Abstract
Long-term cross-correlational structures are examined for pairs of sea surface temperature anomalies (SSTAs) and advective forcing parameters and sea surface height anomalies (SSHAs) and current velocity anomalies (CVAs) in the East/Japan Sea (EJS); all these satellite datasets were collected between 1993 and 2023. By utilizing newly modified detrended cross-correlation analysis algorithms, incorporating local linear trend and local fluctuation level of an SSTA, the analyses were performed on timescales of 400–3000 days. Long-term cross-correlations between SSTAs and SSHAs are strongly persistent over nearly the entire EJS; the strength of persistence is stronger during rising trends and low fluctuations of SSTAs, while anti-persistent behavior appears during high fluctuations of SSTAs. SSTA-CVA pairs show high long-term persistence only along main current pathways: the zonal currents for the Subpolar Front and the meridional currents for the east coast of Korea. SSTA-CVA pairs also show negative long-term persistent behaviors in some spots located near the coasts of Korea and Japan: the zonal currents for the eastern coast of Korea and the meridional currents for the western coast of Japan; these behaviors seem to be related to the coastal upwelling phenomena. Further, these persistent characteristics are more conspicuous in the recent decades (2008~2023) rather than in the past (1993~2008).
1. Introduction
Sea surface temperature (SST) variability is an important issue in oceanography as well as in climate science. As a representative property for a variety of energy exchanges occurring at the sea surface, SST variability has a lot of information about forcing parameters, which can be greatly categorized into the oceanic, atmospheric, and coupled ocean–atmospheric physical processes [1]. Since the impacts from these forcing parameters are imprinted on the SST variability in a complex manner, we can obtain useful information from the auto- and cross-correlation structures of SST anomalies (SSTAs) [2]. In our recent study [3], it was reported that SSTAs in the East/Japan Sea (EJS) show scale-dependent long-term persistent behaviors in auto- and cross-correlation structures constructed from multivariate SSTA datasets; there were also region-specific features.
There are many physical processes closely related to SST variability. For example, SST is varied via lateral energy transports by geostrophic velocity and Ekman current, vertical energy exchanges by vertical entrainment and Ekman pumping, turbulent energy fluxes through various air–sea interactions, and radiative fluxes [1]. Since these factors have their own spatiotemporal scales, SST variability is also spatially and temporally characterized by spatiotemporal scales involved in driving forcing parameters. In a recent study [4], it was shown that the spatial pattern of SST variability in the East/Japan Sea is scale-sensitive; SST variability with smaller scales (less than 60 days) affects the basin-wide area, while the spatial extent of SST variability with larger scales (more than 90 days) tends to be focused on the tongue-shaped region from the East Korea Bay (EKB) to the Subpolar Front (SPF) [4].
These region-specific and scale-dependent behaviors solely coming from SST variability can be mainly due to the features of various driving forcing parameters. Thus, in order to reveal the relationship between SST variability and its driving forces, it is urgent to investigate the cross-correlational structures between SST variability and some advective forcing parameters, indicated as SSHAs and current intensity (zonal, meridional, and total). Further, in order to examine the long-term persistence in their cross-correlations, we utilize the widely used detrended cross-correlation analysis (DCCA) algorithm [5] and its modified versions.
Most real-world systems, including oceanic systems, are complex, in terms of consisting of many degrees of freedom which are interacting in a very complex manner. As a result of this, there have been a lot of analyzing tools suggested for examining the cross-correlational structure among the constituents of a complex system; the traditional Pearson cross-correlation (PCC) tool was proved to be restricted when dealing with nonstationary time series. As its alternatives, the detrended fluctuation analysis (DFA) [6] and its multifractal version, called multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis (MFDFA), were introduced for examining the auto-correlation structure of a complex singular time series [7]. Since then, the detrended cross-correlation analysis (DCCA) was introduced in order to detect the long-range persistence in the cross-correlations between synchronously observed nonstationary time series. These analysis tools have been successfully applied to a variety of scientific fields, including finance, physics, and earth sciences [8,9,10,11,12,13,14].
However, the aforementioned methodologies have a clear shortcoming in analyzing a complex system under the influences of strong external forces; most geophysical systems, including oceanic systems, are governed by a lot of external forcing parameters evolving with a composite spatiotemporal scale. Often, the long-term persistent behaviors (generally appearing as a power-law scaling) are dependent on the characteristics of the given original time series directly related to the external forces; however, DFA and its variant algorithms [5,6,7] do not consider the partwise characteristics of the original time series. In order to overcome these limitations, the original time series should be divided into separate parts according to the partwise characteristics of the original time series, and the separated parts must be, respectively, dealt with in the procedural process of these algorithms. The asymmetric DFA (ADFA) [15] and the multifractal asymmetric detrended cross-correlation analysis (MF-ADCCA) [16] are the first modified algorithms for incorporating the local linear trend of the original time series; therein, the characteristic for dividing the original time series is the local linear trend. In this study, we further consider the local level of fluctuation as another characteristic for the dividing criterion and present a new fluctuation-dependent DCCA (F-DCCA) algorithm.
To summarize, our goal in this study is to examine the long-term persistence in the cross-correlational structures between the SSTAs and the advective forcing parameters in the East/Japan Sea (EJS), in terms of ADCCA, F-DCCA, and DCCA algorithms; we think that the EJS is a good testbed for examining the effect of advective forcing parameters on SSTA variability because it is a semi-enclosed marginal sea and mimics the ocean’s characteristics well. Although the algorithms utilized in this study have some novel aspects in examining the dynamic persistent structures depending on local trends and local fluctuation levels, they still have some limitations in revealing the persistent structures of SSTAs influenced by teleconnection mechanisms. For the latter, a new algorithm should be devised.
This article is organized as follows: In the Materials and Methods section, descriptions of satellite datasets and analysis tools are presented. The subsequent analysis Results section contains all the analysis results as well as their interpretations. In the Discussion section, comparisons with the previous studies and new implications are presented, and lastly, the Conclusion section summarizes the meaningful results and describes the direction of further research in terms of correlational structures under the effect of various climate factors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gridded Satellite Data
In this study, three kinds of satellite-derived daily gridded datasets are used for examining their long-term persistent cross-correlational structures. They are briefly described below.
The satellite-derived daily SST data were obtained from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Optimum Interpolation SST (OISST) version 2.1 software [17,18]. This NOAA 0.25° daily OISST is a long-term climate data record incorporating observations from different platforms (satellites, ships, buoys, and Argo floats) into a regular global grid and is currently available from 1 September 1981 to 4 April 2023. SST anomalies (SSTAs) represent departures from normal or average conditions and are computed via the daily OISST minus a 30-year climatological mean from 1971 to 2000.
The SSH data as well as the derived geostrophic currents are DUACS delayed-time altimeter-gridded (0.25° × 0.25° in latitude and longitude) maps over the global ocean. These products are produced and distributed by the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S, https://climate.copernicus.eu/, accessed on 8 April 2024). These datasets are currently available from 1 January 1993 to 4 April 2023. The anomalies of SSH and geostrophic currents were computed with respect to the full-duration climatological mean.
For the goal of this study, we confined the spatial coverage of all the datasets into the East/Japan Sea (EJS) with latitude of 34~45°N and longitude of 127~144°E, and also, the temporal coverage of all these satellite datasets with different observation periods was set to the same duration from 1 January 1993 to 4 April 2023 for a consistent cross-correlation analysis. Further, in order to compare the decadal change in cross-correlational structures, we divided the whole timespan into two domains, namely the first domain of 1993 to 2008 and the second domain of 2008 to 2023.
2.2. Characteristics of SSTAs
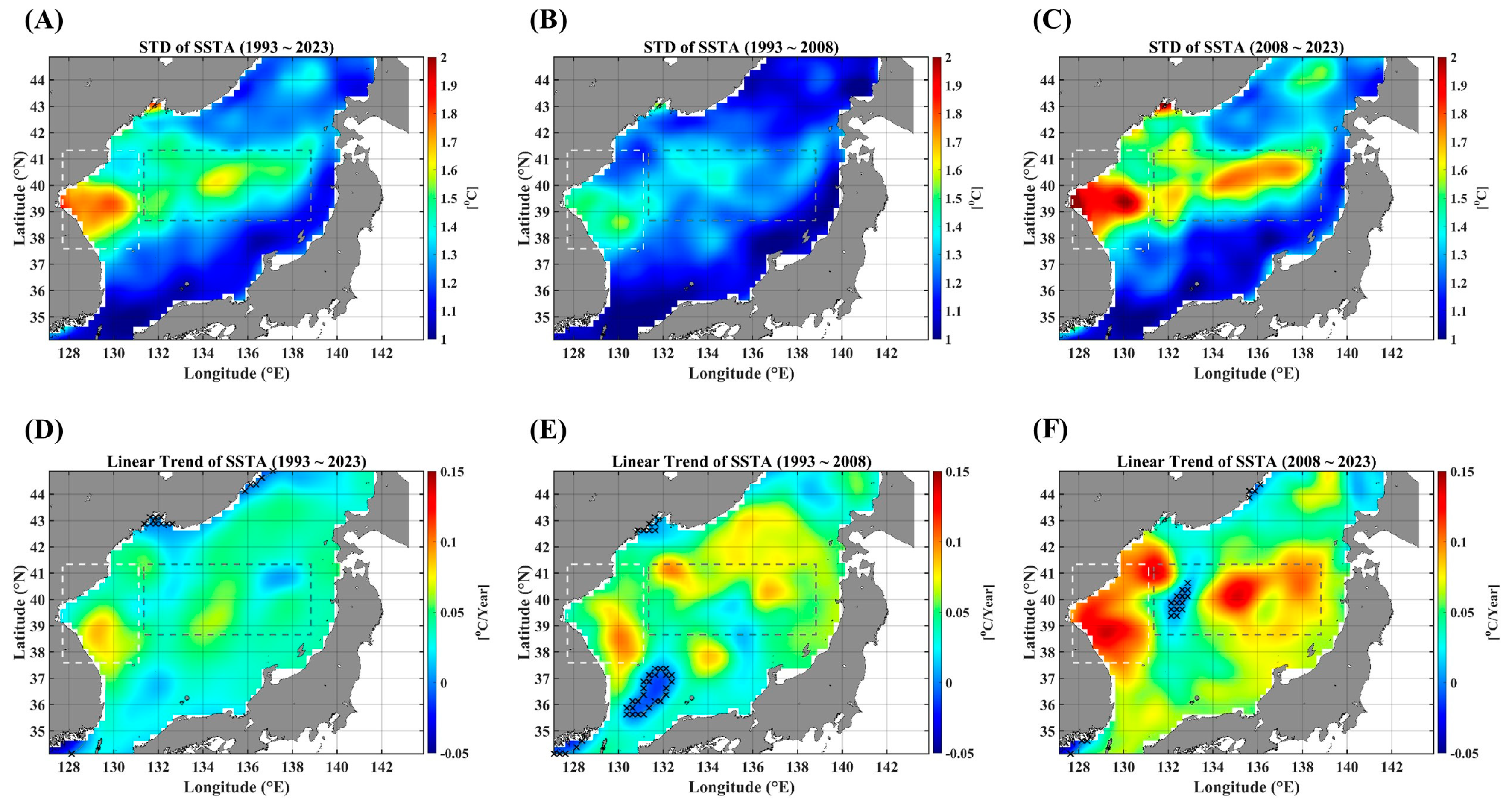
In this section, we present the statistical characteristics of SSTAs in the EJS through the standard deviation (STD) and linear trends. Figure 1 illustrates the spatial distribution of fluctuation levels of SSTAs (Figure 1A–C) denoted by the standard deviation and the spatial pattern of linear trends (Figure 1D–F). As shown in Figure 1B,C as well as Figure 1E,F, the fluctuation levels and linear trends are strengthened in the recent decade from 2008 to 2023, particularly in specific regions. This strengthened warming in the recent decade in the EJS was also reported in the previous study [19]. The STD values are high along the region extending from the EKB to the SPF, and the linear trends are strong in areas near the east coast of Korea, including the EKB and the western part of the SPF. The regions along the west coast of Japan show a relatively low fluctuation over the full duration (Figure 1A–C). These distinct spatial features might be related to the spatial pattern of cross-correlations between SSTAs and advective forcing parameters.
