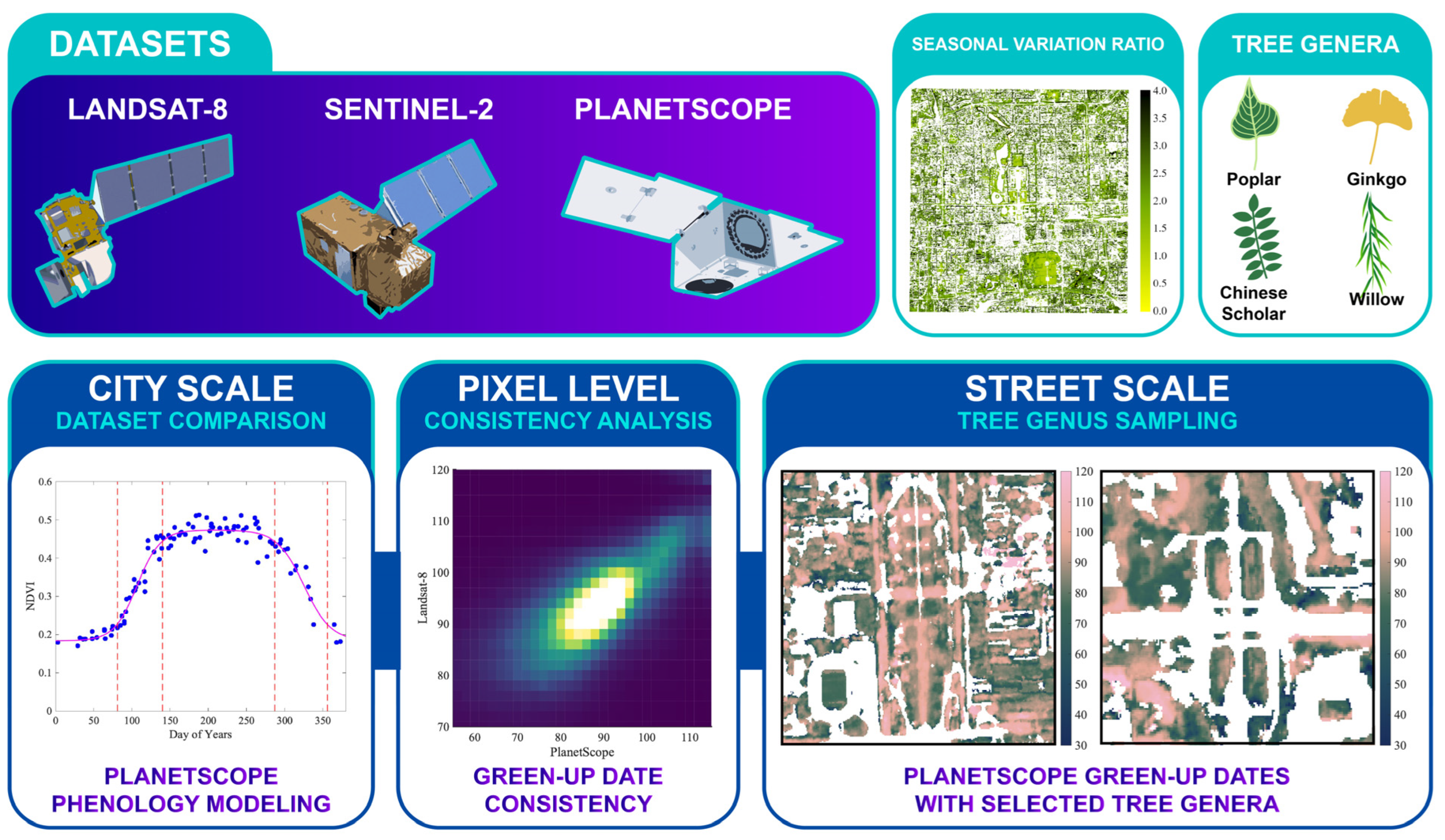
In this study, three NDVI data sources—Landsat 8, Sentinel 2, and PlanetScope—are used (Figure 1). The overall study period spans from 1 January 2019 to 28 February 2023. The whole study period covers four years. Each study year spans from day 1 (1 January) to day 424 (approximately February of the following year), allowing greater flexibility for modeling dormancy dates. This approach contributes to smooth regression curves. For example, the study year 2019 spans from 1 January 2019 to 28 February 2020. The three NDVI data sources are introduced as follows:
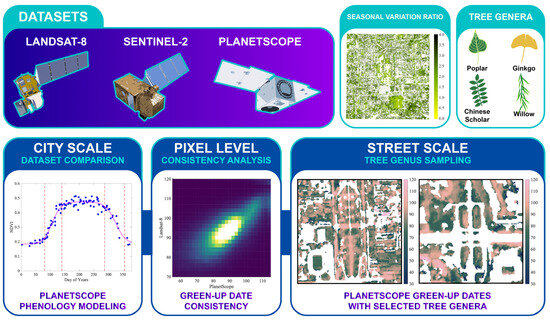
Figure 1.
The research design includes the utilization of Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope datasets and the analysis of urban tree phenology at the city and street scales. The seasonal variation ratio of NDVI is used as an indicator to extract urban deciduous vegetation. The phenology of four tree genera is analyzed and compared in Section 3.4.
(1) The USGS Landsat 8 Level 2 (30 m resolution) NDVI data are obtained from Google Earth Engine (GEE) [32]. Landsat-8 scenes containing 40% or more NaN pixels are excluded.
(2) Harmonized Sentinel-2 MultiSpectral Instrument (MSI; 10 m resolution) Level-2A NDVI data are also obtained from GEE (COPERNICUS/S2_SR_HARMONIZED) [24]. Due to the lower stability of NDVI observations, the default cloud mask to filter out Sentinel-2 scenes is set to 10% in GEE. Due to the limited performance of the cloud mask, each Sentinel-2 scene is manually inspected. Scenes exhibiting obvious cloud cover, abnormally low values, and noisy pixels with very high values are excluded from the analysis.
(3) Harmonized PlanetScope surface reflectance imagery (3 m resolution) is downloaded from Planet Explorer [33]. Due to the large size of the PlanetScope dataset, we have manually selected high-quality scenes that cover the entire study period.
Data preprocessing is conducted in ArcGIS Pro using geoprocessing tools. Initially, the mosaic tool is used to mosaic multiple tiles, and then we use the Raster Calculator tool to calculate NDVI. For images where the mosaic tool failed, we reverse the process and use the Raster Calculator tool to calculate NDVI first, followed by using the mosaic tool to mosaic the NDVI tiles in ArcGIS Pro. In total, there are 73 Landsat-8 scenes, 268 Sentinel-2 scenes, and 110 PlanetScope scenes for further analysis.
2.2. Study Area
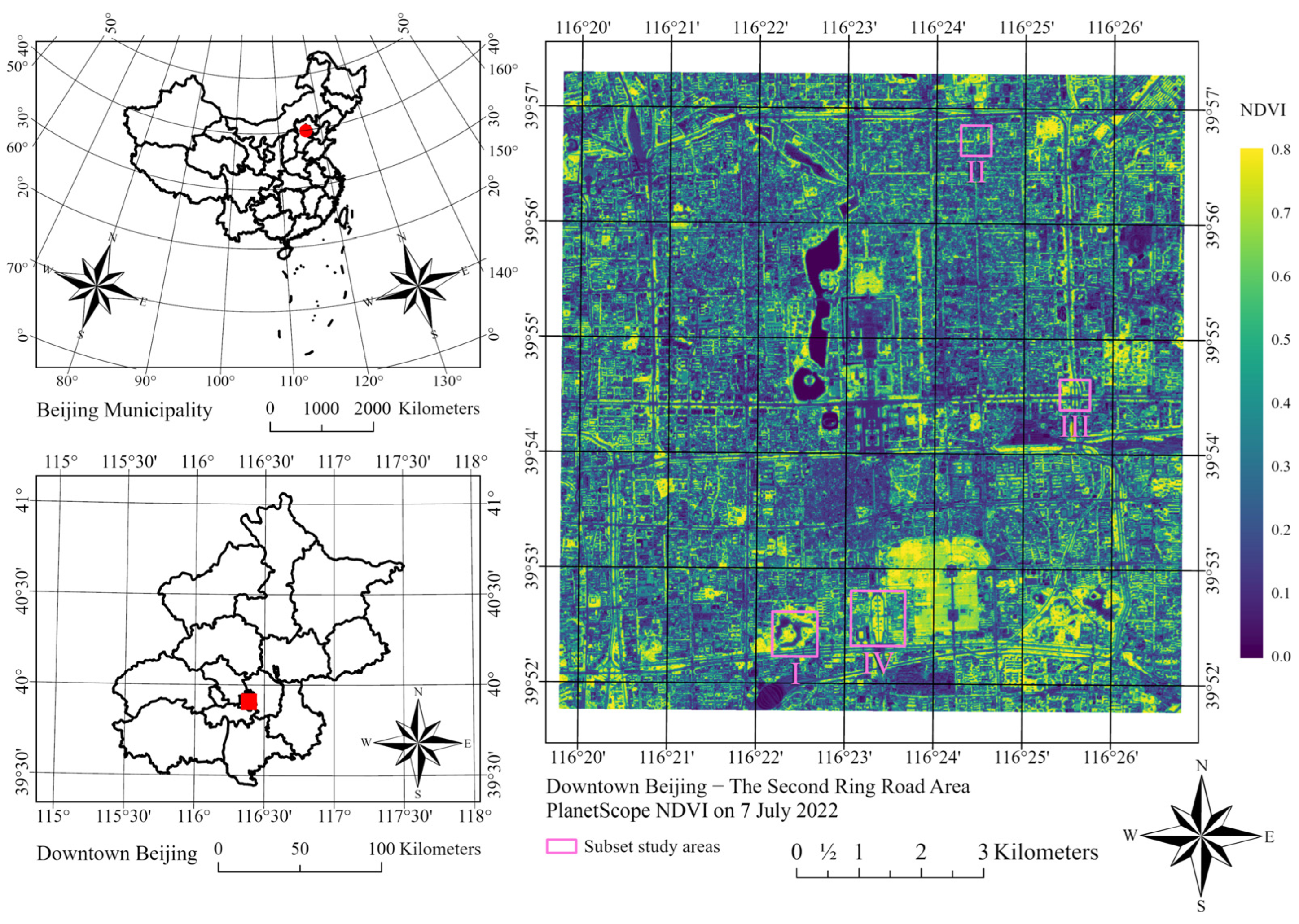
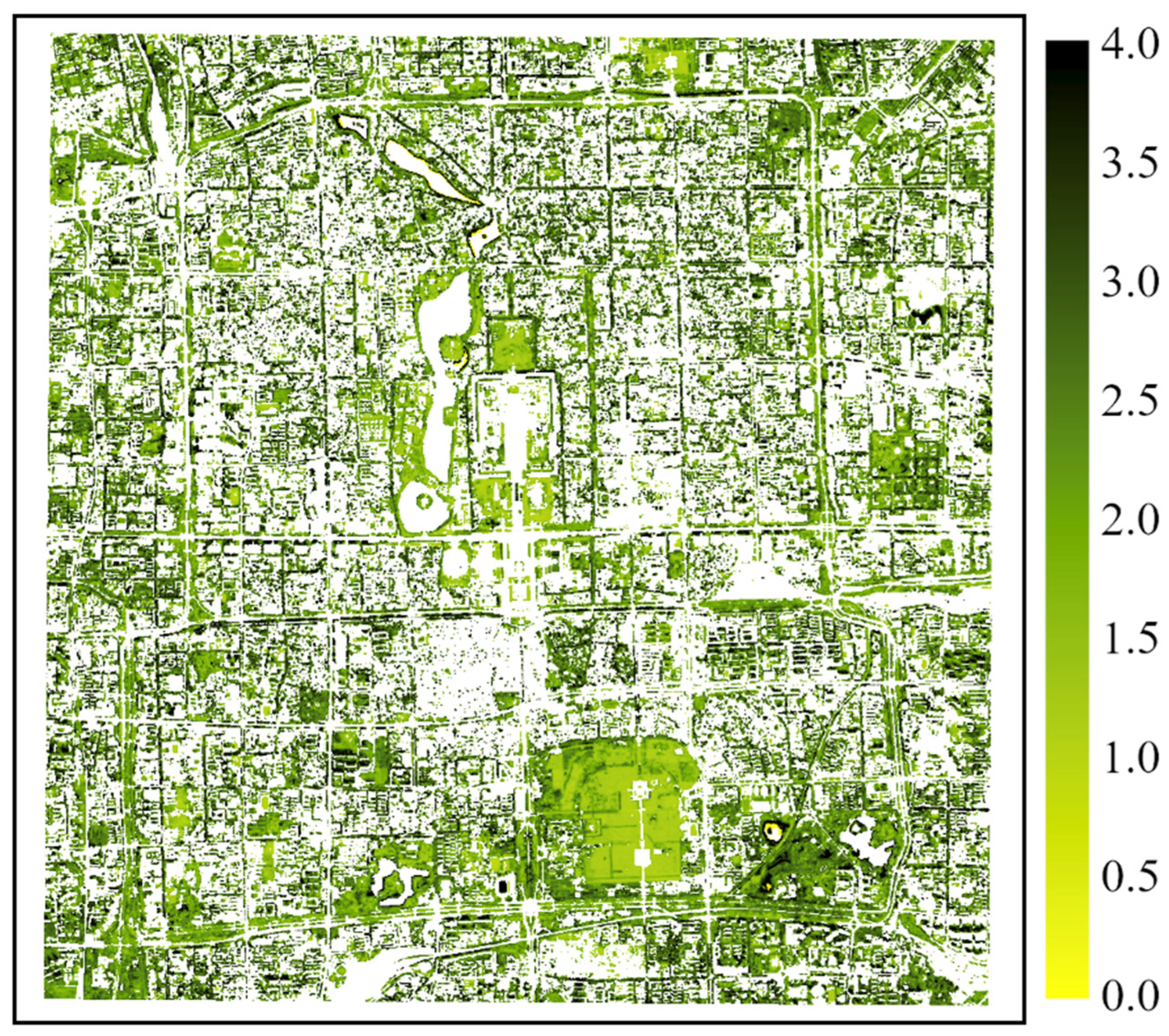
Following our previous study [22], we chose the core urban area enclosed by the Second Ring Road and surrounding areas of Beijing as the study area. The study area extends from 39.86 N to 39.95 N and from 116.33 E to 116.45 E (Figure 2). In 2020, the total population of Beijing was about 22 million [34]. This area constitutes the inner city of Beijing, with Zijincheng (Forbidden City) located in the center. Government buildings, traditional neighborhoods, historic parks, and other function zones characterized a diverse spatial pattern within the study area. Additionally, we have defined four subset study areas to investigate street-scale tree phenology. In the study area, evergreen vegetation with a smaller seasonal variation ratio (SVR, NDVI contrast between August and February) is primarily in parks, while deciduous trees are the major type of street vegetation (Figure 3). To extract deciduous vegetation and underscore its significance, the SVR is defined as the ratio calculated by using the mean August NDVI divided by the mean February NDVI. This calculation involves merging 10 PlanetScope scenes obtained in August from 2019 to 2022 and 8 PlanetScope scenes obtained in February from 2019 to 2023.
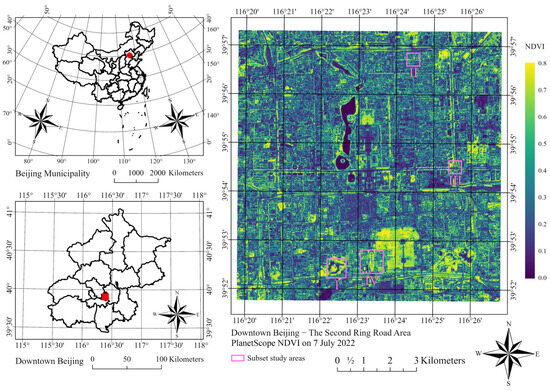
Figure 2.
The study area includes the core urban area enclosed by the Second Ring Road and surrounding areas of Beijing. The subset study areas are (I) Taoranting Park, (II) Yonghe Temple, (III) Jianguomen Bridge, and (IV) Yongdingmen Park.
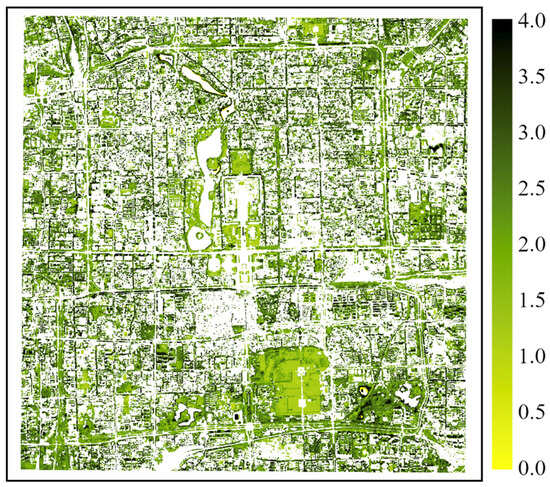
Figure 3.
Seasonal variation ratio (SVR) of NDVI within the study area. SVR is calculated by using the PlanetScope August composite NDVI divided by the PlanetScope February composite NDVI. The visualized pixels have a mean NDVI value greater than 0.3 from the PlanetScope August composite.
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Phenology Modeling
The purpose of phenology modeling using NDVI time series is to derive green-up, maturity, senescence, and dormancy dates. Common methods to achieve this goal include Savitzky–Golay filtering [15,35,36], asymmetric Gaussian model functions [20,37], and asymmetric logistic functions for vegetation dynamics [31,32]. Zhang et al. [38] proposed a logistic function with four learnable parameters using MODIS EVI data. This study follows the widely used modeling method proposed by Zhang et al. [38] for modeling vegetation dynamics. The equation for modeling is given by:
