Abstract
Various species of Alexandrium can produce a number of bioactive compounds, e.g., paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs), spirolides, gymnodimines, goniodomins, and also uncharacterised bioactive extracellular compounds (BECs). The latter metabolites are released into the environment and affect a large range of organisms (from protists to fishes and mammalian cell lines). These compounds mediate allelochemical interactions, have anti-grazing and anti-parasitic activities, and have a potentially strong structuring role for the dynamic of Alexandrium blooms. In many studies evaluating the effects of Alexandrium on marine organisms, only the classical toxins were reported and the involvement of BECs was not considered. A lack of information on the presence/absence of BECs in experimental strains is likely the cause of contrasting results in the literature that render impossible a distinction between PSTs and BECs effects. We review the knowledge on Alexandrium BEC, (i.e., producing species, target cells, physiological effects, detection methods and molecular candidates). Overall, we highlight the need to identify the nature of Alexandrium BECs and urge further research on the chemical interactions according to their ecological importance in the planktonic chemical warfare and due to their potential collateral damage to a wide range of organisms.
Keywords:
dinoflagellate; paralytic shellfish toxin; lytic; allelopathy; bioactivity; chemical ecology; secondary metabolite Key Contribution:
This review highlights the importance of bioactive extracellular compounds within the genus Alexandrium. We report the wide spectra of activities of these unknown metabolites, their physiological effects on organisms, the available chemical information, and we point out the need to quantify these activities and underline the need to identify these metabolites.
1. Introduction
1.1. Alexandrium, a Potentially Toxic Genus
Exceptional densities of marine microalgae, commonly reported as blooms, are recurrently observed in many coastal areas around the world. A number of dinophyceae microalgae are producers of potent phycotoxins which, during such blooms, may have major economic (e.g., on tourism or exploitation of marine resources) and/or health impacts (e.g., human poisoning). Among toxigenic and bloom-forming dinophytes, the genus Alexandrium Halim is perhaps the most intensely studied. This is largely related to the ability of several Alexandrium species to produce paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs; saxitoxin and analogues) responsible for life-threatening human poisoning (paralytic shellfish poisoning, PSP) trough consumption of contaminated seafood [1]. Other species of Alexandrium may produce other phycotoxins such as the spirolides and/or gymnodimines produced by A. ostenfeldii (Paulsen) Balech and Tangen (reported as A. peruvianum by [2]), or goniodomins produced by a few other Alexandrium species [3]. Moreover, many species are described to produce poorly characterised extracellular compounds with lytic capacity [4]. All these traits may contribute to the devastating consequences of toxic Alexandrium blooms including human poisoning, fish kills, socio-economic losses to aquaculture and fisheries, marine fauna mortality and food web disruptions [5].
1.2. Ecology of Alexandrium
Blooms of Alexandrium are favoured by suitable biotic and abiotic environmental conditions and may be triggered and enhanced by increased water temperature, high irradiance, high nutrient supply or water stratification [6,7,8]. Blooms of Alexandrium can be of high biomass with maximum cell densities up to 107–108 cells L−1 [9,10], and at times can be almost monospecific [6,11,12,13,14]. Blooms may occur as both large scale coastal events [15,16,17,18] as well as regional events in estuaries and coastal embayments [19,20] and are often associated with substantial economic losses due to the closure of shellfish beds or even mortality of shellfish [17]. The success and dominance of Alexandrium species in plankton communities and the ability for blooms to persist and to attain high cell densities highlight their well-developed adaptative capacities including competition and/or defensive mechanisms against biotic pressures (e.g., competitors, grazers and parasites). All species of Alexandrium have typical peridinin plastids and are phototrophic. A number of species, however, have been shown to be mixotrophic [21,22], and this trophic versatility may also contribute to bloom formation. Another important factor of recurrent blooms of Alexandrium are cysts beds. As part of their life cycle, many species of Alexandrium can form benthic cysts (in most cases hypnozygotes), that allow cells in dormancy to stand unfavourable temperature or nutrient conditions [23]. Subsequent cyst germination can occur during suitable growth conditions and inoculate vegetative cells into the water column. This can thus initiate blooms, the extent of which may depend on cyst bed distribution as well as on abundance of cysts formed at the end of previous vegetative periods [23,24]. Cysts are also critical in species dispersal, as cells transported to new locations by storms, currents, or humans (e.g., in ballast water), can colonise an area by depositing cysts that can germinate in the subsequent years [24].
1.3. Taxonomy and Nomenclature of Alexandrium
Alexandrium, a typical gonyaulacoid genus in the subfamily Ostreopsidoideae [25] was erected by Halim [26]. The taxonomic history of the genus is quite complex and include numerous rearrangements of species formerly classified in Gonyaulax Diesing, Protogonyaulax F.J.R.Taylor, Gessnerium Halim, Goniodoma F.Stein, and Pyrodinium L.Plate [5,27]. The very first species assignable to Alexandrium was described by Paulsen back in 1904 as Goniodoma ostenfeldii Paulsen (=Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Paulsen) Balech and Tangen) from plankton samples from Iceland [28], followed by the description of Gonyaulax tamarensis Lebour (=Alexandrium tamarense (Lebour) Balech) from the Tamar estuary (southern England) in 1925 [29], and the description of Gonyaulax catenella Whedon and Kofoid (=Alexandrium catenella (Whedon and Kofoid) Balech) from the north-western Pacific Ocean off San Diego [30]. After rearranging these and other species into Gessnerium [31] and/or Protogonyaulax [32], a scientific consensus for the taxonomy of these species was finally reached when Balech [33,34] redefined Halim’s genus Alexandrium and transferred a total of 22 species into Alexandrium. Enrique Balech (1912–2007), an eminent taxonomist from Argentina, greatly impacted our knowledge on Alexandrium by describing as much as eleven new Alexandrium species and by transferring many other species into Alexandrium. His monograph on the genus [35], where he compiled all available information on how to identify and differentiate the species, is still the benchmark in the field. Despite the thorough work of Balech, a number of new Alexandrium species have been discovered in the 20th century. In 2004, A. tamutum M. Montresor, U. John and A. Beran, A. gaarderae L. Nguyen-Ngoc and J. Larsen, and A. globosa L. Nguen-Ngoc and J. Larsen were added, followed by A. diversaporum S.Murray et al., A. pohangense A.S. Lim and H.J. Jeong, and A. fragae S. Branco and M. Menezes [36,37,38,39,40]. All these new species, as far as tested with cultured strains, are not producing PSTs. Moreover, in 2020, a molecular characterisation of multiple strains isolated from marine macroalgae revealed three novel phylotypes of predominantly coccoid live stages. The phylotypes nested in Alexandrium but low availability of motile cells yet prevented a thecal plate analysis and a formal species description and diagnosis [41]. Finally, with the availability of first sequence data of the fusiform gonyaulacoid genus Centrodinium Kofoid [42] it became clear that at least three of their species (C. punctatum (Cleve) Taylor, C. eminens Böhm, C. intermedium Pavillard) form a clade nesting within Alexandrium [42,43]. Moreover, it was also shown that C. punctatum produces exceptionally large amounts of PSP toxins [44]. Notably, the phylogenetic nesting of Centrodinium in Alexandrium makes the latter paraphyletic. The nomenclatural consequences are not clear yet, especially as morphological and molecular details on the type species of Centrodinium, C. elongatum Kofoid, are not available. Recently, Gómez and Artigas [43] in an attempt to “solve” Alexandrium´s paraphyly, proposed to split Alexandrium into four genera (retaining Alexandrium, resurrecting Gessnerium and Protogonyaulax, and newly erecting Episemicolon). However, as argued by Mertens and collaborators [45], these reintroduced taxa were not based on monophyletic groups, and accepting the Gómez and Artigas proposal would result in replacing a single paraphyletic taxon with several non-monophyletic ones so that the proposal [43] to split Alexandrium, on the basis of our current knowledge, should be rejected.
The general problem of reliable species identification in the protistan realm especially refers to Alexandrium, where most taxa are rather similar in general size and shape [35] but where the presence of toxigenic species calls for a sound and reliable species determination. Identification of Alexandrium species is not a simple task and requires a thorough examination of morphological differences in cell size, shape, or chain formation. Most importantly, morphological species identification requires to reveal a suite of subtle details of the theca such as ornamentation, presence and development of cingular and sulcal lists and excavations, the presence and location of attachment pores and of a ventral pore, and shape and arrangement of diagnostic thecal plates such as the apical pore plate, the first apical plate, or the sulcal plates [1,35]. While advanced molecular techniques are of increasing value to support and to ease species identification, a number of phylogenetic studies related to Alexandrium revealed cryptic speciation and also invalidated some of the described morphospecies [46,47]. This is especially important as it particularly concerns the most important PSTs producing species complexes of A. minutum Halim and the former A. tamarense/catenella/fundyense species complex.
Within the A. minutum group sensu Balech (1995), several morphospecies have been described (A. minutum, A. ibericum Balech, A. angustitabulatum F.J.R.Taylor, and A. lusitanicum Balech) with rather similar morphological characteristics and almost identical PSP toxin profiles. A detailed molecular ribosomal gene sequence analysis of members of the A. minutum group convincingly revealed that A. lusitanicum and A. angustitabulatum are in fact synonymous with A. minutum, whereas other morphologically similar species such as A. tamutum, A. insuetum, and A. andersonii were confirmed to be valid species [46].
The most prominent example of an Alexandrium morphospecies concept failure for species circumscriptions is the former A. tamarense species complex consisting of the morphospecies A. tamarense, A. catenella, and A. fundyense Balech [47,48,49]. For several decades these morphospecies were reported and named in the literature based on whether cells were anterior-posteriorly compressed and formed chains (“A. catenella” morphospecies) or not (“A. tamarense” and “A. fundyense” morphospecies) and based on the presence (“A. tamarense” morphospecies) or absence (“A. fundyense” morphospecies) of a ventral pore. However, the first molecular phylogenetic studies of RNA sequences obtained from numerous strains from globally distributed localities of the species complex revealed five distinct ribotypes (named groups I to V) which however did not conform with the morphological criteria [50]. Consequently, in a detailed study including morphology, molecular phylogeny based on multiple marker genes, mating compatibility and presence/absence of STX-coding genes, the five ribotypes where described as distinct species, i.e., A. catenella for group I, A. mediterraneum U.John for group II, A. tamarense for group III, A. pacificum R.W.Litaker for group VI, and A. australiense Sh.Murray for group V [48,51]. These nomenclatural changes have important implications [52]. While it is clear that current and future identification of Alexandrium species of this group has to be based on rRNA marker gene sequencing and/or use of species–specific molecular assays, the use of previous paper information to compile and/or compare species-based information is challenging. A strain previously reported as “A. tamarense” does not necessarily (and in fact in many cases probably does not) provide trait description for the species A. tamarense as it is described today. There is no doubt that species can/do differ in trait and thus reliable species identification and an unambiguous use of scientific names is an indispensable base for any communication about biological species and their traits. In the following review we thus report and compile information of older papers as follows: (1) if the previous work using strains of the tamarense/catenella/fundyense species complex provide molecular data or a strain identifier for which molecular data are available elsewhere, we report the results under the new correct name, followed by the name reported in that paper in parenthesis (e.g., A. catenella (reported as A. tamarense)). As a comprehensive compilation of strain identifiers linked with molecular data, we used the supplementary file S9 provided in [48]. When we were unable to locate/identify sequence data for a particular strain reported in the literature, we reported the species name using quotation marks and adding (not further characterised) (e.g., “A. tamarense” (not further characterised). In some cases, where additional data of the respective paper (e.g., geographical origin, presence/absence of PSTs) are available, this information was included in the parentheses (e.g., “A. tamarense” (likely to represent A. catenella as the strain produce PSTs)). For all other species names of Alexandrium, we conformed to synonymies as reported in AlgaeBase [53] and corrected species names from previous papers accordingly.
1.4. Effects of Alexandrium on Marine Biota
Because of the economic importance of PST-producing species, direct effects of Alexandrium on marine biota have long been studied, especially on the physiology of economically important shellfish, but also on finfish and commercial fisheries. Deleterious physiological effects and marine biota mortality events have been associated with Alexandrium outbreaks [17,54,55,56,57]. So far, these deleterious effects have largely been attributed to the neurotoxic PSTs. But the general problem is that PSTs are not the only bioactive compounds produced by Alexandrium, which makes it difficult or often impossible to pinpoint the ultimate cause of these negative effects. As will be discussed in detail below, many, if not all, species of Alexandrium are known to release bioactive extracellular compounds (BECs) that induce deleterious (mostly lytic) effects against a wide range of cells from protists to mammalian cell lines. In the plankton realm, BECs may negatively affect competing protists [58,59,60], immobilise prey [61,62] and predators [4,63], inhibit putative parasites [64], or affect grazing of copepods [65]. Moreover, there is growing evidence that BECs might also be responsible for physiological incapacitation of shellfish [66,67,68,69,70,71,72] or fish [73]. Nevertheless, detailed knowledge on chemical details of the metabolites mediating these interactions is largely lacking. Most of the toxic effects of Alexandrium on commercial species have been attributed to the known toxins while BECs were not investigated. The objective of this review is to summarise and merge the current knowledge from different fields on BECs within the genus Alexandrium.
2. Known Toxins of Alexandrium and Their Effects
An extraordinary characteristic of Alexandrium is the diversity of toxins that a number of species produce (Figure 1, Table 1). This does not only refer to the chemical variability of a toxin and its derivatives, but also includes the presence of chemically very different toxin classes. Currently, the known toxins associated with species of Alexandrium are hydrophilic paralytic shellfish toxins (PST), and various lipophilic compounds such as spirolides (SPX), gymnodimines (GYM), and goniodomins (GD).
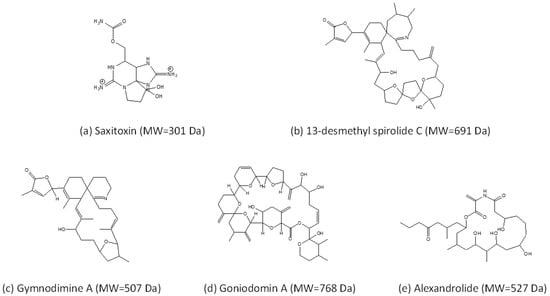
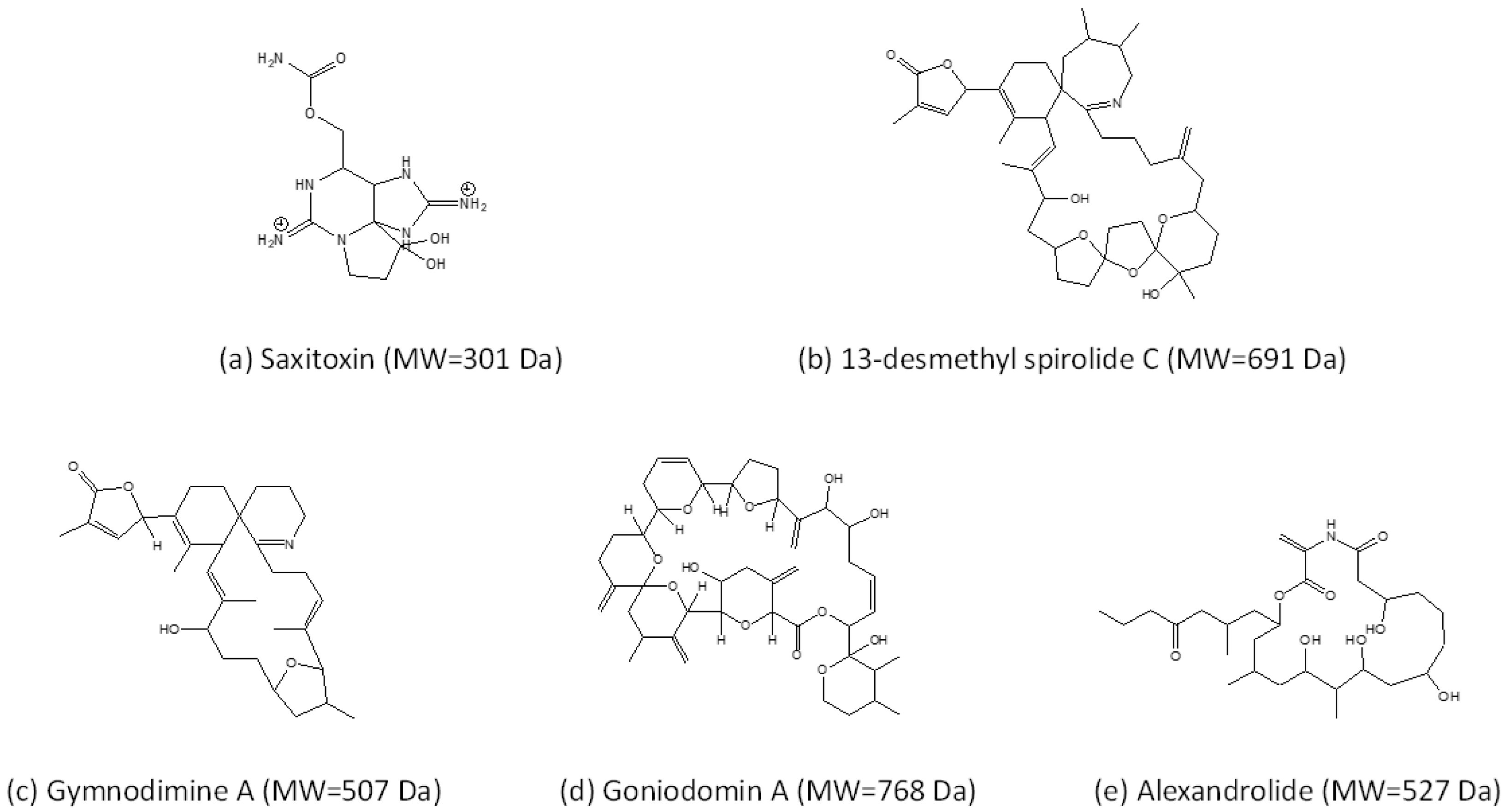
Figure 1.
Examples of the diversity of toxins produced within the genus Alexandrium. (a) Saxitoxin, one of the most common PSTs; (b) 13-desmethyl spirolide C (SPX 1) and (c) Gymnodimine A (GYM A) are cycloimine toxins; (d) Goniodomin A (GDA) is a macrocyclic polyketide; (e) Alexandrolide is a putative allelochemical.