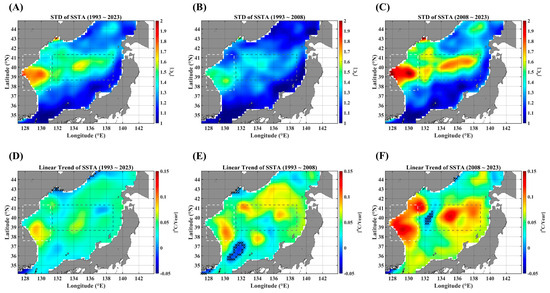
Figure 1.
STD maps of SSTAs for three durations: the full observation period (A), the 1st decades (B), and the 2nd decades (C). The linear trends are illustrated in (D–F), respectively, corresponding to their different observation durations. The light gray dashed-line box indicates the EKB region, and the dark gray dashed-line box denotes the SPF region. Note that the areas marked “x” are not statistically significant for the linear trends at the 95% significance level.
Further, for comparison, we presented the STD and linear trends map for the SSHAs and current intensity (UA, VA, and UVA) in Figure A1, Figure A2, Figure A3 and Figure A4. The pattern of STD maps is very similar for all those parameters, indicating that SSHA and surface currents are closely related to each other, with a high STD in the southern part and a low STD in the northern part. However, the maps of linear trends show a dramatic decadal change.
2.3. Cross-Correlational Analysis
2.3.1. Pearson Cross-Correlation
The traditional Pearson cross-correlations were used to exhibit the spatial distribution of synchronized features with no delay time between SSTAs and advective forcing parameters, such as SSHAs and current intensity (zonal, meridional, and total). This method has some limitations on examining the long-term persistence between a pair of time series under a variety of polynomial trends; firstly, the long-term persistence of a bivariate time series incorporates a long-ranged time-delay cross-correlation, and secondly, the polynomial trends can lead to spurious cross-correlations. Nonetheless, they give us a good benchmark for the alternative analyses. In this study, we use this method as the baseline.
2.3.2. Detrended Cross-Correlation Analysis
This algorithm [5] allows us to compute the long-term persistent cross-correlation of any two nonstationary signals. The procedure is given below.
Step 1: We considered two nonstationary time series , for where is the length of the series. Then, we constructed the signal profile:
where denotes averaging over an entire time series.
Step 2: Both signal profiles are divided into disjoint segments of length . Because of the cases of the length N not divided exactly by s, the segmentation procedure is repeated starting from the end of the signal. Thus, we obtain 2 segments in total.
Step 3: For each segment , the local trend is estimated by fitting a polynomial of order ( for and for ). In this study, we use a polynomial of order . Then, the local trend is subtracted from the profile.
Step 4: The detrended cross-covariance within each segment is computed,
Step 5: In order to see the scaling behavior of the covariant function, we averaged all segments and computed the detrended covarying fluctuation function,
Step 6: The scaling behavior of the covariance function , in case that the function develops scaling, is manifested in the power-law dependence of as follows:
where , known as the cross-correlation Hurst exponent, quantitatively characterizes fractal properties of the covariance, that is, the long-term cross-correlational persistence. In case the function is alternating across zero, it is said that there is no scaling or long-term persistence.
When estimating the Hurst exponent, it is very important to determine a scaling range over which a power-law scaling of Equation (4) is well established and its double logarithmic linear fit yields a robust singular value, which is said to be the Hurst exponent. In this study, the scaling range was set to be a segment scale range of 400~3000 days; herein, the segment scale denotes the segment length, . For the smaller segment sizes (less than 400 days), a Hurst exponent near the value of 1.5 was observed); this value indicates that the considered time series is likely to be a Brownian motion, which is a cumulative sum of random noises. Thus, in this study, we only consider the larger scales, and the smaller scales will be dealt with in future work. The scaling range of 400~3000 days is equally applied to all the DCCA-based algorithms below through this study because all show a similar power-law scaling behavior.
There is another caution to be noted. From Equation (2), the local detrended covariance, , can be consistently negative over all segment sizes, yielding a negative power-law scaling. In this case, the Hurst exponent can be estimated by assigning the minus sign to all in Equation (3), and this behavior is also interpreted as a long-term persistent feature in a negative manner. In this study, we assign the minus sign to the Hurst exponent obtained from the negative series, and this Hurst exponent indicates that there is a negative long-persistent behavior between the two considered nonstationary time series.
The interpretation of is the same as that of the traditional Hurst exponent. That is, when , the cross-correlation of both time series is said to be persistent, implying that an increase in one time series is followed by an increase in the other. In the case of , the cross-correlation is said to be anti-persistent, meaning that an increase in one signal is likely to be followed by a decrease in the other. Lastly, the case of indicates a short-range or no cross-correlation. As mentioned in the previous paragraph, the negatively persistent behaviors are interpreted in the same manner, except for the direction due to the sign; that is, in the case of , the cross-correlation is said to be negatively persistent, implying that an increase in one signal is likely to be followed by a negative increase in the other. These interpretations are also valid in the modified versions of the DCCA algorithm below.
2.3.3. Asymmetric Detrended Cross-Correlation Analysis
This algorithm is a modified version of the DCCA, which incorporates the local linear trend of the original time series in the process of computation of covariances of a pair of two nonstationary time series; this can be an extension of an asymmetric detrended fluctuation analysis (ADFA) to a bivariate time series [13]. The whole procedure is given below; the first two steps are nearly the same as those of the DCCA algorithm.
Step 1: We considered two nonstationary time series , for where is the length of the series. Then, their profiles are computed via a cumulative summation,
where denotes averaging over an entire time series, that is, computed as .
Step 2: We divided each of the time series {, } into non-overlapping segments of equal length . Likewise, the profiles are also divided into non-overlapping segments of equal length , respectively, and into int non-overlapping segments of equal length s, respectively. In order to incorporate a short-end part of the signal in case the record length is not divided by , the same procedure is repeated from the end of the signal. Thus 2 segments are obtained. Then, in the -th segment (), we have two pairs of segmented time series and for .
Step 3: For each segment time series of a pair of segmented time series , we computed the local linear fits (equivalent to local linear trends) using the least squares regression, each of which is expressed as and , respectively. In another pair of time series, , it is the same. The linear fit is used to determine whether the trend of the -th segment {} is positive (rising) or negative (falling), while the linear fit is used to locally detrend the -th profile segment {}. The linear trends of a pair of original time series are said to be asymmetric; this is why this algorithm is said to be an asymmetric DCCA. Thus, the detrended cross-covariance is computed as
Step 4: The detrended covariances {} are classified into two classes according to the piecewise trend of the corresponding time series , and the classified segments are used to assess the asymmetric cross-correlation scaling properties. As mentioned in Step 3, the local trend is determined by the sign of the slope or . By, for example, taking the trend of {} as the reference (herein, the SSTA is the reference), we computed the so-called directional detrended covariances as follows:
where and denote the number of segments with positive and negative trends, respectively. In case for all segments, .
When the piecewise linear trend of is ignored, the traditional DCCA [5] is restored:
As a result, if there are power-law cross-correlations, the following scaling law is established:
where and denote positive (rising) and negative (falling) scaling exponents, respectively. The scaling behaviors in Equation (11) are determined in the log–log plots, and the exponents are estimated via a linear fit over the scaling range.
The interpretation of the exponent is the same as that of the DCCA. However, for the symmetricity of the cross-correlation of a pair of time series, the relation of indicates that the cross-correlation is symmetric. If , the cross-correlation is said to be asymmetric, meaning that there is a trend-dependent scaling behavior. Further, the degree of cross-correlation asymmetry is measured via the following formula:
The greater the magnitude of , the more pronounced the asymmetry of the cross-correlation. The sign of indicates the dependence on the trending behavior of the chosen time series, herein {}, that is, the SSTA time series.
2.3.4. Fluctuation-Dependent Detrended Cross-Correlation Analysis
We present a new DCCA algorithm by making a little modification to ADCCA. This algorithm is based on the fact that the nonstationarity inherent in the original time series is caused by different dynamical processes and results in a noticeable variation in the fluctuation level. To this end, we consider the fluctuation level of the segmented original time series instead of its linear trend. Thus, the algorithm is very similar to the ADCCA; from now on, this algorithm is called the F-DCCA. The whole procedure is below; since the first two steps are completely the same as those in the ADCCA, Steps 1 and 2 are ignored.
Step 3: For each segment time series of a pair of segmented time series , we compute the local standard deviation (STD) and the local linear fits (equivalent to local linear trends), , respectively. The local STD is used to determine whether the level of fluctuation of the -th segment {} is high or low; the linear fit of the profile series is used to locally detrend its corresponding segment {}. Then, we compute the fluctuation-dependent detrended covariance given as follows:
Step 4: The detrended covariances {} are classified into two classes, high and low, according to the segment-wise level of fluctuation. In this study, the STD criterion is set to be the STD, , of the full-length time series {}; if the local is greater (less) than , the local segment indicator becomes (), which indicates a local high (low) fluctuation level. In this study, the referenced series {} is the SSTA signal. Then, we compute the so-called fluctuational detrended covariances as follows:
where and denote the number of segments with high- and low-fluctuation levels, respectively.
Likewise, the traditional DCCA is restored when the fluctuation criterion is ignored. Further, if there are power-law cross-correlations, the following scaling law is established:
where and denote high- and low-fluctuation scaling exponents, respectively. The scaling behaviors in Equation (11) are determined in the log–log plots, and the exponents are estimated via a linear fit over the scaling range.
The interpretation of the exponent is the same as those of the DCCA and ADCCA. Similar to the symmetricity of the ADCCA algorithm, we can define a new fluctuation–asymmetry metric given as follows:
This metric indicates the degree of fluctuation-dependency of the cross-correlational structure of two signals, while the cross-correlation asymmetry quantifies the degree of trend-dependency in the cross-correlational structure of two signals. Finally, these metrics could be said to represent the change in underlying dynamics.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Pattern of Pearson Cross-Correlation
The PCC is a tool for quantifying the level of synchronized co-movement of two stationary time series. Thus, if there is a phase lag or a nonstationary feature between both signals, a spurious result can come out. Nonetheless, this approach has been long used in oceanography, especially in terms of empirical orthogonal function algorithms. In this study, we use the PCC map as a baseline for alternative long-persistence analysis tools.
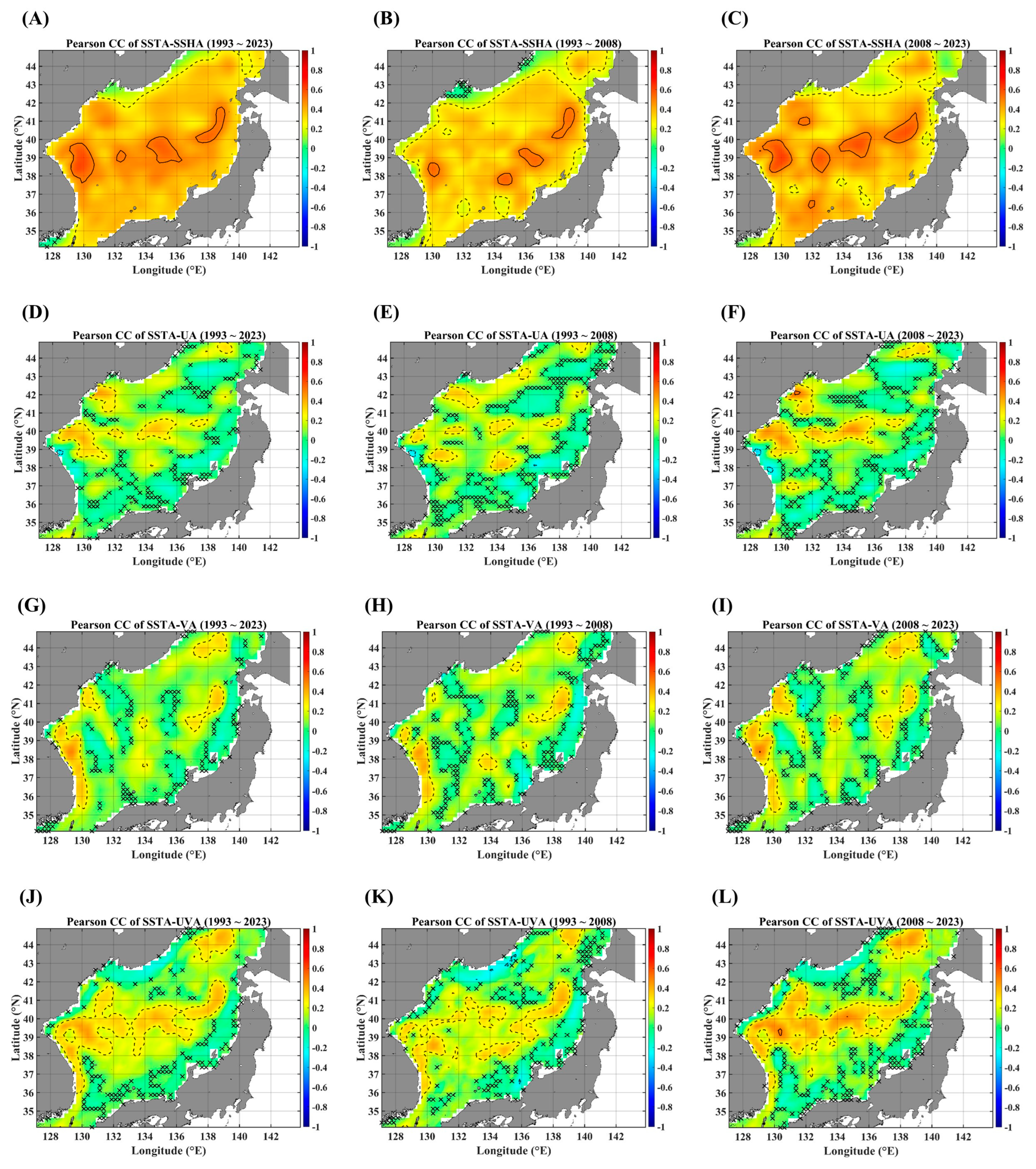
Figure 2 illustrates four PCC maps, which represent a pairwise cross-correlation level between SSTAs and the rest of the four advective forcing parameters, namely SSHAs, the zonal current anomaly (UA), the meridional current anomaly (VA), and the total current anomaly (UVA), respectively. The solid line indicates a PCC value of 0.5 and the dotted line denotes a value of 0.25; they are interpreted as strong and weak correlations, in an ad hoc way. The most intriguing feature is that the region with a strong cross-correlation is focused on the tongue-shaped area connecting the EKB and the SPF and has become conspicuous in the recent decade from 2008 to 2023. Especially, the current speed seems to play a major role (Figure 2L). It should be noted that the SSHA can incorporate other forcing parameters not directly linked to advection.
