Overweight, Obesity, and Depression in Multimorbid Older Adults: Prevalence, Diagnostic Agreement, and Associated Factors in Primary Care—Results from a Multicenter Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What are the age- and gender-specific prevalence rates of depression, and how do they differ between individuals with under- and normal weight, overweight, and with varying degrees of obesity?
- What is the rate of agreement comparing depression diagnoses made by GPs and detected by a validated instrument (GDS) with regards to different BMI classes?
- Which factors are associated with a match (True Positive or True Negative), and which factors are associated with a mismatch (False Positive or False Negative) between the GP’s clinical judgment and the GDS-based screening outcome? What role does the BMI class play in this context?
2. Materials and Methods
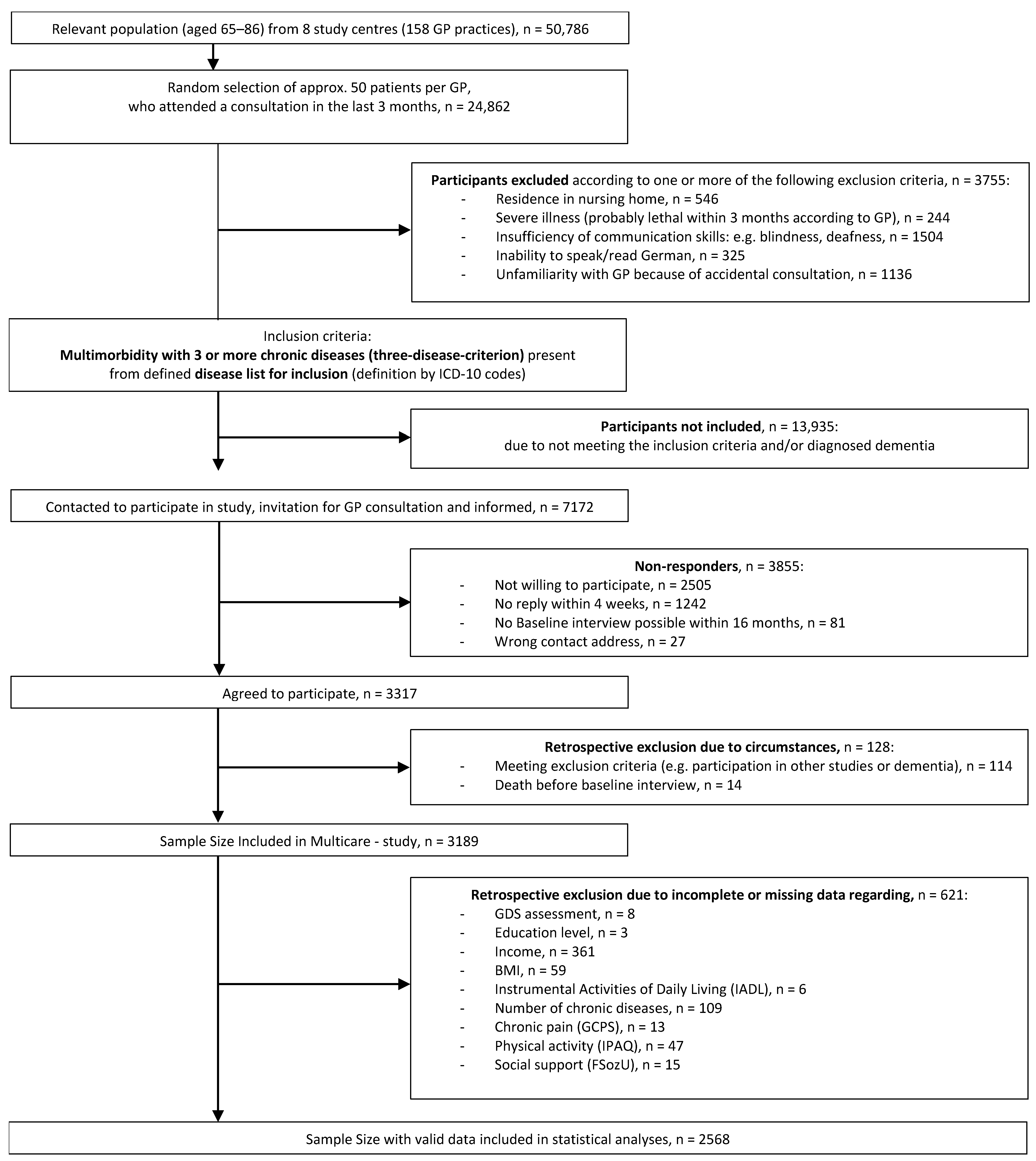
2.1. Sample
2.2. Data Collection and Assessment Procedure
2.3. Sociodemographic Data
2.4. Resources and Risk Factors
2.5. Dependent Variables
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Prevalence of Depressive Symptoms According to Body Mass Index, Gender, and Age
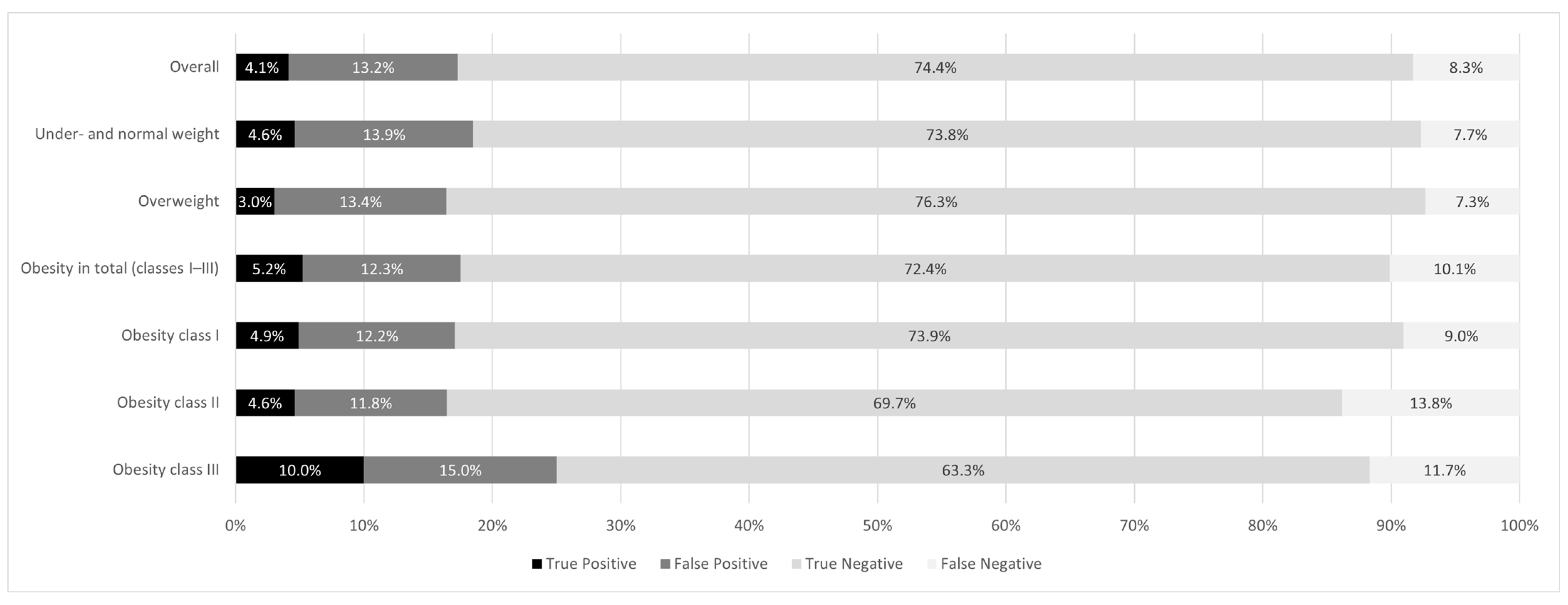
3.3. Diagnostic Agreement of Depression Analyzed by BMI Classes
3.4. Patient-Specific Factors and Their Influence on the Outcome of GP Diagnosis Versus GDS-Based Depression Assessment
3.5. Concordance in Indicating and Not Indicating Depression
3.6. Discordance in Indicating and Not Indicating Depression
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CASMIN | Comparative Analysis of Social Mobility in Industrial Nations |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| GCPS | Graded Chronic Pain Scale |
| GDS | Geriatric Depression Scale |
| GP | General practitioner |
| IADL | Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (scale) |
| ICD | International Classification of Diseases |
| IPAQ | International Physical Activities Questionnaire |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SCID | Structured Clinical Interview for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- World Health Organization. MhGAP: Mental Health Gap Action Programme: Scaling up Care for Mental, Neurological, and Substance Use Disorders; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; ISBN 978-92-4-159620-6.
- World Health Organization (Ed.) Mental Health Atlas 2017; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-92-4-151401-9.
- World Health Organization (Ed.) Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; ISBN 92-4-159222-2.