where t is the number of days, and y(t) is the value of the vegetation index (NDVI in this study) at time t. a1, a2, a3, and a4 are parameters for the regression model to learn. The maximum value of the fitted curve is represented by (a3 + a4), and a4 is the initial background vegetation index value. There are two widely used ways to identify phenological transition dates. First, phenological transition dates can be derived from four extrema on the change rate of the curvature of the vegetation curve [38]. Alternatively, those transition dates can be defined by the day when the vegetation curve reaches certain thresholds between the peak values (a3 + a4) and the background values a4 [39,40]. Acknowledging that different sensors generate different phenological transition dates, this study follows the thresholds from the MODIS Land Cover Dynamics (MCD12Q2) Product [39] to identify phenological indicators, including green-up, maturity, senescence, and dormancy dates. This method allows an easier comparison among datasets from other studies.
The green-up and dormancy dates are the intersections between the fitted NDVI curves and a horizontal line . The maturity and senescence dates are the intersections between the fitted NDVI curves and a horizontal line . In addition to the threshold to identify dormancy dates, this study also tests and compares the performance of another threshold in Section 3.2 and Section 3.4.
In this study, the first half of a study year for modeling (spring–summer growth period) spans from day 1 to day 212 (approximately 7 months), and the second half of a study year (autumn–winter growth period) spans from day 213 to day 424 (approximately 7 months). The extended study year accounts for trees reaching the deep dormancy stage in January of the following year, which is the coldest month in Beijing. An extended study year improves the quality of phenology modeling in this study area. To calculate the parameters of vegetation dynamics, we used the nonlinear regression function in MATLAB (version R2022a).
2.3.2. City-Scale Vegetation Phenology Comparison
The mean NDVI value of each remote sensing image is used for city-scale vegetation phenology comparison. After the regression coefficients are calculated for the spring–summer growth period, a3 and a4 in Equation (1) derived from the spring–summer growth period are used for the autumn–winter growth period to keep the same maximum value of the fitted curves. This treatment keeps the fitted curves more continuous between the early and later halves of the year. At this scale, study years are overlaid to ensure sufficient data for a more reliable regression curve. As mentioned in Section 2.3.1, we extend the temporal scale of the modeling year to 424 days to cover January and February in the following year.
2.3.3. Pixel-Level Phenology Comparison
Since the preliminary results indicated that Landsat-8 has limited ability to identify the senescence day due to limited observations and a lower spatial resolution, we primarily focus on the two phenological indicators of the spring–summer growth period and briefly discuss the two phenological indicators of the autumn–winter growth period. We use the “imresize” function with the “box” interpolation kernel in MATLAB to resize Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 images to the pixel size of PlanetScope for this analysis. In MATLAB, we have layered available NDVI maps, extracted NDVI values for each pixel, and applied Equation (1) with thresholds (as mentioned in Section 2.3.1) to derive green-up, maturity, senescence, and dormancy dates. However, due to the uncertainty at the pixel level, we have designed the following filters: (1) pixels containing 70% or more NaN values are excluded; (2) pixels with a mean NDVI of 0.3 or lower in PlanetScope images obtained in August are excluded (no clear evidence of vegetation cover; more strict criteria are also evaluated in Section 3.3); (3) pixels of evergreen vegetation are excluded, while deciduous vegetation is estimated by PlanetScope SVR greater than 1.5 (as mentioned in Section 2.2); and (4) abnormal outliers of phenological indicators are excluded. This refers to green-up dates less than or equal to day 0 or greater than or equal to day 180; maturity dates less than or equal to day 60 or greater than or equal to day 210; senescence dates less than or equal to day 240 or greater than or equal to day 330; and dormancy dates less than or equal to day 270 or greater than or equal to day 390. The objective of filtering out evergreen vegetation is to highlight changes in deciduous vegetation. After the data filtering, the proportion of available pixels is about 40% for all datasets for identifying green-up and maturity dates. Landsat-8 has about 22% of pixels for identifying senescence dates and about 29% for identifying dormancy dates. Sentinel-2 has around 32% of pixels for identifying senescence and dormancy dates. PlanetScope has about 34% for identifying senescence dates and about 40% for identifying dormancy dates. Detailed proportions will be mentioned in Section 3.3.