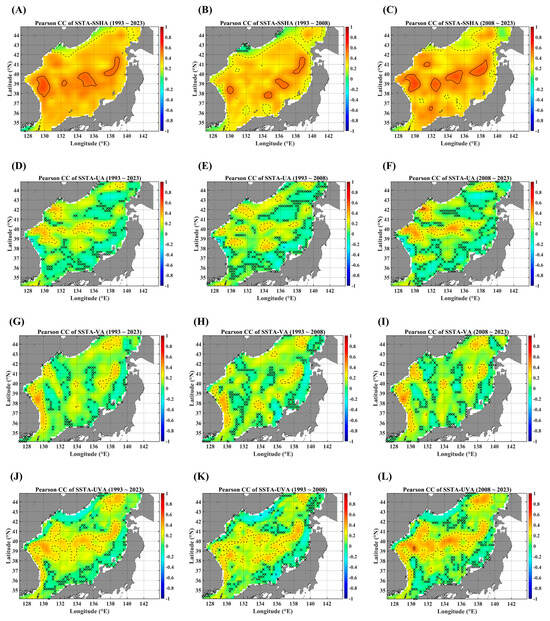
Figure 2.
PCC maps between SSTAs and advective parameters, in terms of different temporal ranges. PCC maps between SSTAs and SSHAs for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. PCCs map between the SSTA and zonal current anomaly for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. PCC maps between the SSTA and meridional current anomaly for (G) 1993–2023, (H) 1993–2008, and (I) 2008–2023. PCC maps between the SSTA and total current anomaly for (J) 1993–2023, (K) 1993–2008, and (L) 2008–2023. The contour line notation: the solid black line for 0.5 (strong correlation), the dotted line for 0.25 (weak correlation), and the dashed black line for −0.25. Note that the areas marked “x” are not statistically significant for the linear trends at the 95% significance level.
As for a negative PCC, there are nearly no noticeable negative cross-correlations over almost the entire EJS region. If any exist, their strength is too weak, with most values below 0.25 in magnitude. However, it should be noted that the regions with negative PCC values are mainly located along the coastal area for the pairs of the SSTA and current velocity. One interesting feature is that there is a point with a negative PCC value greater than 0.25 in magnitude between the SSTA and zonal velocity, which is indicated as a dashed contour line (Figure 2D–F); this point may be related to the effect of significant negative wind stress curl [20].
3.2. Spatial Pattern of DCCA
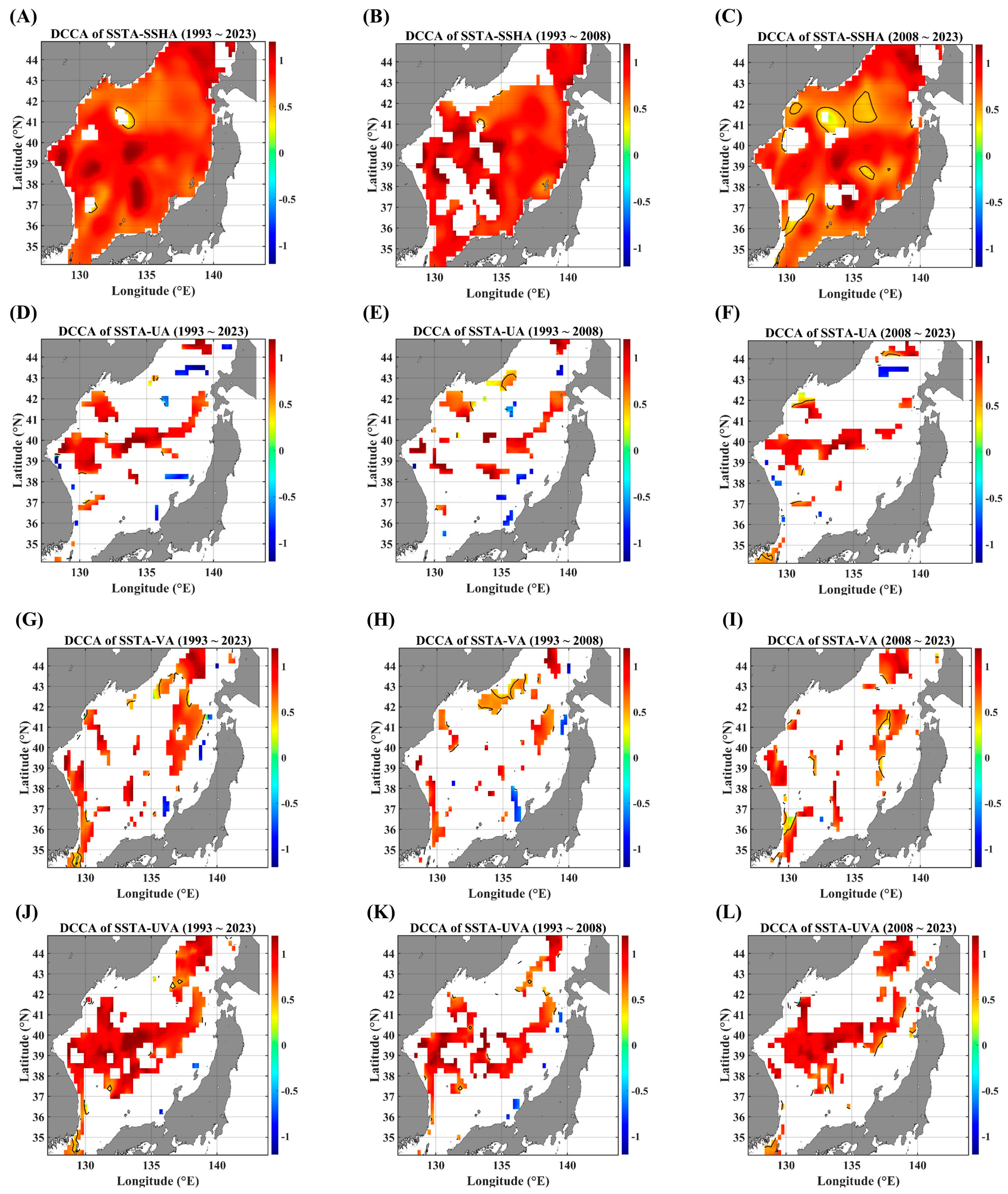
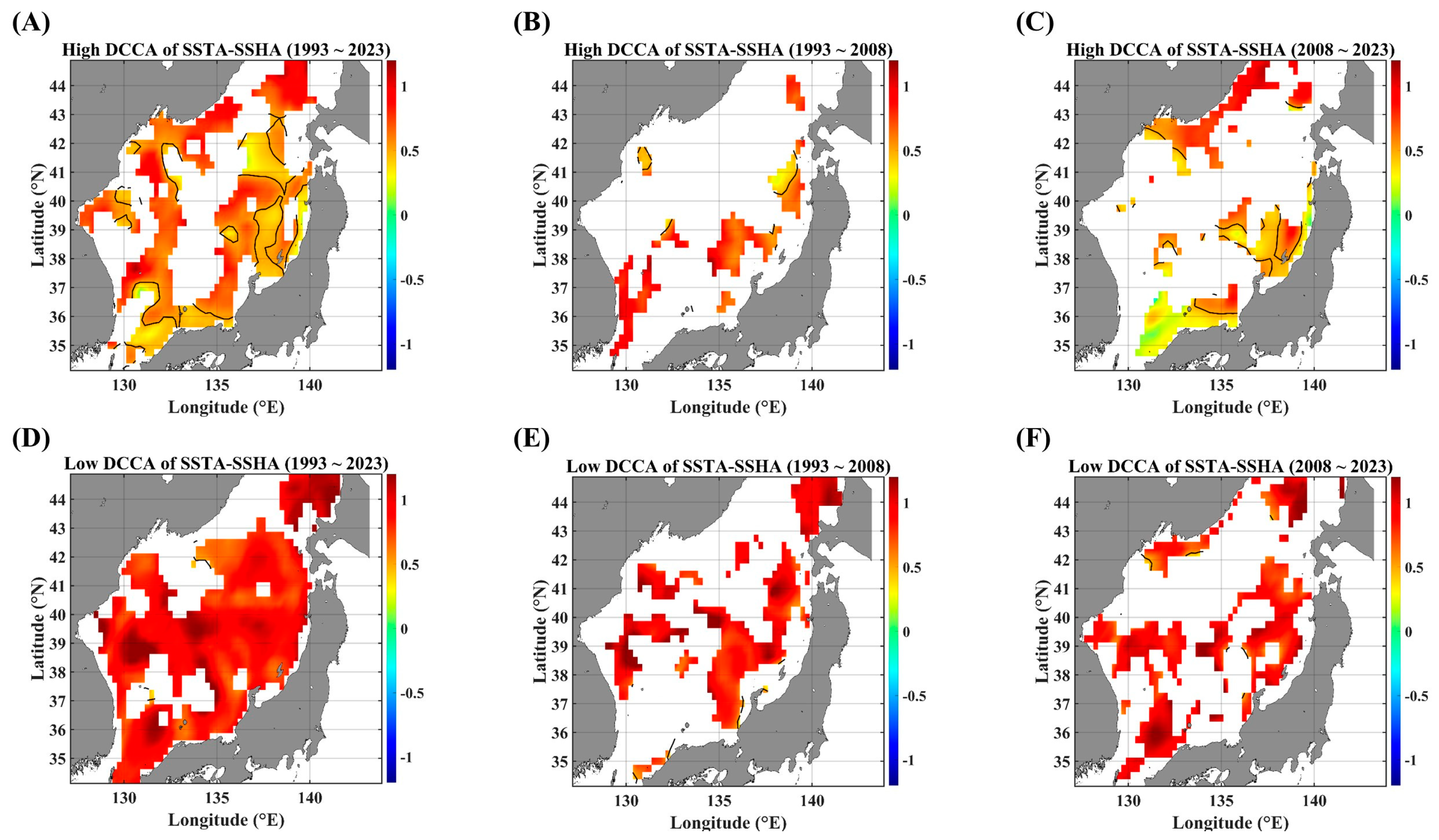
For comparison with PCC maps, DCCA maps are presented in Figure 3. The biggest difference between the two algorithms lies in the quantification of long-term persistence. Generally, persistence means slow-decaying auto- and/or cross-correlational behaviors. The DCCA algorithm is a more appropriate tool compared to the traditional time-delayed PCC methodology because DCCA can yield a reliable result even for both nonstationary time series while the PCC tool is theoretically reliable only under the constraint of stationarity. The PCC algorithm can yield a spurious result when there are polynomial trends in both signals, respectively.
