Impacts of Water Diversion Projects on Vegetation Coverage in Central Yunnan Province, China (2017–2022)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
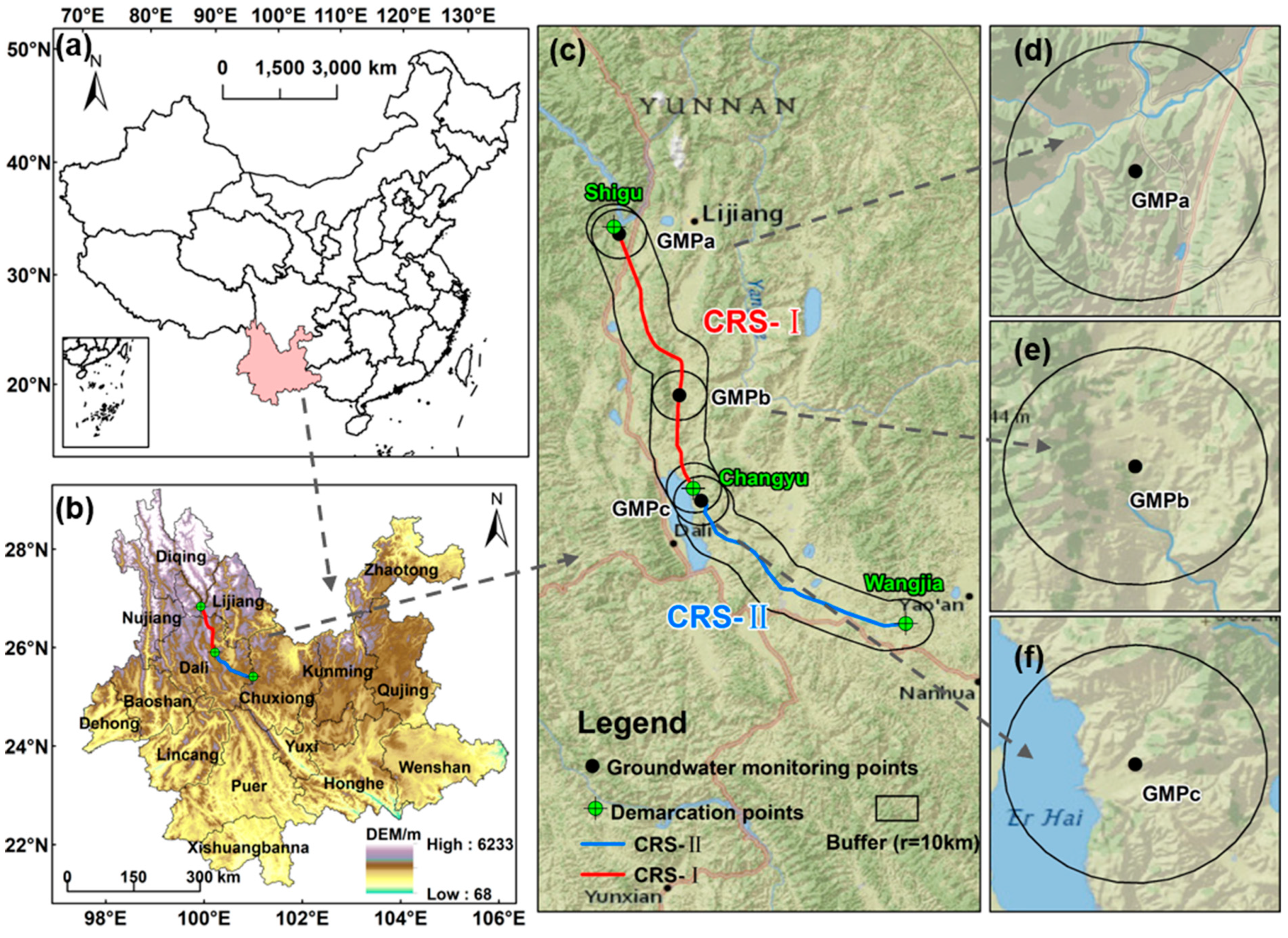
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. FVC Calculation
2.4. Transfer Matrix of the Vegetation Types
2.5. Buffer Analysis Method
3. Results
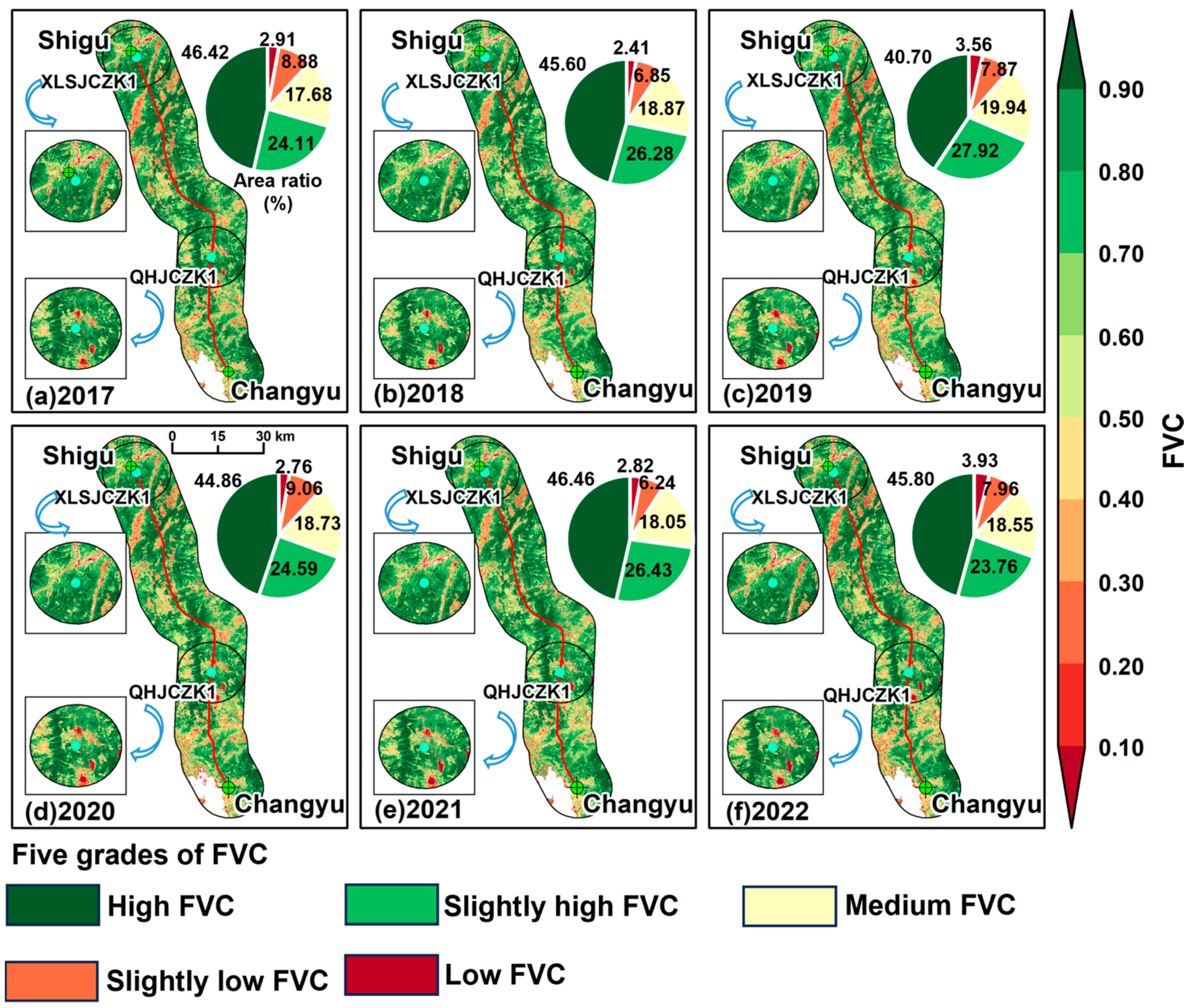
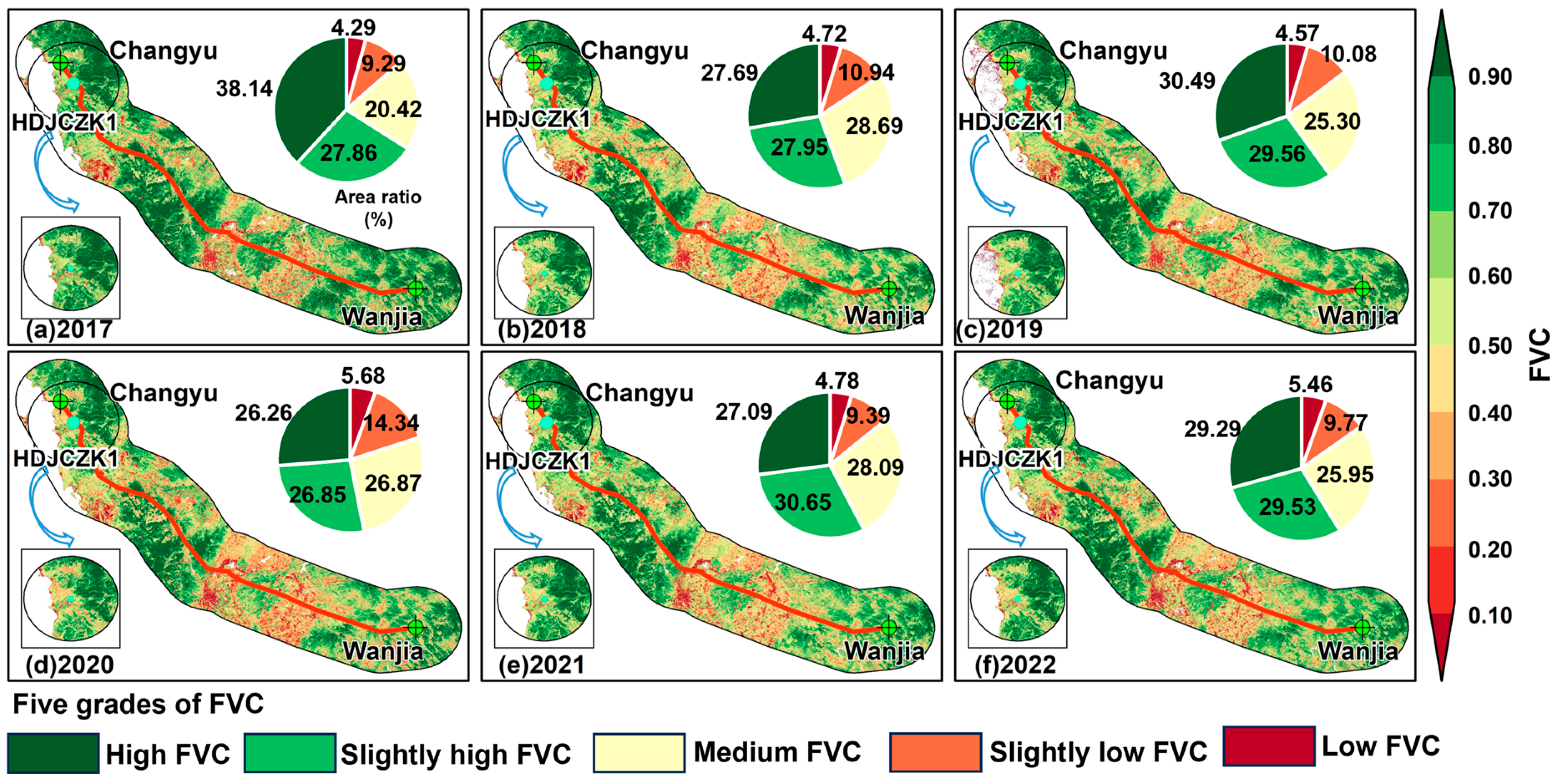
3.1. Spatiotemporal Pattern of FVC on Both Sides of the Tunnel Construction Route
3.1.1. Spatiotemporal Changes in FVC on Both Sides of CRS-I
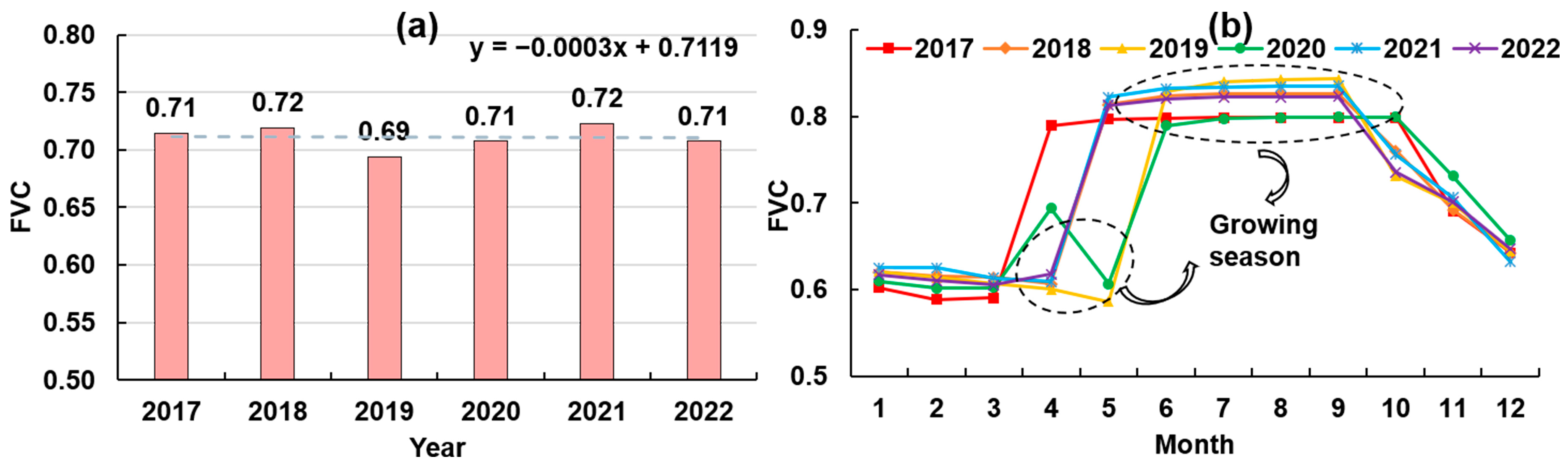
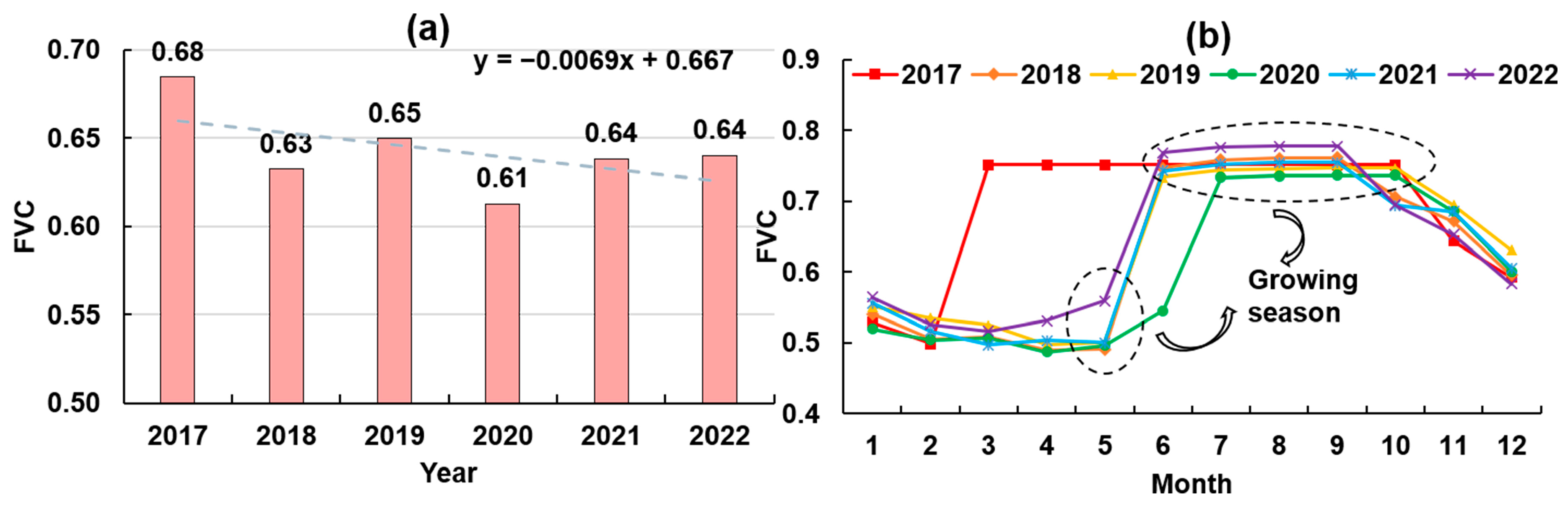
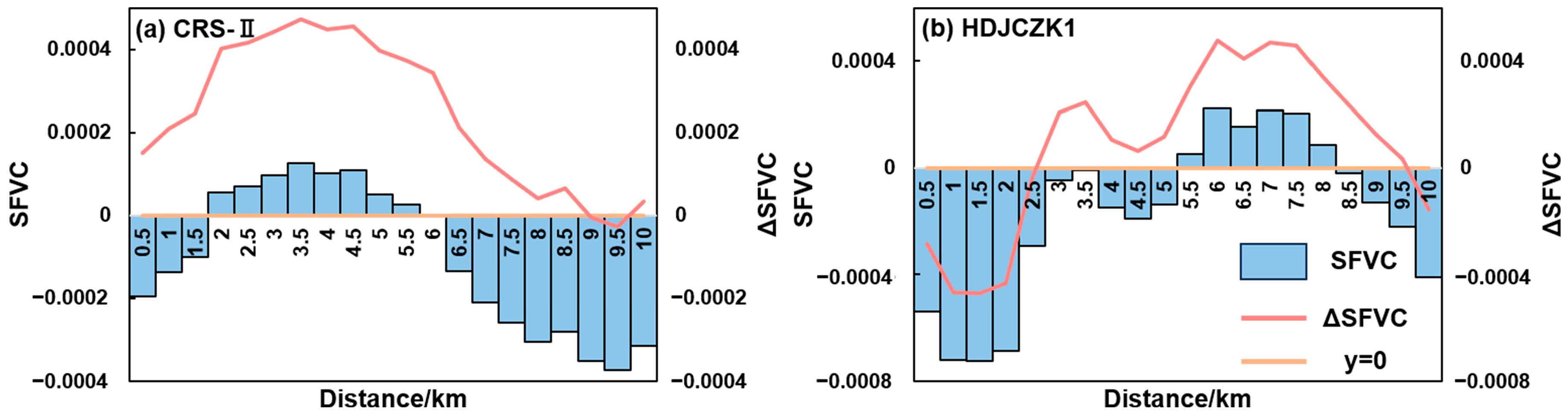
3.1.2. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Changes in FVC on Both Sides of CRS-II
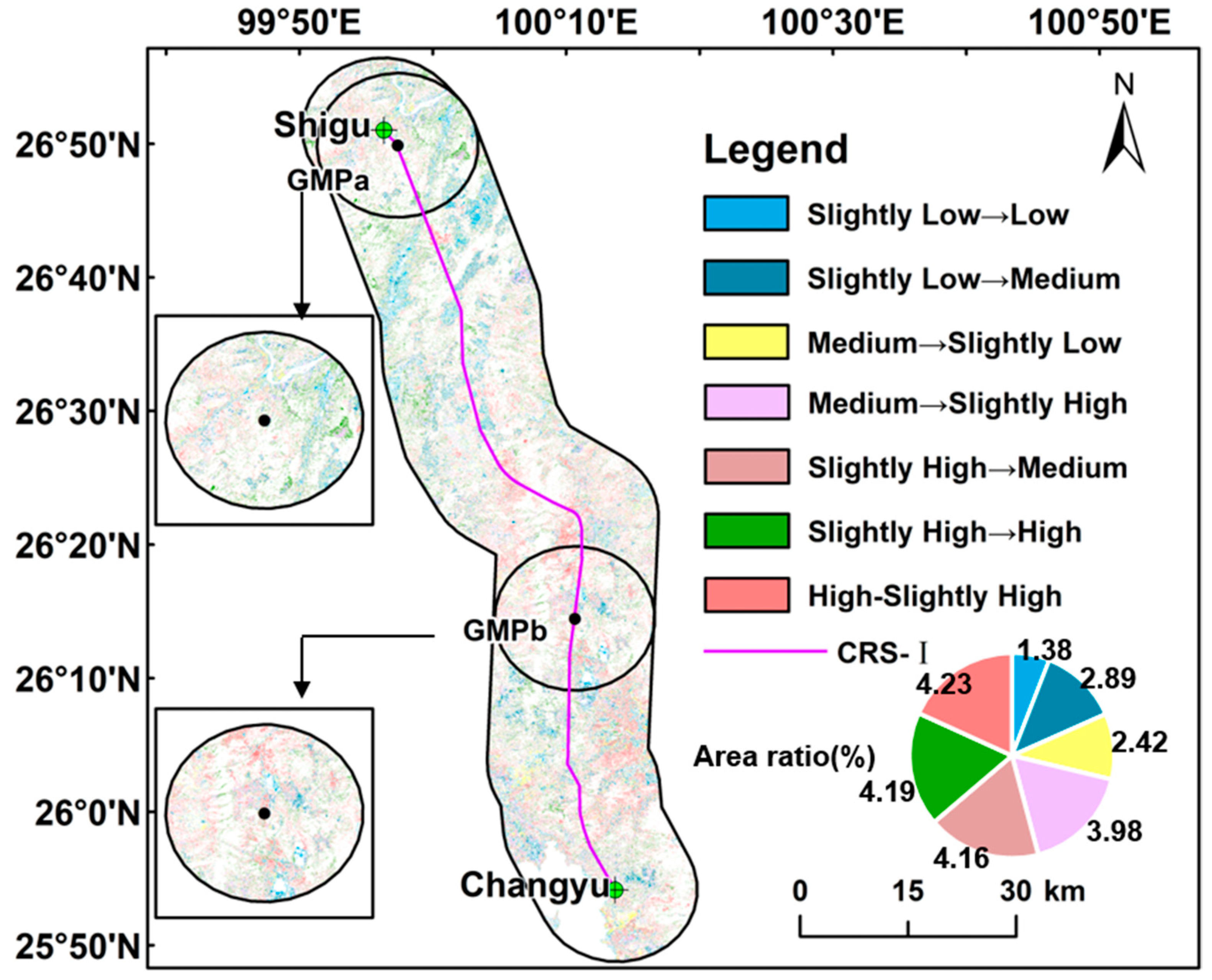
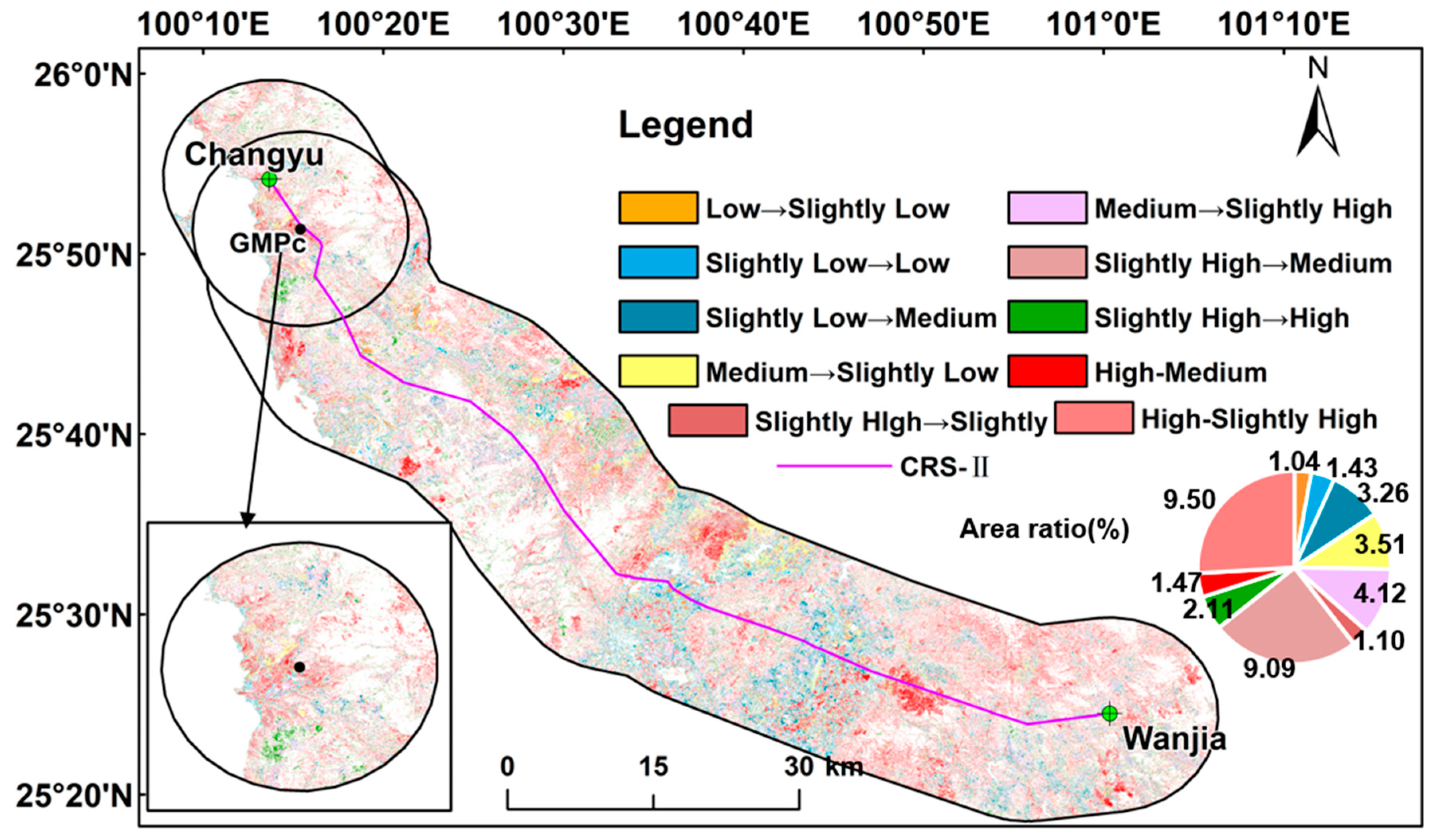
3.2. Conversion of FVCs on Both Sides of the Project
3.2.1. Conversion of FVCs on Both Sides of CRS-I
3.2.2. Conversion of FVC Types on Both Sides of CRS-II
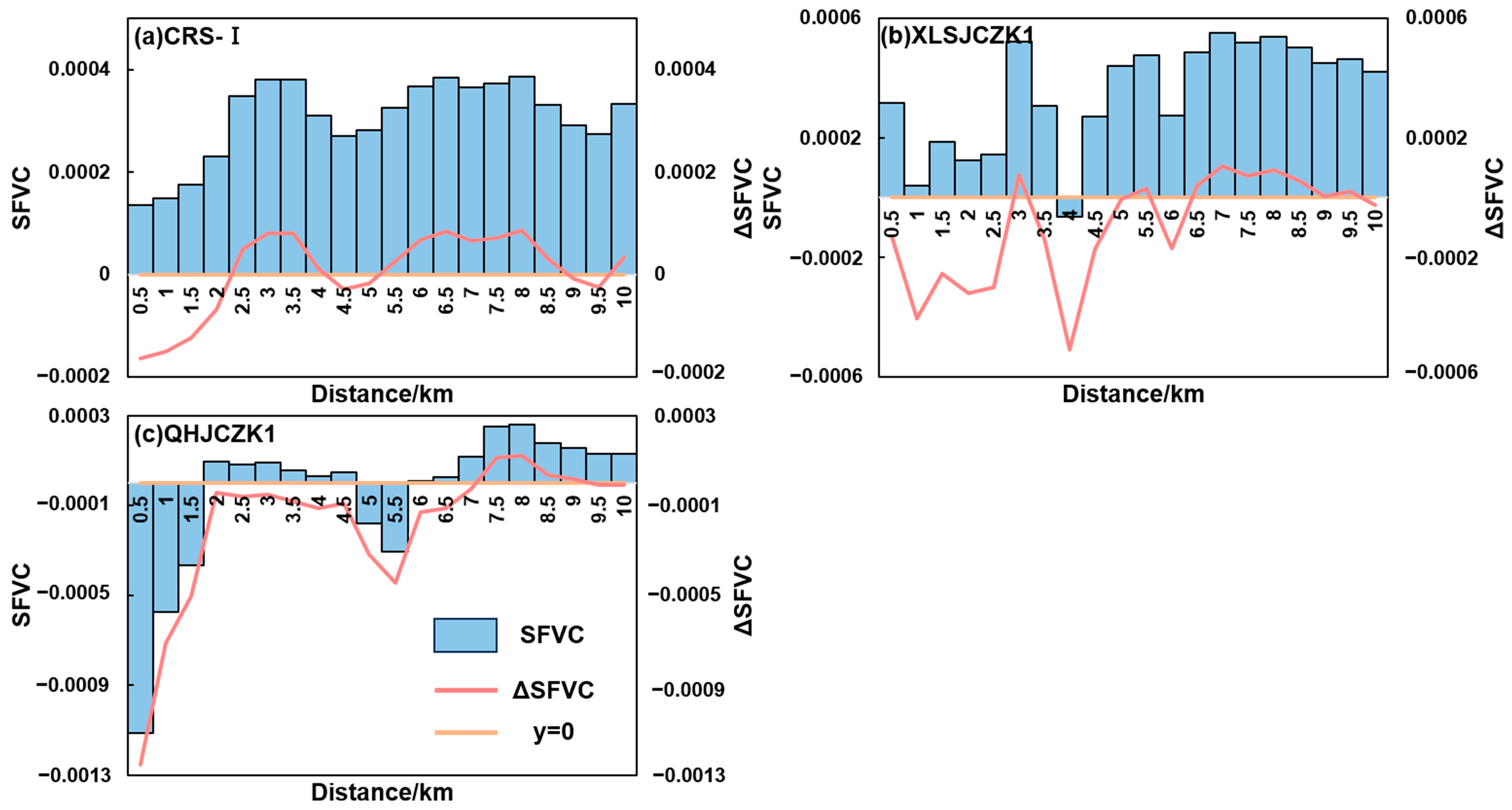
3.3. Composite Impact Footprint of FVC in the Context of Climate Change
3.3.1. Impact Footprint of FVC Changes on Both Sides of CRS-Ⅰ
3.3.2. Impact Footprint of FVC Changes on Both Sides of CRS-II
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russell, R.; Guerry, A.D.; Balvanera, P.; Gould, R.K.; Basurto, X.; Chan, K.M.; Klain, S.; Levine, J.; Tam, J. Humans and nature: How knowing and experiencing nature affect well-being. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2013, 38, 473–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speldewinde, P.; Slaney, D.; Weinstein, P. Is restoring an ecosystem good for your health? Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Zhang, J.; Han, H.; Cheng, X.; Kang, F. Study on the impact of vegetation change on ecosystem services in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Hao, X.; Hua, D.; Hao, H. Assessment of ecosystem resilience in Central Asia. J. Arid. Environ. 