2.3.4. Street-Scale Tree Genus Phenology Comparison
To test the performance of PlanetScope in detecting important phenological transition dates of street trees, we have selected four common genera of street trees in Beijing: Populus sp. (Poplars), Ginkgo sp. (Ginkgos), Styphnolobium sp. (Chinese scholar/pagoda trees), and Salix sp. (Willows). The illustrations and images of these selected common tree genera are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 4. These are common deciduous street tree genera in downtown Beijing. Tree samples are determined by Baidu street view images and double-checked by field inspection. Bounding boxes for each tree genus are defined by examining the satellite images in ArcGIS Pro, Google Maps, and Baidu Maps. This workflow ensures that a single target tree genus dominates the bounding box and that the coordinates of each sampling location are precise. Populus sp., Ginkgo sp., Styphnolobium sp., and Salix sp. have 96, 367, 635, and 126 pixels of the PlanetScope pixel size, respectively. Different from the city-scale vegetation phenology comparison, the regression coefficients in this section are independent in the spring–summer and autumn–winter growth periods. In the four subset study areas, we have selected tree plots and analyzed phenology based on mean NDVI change by genus. In Section 3.4, the four filters (mentioned in Section 2.3.3) are only used for street-scale phenology mapping but not applied to tree genus phenology modeling.

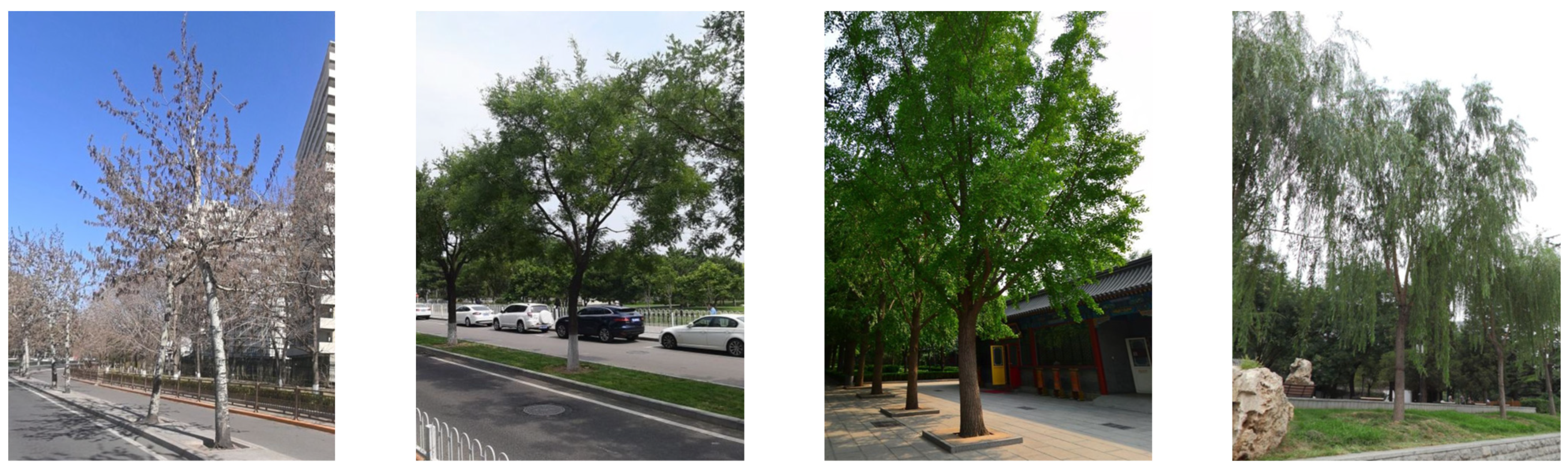
Figure 4.
Images of the selected tree genera, including (a) Populus sp. in Jianguomen Bridge, (b) Styphnolobium sp. in Yongdingmen Park, (c) Ginkgo sp. in Yonghe Temple, and (d) Salix sp. in Taoranting Park. These four selected tree genera are used to show the street-scale phenology by genus in Section 3.4 of this study. These images are obtained from Baidu Maps.
3. Results
3.1. Correlations in the Spatial Distribution of NDVI in Downtown Beijing
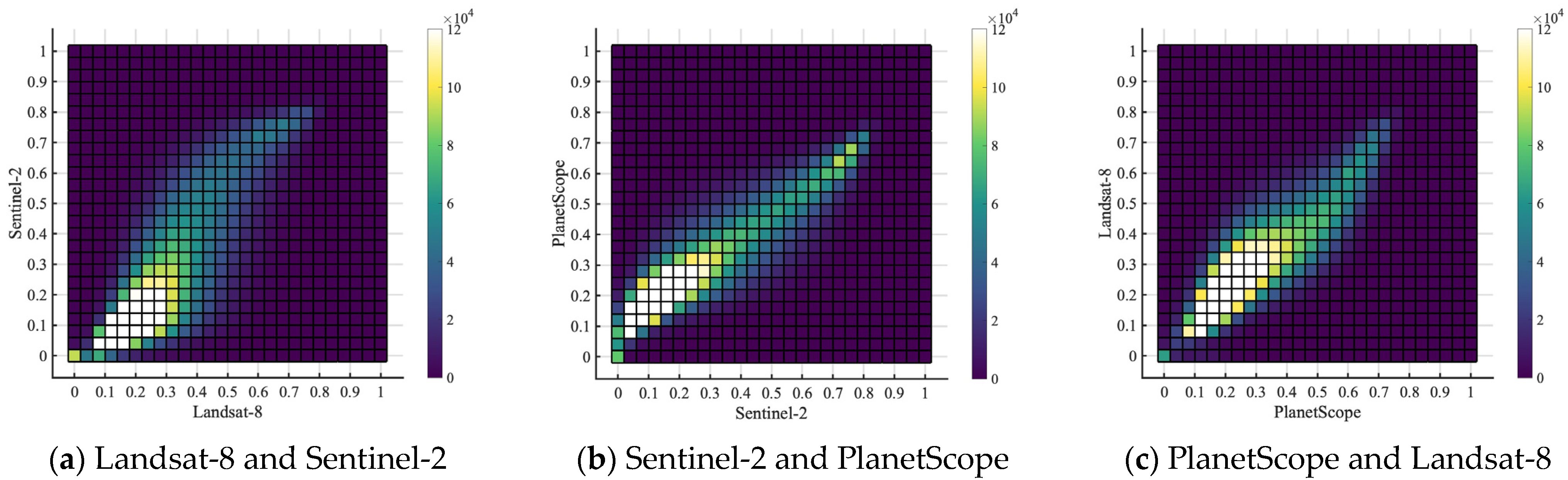
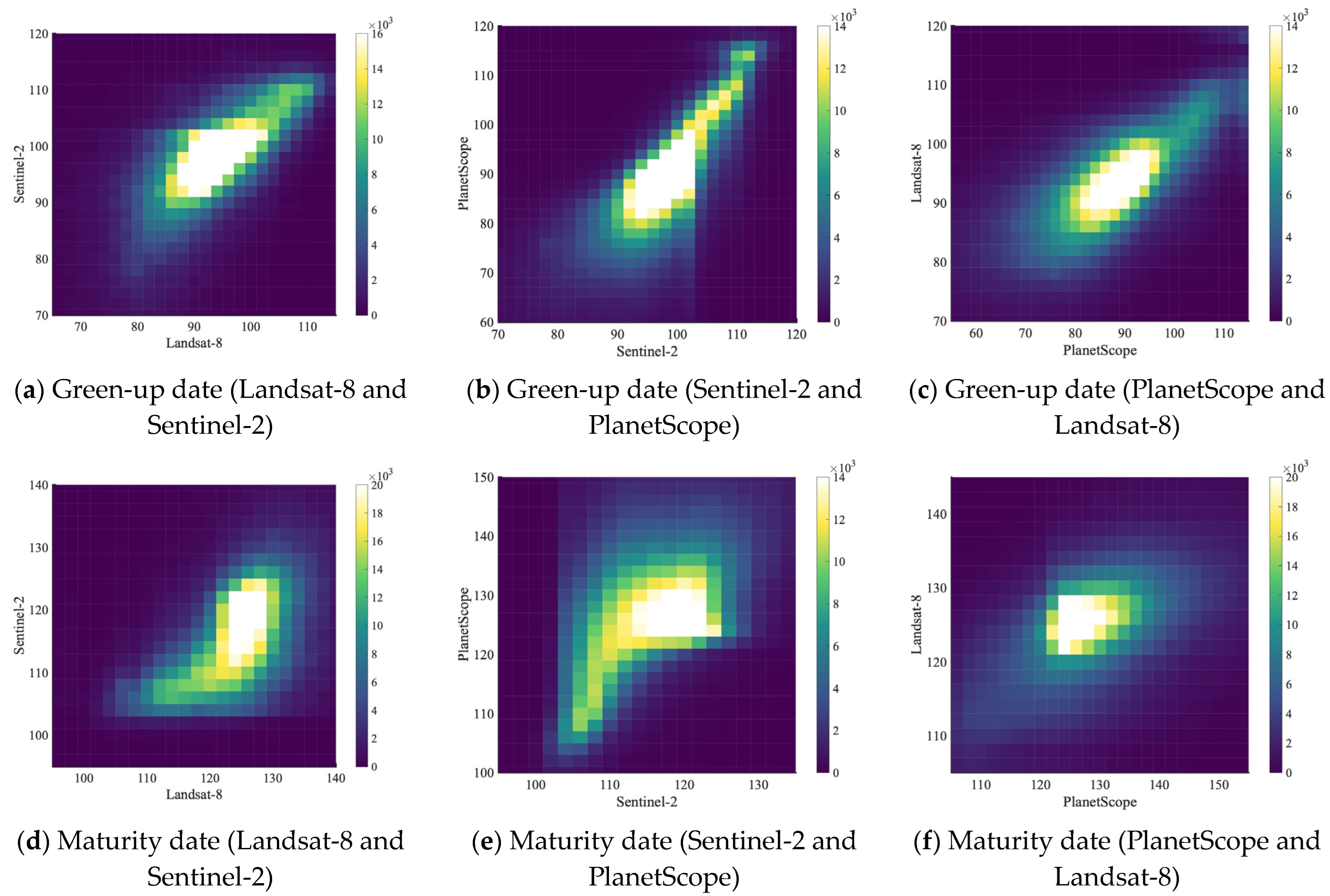
Different NDVI datasets are compared to evaluate their consistency for the purpose of modeling vegetation phenology based on NDVI. The coefficient of determination (R2) value between Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 is 0.63 (Figure 5a), while the R2 value between Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope is 0.78 (Figure 5b), and the R2 value between PlanetScope and Landsat-8 is 0.71 (Figure 5c). The density histograms in Figure 5 show nonlinear correlations, especially between Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 and between PlanetScope and Landsat-8. The standard deviations of the three datasets (mean August 2021 NDVI) are similar, which are 0.17, 0.22, and 0.17 for Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope, respectively. From the figure, we observe that (a) Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 show a convex shape in low NDVI values and a concave shape in high NDVI values; (b) Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope show the highest consistency; and (c) PlanetScope and Landsat-8 show a linear correlation with slight heteroscedasticity in low NDVI values and a convex shape in high NDVI values. Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope have a much more linear relationship, probably because the PlanetScope dataset has been harmonized with Sentinel-2 since it was obtained. These results from comparisons are consistent with previous studies. For example, Moon et al. [24] compared the NDVI consistency between the PlanetScope dataset and the harmonized Landsat and Sentinel dataset, and their results show high agreement in time series. Moreover, Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 are tested to have high consistency in monthly mean NDVI at the neighborhood scale without sensor harmonization [22]. We conclude that the three data products are generally consistent with each other when NDVI values are compared at the PlanetScope pixel level.