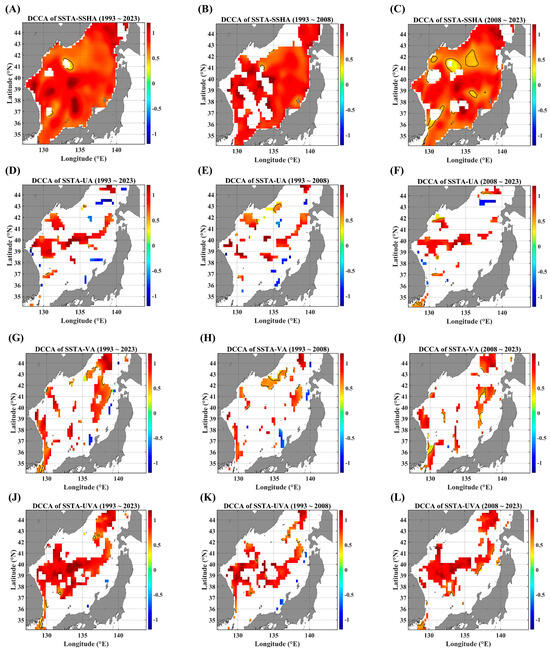
Figure 3.
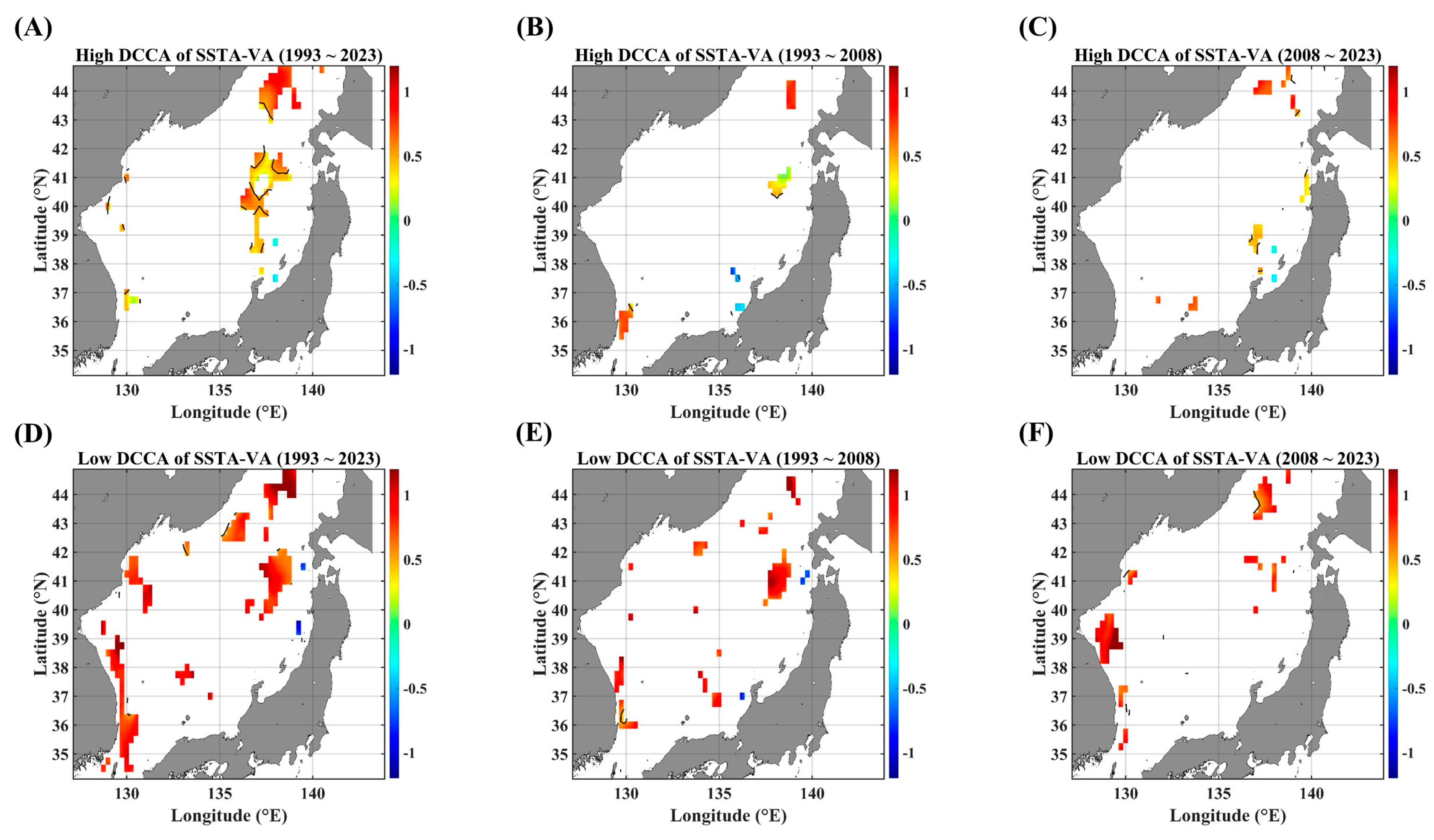
DCCA maps between SSTAs and advective parameters, in terms of different temporal ranges. DCCA maps between SSTAs and SSHAs for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. DCCA maps between the SSTA and zonal current anomaly for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. DCCA maps between the SSTA and meridional current anomaly for (G) 1993–2023, (H) 1993–2008, and (I) 2008–2023. DCCA maps between the SSTA and total current anomaly for (J) 1993–2023, (K) 1993–2008, and (L) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
As shown in Figure 3, long-term cross-correlational persistence is very rare, except for the case of a pair of SSTAs and SSHAs. Firstly, SSHAs seem to be a combination of various forcing parameters, while the current velocity anomalies show a region-specific feature; the zonal velocity is strongly related to zonal currents (SPF area), and the meridional velocity is securely related to the meridional currents (near the coast of Korea). As for the current speed, the SPF area and the east coast of Korea seem to be a hot spot for the long-term persistent interactions between SSTAs and currents.
The presence of negative long-term persistence is notable, although the spatial coverage is too small (Figure 3D–I); these behaviors are observed only in the pairs of SSTAs and current velocities. The pair of the SSTA and zonal current velocity leads to a negative long-term persistent feature along the east coast of Korea (Figure 3D,F), while another pair of the SSTA and meridional current velocity seems to contribute to long-term persistence near the Japan coast and the Tsugaru strait (Figure 3G,H). There could be a possibility for upwelling phenomena due to coastal currents; in a recent study [21], current-driven upwelling prevailed off the southern coast while wind-driven upwelling is dominant off the northern coast.
3.3. Spatial Pattern of ADCCA
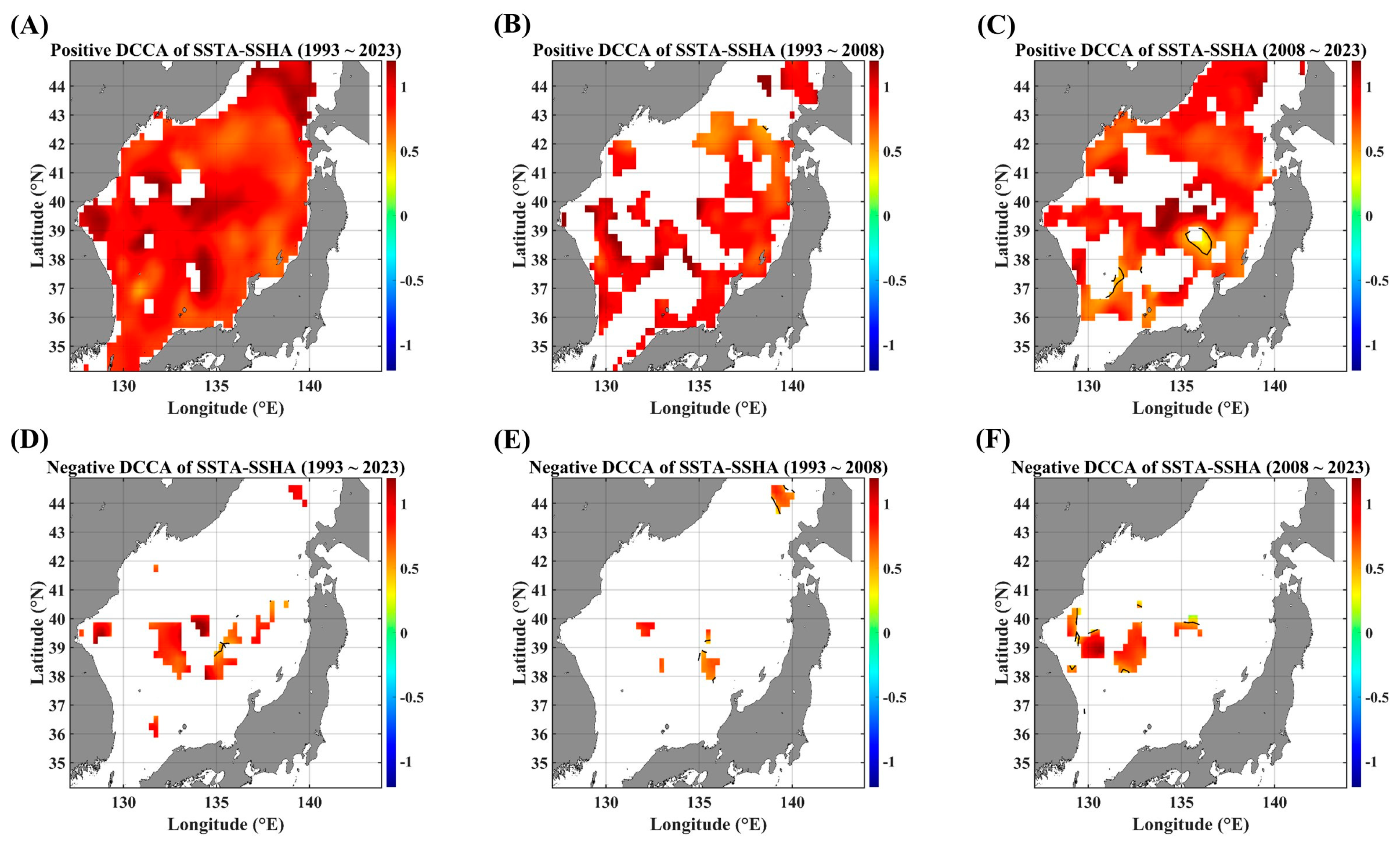
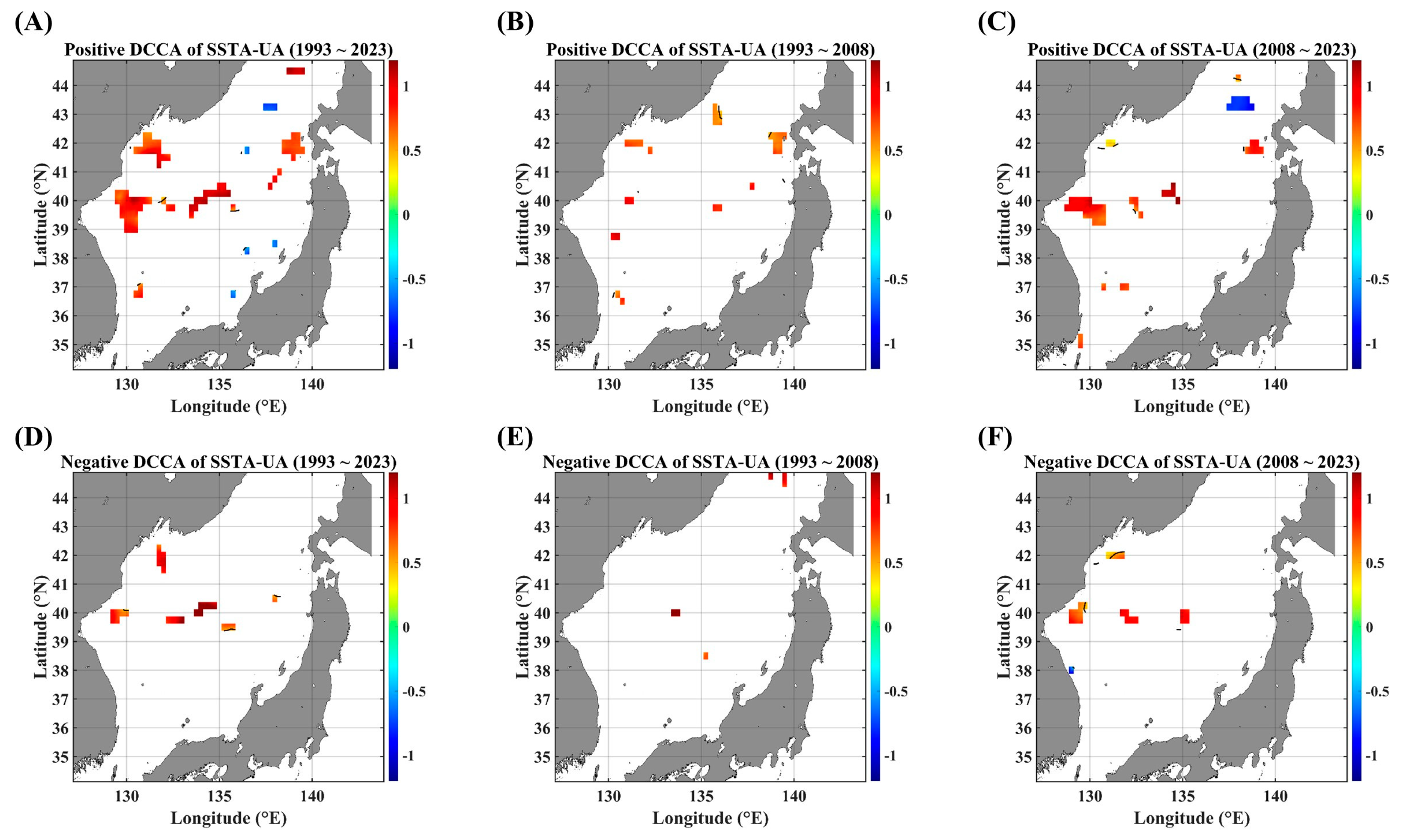
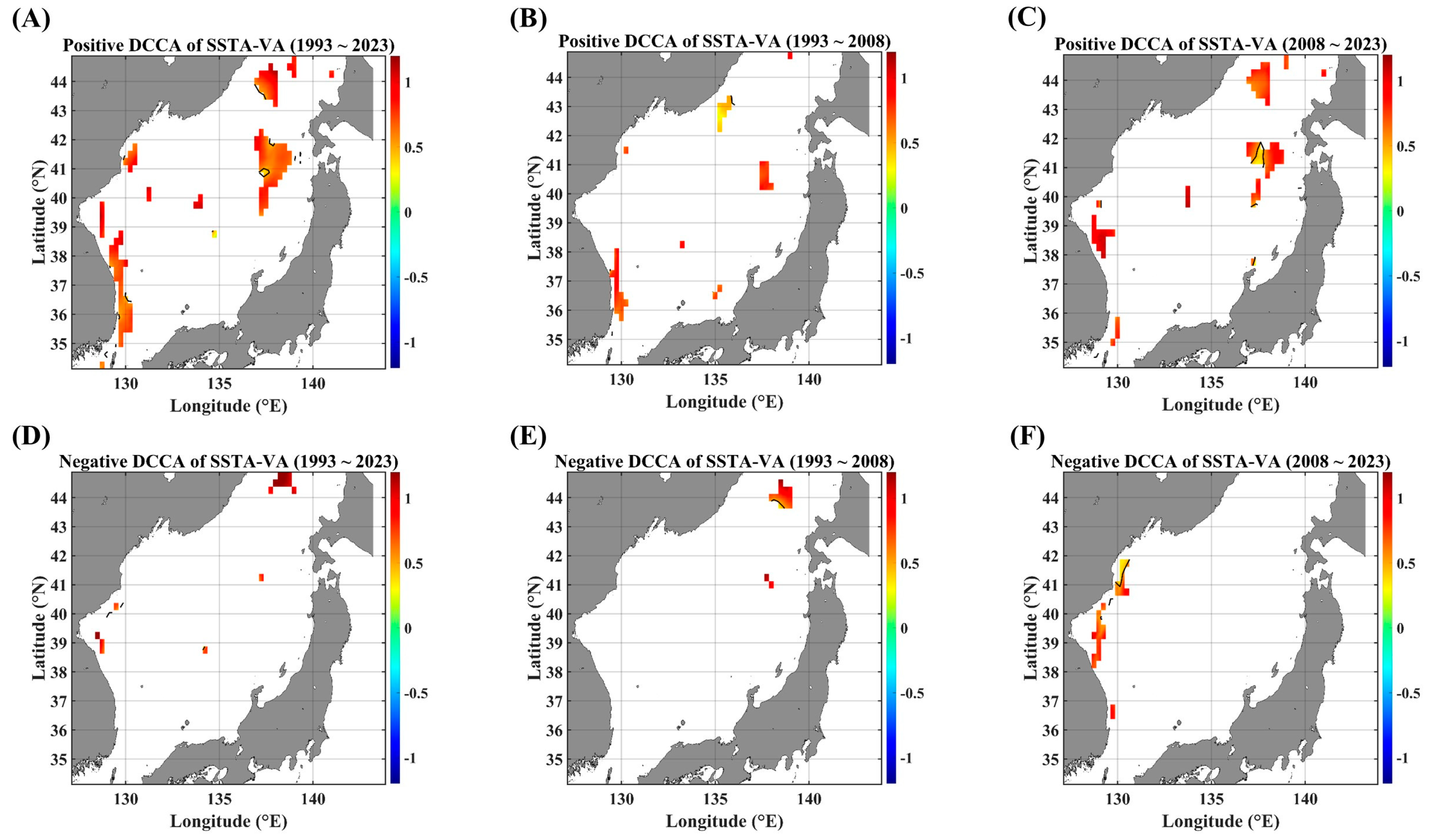
As a kind of conditional DCCA, the asymmetric DCCA was performed on pairs of SSTAs and advective forcing parameters. Since, generally, the advective forcing parameters (herein, SSHA, UA, VA, and UVA are considered) make a more direct impact on SSTA variability than the other way around, the local linear trend of segmented SSTA series was used as a separating criterion. Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the ADCCA map between the SSTA and the respective advective forcing parameter, where “Positive” denotes the rising-up behavior of a local linear trend in the segmented SSTA variability, and “Negative” denotes the falling-down behavior of the SSTA’s local linear trend.
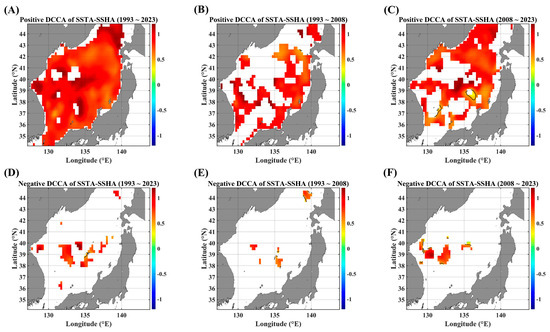
Figure 4.
ADCCA maps between SSTAs and SSHAs, in terms of different temporal ranges. ADCCA maps during the positive (rising) phase for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. ADCCA maps during the negative (falling) phase for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
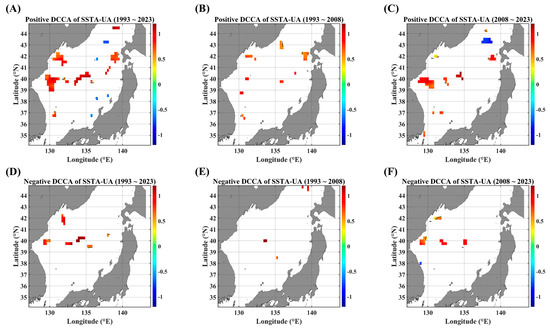
Figure 5.
ADCCA maps between the SSTA and UA, in terms of different temporal ranges. The ADCCA maps during the positive (rising) phase for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. ADCCA maps during the negative (falling) phase for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