2.1. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins
The best studied group of Alexandrium toxins are PSTs. This probably is due to their rapid accumulation in filter-feeding bivalves and their high toxicity in humans after consumption of contaminated shellfish [74]. PSTs are also associated with deleterious effects in seabirds [75] and marine mammals [56,76]. PSTs were already reported in the first half of the 20th century [77] and comprise a group of over 40 variants, not only produced by Alexandrium (including Centrodinium punctatum, which cluster within Alexandrium) but also by two other species of different genera (Gymnodinium catenatum H.W.Graham and Pyrodinium bahamense L.Plate), as well as several species of different genera of freshwater cyanobacteria. The PSTs produced by Alexandrium are constrained to 12 structural variants namely carbamoyl and N-sulfocarbamoyl toxins. The composition of these variants is a stable phenotypic trait, but the amounts of PSTs derivatives vary between and within strains [1]. In vertebrates including humans, PST target voltage-gated sodium channels inducing a blockage of ion transport and action potential of excitable membranes and are accordingly classified as neurotoxins. PSTs accumulation and shellfish contamination may be responsible for PSP outbreaks, thus leading to economic losses linked with fishery closures or recreational activities, and human intoxications. Moreover, PSTs have been associated with ichthyotoxicity [78,79], toxicity in shellfish [80], and deterrence or toxicity to copepods [81,82].
2.2. Cycloimines (Spirolides and Gymnodimines)
Cycloimines are a group of marine biotoxins characterised by a macrocyclic carbon skeleton and an additional six or seven membered rings with an imine functional group [83]. Within this group, spirolides are characterised by a seven membered cyclic imine moiety, which were first discovered in shellfish, because of their fast neurotoxic properties (so-called fast-acting toxins) detected in the mouse bioassay [84]. Later, spirolides were reported to be produced by Alexandrium ostenfeldii [85], the only known species producing spirolides. In recent years, increasingly more spirolide variants were detected in A. ostenfeldii from different geographic regions [2,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97]. Chemically related gymnodimines were originally detected in shellfish in New Zealand [98] and soon associated with the naked marine dinoflagellate Karenia selliformis A.J. Haywood, K. Steidinger and L. MacKenzie (initially reported as Gymnodinium sp.) [99]. Later, 12-methyl gymnodimine was detected in A. ostenfeldii (reported as A. peruvianum (Balech and Mendiola) Balech and Tangen) [2] and since then many other gymnodimine variants were found in this species [87,89,100].
Despite their very high intraperitoneal toxicity, cycloimines are far less toxic when administered orally [101]. Functional bioassays on gymnodimine A (GYM A) and 13-desmethyl spirolide C (SPX 1) revealed a similar bioactivity of these toxins as both GYM A and SPX 1 induced rapid neurotoxic symptoms in mice, suggesting that both are fast-acting toxins [102]. The common symptoms induced by GYM A and SPX 1 via different routes were proven to be caused by binding of cycloimines to acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) [103,104]. Electrophysiological inhibition assays on GYM A [105] and SPX 1 [106] described the capacity of the toxins to inhibit AChRs. However, a reversible effect was only apparent in treatments with GYM A [105] indicating slightly different modes of action of these chemically very similar compounds. This was further supported by Nieva and collaborators, who showed that GYM A and SPX 1 activated nicotinic AChRs, but that only GYM A activated muscarinic AChRs [107].
2.3. Goniodomins
The first report of goniodomin (GD) dates back to 1968 in Puerto Rico, when Goniodoma sp. (later specified as G. pseudogonyaulax Biecheler and subsequently revised as the new species A. hiranoi Kita and Fukuyo [108]) was described as a source of GD [109]. At that time the structure of this GD was not fully elucidated, but twenty years later the compound was isolated again from a bloom of A. hiranoi and described as the macrocyclic polyketide goniodomin A (GDA) [110]. Recent compelling evidence shows that goniodomin and GDA in fact are the same compound [111]. Later reports added that GDA is also produced by A. monilatum (J.F.Howell) Balech [112], A. pseudogonyaulax (Biecheler) Horiguchi ex K.Yuki and Y.Fukuyo [113], and A. taylorii Balech [3]. In 2008 an isomer of GDA was structurally elucidated and named GDB [114]. Already Sharma and collaborators [109] described an antibiotic activity of GD and later other biological effects have been added, such as antifungal activity [110], cell division inhibition of sea urchin eggs [110], antiangiogenic activity [115], and perhaps most significantly in terms of its adverse effects on marine ecosystems, it has been associated with mortality in aquatic invertebrates [116]. Not much is known about the transfer of GDA in food webs, but GDA has been shown to accumulate in the marine snail Rapana venosa in controlled exposure experiments [116]. Cytotoxicity and effects on actin levels in human neuroblastoma cells of GDA and GDB were reported [117]. Moreover, it was shown that GDA forms potassium (and other alkali ion) complexes with potentially ionophoric properties, which may be involved in allelochemical interactions and ichthyotoxicity [118].


Table 1.
Compilation of toxin information and trophy of Alexandrium species. No published information was found for the following species: A. balechii, A, compressum, A. camurascutulum, A. concavum, A. depressum, A. foedum, A. fraterculus, A. gaarderae, A. globosum, A. kutnerae, A. satoanum, A. tropicale, and A. acatenella. Detailed information on BECs activity is available in Table 2. In the table, “+” indicates that the vast majority of strain of the species produce toxins, “−” indicates that in the cited reference, the presence of the compound was specifically looked for but it was not detected. Presence of “±” indicates that both toxigenic and non-toxigenic strains of the species have been described or that contrasting results about toxin production exist. Absence of symbol indicates that no information is available from the literature. All species of Alexandrium have plastids and are photosynthetic. For a couple of species mixotrophic capability have been tested, and these species are marked here as “P” (i.e., phototroph, phagotrophy was not observed (but note that always a limited number of different strains has been tested) or “M” (i.e., mixotroph, phagotrophy was observed).
Table 1.
Compilation of toxin information and trophy of Alexandrium species. No published information was found for the following species: A. balechii, A, compressum, A. camurascutulum, A. concavum, A. depressum, A. foedum, A. fraterculus, A. gaarderae, A. globosum, A. kutnerae, A. satoanum, A. tropicale, and A. acatenella. Detailed information on BECs activity is available in Table 2. In the table, “+” indicates that the vast majority of strain of the species produce toxins, “−” indicates that in the cited reference, the presence of the compound was specifically looked for but it was not detected. Presence of “±” indicates that both toxigenic and non-toxigenic strains of the species have been described or that contrasting results about toxin production exist. Absence of symbol indicates that no information is available from the literature. All species of Alexandrium have plastids and are photosynthetic. For a couple of species mixotrophic capability have been tested, and these species are marked here as “P” (i.e., phototroph, phagotrophy was not observed (but note that always a limited number of different strains has been tested) or “M” (i.e., mixotroph, phagotrophy was observed).
| Species | PSP | Spiro-Imine | Gonodiomin | Trophy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. affine | ± a | P [21] | ||
| A. andersonii | ± b | M [21] | ||
| A. australiense | ± c | |||
| A. catenella | + d | − e | M [119] | |
| A. cohorticula | ± f | |||
| A. concavum | − g | |||
| A. diversaporum | − h | |||
| A. fragae | + i | |||
| A. fraterculus | − j | P [21] | ||
| A. hiranoi | + k | P [120] | ||
| A. insuetum | − l | P [121] | ||
| A. leei | ± m | |||
| A. margalefii | − n | P [120] | ||
| A. mediterraneum | − o | P [121] | ||
| A. minutum | ± p | M [119] | ||
| A. monilatum | − q | + r | ||
| A. ostenfeldii | ± s | ± s | M [122] | |
| A. pacificum | + t | P [121] | ||
| A. pohangense | − u | M [61] | ||
| A. pseudogonyaulax | − v | + v | M [120] | |
| A. tamarense | − w | M [123] | ||
| A. tamiyavanichii | + x | |||
| A. tamutum | − y | P [121] | ||
| A. taylorii | − z | − z | + z | P [120] |
(a) Negative for PST in [124], the only positive record comes from [125]. HPLC estimates, but without any details on methods. (b) PSTs reported in [126], but: negative for PSP [127], also negative for PST [124]. Negative for PSP also in [128] (but no limit of detection (LOD) reported), negative for PSP [129] (including a lack of STX genes). (c) PSTs and stxA confirmation but for only one strain in [130]. Species otherwise considered to be non-PST [131,132]. (d) Characterisation of PSTs production in [133]. (e) Lack of spirolides reported in [134] for strains of “A. tamarense” likely to be A. catenella (no LOD given). (f) Comment in [1]: Japanese strains reportedly toxigenic, but possible misidentification of A. tamiyavanichii. (g) Lack of PSP in [135] but their strain designated as A. gaarderae is not A. gaarderae as described by Gaarder but corresponds to A. gaarderae as defined in [39]. (h) Lack of PSTs and lack of sxtA documented in [36]. (i) PSP in [38]. (j) Lack of PST in [136], also in [135], also in [124]. (k) Goniodomin A was isolated from a bloom of A. hiranoi (the strain was initially described as Goniodoma pseudogonyaulax [110]). (l) Lack of PSP in [137] (in Japanese, also in [124]. (m) Comment in [1]: “Typically non-toxic, but low level of saxitoxin derivative reported from Vietnamese strain”. The positive record comes from [125] but no details (e.g., no strain identifier, no sequence data, and no morphology) on A. leei given and very low levels or even no toxins (but without LODs). Negative record for PSP in [138] (but only receptor assay, no LOD given). (n) Lack of PSP in [135], also in [128] (no LOD reported). (o) Claimed as no PSP [48]. (p) PST producing species [139,140] but non-PSP strains reported in [141,142]. (q) Lack of saxitoxin in A. monilatum extracts and different mode of toxicity in [143,144] (r) Goniodomin A reported in [112]. (s) Strains can be PST or non-PST producers [1]. The strain variability in spiroimines refers to gymnodimines. Spirolides seem to be produced by all strains [145]. There is one report of a strain from Chile [146] reporting lack of spirolides, but this needs re-investigation, as recent analyses indicate that this strain may produce previously unknown spirolides (Krock, unpublished). (t) PST production characterised in [140]. (u) Absence of sxtA documented in [37]. (v) Lack of PST documented in [135,147], also [128] (no LOD reported). Goniodomin A and B reported in some strains [147]. (w) Claimed as no PSP [48]. A PSTs producing strain of A. tamarense was recently reported from the Mediterranean [148], but, as stated by the authors, toxin analysis of this strain was carried out at the beginning of the 2000s, and toxin data of Mediterranean A. tamarense strains should be confirmed in the future using more recent and proven methods and instruments. (x) Presence of sxtA documented in [149]; PSP analysis in [124,150,151,152]. (y) Negative for PSP in species description paper [40]. Confirmed negative for PSP by [141,153,154], negative also in [127,128] (but no details on LOD). (z) Mediterranean strains of A. taylorii do not produce PSP [3,4] nor spiroimines, but do produce Goniodomin A [3]. A Pacific strain designated as A. taylorii without accompanying sequence data has been claimed as a PSP producer [155], but this report is questionable and needs re-investigation: the cell quotas were very low and the “toxin profile” had a 100% match with the PSP profile of a A. ostenfeldii strain which was simultaneously studied, and thus strain cross-contamination and not PSP production of A. taylorii is the likely cause of this report.
3. Uncharacterised Extracellular Bioactivities
Species of Alexandrium not only produce the known toxins listed above, but also uncharacterised bioactive extracellular compounds (BECs), which at present are mainly described by their lytic activity against a wide range of organisms. Lytic activity has been studied with standard haemolytic assays or with protistan competitors or predators as target species. However, lysis has also been reported against other cell types, such as para-sites, fish gill cells and shellfish tissue (Table 2).
Effects of BECs have been reported for many species of Alexandrium (Table 2). A high variability in the potency is observed among strains of the same species [4,156,157], even within strain from the same population [158,159,160,161].
There is experimental evidence that BECs activities are not mediated by PSTs or cycloimines (including gymnodimines and spirolides) but by other compounds, which we qualify as BECs [4,162,163]. These metabolites seem of dinoflagellate origin as allelochemical potency persisted when bacterial load was drastically decreased by using antibiotics [58,164,165]. However, full axenia may not have been reached and, therefore, it cannot be excluded that bacteria may play a role in the potency of BECs. For Alexandrium monocultures grown in the laboratory, there is a constitutive release of BECs in both exponential and stationary growth phases [157,166]. The production of BECs, like the production of any organic molecule, has an energetic cost, but the implications for the production of BECs is not clear yet. Preliminary comparison of a number of Alexandrium strains indicates that, to some extent, lytic activity and growth rate are inversely correlated, but only when PST-producing strains are included and non-lytic strains are excluded [167]. Another study [168] evidenced a trade-off between lytic potency and feeding ability (i.e., mixotrophic behaviour) of one strain of A. pseudogonyaulax, thus supporting the idea that BECs impose a significant energetic cost on the cell.

Table 2.
Studies reporting bioactivities originating from unknown bioactive compounds within the genus Alexandrium. Details about possible misidentification of strains are given in the footnote. No published information on bioactive compounds were found for the following species: A. balechii, A. compressum, A. camurascutulum, A. concavum, A. depressum, A. foedum, A. fraterculus, A. gaarderae, A. globosum, A. kutnerae, A. satoanum, A. tropicale, A. acatenella. Absence of references indicates that no information is available from the literature.
Table 2.
Studies reporting bioactivities originating from unknown bioactive compounds within the genus Alexandrium. Details about possible misidentification of strains are given in the footnote. No published information on bioactive compounds were found for the following species: A. balechii, A. compressum, A. camurascutulum, A. concavum, A. depressum, A. foedum, A. fraterculus, A. gaarderae, A. globosum, A. kutnerae, A. satoanum, A. tropicale, A. acatenella. Absence of references indicates that no information is available from the literature.
| Species | Hemolytic | Anti-Pathogen | Allelopathy | Anti-Grazer | Toxicity to Bivalves | Ichthyotoxic (Fishes) | Cytotoxic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. affine | [4] | [169] | [170] | ||||
| A. andersonii | [171] | [21] | [172] | ||||
| A. catenella | [173] a | [60] b | [164] c | [66] | [73] | ||
| A. fraterculus | [21] | ||||||
| A. insuetum | [121] | ||||||
| A. leei | [174] | ||||||
| A. margalefii | [121] | ||||||
| A. mediterraneum | [121] | ||||||
| A. minutum | [157] | [64] | [157] | [175] d | [68] | [176] e | |
| A. monilatum | [143] f | [177] f | |||||
| A. ostenfeldii | [163] | [85] | |||||
| A. pacificum | [178] g | [121] | |||||
| A. pohangense | [61] | ||||||
| A. pseudogonyaulax | [62] | [65] h | |||||
| A. tamarense | [173] i | [72] | [66] | ||||
| A. tamutum | [153] | [179] j | |||||
| A. taylorii | [180] k | [3] | [180] l | ||||
| Undefined strains of catenella/tamarense/ fundyense species complex | [181] m, [157] n | [182] o, [183] p |
(a) Strain of A. catenella. Hemolytic activity of cell extract but not of the filtrate. Ref. [48] previously identified as a A. fundyense. (b) Strain of A. catenella reported as A. fundyense. (c) Strain of A. tamarense reported as A. fundyense. (d) A. minutum reported as A. lusitanicum. (e) The role of PSTs cannot be excluded as the toxin profile of the strain is not given. (f) A. monilatum reported as Gonyaulax monilatum. (g) A. pacificum reported as A. catenella. (h) The strain of A. pseudogonyaulax used in this study contained Goniodimin A, the role of which in anti-grazing activity remains to be investigated. (i) Hemolytic activity of cell extract but not of the filtrate. (j) Strain of A. tamutum reported as A. tamarense. (k) No details (e.g., no strain identifier, no sequence data, and no morphology). (l) No details (e.g., no strain identifier, no sequence data, and no morphology). (m) Strain identified as A. catenella but no details (e.g., no strain identifier, no sequence data, and no morphology). Hemolytic activity of cells but not of filtrate. (n) Strain identified as A. tamarense but unlikely to be a true A. tamarense because of PSTs production. No sequence data and morphology found for this strain. (o) Strain identified as A. tamarense but no details (e.g., no strain identifier, no sequence data, and no morphology). (p) Strain identified as A. catenella but no details (e.g., no strain identifier, no sequence data, and no morphology).
3.1. Effect of BECs on Marine Organisms
When describing chemical interactions between photosynthetic plankton species and other marine organisms, the concept of allelopathy is often used. Allelopathy is commonly referred to in terrestrial systems and refers to “the impact of plants upon neighboring plants and/or their associated microflora and/or macrofauna by the production of allelochemicals; often these allelochemicals interfere with plant growth but they may also result in stimulation of growth” [184]. Applying the terrestrial concept of allelopathy on plankton systems, some authors only include phytoplankton–phytoplankton interactions [185,186,187]. However, in the marine realm of protist communities, the typical plant–animal dichotomy is not applicable: in fact, many planktonic organisms are mixotrophs, meaning that they combine photo- and heterotrophy [188,189]. Consequently, other authors broaden the allelochemical concept to comprise interactions of protists and bacteria in general, thereby including, grazers or any organisms competing with protists [4,162,163,190,191]. In this review, we follow such broad concepts defining allelochemical interactions as negative effects of a protist on accompanying organisms, through the release of chemicals, named allelochemicals. These BECs-based chemical interactions might cause various effects and thus may have several ecological roles. In the following chapters the effects are subdivided according to the target organisms and cells, including physiological incapacitation and toxicity to shellfish and fishes.
3.1.1. Allelochemical Activities
Anti-Pathogen Activities
Species of Alexandrium, like other dinoflagellates, are subject to pathogens (e.g., viruses, parasites, and bacteria) that at times contribute to the loss of biomass [192] and even bloom demise. Exudates with allelochemical properties of A. minutum showed anti-parasitic activity against the Syndinialean Amoebophrya sp. in co-cultures [64]. Exposure of free-living infectious spores of Amoebophrya sp. to A. minutum filtrates rapidly resulted in a permeabilization of their membranes. This eventually led to a loss of virulence of the parasite in cultures. When the herpesvirus OSHV-1 µVar, a common pathogen of oysters Magallana gigas (previously referred as Crassostrea gigas) was exposed to A. pacificum (initially reported as A. catenella), the prevalence of viral infection in M. gigas decreased [178]. Potential direct deleterious effects of Alexandrium BECs on marine viruses may thus mitigate infection by decreasing the viral load. Effects of BECs on pathogenic bacteria have not been studied yet. Generally, the bacterial consortium associated with Alexandrium cultures are not negatively affected [162,193], rather their growth is enhanced by the presence of allelochemicals, and this increased growth might be due to the release of organic matter from lysing cells.
