Interruptins Extracted from Cyclosorus terminans Protect Gut Pathologies Induced by High-Fat Diet in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
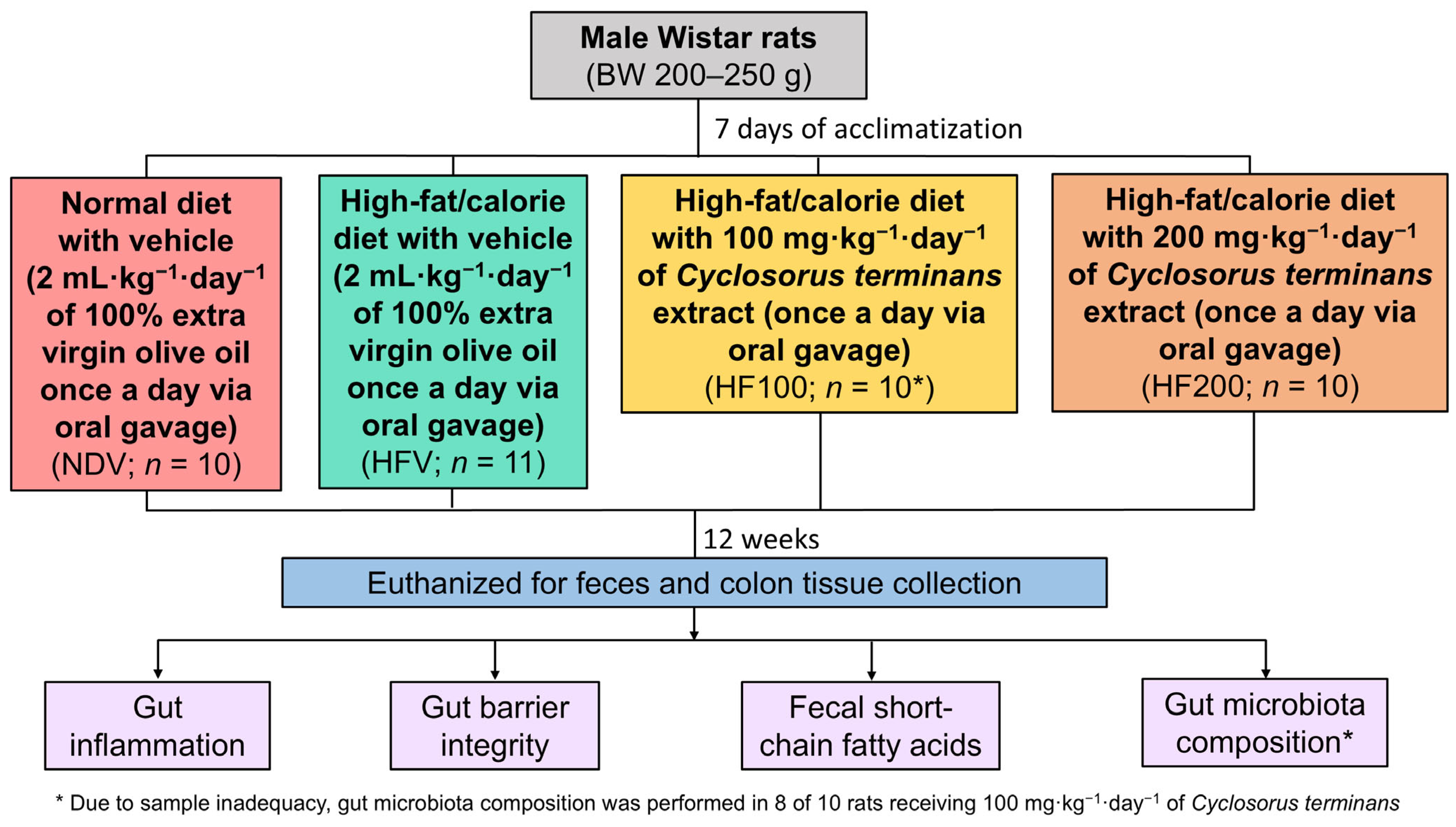
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Plant Extraction
2.3. Sample Size Calculation
2.4. The Expression of mRNA Analyses to Evaluate Gut Inflammation
2.5. Protein Expression Analyses to Evaluate Gut Barrier Integrity
2.6. Quantification of Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids
2.7. Identification of Gut Microbiota Composition
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
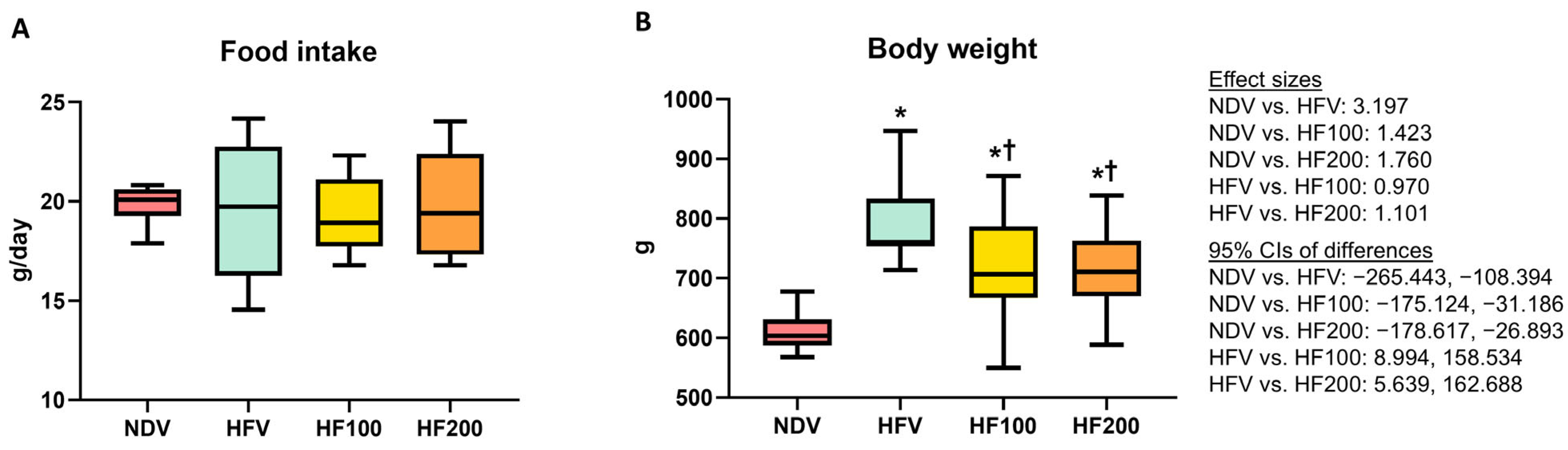
3.1. C. terminans Extract Attenuated an Increase in Body Weight in Rats Exposed to High-Fat/Calorie Diet
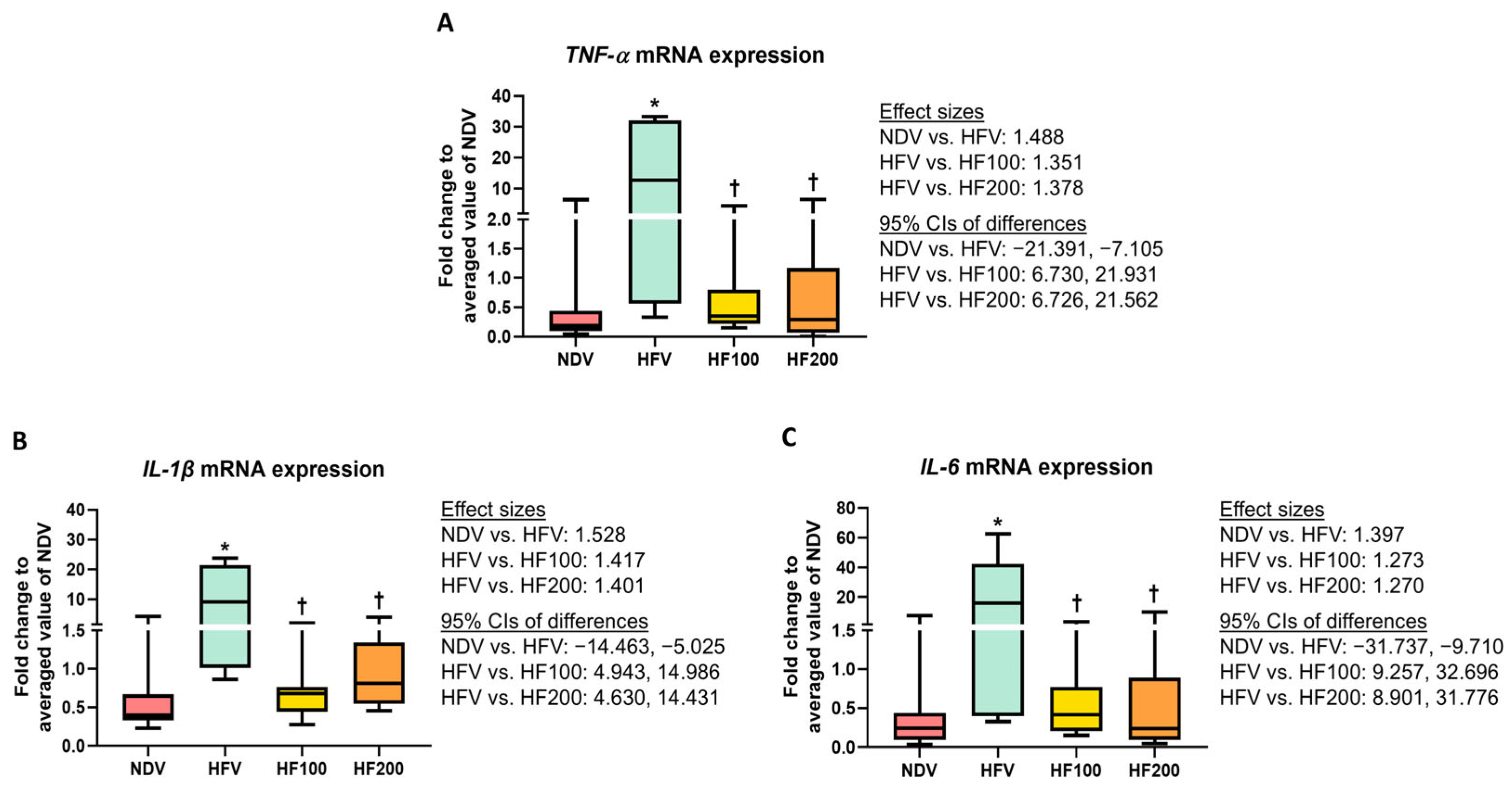
3.2. C. terminans Extract Exerted a Prophylactic Effect Against Gut Inflammation in Rats Exposed to High-Fat/Calorie Diet
3.3. C. terminans Extract Exerted a Prophylactic Effect Against Gut Barrier Disruption in Rats Exposed to High-Fat/Calorie Diet
3.4. C. terminans Extract Exerted a Prophylactic Effect Against the Alterations of Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acid Levels in Rats Exposed to High-Fat/Calorie Diet
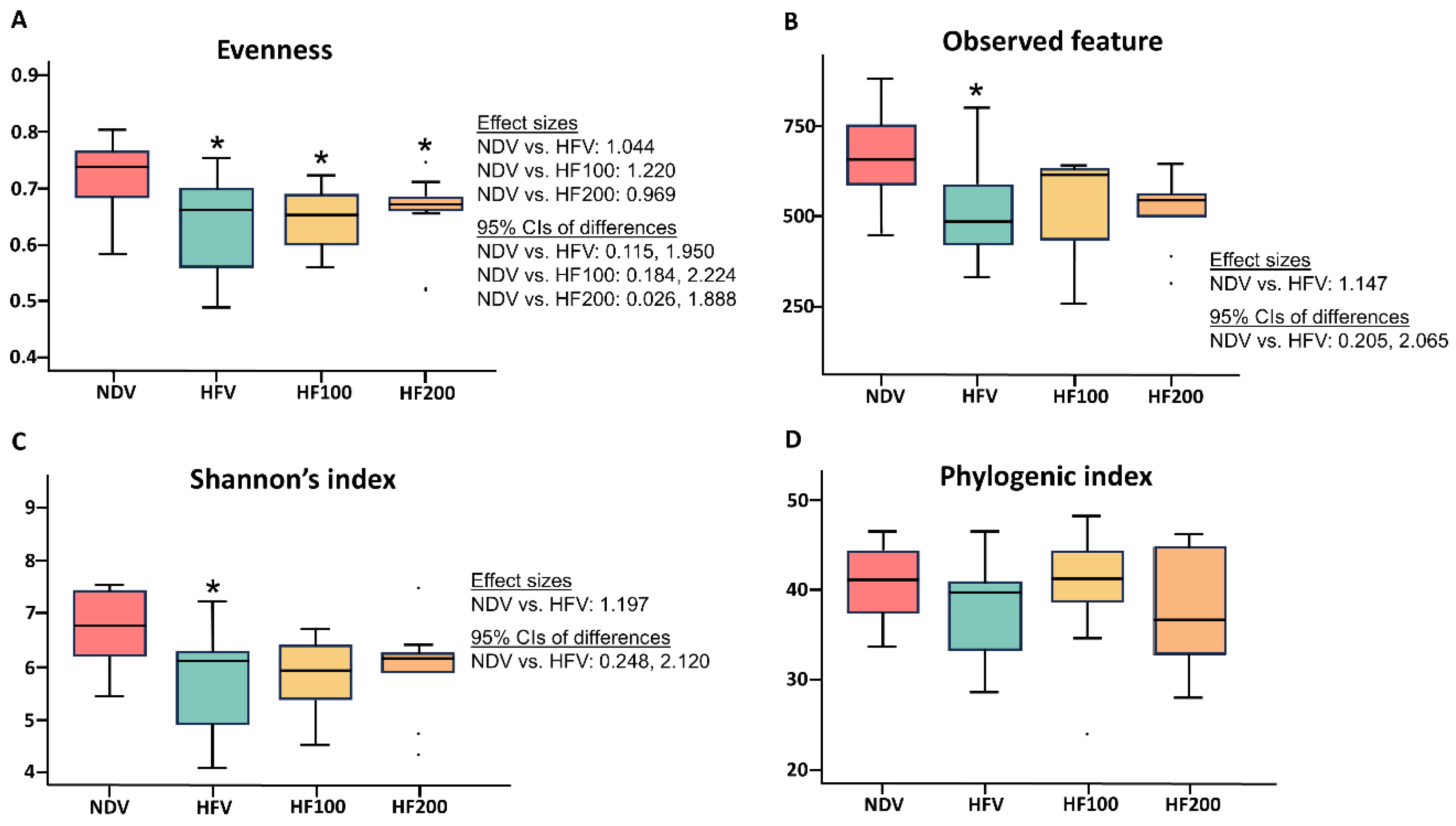
3.5. C. terminans Extract Exerted a Prophylactic Effect Against the Alteration of Alpha Diversity in Rats Exposed to High-Fat/Calorie Diet
3.6. C. terminans Extract Did Not Improve Beta Diversity in Rats Fed High-Fat/Calorie Diet
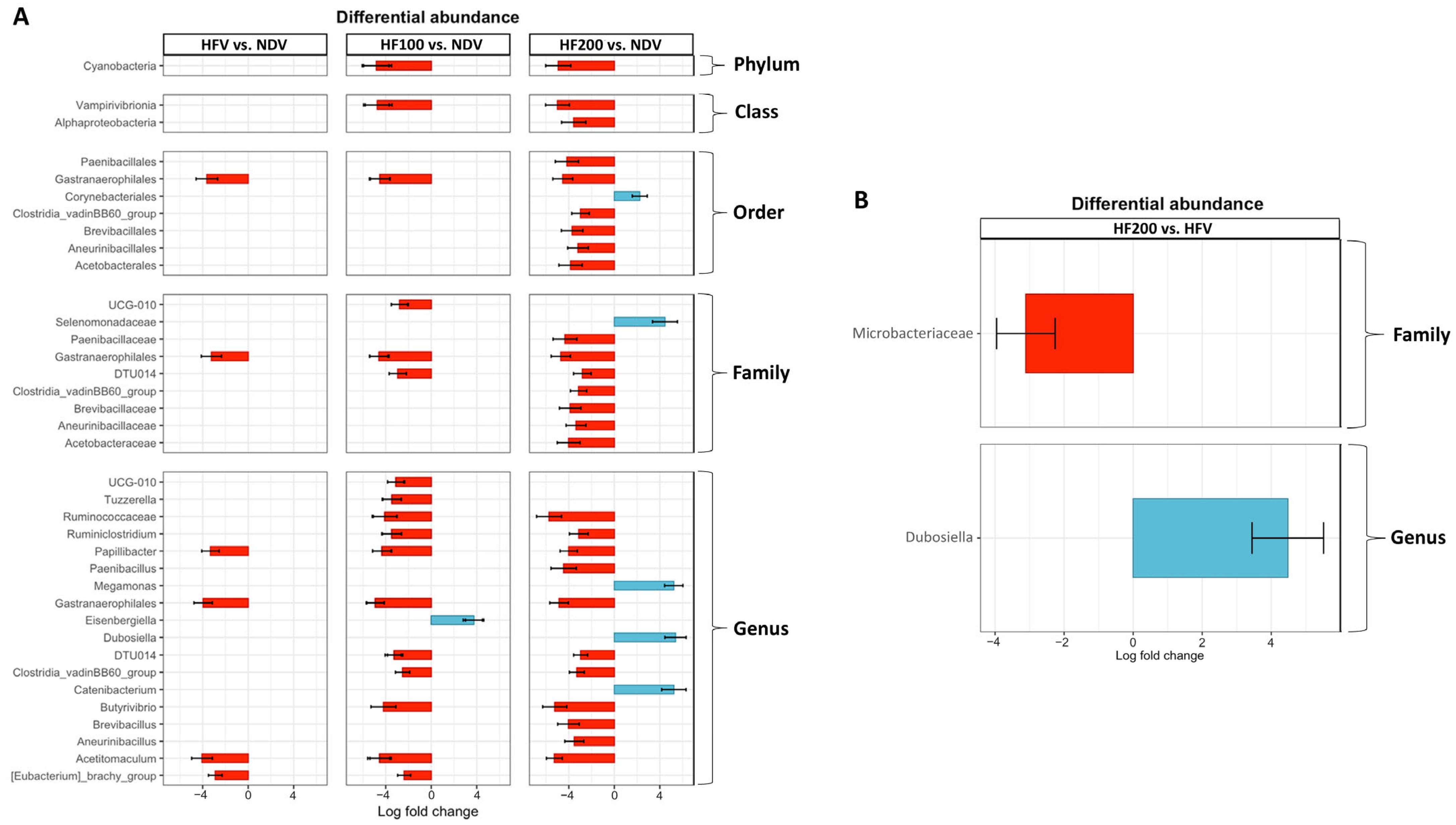
3.7. Differential Abundance of Gut Microbiota Composition
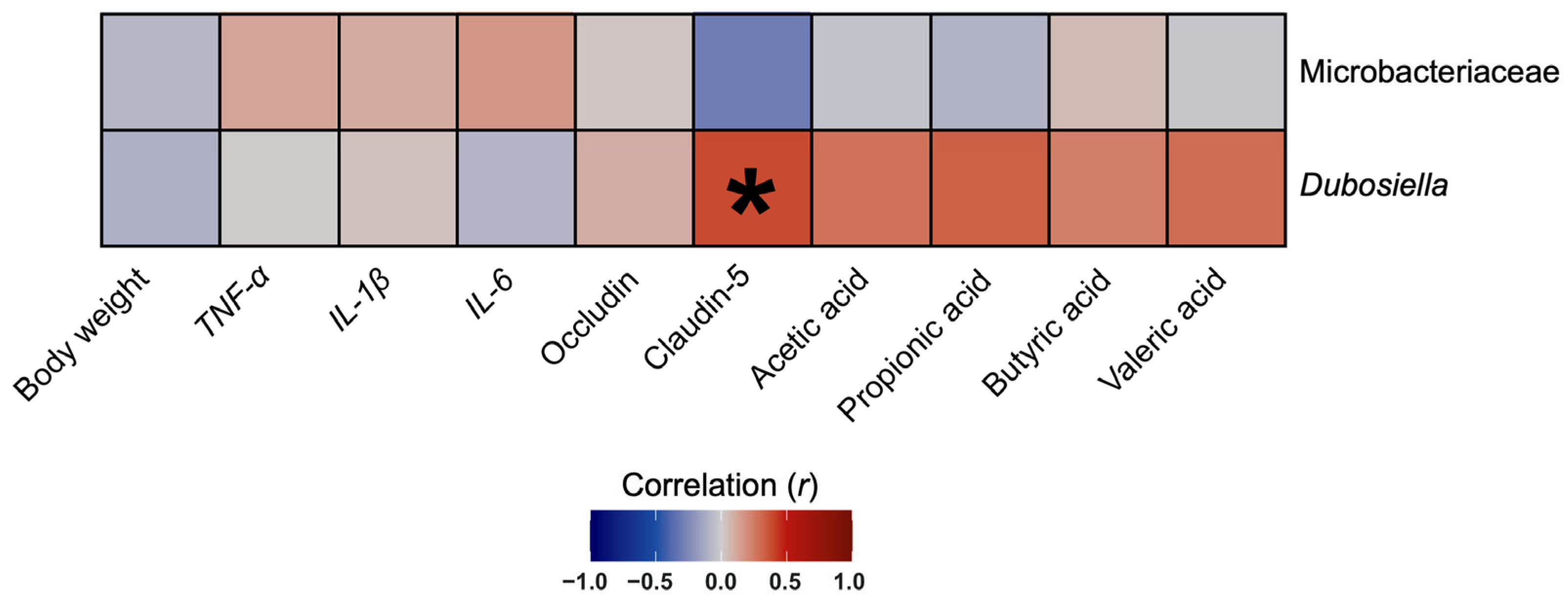
3.8. The Abundance of Genus Dubosiella Was Positively Correlated with Claudin-5 Protein Expression in Colon Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C. terminans | Cyclosorus terminans |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| HFV | high-fat/calorie diet treated with vehicle |