- Bentham, J.; Di Cesare, M.; Bilano, V. Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128·9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 21 February 2025).
- Batsis, J.A.; Zagaria, A.B. Addressing Obesity in Aging Patients. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Kruszon-Moran, D.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Trends in Obesity Among Adults in the United States, 2005 to 2014. JAMA 2016, 315, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Max Rubner-Institut. Ergebnisbericht, Teil 1 Nationale Verzehrsstudie II; 2008. Available online: https://www.mri.bund.de/fileadmin/MRI/Institute/EV/NVS_II_Abschlussbericht_Teil_1_mit_Ergaenzungsbericht.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Haslam, D.W.; James, W.P.T. Obesity. Lancet 2005, 366, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpino, F.M.; dos Santos Rodrigues, A.P.; Petarli, G.B.; Machado, K.P.; Flores, T.R.; Batista, S.R.; Nunes, B.P. Overweight, Obesity and Risk of Multimorbidity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivimäki, M.; Strandberg, T.; Pentti, J.; Nyberg, S.T.; Frank, P.; Jokela, M.; Ervasti, J.; Suominen, S.B.; Vahtera, J.; Sipilä, P.N.; et al. Body-Mass Index and Risk of Obesity-Related Complex Multimorbidity: An Observational Multicohort Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebenbaum, M.; Zaric, G.S.; Thind, A.; Sarma, S. Trends in Obesity and Multimorbidity in Canada. Prev. Med. 2018, 116, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, C.; Luppa, M.; Weyerer, S.; König, H.-H.; Maier, W.; Schön, G.; Petersen, J.J.; Gensichen, J.; Fuchs, A.; Bickel, H.; et al. Obesity and Associated Lifestyle in a Large Sample of Multi-Morbid German Primary Care Attendees. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speerforck, S.; Schomerus, G. “Mental Health Awareness”—Eine Entwicklung ohne Nebenwirkungen? Psychiatr. Prax. 2024, 51, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global Burden of 369 Diseases and Injuries in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 310 Diseases and Injuries, 1990–2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1545–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.; Xie, R.; Mishra, S.R.; Dai, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Yuan, C.; Xu, X. Bidirectional Association between Physical Multimorbidity and Subclinical Depression in Chinese Older Adults: Findings from a Prospective Cohort Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 296, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangenberg, L.; Forkmann, T.; Brähler, E.; Glaesmer, H. The Association of Depression and Multimorbidity in the Elderly: Implications for the Assessment of Depression. Psychogeriatrics 2011, 11, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustini, B.; Lotfaliany, M.; Woods, R.L.; McNeil, J.J.; Nelson, M.R.; Shah, R.C.; Murray, A.M.; Ernst, M.E.; Reid, C.M.; Tonkin, A.; et al. Patterns of Association between Depressive Symptoms and Chronic Medical Morbidities in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 68, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moetteli, S.; Mueller-Stierlin, A.S. Ernährungsinterventionen in der Psychiatrie—Ein vernachlässigter Baustein für einen gesünderen Lebensstil. Psychiatr. Prax. 2024, 51, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quek, Y.-H.; Tam, W.W.S.; Zhang, M.W.B.; Ho, R.C.M. Exploring the Association between Childhood and Adolescent Obesity and Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannan, M.; Mamun, A.; Doi, S.; Clavarino, A. Is There a Bi-Directional Relationship between Depression and Obesity among Adult Men and Women? Systematic Review and Bias-Adjusted Meta Analysis. Asian J. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.; Sun, Q.; Czernichow, S.; Kivimaki, M.; Okereke, O.I.; Lucas, M.; Manson, J.E.; Ascherio, A.; Hu, F.B. Bidirectional Association between Depression and Obesity in Middle-Aged and Older Women. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, L.T.; Zarate, C.A. Depression in the Primary Care Setting. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzbach, M.; Luppa, M.; Hansen, H.; König, H.-H.; Gensichen, J.; Petersen, J.J.; Schön, G.; Wiese, B.; Weyerer, S.; Bickel, H.; et al. A Comparison of GP and GDS Diagnosis of Depression in Late Life among Multimorbid Patients—Results of the MultiCare Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 168, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorow, M.; Stein, J.; Pabst, A.; Weyerer, S.; Werle, J.; Maier, W.; Miebach, L.; Scherer, M.; Stark, A.; Wiese, B.; et al. Categorical and Dimensional Perspectives on Depression in Elderly Primary Care Patients—Results of the AgeMooDe Study. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 27, e1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, I.; Hansen, H.; Schön, G.; Maier, W.; Höfels, S.; Altiner, A.; Fuchs, A.; Gerlach, F.M.; Petersen, J.J.; Gensichen, J.; et al. The German MultiCare-Study: Patterns of Multimorbidity in Primary Health Care—Protocol of a Prospective Cohort Study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2009, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van Den Bussche, H.; Scherer, M. Das Verbundvorhaben “Komorbidität und Multimorbidität in der hausärztlichen Versorgung” (MultiCare). Z. Gerontol. Geriatrie 2011, 44, 73–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Die Generation 65+ in Deutschland 2015. Statistisches Bundesamt, Wiesbaden. Available online: https://www.statistischebibliothek.de/mir/servlets/MCRFileNodeServlet/DEMonografie_derivate_00001454/Generation65.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Lachman, M.E. Psychology of Adult Development. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glossary: Equivalised Disposable Income. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Glossary:Equivalised_disposable_income (accessed on 21 February 2025).