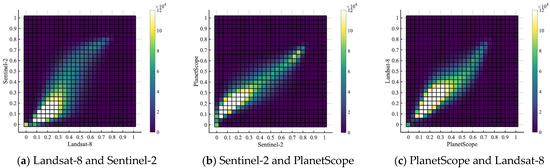
Figure 5.
Scatter plots of summer 2021 pixel-level mean NDVI correlation for (a) Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 with an R2 of 0.63, (b) Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope with an R2 of 0.78, and (c) PlanetScope and Landsat-8 with an R2 of 0.71. The color bars show the number of pixels that fall into each scatter plot cell. This scatter plot includes pixels that have valid NDVI values in all three datasets.
3.2. City-Scale Vegetation Phenology in Downtown Beijing, Inferred from PlanetScope, Landsat-8, and Sentinel-2
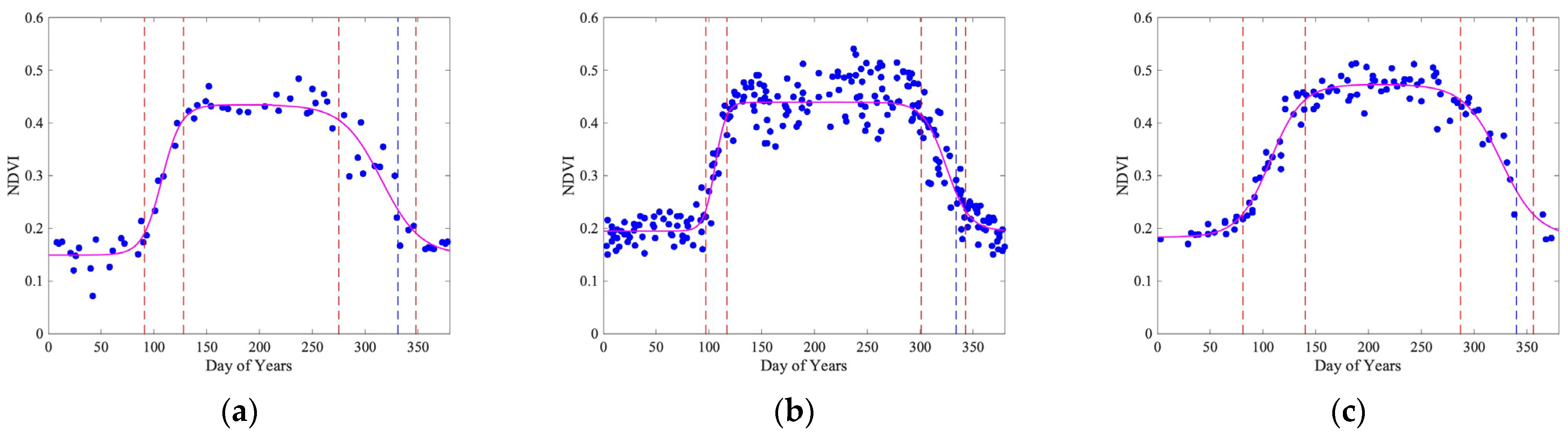
At the city scale, the study year overlay analysis shows that Landsat-8 identifies four phenological transition dates of 91, 128, 275, and 348, as shown in Figure 6a. The spring–summer growth period (between the green-up point and the maturity point) is 37 days. The maturity plateau length (between the maturity point and the senescence point) is 147 days. The autumn–winter growth period (between the senescence point and the dormancy point) is 73 days. The dormancy valley (between the dormancy point and the following green-up point) is 108–109 days. Similarly, Sentinel-2 identifies four phenological transition dates of 97, 117, 301, and 343, as shown in Figure 6b. The spring–summer growth period is 20 days, the maturity plateau length is 184 days, and the autumn–winter growth period is 42 days. The dormancy valley is 119–120 days. Lastly, PlanetScope identifies four phenological transition dates of 81, 140, 287, and 356, as shown in Figure 6c. The spring–summer growth period is 59 days, the maturity plateau length is 147 days, and the autumn–winter growth period is 69 days. While these important phenological dates show similar results, we do observe some differences. For example, Sentinel-2 shows the longest maturity plateau length, while Landsat-8 and PlanetScope have identified the same length. PlanetScope shows very smooth curves depicting the vegetation phenology at the city scale, which identifies the dormancy dates later than 350.
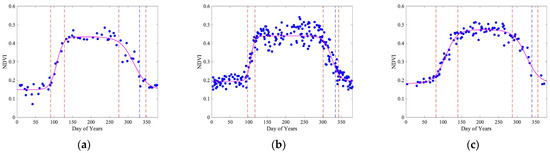
Figure 6.
City-scale vegetation phenology was estimated from Landsat-8 in (a), Sentinel-2 in (b), and PlanetScope in (c). The blue dots are NDVI observations. The magenta curves following the NDVI observations are modeled phenology using Equation (1). Phenological transition dates (shown by vertical dash lines) are identified using the thresholds mentioned in Section 2.3.1. In this figure, we use overlaid yearly data from 1 January 2019 to 28 February 2023. Blue dashed lines show the dormancy dates estimated using the threshold .
The independent study year analysis is shown in Table 1. The results show that the three datasets have identified similar green-up dates in the study year 2020, while PlanetScope has identified the earliest green-up date in the study years 2019, 2021, and 2022. Among independent study years, the standard deviations of Landsat-8 are 8.66, 17.90, 9.11, and 13.18 days for the green-up, maturity, senescence, and dormancy dates, respectively. The standard deviations of Sentinel-2 are 4.65, 4.99, 2.65, and 9.78 days, respectively. The standard deviations of PlanetScope are 2.75, 2.45, 10.05, and 7.35 days, respectively. Among the three datasets, the standard deviations show that PlanetScope has the most stable estimation of the green-up, maturity, and dormancy dates. Sentinel-2 has the most stable estimation of the senescence date. At the city scale, the maturity and dormancy date estimations of Landsat-8 and the senescence date estimation of PlanetScope are highly variable. Additionally, due to relatively late dormancy dates estimated using the threshold , we also test the threshold to calculate the dormancy dates, where Landsat-8 yields the earliest dormancy date using the overlaid four-year dataset. The standard deviations of the dormancy dates of four individual study years using this threshold are 8.54, 7.07, and 6.95 days for Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope, respectively, which are lower than those using the threshold .

Table 1.
Phenological transition dates, including green-up, maturity, senescence, and dormancy dates of the year(s) at the city scale, are estimated from Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope.
3.3. Pixel-Level Growth Period Phenology
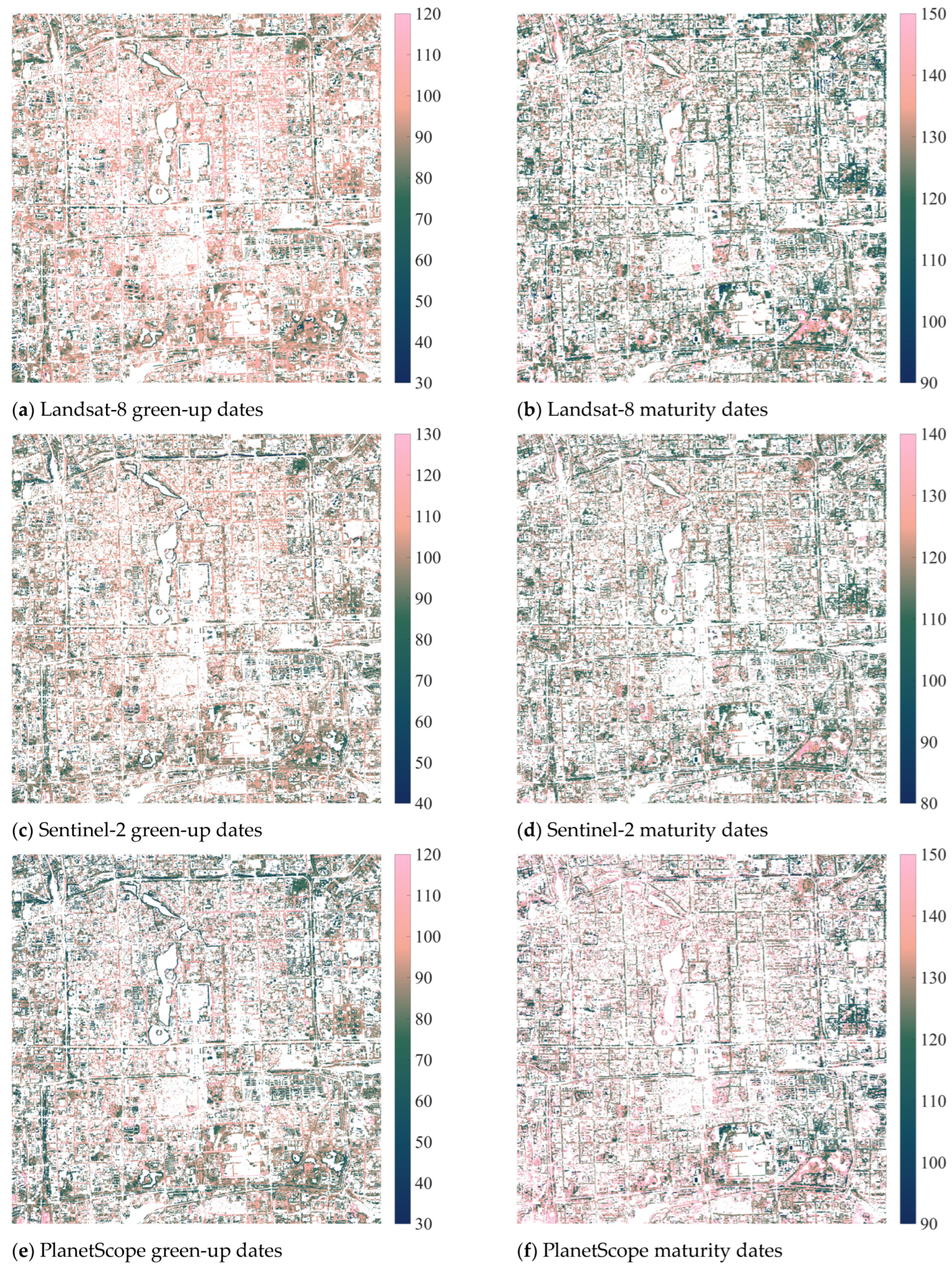
The spring–summer growth period phenology, including green-up and maturity dates, is further investigated for the pixel level. After applying the filters (as mentioned in Section 2.3.3), the proportions of available pixels are 42.97% for Landsat-8 green-up dates, 42.34% for Landsat-8 maturity dates, 40.25% for Sentinel-2 green-up dates, 40.69% for Sentinel-2 maturity dates, 41.93% for PlanetScope green-up dates, and 40.62% for PlanetScope maturity dates (Figure 7). The pixel-level spring–summer growth period phenology analysis shows similar temporal patterns (as shown in Figure 7) compared to the city-scale analysis (as shown in Figure 6). Landsat-8 identifies the mean green-up date (with one standard deviation) of 91.07 (±13.99) and the mean maturity date of 126.71 (±13.24). Moreover, Sentinel-2 identifies the mean green-up date of 95.54 (±16.30) and the mean maturity date of 118.41 (±14.79). Lastly, PlanetScope identifies the mean green-up date of 83.48 (±20.00) and the mean maturity date of 135.29 (±21.70). The results show that PlanetScope identifies the earliest mean green-up date with the greatest standard deviation and the latest mean maturity date with the greatest standard deviation. The high spatial resolution can explain the high standard deviation from PlanetScope. Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 show similar results in the mean green-up dates, while Sentinel-2 shows the earliest mean maturity date among the three datasets.