| HF100 | high-fat/calorie diet treated with 100 mg·kg−1·day−1 of C. terminans extract |
| HF200 | high-fat/calorie diet treated with 200 mg·kg−1·day−1 of C. terminans extract |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1beta |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| mg·kg−1·day−1 | milligram per kilogram per day |
| mRNA | messenger ribonucleic acid |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| NDV | normal diet treated with vehicle |
| SRA | Sequence Read Archive |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
References
- Davis, C.D. The Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Obesity. Nutr. Today 2016, 51, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, J.; Galmiche, M.; Déchelotte, P. Dysbiotic Gut Bacteria in Obesity: An Overview of the Metabolic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives of Next-Generation Probiotics. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumpertz, R.; Le, D.S.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Trinidad, C.; Bogardus, C.; Gordon, J.I.; Krakoff, J. Energy-balance studies reveal associations between gut microbes, caloric load, and nutrient absorption in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalliomäki, M.; Collado, M.C.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Early differences in fecal microbiota composition in children may predict overweight. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Bäckhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the complications. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2017, 13, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Khanna, S.; Khanna, P.; Kahar, P.; Patel, B.M. Obesity: A Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation and Its Markers. Cureus 2022, 14, e22711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotova, N.V.; Chereshnev, V.A.; Gusev, E.Y. Systemic Inflammation: Methodological Approaches to Identification of the Common Pathological Process. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.G.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Murphy, A.J.; Febbraio, M.A. Diet-induced gut dysbiosis and inflammation: Key drivers of obesity-driven NASH. iScience 2023, 26, 105905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, S.K.; Ghimire, S.; Lehman, P.; Mangalam, A.K. Obesity induced gut dysbiosis contributes to disease severity in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 966417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.I.; Gill, A.L.; Mooney, R.A.; Gill, S.R. Modulation of Gut Microbiota Metabolism in Obesity-Related Type 2 Diabetes Reduces Osteomyelitis Severity. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0017022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.N.; Liu, X.T.; Liang, Z.H.; Wang, J.H. Gut microbiota in obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Chu, H. The critical role of gut microbiota in obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1025706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amabebe, E.; Robert, F.O.; Agbalalah, T.; Orubu, E.S.F. Microbial dysbiosis-induced obesity: Role of gut microbiota in homoeostasis of energy metabolism. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 123, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.P.; Wang, B.; Jain, S.; Ding, J.; Rejeski, J.; Furdui, C.M.; Kitzman, D.W.; Taraphder, S.; Brechot, C.; Kumar, A.; et al. A mechanism by which gut microbiota elevates permeability and inflammation in obese/diabetic