- Hauner, H.; Moss, A.; Berg, A.; Bischoff, S.C.; Colombo-Benkmann, M.; Ellrott, T.; Heintze, C.; Kanthak, U.; Kunze, D.; Stefan, N.; et al. Interdisziplinäre Leitlinie der Qualität S3 zur “Prävention und Therapie der Adipositas”: Der Deutschen Adipositas-Gesellschaft e.V.; der Deutschen Diabetes Gesellschaft; der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Ernährung e.V.; der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Ernährungsmedizin e.V. Version 2.0 (April 2014); AWMF-Register Nr. 050-001. Adipositas Ursachen Folgeerkrankungen Ther. 2014, 8, 179–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, M.P.; Brody, E.M. Assessment of Older People: Self-Maintaining and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living. Gerontologist 1969, 9, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, C. Lawton—Brody Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Scale (IADL). AJN Am. J. Nurs. 2008, 108, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Klasen, B.W.; Hallner, D.; Schaub, C.; Willburger, R.; Hasenbring, M. Validation and Reliability of the German Version of the Chronic Pain Grade Questionnaire in Primary Care Back Pain Patients. Psychosoc. Med. 2004, 1, Doc07. [Google Scholar]
- The IPAQ Group. Guidelines for Data Processing and Analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)—Short and Long Forms; 2005. Available online: https://biobank.ndph.ox.ac.uk/showcase/ukb/docs/ipaq_analysis.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Fydrich, T.; Geyer, M.; Hessel, A.; Sommer, G.; Brähler, E. Fragebogen Zur Sozialen Unterstützung (F-SozU): Normierung an Einer Repräsentativen Stichprobe. Diagnostica 1999, 45, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fydrich, T.; Sommer, G.; Tydecks, S.; Brähler, E. Fragebogen zur sozialen Unterstützung (F-SozU): Normierung der Kurzform (K-14). Z. Med. Psychol. 2009, 18, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Stone-Bury, L.; Granier, K.; Segal, D. Geriatric Depression Scale. In Encyclopedia of Gerontology and Population Aging; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-3-319-69892-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauggel, S.; Birkner, B. Validität und Reliabilität einer deutschen Version der Geriatrischen Depressionsskala (GDS). Z. Klin. Psychol. Psychotherapie 1999, 28, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppermann, K.-M.; Friedrich, C.; Herth, F.; Huber, R.M. Geriatrische Assessments Und Diagnostik Beim Älteren Patienten. Onkologie 2008, 31, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BfArM—ICD-10-GM Version 2024. Available online: https://klassifikationen.bfarm.de/icd-10-gm/kode-suche/htmlgm2024/block-f30-f39.htm (accessed on 21 February 2025).