Effects on Protist Competitors
Allelochemical activity of Alexandrium strains on protist competitors is usually assessed using co-cultures, or by adding cell-free medium (either supernatant or filtrate) to test target organism responses [4,58,163,165,194,195]. In such experiments, it is usually reported that activity of whole cultures is slightly stronger than supernatant or filtrate [165], likely because in co-culture allelochemicals are continuously released during the incubation period. Nothing is known about potential modulation of allelochemical production/release in presence of target cells, either caused by cell-to-cell contact or by target-based chemical cues. The latter process is known for PSTs, where the production increases in response to chemical cues from dead microalgal cells that are potential competitors [196] and in response to copepod chemical cues [197]. Conversely, lytic potency can be significantly enhanced in Alexandrium under certain environmental conditions such as P-starvation [166], low light [167], reduced salinity [198], or upon Cu addition [199]. Generally, reduced growth or exhaustive growth cessation at stationary phase may lead to significant BECs accumulation [157].
Allelochemical activity of Alexandrium spp. is mostly reported as growth inhibition [60,195,200] or cell lysis [4,58,163]. Other visible effects on target cells in contact with allelochemicals of Alexandrium spp., such as aberrant behaviour (e.g., backward swimming [201]), immobilisation of motile cells [4], cell deformation [163], or cell bleaching [165,200] might be considered as pre-lytic stages. For some target species, the formation of temporary cysts in response to Alexandrium allelochemicals has been observed [162,163]. While the gross effects of BECs have been widely described, the precise mode(s) of action of allelochemicals remain(s) to be confirmed. The thorough studies of allelochemical interactions between A. catenella—Rhodomonas salina (Wislouch) D.R.A. Hill and R. Wetherbee [58,194,202], A. minutum—Chaetoceros muelleri Lemmermann [165,199,203,204], or co-cultures between A. pacificum (reported as as A. tamarense)—Pheodactylum tricornutum Bohlin [195] foster the hypothesis that allelochemicals of A. minutum and of species of the former A. tamarense species complex are fast-acting membrane disruptive compounds [202,204]. A membrane-disrupting effect was confirmed on artificial liposomes [202]. When testing photosynthetic target species, the fluorescence yield (estimated by pulse-amplitude modulation fluorometry) during the first 3 h of incubation, as long as cells were not lysed, did not significantly change, suggesting that allelochemicals produced by A. ostenfeldii cause no short-term negative effects on the photosynthetic apparatus [163]. In the long run, however, photosynthesis is also impaired with reports of blurred and disintegrated chloroplast membranes in P. tricornutum in co-culture with “A. tamarense” (not further characterised) [195] and inhibition of photosynthetic electron flow between the two photosystems [204]. The inhibition of photosynthesis seems to originate from an impaired electron flux that leads to larger inhibitions of photosystem I (PSI) and photosystem II (PSII) [165,203,204]. Eventually, the deleterious effects lead to the death and the lysis of microalgal cells.
Inhibiting, impairing, or even eliminating competitors provides an advantage with respect to competition for limiting resources. Another additional level of benefit is when organic matter of competitors (either particulate or dissolved) is used by the allelochemical donor species, a “kill and eat your competitor” strategy [205,206]. In fact, a number of Alexandrium species are known to be mixotrophs and to ingest other protistan species (Table 1, [22]), and here phagotrophy is likely to be supported by a chemically mediated prey immobilisation. Among phagotrophic species of Alexandrium, A. pohangense was shown to ingest Margalefidinium polykrikoides (Margalef) F. Gomez, Richlen and D.M.Anderson cells by engulfment, after immobilizing the prey cell using exuded materials [61]. Cells of Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax use a mucus trap for feeding. In co-culture with A. pseudogonyaulax, various protists are immobilised [62,120], and video observations of prey being immobilised in the mucus indicate that A. pseudogonyaulax might “fish” prey with a toxic net made of mucus and allelochemicals.
Lytic potency of mixotrophic Alexandrium might be partly responsible for an overestimation of grazing rates when their calculation is based on the decline of prey concentration (e.g., [61,157]) and when an unknown portion of prey cells were lysed and not ingested.
Allelochemicals produced by the genus Alexandrium affect a large range of marine protists including phototrophic and heterotrophic organisms, but not all species or strains are affected with the same intensity [58,59,162,163]. Moreover, pairwise mixing different targets with different Alexandrium (A. catenella, A. ostenfeldii, A. minutum) revealed different sensitivities of target species to allelochemicals of different Alexandrium species. This indicate that different Alexandrium species may produce different compounds or different “cocktails” of similar compounds [58]. When natural communities were exposed to a lytic A. catenella filtrate in controlled conditions [60,193] (reported as A. fundyense, and A. tamarense, respectively), a decrease in populations of ciliates and various other plankton organisms (e.g., diatoms, nanoflagellates) was observed except for the group of small (<30 µm) dinoflagellates. Field observations confirmed the same patterns: decrease in nanoflagellate and diatom abundances and increase in dinoflagellate densities [60] suggesting that dinoflagellates might have protective mechanisms. However, controlled co-culture experiments of A. catenella (reported as A. tamarense) and different target species revealed that growth of all five tested dinophyte species were negatively affected and four of the five species finally died off at the end [59]. Generally, self-protection of cells that produce bioactive extracellular compounds is an obvious need. As for allelochemicals of Karlodinium veneficum (detailed in the chapter “3.3.3 BECs of other microalgal species”), the protection might originate from the biochemistry of the membrane [202].
Another protective mechanism of some dinoflagellates against allelochemicals is the formation of temporary cysts [59,162], where the dinophyte cells shed their theca and stay alive in pellicle cysts and are able to hatch and grow once the allelochemical concentration decreased significantly. Cell size can also influence the sensitivity to allelochemicals [200], in the diatom Thalassiosira cf. gravida, the larger cells that had undergone sexual reproduction were more resistant to “A. fundyense” (not further characterised).
Anti-Grazing Activities
Allelochemicals produced by Alexandrium do not only affect protistan competitors but also protistan grazers. An “anti-grazing effect” is obvious when phagotrophic protists show aberrant swimming behaviour and are immobilised or lysed in presence of the putative prey or its BECs [4,85,163,164,201,207,208]. A case-study is the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Polykrikos kofoidii Chatton, an abundant and voracious grazer of large dinoflagellates such as Alexandrium. The feeding and growth responses of P. kofoidii to various Alexandrium spp. strains (including both PSP and non-PSP strains) varied depending on the strain. Some Alexandrium strains supported rapid growth of the predator, whereas others rapidly caused cell death of the heterotrophic dinoflagellate [209,210]. Polykrikos kofoidii was shown to be negatively affected by lytic A. catenella strains (reported as A. tamarense) while a non-lytic A. catenella strain Alex5 (reported as A. tamarense or A. fundyense, respectively) was ingested and allowed rapid growth of the grazer [165,211]. Deleterious effects of Alexandrium on P. kofoidii (and to the ciliate Tiarina fusus Bergh, 1981) were not related to PSTs [207]. Notably, in multi-strain incubations the presence of lytic compounds did not only protect the producer strains but also mitigated the grazing on a non-lytic strain, therefore protecting the whole community [164]. Negative effects of A. catenella (reported as A. tamarense) and A. ostenfeldii on the tintinnid Favella ehrenbergii (Claparède and Lachmann, 1858) Jörgensen, 1924 were initially speculated to be caused by PSTs [85,201], but in light of the data presented above, it is very likely that lytic compounds (not known at that time) and not PSTs in fact were responsible.
There is a plethora of evidence that Alexandrium spp. chemically affects non-protistan grazers of the metazooplankton [65,179,180,212,213]. While available data suggest that protists are not affected by PSTs, the neurotoxins have demonstrated anti-grazing effects against non-protist grazers [81,82]. An anti-grazing activity of a PSTs standard mixture was shown on the marine copepod Tigriopus californicus [81], while toxic effects of purified gonyautoxin (analogues of STX) standards were evidenced on the crustacean Artemia salina [82]. Another strong argument in favour of PST anti-grazing activity is drastic enhancement of PSTs production in the presence of some copepods or their chemical cues [197,214,215,216].
While many studies highlighted toxic effects of PST-producing cells on copepods (e.g., [213,217,218]), it must be noted that in most of the copepod—Alexandrium grazing studies BECs were not considered. However, few studies highlighted deleterious effects of non-PST but lytic strains. For example, lytic compounds of “A. taylorii” (A. taylorii is regarded as a non-PST-producing species [3], but note that in the study of Emura and collaborators [180] no strain identifier, no morphology and no sequence data were provided, which would allow confirmation of the Alexandrium species determination) were shown to be toxic against Artemia salina [180]. The crustaceans were immobilised and died when exposed to the supernatant or the whole culture. Non-neurotoxic compounds of A. tamutum (reported as A. tamarense) were also involved in reprotoxic effects against the copepod Temora stylifera [179].
The situation might be even more complex as anti-grazing activities may not be limited to PSTs or lytic compounds alone. In a comparative approach using lytic and non-lytic Alexandrium strains (based on a microalgal bioassay), as well as PST-producing and non-producing Alexandrium strains, Xu and collaborators [65] highlighted that the behaviour of the copepod Temora longicornis was modified (i.e., reduction of feeding activity or regurgitation of cells) when fed on Alexandrium spp., but the modification was neither linked to PST nor to lytic compounds. It seems that in fact several different groups of bioactive compounds are potentially involved in anti-grazing activities. A high diversity and potentially a target specificity of anti-grazing compounds might reflect different stages of the ever-going arms race between phytoplankton and grazers [219].
Overall, the anti-grazing compounds highlight the general problem of the simultaneous presence of different compound classes in Alexandrium and the associated problem of identifying the compounds responsible for a specific bioactivity. Since the compounds are not chemically identified it is impossible to attribute the different effects to a specific group of toxins. Further comparative analysis with Alexandrium strains with specific bioactivities (e.g., only PSTs, only lytic, only anti-grazing) or mixed bioactivities are required to assign observed effects to a single group of compounds or to a mixture of known toxins and BECs. This would allow to retrospectively evaluate the effects already observed on copepods [220] or benthic gastropods [175,221], for example.
3.1.2. Toxicity towards Shellfish
Toxicity of Alexandrium spp. towards shellfish has been widely reported and historically associated to PSTs. Until recently, in most of such studies, only the PSTs content of the Alexandrium strain(s) was reported. A potential production of BECs was not assessed, which renders it impossible to clearly identify and distinguish the effects of PSTs from BECs. Several studies on shellfish hypothesised a production of BECs by experimental Alexandrium strains, but without actually assessing the hemolytic or allelochemical potency. This is for example the case of a study by Ford and collaborators [222], showing inhibition of adherence and phagocytosis of hemocytes from the clams Ruditapes philippinarum and Mya arenaria by a filtrate of a non-PST producing strain of A. tamarense.
A number of recent studies used a comparative approach with strains that were thoroughly characterised with respect to different bioactive compounds, enabling the distinction between effects from PSTs or BECs (Figure 2). In particular, some of these new studies [66,67,68,70,71,72] exposed bivalve species (M. gigas, Mytilus edulis, Pecten maximus) to different strains of Alexandrium spp., for which PST production and BECs potency (measured as allelochemical or hemolytic potencies) were characterised. These studies clearly highlight that a majority of the deleterious effects observed on bivalves might indeed be due to BECs produced by Alexandrium spp. rather than by PSTs. These observations might also explain the diversity and/or controversy of effects on fish and shellfish reported in the literature. Borcier and collaborators [67] highlighted harmful effects of extracellular compounds when juveniles of the great scallop P. maximus were fed with a mix of microalgae containing strain CCMI1002 of A. minutum, which only produces allelochemicals but no PST. Daily shell growth was delayed, tissues in direct contact with A. minutum cells were altered, and reaction time decreased when the scallops were exposed to predators. Similarly, different effects were visible when M. gigas was exposed to different strains of A. minutum producing either only BECs (strain CCMI1002), only PSTs (strain DA1257), or both (strain AM89BM) [68]. This later study demonstrated that the majority of the physiological effects (e.g., modification of valve-activity, hemocyte mobilisation in the gills) of A. minutum on oysters were attributable to BECs. Other comparative studies were conducted on mussels exposed to three different strains of Alexandrium [66]. Two strains of A. catenella (Alex2 and Alex5) were producing PSTs, but only one of them (Alex2) was also lytic. The third strain (A. tamarense NX-57-08) was lytic but non-PST producer. The authors demonstrated cytotoxic effects of bioactive (i.e., lytic) extracellular compounds. Effects of these lytic compounds comprised also other deleterious effects such as immune impairment or lysosomal membrane destabilisation. These immunosuppressive effects were further confirmed in vitro, on hemocytes from the mussel M. edulis exposed to a lytic supernatant of A. tamarense (strain NX-57-08) [72].
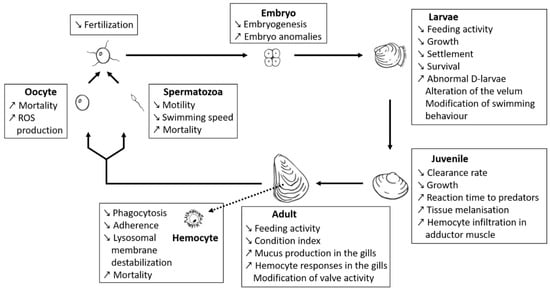
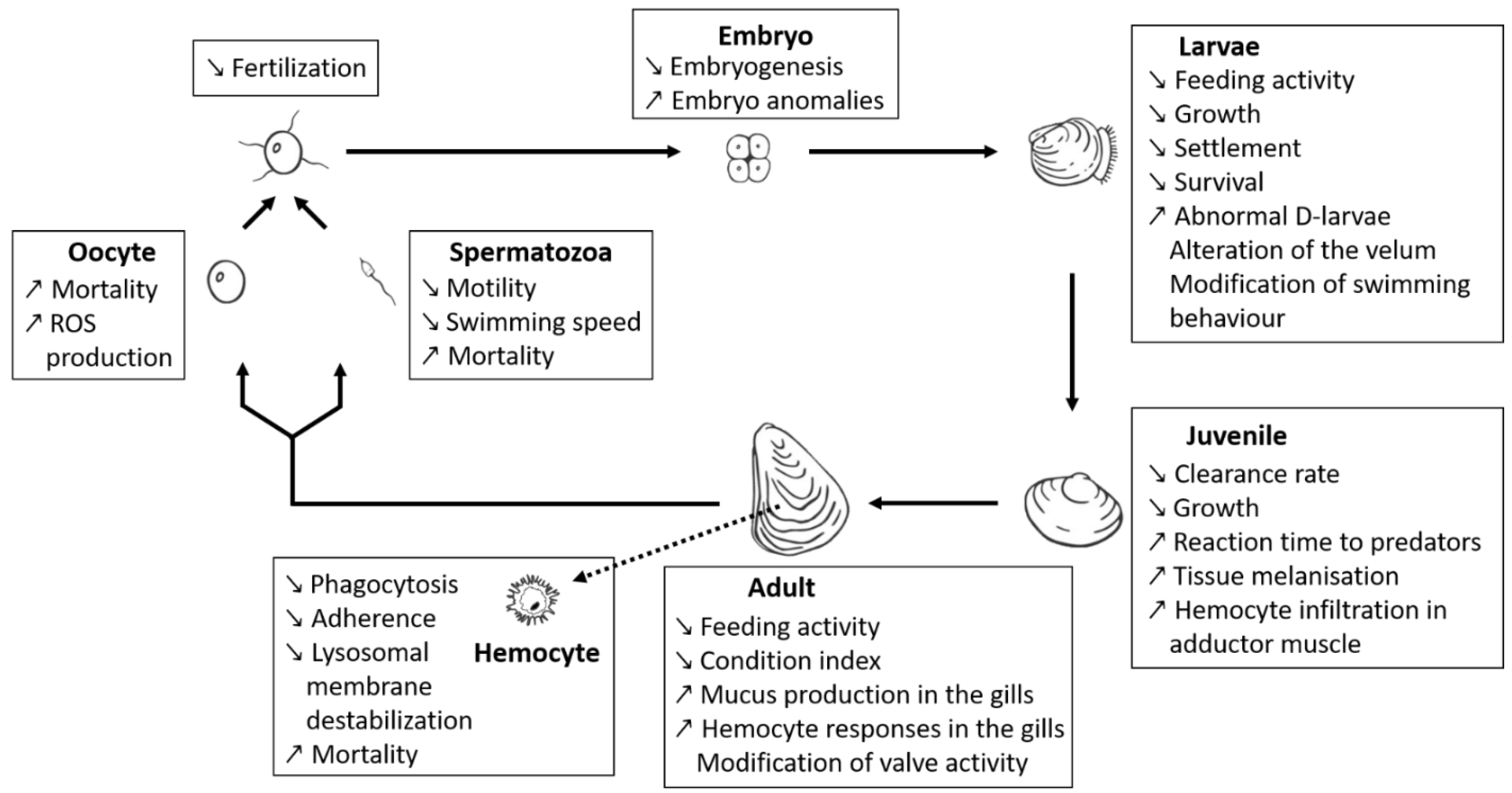
Figure 2.
A general overview of the current knowledge from the literature on the effects of BECs produced by Alexandrium on different life stages of various marine bivalves (exemplified here for oysters). Bold arrows highlight the life cycle of marine bivalves, life stages are indicated in bold in the box. Small arrows in the boxes indicate significant differences that are either lower or higher from control: downward arrow indicate a decrease and upward arrow indicate an increase in the parameter as compared to the control.
Early planktonic and larval stages of shellfish are also strongly affected by BEC. The A. minutum strain CCMI1002 (BECs but non-PST producer) showed deleterious effects of BECs on developmental stages of oysters. Specifically, this A. minutum strain caused lysis of embryos (the most sensitive stage to A. minutum toxicity among planktonic life-stages of oysters), inhibited hatching into D-larvae, disrupted larval swimming behaviour, feeding and growth, and induced decreases in survival and settlement of umbonate and eyed larvae [70]. Lytic activity of non-PST A. affine was reported on gametes, embryos and larval stages of the pearl oyster Pinctada imbricata (reported as Pinctada fucata martensi) [169,223]. The deleterious effects of “A. catenella” (not further characterised) exudates were also evidenced upon Pacific oyster (M. gigas) and Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) larvae [224]. The deleterious effects comprised larval mortality and histopathological changes of the digestive apparatus. The lytic potency of the particular Alexandrium strain was not assessed but it is likely that BECs are involved in these effects.
Now that some specific Alexandrium strains have been better characterised with respect to their PSTs and BECs production potential, it is instructive to retrospectively evaluate earlier exposure studies using these strains. This is especially the case with the A. minutum strain AM89BM (lytic and PSTs), which was used in many previous exposure experiments [54,225,226,227]. The immuno-suppressive effects on hemocytes from the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica [54], or the production of reactive oxygen species by M. gigas gametes [227] exposed to the supernatant of this A. minutum strain might retrospectively be attributed to lytic compounds. A modelling approach (Dynamic Energy Budget modelling [228]), using the AM89BM strain, also revealed putative effects of A. minutum BECs on the physiology of oysters. Knowledge of the production of lytic compounds by this strain [67,68], enabled the authors to better constrain their model when they considered the production of BECs. They hypothesised that BECs alter the feeding behaviour of oysters, causing a decrease in the ingestion rate.