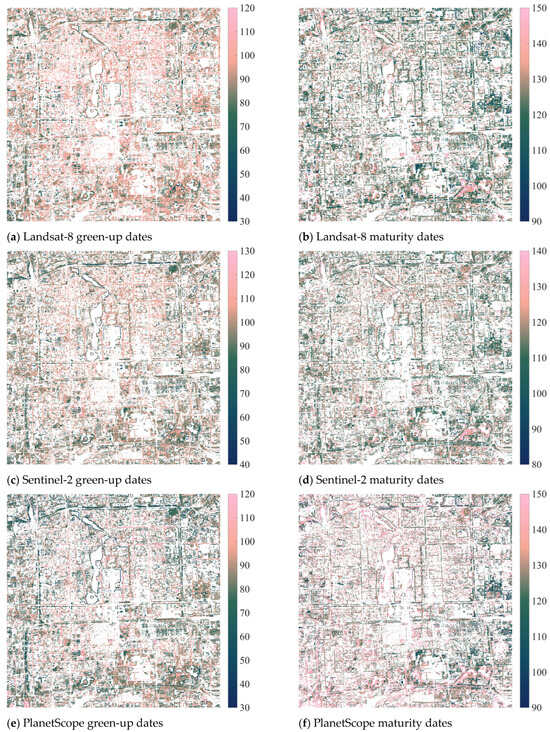
Figure 7.
Vegetation phenology maps at the pixel level were calculated using Equation (1) and filtered by the PlanetScope August composite NDVI > 0.3, the PlanetScope August/February seasonal variation ratio (SVR) > 1.5, and extreme value thresholds. (a) 30 m Landsat-8 green-up dates have a mean value (standard deviation) of 91.07 (±13.99). (b) Landsat-8 maturity dates have a mean value of 126.71 (±13.24). (c) 10 m Sentinel-2 green-up dates have a mean value of 95.54 (± 16.30). (d) Sentinel-2 maturity dates have a mean value of 118.41 (±14.79). (e) 3 m PlanetScope green-up dates have a mean value of 83.48 (±20.00). (f) PlanetScope maturity dates have a mean value of 135.29 (±21.70).
There is a medium level of correlation between each pair of datasets identifying the green-up date at the pixel level, as shown in Figure 8a–c and Table 2. When the NDVI filter is 0.3 (to filter out pixels with an NDVI value equal to or smaller than 0.3) and the evergreen/deciduous filter is 1.5, the R2 values are 0.22 between Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2, 0.25 between Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope, and 0.20 between PlanetScope and Landsat-8. The R2 values significantly increase when the NDVI filter increases to 0.5. When the NDVI filter increases to 0.7, the R2 values of green-up dates between Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 and between Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope increase, while the R2 value between the PlanetScope and Landsat-8 decreases (Table 2). This result indicates that these three datasets have high consistency in estimating the green-up date in medium-to-dense vegetation (PlanetScope August mean NDVI > 0.5). The identification of maturity dates yields much lower R2 values when the NDVI filter is 0.3 and the evergreen/deciduous filter is 1.5, as shown in Figure 8d–f and Table 2. When the NDVI filter increases to 0.5 and 0.7, there is a significant increase in R2 values between the datasets. This result suggests that these three datasets have high consistency in estimating the maturity date in dense vegetation (PlanetScope August mean NDVI > 0.7, as mentioned in Table 2).
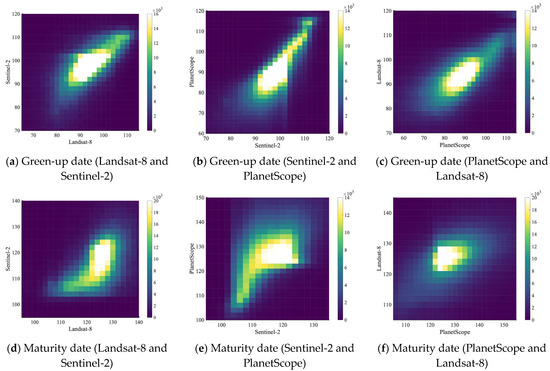
Figure 8.
Density plots show the consistency of the estimated phenological transition dates during the spring–summer growth period at the pixel level. Colorbars show the number of pixels. Filters include NDVI > 0.5 and SVR > 1.5. (a) Green-up date comparison between Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2; (b) green-up date comparison between Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope; (c) green-up date comparison between PlanetScope and Landsat-8; (d) maturity date comparison between Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2; (e) maturity date comparison between Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope; (f) maturity date comparison between PlanetScope and Landsat-8.

Table 2.
Consistency of the estimated phenological transition dates during the spring–summer growth period at the pixel level (R2 values).
The proportions of available pixels are 22.40% for Landsat-8 senescence dates, 28.86% for Landsat-8 dormancy dates, 31.28% for Sentinel-2 senescence dates, 32.64% for Sentinel-2 dormancy dates, 34.36% for PlanetScope senescence dates, and 40.36% for PlanetScope dormancy dates. The R2 values between datasets in identifying senescence and dormancy dates are generally low (Figure A1 and Table A1), except that three datasets have a medium consistency in identifying dormancy dates when the NDVI filter is 0.7 and the evergreen/deciduous filter is 1.5. These results indicate that the three datasets have very different characteristics during the autumn–winter growth period.
3.4. Street-Scale Tree Genus Phenology Comparison
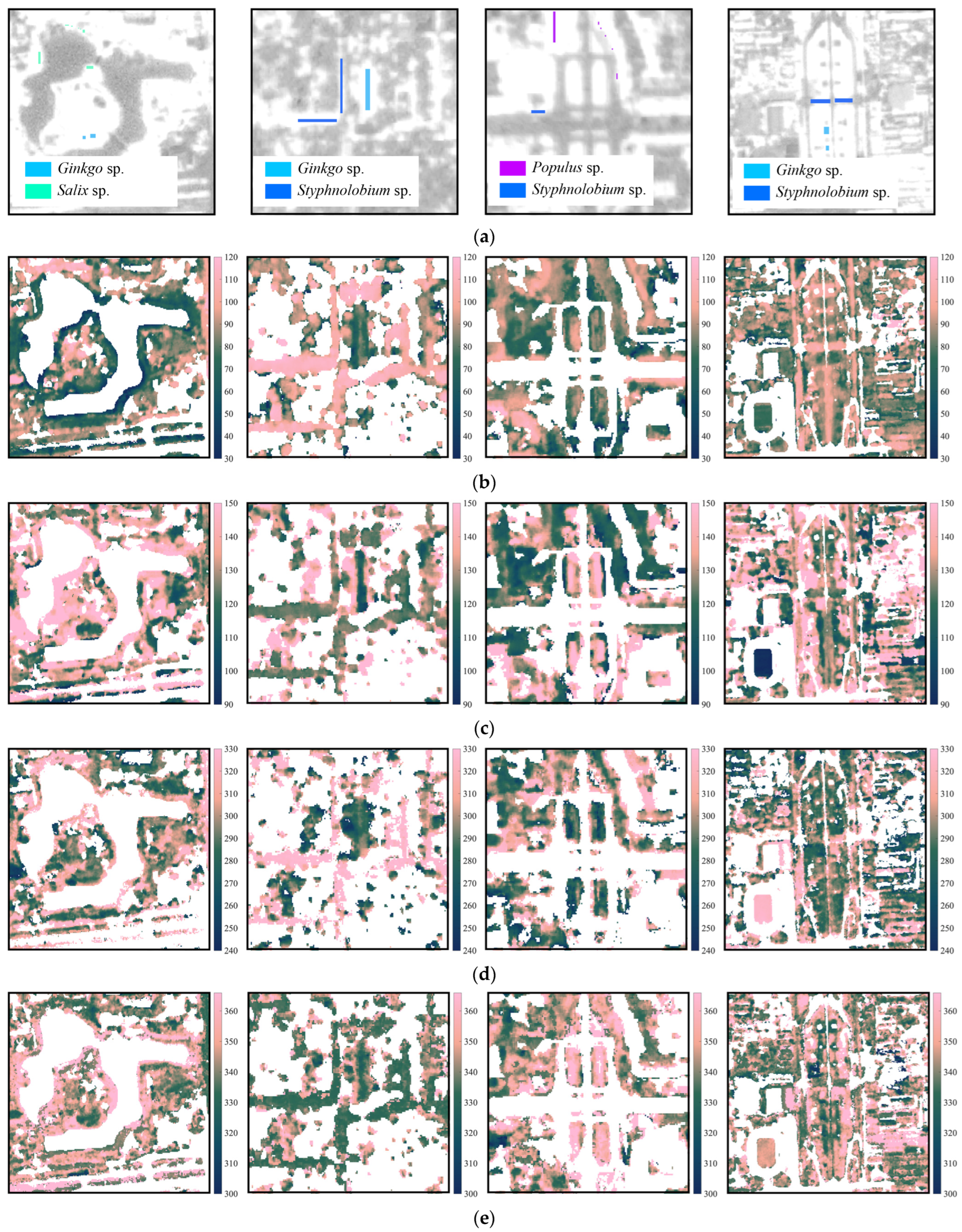
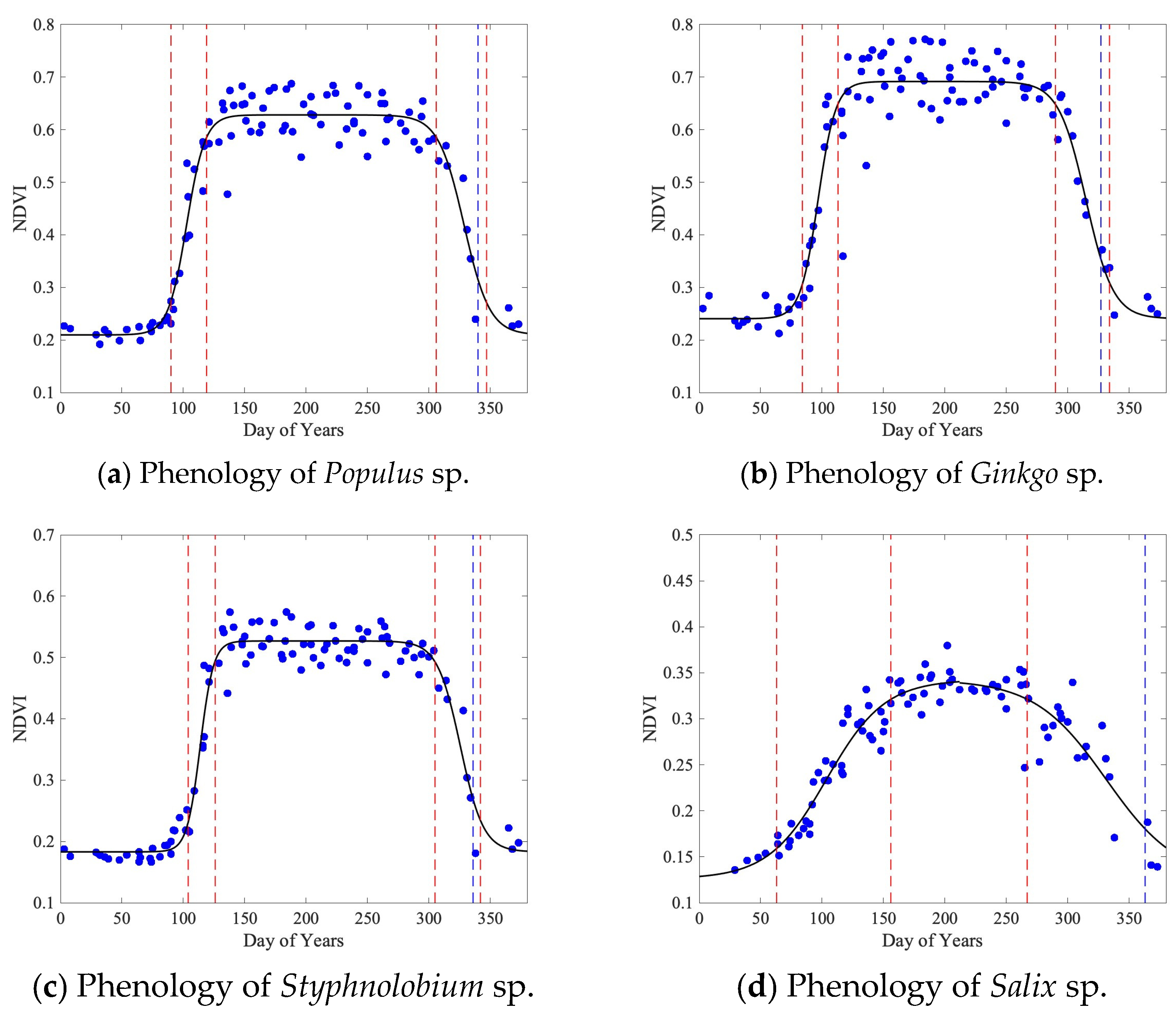
Zooming into the street scale, PlanetScope images can distinguish tree genera (Figure 9 and Figure 10). Within the sample tree points labeled in Figure 9a, the mean phenological transition dates and the three phenological periods of the four tree genera are calculated, as shown in Figure 10 and Table 3. Results estimated using PlanetScope images show that the spring–summer growth periods of the four genera are 29 days, 29 days, 25 days, and 93 days, respectively. The maturity plateau lengths are 187 days, 177 days, 179 days, and 111 days, respectively. The autumn–winter growth periods are 41 days, 44 days, 37 days, and 115 days, respectively. The dormancy lengths are 108–109 days, 115–116 days, 124–125 days, and 46–47 days, respectively. Maximum fitted NDVI values are 0.63, 0.69, 0.53, and 0.34, respectively. Due to the impact of nearby waterbodies on the reflectance of vegetation pixels, outliers of land observation are removed when modeling Salix sp. The estimated dormancy dates of the four tree genera, especially Salix sp., do not capture the real timing due to complex urban surface reflectance and waterbody reflectance. To resolve this problem, different thresholds are tested and listed in Figure 10 and Table 3.
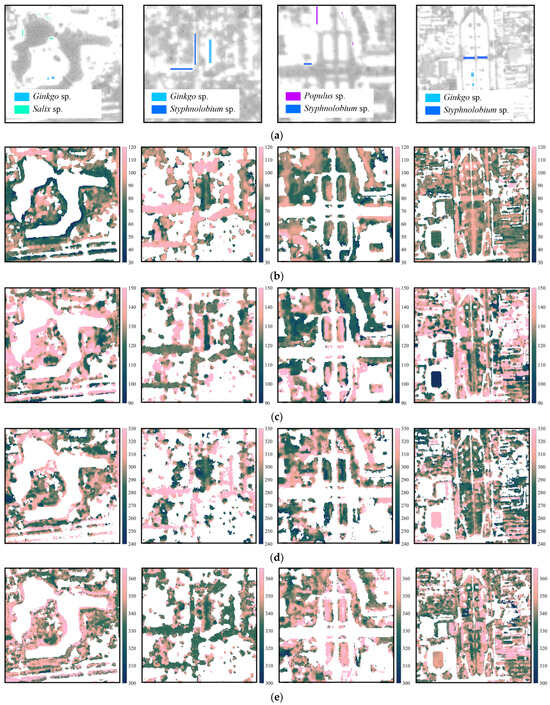
Figure 9.
(a) Sample pixels of the four target tree genera in sample neighborhoods. These sample neighborhoods are Taoranting Park, Yonghe Temple, Jianguomen Bridge, and Yongdingmen Park from left to right, which have also been labeled in Figure 2 as subset study areas. Spatial distributions of phenological transition dates of (b) green-up, (c) maturity, (d) senescence, and (e) dormancy in sample neighborhoods. These dates are derived from PlanetScope images at the street scale with a spatial resolution of 3 m. Tree stands show different spatial and temporal phenology patterns. The illustrations and images of the selected tree genera is shown in Figure 1 and Figure 4.
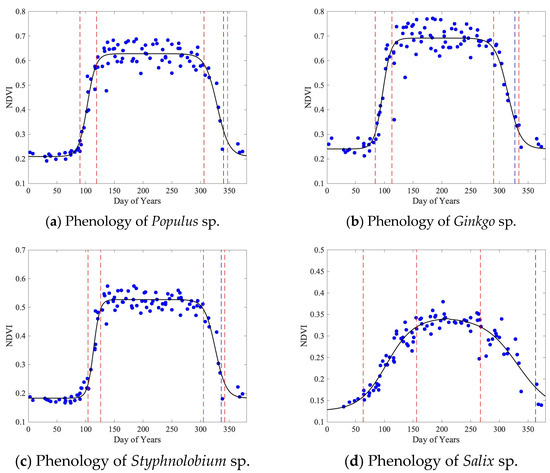
Figure 10.