- Schienkiewitz, A.; Kuhnert, R.; Blume, M.; Mensink, G.B.M. Overweight and Obesity among Adults in Germany—Results from GEDA 2019/2020-EHIS. J. Health Monit. 2022, 7, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peralta, M.; Ramos, M.; Lipert, A.; Martins, J.; Marques, A. Prevalence and Trends of Overweight and Obesity in Older Adults from 10 European Countries from 2005 to 2013. Scand. J. Public Health 2018, 46, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearl, R.L.; Hernandez, M.; Bach, C.; Groshon, L.; Wadden, T.A. Prevalence of Diagnosed Psychiatric Disorders among Adults Who Have Experienced and Internalized Weight Stigma. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2023, 9, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagar, S.; Patel, H.B.; Nagar, N.; Mahyavanshi, D.; Nagar, S.S.; Godara, N. Study on Factors Associated with Depression among Elderly and Comparison of Two Scales Used for Screening. Indian J. Community Med. 2021, 46, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansen, C.B.; Kjær, J.N.; Hjorth, P.; Andersen, K.; Prina, A.M. The Association of Time since Spousal Loss and Depression in Widowhood: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2019, 54, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, W.; Luo, J.; Huang, H. Associations between Education Levels and Prevalence of Depressive Symptoms: NHANES (2005–2018). J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 301, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryhorczuk, C.; Sharma, S.; Fulton, S.E. Metabolic Disturbances Connecting Obesity and Depression. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.-H.; Lee, J.J.; Yu, E.W.-R.; Hu, H.-Y.; Lin, S.-Y.; Ho, C.-Y. Association between Obesity and Education Level among the Elderly in Taipei, Taiwan between 2013 and 2015: A Cross-Sectional Study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kang, H.; Choi, S.; Choi, J. Exploring Social Activity Patterns among Community-Dwelling Older Adults in South Korea: A Latent Class Analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yao, L.; Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Liu, L. Prevalence and Factors Influencing Depression among Empty Nesters in China: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilbert, A.; Braehler, E.; Haeuser, W.; Zenger, M. Weight Bias Internalization, Core Self-Evaluation, and Health in Overweight and Obese Persons. Obesity 2014, 22, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhl, R.M.; Heuer, C.A. The Stigma of Obesity: A Review and Update. Obesity 2009, 17, 941–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmer, C.; Bosnjak, M.; Mata, J. The Association between Weight Stigma and Mental Health: A Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e12935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, M.; Qiu, L.; Levis, B.; Fan, S.; Sun, Y.; Amiri, L.S.N.; Harel, D.; Markham, S.; Vigod, S.N.; Ziegelstein, R.C.; et al. Depression Prevalence of the Geriatric Depression Scale-15 Was Compared to Structured Clinical Interview for DSM Using Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, Y.; Rajaa, S.; Rehman, T. Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Forms of Geriatric Depression Scale for Screening of Depression among Older Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 87, 104002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joling, K.J.; Van Marwijk, H.W.J.; Piek, E.; Der Horst, H.E.V.; Penninx, B.W.; Verhaak, P.; Van Hout, H.P.J. Do GPs’ Medical Records Demonstrate a Good Recognition of Depression? A New Perspective on Case Extraction. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 133, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hung, C.-F.; Rivera, M.; Craddock, N.; Owen, M.J.; Gill, M.; Korszun, A.; Maier, W.; Mors, O.; Preisig, M.; Rice, J.P.; et al. Relationship between Obesity and the Risk of Clinically Significant Depression: Mendelian Randomisation Study. Br. J. Psychiatry 2014, 205, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.J.; Cho, C.; Berk, A.R.; Holland, J.; Roth, A.J. Are Gold Standard Depression Measures Appropriate for Use in Geriatric Cancer Patients? A Systematic Evaluation of Self-Report Depression Instruments Used With Geriatric, Cancer, and Geriatric Cancer Samples. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanowski, P.; Wagner, E.; Schmaling, K.; Schwartz, S.; Williams, B.; Diehr, P.; Kulzer, J.; Gray, S.; Collier, C.; LoGerfo, J. Community-Integrated Home-Based Depression Treatment in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 2004, 291, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J.; Vaze, A.; Rao, S. Clinical Diagnosis of Depression in Primary Care: A Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2009, 374, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtamu, K.; Birhane, R.; Demissie, M.; Fekadu, A. Interventions to Improve the Detection of Depression in Primary Healthcare: Systematic Review. Syst. Rev. 2023, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Overall (n, (%)) | Women (n, (%)) | Men (n, (%)) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 2568 | (100) | 1498 | (58.3) | 1070 | (41.7) | |
| Age | 0.169 a | ||||||
| <75 years old | 1505 | (58.6) | 861 | (57.5) | 644 | (60.2) | |
| ≥75 years old | 1063 | (41.4) | 637 | (42.5) | 426 | (39.8) | |
| Education | <0.001 a | ||||||
| Low | 1579 | (61.5) | 966 | (64.5) | 613 | (57.3) | |
| Middle | 694 | (27.0) | 443 | (29.6) | 251 | (23.5) | |
| High | 295 | (11.5) | 89 | (5.9) | 206 | (19.3) | |
| Marital status | <0.001 a | ||||||
| Married | 1506 | (58.6) | 664 | (44.3) | 842 | (78.7) | |
| Single | 156 | (6.1) | 110 | (7.3) | 46 | (4.3) | |
| Divorced | 209 | (8.1) | 154 | (10.3) | 55 | (5.1) | |
| Widowed | 697 | (27.1) | 570 | (38.1) | 127 | (11.9) | |
| Income | <0.001 b | ||||||
| Mean (s.d.) | 1.4 | (0.7) | 1.3 | (0.6) | 1.5 | (0.8) | |
| BMI | <0.001 a,d | ||||||
| Under- and normal weight | 627 | (24.4) | 393 | (26.2) | 234 | (21.9) | |
| Overweight | 1120 | (43.6) | 579 | (38.7) | 541 | (50.6) | |
| Obesity in total (I–III) | 821 | (32.0) | 526 | (35.1) | 295 | (27.6) | |
| Obesity I | 609 | (23.7) | 379 | (25.3) | 230 | (21.5) | |
| Obesity II | 152 | (5.9) | 101 | (6.7) | 51 | (4.8) | |
| Obesity III | 60 | (2.3) | 46 | (3.1) | 14 | (1.3) | |
| IADL | 0.901 a | ||||||
| Limited | 628 | (24.5) | 365 | (24.4) | 263 | (24.6) | |
| Not limited | 1940 | (75.6) | 1133 | (75.6) | 807 | (75.4) | |
| GCPS pain presence | <0.001 a | ||||||
| Yes | 2019 | (78.6) | 1258 | (84.0) | 761 | (71.1) | |
| No | 549 | (21.4) | 240 | (16.0) | 309 | (28.9) | |
| GCPS pain intensity (0–100) | <0.001 b | ||||||
| Mean (s.d.) | 34.0 | (25.1) | 38.2 | (24.8) | 28.2 | (24.2) | |
| Number of chronic diseases | <0.001 b | ||||||
| Mean (s.d.) | 7.4 | (3.1) | 7.7 | (3.1) | 7.1 | (3.2) | |
| IPAQ | <0.001 a | ||||||
| Low | 805 | (31.4) | 524 | (35.0) | 281 | (26.3) | |
| Moderate | 1121 | (43.7) | 647 | (43.2) | 474 | (44.3) | |
| High | 642 | (25.0) | 327 | (21.8) | 315 | (29.4) | |
| Social support | 0.507 b | ||||||
| Mean (s.d.) | 4.1 | (0.7) | 4.1 | (0.7) | 4.1 | (0.7) | |
| GDS | <0.001 c | ||||||
| Mean (s.d.) | 2.5 | (2.6) | 2.7 | (2.7) | 2.3 | (2.5) | |