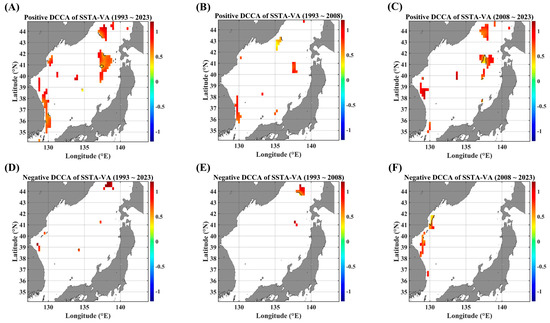
Figure 6.
ADCCA maps between the SSTA and VA, in terms of different temporal ranges. ADCCA maps during the positive (rising) phase for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. ADCCA maps during the negative (falling) phase for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
In the pair of SSTAs and SSHAs (Figure 4), the positive ADCCA shows a strong long-term persistent behavior over almost the entire EJS region when the full duration was considered (Figure 4A). However, the negative ADCCA exhibits nearly no long-term persistence (Figure 4D–F). This distinct behavior seems to be mainly due to the strong rising tendency of SSTAs in the EJS. Also, there is a difference between the first and second decades. For the positive ADCCA, the recent decade (Figure 4C) shows a more complex spatial distribution rather than the former decade (Figure 4B). The area eastward from 135°E to 38.5°N shows a transition from persistent to anti-persistent behavior (the solid black contour line in Figure 4C). Nonetheless, it is noteworthy that the tongue-shape area from the EKB to the SPF has become highly persistent in the recent decade. Further, there is no region showing a negative long-term persistent behavior.
As for the pairs of SSTAs and current velocities, UA and VA, nearly no long-term persistence is observed. However, the high persistent behaviors are observed along the obvious zonal and meridional current areas, respectively. Although it is small in the area portion, a high persistence of the positive ADCCA between the SSTA and UA is observed along the SPF area (Figure 5A,C) while the positive ADCCA of a pair of the SSTA and VA shows a high persistent behavior along the east coast of Korea (Figure 6A,C). These behaviors are also relatively more conspicuous in the recent decade than in the former decade.
The negative long-term persistent behaviors are nearly not observed from the perspective of linear-trend asymmetry (Figure 5 and Figure 6), compared to those of DCCA cases (Figure 3). This distinct contrast directly implies that there is no long-term persistence depending on the local linear trend. Instead, a negative long-term persistence is established only when all segments are considered. Since power-law scaling features in DCCA-based algorithms are determined by an ensemble average of local detrended fluctuation functions, no power-law scaling can be established according to constraints such as local linear trend and local fluctuation level.
Concerning the long-term persistent behavior of ADCCA between the SSTA and current speed (UVA), Figure A5 shows more clearly a high persistence along the SPF area in the recent decade, and the extent of the spatial area with a high persistence is greater compared to the single current velocity (Figure 5 and Figure 6). This contrast can be mainly due to the directionality of the current velocity.
Also, as mentioned in the section of the DCCA map, the spatial extent of the high persistence of the ADCCA becomes wider in the pair of SSTAs and SSHAs compared to other pairs. This feature seems to be mainly due to the fact that the SSHA component includes more composite factors, even relating to vertical advection. A wide spatial coverage with a strong cross-correlation between SSTAs and SSHAs is also observed in PCC maps in Figure 3A–C.