Phenology of four common street tree genera. The pixels are selected as shown in Figure 9a. Populus sp., Ginkgo sp., Styphnolobium sp., and Salix sp. have 96, 367, 635, and 126 pixels, respectively, with a spatial resolution of PlanetScope. The phenology of each tree genus is calculated directly from the cleaned-up datasets with only cloud removal and without using the NDVI filter and the evergreen/deciduous filter. The standard deviation is calculated using the pixel values from the original vegetation phenology maps (Figure 7). Blue dash lines show the dormancy results using the threshold .

Table 3.
Combined phenological transition dates (with standard deviation at the pixel level) and mean time intervals of selected tree genera.
4. Discussion
4.1. Dataset Selection for Urban Tree Phenology Analysis
Although Landsat-8 has a stable NDVI observation curve, the 30 m spatial resolution is too coarse to capture smaller-scale variations and textures, especially when streetscape management requires detailed information and a clear delineation between tree canopy and built-up surfaces. The longer revisit interval makes it difficult to obtain enough data in a shorter period, such as one or two study years. The low temporal resolution also makes Landsat-8 susceptible to clouds because clouds will further decrease available observations at the pixel level. Sentinel-2 achieves a good balance between spatial resolution and revisit intervals. The 10 m spatial resolution is close to larger street trees. The 5-day temporal resolution makes it comparatively easy to form a time series by using observations obtained in a single year. However, the NDVI observations fluctuate more because the cloud mask on GEE does not always identify cloud pixels. Therefore, manual image inspection is required. Compared to Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2, the much higher spatial resolution of PlanetScope allows tree phenology estimation at the street scale because the 3 m spatial resolution is smaller than many tree crowns. However, during data exploration and analysis, we also found that built-up surfaces and water bodies might impact NDVI and the estimated phenological transition dates of adjacent tree pixels. The boundary between the tree canopy and the surrounding non-vegetated area is not very clearly delineated. Moreover, a mixed urban forest stand may lead to an averaged estimation result. This is the reason why we select street-scale tree points only in monoculture areas with one genus. This limitation requires future investigation with precisely geolocated tree points for comparison.
4.2. Result Interpretation
The pixel-level comparison between datasets shows lower consistency compared to previous studies for the following reasons: First, Moon et al. [24] focus on very natural environments with minimal built-up disturbances. In contrast, our study focuses on downtown Beijing, where the built-up areas are the predominant land cover type. Maintained landscapes form vertically hierarchical structures, ranging from groundcovers and shrubs to understory canopy and overstory canopy. The lower layer of maintained groundcovers and shrubs may be a disturbing background for tree phenology analysis. Second, Moon et al. [24] have resampled PlanetScope to a much coarser spatial resolution from 3 m to 9 m, using the median value for representation. Extracting the median value from 9 pixels may decrease the variability of the PlanetScope dataset. In our study, we have used the original spatial resolution of PlanetScope to evaluate the consistency among the three datasets. This method preserves the detailed information of datasets with higher spatial resolutions; therefore, PlanetScope can detect more edges between densely vegetated areas, sparsely vegetated areas, and non-vegetated areas. Consequently, the pixel-level comparison resulted in lower R2 values. The different NDVI filters used in this study lead to distinct levels of consistency among the three datasets in estimating phenological transition dates during the entire growth period. This finding indicates the distinct challenges in identifying phenological transition dates in the natural environment (dense vegetation) versus urban landscapes (mixed density of vegetation).
The spatial patterns of the pixel-level growth period phenology show that certain streets have noticeably later green-up dates and earlier maturity dates than other streets and urban green space patches. In a larger area, Zhang et al. [18] examined the impact of the impervious surface area on phenological indicators using the 500 m spatial resolution MODIS vegetation phenology data. Their results indicate that there is a general increase in the green-up date and a decrease in the dormancy date as the impervious surface area increases. Wang et al. [19] concluded that warming advanced the green-up date in 78.3% of the urban areas and 72.8% of the rural areas using MODIS datasets focusing on 292 studied cities in China. Similarly, the urbanization level contributes to the advancement of the green-up date in New York State, but the average green-up dates also vary noticeably by land cover type [16]. In contrast, our study excluded impervious surface areas, and the spatial pattern at a finer pixel level (Figure 7 and Figure 9) indicates that the composition of the vegetation community at the street scale may have a stronger impact on the phenological indicators.
At the street scale, one limitation is a lack of comparison between multiple datasets, which is more desirable to obtain more convincing results in estimating urban tree phenology. This limitation can be improved using Jilin-1 satellite images with a very high spatial resolution. Moreover, Alonzo et al. [31] used a much more complete dataset of tree points. However, our study does not obtain such detailed information on tree species. Future studies may focus on collecting more tree samples to enhance the robustness of the tree genus analysis at the street scale.