3.1.3. Ichthyotoxicity
In addition to the numerous studies regarding PSTs accumulation and/or direct effects of Alexandrium on shellfish, there are a number of cases, where blooms of Alexandrium spp. were linked to fish kills [56,57,229,230,231,232,233,234]. Toxicity of unknown compounds toward fish was first shown with A. monilatum, a species not identified as a PSTs producer (Table 1), on the guppy Lebistes reticulatus [177]. Signs of hypoxia were observed on the surf smelt Hypomesus pretiosus japonicus exposed to culture filtrate of two Alexandrium strains (reported as “Protogonyaulax catenella” and “P. tamarense”, not further characterised) [235]. The ichthyotoxicity was attributed to extracellular compounds as the filtrate was free of cells and PSTs (estimated with a mouse assay). Extracellular toxins were found to swell and exfoliate fish gills, as well as decreasing membrane elasticity of rainbow trout eggs. Similarly, the ichthyotoxicity of A. leei against Asian sea bass fishes was not correlated to PSTs but was attributed to extracellular compounds present in cell-free culture medium [174]. Toxicity of supernatants of different strains of A. catenella was also observed on cell lines of rainbow trout (RTgill-W1) [73]. The toxicity varied with strains and sample source (i.e., whole culture, cell extracts, or supernatant) but was not correlated to the varying PSTs content of the different strains, and was therefore linked to other group(s) of compounds. In a later study [170], the exposure of red seabream to cells of non-PST A. affine resulted in the death of fishes. Sublethal effects of A. affine on fishes comprised decrease in respiration rates, immunosuppression and hepathic impairment in tissues. Although the authors concluded that deleterious effects originated from the attachment of the dinoflagellate to gill tissue, they did not take into consideration the potential production of unknown BECs and its role in ichthyotoxicity. Regarding the putative ichthyotoxicity of BECs, in the absence of their chemical identification, it is essential to compare the effects of only-BECs and only-PST Alexandrium strains on fish gill cells and whole fish to further evaluate their role in fish kills.
3.2. Methods for the Detection, Quantification and Study of BECs
Standard methods for the detection and quantification of phycotoxins involve chemical methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) or to a fluorescence detector (HPLC-FLD), or immunosorbent assays (i.e., enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ELISA). BECs, however, are largely uncharacterised compounds and are thus impossible to detect and quantify using these chemical methods. Nevertheless, several bioassays based on different bioactivities (e.g., lysis of blood cells or protists, effects on microalgal photosynthesis, or ichthyotoxicity) have been used to detect and quantify BECs in culture or cell extracts. As opposed to classic experiments made to characterise the toxic effects, bioassays can be defined as biological tests where organisms living under laboratory conditions are exposed to various concentrations of a toxicant, thus allowing quantification of their potency. In the future, a limited number of standard bioassays should be favoured to study BECs thus allowing better comparison between studies and between algal species and strains. In the case of bioassays with cell lines (e.g., hemocytes, microalgae, and fish gill cell lines), target strains available from culture collections should be favoured.
There are some methodological aspects and challenges when working with BECs, and not considering these in the experimental protocols might lead to substantial losses of BECs, and consequently, to misinterpretations. The first crucial step is to decide which fraction of a culture or field sample to analyse. Bioassays for the study of BECs can be performed with supernatants, filtrates or cell extracts of microalgal cultures or field samples. Some filters can retain allelochemical activity and therefore the use of supernatants [194] or specific filters (acetate cellulose or asymmetric polyethersulfone) is recommended [156]. Care must be taken during the storage of samples: it is recommended to limit the use of plastics [194] that are capable of adsorbing some allelochemical BECs. If the use of plastics cannot be avoided, their utilisation should be mentioned. Available data on BECs indicate that they are relatively resistant to cold, heat, and pH changes [73,165,174,182,194].
3.2.1. Hemolytic Bioassay
It is unlikely that blood cells are directly exposed to the toxins and thus are not the ecologically relevant targets, but blood cells of various organisms (including humans) are commonly used in toxicity assays. In haemolytic bioassays, red blood cells are exposed to samples and the lysis of erythrocytes (haemolysis) is quantified fluorometrically. Haemolytic activity of compounds in the culture medium have been shown for different Alexandrium species (Table 2 and [157,173,180,182,235,236,237]). Haemolytic activity of Alexandrium spp. is not correlated to PSTs content [236,237] but is positively correlated with Alexandrium spp. cell density and culture age [157]. Haemolytic activity is usually accompanied by other bioactivities such as allelochemical activity [157,236,237], and anti-grazers activity [180]. While haemolytic bioassays are reproducible and efficient in highlighting extracellular toxicity, these bioassays are not specific to give information on the ecological roles and potential targets of the compounds: haemolytic and allelochemical potency did not always correlate [236], suggesting the production of several BECs.
3.2.2. Protistan Bioassay
Allelochemical potency of Alexandrium spp. is most often quantified through inhibition of growth or photosynthesis and through lysis of other protists. Alexandrium affects many marine protists including photototrophic and heterotrophic organisms [58,59,162,163] so there is a wide range of bioassay target species available. However, variability in the sensitivity of microalgal species and strains to Alexandrium spp. allelochemicals [58,59,238] has to be considered, and using exclusively a resistant target strain would lead to false conclusions. For the better comparability of BECs detection and quantification between different studies and laboratories, we therefore recommend the use of a limited number of strains that are available in culture collections.
A frequently used protistan bioassay is the Rhodomonas salina assay [58,66,161,163,166,167,194,198,239,240]. In this bioassay, the cryptophyte R. salina (e.g., strain KAC 30 from the Kalmar culture collection) is exposed to donor species whole cells, culture filtrates/supernatants or cell extracts, for a defined incubation period (usually 3–24 h). The decrease in cell density compared to a control is then quantified microscopically (e.g., [163]), but can also be quantified fluorometrically [241]. This bioassay has also shown its benefits in bioassay-guided fractionation protocols to purify allelochemicals [194,239]. Another bioassay [156] used in several studies [67,68], is based on the inhibition of photosynthesis in the diatom Chaetoceros muelleri (Strain CCAP 1010/3 from the culture collection of algae and protozoa (CCAP)). In this bioassay, C. muelleri cells are exposed to Alexandrium spp. filtrates or supernatants for 2 h before quantifying the inhibition of maximum photosystem II quantum yield (Fv/Fm), which has been identified as a sublethal effect before cell lysis [204]. These two bioassays are based on different target species and therefore it is possible, that in fact, different compounds are quantified, i.e., compounds inducing cryptophyte lysis versus compounds inducing diatom lysis. To clarify this issue, extended intercomparisons of both bioassays are needed.
3.2.3. Anti-Grazer Bioassay
Next to classical grazing experiments [242,243] there seem to be no standardised bioassay-type setups to specifically study anti-grazing bioactivities of Alexandrium. A widely applied bioassay uses the brine shrimp Artemia spp., which is at least a potential grazer of microalgae (e.g., [244,245]). However, this bioassay does not specifically quantify anti-grazing or repellent activity. Artemia spp. individuals are exposed to microalgal cells or filtrates, then immobile or dead Artemia individuals are quantified to estimate lethal concentrations. In the context of Alexandrium, the Artemia assay has been used to highlight the presence of “A. taylorii” (not further characterised) exotoxins [180]. This bioassay highlighting toxicity should be complemented with a more specific bioassay quantifying ingestion rate of Alexandrium cells by zooplankton (e.g., [246]) to highlight anti-grazing activity. Video observation and quantification of ingestion or rejection events of Alexandrium cells by copepods, as performed in [65] might also be adapted in a bioassay to quantify anti-grazing bioactivities.
3.2.4. Ichthyotoxicity Bioassays
In the first ichthyotoxicity bioassay highlighting Alexandrium BECs [174], whole fishes (Later calcacifer) were exposed to A. leei cultures, filtrates or different extracts for 3–7 days. The percentage of mortality, the death time, and the size of fish were then estimated. This bioassay highlighted that ichthyotoxicity of culture originated from exudates and allowed a partial characterisation of the chemical properties of A. leei ichthyotoxin(s). While whole fish bioassays give robust and ecologically relevant results, they require special aquarium facilities and ethics approvals to work with whole fish. Later, the use of ichthyotoxicity bioassays using rainbow fish gill cell lines [247,248,249] was applied to the genus Alexandrium [73,250]. In a first approach, Mardones and collaborators [73] monitored gill cell (RTgill-W1) lysis with a fluorometric assay, later the Ca2+, H+, and K+ ion fluxes were measured with microelectrodes [250], following the addition of culture supernatant or cell extract. Both versions of the fish-gill bioassay provide rapid results after 1–2 h of incubation and allow the detection and quantification of ichthyotoxic BECs in cultures. Thus, in vitro fish-gill bioassays allow a rapid screening of samples and, when performed under controlled conditions, allow comparative studies [248] between different Alexandrium species or strains. However, it has to be kept in mind that the response of isolated gill cells does not necessarily represent the complex response of the whole organism. No specific bioassay has been developed for shellfish but bivalve haemocytes and gametes isolated from whole organisms were used in many studies [72,222,227,251] and can allow a rapid detection (2 h) of BECs toxicity to bivalves [227]. However, there are currently no long-term marine invertebrate cell lines available. The use of standardised and free of pathogen shellfish [252] such as the standardised oyster seed used in [253] should be generally considered and might improve the comparability between studies and between different laboratories.
3.3. State of the Art of Characterisation of Alexandrium BECs
Attempts of a chemical characterisation of bioactive extracellular compounds produced by Alexandrium spp. have been based on the different bioassays and thus potentially on different bioactivities. The standard haemolytic assays are described in Section 3.2.1. Haemolytic bioassays have been used for some early attempts to characterise BECs of Alexandrium [180,182]. Other studies focused on the characterisation of BECs based on their allelochemical potential [183,194,195,207,239,254] or on ichthyotoxic effects [73,174,255]. This section compiles the information regarding various attempts to characterise BECs, including detailed information on the various sample preparation or extraction protocols (Table 3) and an overview of current knowledge and hypotheses about the nature of BECs (Table 4).

Table 3.
Diversity of protocols used for the chemical characterisation of Alexandrium BECs (and unknown intracellular cytotoxins).

Table 4.
Chemical characteristics of Alexandrium BECs (and unknown intracellular cytotoxins) or hypothesis made on their nature.
3.3.1. Characterisation of BECs Based on Haemolytic and Allelochemical Properties
Different hypotheses were provided regarding the nature of Alexandrium allelochemicals and were controversial (Table 4), especially regarding the potential proteinaceous nature. Although it is not proof of their implication in bioactivity, the presence of polypeptides was reported in the supernatant extract of an allelochemical strain of “A. tamarense” (not further characterised) by ultra-performance liquid matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometric (UPLC-MALDI-MS) [195]. In A. minutum cellular extracts with anti-cancer activity, three major proteins were found in the active fraction [176]; however, the activity of the extracellular fraction remains to be investigated. In these two studies, proteins were detected; however, their implication in activities was not thoroughly investigated (i.e., the activity of the purified polypeptides/proteins was not tested nor was a mitigation of the activity with a peptidase examined) and remains to be confirmed. A potential role of proteins in lytic activity was first hypothesised by Emura and collaborators [180]. The authors studied the haemolytic activity of a cell-free supernatant of “A. taylorii” (not further characterised) culture. They based the assumption of a proteinaceous compound on the temperature-dependant activity of the lytic activity but also on the mitigation of this activity when trypsin (a peptidase) was added. The authors further identified that lytic activity was associated with large compounds (>10 kDa) as the activity was concentrated by ultrafiltration and no activity was measured in the filtrate. Flores and collaborators [207] presented data related to the involvement of proteinaceous compounds in lytic activity of Alexandrium strains (all three reported as A. tamarense species complex; two strains likely to represent A. catenella as they originate from the US east coast and have PSTs, and one strain of A. tamarense) against the ciliate Tiarina fusus and the dinoflagellate Polykrikos kofoidii: the addition of peptidase (trypsin) mitigated the lytic activity of A. tamarense only, but toxicity of both A. catenella strains were not mitigated by trypsin addition. It is unclear at present, however, if these differences reflect assay or strain variability or true species–specific differences between A. catenella and A. tamarense. Neither hemolytic and cytotoxic activities from “A. tamarense” (not further characterised) exudates [182,236] nor the lytic fraction from A. catenella [194,239] revealed proteinaceous characteristics (trypsin or heat sensitivity, or Coomassie staining). Next to the potential proteinaceous nature of Alexandrium BECs, Flores and collaborators [207] also suggested a possible involvement of reactive oxygen species as they observed an alleviation of lytic activities after the addition of antioxidant enzymes (peroxidase and superoxide dismutase). Contrasting results on the proteinaceous nature of BECs might be explained by different Alexandrium species releasing different groups of lytic compounds with different nature, e.g., non-proteinaceous compounds in “A. tamarense” (not further characterised) [182,236] and protein-like compounds in “A. taylorii” (not further characterised) [180] and in A. tamarense [207]. However, the unclear species identification in some studies [180,236] precludes such interpretations.
Another candidate compound was further isolated by electrophoresis from “A. tamarense” (not further characterised) cell-free medium [182]. The putative “AT-toxin” has a high molecular weight, estimated to be around 1000 kDa, and does not contain significant amounts of amino acids but contains sugars. The sugar composition was thoroughly described by the authors who consequently hypothesised that an extracellular polysaccharide-based toxin was responsible for haemolytic activity and induction of apoptosis in a human myeloid leukemia cell line. Similarly, the presence of saccharides has been reported in an A. minutum cytotoxic fraction with anti-proliferative activity against cancer [176]. In the later study, the authors identified that the bioactive fraction contained glycoprotein(s) with molecular weight(s) above 20 kDa, the involvement of which in activity remains to be investigated. An involvement of sugars in bioactivities remains to be confirmed through further purification steps and/or by testing the bioactivity of the extract following polysaccharide degradation. In contrast, in A. catenella (reported as A. tamarense) the role of sugar in lytic activity from culture supernatant seems unlikely [239].
Hydrophobicity is a shared feature of BECs from at least three species, A. catenella (reported as A. tamarense) [194,202,239], A. tamutum (reported as A. tamarense) [179] and A. minutum [254]. Characterisation of hydrophobic Alexandrium BECs has mainly relied on methanolic extraction of allelochemical activity from the supernatant [194,239,254]. Allelochemicals were extracted from A. catenella and A. minutum supernatant through solid phase extraction (LC-18 SPE) allowing separation of a hydrophobic fraction (eluted with 80% of methanol) which was much more potent than the others [194,239,254]. A common notion, which is in accordance with the hydrophobic nature, is that during preparation and sample handling there are significant losses of biological activities probably due to stickiness to surfaces, with plastic material causing larger loss compared to glass. When stored in glass flasks, an apparent “loss” of activity was observed but could be recovered by vigorous shaking [194]. Allelochemicals of A. catenella (reported as A. tamarense) were hypothesised to be amphipathic (i.e., compounds with a polar head and a hydrophobic part) according to liquid/liquid partitioning [194,239]. Based on further separation methods (ultrafiltration, reversed phase chromatography, and hydrophilic interaction ion-chromatography) followed by LC-TOFMS analysis, the authors eventually concluded that the putative allelochemicals of A. catenella are large (7–15 kDa), non-proteinaceous, and probably non-polysaccharidic molecules, but they could not isolate defined mass candidates. Such a large size (which is common in surfactants and detergents) corroborates the nature of allelochemicals as amphipathic compounds. Involvement of fatty acids as potential allelochemicals was much less likely, because the n-hexane phase of liquid/liquid partitioning did not exhibit allelochemical activity [194,239].
Despite the numerous attempts to characterise BECs of Alexandrium spp., only one molecular candidate from a single strain from “A. catenella” (not further characterised) was structurally identified: alexandrolide (Figure 1), a microalgal growth inhibitor [183]. Alexandrolide is a non-proteinaceous, non-saccharidic, hydrophobic compound isolated by bioassay-guided purification. The allelochemical with a molecular formula of C28H49NO8 and a pseudo molecular weight [M + H]+ of 528.3537 Da has a maximum ultraviolet absorption of 235 nm and infrared absorption at 1640 and 3400 cm−1. The fraction containing the newly identified molecule inhibited the growth of microalgae and was cytotoxic to mouse lymphoid P388. It was particularly potent against Skeletonema costatum (Greville) Cleve and Chattonella antiqua (Y.Hada) C.Ono but had much lesser effects on three dinoflagellate species tested. Notably, the chemical structure of alexandrolide is unlikely to induce a permeabilization of membranes as observed with some BECs. Experiments adding purified alexandrolides or determination of intra- and extracellular levels of alexandrolides are not yet available so its allelochemical function cannot be regarded as proven yet. Development of protocols is needed to allow the detection and quantification of alexandrolide in order to properly address its role in Alexandrium allelochemical interactions.
3.3.2. Ichthyotoxic BECs
The study by Tang and collaborators [174] is the first to report basic chemical information on non-PST ichthyotoxins produced within the genus Alexandrium. The authors evidenced the presence of heat-stable and water-soluble ichthyotoxin(s) in exudates of a A. leei culture inducing the death of fishes (Lates calcarifer), but the precise nature of the ichthyotoxin(s) remains unknown. Later studies [73,255] investigated the nature of ichthyotoxins of A. catenella. These authors highlighted the presence of light sensitive, heat resistant and hydrophilic compounds [255] in both culture supernatant and extracts from lysed cells through an in vitro fish gill assay.
Mardones and collaborators [73] did not perform a bioassay-guided purification of ichthyotoxic extracts but tested the hypothesis that a synergistic action of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free fatty acids (FA) were responsible for ichthyotoxicity, as was proposed for Chattonella marina [256]. Therefore, they investigated the lipid composition of A. catenella strains and highlighted that polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) accounted for more than 50% of total FA including docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; 22:6n-3), that counted for 16 to 20% of total FA [73]. Then, they tested the ichthyotoxicity of these FA alone or in combination with ROS in fish-gills based bioassays. DHA was highlighted to be the most ichthyotoxic FA to fish larvae and its toxicity was greatly enhanced when coupled to superoxide anions. It was thus hypothesised that oxidation products of FA play a dominant major role in ichthyotoxicity [73]. This toxicity would be particularly relevant for microalgal cells in contact with gills: the breakdown of cells would release FA and superoxide anions and result in lipid peroxidation and gill damages [256]. However, this scenario is unlikely to explain the ichthyotoxicity of supernatants that are free of cells, unless cells can exudate FA into the culture medium or centrifugation resulted in a significant breakdown of cells. The presence of significant amounts of FA or peroxides in culture supernatant has not yet been proven. It is thus still an open question if and how PUFAs and superoxide anions are involved in Alexandrium ichthyotoxicity.