2021, 195, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, A.W.; Macias-Fauria, M.; Long, P.R.; Benz, D.; Willis, K.J. Sensitivity of global terrestrial ecosystems to climate variability. Nature 2016, 531, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Hou, H. Integrating the impacts of vegetation coverage on ecosystem services to determine ecological restoration targets for adaptive management on the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 5697–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Tang, X.; Gu, Q.; Wang, T.; Wei, J.; Song, L.; Ma, M. Climatic anomaly and its impact on vegetation phenology, carbon sequestration and water-use efficiency at a humid temperate forest. J. Hydrol. 2018, 565, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.I.; Conradi, T.; Muhoko, E. Shifts in vegetation activity of terrestrial ecosystems attributable to climate trends. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, L.-J.; Jiang, J.; Chu, L.; Zhang, J.-C. Threshold effect of ecosystem services in response to climate change and vegetation coverage change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau ecological shelter. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 318, 128592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Yao, W.-Q.; Wang, J.-H.; Song, X.-Y. A study on the relationship between dynamic change of vegetation coverage and precipitation in Beijing’s mountainous areas during the last 20 years. Math. Comput. Model. 2011, 54, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, H.; Ye, J.; Han, L.; Gong, Y.; Cai, D. Vegetation coverage of desert ecosystems in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is underestimated. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Song, W.; Gao, Z.; McVicar, T.R.; Donohue, R.J.; Yan, G. Fractional vegetation cover estimation by using multi-angle vegetation index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, F. Spatiotemporal Variations in Fractional Vegetation Cover and Their Responses to Climatic Changes on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Gu, X.; Baret, F.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Fractional vegetation cover estimation algorithm for Chinese GF-1 wide field view data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, Q.; Tong, X. Integrating 250 m MODIS data in spectral unmixing for 500 m fractional vegetation cover estimation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Ma, X.; Huo, T.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, C. Assessment of the environmental effects of ecological water conveyance over 31 years for a terminal lake in Central Asia. Catena 2022, 208, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapinel, S.; Mony, C.; Lecoq, L.; Clément, B.; Thomas, A.; Hubert-Moy, L. Evaluation of Sentinel-2 time-series for mapping floodplain grassland plant communities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Fu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Attributing vegetation change in an arid and cold watershed with complex ecosystems in northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Peng, W. Quantifying spatiotemporal dynamics of vegetation and its differentiation mechanism based on geographical detector. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32016–32031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Gao, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Effects of coal mining and climate-environment factors on the evolution of a typical Eurasian grassland. Environ. Res. 2024, 244, 117957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zhang, J.; Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Lu, X.; Jiang, M. Impacts of climate change on fractional vegetation coverage of temperate grasslands in China from 1982 to 2015. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 350, 119694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Gui, D.; Liu, Q.; Feng, X.; Qu, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Wei, G. Vegetation coverage precisely extracting and driving factors analysis in drylands. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 79, 102409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D. Effects of climate change and human activities on vegetation coverage change in northern China considering extreme climate and time-lag and-accumulation effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Kong, H. Dynamic changes of vegetation coverage in China-Myanmar economic corridor over the past 20 years. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Q.; Yang, M. Spatio-temporal patterns and driving factors of vegetation change in the Pan-Third Pole Region. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Tian, H.; Wu, X.; Gao, Z.; Feng, Y.; Piao, S.; Lv, N.; Pan, N.; Fu, B. Accelerated increase in vegetation carbon sequestration in China after 2010: A turning point resulting from climate and human interaction. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 5848–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Z.; Ling, H.; Deng, M.; Han, F.; Yan, J.; Deng, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, W. Past and projected future patterns of fractional vegetation coverage in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, C.H.; Ndangalasi, H.J.; Gerstle, J.; Lovett, J.C. Effect of the Lower Kihansi Hydropower Project and post-project mitigation measures on wetland vegetation in Kihansi Gorge, Tanzania. Biodivers. Conserv. 2005, 14, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z. Remote Sensing Analysis of Fractional Vegetation Cover Change Triggered by Island Construction. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2017, 19, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Li, L.; Liu, Q.; Xin, X.; Peng, Z.; Wu, M.; Niu, Z.; Tian, H. Monitoring and analyzing ecosystem impact on hydropower projects by remote sensing in the Belt and Road region. J. Geo-Inf. Sci 2020, 22, 1424–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Zhao, X.; Pu, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, S.; He, C. Spatio-temporal Evolution and Attribution of Landscape Ecological Security at Patch Scale in Yunnan Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 8087–8098. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W. Temporal and Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Vegetation NDVI and Its Driving Factors in Central Yunnan Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 252–257. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Donghao, Y.; Jianxiong, W. Analysis on dynamic change characteristics and driving forces of vegetation coverage in Southwestern Yunnan. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Peng, C.; Cheng, W.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Fan, C.; Sun, H. Analysis of vegetation coverage change in Yunnan Province based on MODIS-NDVI. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 20, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, H. Driving force of vegetation cover change in Yunnan province from 2001 to 2018. Mt. Res. 2022, 40, 531–541. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; He, Y.; Cai, Y.; Qu, X.; Cui, X. Relationship between extreme climate indices and spatiotemporal changes of vegetation on Yunnan Plateau from 1982 to 2019. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 31, e01813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tang, L.; Hupy, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Shao, G. A commentary review on the use of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) in the era of popular remote sensing. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Fan, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wu, H.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, K.; Shi, M.; Yang, Q. The Spatio-Temporal Evolution Characteristics of the Vegetation NDVI in the Northern Slope of the Tianshan Mountains at Different Spatial Scales. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tong, S.; Guo, E. Monitoring the trends of aeolian desertified lands based on time-series remote sensing data in the Horqin Sandy Land, China. Catena 2017, 157, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, T.; Qiu, Z.; Guan, Z.; Ma, X. Effects of precipitation changes on fractional vegetation cover in the Jinghe River basin from 1998 to 2019. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Mu, X.; McVicar, T.R.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Niu, Z.; Yan, G. Global quasi-daily fractional vegetation cover estimated from the DSCOVR EPIC directional hotspot dataset. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liao, C.; Li, J.; Sun, Q. Fractional vegetation cover estimation in arid and semi-arid environments using HJ-1 satellite hyperspectral data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Duan, P.; Jim, C.Y.; Chan, N.W.; Shi, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Bahtebay, J.; Ma, X. Vegetation cover changes in China induced by ecological restoration-protection projects and land-use changes from 2000 to 2020. Catena 2022, 217, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Singh, V.P.; Zhao, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, T.; Duan, L. Ecological degradation in the Inner Mongolia reach of the Yellow River Basin, China: Spatiotemporal patterns and driving factors. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, H. Response analysis of land use change to the degree of human activities in Beiluo River basin since 1976. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Henebry, G.M.; Liu, L. Urbanization imprint on land surface phenology: The urban–rural gradient analysis for Chinese cities. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, C. Surface urban heat island in China’s 32 major cities: Spatial patterns and drivers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Su, Q.; Yang, R. Interannual covariability of summer monsoon precipitation in Yunnan, China, and diabatic heating anomalies over the Arabian Sea–Bay of Bengal. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 2063–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R. Temperature sensitivity of photosynthesis and respiration in terrestrial ecosystems globally. Acta Ecol. Sin 2018, 38, 8392–8399. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.-W.; Jin, T.; Chen, Y.-M. Machine learning-based forecasting of soil settlement induced by shield tunneling construction. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Boers, N. Global vegetation resilience linked to water availability and variability. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.-Q.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y.-P.; Gao, S.; Wang, Z.; Feng, G.-L. Impacts of climate change on vegetation pattern: Mathematical modeling and data analysis. Phys. Life Rev. 2022, 43, 239–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Bi, P. Spatiotemporal changes and driving factors of vegetation in 14 different climatic regions in the global from 1981 to 2018. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75322–75337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, J. Dual influence of climate change and anthropogenic activities on the spatiotemporal vegetation dynamics over the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau from 1981 to 2015. Earths Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Song, X. Identifying the Main Factors Influencing Significant Global Vegetation Changes. Forests 2023, 14, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Lu, H.; Yao, T.; Xue, Y.; Feng, W. Enhancing sustainability of vegetation ecosystems through ecological engineering: A case study in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type | FVC Range | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Low FVC | 0~0.2 |
| 2 | Slightly low FVC | 0.2~0.4 |
| 3 | Medium FVC | 0.4~0.6 |
| 4 | Slightly high FVC | 0.6~0.8 |
| 5 | High FVC | 0.8~1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, A.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, F.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Zhang, K.; Wang, G. Impacts of Water Diversion Projects on Vegetation Coverage in Central Yunnan Province, China (2017–2022). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132373
Feng A, Zhu Z, Zhu X, Zhang Q, Yan F, Li Z, Guo Y, Singh VP, Zhang K, Wang G. Impacts of Water Diversion Projects on Vegetation Coverage in Central Yunnan Province, China (2017–2022). Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(13):2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132373
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Anlan, Zhenya Zhu, Xiudi Zhu, Qiang Zhang, Fengling Yan, Zhijun Li, Yiwei Guo, Vijay P. Singh, Kaiwen Zhang, and Gang Wang. 2024. "Impacts of Water Diversion Projects on Vegetation Coverage in Central Yunnan Province, China (2017–2022)" Remote Sensing 16, no. 13: 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132373
APA StyleFeng, A., Zhu, Z., Zhu, X., Zhang, Q., Yan, F., Li, Z., Guo, Y., Singh, V. P., Zhang, K., & Wang, G. (2024). Impacts of Water Diversion Projects on Vegetation Coverage in Central Yunnan Province, China (2017–2022). Remote Sensing, 16(13), 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132373