Additionally, our method of estimating the dormancy date at both the city scale and the street scale using the threshold from the MODIS MCD12Q2 product results in later values, while the threshold results in a more reasonable outcome. This finding suggests that the spatial resolution of the datasets may impact the estimated dormancy date, given that the three datasets have a much higher spatial resolution than MODIS. To further investigate this phenomenon, more available winter observations and dataset harmonization are expected to reduce uncertainty.
4.3. Implications on Urban Environmental Planning
This study enables urban planners to measure tree phenology at the street scale. As confirmed by checking Baidu street view photos, the vegetation phenology maps also show a problem of homogenous street tree plantation in Beijing (Figure 7). Therefore, streetscapes lack aesthetic appeal. For example, Styphnolobium sp. is a very dominant tree genus along many streets within the study area. However, based on PlanetScope observations, Styphnolobium sp. typically experiences a late mean green-up date around mid-April. This results in the streets in Beijing not being green enough in the early spring. Planners might consider a mix of tree genera with different seasonal characteristics for street-scale greening initiatives. This can improve street-scale species richness and enhance people’s perception of biodiversity. Future studies may use PlanetScope to estimate urban biomass at the street scale. This could be beneficial for achieving carbon net zero goals and controlling urban air pollution in the early spring. Future studies may use planning metrics for other types of analysis. This could involve examining factors such as land use and land cover maps and zoning maps to investigate street tree phenology and the urban function distribution behind it. Future studies may explore the design of a map showing areas with phenologically monotonous vegetation. This may help local governments visualize priority areas for intervention.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we have compared vegetation phenology metrics derived from Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope at the city scale and the pixel level in downtown Beijing. Moreover, we compared the phenological metrics of four common street tree genera in Beijing using the PlanetScope dataset. The city-scale comparison shows slightly different phenological signals from the three datasets due to the different sensor properties. From the pixel-level maps (Figure 7), the mean green-up date is 91.07 (±13.99) using Landsat-8, 95.54 (±16.30) using Sentinel-2, and 83.48 (±20.00) using PlanetScope. The mean maturity date is 126.71 (±13.24) using Landsat-8, 118.41 (±14.79) using Sentinel-2, and 135.29 (±21.70) using PlanetScope. For spring–summer growth period phenology, the results show that PlanetScope identifies the earliest mean green-up date with the greatest standard deviation and the latest mean maturity date with the greatest standard deviation. The high spatial resolution can explain the high standard deviation from PlanetScope. Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 show very similar results in the mean green-up dates, while Sentinel-2 shows the earliest mean maturity date among the three datasets. The pixel-level comparison shows medium-to-high consistency in estimating green-up and maturity dates in areas with medium-to-high vegetation cover (Table 2), while the consistency between the datasets in identifying senescence and dormancy dates is generally low (Table A1). In conclusion, the three satellite observation datasets prove to be effective in monitoring street tree phenology during the spring–summer growth period in Beijing; PlanetScope is effective in monitoring tree phenology at the street scale; however, Landsat-8 may be affected by the mixture of land covers due to its relatively coarse spatial resolution.
At the street scale, this study emphasizes the efficacy of NDVI time series derived from PlanetScope in estimating the phenology of common street tree genera, including Poplars (Populus), Ginkgos (Ginkgo), Chinese Scholars (Styphnolobium), and Willows (Salix), in downtown Beijing to improve urban vegetation planning. Based on PlanetScope observations, we found that the four street tree genera have unique phenological patterns. For instance, Chinese Scholars have a late green-up date of 101 and a comparatively early late senescence date of 305 on average. We have observed the late green-up timing along many major streets in downtown Beijing, where Chinese Scholars is the major tree genus. This phenomenon can also be observed from the Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 datasets. For future studies, the exploration of street-scale biomass estimation, integration of urban land use and zoning maps, and in-depth analysis of the phenological diversity of urban landscapes are potential directions. This trajectory seeks to elevate the field of urban vegetation phenology, transforming it into a more application-centric pursuit.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.-Y.G.; methodology, F.-Y.G.; software, H.W.; validation, F.-Y.G.; formal analysis, H.W.; investigation, H.W.; resources, H.W. and F.-Y.G.; data curation, H.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.W. and F.-Y.G.; writing—review and editing, F.-Y.G.; visualization, H.W.; supervision, F.-Y.G.; project administration, F.-Y.G.; funding acquisition, F.-Y.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42301477), the Humanities and Social Science Fund of Ministry of Education (Grant No. 22YJCZH034), and Capital Development and Governance Institute, Renmin University of China (Grant No. 2024B-11).
Data Availability Statement
Remote sensing data are downloaded from Google Earth Engine (Available online: http://earthengine.google.com (accessed on 23 June 2024)) and Planet Labs (Available online: https://www.planet.com (accessed on 23 June 2024)).
Acknowledgments
Hexiang Wang was supported by the Presidential Graduate Fellowship 2022–2026 at the University of Georgia. This work was also supported by the supercomputing center at Renmin University of China. We thank Google Earth Engine for offering access to Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 data, Planet Labs for providing high-resolution satellite imagery. The computer resources were supported by the lab computers at the University of Georgia and Public Computing Cloud at Renmin University of China (PCC@RUC).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
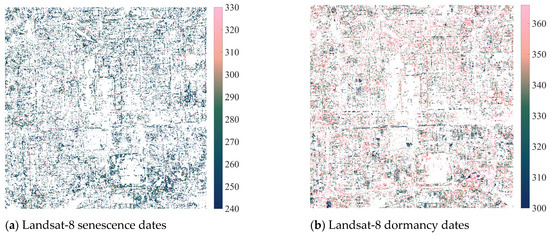
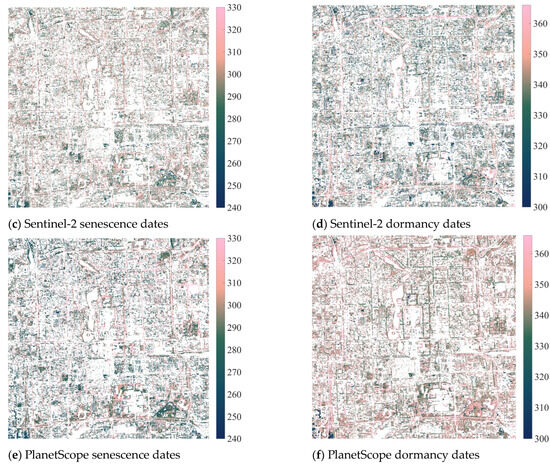
Figure A1.
Vegetation phenology maps at the pixel level were calculated using Equation (1) filtered by the PlanetScope August composite NDVI > 0.3, the PlanetScope August/February seasonal variation ratio (SVR) > 1.5, and extreme value thresholds. (a) 30 m Landsat-8 senescence dates with a mean value (standard deviation) of 271.51 (±23.44). (b) Landsat-8 dormancy dates with a mean value of 347.12 (±20.05). (c) 10 m Sentinel-2 senescence dates with a mean value of 294.81 (±17.96). (d) Sentinel-2 dormancy dates with a mean value of 336.17 (±17.99). (e) 3 m PlanetScope senescence dates with a mean value of 292.64 (±22.96). (f) PlanetScope dormancy dates with a mean value of 346.65 (±15.15).
Figure A1.
Vegetation phenology maps at the pixel level were calculated using Equation (1) filtered by the PlanetScope August composite NDVI > 0.3, the PlanetScope August/February seasonal variation ratio (SVR) > 1.5, and extreme value thresholds. (a) 30 m Landsat-8 senescence dates with a mean value (standard deviation) of 271.51 (±23.44). (b) Landsat-8 dormancy dates with a mean value of 347.12 (±20.05). (c) 10 m Sentinel-2 senescence dates with a mean value of 294.81 (±17.96). (d) Sentinel-2 dormancy dates with a mean value of 336.17 (±17.99). (e) 3 m PlanetScope senescence dates with a mean value of 292.64 (±22.96). (f) PlanetScope dormancy dates with a mean value of 346.65 (±15.15).