| Overall | Under- and Normal Weight | Overweight | Obesity in Total (Classes I–III) | Obesity Class I | Obesity Class II | Obesity Class III | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | p | n (%) | p | n (%) | p | n (%) | p | n (%) | p | n (%) | p | n (%) | p | ||||||||
| Depression prevalence according to GP | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 444 | (17.3) | 116 | (18.5) | 184 | (16.4) | 144 | (17.5) | 104 | (17.1) | 25 | (16.5) | 15 | (25.0) | |||||||
| Gender | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Female | 331 | (22.1) | <0.001 | 85 | (21.6) | 0.009 | 126 | (21.8) | <0.001 | 120 | (22.8) | <0.001 | 86 | (22.7) | <0.001 | 21 | (20.8) | 0.062 a | 13 | (28.3) | 0.483 a |
| Male | 113 | (10.6) | 31 | (13.3) | 58 | (10.7) | 24 | (8.1) | 18 | (7.8) | 4 | (7.8) | 2 | (14.3) | |||||||
| Age | |||||||||||||||||||||
| <75 years old | 274 | (18.2) | 0.144 | 78 | (21.9) | 0.012 | 108 | (17.1) | 0.498 | 88 | (17.0) | 0.611 | 63 | (16.6) | 0.674 | 13 | (13.4) | 0.182 | 12 | (30.0) | 0.343 a |
| ≥75 years old | 170 | (16.0) | 38 | (14.0) | 76 | (15.6) | 56 | (18.4) | 41 | (17.9) | 12 | (21.8) | 3 | (15.0) | |||||||
| Depression prevalence according to GDS questionnaire | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 319 | (12.4) | 77 | (12.3) | 116 | (10.4) | 126 | (15.4) | 85 | (14.0) | 28 | (18.4) | 13 | (21.7) | |||||||
| Gender | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Female | 216 | (14.4) | <0.001 | 56 | (14.3) | 0.052 | 74 | (12.8) | 0.006 | 86 | (16.4) | 0.288 | 59 | (15.6) | 0.142 | 18 | (17.8) | 0.790 | 9 | (19.6) | 0.478 a |
| Male | 103 | (9.6) | 21 | (9.0) | 42 | (7.8) | 40 | (13.6) | 26 | (11.3) | 10 | (19.6) | 4 | (28.6) | |||||||
| Age | |||||||||||||||||||||
| <75 years old | 170 | (11.3) | 0.040 | 44 | (12.4) | 0.945 | 57 | (9.0) | 0.095 | 69 | (13.4) | 0.039 | 44 | (11.6) | 0.030 | 13 | (13.4) | 0.036 | 12 | (30.0) | 0.043 a |
| ≥75 years old | 149 | (14.0) | 33 | (12.2) | 59 | (12.1) | 57 | (18.8) | 41 | (17.9) | 15 | (27.3) | 1 | (5.0) | |||||||
|
True Positive
Pseudo-R2: 0.198 |
True Negative
Pseudo-R2: 0.110 |
False Positive
Pseudo-R2: 0.035 |
False Negative
Pseudo-R2: 0.186 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | (95% CI) | p -Value | OR | (95% CI) | p -Value | OR | (95% CI) | p -Value | OR | (95% CI) | p -Value | |
| Gender (Ref.: men) | ||||||||||||
| Women | 1.83 | (1.05–3.18) | 0.033 | 0.58 | (0.47–0.73) | <0.001 | 2.01 | (1.51–2.68) | <0.001 | 0.96 | (0.68–1.36) | 0.824 |
| Age (Ref.: <75 years old) | ||||||||||||
| ≥75 years old | 0.66 | (0.43–1.01) | 0.057 | 1.34 | (1.09–1.65) | 0.005 | 0.79 | (0.61–1.02) | 0.070 | 0.99 | (0.71–1.38) | 0.952 |
| Marital status (Ref.: married) | Wald/F: 13.75 | 0.003 | Wald/F: 8.68 | 0.034 | Wald/F: 2.30 | 0.513 | Wald/F: 0.47 | 0.925 | ||||
| Single | 0.91 | (0.35–2.41) | 0.855 | 0.85 | (0.57–1.28) | 0.437 | 1.15 | (0.70–1.89) | 0.587 | 1.20 | (0.66–2.18) | 0.553 |
| Divorced | 1.57 | (0.76–3.27) | 0.227 | 0.67 | (0.47–0.95) | 0.024 | 1.37 | (0.91–2.07) | 0.135 | 1.14 | (0.64–2.01) | 0.656 |
| Widowed | 2.43 | (1.47–4.01) | 0.001 | 0.75 | (0.59–0.94) | 0.015 | 1.07 | (0.79–1.44) | 0.665 | 1.03 | (0.70–1.51) | 0.880 |
| Education (Ref.: low) | Wald/F: 7.96 | 0.019 | Wald/F: 0.72 | 0.698 | Wald/F: 5.77 | 0.056 | Wald/F: 2.98 | 0.226 | ||||
| Middle | 1.05 | (0.64–1.72) | 0.860 | 1.06 | (0.85–1.32) | 0.630 | 0.78 | (0.59–1.03) | 0.077 | 1.31 | (0.93–1.86) | 0.127 |
| High | 2.48 | (1.30–4.72) | 0.006 | 0.91 | (0.65–1.27) | 0.571 | 0.63 | (0.40–1.00) | 0.050 | 1.38 | (0.79–2.41) | 0.253 |
| Income | 0.90 | (0.66–1.22) | 0.483 | 1.38 | (1.16–1.64) | <0.001 | 0.96 | (0.80–1.16) | 0.678 | 0.47 | (0.33–0.66) | <0.001 |
