The Influences of Environmental Factors on the Microwave Scattering Coefficient from the Sea Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. The Impact of Oceanic Atmospheric Stability on the Scattering Coefficient
2.2. Data Processing Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Data Used in This Work
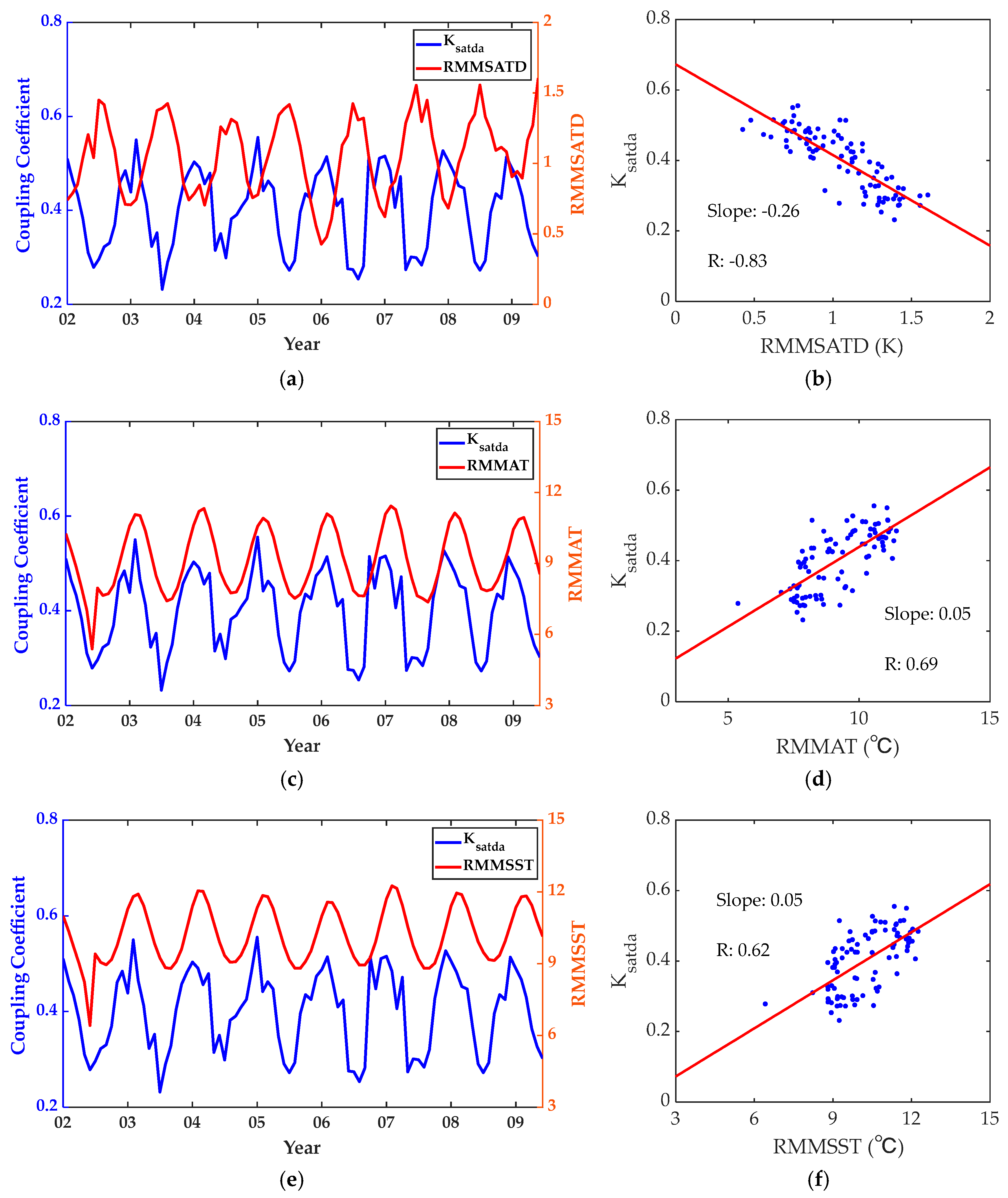
3.2. Definition and Discussion of the Coupling Coefficient
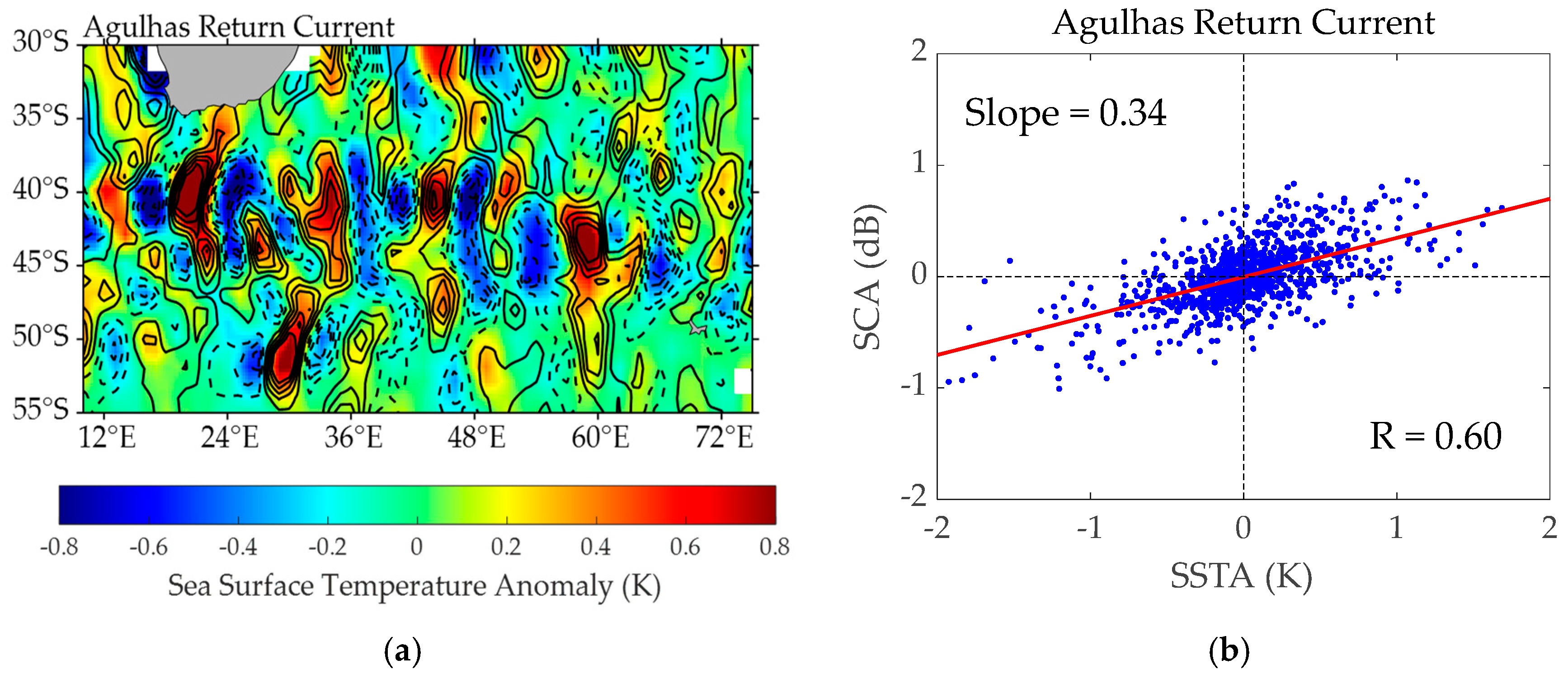
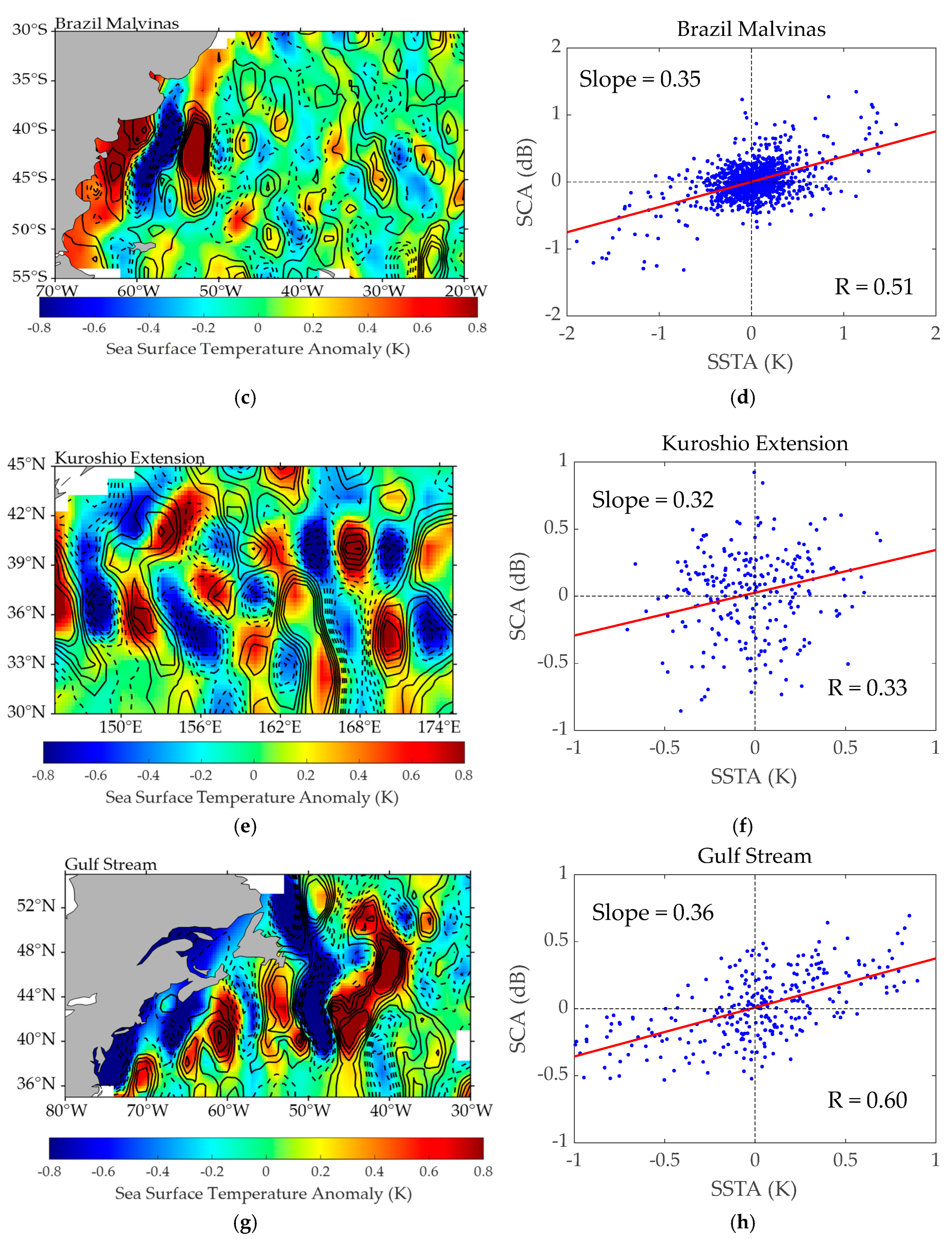
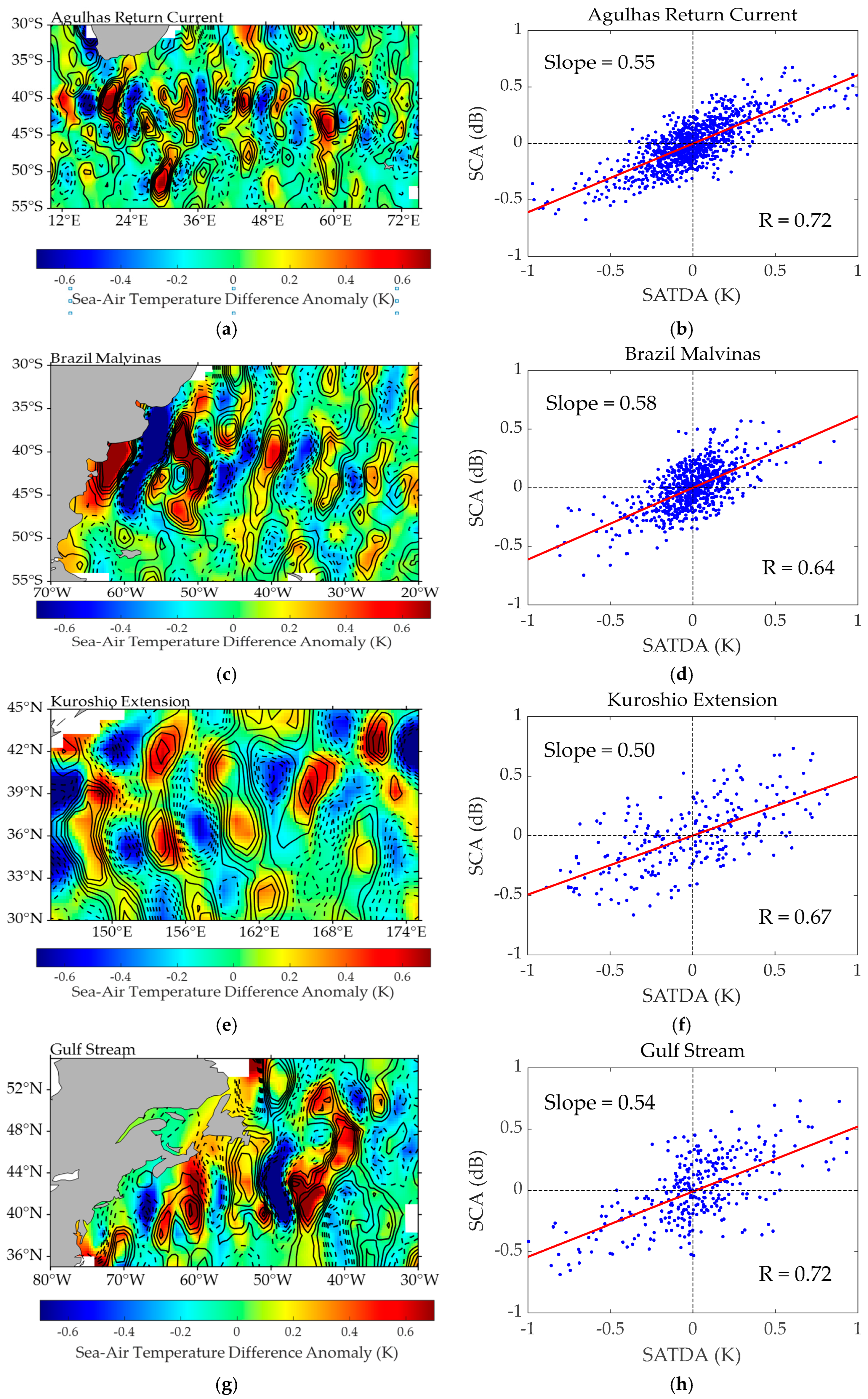
3.2.1. The Response Relationship Between the SSTA and SCA
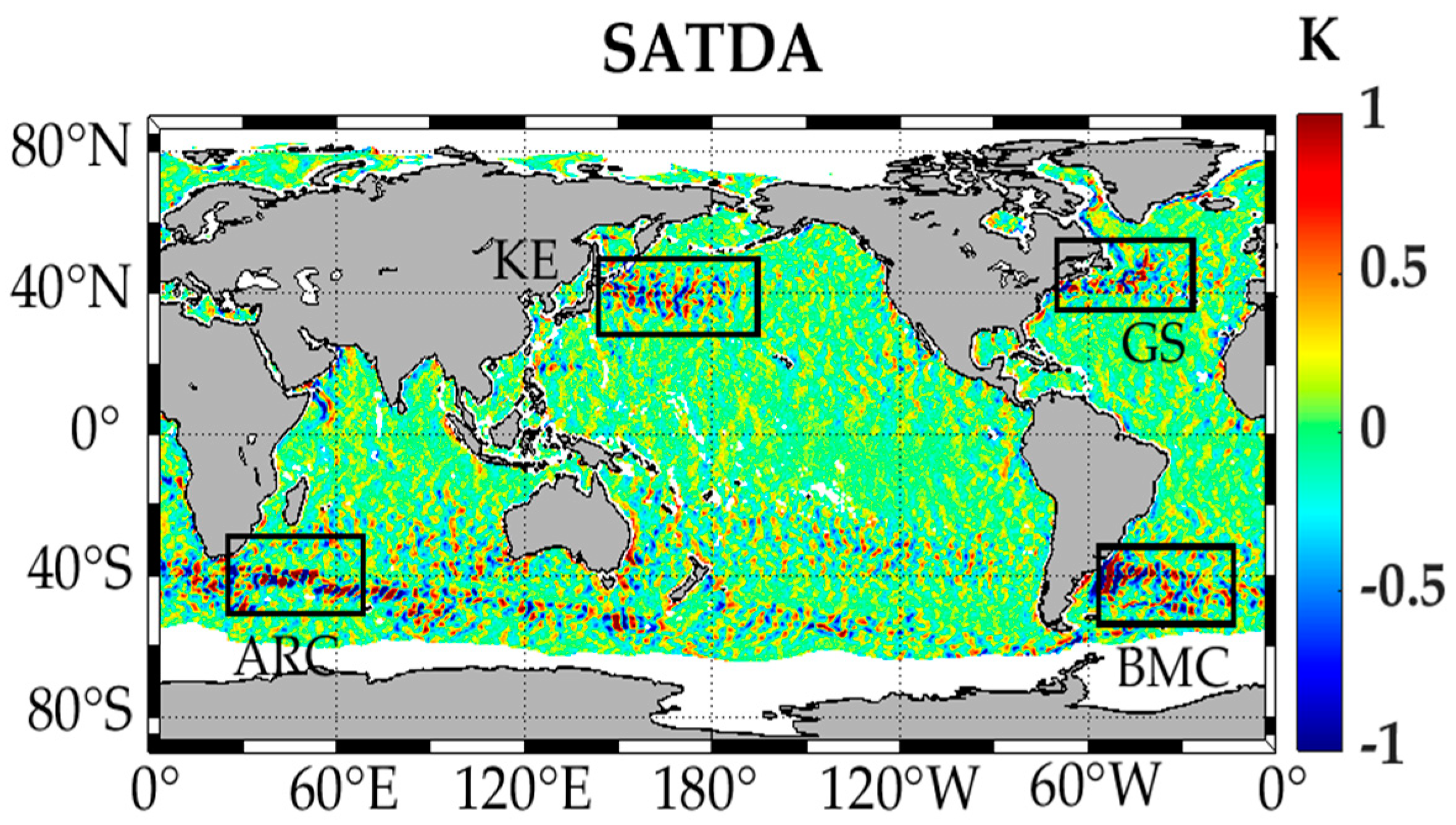
3.2.2. The Response Relationship Between the SATDA and SCA
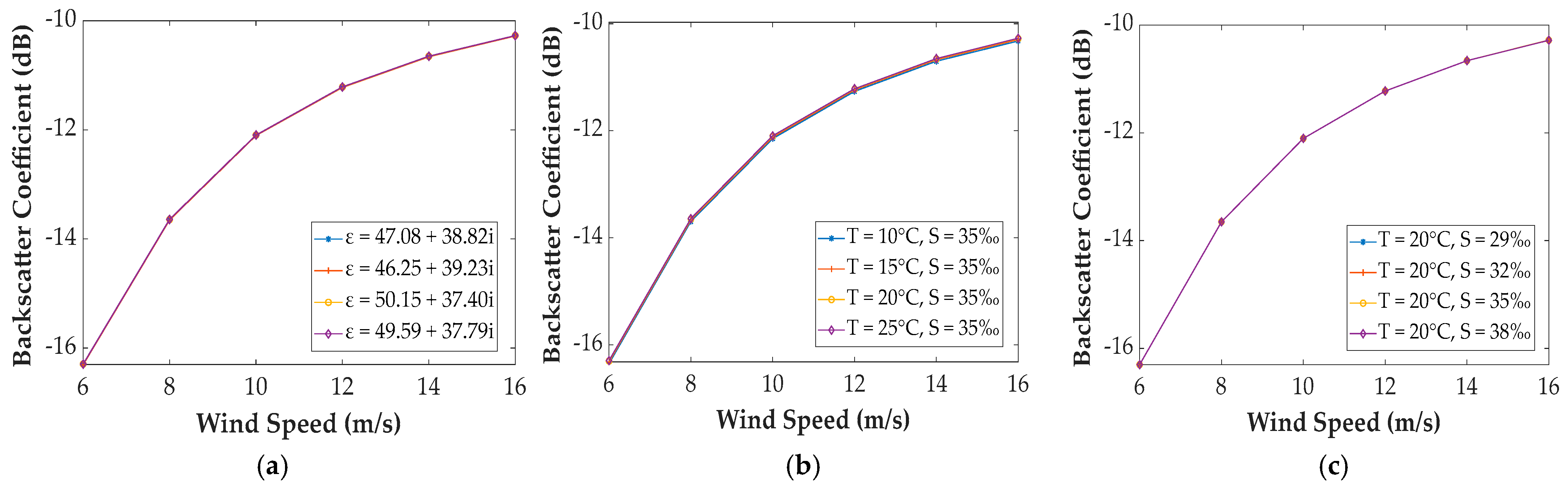
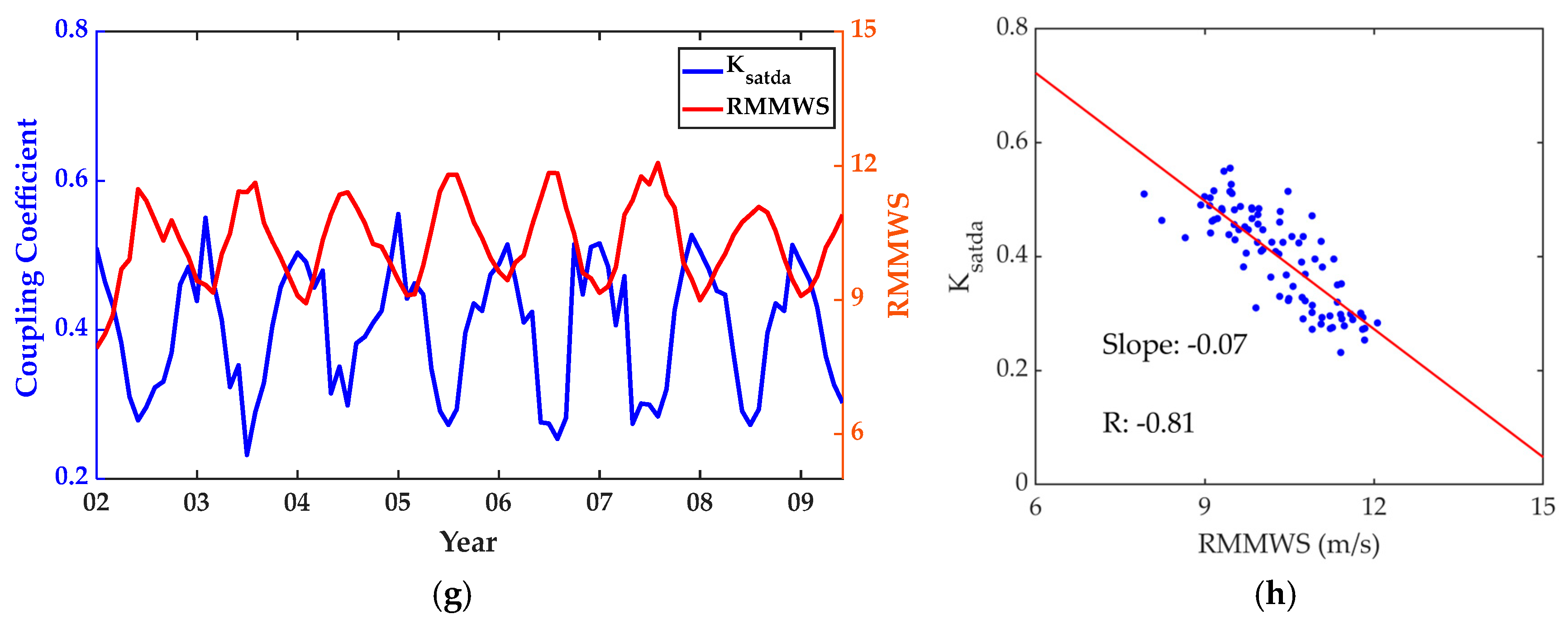
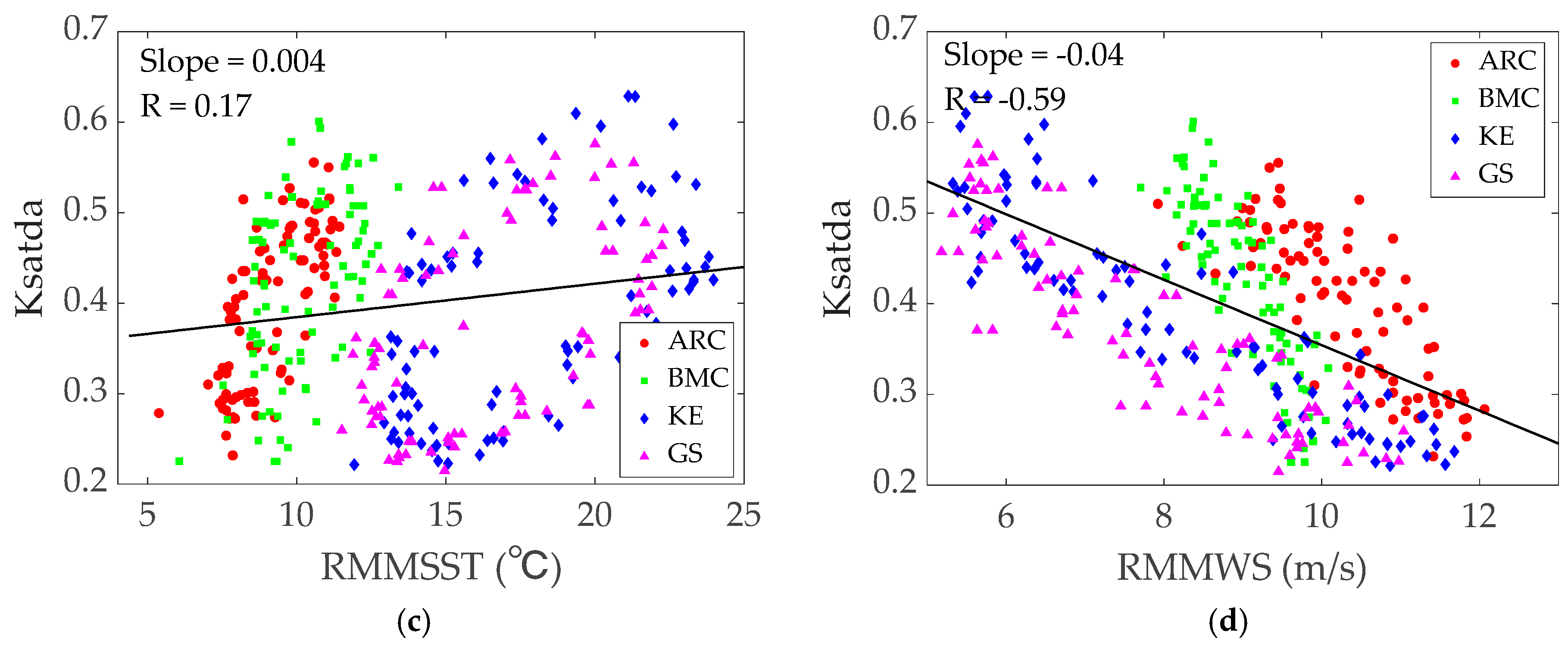
3.3. The Impact of the Marine Environmental Parameters on
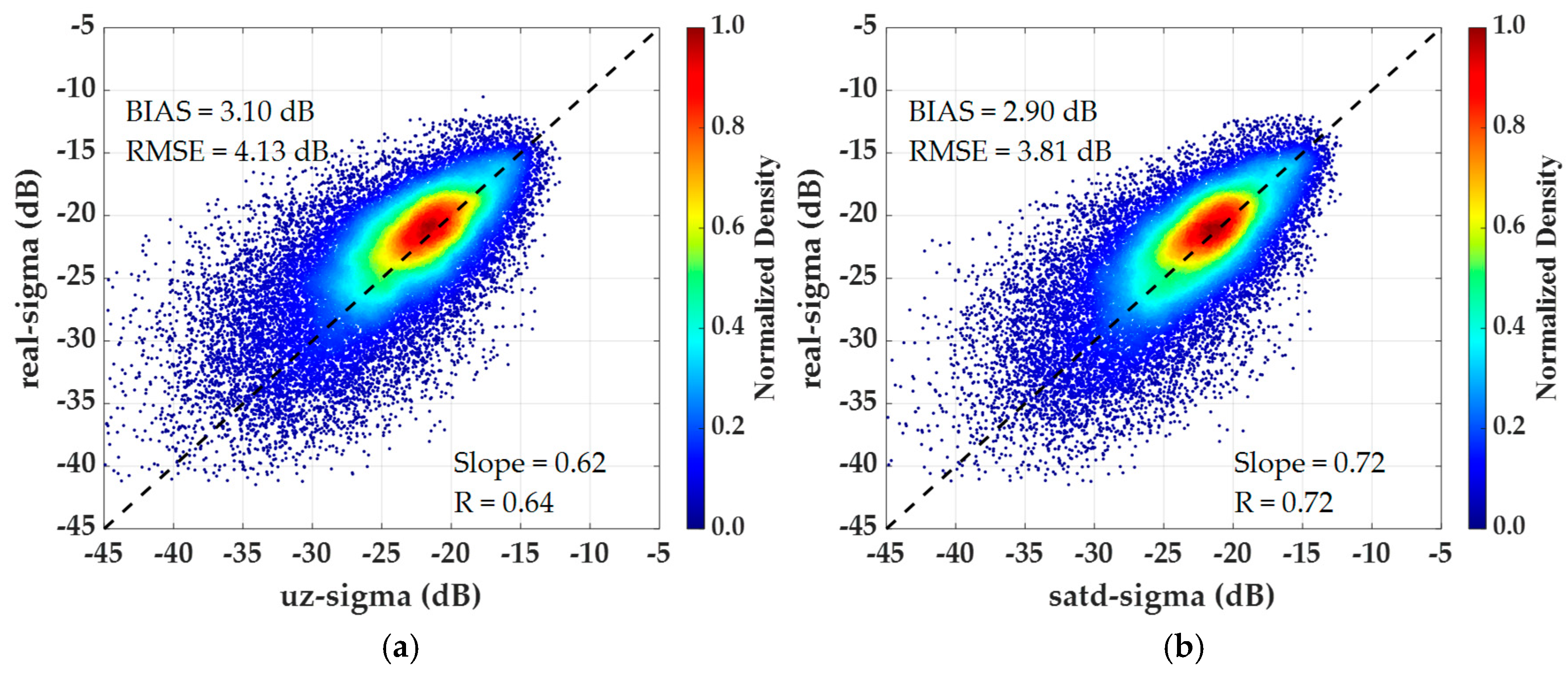
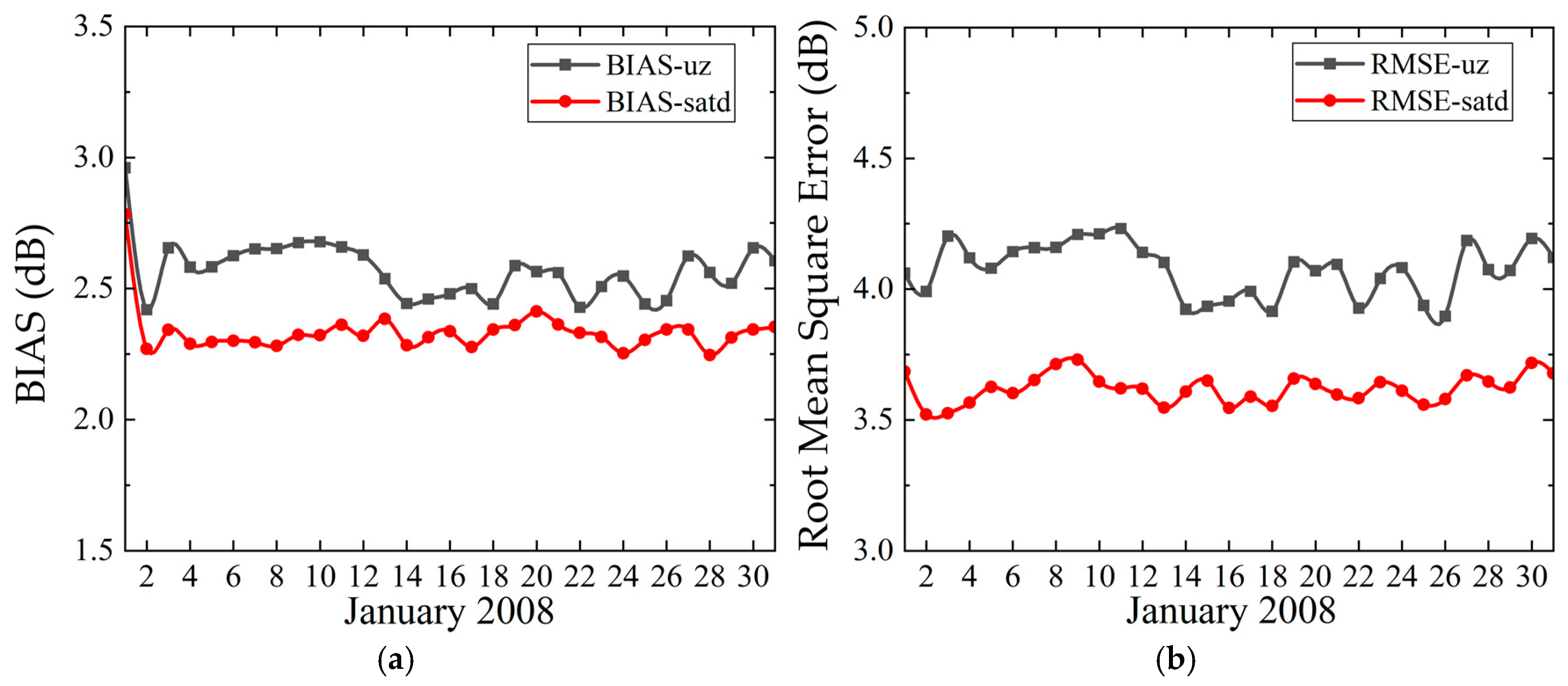
3.4. Improving the Scattering Coefficient Accuracy by Introducing SATD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jafari, Z.; Bobby, P.; Karami, E.; Taylor, R. A Novel Method for the Estimation of Sea Surface Wind Speed from SAR Imagery. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, W.J. A relationship between wind stress and wave slope. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1982, 87, 1961–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Shin, I. Wind speed retrieval based on sea surface roughness measurements from spaceborne microwave radiometers. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.; Mouche, B.; Chapron, B. On the use of Doppler shift for SAR wind retrieval. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop SeaSAR 2010, Frascati, Italy, 25–29 January 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Lin, M.; Zou, J.; Mu, B.; Peng, H. Evaluation of Sea Surface Wind Products from Scatterometer Onboard the Chinese HY-2D Satellite. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Chen, K.S.; Yang, X. Effects of wind wave spectra on radar backscatter from sea surface at different microwave bands: A numerical study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6325–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.K.; Li, Z.; Chen, K.S. Backscattering from a randomly rough dielectric surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsos, E.I. The validity of the Kirchhoff approximation for rough surface scattering using a Gaussian roughness spectrum. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1988, 83, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsos, E.I.; Jackson, D.R. The validity of the perturbation approximation for rough surface scattering using a Gaussian roughness spectrum. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 86, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Crespo, J.; Friberg, A.; Nieto-Vesperinas, M. Scattering from slightly rough random surfaces: A detailed study on the validity of the small perturbation method. J. Ootical Soc. Am. A-Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 1990, 7, 1185–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.; Fung, A.K. A theory of sea scatter at large incident angles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1977, 82, 3439–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, L.; He, Q. Hybrid FE-BI-KA method in analysing scattering from dielectric object above sea surface. Electron. Lett. 2011, 47, 1147–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Mouche, A.; Lu, Y.; Perrie, W.; Zhang, G. A geophysical model function for wind speed retrieval from C-band HH-polarized synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffelen, A.; Verspeek, J.A.; Vogelzang, J.; Verhoef, A. The CMOD7 geophysical model function for ASCAT and ERS wind retrievals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Gairola, R.M. Fostering the need of L-band radiometer for extreme oceanic wind research. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardulli, L.; Wentz, F. Reprocessed QuikSCAT (V04) wind vectors with Ku-2011 geophysical model function. In Remote Sensing Systems Technical Report 043011; Remote Sensing Systems: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Panfilova, M.; Karaev, V. Gale Wind Speed Retrieval Algorithm Using Ku-Band Radar Data Onboard GPM Satellite. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.M.; Mitchell, T.P.; Deser, C. The influence of sea-surface temperature on surface wind in the eastern equatorial Pacific: Seasonal and interannual variability. J. Clim. 1989, 2, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.P.; McPhaden, M.J.; Wallace, J.M. The influence of sea-surface temperature on surface wind in the eastern equatorial Pacific: Weekly to monthly variability. J. Clim. 1989, 2, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.B.; Esbensen, S.K.; Schlax, M.G.; Thum, N.; Freilich, M.H.; Wentz, F.J.; Gentemann, C.L.; McPhaden, M.J.; Schopf, P.S. Observations of coupling between surface wind stress and sea surface temperature in the eastern tropical Pacific. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 1479–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.W.; Chelton, D.B.; Esbensen, S.K.; Wentz, F.J. High-resolution satellite measurements of the atmospheric boundary layer response to SST variations along the Agulhas Return Current. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 2706–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, A.S.; Jaglom, A.M.; Lumley, J.L. Statistical Fluid Mechanics: Mechanics of Turbulence; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. The Effects of MSATD and MWS on the Coupling Coefficient Between SATDA And WSA. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 8117–8120. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, R.-H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H. Mesoscale Surface Wind-SST Coupling in a High-Resolution CESM Over the KE and ARC Regions. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2021, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, C. The influences of environmental factors on the air-sea coupling coefficient. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, L. Effects of atmospheric stability and wind fetch on microwave sea echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing Active and Passive-Volume II: Radar Remote Sensing and Surface Scattering and Enission Theory; Addison-Wesley: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 922–982. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, W.; Balana, A.; Delbos, G.; Lamkaouchi, K.; Eymard, L.; Guillou, C.; Prigent, C. New permittivity measurements of seawater. Radio Sci. 1998, 33, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Weng, F.; English, S.J. An improved fast microwave water emissivity model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 49, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfouhaily, T.; Chapron, B.; Katsaros, K.; Vandermark, D. A Unified Directional Spectrum for Long and Short Wind-Driven Waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 15781–15796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A. Observations of swell influence on ocean surface roughness. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A. A note on the ocean surface roughness spectrum. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, W.; Fett, R.; Kerling, J.; La Violette, P. Air-Sea Interaction Effects in the Lower Troposphere Across the North Wall of the Gulf Stream. Mon. Weather Rev. 1981, 109, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xue, H.; Bane, J.M. A 3D Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean Model Study of Air-Sea Interactions during a Passing Winter Storm over the Gulf Stream. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 128, 973–996. [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith, P.S.; Larouche, P.; Chasse, J.; Petrie, B. Sea-surface temperature in relation to air temperature in the Gulf of St. Lawrence: Interdecadal variability and long term trends. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2012, 77, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.T.; Xie, X. Ocean-atmosphere momentum coupling in the Kuroshio Extension observed from space. J. Oceanogr. 2005, 64, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseki, S.; Watanabe, M. Atmospheric Boundary Layer Response to Mesoscale SST Anomalies in the Kuroshio Extension. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2492–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xu, H. Atmospheric Responses to Kuroshio SST Front in the East China Sea under Different Prevailing Winds in Winter and Spring. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 3191–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokinaga, H.; Tanimoto, Y.; Xie, S.P. SST-Induced Surface Wind Variations over the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence: Satellite and In Situ Observations. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3470–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.; Pezzi, L.; Swart, S.; Oliveira, F.; Santini, M. Air-sea interactions over eddies in the Brazil-Malvinas confluence. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, R.A.P.; de Souza, R.B.; Reis, R.A.d.N.; de Mendonca, L.F.F.; da Silva Lindermann, D. Satellite and in situ measurements of water vapour in the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence region. Int. J. Climatol. 2024, 44, 4286–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, M.; Leethorp, A.M.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E. The Atmospheric Boundary Layer above the Agulhas Current during a long current Winds. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 30, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leon, S.; Soares, C.G. Numerical study of the effect of current on waves in the Agulhas Current Retroflection. Ocean Eng. 2022, 264, 112333–112343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arne, B.; Ruhs, S.; Ivanciu, I.; Žschwarzkopf, F.U.; Veitch, J.; Reason, C.; Zorita, E.; Tim, N.; Hunicke, B.; Vafeidis, A.T.; et al. The Agulhas Current System as an Important Driver for Oceanic and Terrestrial Climate. In Sustainability of Southern African Ecosystems Under Global Change: Science for Management and Policy Interventions; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 191–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, R.N.; Leidner, S.M. An introduction to the near–real–time QuikSCAT data. Weather Forecast. 2005, 20, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, T.; Callahan, P.S. QuikSCAT Science Data Product User’s Manual: Overview and Geophysical Data Products, D-18053-Rev A, Version 3; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nakata, K.; Ohshima, K.I.; Nihashi, S. Estimation of thin-ice thickness and discrimination of ice type from AMSR-E passive microwave data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, F.; Sun, D. The Influences of Environmental Factors on the Microwave Scattering Coefficient from the Sea Surface. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081405
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Su F, Sun D. The Influences of Environmental Factors on the Microwave Scattering Coefficient from the Sea Surface. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(8):1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081405
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yitong, Yanmin Zhang, Yunhua Wang, Fanwei Su, and Daozhong Sun. 2025. "The Influences of Environmental Factors on the Microwave Scattering Coefficient from the Sea Surface" Remote Sensing 17, no. 8: 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081405
APA StyleJiang, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Su, F., & Sun, D. (2025). The Influences of Environmental Factors on the Microwave Scattering Coefficient from the Sea Surface. Remote Sensing, 17(8), 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081405