3.3.3. BECs of Other Microalgal Species
To better understand Alexandrium BECs activity, it is instructive to compile and compare knowledge about other toxins of microalgal origin known to be involved in the several toxic and lytic activities. Such compounds are karlotoxins produced by Karlodinium veneficum [257,258,259,260,261,262], karmitoxin produced by Karlodinium armiger Berholtz, Daugbjerg and Moestrup [263], amphidinols produced by Amphidinium spp. [264,265], or prymnesins produced by the haptophyte Prymnesium parvum N.Carter [266,267]. However, the allelochemical potency of prymnesins still remains to be confirmed [268]. All these ichthyotoxins, are polyketides, like the majority of dinoflagellate toxins [269]. Polyketides are a highly diverse class of secondary metabolites that are produced through polyketide synthases [270,271]. Polyketide diversity is based on variable compound structures (Figure 3A) and on the diversity of biological activities [272], including cytotoxic, ichthyotoxic, and hemolytic activities [273]. Notably, all the previously mentioned ichthyotoxins (i.e., karlotoxins, karmitoxins, prymnesins, and amphidinols), are putative allelochemicals and share a similar chemical feature: a hairpin structure with a polar head and a hydrophobic structure.
Karlotoxins, produced by Karlodinium veneficum [262] are particularly well described and reveal many analogies with BECs from Alexandrium. Karlotoxins are lytic compounds with ichthyotoxic activity [274], are toxic to bivalves [275,276], have anti-grazing activities [258,277,278], and have anti-parasitic activity against the genus Amoebophrya [279,280]. Karlotoxins are amphipathic compounds [281] with hairpin conformation including a large hydrophobic part that non-specifically increases membrane permeability [282]. Karlotoxins are suggested to form pores in membranes. The hydrophobic part of the toxin is inserted within the membrane and likely interacts with specific phospholipids, while the hydrophilic part is outside the membrane and interacts with cholesterols [283]. This organisation of toxins in membranes generates pores that result in membrane depolarisation, disruption of cellular functions [262], and eventually lead to anosmotic lysis of the cells. Karlotoxins, amphidinols, and karmitoxin are variants of the same core structure. While prymnesins are chemically quite different, they also share a common feature with the hairpin-like toxins: a large hydrophilic and a smaller lipophilic part. This amphipathic structure is likely linked to their affinity to cholesterols [265,284] and the disruption of membranes (Figure 3B). Polyketides are a promising track in the investigation of the chemical structure of the unknown bioactive compounds produced by the genus Alexandrium, regarding the variety of their bioactivities and mode of action.
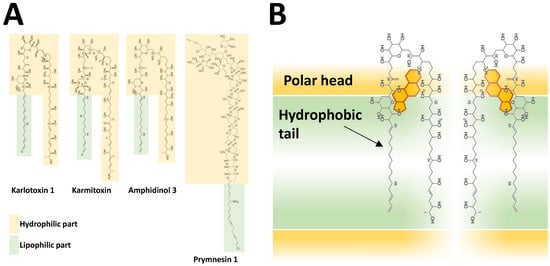
Figure 3.
(A) Polyketides sharing the structures associated with the permeabilization of membranes and lytic activity. The green boxes represent the large hydrophobic part, and the yellow boxes represent the hydrophilic part of the toxin. (B) Proposed pore formation of the cell membrane by multiple karlotoxin molecules according to [283]. The simplified biphasic/lipidic membrane is represented by the rectangles with lipid polar heads in yellow and their hydrophobic tails in green. Karlotoxin are surrounding cholesterol molecules (in orange).
Figure 3.
(A) Polyketides sharing the structures associated with the permeabilization of membranes and lytic activity. The green boxes represent the large hydrophobic part, and the yellow boxes represent the hydrophilic part of the toxin. (B) Proposed pore formation of the cell membrane by multiple karlotoxin molecules according to [283]. The simplified biphasic/lipidic membrane is represented by the rectangles with lipid polar heads in yellow and their hydrophobic tails in green. Karlotoxin are surrounding cholesterol molecules (in orange).
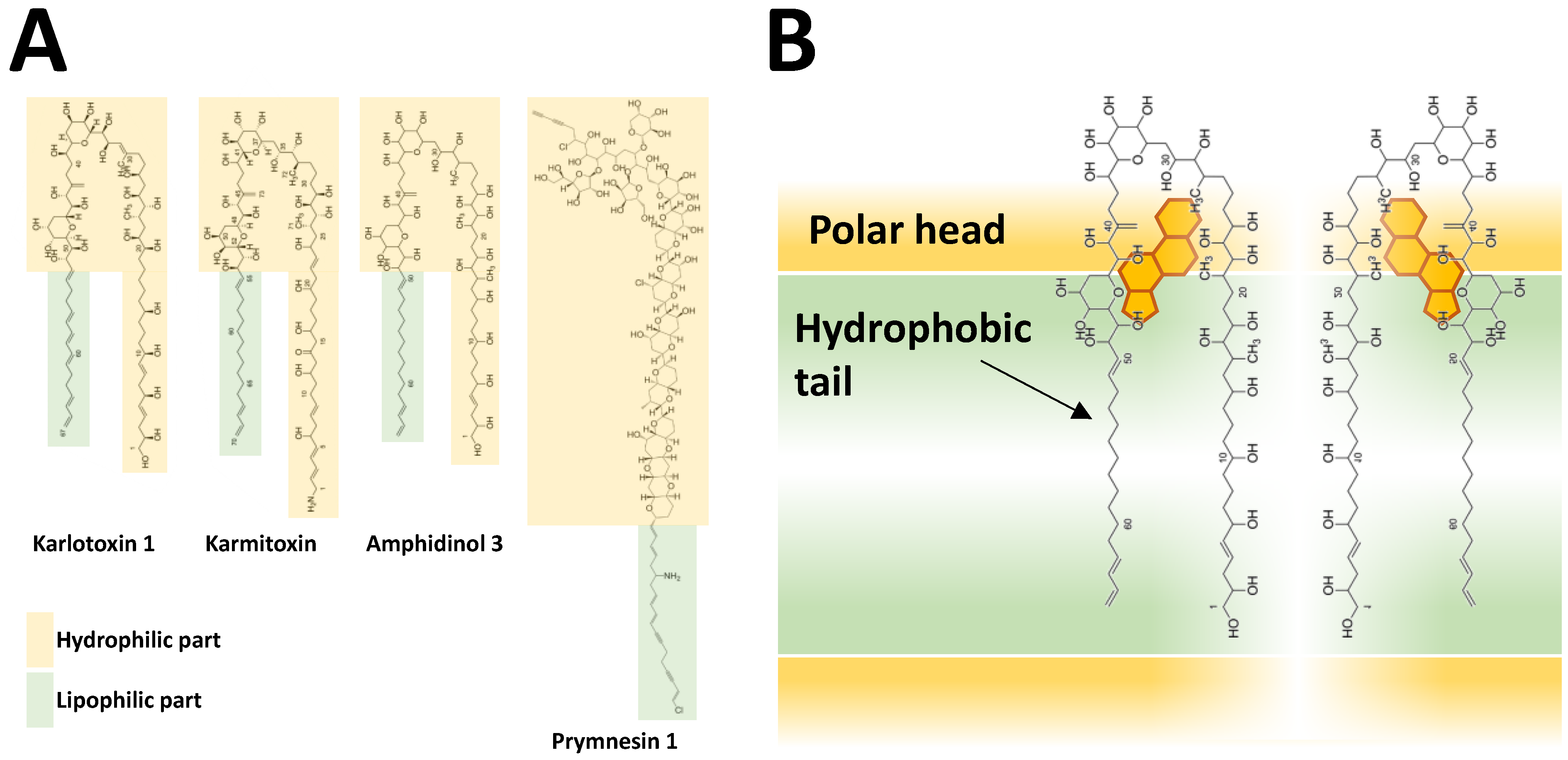
4. Synthesis
4.1. Ecological Role of BECs
Paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs) are well known and thoroughly described in terms of chemistry and toxicology; however, their ecological role remains to be fully understood [285]. While PSTs are potent neurotoxins to mammals and seabirds, it is unlikely that their ecological function is to block mammalian ion channels [286]. Therefore, these toxins were hypothesised to act as pheromones [287] or as grazing deterrents [286], with the latter hypothesis substantiated by experimental evidence with copepods. Toxic effects to mammals are likely only collateral damages as no significant and direct biological interactions exist between them.
The ecological role(s) of BECs of the genus Alexandrium are also difficult to evaluate, especially when considering the wide range of organisms affected. The present literature review clearly emphasised the fact that many Alexandrium species and strains, even without producing PSTs or the known toxins, exhibit various bioactivities. While it is unknown whether all effects on marine organisms are based on the same or on a variety of different compounds, the different bioactivities investigated in a few particular strains suggest that they might be related (Table 5). Even though BECs might give a competitive advantage to Alexandrium by decreasing the grazing pressure of shellfish and or other benthic filter-feeders, Alexandrium are plankton organisms and thus toxicity to bivalves and ichthyotoxicity may be interpreted as collateral damage from the planktonic chemical warfare.

Table 5.
Similarities in bioactivities from A. minutum and A. catenella strains [59,64,66,67,68,156,157]. The potency is indicated as low, +; moderate, ++; or high, +++. The − sign indicates that no activity was detected. The / sign indicates that the activity was not investigated.
The haziness around the chemical identity of BECs and their putative variety make it impossible to conclude on a main role. Allelochemicals are usually discussed in association with the competition for resources or to facilitate feeding, but they can also be involved in defence against pathogens or predators [186,191]. Allelochemicals of Alexandrium might explain how Alexandrium blooms persist for longer periods and can reach extreme densities [6,9]. Allelochemicals provide a competitive advantage to Alexandrium cells by inhibiting competitors and parasites, and by limiting predation and grazing. Allelochemical interactions might also be a strategy developed by various mixotrophic species to immobilise prey [206,288,289] thus enhancing their competitiveness.
Understanding the evolution of allelochemical production and the variation of this genotypic trait in genotypically diverse dinoflagellate populations is challenging. The production of BECs might first be seen as a private good benefiting only the producer. But above a cell concentration threshold, the private BECs might become a “public” good [290] and favour the whole community by decreasing grazing, competition, and parasitism. This intraspecific facilitation has already been experimentally evidenced, where the presence of BEC-producing cells was protecting non-lytic cells from the same species against grazers [164] or cells from another genus against parasitism [64]. Both the rapid dilution of extracellular compounds and the related effective cell density threshold have been raised as a limit to the public good [291], as sufficiently high abundances would only be observed under bloom conditions and allelochemical are thus unlikely to support bloom development. However, at micro-scales where cell interactions occur, phytoplankton can form dense patches with concentrations orders of magnitude higher than background [292,293,294,295].
4.2. Toward the Essential Identification of BECs
To better understand compound-specific cause/effect relationships it is necessary to evaluate the presence/absence of both the known toxins and unknown BECs before assessing the effect of an Alexandrium strain on other organisms. As long as the BECs metabolites are not identified, the bioassays previously described can be used to quantify the different bioactivities. Even though some BECs bioactivities may be linked to a single class of compounds, one single bioassay probably will not yield a sufficient proxy for the quantification of the different bioactivities. Studies performing simultaneous analyses of different bioactivities of several strains with standard bioassay (e.g., [268] for Prymnesium parvum) are needed to better disentangle the possible link between activities.
To fully understand the ecological roles of BECs and their putative ichthyotoxicity and toxicity to bivalves, it is essential to isolate, characterise, and assess the diversity, the compound-specific toxicity, and mode of action of BECs. With respect to structural characterisation, a broad variety of different suggestions on the chemical nature of BECs can be found in different studies, such as proteinaceous compounds, saccharides, fatty acids, polyketides, and reactive oxygen species (ROS). To shed more light on this confusion, it still has to be worked out if, and to what extent, different species of Alexandrium may indeed produce different BECs. From literature data this is sometimes difficult to evaluate, as species determinations of the studied Alexandrium strains are not always sufficiently and reliably documented. Moreover, the chemical nature of Alexandrium BECs has so far only been investigated on semi-purified extract, and for only four out of the 17 Alexandrium species for which BECs have been reported. Next to Alexandrium species specificity, inconsistencies in BECs type suggestions likely originate also from varying experimental protocols for sample treatments and compound purifications. Partially, these protocols follow bioassay-guided fractionation, whereas others follow natural chemistry approaches without any functional control or verification of toxicity. Furthermore, a plethora of different treatments between working groups has been used in these studies that result in different biases in each of them. These different methods include precipitation of culture medium by high pH and solvation of the precipitate, ultrafiltration with different cut-offs, or dialysis. Also, loss of some BECs due to stickiness and surface adsorption has not been considered by many studies.
Compilation of available information emphasises that the chemical nature of BECs of Alexandrium remains largely unknown at present: only alexandrolide has been structurally elucidated so far [184]. It is now necessary to determine naturally occurring alexandrolide abundances and study the activity and mode of action of this compound at environmentally relevant concentrations. If these experiments indicate ichthyotoxic or allelochemical effects, it will become interesting to screen other Alexandrium species for this or related compounds. In any case, alexandrolide does not seem to share the chemical properties evidenced for A. minutum and A. catenella allelochemicals.
In the past, full identification of A. minutum or A. catenella BECs was hampered by several constraints: (i) low yields of extraction and purification, (ii) possibly large molecule size and amphipathic nature, and (iii) complexity of the exometabolome (i.e., chemical noise).
The substantial losses of allelochemical potency during the purification process does not ease their identification. The allelochemicals of the genus Alexandrium are particularly prone to adsorption on plastics [194,239]. Pre-filtration of fractions is one more step that induces a substantial loss of compounds. Optimisation of the protocol (e.g., investigating different filters, limiting the number of filtration steps or substituting filtration by centrifugation) is necessary to minimise losses. This implies that standard techniques of natural product chemistry may not be adequate for large amphipathic compounds. In addition, chemical noise is a major barrier for the identification of BEC. While comparative metabolomic (between lytic and non-lytic strains) is a way to identify candidates, allelochemicals still have to be isolated for further characterisation. As allelochemicals are likely to be potent at low concentrations, their signal is likely below the chemical noise (detection limit) of the fraction. While there is no evidence for a bacterial origin of allelochemicals [58,162,164], exudates of bacteria also add complexity to the organic fraction. Using axenic cultures [296] and artificial seawater [254] could ease the purification process by decreasing fraction complexity. Moreover, culturing conditions could be optimised to increase BECs yield. An increase in allelochemical potency was reported upon exposure of A. minutum to toxic concentrations of copper and allelochemicals were hypothesised to be copper chelators [199]. It may be possible to take advantage of this potential feature to isolate allelochemicals using immobilised metal affinity chromatography. This technique is used for the isolation of proteins exhibiting affinity to metals [297,298] and may be relevant to isolate A. minutum allelochemicals. Overall, new and standardised purification techniques based on the unusual behaviour of BECs should be applied to isolate them and ease their characterisation.
5. Concluding Remarks
The toxic effects of unknown/uncharacterised BECs of Alexandrium have largely been described on a wide range of marine organisms. These compounds can induce lysis of protists but also of haemocytes of various animals and mammalian cell lines. Regarding their various ecological functions/roles (affecting competitor, grazers, and parasites) BECs are likely to play an essential role in the dynamic of Alexandrium blooms. Despite numerous attempts to characterise them, the chemical nature(s) of BECs remain(s) poorly known or uncertain. The best-described BECs are those from A. catenella and A. minutum with allelochemical activity. They comprise unknown large amphipathic compounds that presumably target cell membranes and induce cell lysis. One compound, alexandrolide, a putative microalgal-growth inhibitor is structurally identified, but its ecological relevance remains to be confirmed. This review highlights the need to further characterise and quantify the chemicals responsible for numerous extracellular bioactivities. Due to BECs’ unusual chemical behaviours, new purification techniques are required to isolate BECs before assessing their characterisation. While BECs might be a limited group of compounds with wide bioactive spectra, the genus Alexandrium comprises several species, therefore potential chemical differences between species should be considered. It is essential to properly identify and document Alexandrium species, as this may be a source of inconsistencies between studies. BECs might have effects on the outcome and conclusions of studies targeting interactions of Alexandrium spp. and other marine organisms (especially ichthyotoxic and mixotrophy related studies). When performing such experiments, extracellular bioactivities should always be characterised together with detection and quantification of other known toxins. Until the nature of BECs is elucidated, we recommend the use of standard bioassays to quantify the different bioactivities. Intercalibration between bioassays should also be performed to shed light on the link between the different bioactivities. Once their structure(s) have been elucidated, the effects of purified compounds, and mixtures of compounds, on other cells should be screened and characterised, not only for toxicology purposes but also for potential biotechnological applications (e.g., anti-cancer [172,176], antiviral, antibacterial, and antiparasitic applications).