mice and human gut. Gut 2023, 72, 1848–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, S.A.; Fu, J.; Chang, P.V. Microbial tryptophan metabolites regulate gut barrier function via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 19376–19387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Tian, H.; Xue, Y.; Ren, P.; Kuang, X.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates obesity in mice through modulation of gut microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal permeability. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 106020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandsma, E.; Kloosterhuis, N.J.; Koster, M.; Dekker, D.C.; Gijbels, M.J.J.; van der Velden, S.; Ríos-Morales, M.; van Faassen, M.J.R.; Loreti, M.G.; de Bruin, A.; et al. A Proinflammatory Gut Microbiota Increases Systemic Inflammation and Accelerates Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefley, S.; Howard, N.; Crasto, C.; Vasylyeva, T. Microbiome Dysbiosis in Obese Adolescents: A Potential Contributor to Inflammation. FASEB J. 2021, 35, 02509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemniak-Wojtowicz, D.; Kucharska, A.M.; Pyrżak, B. Obesity and chronic inflammation crosslinking. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 45, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.N.; Wu, T.Y.; Chau, C.F. Natural Dietary and Herbal Products in Anti-Obesity Treatment. Molecules 2016, 21, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songtrai, S.; Pratchayasakul, W.; Arunsak, B.; Chunchai, T.; Kongkaew, A.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Kaewsuwan, S. Cyclosorus terminans Extract Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Induced Obese Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, D.; Rali, T. A Survey of Medicinal Plants of the Southern Highlands, Papua New Guinea. Int. J. Crude Drug Res. 1989, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nick, A.; Rali, T.; Sticher, O. Biological screening of traditional medicinal plants from Papua New Guinea. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 49, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, C.; Fu, W.; Ruan, J. Extract of Cyclosorus acuminatus attenuates diabetic nephropathy in mice via modifying peroxisome proliferators activated receptor signalling pathway. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewsuwan, S.; Plubrukarn, A.; Utsintong, M.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Cho, J.G.; Park, S.G.; Sung, J.H. Interruptin B induces brown adipocyte differentiation and glucose consumption in adipose-derived stem cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thonusin, C.; Apaijai, N.; Jaiwongkam, T.; Kerdphoo, S.; Arunsak, B.; Amput, P.; Palee, S.; Pratchayasakul, W.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. The comparative effects of high dose atorvastatin and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor on the mitochondria of oxidative muscle fibers in obese-insulin resistant female rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 382, 114741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwong, S.; Puttarak, P.; Kaewsuwan, S. Anti propionibacterium acnes activity, HPLC method validation for simultaneous analysis and extraction of coumarins from the fern cyclosorus terminans. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2018, 37, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar]
- Brochot, A.; Azalbert, V.; Landrier, J.F.; Tourniaire, F.; Serino, M. A Two-Week Treatment with Plant Extracts Changes Gut Microbiota, Caecum Metabolome, and Markers of Lipid Metabolism in ob/ob Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiennimitr, P.; Yasom, S.; Tunapong, W.; Chunchai, T.; Wanchai, K.; Pongchaidecha, A.; Lungkaphin, A.; Sirilun, S.; Chaiyasut, C.; Chattipakorn, N.; et al. Lactobacillus paracasei HII01, xylooligosaccharides, and synbiotics reduce gut disturbance in obese rats. Nutrition 2018, 54, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suparan, K.; Sriwichaiin, S.; Thonusin, C.; Sripetchwandee, J.; Khuanjing, T.; Maneechote, C.; Nawara, W.; Arunsak, B.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Donepezil ameliorates gut barrier disruption in doxorubicin-treated rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 189, 114741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwichaiin, S.; Thiennimitr, P.; Thonusin, C.; Sarichai, P.; Buddhasiri, S.; Kumfu, S.; Nawara, W.; Kittichotirat, W.; Fucharoen, S.; Chattipakorn, N.; et al. Deferiprone has less benefits on gut microbiota and metabolites in high iron-diet induced iron overload thalassemic mice than in iron overload wild-type mice: A preclinical study. Life Sci. 2022, 307, 120871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; De Cáceres, M. Beta diversity as the variance of community data: Dissimilarity coefficients and partitioning. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassol, I.; Ibañez, M.; Bustamante, J.P. Key features and guidelines for the application of microbial alpha diversity metrics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá, M.; Calderon-Dominguez, M.; Serra, D.; Herrero, L.; Viana, M. Mechanisms of Impaired Brown Adipose Tissue Recruitment in Obesity. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabner, G.F.; Xie, H.; Schweiger, M.; Zechner, R. Lipolysis: Cellular mechanisms for lipid mobilization from fat stores. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1445–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.X.; Goh, W.R.; Wu, R.N.; Yue, X.Q.; Luo, X.; Khine, W.W.T.; Wu, J.R.; Lee, Y.K. Revisit gut microbiota and its impact on human health and disease. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, J.C.; Ursell, L.K.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: An integrative view. Cell 2012, 148, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.H.; Kitai, T.; Hazen, S.L. Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Han, J. The impact of the intestinal microbiome on bone health. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2018, 7, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbierski-Kind, J.; Grenkowitz, S.; Schlickeiser, S.; Sandforth, A.; Friedrich, M.; Kunkel, D.; Glauben, R.; Brachs, S.; Mai, K.; Thürmer, A.; et al. Effects of caloric restriction on the gut microbiome are linked with immune senescence. Microbiome 2022, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.K.; Lamb, C.; Hassan, W.M.; Foxworth, J. Brevibacillus Laterosporus Bacteremia in an Adult. Cureus 2020, 12, e10481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaniawski, M.A.; Spivak, A.M. Recurrent Paenibacillus infection. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 2019, omz034. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Wu, T.L.; Dai, Y.Y.; Sheng, Y.Y.; Ren, Y.L.; Xue, Y.Z. Gut microbial evidence chain in high-salt diet exacerbates intestinal aging process. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1046833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.N.; Bazzano, L.A.; Ajami, N.J.; He, H.; Zhao, J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Correa, A.; He, J. Gut Microbiome Associates With Lifetime Cardiovascular Disease Risk Profile Among Bogalusa Heart Study Participants. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tu, S.; Ji, X.; Wu, J.; Meng, J.; Gao, J.; Shao, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, G.; Qiu, J.; et al. Dubosiella newyorkensis modulates immune tolerance in colitis via the L-lysine-activated AhR-IDO1-Kyn pathway. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thonusin, C.; Suparan, K.; Kunasol, C.; Lungruammit, N.; Nawara, W.; Arunsak, B.; Kerdphoo, S.; Kongkaew, A.; Songtrai, S.; Pintana, H.; et al. Interruptins Extracted from Cyclosorus terminans Protect Gut Pathologies Induced by High-Fat Diet in Rats. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081387
Thonusin C, Suparan K, Kunasol C, Lungruammit N, Nawara W, Arunsak B, Kerdphoo S, Kongkaew A, Songtrai S, Pintana H, et al. Interruptins Extracted from Cyclosorus terminans Protect Gut Pathologies Induced by High-Fat Diet in Rats. Nutrients. 2025; 17(8):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081387
Chicago/Turabian StyleThonusin, Chanisa, Kanokphong Suparan, Chanon Kunasol, Nopphakhun Lungruammit, Wichwara Nawara, Busarin Arunsak, Sasiwan Kerdphoo, Aphisek Kongkaew, Sujinda Songtrai, Hiranya Pintana, and et al. 2025. "Interruptins Extracted from Cyclosorus terminans Protect Gut Pathologies Induced by High-Fat Diet in Rats" Nutrients 17, no. 8: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081387
APA StyleThonusin, C., Suparan, K., Kunasol, C., Lungruammit, N., Nawara, W., Arunsak, B., Kerdphoo, S., Kongkaew, A., Songtrai, S., Pintana, H., Maneechote, C., Pratchayasakul, W., Kaewsuwan, S., Chattipakorn, N., & Chattipakorn, S. C. (2025). Interruptins Extracted from Cyclosorus terminans Protect Gut Pathologies Induced by High-Fat Diet in Rats. Nutrients, 17(8), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081387