3.4. Spatial Pattern of F-DCCA
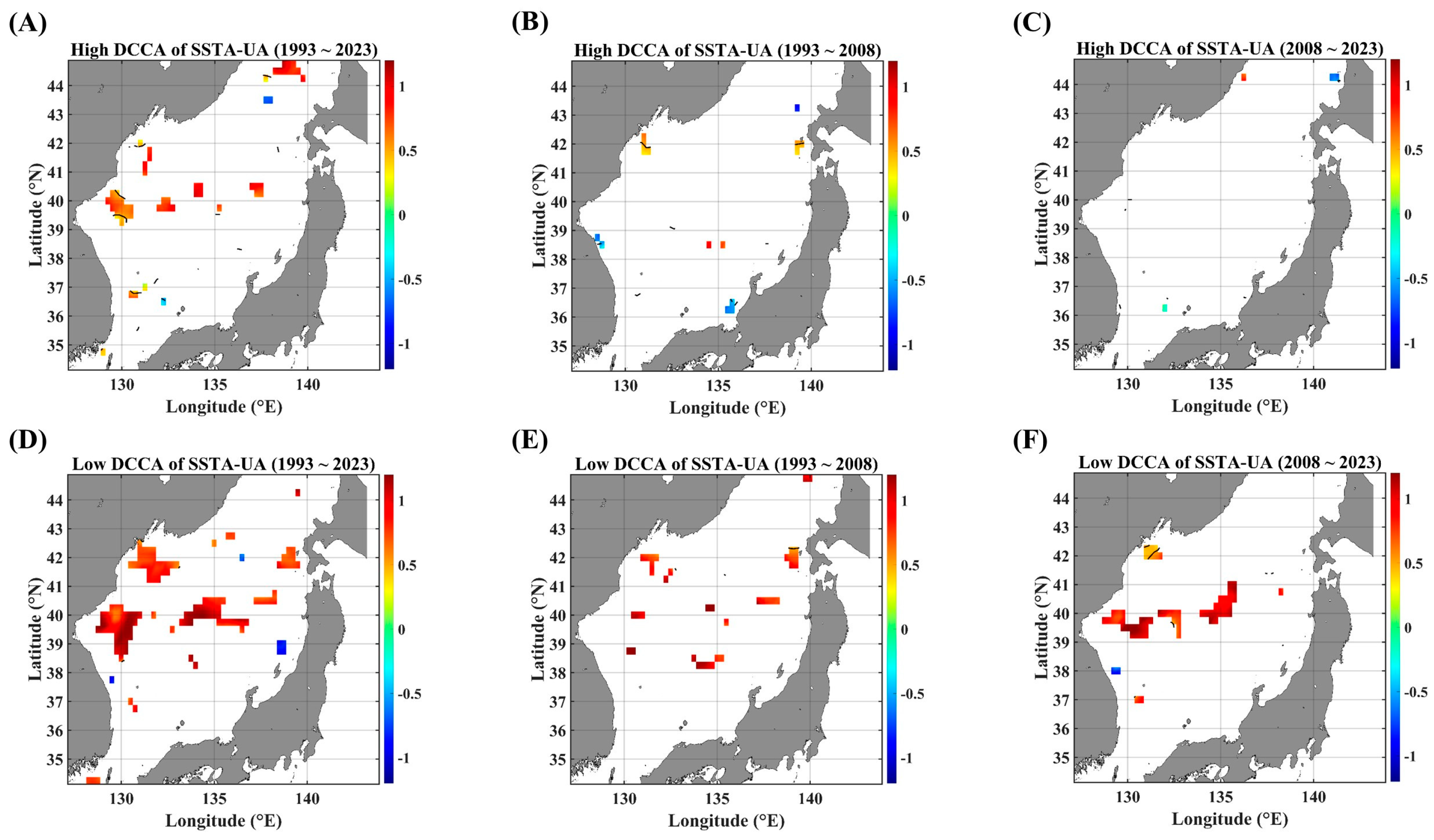
Secondly, as another conditional DCCA, the F-DCCA algorithm was applied to all pairs of SSTAs and advective forcing parameters. Different from the case of the ADCCA algorithm, the local level of fluctuation of SSTAs can also lead to different cross-correlational long-term persistence between SSTAs and advective forcing parameters; all the relevant F-DCCA maps are given in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9, where “High” means that the STD of the local fluctuation is greater than the STD of the full-length fluctuations while “Low” indicates that the local STD is smaller than the full-length STD.
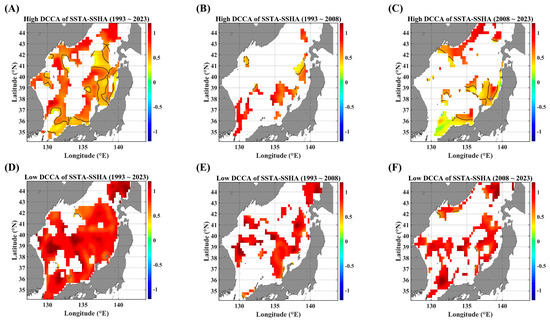
Figure 7.
F-DCCA maps between SSTAs and SSHAs, in terms of different temporal ranges. F-DCCA maps with high fluctuations for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. F-DCCA maps with low fluctuations for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
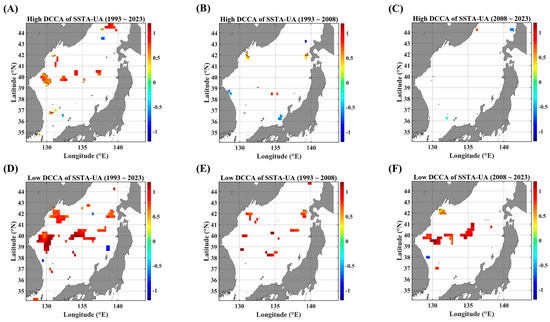
Figure 8.
F-DCCA maps between the SSTA and UA, in terms of different temporal ranges. F-DCCA maps with high fluctuations for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. F-DCCA maps with low fluctuations for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
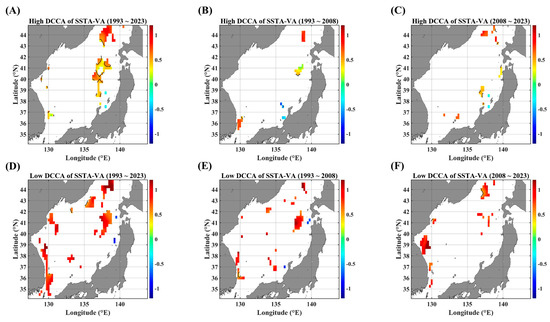
Figure 9.
F-DCCA maps between the SSTA and VA, in terms of different temporal ranges. F-DCCA maps with high fluctuations for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. F-DCCA maps with low fluctuations for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
Figure 7 shows the clearly distinct behaviors of long-term persistence in high and low levels of SSTA fluctuations, respectively. In low fluctuations, highly persistent behaviors are mostly observed all over the EJS (Figure 7D–F), while anti-persistent behaviors are strengthened in high fluctuations (Figure 7A–C). Especially, near the Korea–Tsushima strait (KTS), the long-term persistence shows a harsh contrast: strong persistence in low fluctuations and weak or anti-persistence in high fluctuations. This feature is noteworthy because the KTS is the major in-flux gate of warm waters. Also, along the SPF line, a highly persistent behavior is observed only in the low-fluctuating phase (Figure 7A,D).
Even in F-DCCA maps between the SSTA and a singular current velocity component (Figure 8 and Figure 9), as already clearly observed in Figure 7, noticeable persistent behaviors are only seen in the low-fluctuating phases (Figure 8F and Figure 9F). These behaviors become more conspicuous in the recent decade (2008–2023) rather than in the former decade (1993–2008). Also, the regions showing a strong persistence seem to be closely related to the current paths. The zonal current leads to a high persistence along the SPF region (Figure 8F) while the meridional current leads to a high persistence along the east coast of Korea (Figure 9F), strongly influenced by the East Korea Warm Current (EKWC).
As for the negative long-term persistence in the aspect of the F-DCCA, there is nearly no region compared to those of the DCCA. If any exist, they are very sparsely located along the Japanese coast as well as the Tsugaru strait (Figure 9B,E). Thus, it can be concluded that there is no long-term scaling behavior in negatively fluctuating pairs of SSTAs and advective forcing parameters under constraints such as local fluctuation levels and local linear trends.
Considering the case of the current speed (Figure A6), the wider spatial area is affected by a strong persistence only in the low-fluctuating phase. Further, the highly persistent region seems to be dependent on the observation period. The pathway region of the EKWC shows a highly persistent behavior in the former decade (Figure A6E) while the SPF region exhibits a stronger persistence in the recent decade (Figure A6F).
Already confirmed in previous analysis results, the spatial extent with long-term persistent and/or anti-persistent behaviors is robustly wider in the pair of SSTAs and SSHAs compared to other pairs. This behavior seems to be due to the fact that an SSHA represents a mixture of various forcing parameters. Nevertheless, there is one big difference; the persistent behavior seems to be more strongly dependent on the level of SSTA fluctuations (Figure 7). Specifically, the area along the Japanese coast exhibits a highly anti-persistent behavior in the pair of SSTAs and SSHAs. This finding should be necessarily noted for future research because there can be an upwelling process.
4. Discussion
In this study, we have examined the long-term persistence of cross-correlational structures between SSTAs and advective forcing parameters using DCCA-based algorithms because the traditional time-lagged Pearson cross-correlation tool is not appropriate for dealing with a pair of nonstationary time series, especially oceanic time series with a variety of strong periodic trends. The cross-correlational long-term persistence of a pair of time series is an important feature, especially in predicting the future variations of one parameter based on the present variations of another parameter: herein, SSTAs and three advective forcing parameters (SSHAs, UA, and VA). Also, a complexity underlying SSTA variability can be qualitatively assessed, according to whether power-law scaling relations for those pairs are established or not. The unestablished regions of power-law scaling can be said to be more complex.
There naturally arises a question about the origin of long-term persistence in cross-correlational structure. According to the simulation study [5], both signals can exhibit a cross-correlational power-law scaling under a strong common term, the so-called interaction term, if only one of them exhibits a power-law scaling. Since it was already confirmed that the SSTA exhibits a power-law scaling [3], the presence of strong persistence among pairs considered in this study indicates that the interaction term between them must be strong enough to influence their joint behavior.
Further, these long-term persistent behaviors can be dependent on the characteristics of the SSTA’s variability characteristics. Thus, to unveil these constraint-dependent features, we additionally utilized the modified versions of the DCCA algorithm, namely ADCCA and F-DCCA, which deal with the local linear trend and the local fluctuation level of SSTAs, respectively. In the applications of DCCA-based algorithms as well as DFA-based algorithms, the step of estimating the generalized Hurst exponents from the power-law scaling functions (Equations (4), (10) and (15)) is very important because various crossover behaviors are very often observed in cases of geophysical time series [3,11,13,14]. In this study, the scaling range from 400 to 3000 days was used because Brownian motion behaviors were observed for the smaller scales (less than 400 days). The Hurst exponent is about 1.5 for Brownian motions, and a Brownian motion can be explained in terms of stochastic processes with no or short-term correlations [22].
In STD and linear trend maps (Figure 1), the tongue-shaped region, extending from the EKB toward the eastern end of the SPF, shows a high value in two measures. And, this region is also well consistent with the areas of relatively high PCC values for all pairs between SSTAs and advective forcing parameters (Figure 2). However, these consistent behaviors seem to be valid only for two pairs of the SSTA and UA as well as the SSTA and UVA (Figure 3). As for the pair of SSTAs and SSHAs, strongly persistent behaviors are not restricted to that region but pervasive nearly all over the EJS. In the case of the pair of the SSTA and VA, the coast regions, along which main meridional currents flow, show a strong long-term persistence. These observational findings imply that the SSTA variability in the tongue-shape region is greatly affected by the zonal current and the current speed in a long-term persistent manner.
Concerning the impact of constraints on long-term persistent behaviors, any constraint on SSTA variability seems to surely increase the system’s complexity. Compared to DCCA results (Figure 3), ADCCA and F-DCCA results showed nearly no areas in the EJS where any long-term persistent behaviors are established (Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9). Nonetheless, there are noticeable findings supporting that long-term persistent behaviors for all the pairs are dependent on local linear trends as well as local fluctuation levels; relatively strong persistence appeared in the rising-up (positive) phases of the SSTA and in the low-fluctuating phases of the SSTA. There are also region-specific features between the SSTA and current velocity (UA and VA); zonal currents (UA) show a strong persistent behavior along its main pathway from the EKB to the eastern end of the SPF, while meridional currents show a strong persistence along the coasts of Korea and Japan. These coastal regions should be cautiously dealt with because of the poor resolution of satellite-gridded datasets on the coasts. Nonetheless, the relations between SSTAs and current velocity anomalies along the major pathways of surface currents are noteworthy.
One noticeable finding is that these long-term persistent behaviors between SSTAs and advective forcing parameters are stronger in the recent decade (2008–2023) than in the former decade (1993–2008). Specifically, during the rising phase of SSTAs, the long-term persistence becomes more pronounced. This may be related to the increasing role of oceanic dynamics in recent decades [23].
We have to note a clear limitation in establishing the constraints; in this study, two constraints are characterized solely by SSTA variability. Generally, SST variability in the EJS is greatly influenced by climate forcing parameters, such as Arctic Oscillation (AO), North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), West Pacific (WP) pattern, and El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) [24,25,26]. Thus, these climate factors should be also considered as constraints on long-term persistence examinations between SSTAs and various forcing parameters. To this end, an analysis algorithm is under study.