Author Contributions
All authors participated equally in the conceptualization, writing, editing and reviewing of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received no external funding and was carried out with the financial support of the centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, the Région Bretagne, the University of Wollongong, IFREMER and the GDR Phycotox. This work was also funded by the Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Deutscher Forschungszentren through the research programme PACES II of the Alfred Wegener Institut—Helmholtz Zentrum für Polar- und Meeresforschung.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This idea for this review was initiated during Marc Long’s Ph.D. thesis, therefore the authors want to warmly thank the co-supervisors Hélène Hégaret, Dianne F. Jolley, Philippe Soudant, and Géraldine Sarthou for their contributory comments. The authors would also like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagoner, R.M.; Misner, I.; Tomas, C.R.; Wright, J.L.C. Occurrence of 12-methylgymnodimine in a spirolide-producing dinoflagellate Alexandrium peruvianum and the biogenetic implications. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 4243–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Wietkamp, S.; Beran, A. A Mediterranean Alexandrium taylorii (Dinophyceae) strain produces goniodomin A and lytic compounds but not paralytic shellfish toxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; John, U. Toxic effects of Alexandrium spp. on heterotrophic dinoflagellates: An allelochemical defence mechanism independent of PSP-toxin content. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 230, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D. Harmful algal species fact sheets: Alexandrium. In Harmful Algal Blooms: A Compendium Desk Reference; Shumway, S.E., Burkholder, J.M., Morton, S.L., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 563–574. ISBN 978-1-118-99465-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chapelle, A.; Le Gac, M.; Labry, C.; Siano, R.; Quere, J.; Caradec, F.; Le Bec, C.; Nezan, E.; Doner, A.; Gouriou, J. The Bay of Brest (France), a new risky site for toxic Alexandrium minutum blooms and PSP shellfish contamination. Harmful Algae News 2015, 51, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Guallar, C.; Bacher, C.; Chapelle, A. Global and local factors driving the phenology of Alexandrium minutum (Halim) blooms and its toxicity. Harmful Algae 2017, 67, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasiewicz, S.; Chapelle, A.; Bacher, C.; Soudant, D. Harmful algae niche responses to environmental and community variation along the French coast. Harmful Algae 2020, 93, 101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, E.; Bravo, I.; Vila, M.; Figueroa, R.I.; Masó, M.; Sampedro, N. Relationship between vegetative cells and cyst production during Alexandrium minutum bloom in Arenys de Mar harbour (NW Mediterranean). J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapelle, A.; Le Bec, C.; Le Gac, M.; Labry, C.; Amzil, Z.; Guillou, L.; Dreanno, C.; Klouch, K.; Siano, R.; Pineau, L.; et al. Étude sur la Prolifération de la Microalgue Alexandrium Minutum en Rade de Brest. Projet Daoulex. Rapport d’avancement n° 2: Analyse des Traces Biologiques d’Alexandrium Minutum dans les sédiments de la Rade de Brest. 2014. Available online: https://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00191/30231/ (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Carreto, J.I.; Benavides, H.R.; Negri, R.M.; Glorioso, P.D. Toxic red-tide in the Argentine Sea. phytoplankton distribution and survival of the toxic dinoflagellate Gonyaulax excavata in a frontal area. J. Plankton Res. 1986, 8, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M.; Steffensen, D.A.; Wetherbee, R. Three estuarine Australian dinoflagellates that can produce paralytic shellfish toxins. J. Plankton Res. 1988, 10, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, G.C.; Cembella, A.D.; Joyce, L.B.; Larsen, J.; Probyn, T.A.; Ruiz Sebastián, C. The dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum in Cape Town harbour (South Africa): Bloom characteristics, phylogenetic analysis and toxin composition. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, M.; Camp, J.; Garcés, E.; Masó, M.; Delgado, M. High resolution spatio-temporal detection of potentially harmful dinoflagellates in confined waters of the NW Mediterranean. J. Plankton Res. 2001, 23, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D. A Diversity of harmful algal blooms in coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.W.; Pettigrew, N.R.; Thomas, A.C. On the nature of Alexandrium fundyense blooms in the Gulf of Maine. Deep. Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2005, 52, 2603–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, G.; Díaz, P.A.; Godoy, M.; Araya, M.; Ganuza, I.; Pino, R.; Álvarez, F.; Rengel, J.; Hernández, C.; Uribe, E.; et al. Paralytic shellfish toxins in surf clams Mesodesma donacium during a large bloom of Alexandrium catenella dinoflagellates associated to an intense shellfish mass mortality. Toxins 2019, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, P.A.; Álvarez, G.; Varela, D.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Díaz, M.; Molinet, C.; Seguel, M.; Aguilera-Belmonte, A.; Guzmán, L.; Uribe, E.; et al. Impacts of harmful algal blooms on the aquaculture industry: Chile as a case study. Perspect. Phycol. 2019, 6, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattenrath, T.K.; Anderson, D.M.; Gobler, C.J. The influence of anthropogenic nitrogen loading and meteorological conditions on the dynamics and toxicity of Alexandrium fundyense blooms in a New York (USA) estuary. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, M.; Grazia, M.; Maso, M.; Gangemi, E.; Penna, A.; Sampedro, N.; Azzaro, F.; Camp, J.; Galluzzi, L. A comparative study on recurrent blooms of Alexandrium minutum in two Mediterranean coastal areas. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 673–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Kwon, J.E.; Kang, H.C.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Yoon, E.Y.; Kim, J.S. Mixotrophic ability of the phototrophic dinoflagellates Alexandrium andersonii, A. affine, and A. fraterculus. Harmful Algae 2016, 59, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.J.; Tillmann, U. Mixotrophy among dinoflagellates—Prey selection, physiology and ecological imporance. In Dinoflagellates: Classification, Evolution, Physiology and Ecological Significance; DV, S.R., Ed.; Nova Science: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 201–260. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.M. Physiology and bloom dynamics of toxic Alexandrium species, with emphasis on life cycle transitions. In Physiology and Ecology of Harmful Algal Bloom; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; NATO ASI Series; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; Volume G41, pp. 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Richlen, M.L.; Zielinski, O.; Holinde, L.; Tillmann, U.; Cembella, A.; Lyu, Y.; Anderson, D.M. Distribution of Alexandrium fundyense (Dinophyceae) cysts in Greenland and Iceland, with an emphasis on viability and growth in the Arctic. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 547, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillmann, U.; Bantle, A.; Krock, B.; Elbrächter, M.; Gottschling, M. Recommendations for epitypification of dinophytes exemplified by Lingulodinium polyedra and molecular phylogenetics of the Gonyaulacales based on curated rRNA sequence data. Harmful Algae 2021, 104, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, Y. Alexandrium minutum nov. g. nov. sp. dinoflagellé provocant des «eaux rouges». Vie Milieu 1960, 11, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, F.J.R.; Fukuyo, Y. The Neurotoxigenic Dinoflagellate Genus Alexandrium Halim: General Introduction. In Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen, O. Plankton investigations in the waters round Iceland in 1903. Medd. Komm. Havunders. Kobenhaven Ser. Plankt. 1904, 1, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lebour, M.V. The Dinoflagellates of Northern Seas; Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom: Plymouth, UK, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Whedon, W.F. Dinoflagellates of the San Francisco region. I. On the skeletal morphology of two new species, Gonyaulax catenella and G. acatenella. Univ. Calif. Publ. Zool. 1936, 41, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Loeblich, A.R., III; Loeblich, L.A. The systematics of Gonyaulax with special reference to the toxic species. In Toxic Dinoflagellate Blooms; Taylor, D.J., Seliger, H.H., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, F.J.R. The toxigenic gonyaulacoid dinoflagellates. In Toxic Dinoflagellate Blooms; Taylor, D.L., Seliger, H.H., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Balech, E. The genus Alexandrium or Gonyaulax of the tamarensis group. In Toxic Dinoflagellates; Anderson, D.W., White, A.W., Baden, D.G., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Balech, E. Redescription of Alexandrium minutum Halim (Dinophyceae) type species of the genus Alexandrium. Phycologia 1989, 28, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balech, E. The Genus Alexandrium Halim (Dinoflagellata); Sherkin Island Marine Station: Cork, Ireland, 1995; Volume 452. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, S.A.; Hoppenrath, M.; Orr, R.J.S.; Bolch, C.; John, U.; Diwan, R.; Yauwenas, R.; Harwood, T.; de Salas, M.; Neilan, B.; et al. Alexandrium diversaporum sp. nov., a new non-saxitoxin producing species: Phylogeny, morphology and sxtA genes. Harmful Algae 2014, 31, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.S.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.Y. Description of the new phototrophic dinoflagellate Alexandrium pohangense sp. nov. from Korean coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2015, 46, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, S.; Oliveira, M.M.M.; Salgueiro, F.; Vilar, M.C.P.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Menezes, M. Morphology and molecular phylogeny of a new PST-producing dinoflagellate species: Alexandrium fragae sp. nov. (Gonyaulacales, dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2020, 95, 101793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.; Nguyen, N.L. Potentially Toxic Microalgae of Vietnamese Waters; Council for Nordic Publications in Botany: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004; ISBN 8788702855. [Google Scholar]
- Montresor, M.; John, U.; Beran, A.; Medlin, L.K. Alexandrium tamutum sp. nov. (Dinophyceae): A new nontoxic species in the genus Alexandrium. J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Kuribara, Y.; Fukuzawa, R.; Mimura, K.; Funaki, H.; Tanaka, K.; Watanabe, R.; Uchida, H.; Suzuki, T.; Adachi, M. First report of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) associated with marine macroalgae off Japan: Diversity, distribution, and toxicity. Harmful Algae 2021, 104, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mertens, K.N.; Nézan, E.; Chomérat, N.; Bilien, G.; Iwataki, M.; Shin, H.H. Discovery of a new clade nested within the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae): Morpho-molecular characterization of Centrodinium punctatum (Cleve) F.J.R. Taylor. Protist 2019, 170, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.; Artigas, L.F. Redefinition of the dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium based on Centrodinium: Reinstatement of Gessnerium and Protogonyaulax, and Episemicolon gen. nov. (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae). J. Mar. Biol. 2019, 2019, 1284104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.H.; Li, Z.; Réveillon, D.; Rovillon, G.A.; Mertens, K.N.; Hess, P.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, D.; et al. Centrodinium punctatum (Dinophyceae) produces significant levels of saxitoxin and related analogs. Harmful Algae 2020, 100, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, K.N.; Adachi, M.; Anderson, D.M.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Bravo, I.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Bolch, C.J.S.; Calado, A.J.; Carbonell-Moore, M.C.; Chomérat, N.; et al. Morphological and phylogenetic data do not support the split of Alexandrium into four genera. Harmful Algae 2020, 98, 101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilly, E.L.; Halanych, K.M.; Anderson, D.M. Phylogeny, biogeography, and species boundaries within the Alexandrium minutum group. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, E.L.; Halanych, K.M.; Anderson, D.M. Species boundaries and global biogeography of the Alexandrium tamarense complex (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, U.; Litaker, R.W.; Montresor, M.; Murray, S.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Formal revision of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex (dinophyceae) taxonomy: The introduction of five species with emphasis on molecular-based (rDNA) classification. Protist 2014, 165, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Lin, S. DNA barcoding species in Alexandrium tamarense complex using ITS and proposing designation of five species. Harmful Algae 2014, 31, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholin, C.A.; Herzog, M.; Sogin, M.; Anderson, D.M. Identification of a group- and strain-specific genetic markers for globally distributed Alexandrium (dinophyceae). II. Sequence analysis of a fragment of the LSU rRNA gene. J. Phycol. 1994, 30, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Sampedro, N.; Larsen, J.; Moestrup, Ø.; Calado, A.J. Arguments against the proposal 2302 by John & al. to reject the name Gonyaulax catenella (Alexandrium catenella). Taxon 2015, 64, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Fraga, S.; Montresor, M.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Hoppenrath, M.; Murray, S.; Calado, A.J. A practical guide to new nomenclature for species within the “Alexandrium tamarense species complex”. Harmful Algae News 2018, 61, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. 2021. Available online: https://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- Hégaret, H.; Da Silva, P.M.; Wikfors, G.H.; Haberkorn, H.; Shumway, S.E.; Soudant, P. In Vitro interactions between several species of harmful algae and haemocytes of bivalve molluscs. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2011, 27, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, S.P.; Burkholder, J.A.M.; Shumway, S.E.; Hégaret, H.; Wikfors, G.H.; Frank, D. Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium monilatum on survival, grazing and behavioral response of three ecologically important bivalve molluscs. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, M.; Lair, S.; Michaud, S.; Scarratt, M.; Quilliam, M.; Lefaivre, D.; Robert, M.; Wotherspoon, A.; Michaud, R.; Ménard, N.; et al. Multispecies mass mortality of marine fauna linked to a toxic dinoflagellate bloom. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cembella, A.D.; Quilliam, M.A.; Lewis, N.I.; Bauder, A.G.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Thomas, K.; Jellett, J.; Cusack, R.R. The toxigenic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense as the probable cause of mortality of caged salmon in Nova Scotia. Harmful Algae 2002, 1, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Alpermann, T.; John, U.; Cembella, A. Allelochemical interactions and short-term effects of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium on selected photoautotrophic and heterotrophic protists. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Hansen, P.J. Allelopathic effects of Alexandrium tamarense on other algae: Evidence from mixed growth experiments. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Gobler, C.J. Allelopathic inhibition of competing phytoplankton by North American strains of the toxic dinoflagellate, Alexandrium fundyense: Evidence from field experiments, laboratory experiments, and bloom events. Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.S.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.H.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, K. Mixotrophy in the newly described dinoflagellate Alexandrium pohangense: A specialist for feeding on the fast-swimming ichthyotoxic dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Daugbjerg, N.; Hansen, P.J. Toxic mucus traps: A novel mechanism that mediates prey uptake in the mixotrophic dinoflagellate Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax. Harmful Algae 2012, 17, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Lim, A.S.; Rho, J.R.; Lee, S.B. Killing potential protist predators as a survival strategy of the newly described dinoflagellate Alexandrium pohangense. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.; Marie, D.; Szymczak, J.; Toullec, J.; Bigeard, E.; Sourisseau, M.; Le Gac, M.; Guillou, L.; Jauzein, C. Dinophyceae can use exudates as weapons against the parasite Amoebophrya sp. (Syndiniales). ISME Commun. 2021, 1, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Hansen, P.; Nielsen, L.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Kiørboe, T. Distinctly different behavioral responses of a copepod, Temora longicornis, to different strains of toxic dinoflagellates, Alexandrium spp. Harmful Algae 2016, 62, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, V.A.; Langeloh, H.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Müller, A.; Bickmeyer, U.; Abele, D. Separate and combined effects of neurotoxic and lytic compounds of Alexandrium strains on Mytilus edulis feeding activity and hemocyte function. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcier, E.; Morvezen, R.; Boudry, P.; Miner, P.; Charrier, G.; Laroche, J.; Hegaret, H. Effects of bioactive extracellular compounds and paralytic shellfish toxins produced by Alexandrium minutum on growth and behaviour of juvenile great scallops Pecten maximus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 184, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrec, J.; Soudant, P.; Payton, L.; Tran, D.; Miner, P.; Lambert, C.; Goïc, N.L.; Huvet, A.; Quillien, V.; Boullot, F.; et al. Bioactive extracellular compounds produced by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum are highly detrimental for oysters. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 199, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrec, J.; Hégaret, H.; Alunno-Bruscia, M.; Picard, M.; Soudant, P.; Petton, B.; Boulais, M.; Suquet, M.; Quéau, I.; Ratiskol, D.; et al. The dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum affects development of the oyster Crassostrea gigas, through parental or direct exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrec, J.; Hégaret, H.; Huber, M.; Le Grand, J.; Huvet, A.; Tallec, K.; Boulais, M.; Soudant, P.; Fabioux, C. The toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum impairs the performance of oyster embryos and larvae. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrec, J.; Fabioux, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Boulais, M.; Soudant, P.; Hégaret, H. The toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum affects oyster gamete health and fertilization potential. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 169, 105401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, V.A.; Bickmeyer, U.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Müller, A.; Abele, D. In Vitro effects of paralytic shellfish toxins and lytic extracellular compounds produced by Alexandrium strains on hemocyte integrity and function in Mytilus edulis. Toxins 2021, 13, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, J.I.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Nichols, P.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Fish gill damage by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella from Chilean fjords: Synergistic action of ROS and PUFA. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Shumway, S.E. Paralytic shellfish toxins in bivalve molluscs: Occurrence, transfer kinetics, and biotransformation. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1998, 6, 315–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gigirey, B.; Soliño, L.; Bravo, I.; Rodríguez, F.; Casero, M.V.M. Paralytic and amnesic shellfish toxins impacts on seabirds, analyses and management. Toxins 2021, 13, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Quakenbush, L.; Frame, E.; Huntington, K.B.; Sheffield, G.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Bryan, A.; Kendrick, P.; Ziel, H.; Goldstein, T.; et al. Prevalence of algal toxins in Alaskan marine mammals foraging in a changing arctic and subarctic environment. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, H.; Meyer, K.F. Paralytic Shell-Fish Poisoning. Arch. Pathol. 1937, 24, 560–598. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.W. Seafood Toxins; Ragelis, E., Ed.; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; pp. 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chou, H.N. Ichthyotoxicity studies of milkfish Chanos chanos fingerlings exposed to a harmful dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2001, 262, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, D.F.; Da Silva, P.M.; Barracco, M.A.; Soudant, P.; Hégaret, H. Effects of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum and its toxin (saxitoxin) on the functional activity and gene expression of Crassostrea gigas hemocytes. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.A.; Andersen, R.J.; Harrison, P.J. Feeding deterrent and toxicity effects of apo-fucoxanthinoids and phycotoxins on a marine copepod (Tigriopus californicus). Mar. Biol. 1997, 128, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhan, J.; Liu, L.; Gong, Y. Transcriptomic responses of Artemia salina exposed to an environmentally relevant dose of Alexandrium minutum cells or Gonyautoxin 2/3. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stivala, C.E.; Benoit, E.; Aráoz, R.; Servent, D.; Novikov, A.; Molgó, J.; Zakarian, A. Synthesis and biology of cyclic imine toxins, an emerging class of potent, globally distributed marine toxins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 411–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Curtis, J.M.; Oshima, Y.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Watson-Wright, W.M.; Wright, J.L.C. Spirolides B and D, two novel macrocycles isolated from the digestive glands of shellfish. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 97, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Moestrup, Ø. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii: Paralytic shellfish toxin concentration, composition, and toxicity to a tintinnid ciliate. J. Phycol. 1992, 28, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Burton, I.W.; Cembella, A.D.; Curtis, J.M.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Characterization of Spirolides A, C, and 13-Desmethyl C, New Marine Toxins Isolated from Toxic Plankton and Contaminated Shellfish. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, H.; Tillmann, U.; Harju, K.; Aversano, C.D.; Tartaglione, L.; Krock, B. Toxin variability estimations of 68 Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains from the Netherlands reveal a novel abundant gymnodimine. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieva, J.A.; Tebben, J.; Tillmann, U.; Wohlrab, S. Mass spectrometry-based characterization of new spirolides from Alexandrium ostenfeldii. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurhelle, C.; Nieva, J.; Tillmann, U.; Harder, T.; Krock, B.; Tebben, J. Identification of novel gymnodimines and spirolides from the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, J.; Mackinnon, S.L.; Leblanc, P.; Walter, J.A.; Hovgaard, P.; Aune, T.; Quilliam, M.A. Detection and identification of spirolides in Norwegian shellfish and plankton. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Magno, S.; Tartaglione, L.; Cangini, M.; Pompei, M.; Guerrini, F.; Boni, L.; Pistocchi, R. Toxin profile of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) from the Northern Adriatic Sea revealed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2006, 47, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackinnon, S.L.; Walter, J.A.; Quilliam, M.A.; Cembella, A.D.; Leblanc, P.; Burton, I.W.; Hardstaff, W.R.; Lewis, N.I. Spirolides isolated from Danish strains of the toxigenic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, J.S.; Leblanc, P.; Lewis, N.I.; Munday, R.; Quilliam, M.A.; Mackinnon, S.L. Characterization of a dispiroketal spirolide subclass from Alexandrium ostenfeldii. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Iacovo, E.D.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Grauso, L.; Tartaglione, L.; Guerrini, F.; Pezzolesi, L.; Pistocchi, R. Characterization of 27-hydroxy-13-desmethyl spirolide C and 27-oxo-13,19-didesmethyl spirolide C. Further insights into the complex Adriatic Alexandrium ostenfeldii toxin profile. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Kremp, A.; Tahvanainen, P.; Krock, B. Characterization of spirolide producing Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) from the western Arctic. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinder, V.A.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Delgado, A.L.; Krohn, T.; Garzón Cardona, J.E.; Metfies, K.; López Abbate, C.; Silva, R.; Lara, R. Plankton multiproxy analyses in the northern Patagonian shelf, Argentina: Community structure, phycotoxins, and characterization of toxic Alexandrium strains. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Rafuse, C.; Lewis, N.I.; Li, A.; Meng, F.; Beach, D.G.; McCarron, P. Screening of cyclic imine and paralytic shellfish toxins in isolates of the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) from Atlantic Canada. Harmful Algae 2018, 77, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Satake, M.; Mackenzie, L.; Kaspar, H.F.; Yasumoto, T. Gymnodimine, a new marine toxin of unprecedented structure isolated from New Zealand oysters and the dinoflagellate, Gymnodinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 7093–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Satake, M.; MacKenzie, L.; Kaspar, H.F.; Yasumoto, T. Gymnodimine, A novel toxic imine isolated from the Foveaux Strait oysters and Gymnodinium sp. In Harmful Toxic Algal Bloom; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 1996; pp. 495–498. [Google Scholar]