| BMI (Ref.: ≤ 24.9 kg/m2) | Wald/F: 3.11 | 0.539 | Wald/F: 6.24 | 0.182 | Wald/F: 3.25 | 0.517 | Wald/F: 6.83 | 0.145 | ||||
| Overweight | 0.63 | (0.36–1.08) | 0.092 | 1.14 | (0.89–1.45) | 0.312 | 1.04 | (0.78–1.40) | 0.769 | 0.84 | (0.56–1.27) | 0.413 |
| Obesity I | 0.76 | (0.42–1.37) | 0.366 | 1.35 | (1.02–1.78) | 0.036 | 0.82 | (0.58–1.15) | 0.252 | 0.75 | (0.47–1.19) | 0.217 |
| Obesity II | 0.63 | (0.25–1.56) | 0.314 | 1.21 | (0.79–1.84) | 0.377 | 0.77 | (0.45–1.33) | 0.353 | 1.08 | (0.57–2.04) | 0.822 |
| Obesity III | 0.65 | (0.20–2.07) | 0.461 | 1.79 | (0.94–3.41) | 0.076 | 0.93 | (0.44–1.99) | 0.859 | 0.33 | (0.13–0.84) | 0.020 |
| IADL (Ref.: not limited) | ||||||||||||
| Limited | 3.14 | (1.98–5.00) | <0.001 | 0.61 | (0.49–0.76) | <0.001 | 0.82 | (0.61–1.11) | 0.203 | 2.14 | (1.54–2.99) | <0.001 |
| GCPS pain presence (Ref.: no) | ||||||||||||
| Yes | 1.07 | (0.44–2.57) | 0.884 | 0.97 | (0.68–1.37) | 0.842 | 1.41 | (0.93–2.13) | 0.106 | 0.73 | (0.40–1.33) | 0.301 |
| GCPS pain intensity | 1.01 | (0.99–1.02) | 0.281 | 0.99 | (0.98–1.00) | <0.001 | 1.00 | (1.00–1.01) | 0.449 | 1.02 | (1.01–1.02) | <0.001 |
| Number of chronic diseases | 1.05 | (0.98–1.12) | 0.161 | 0.95 | (0.91–0.98) | 0.001 | 0.99 | (0.95–1.03) | 0.509 | 1.13 | (1.07–1.18) | <0.001 |
| IPAQ (Ref.: low) | Wald/F: 1.63 | 0.442 | Wald/F: 13.18 | 0.001 | Wald/F: 1.10 | 0.576 | Wald/F: 13.31 | 0.001 | ||||
| Moderate | 0.89 | (0.54–1.46) | 0.644 | 1.24 | (1.00–1.55) | 0.055 | 1.01 | (0.76–1.34) | 0.969 | 0.71 | (0.50–1.01) | 0.059 |
| High | 0.62 | (0.30–1.29) | 0.202 | 1.68 | (1.27–2.22) | <0.001 | 0.86 | (0.61–1.21) | 0.395 | 0.37 | (0.22–0.64) | <0.001 |
| Social support | 0.36 | (0.28–0.46) | <0.001 | 1.74 | (1.51–2.00) | <0.001 | 1.16 | (0.97–1.38) | 0.102 | 0.49 | (0.40–0.60) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bludau, D.C.; Pabst, A.; Bleck, F.; Weyerer, S.; Maier, W.; Gensichen, J.; Mergenthal, K.; Bickel, H.; Fuchs, A.; Schäfer, I.; et al. Overweight, Obesity, and Depression in Multimorbid Older Adults: Prevalence, Diagnostic Agreement, and Associated Factors in Primary Care—Results from a Multicenter Observational Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081394
Bludau DC, Pabst A, Bleck F, Weyerer S, Maier W, Gensichen J, Mergenthal K, Bickel H, Fuchs A, Schäfer I, et al. Overweight, Obesity, and Depression in Multimorbid Older Adults: Prevalence, Diagnostic Agreement, and Associated Factors in Primary Care—Results from a Multicenter Observational Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(8):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081394
Chicago/Turabian StyleBludau, Daniel Christopher, Alexander Pabst, Franziska Bleck, Siegfried Weyerer, Wolfgang Maier, Jochen Gensichen, Karola Mergenthal, Horst Bickel, Angela Fuchs, Ingmar Schäfer, and et al. 2025. "Overweight, Obesity, and Depression in Multimorbid Older Adults: Prevalence, Diagnostic Agreement, and Associated Factors in Primary Care—Results from a Multicenter Observational Study" Nutrients 17, no. 8: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081394
APA StyleBludau, D. C., Pabst, A., Bleck, F., Weyerer, S., Maier, W., Gensichen, J., Mergenthal, K., Bickel, H., Fuchs, A., Schäfer, I., König, H.-H., Wiese, B., Schön, G., Wegscheider, K., Scherer, M., Riedel-Heller, S. G., & Löbner, M. (2025). Overweight, Obesity, and Depression in Multimorbid Older Adults: Prevalence, Diagnostic Agreement, and Associated Factors in Primary Care—Results from a Multicenter Observational Study. Nutrients, 17(8), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081394