Lastly, there is another noticeable finding on the negative long-term persistent behavior between SSTAs and current velocity anomalies in terms of the DCCA. The negative persistence means that the SSTA increases as UA (or VA) negatively increases, and vice versa. It should be noted that these behaviors are observed only along the coasts although the spots are too small. There is a possibility that these spots are related to the current-driven upwelling process [21]. In future research, this topic will be more closely analyzed in terms of cross-correlational characteristics by considering wind and current.
5. Conclusions
Our main results in this study can be summarized as follows:
- A strong long-term persistent behavior is observed nearly all over the EJS for the pair of SSTAs and SSHAs in terms of the DCCA.
- The long-term persistence between SSTAs and SSHAs is strong only for the rising phases of SSTAs as well as the small fluctuating phases of SSTAs in terms of the ADCCA and F-DCCA, respectively.
- The pairs of the SSTA and current velocity (UA and VA) show a region-specific long-term persistence; a strong persistent behavior is observed along the coasts of Korea and Japan for the pair of the SSTA and VA and along the tongue-shaped region for the pair of the SSTA and UA.
- There are a small number of spots where a negatively long-term persistent behavior is observed: along the east coast of Korea for the SSTA-UA pair, and along the west coast of Japan for the SSTA-VA pair.
The long-term persistent features in cross-correlational structures for pairs between SSTAs and advective forcing parameters can give us insights into a variety of physical processes underlying SSTA dynamics in the EJS. Especially, the region-specificity and the SSTA feature-dependency of long-term cross-correlational persistence for those pairs can greatly contribute to the SSTA’s prediction based on machine learning algorithms as well as the structural variability of the SSTA system on a longer time scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.L. and J.-J.P.; methodology, G.L; validation, G.L. and J.-J.P.; formal analysis, G.L.; investigation, G.L.; data curation, G.L.; writing—original draft preparation, G.L.; writing—review and editing, G.L. and J.-J.P.; visualization, G.L.; supervision, J.-J.P.; project administration, J.-J.P.; funding acquisition, J.-J.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Korea Institute of Marine Science & Technology Promotion (KIMST) funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries (RS-2023-00256005). This work was also supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (NRF-2022R1A2C1004059).
Data Availability Statement
The SST data presented in this study are openly available in NCEI at https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/products/optimum-interpolation-sst (accessed on 4 April 2023).
Acknowledgments
NOAA OI SST V2 high-resolution dataset data were provided by the NOAA, PSL, Boulder, CO, USA, from their website at https://psl.noaa.gov (accessed on 4 April 2023). This study has been conducted using E.U. Copernicus Marine Service Information; https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00145 (accessed on 8 April 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
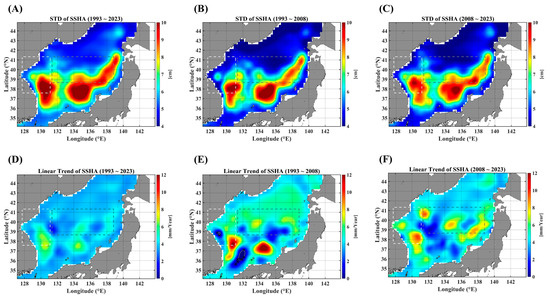
Figure A1.
STD maps of SSHAs for three durations: the full observation period (A), the 1st decades (B), and the 2nd decades (C). The linear trends are illustrated in (D–F), respectively, corresponding to their different observation durations. The light gray dashed-line box indicates the EKB region, and the dark gray dashed-line box denotes the SPF region. Note that the areas marked “x” are not statistically significant for the linear trends at the 95% significance level.
Figure A1.
STD maps of SSHAs for three durations: the full observation period (A), the 1st decades (B), and the 2nd decades (C). The linear trends are illustrated in (D–F), respectively, corresponding to their different observation durations. The light gray dashed-line box indicates the EKB region, and the dark gray dashed-line box denotes the SPF region. Note that the areas marked “x” are not statistically significant for the linear trends at the 95% significance level.
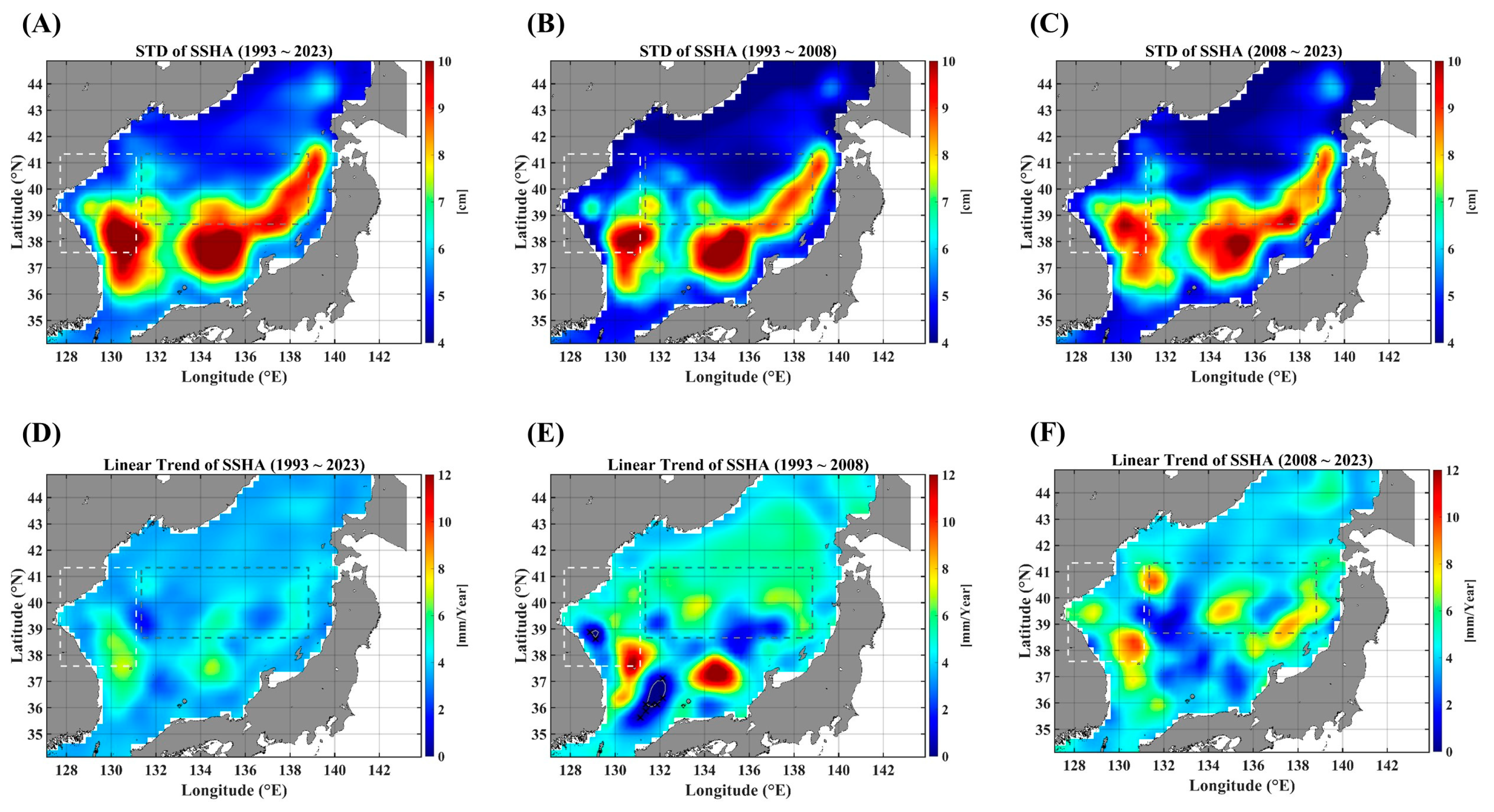
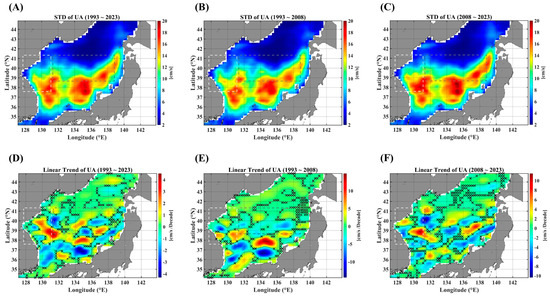
Figure A2.
STD maps of the UA for three durations: the full observation period (A), the 1st decades (B), and the 2nd decades (C). The linear trends are illustrated in (D–F), respectively, corresponding to their different observation durations. The light gray dashed-line box indicates the EKB region, and the dark gray dashed-line box denotes the SPF region. Note that the areas marked “x” are not statistically significant for the linear trends at the 95% significance level.
Figure A2.
STD maps of the UA for three durations: the full observation period (A), the 1st decades (B), and the 2nd decades (C). The linear trends are illustrated in (D–F), respectively, corresponding to their different observation durations. The light gray dashed-line box indicates the EKB region, and the dark gray dashed-line box denotes the SPF region. Note that the areas marked “x” are not statistically significant for the linear trends at the 95% significance level.
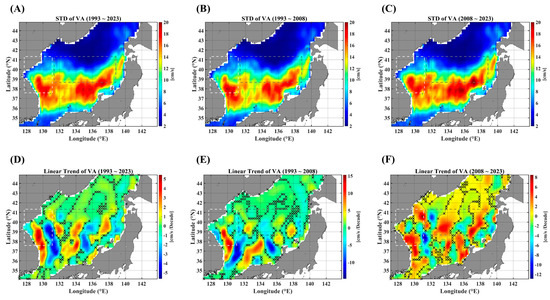
Figure A3.
STD maps of the VA for three durations: the full observation period (A), the 1st decades (B), and the 2nd decades (C). The linear trends are illustrated in (D–F), respectively, corresponding to their different observation durations. The light gray dashed-line box indicates the EKB region, and the dark gray dashed-line box denotes the SPF region. Note that the areas marked “x” are not statistically significant for the linear trends at the 95% significance level.
Figure A3.
STD maps of the VA for three durations: the full observation period (A), the 1st decades (B), and the 2nd decades (C). The linear trends are illustrated in (D–F), respectively, corresponding to their different observation durations. The light gray dashed-line box indicates the EKB region, and the dark gray dashed-line box denotes the SPF region. Note that the areas marked “x” are not statistically significant for the linear trends at the 95% significance level.
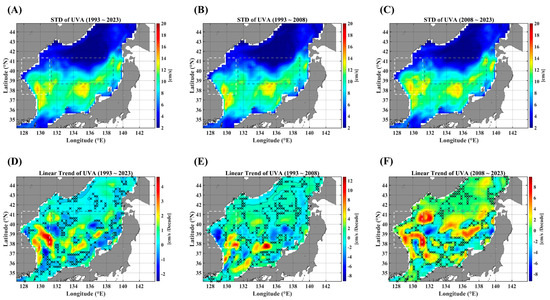
Figure A4.
STD maps of the UVA for three durations: the full observation period (A), the 1st decades (B), and the 2nd decades (C). The linear trends are illustrated in (D–F), respectively, corresponding to their different observation durations. The light gray dashed-line box indicates the EKB region, and the dark gray dashed-line box denotes the SPF region. Note that the areas marked “x” are not statistically significant for the linear trends at the 95% significance level.
Figure A4.
STD maps of the UVA for three durations: the full observation period (A), the 1st decades (B), and the 2nd decades (C). The linear trends are illustrated in (D–F), respectively, corresponding to their different observation durations. The light gray dashed-line box indicates the EKB region, and the dark gray dashed-line box denotes the SPF region. Note that the areas marked “x” are not statistically significant for the linear trends at the 95% significance level.