- Harju, K.; Koskela, H.; Kremp, A.; Suikkanen, S.; de la Iglesia, P.; Miles, C.O.; Krock, B.; Vanninen, P. Identification of gymnodimine D and presence of gymnodimine variants in the dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii from the Baltic Sea. Toxicon 2016, 112, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R.; Selwood, A.I.; Rhodes, L. Acute toxicity of pinnatoxins E, F and G to mice. Toxicon 2012, 60, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Alfonso, A.; Rodríguez, P.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Manuel, J.; Bermúdez, R.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Pharmacokinetic and toxicological data of spirolides after oral and intraperitoneal administration. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, Y.; Radic, Z.; Aráoz, R.; Talley, T.T.; Benoit, E.; Servent, D.; Taylor, P.; Molgó, J.; Marchot, P. Structural determinants in phycotoxins and AChBP conferring high affinity binding and nicotinic AChR antagonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6076–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, T.A.; Hepler, C.D.; Kombo, D.C.; Grinevich, V.P.; Kiser, M.N.; Hooker, D.N.; Zhang, J.; Mountfort, D.; Selwood, A.; Akireddy, S.R.; et al. Comparison of acetylcholine receptor interactions of the marine toxins, 13-desmethylspirolide C and gymnodimine. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2238–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrat, R.; Servent, D.; Girard, E.; Ouanounou, G.; Amar, M.; Marrouchi, R.; Benoit, E.; Molgó, J. The marine phycotoxin gymnodimine targets muscular and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes with high affinity. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aráoz, R.; Ouanounou, G.; Iorga, B.I.; Alili, D.; Amar, M.; Benoit, E.; Molgo, J.; Servent, D.; Paris-saclay, I.N.; Yvette, G.; et al. The neurotoxic effect of 13, 19-didesmethyl and 13-desmethyl spirolide C phycotoxins is mainly mediated by nicotinic rather than muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 147, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieva, J.A.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Tebben, J.; Zurhelle, C. Gymnodimine A and 13-desMethyl spirolide C alter intracellular calcium levels via acetylcholine receptors. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Fukuyo, Y.; Tokuda, H.; Hirano, R. Sexual reproduction of Alexandrium hiranoi (Dinophyceae). Bull. Plankt. Soc. Jpn. 1993, 39, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.M.; Michaels, L.; Burkholder, P.R. Goniodomin, a new antibiotic from a dinoflagellate. J. Antibiot. 1968, 21, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Makabe, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Konosu, S.; Wälchli, M.R. Goniodomin A, a novel polyether macrolide from the dinoflagellate Goniodoma pseudogoniaulax. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988, 29, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.M.; Reece, K.S.; Stec, D.F.; Scott, G.P.; Jones, W.M.; Hobbs, P.L.M.; Harris, T.M. The toxin goniodomin, produced by Alexandrium spp., is identical to goniodomin A. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, M.H.; Morton, S.L.; Smith, L.L.; Beauchesne, K.R.; Huncik, K.M.; Moeller, P.D.R. Production of goniodomin A by the planktonic, chain-forming dinoflagellate Alexandrium monilatum (Howell) Balech isolated from the Gulf Coast of the United States. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triki, H.Z.; Laabir, M.; Moeller, P.; Chomérat, N.; Daly-Yahia, O.K. First report of goniodomin A production by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax developing in southern Mediterranean (Bizerte Lagoon, Tunisia). Toxicon 2016, 111, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y. Stereochemical Assignment of Goniodomin A, an Actin-Targeting Polyether Macrolide. Ph.D. Thesis, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, M.; Inoue, D.; Matsunaga, K.; Ohizumi, Y.; Ueda, H.; Asano, T.; Murakami, M.; Sato, Y. Goniodomin A, an antifungal polyether macrolide, exhibits antiangiogenic activities via inhibition of actin reorganization in endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 116, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.M.; Mann, R.; Moeller, P.; Hsia, M.S. Mortality of the veined rapa whelk, Rapana Venosa, in relation to a bloom of Alexandrium monilatum in the York River, United States. J. Shellfish Res. 2009, 28, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espiña, B.; Cagide, E.; Louzao, M.C.; Vilariño, N.; Vieytes, M.R.; Takeda, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Botana, L.M. Cytotoxicity of goniodomin A and B in non contractile cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 251, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tainter, C.J.; Schley, N.D.; Harris, C.M.; Stec, D.F.; Song, A.K.; Balinski, A.; May, J.C.; Mclean, J.A.; Reece, K.S.; Harris, T.M. Algal toxin goniodomin A binds potassium ion selectively to yield a conformationally altered complex with potential biological consequences. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hae, J.J.; Jae, Y.P.; Jae, H.N.; Myung, O.P.; Jeong, H.H.; Kyeong, A.S.; Jeng, C.; Chi, N.S.; Kwang, Y.L.; Won, H.Y. Feeding by red-tide dinoflagellates on the cyanobacterium Synechococcus. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 41, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Bædkel, T.D.; Tillmann, U.; Hansen, P.J. A search for mixotrophy and mucus trap production in Alexandrium spp. and the dynamics of mucus trap formation in Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax. Harmful Algae 2017, 64, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.S.; Jeong, H.J.; Ok, J.H. Five Alexandrium species lacking mixotrophic ability. Algae 2019, 34, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, D.M.; Anderson, D.M. Widespread phagocytosis of ciliates and other protists by marine mixotrophic and heterotrophic thecate dinoflagellates. J. Phycol. 1996, 32, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Yoo, Y.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, N.S.; Song, J.Y.; Shin, W.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, K. Feeding by phototrophic red-tide dinoflagellates on the ubiquitous marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2009, 56, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, R.J.S.; Stüken, A.; Rundberget, T.; Eikrem, W.; Jakobsen, K.S. Improved phylogenetic resolution of toxic and non-toxic Alexandrium strains using a concatenated rDNA approach. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Ngoc, L. An autecological study of the potentially toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium affine isolated from Vietnamese waters. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Montresor, M. Saxitoxin and neosaxitoxin as toxic principles of Alexandrium andersoni (Dinophyceae) from the Gulf of Naples, Italy. Toxicon 2000, 38, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzet, N.; Franco, J.M.; Raine, R. Morphogenetic diversity and biotoxin composition of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) in Irish coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zeng, N.; Liu, T.; Yang, W.; Müller, A.; Krock, B. Morphology, toxicity, and phylogeny of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species along the coast of China. Harmful Algae 2013, 27, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savela, H.; Harju, K.; Spoof, L.; Lindehoff, E.; Meriluoto, J.; Vehniäinen, M.; Kremp, A. Quantity of the dinoflagellate sxtA4 gene and cell density correlates with paralytic shellfish toxin production in Alexandrium ostenfeldii blooms. Harmful Algae 2016, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.A.; Wiese, M.; Neilan, B.A.; Orr, R.J.S.; de Salas, M.; Brett, S.; Hallegraeff, G. A reinvestigation of saxitoxin production and sxtA in the “non-toxic” Alexandrium tamarense Group V clade. Harmful Algae 2012, 18, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, C.J.S.; de Salas, M.F. A review of the molecular evidence for ballast water introduction of the toxic dinoflagellates Gymnodinium catenatum and the Alexandrium “tamarensis complex” to Australasia. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M.; Bolch, C.; Blackburn, S.I.; Oshima, Y. Species of the toxigenic dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium in southeastern Australian waters. Bot. Mar. 1991, 34, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.E.; Park, G.; Dam, H.G. Relative importance of nitrogen sources, algal alarm cues and grazer exposure to toxin production of the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Harmful Algae 2019, 84, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) as the causative organism of spirolide shellfish toxins. Phycologia 2000, 8884, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, L.; De Salas, M.; Adamson, J.; Beuzenberg, V. The dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium (Halim) in New Zealand coastal waters: Comparative morphology, toxicity and molecular genetics. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.J.; Kim, C.H.; Sako, Y. Paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin analysis of the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) occurring in Korean coastal waters. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaga, S.; Sekiguchi, K.; Yoshida, M.; Ogata, T. Occurrence and toxin production of Alexandrium spp. (Dinophyceae) in coastal waters of Iwate Prefecture, Japan. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 2006, 72, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gires, U.; Leaw, C.P.; Asmat, A.; Lim, P.T. Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species in Malaysian waters. Harmful Algae 2002, 1, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Perini, F.; Galluzzi, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Iacovo, E.D.; Tartaglione, L.; Ricci, F.; Forino, M.; Ciminiello, P.; Penna, A. SxtA and sxtG gene expression and toxin production in the mediterranean Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae). Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5258–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffroy, S.; Lechat, M.M.; Le Gac, M.; Rovillon, G.A.; Marie, D.; Bigeard, E.; Malo, F.; Amzil, Z.; Guillou, L.; Caruana, A.M.N. From the sxtA4 gene to saxitoxin production: What controls the variability among Alexandrium minutum and Alexandrium pacificum strains? Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Bresnan, E.; Graham, J.; Lacaze, J.P.; Turrell, E.; Collins, C. Distribution, diversity and toxin composition of the genus Alexandrium (dinophyceae) in Scottish waters. Eur. J. Phycol. 2010, 45, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzet, N.; Franco, J.M.; Raine, R. Characterization of nontoxic and toxin-producing strains of Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae) in Irish coastal waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3333–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemons, G.P.; Pinion, J.P.; Bass, E.; Pham, D.V.; Sharif, M.; Wutoh, J.G. A hemolytic principle associated with the red-tide dinoflagellate Gonyaulax monilata. Toxicon 1980, 18, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemons, G.P.; Pham, D.V.; Pinion, J.P. Insecticidal activity of Gonyaulax (dinophyceae) cell powders and saxitoxin to the german cockroach. J. Phycol. 1980, 16, 305–307. [Google Scholar]
- Suikkanen, S.; Kremp, A.; Hautala, H.; Krock, B. Paralytic shellfish toxins or spirolides? The role of environmental and genetic factors in toxin production of the Alexandrium ostenfeldii complex. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Franco, J.M.; Bravo, I. Differences in the toxin profiles of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains isolated from different geographic origins: Evidence of paralytic toxin, spirolide, and gymnodimine. Toxicon 2015, 103, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Wen, Y.; Hansen, P.J.; Larsen, T.O.; Andersen, A.J.C. Development of a LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of goniodomins A and B and its application to Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax strains and plankton field samples of Danish coastal waters. Toxicon 2018, 155, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugliè, A.; Giacobbe, M.G.; Riccardi, E.; Bruno, M.; Pigozzi, S.; Mariani, M.A.; Satta, C.T.; Stacca, D.; Bazzoni, A.M.; Caddeo, T.; et al. Paralytic shellfish toxins and cyanotoxins in the Mediterranean: New data from sardinia and Sicily (Italy). Microorganisms 2017, 5, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hii, K.S.; Lim, P.T.; Tan, T.H.; Leaw, C.P. Characterization of the Saxitoxin Biosynthetic Starting Gene, sxta in the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamiyavanichii. In Proceedings of the 12th Symposium of the Malaysian Society of Applied Biology: Solutions to Global Challenges and Issues, Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia, 1–3 June 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, M.; Varela, D.; De Oliveira Proença, L.A.; Da Silva Tamanaha, M.; Paredes, J. Identification of the toxic alga Alexandrium tamiyavanichi (dinophyceae) from Northeastern Brazil: A combined morphological and rDNA sequence (partial lsu and its) approach. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.T.; Ogata, T. Salinity effect on growth and toxin production of four tropical Alexandrium species (Dinophyceae). Toxicon 2005, 45, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.T.; Leaw, C.P.; Usup, G.; Kobiyama, A.; Koike, K.; Ogata, T. Effects of light and temperature on growth, nitrate uptake, and toxin production of two tropical dinoflagellates: Alexandrium tamiyavanichii and Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A. Bioactive compounds of marine dinoflagellate isolates from western Greenland and their phylogenetic association within the genus Alexandrium. Harmful Algae 2016, 51, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremp, A.; Hansen, P.J.; Tillmann, U.; Savela, H.; Suikkanen, S.; Voß, D.; Barrera, F.; Jakobsen, H.H.; Krock, B. Distributions of three Alexandrium species and their toxins across a salinity gradient suggest an increasing impact of GDA producing A. pseudogonyaulax in shallow brackish waters of Northern Europe. Harmful Algae 2019, 87, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.T.; Usup, G.; Leaw, C.P.; Ogata, T. First report of Alexandrium taylori and Alexandrium peruvianum (Dinophyceae) in Malaysia waters. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Tallec, K.; Soudant, P.; Lambert, C.; Le Grand, F.; Sarthou, G.; Jolley, D.; Hégaret, H. A rapid quantitative fluorescence-based bioassay to study allelochemical interactions from Alexandrium minutum. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzul, G.; Seguel, M.; Guzman, L.; Denn, E.E. Comparison of allelopathic properties in 3 toxic Alexandrium species. J. Exp. Bot. 1999, 232, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Alpermann, T.L.; da Purificação, R.C.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A. Intra-population clonal variability in allelochemical potency of the toxigenic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpermann, T.J.; Tillmann, U.; Beszteri, B.; Cembella, A.D.; John, U. Phenotypic variation and genotypic diversity in a planktonic population of the toxigenic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Tillmann, U.; Martens, H.; Krock, B.; van Scheppingen, Y.; John, U. Characterization of multiple isolates from an Alexandrium ostenfeldii bloom in The Netherlands. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, K.M. Intraspecific trait variation and trade-offs within and across populations of a toxic dinoflagellate. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fistarol, G.O.; Legrand, C.; Selander, E.; Hummert, C.; Stolte, W.; Granéli, E. Allelopathy in Alexandrium spp.: Effect on a natural plankton community and on algal monocultures. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 35, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; John, U.; Cembella, A. On the allelochemical potency of the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii against heterotrophic and autotrophic protists. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, U.; Tillmann, U.; Hulskotter, J.; Alpermann, T.J.; Wohlrab, S.; Van de Waal, D.B. Intraspecific facilitation by allelochemical mediated grazing protection within a toxigenic dinoflagellate population. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20141268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelong, A.; Haberkorn, H.; Le Goïc, N.; Hégaret, H.; Soudant, P. A new insight into allelopathic effects of Alexandrium minutum on photosynthesis and respiration of the diatom Chaetoceros neogracile revealed by photosynthetic-performance analysis and flow cytometry. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Tillmann, U. Nutrient starvation effects on the allelochemical potency of Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae). Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Markussen, B.; Daugbjerg, N.; Krock, B.; Norlin, A.; Hansen, P.J. The cost of toxicity in microalgae: Direct evidence from the dinoflagellate Alexandrium. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Hansen, P.J. The loss of mixotrophy in Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax: Implications for trade-offs between toxicity, mucus trap production, and phagotrophy. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basti, L.; Nagai, S.; Go, J.; Okano, S.; Nagai, K.; Watanabe, R.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, Y. Differential inimical effects of Alexandrium spp. and Karenia spp. on cleavage, hatching, and two larval stages of Japanese pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii. Harmful Algae 2015, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, N.; Nam, S.-E.; Shin, Y.K.; Rhee, J.-S. The dinoflagellate Alexandrium affine acutely induces significant modulations on innate immunity, hepatic function, and antioxidant defense system in the gill and liver tissues of red seabream. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 240, 105985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro, N.; Franco, J.M.; Zapata, M.; Riobó, P.; Garcés, E.; Penna, A.; Caillaud, A.; Diogène, J.; Cacho, E.; Camp, J. The toxicity and intraspecific variability of Alexandrium andersonii Balech. Harmful Algae 2013, 25, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, C.; Nuzzo, G.; Galasso, C.; Casotti, R.; Fontana, A.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium andersoni induces cell death in lung and colorectal tumor cell lines. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschbach, E.; Scharsack, J.P.; John, U.; Medlin, L.K. Improved erythrocyte lysis assay in microtitre plates for senstiive detection and efficient measurement of haemolytic compounds from ichthyotoxic algae. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2001, 21, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Z.; Kong, L.; Holmes, M.J. Dinoflagellate Alexandrium leei (Dinophyceae) from Singapore coastal waters produces a water-soluble ichthyotoxin. Mar. Biol. 2007, 150, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhl, A.R.; Martins, C.A.; Anderson, D.M. Toxicity of Alexandrium lusitanicum to gastropod larvae is not caused by paralytic-shellfish-poisoning toxins. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasso, C.; Nuzzo, G.; Brunet, C.; Ianora, A.; Sardo, A.; Fontana, A.; Sansone, C. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum activates a mitophagic pathway in human lung cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, D.V.; Ray, S.M.; Wilson, W.B. Gonyaulax monilata: Population growth and development of toxicity in cultures. J. Protozool. 1967, 14, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassudrie, M.; Soudant, P.; Nicolas, J.L.; Fabioux, C.; Lambert, C.; Miner, P.; Le Grand, J.; Petton, B.; Hégaret, H. Interaction between toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella exposure and disease associated with herpesvirus OsHV-1μVar in Pacific oyster spat Crassostrea gigas. Harmful Algae 2015, 45, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianora, A.; Turner, J.T.; Esposito, F.; Carotenuto, Y.; D’Ippolito, G.; Romano, G.; Fontana, A.; Guisande, C.; Miralto, A. Copepod egg production and hatching success is reduced by maternal diets of a non-neurotoxic strain of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 280, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emura, A.; Matsuyama, Y.; Oda, T. Evidence for the production of a novel proteinaceous hemolytic exotoxin by dinoflagellate Alexandrium taylori. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Fujita, M.; Kawano, S.; Baba, T. Effect of salinity on interspecific competition between the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella and the raphidophyte Heterosigma akashiwo. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 81, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Katsuo, D.; Nakayasu, S.; Salati, C.; Duan, J.; Zou, Y.; Matsuyama, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Oda, T. Purification and characterization of a novel high molecular weight exotoxin produced by red tide phytoplankton Alexandrium tamarense. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2008, 22, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satake, M.; Honma, D.; Watanabe, R.; Oshima, Y. Alexandrolide, a diatom growth inhibitor isolated from the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Allelopathy Society. Available online: https://allelopathy-society.osupytheas.fr/about/ (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- Chan, A.T.; Andersen, R.J.; Le Blanc, M.J.; Harrison, P.J. Algal plating as a tool for investigating allelopathy among marine microalgae. Mar. Biol. 1980, 59, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, C.; Rengefors, K.; Fistarol, G.O.; Granéli, E. Allelopathy in phytoplankton—Biochemical, ecological and evolutionary aspects. Phycologia 2003, 42, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, E.M.; Legrand, C.; Rengefors, K.; Tillmann, U. Allelochemical interactions among aquatic primary producers. In Chemical Ecology in Aquatic Systems; Brönmark, C., Hansson, L.A., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 196–209. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, K.J.; Stoecker, D.K.; Mitra, A.; Raven, J.A.; Glibert, P.M.; Hansen, P.J.; Granéli, E.; Burkholder, J.M. Misuse of the phytoplankton-zooplankton dichotomy: The need to assign organisms as mixotrophs within plankton functional types. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, K.J.; Mitra, A.; Anestis, K.; Anschütz, A.A.; Calbet, A.; Ferreira, G.D.; Gypens, N.; Hansen, P.J.; John, U.; Martin, J.L.; et al. Mixotrophic protists and a new paradigm for marine ecology: Where does plankton research go now? J. Plankton Res. 2019, 41, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R.X.; Hogan, S.; Poulson-ellestad, K.L.; Brown, E. Karenia brevis allelopathy compromises the lipidome, membrane integrity, and photosynthesis of competitors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granéli, E.; Hansen, P.J. Allelopathy in Harmful Algae: A mechanism to compete for resources. In Ecology of Harmful Algae; Granéli, E., Turner, J.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 189–201. [Google Scholar]