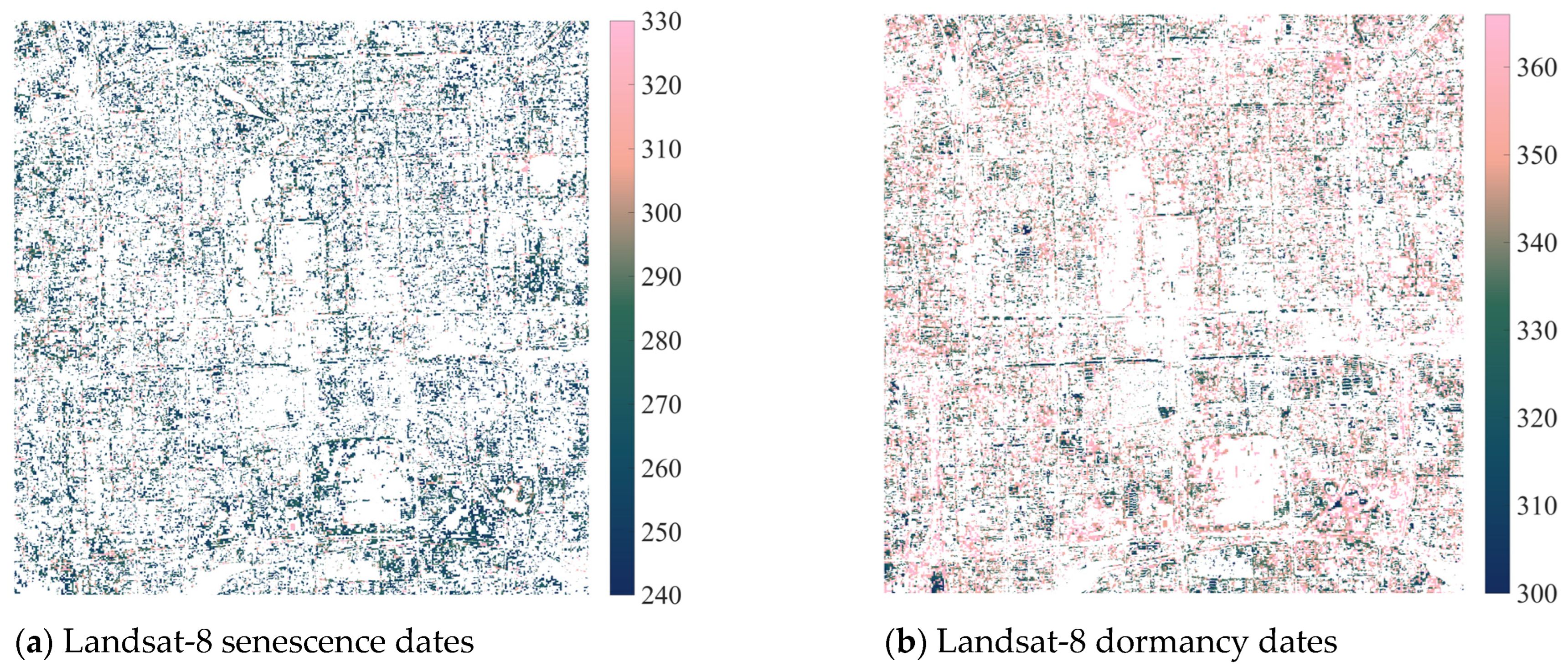
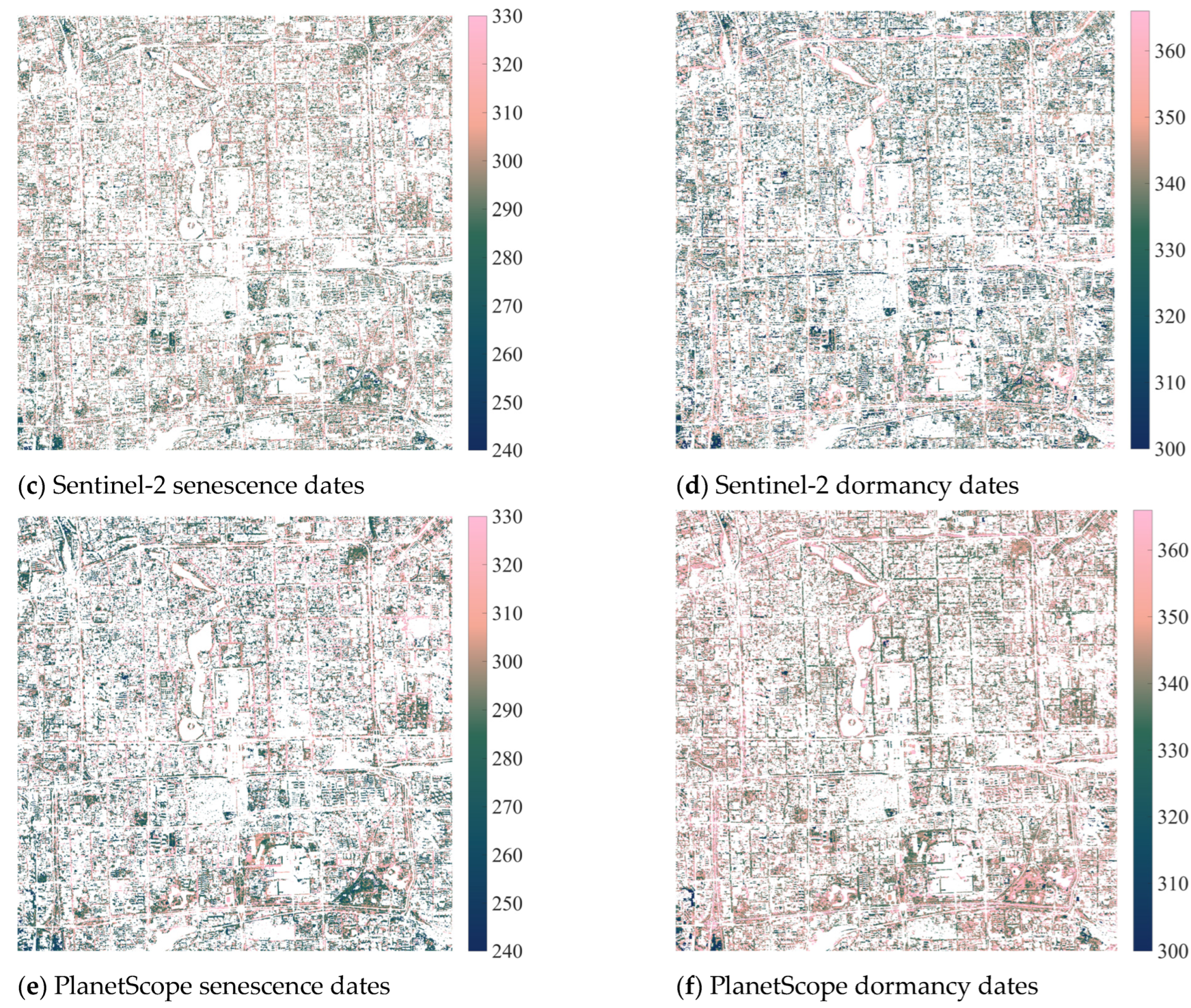

Table A1.
Consistency of the estimated phenological transition dates during the autumn–winter growth period at the pixel level (R2 values).
Table A1.
Consistency of the estimated phenological transition dates during the autumn–winter growth period at the pixel level (R2 values).
| Filtering Criteria | Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 (senescence) | Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope (senescence) | PlanetScope and Landsat-8 (senescence) |
| NDVI > 0.3, SVR > 1.5 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.13 |
| NDVI > 0.5, SVR > 1.5 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.15 |
| NDVI > 0.7, SVR > 1.5 | 0.05 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| Filtering Criteria | Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 (dormancy) | Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope (dormancy) | PlanetScope and Landsat-8 (dormancy) |
| NDVI > 0.3, SVR > 1.5 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| NDVI > 0.5, SVR > 1.5 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.05 |
| NDVI > 0.7, SVR > 1.5 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.19 |
Filtering criteria are designed to exclude pixels based on their properties, ultimately for consistency analysis.
References
- Zhou, Y. Understanding urban plant phenology for sustainable cities and planet. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, D.E.; Buyung-Ali, L.; Knight, T.M.; Pullin, A.S. Urban greening to cool towns and cities: A systematic review of the empirical evidence. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rötzer, T.; Moser-Reischl, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Hartmann, C.; Paeth, H.; Pauleit, S.; Pretzsch, H. Urban tree growth and ecosystem services under extreme drought. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 308, 108532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, Z.G.; Dallimer, M.; Edmondson, J.L.; Leake, J.R.; Gaston, K.J. Identifying potential sources of variability between vegetation carbon storage estimates for urban areas. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chang, Y.; Yan, P. Ranking the suitability of common urban tree species for controlling PM2.5 pollution. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Byrne, J.A.; Pickering, C. A systematic quantitative review of urban tree benefits, costs, and assessment methods across cities in different climatic zones. Urban For. Urban Green. 2012, 11, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowarik, I. Novel urban ecosystems, biodiversity, and conservation. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1974–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.K.; Honold, J.; Botzat, A.; Brinkmeyer, D.; Cvejić, R.; Delshammar, T.; Elands, B.; Haase, D.; Kabisch, N.; Karle, S.J.; et al. Recreational ecosystem services in European cities: Sociocultural and geographic context matters for park use. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, G.R.; Rock, M.; Toohey, A.M.; Hignell, D. Characteristics of urban parks associated with park use and physical activity: A review of qualitative research. Health Place 2010, 16, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariñanos, P.; Casares-Porcel, M. Urban green zones and related pollen allergy: A review. Some guidelines for designing spaces with low allergy impact. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 101, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Jiang, N.; Peng, D.; Rao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fu, Y.H.; Yang, W.; Zhu, X.; Cao, R.; Chen, X.; et al. Can changes in autumn phenology facilitate earlier green-up date of northern vegetation? Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 291, 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Friedl, M.A.; Tan, B.; Zhang, X.; Verma, M. Land surface phenology from MODIS: Characterization of the Collection 5 global land cover dynamics product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Han, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, F. Divergent impacts of droughts on vegetation phenology and productivity in the Yungui Plateau, southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Asrar, G.R.; Meng, L. Characterizing spatiotemporal dynamics in phenology of urban ecosystems based on Landsat data. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Ma, X.; Dou, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, C. Impacts of climate change on vegetation phenology and net primary productivity in arid Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 149055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, X.; Asrar, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, M.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Luo, M.; Sapkota, A.; et al. Detection and attribution of long-term and fine-scale changes in spring phenology over urban areas: A case study in New York State. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 110, 102815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Sharifi, A.; Tahir, M.N.; Tariq, A.; Zhang, L.; Mumtaz, F.; Shah, S.H.I.A. Evaluation of Vegetation Indices and Phenological Metrics Using Time-Series MODIS Data for Monitoring Vegetation Change in Punjab, Pakistan. Water 2021, 13, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, P.; Li, X.; Niu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cao, W.; Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Yao, X.; Yu, L.; et al. The divergent response of vegetation phenology to urbanization: A case study of Beijing city, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; De Boeck, H.J.; Chen, L.; Song, C.; Chen, Z.; McNulty, S.; Zhang, Z. Urban warming increases the temperature sensitivity of spring vegetation phenology at 292 cities across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Song, G.; Liujun, Z.; Yanan, Z.; Di, L. Urban vegetation phenology analysis using high spatio-temporal NDVI time series. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 25, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Song, C.; Li, J. Impacts of Urbanization on Vegetation Phenology over the Past Three Decades in Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zeng, Z.-C. Satellite Observations of Urban Greenery Phenology in Downtown Beijing at Meter to Kilometer Scales. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 6268–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planet Labs. Real-Time Satellite Monitoring with Planet. Available online: https://www.planet.com/products/monitoring/ (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Moon, M.; Richardson, A.D.; Friedl, M.A. Multiscale assessment of land surface phenology from harmonized Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2, PlanetScope, and PhenoCam imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 266, 112716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Yan, Z.; Song, G.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Q.; Deng, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Z.; et al. Monitoring tree-crown scale autumn leaf phenology in a temperate forest with an integration of PlanetScope and drone remote sensing observations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 171, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, E.; Kerekes, J.; Daughtry, C.; Russ, A. Assessing the impact of satellite revisit rate on estimation of corn phenological transition timing through shape model fitting. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, E.; Sheffield, K.; Crawford, D.; Akpa, S.; Clancy, A.; Clark, R. Spatial and Temporal Biomass and Growth for Grain Crops Using NDVI Time Series. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Ong, J.; Theobald, E.J.; Olden, J.D.; Tan, A.; Hillerislambers, J. Detecting montane flowering phenology with cubesat imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jin, Y.; Brown, P. An enhanced bloom index for quantifying floral phenology using multi-scale remote sensing observations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 156, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Chen, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhang, L. An MLC and U-Net Integrated Method for Land Use/Land Cover Change Detection Based on Time Series NDVI-Composed Image from PlanetScope Satellite. Water 2022, 14, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, M.; Baker, M.E.; Caplan, J.S.; Williams, A.; Elmore, A.J. Canopy composition drives variability in urban growth period length more than the heat island effect. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Earth Engine. A Planetary-Scale Platform for Earth Science Data & Analysis. Available online: https://earthengine.google.com (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Planet Labs. Planet Explorer. Available online: https://www.planet.com/explorer/ (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- National Bureau of Statistics. 2021. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/zt_18555/zdtjgz/zgrkpc/dqcrkpc/ (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jonsson, P.; Tamura, M.; Gu, Z.; Matsushita, B.; Eklundh, L. A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time-series data set based on the Savitzky-Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P.; Eklundh, L. Seasonality extraction by function fitting to time-series of satellite sensor data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Hodges JC, F.; Gao, F.; Reed, B.C.; Huete, A. Monitoring vegetation phenology using MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Friedl, M.A. User Guide to Collection 6.1 MODIS Land Cover Dynamics (MCD12Q2) Product. 2022. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/documents/1417/MCD12Q2_User_Guide_V61.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Sun, X.; Yuan, L.; Liu, M.; Liang, S.; Li, D.; Liu, L. Quantitative estimation for the impact of mining activities on vegetation phenology and identifying its controlling factors from Sentinel-2 time series. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).