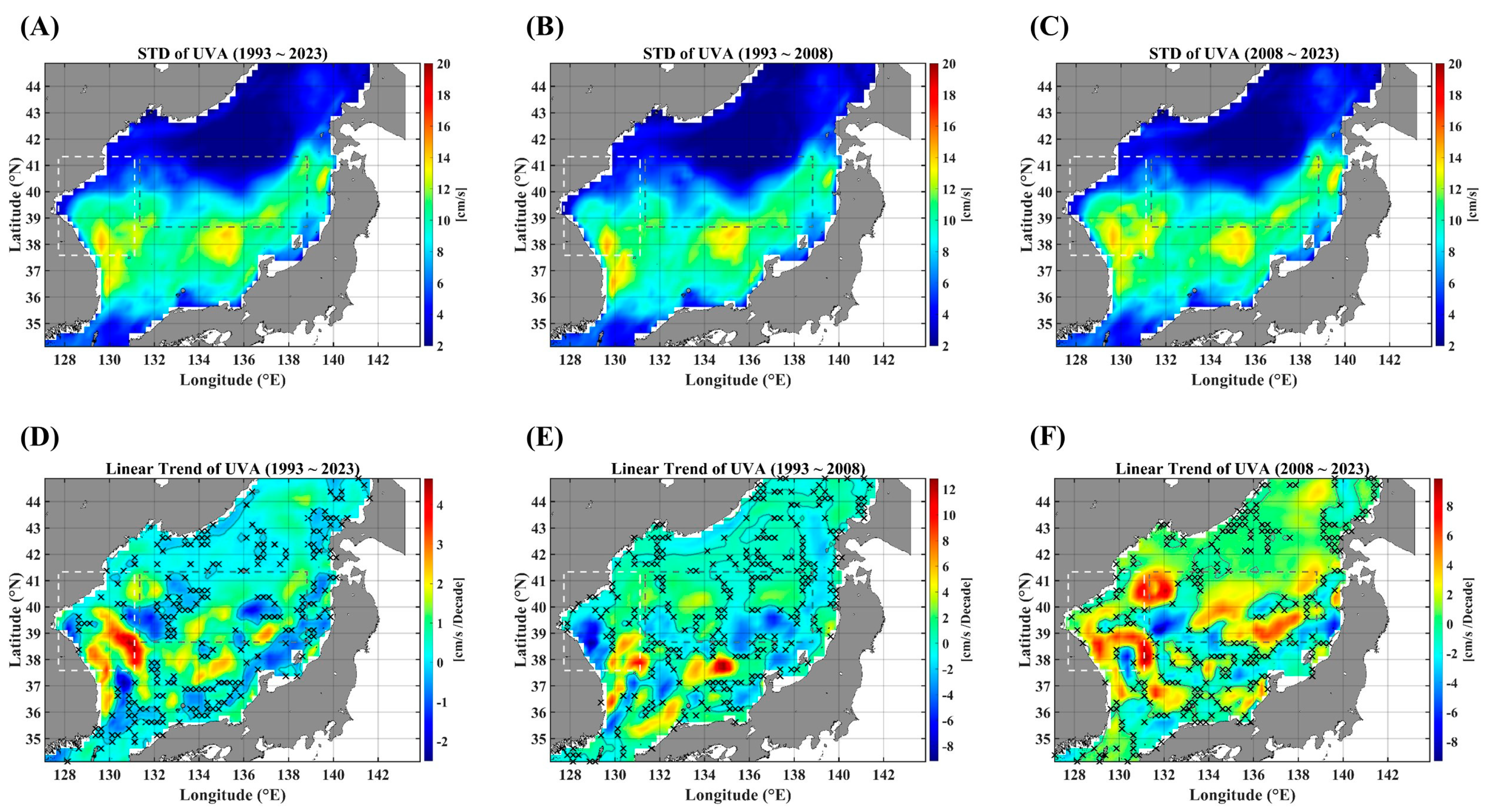
Figure A5.
ADCCA maps between the SSTA and UVA, in terms of different temporal ranges. ADCCA maps during the positive (rising) phase for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. ADCCA maps during the negative (falling) phase for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
Figure A5.
ADCCA maps between the SSTA and UVA, in terms of different temporal ranges. ADCCA maps during the positive (rising) phase for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. ADCCA maps during the negative (falling) phase for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
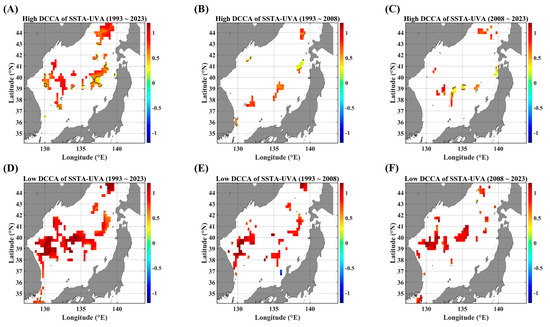
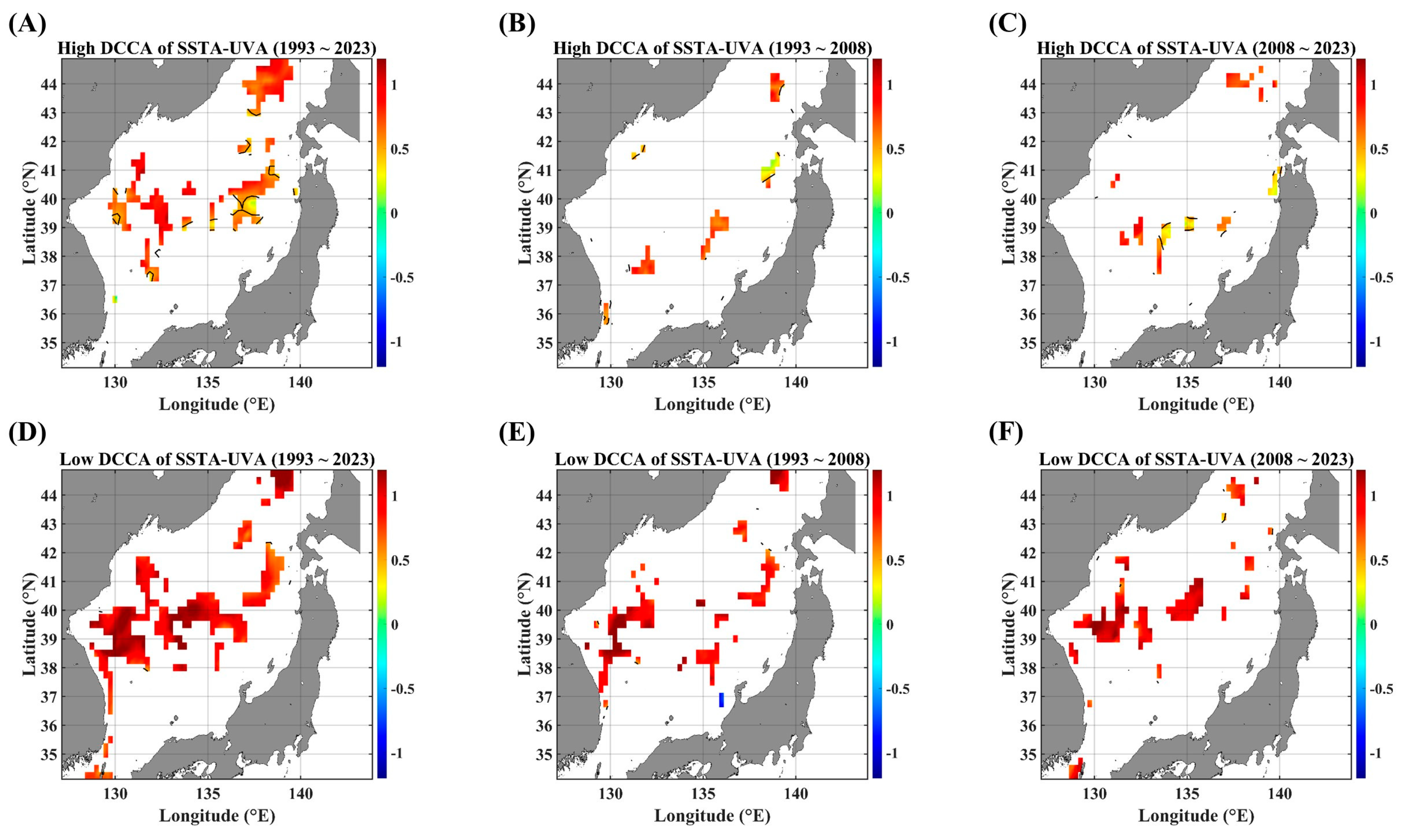
Figure A6.
F-DCCA maps between the SSTA and UVA, in terms of different temporal ranges. F-DCCA maps with high fluctuations for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. F-DCCA maps with low fluctuations for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
Figure A6.
F-DCCA maps between the SSTA and UVA, in terms of different temporal ranges. F-DCCA maps with high fluctuations for (A) 1993–2023, (B) 1993–2008, and (C) 2008–2023. F-DCCA maps with low fluctuations for (D) 1993–2023, (E) 1993–2008, and (F) 2008–2023. All the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are statistically significant at the 95% significance level. Note that the white blanks indicate areas where the power-law scaling is not defined, and therefore the cross-correlational Hurst exponents are also not defined. Also, note that the solid black contour line indicates a Hurst exponent of 0.5, implying that there is a short-ranged or no cross-correlation.
References
- Deser, C.; Alexander, M.A.; Xie, S.-P.; Phillips, A.S. Sea Surface Temperature Variability: Patterns and Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgin, C.E.; Merchant, C.J.; Ferreira, D. Tendencies, variability and persistence of sea surface temperature anomalies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.; Park, J.-J. Auto- and Cross-Correlation Multifractal Analysis of Sea Surface Temperature Variability. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.; Park, J.-J. Intrinsic Mode-Based Network Approach to Examining Multiscale Characteristics of Sea Surface Temperature Variability. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podobnik, B.; Stanley, H.E. Detrended Cross-Correlation Analysis: A New Method for Analyzing Two Nonstationary Time Series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 084102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-K.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Havlin, S.; Simons, M.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 49, 1685–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantelhardt, J.W.; Zschiegner, S.A.; Bunde, E.K.; Havlin, S.; Bunde, A.; Stanley, H.E. Multifractal detrended fluctuation anal-ysis of nonstationary time series. Physica A 2002, 316, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvozdanovic, I.; Podobnik, B.; Wang, D.; Eugene Stanley, H. 1/f behavior in cross-correlations between absolute returns in a US market. Physica A 2012, 391, 2860–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatic, D.; Stanley, H.E.; Podobnik, B. Detrended cross-correlation analysis for non-stationary time series with periodic trends. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2011, 94, 18007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.; Min, S. Effect of Outliers and Non-consecutive Data Points on the Detrended Cross-Correlation Analysis. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2018, 72, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lim, G.; Chang, K.-H.; Jung, J.-W.; Kim, K.; Park, C.H. Multifractal Analysis of Rainfalls in Korean Peninsula. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2008, 52, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.-H.; Lim, G.; Min, S. Dynamics of the Global Stock Market Networks Generated by DCCA Methodology. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-H.; Li, C.-L.; Si, Y.-L. A detrended cross-correlation analysis of meteorological and API data in Nanjing, China. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2015, 419, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.; Min, S. Correlation Structures of PM2.5 Concentration Series in the Korean Peninsula. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Ramirez, J.; Rodriguez, E.; Echeverria, J.C. A DFA approach for assessing asymmetric correlations. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2009, 388, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Cao, J.; Xu, L.; He, L. Detrended cross-correlation analysis approach for assessing asymmetric multifractal detrended cross-correlations and their application to the Chinese financial market. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 393, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M.; Liu, C.; Chelton, D.B.; Casey, K.S.; Schlax, M.G. Daily high-resolution-blended analyses for sea surface temperature. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5473–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, C.; Freeman, E.; Graham, G.; Smith, T.; Zhang, H.-M. Assessment and inter-comparison of NOAA daily opti-mum interpolation sea surface temperature (DOISST) version 2.1. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 7421–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-Y.; Park, K.-A. Change in the recent warming trend of sea surface temperature in the East Sea (Sea of Japan) over decades (1982–2018). Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Jo, H.-J.; Moon, J.-H. Occurrence and Evolution of Mesoscale Thermodynamic Phenomena in the Northern Part of the East Sea (Japan Sea) Derived from Satellite Altimeter Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Choi, J.-G.; Park, J.; Kwon, J.-I.; Kim, M.-H.; Jo, Y.-H. Upwelling processes driven by contributions from wind and current in the Southwest East Sea (Japan Sea). Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1165366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K. Stochastic Climate Models: Part I. Theory. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 1976, 28, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, T.; Fang, G.; Jiang, S.; Wang, G.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of Marine Heatwaves in the Japan/East Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.-H.; Cho, K.-D.; Kim, H.-J. The relationship between ENSO events and sea surface temperature in the East (Japan) Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2001, 49, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, A.; Beardsley, R.C. Atmosphere and marginal-sea interaction leading to an interannual variation in cold-air outbreak activity over the Japan sea. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5707–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Min, H.; Kim, C. Interannual variability and long-term trend of coastal sea surface temperature in Korea. Ocean Polar Res. 2006, 28, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).