- Chambouvet, A.; Morin, P.; Marie, D.; Guillou, L. Control of toxic marine dinoflagellate blooms by serial parasitic killers. Science 2008, 322, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissbach, A.; Tillmann, U.; Legrand, C. Allelopathic potential of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense on marine microbial communities. Harmful Algae 2010, 10, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Cembella, A. Preliminary characterization of extracellular allelochemicals of the toxic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense using a Rhodomonas salina bioassay. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 497–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-W.; Li, D.-W.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, J.-J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W.-D.; Liu, J.-S.; Lu, S.-H.; Li, H.-Y. Molecular exploration of algal interaction between the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum and the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Algal Res. 2016, 17, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.R.; Kubanek, J. Harmful alga trades off growth and toxicity in response to cues from dead phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, E.; Thor, P.; Toth, G.; Pavia, H. Copepods induce paralytic shellfish toxin production in marine dinoflagellates. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, H.; Van de Waal, D.B.; Brandenburg, K.M.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U. Salinity effects on growth and toxin production in Alexandrium ostenfeldii from The Netherlands. J. Plankton Res. 2016, 38, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Holland, A.; Planquette, H.; González Santana, D.; Whitby, H.; Soudant, P.; Sarthou, G.; Hégaret, H.; Jolley, D.F. Effects of copper on the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum and its allelochemical potency. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 210, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyczkowski, E.R.; Karp-Boss, L. Allelopathic effects of Alexandrium fundyense (Dinophyceae) on Thalassiosira cf. gravida (Bacillariophyceae): A matter of size. J. Phycol. 2014, 50, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.J. The red tide dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense: Effects on behaviour and growth of a tintinnid ciliate. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 53, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Bickmeyer, U.; Graeve, M.; Cembella, A. Mode of action of membrane-disruptive lytic compounds from the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Toxicon 2011, 58, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.; Tallec, K.; Soudant, P.; Le Grand, F.; Donval, A.; Lambert, C.; Sarthou, G.; Jolley, D.F.; Hégaret, H. Allelochemicals from Alexandrium minutum induce rapid inhibition and modify the membranes from Chaetoceros muelleri. Algal Res. 2018, 35, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Peltekis, A.; González-Fernández, C.; Hégaret, H.; Bailleul, B. Allelochemicals of Alexandrium minutum: Kinetics of membrane disruption and photosynthesis inhibition in a co-occurring diatom. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thingstad, T.F.; Havskum, H.; Garde, K.; Riemann, B. On the strategy of "eating your competitor": A mathematical analysis of algal mixotrophy. Ecology 1996, 77, 2108–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecker, D.; Tillmann, U.; Graneli, E. Phagotrophy in harmful algae. In Ecology of Harmful Algae; Granéli, E., Turner, J.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, H.S.; Wikfors, G.H.; Dam, H.G. Reactive oxygen species are linked to the toxicity of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium spp. to protists. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 66, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulco, V.K. Harmful effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense on the tintinnids Favella taraikaensis and Eutintinnus sp. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2007, 87, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Cho, H.J.; Jacobson, D.M. Observations of the feeding behavior and growth rates of the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Polykrikos kofoidii (Polykrikaceae, Dinophyceae). Phycologia 2000, 39, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.C.; Jin Jeong, H.; So Jin, K.; You, J.H.; Hee Ok, J. Differential feeding by common heterotrophic protists on 12 different Alexandrium species. Harmful Algae 2018, 78, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; John, U.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A. Allelopathic effects of bioactive compounds produced by harmful algae. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2006; Moestrup, O., Doucette, G., Enevoldsen, H., Godhe, A., Hallegraeff, G., Luckas, B., Lundholm, N., Lewis, J., Rengefors, K., Sellner, K., Eds.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; pp. 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lasley-Rasher, R.S.; Nagel, K.; Angra, A.; Yen, J. Intoxicated copepods: Ingesting toxic phytoplankton leads to risky behaviour. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncalli, V.; Turner, J.T.; Kulis, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Lenz, P.H. The effect of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense on the fitness of the calanoid copepod Calanus finmarchicus. Harmful Algae 2016, 51, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergkvist, J.; Selander, E. Induction of toxin production in dinoflagellates: The grazer makes a difference. Oecologia 2008, 156, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selander, E.; Kubanek, J.; Hamberg, M.; Andersson, M.X.; Cervin, G.; Pavia, H. Predator lipids induce paralytic shellfish toxins in bloom-forming algae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6395–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, E.; Fagerberg, T.; Wohlrab, S.; Pavia, H. Fight and flight in dinoflagellates? Kinetics of simultaneous grazer-induced responses in Alexandrium tamarense. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, S.P.; Dam, H.G. Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense on the copepod Acartia hudsonica: A test of the mechanisms that reduce ingestion rates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 248, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.T. Planktonic marine copepods and harmful algae. Harmful Algae 2014, 32, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kiørboe, T. Toxic dinoflagellates produce true grazer deterrents. Ecology 2018, 99, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagøein, E.; Miranda, A.; Reguera, B.; Franco, J.M. Effects of two paralytic shellfish toxin producing dinoflagellates on the pelagic harpacticoid copepod Euterpina acutifrons. Mar. Biol. 1996, 126, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, R.A.F.; Figueiredo, G.M.; Valentin, J.L.; da Silva Scardua, P.M.; Hégaret, H. Immunological and physiological responses of the periwinkle Littorina littorea during and after exposure to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 160, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, S.E.; Bricelj, V.M.; Lambert, C.; Paillard, C. Deleterious effects of a nonPST bioactive compound(s) from Alexandrium tamarense on bivalve hemocytes. Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, K.; Oda, T.; Nagai, K.; Nagai, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Basti, L. Deleterious effects of harmful dinoflagellates and raphidophytes on egg viability and spermatozoa swimming velocity in the Japanese pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii. J. Shellfish Res. 2018, 37, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supono, S.; Knowles, G.; Bolch, C. Toxicity and histopathological effects of toxic dinoflagellate, Alexandrium catenella exudates on larvae of blue mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis, and Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. J. Ilm. Perikan. Dan Kelaut. 2020, 12, 5965741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéguen, M.; Bardouil, M.; Baron, R.; Lassus, P.; Truquet, P.; Massardier, J. Detoxification of Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas fed on diets of Skeletonema costatum with and without silt, following PSP contamination by Alexandrium minutum. Aquat. Living Ressources 2008, 20, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberkorn, H.; Lambert, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Quéré, C.; Bruneau, A.; Riso, R.; Auffret, M.; Soudant, P. Cellular and biochemical responses of the oyster Crassostrea gigas to controlled exposures to metals and Alexandrium minutum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 147, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Goïc, N.; Hégaret, H.; Boulais, M.; Béguel, J.P.; Lambert, C.; Fabioux, C.; Soudant, P. Flow cytometric assessment of morphology, viability, and production of reactive oxygen species of Crassostrea gigas oocytes. Application to Toxic dinoflagellate (Alexandrium minutum) exposure. Cytom. Part A 2014, 85, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pousse, É.; Flye-Sainte-Marie, J.; Alunno-Bruscia, M.; Hégaret, H.; Rannou, É.; Pecquerie, L.; Marques, G.M.; Thomas, Y.; Castrec, J.; Fabioux, C.; et al. Modelling paralytic shellfish toxins (PST) accumulation in Crassostrea gigas by using Dynamic Energy Budgets (DEB). J. Sea Res. 2019, 143, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.L.; LeGresley, M.M.; Haya, K.; Sephton, D.H.; Burridge, L.E.; Page, F.H.; Chang, B.D. Salmon mortalities associated with a bloom of Alexandrium fundyense in 2003 in the Bay of Fundy, and subsequent early warning approaches for industry. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.L.; LeGresley, M.M.; Hanke, A.; Page, F.H. Alexandrium fundyense-red tides, PSP shellfish toxicity, salmon mortalities and human illnesses in 2003-04–before and after. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2006; Moestrup, O., Doucette, G., Enevoldsen, H., Godhe, A., Hallegraeff, G., Luckas, B., Lundholm, N., Lewis, J., Rengefors, K., Sellner, K., et al., Eds.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; pp. 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Burridge, L.E.; Martin, J.L.; Lyons, M.C.; Legresley, M.M. Lethality of microalgae to farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2010, 308, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranston, E.R.; Webber, D.F.; Larsen, J. The first description of the potentially toxic dinoflagellate, Alexandrium minutum in Hunts Bay. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, C.; Clement, A.; Aguilera, A. Summer Alexandrium catenella bloom and the impact on fish farming, in the XI Aysén Region, Chile. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2006; Moestrup, O., Doucette, G., Enevoldsen, H., Godhe, A., Hallegraeff, G., Luckas, B., Lundholm, N., Lewis, J., Rengefors, K., Sellner, K., et al., Eds.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; pp. 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, C.H.; Bates, S.S.; Martin, J.L.; Haigh, N.; Howland, K.L.; Lewis, N.I.; Locke, A.; Peña, A.; Poulin, M.; Rochon, A.; et al. Three decades of Canadian marine harmful algal events: Phytoplankton and phycotoxins of concern to human and ecosystem health. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, T.; Kodama, M. Ichthyotoxicity found in cultured media of Protogonyaulax spp. Mar. Biol. 1986, 92, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ye, Q.; Gu, H.-F.; Li, H.-Y.; Lv, S.-H.; Liu, J.-S.; Yang, W.-D. Variability in the allelopathic action of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex along the coast of China. Harmful Algae 2015, 47, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.D.; Xie, J.; van Rijssel, M.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, J.S. Allelopathic effects of Alexandrium spp. on Prorocentrum donghaiense. Harmful Algae 2010, 10, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gan, C.; Huang, J.; Zou, C.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, W. Variability of Prorocentrum donghaiense response to allelopathic action from Alexandrium pacificum in laboratory culture. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Muck, A.; Wielsch, N.; Svatoš, A.; Cembella, A. Isolation of activity and partial characterization of large non-proteinaceous lytic allelochemicals produced by the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanen, P.; Suikkanen, S.; Kremp, A. Allelopathic activity of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii: Intra-population variability and response of co-occurring dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Andersen, N.G.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Hansen, P.J. Stability of the intra- and extracellular toxins of Prymnesium parvum using a microalgal bioassay. Harmful Algae 2014, 32, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.W. Effects of size and concentration of food particles on the feeding behavior of the marine planktonic copepod Calanus pacificus1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1972, 17, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, W.R.; Zhang, Q.-X.; Carmichael, W.W. Effects of toxic cyanobacteria and purified toxins on the survival and feeding of a copepod and three species of Daphnia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, R.A.F.; Fernandes, T.; Dos Santos, L.N.; Nascimento, S.M. Toxicity of benthic dinoflagellates on grazing, behavior and survival of the brine shrimp Artemia salina. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anne-Sophie, P.; Julie, R.; Laurence, G.G.; Sophie, M.; Eva, T.; Thomas, O.P.; Rodolphe, L.; Stéphane, G. Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata on survival, feeding and reproduction of a phytal harpacticoid copepod. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2019, 516, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, L.M.; Silva, L.H.S.; Faassen, E.J.; Lürling, M.; Ger, K.A. Copepod prey selection and grazing efficiency mediated by chemical and morphological defensive traits of cyanobacteria. Toxins 2020, 12, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segner, H. Fish cell lines as a tool in aquatic toxicology. EXS 1998, 86, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.E.J.; Dayeh, V.R.; Schirmer, K.; Bols, N.C. Applications and potential uses of fish gill cell lines: Examples with RTgill-W1. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2009, 45, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Waite, T.D.; Godrant, A.; Rose, A.L.; Tovar, C.D.; Woods, G.M.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Novel application of a fish gill cell line assay to assess ichthyotoxicity of harmful marine microalgae. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, J.I.; Shabala, L.; Shabala, S.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Seger, A.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Fish gill damage by harmful microalgae newly explored by microelectrode ion flux estimation techniques. Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goïc, N.; Hégaret, H.; Fabioux, C.; Miner, P.; Suquet, M.; Lambert, C.; Soudant, P. Impact of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella on Pacific oyster reproductive output: Application of flow cytometry assays on spermatozoa. Aquat. Living Resour. 2013, 26, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, F.; Wegner, K.M.; Polz, M.F. Oysters and vibrios as a model for disease dynamics in wild animals. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petton, B.; Boudry, P.; Alunno-Bruscia, M.; Pernet, F. Factors influencing disease-induced mortality of Pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2015, 6, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M. Allelochemical Interactions between the Dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum and the Diatom Chaetoceros muelleri. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Bretagne occidentale, Brest, France, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Seger, A.; Mardones, J.I.; Nichols, P.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Progress in understanding algal bloom-mediated fish kills: The role of superoxide radicals, phycotoxins and fatty acids. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Nichols, P.D.; Hamilton, B.; Lewis, R.J.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Ichthyotoxicity of Chattonella marina (Raphidophyceae) to damselfish (Acanthochromis polycanthus): The synergistic role of reactive oxygen species and free fatty acids. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, J.E.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Krupatkina, D.N.; Nonogaki, H.; Brown, P.J.P.; Lewitus, A.J.; Harvey, H.R.; Place, A.R. Species specificity and potential roles of Karlodinium micrum toxin. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, J.E.; Krupatkina, D.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A.R. Karlotoxin mediates grazing by Oxyrrhis marina on strains of Karlodinium veneficum. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeds, J.R.; Place, A.R. Sterol-specific membrane interactions with the toxins from Karlodinium micrum (Dinophyceae)—A strategy for self-protection? Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbay, G.; Chambliss, S.S.; Wikfors, G.H.; Adolf, J.E.; Chintapenta, L.K.; Place, A.R. The growth response of Prorocentrum minimum Pavill. (Dinophyta) to karlotoxin exposure. Int. J. Algae 2014, 16, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, A.R.; Bowers, H.A.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Adolf, J.E.; Deeds, J.R.; Sheng, J. Karlodinium veneficum-The little dinoflagellate with a big bite. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Malkiel, E.; Katz, J.; Adolf, J.E.; Place, A.R. A dinoflagellate exploits toxins to immobilize prey prior to ingestion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.A.; Binzer, S.B.; Hoeck, C.; Meier, S.; De Medeiros, L.S.; Andersen, N.G.; Place, A.; Nielsen, K.F.; Hansen, P.J.; Larsen, T.O. Karmitoxin: An amine-containing polyhydroxy-polyene toxin from the marine dinoflagellate Karlodinium armiger. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellkamp, M.; García-Camacho, F.; Durán-Riveroll, L.M.; Tebben, J.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B. LC-MS/MS method development for the discovery and identification of amphidinols produced by Amphidinium. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, G.K.; Matsumori, N.; Konoki, K.; Murata, M.; Tachibana, K. Chemical structures of amphidinols 5 and 6 isolated from marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium klebsii and their cholesterol-dependant membrane disruption. J. Mar. Biotechnol. 1997, 5, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Binzer, S.B.; Svenssen, D.K.; Daugbjerg, N.; Alves-de-Souza, C.; Pinto, E.; Hansen, P.J.; Larsen, T.O.; Varga, E. A-, B- and C-type prymnesins are clade specific compounds and chemotaxonomic markers in Prymnesium parvum. Harmful Algae 2019, 81, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, T.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and partial stereochemical assignments for prymnesin-1 and prymnesin-2: Potent hemolytic and ichthyotoxic glycosides isolated from the red tide alga Prymnesium parvum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 8499–8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Andersen, N.G.; Larsen, T.O.; Nielsen, K.F.; Hansen, P.J. Prymnesium parvum revisited: Relationship between allelopathy, ichthyotoxicity, and chemical profiles in 5 strains. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 157, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, K.S.; Snyder, R.V. The biosynthesis of polyketide metabolites by dinoflagellates. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 93–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellmann, R.; Stüken, A.; Orr, R.J.S.; Svendsen, H.M.; Jakobsen, K.S. Biosynthesis and molecular genetics of polyketides in marine dinoflagellates. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1011–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidgewell, K.; Clark, B.R.; Gerwick, W.H. The natural products chemistry of cyanobacteria. In Comprehensive Natural Products II Chemistry and Biology; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 141–188. ISBN 978-0-08-045382-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rein, K.S.; Borrone, J. Polyketides from dinoflagellates: Origins, pharmacology and biosynthesis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 124, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Altares, M. Structural Diversity of Microalgal Marine Toxins; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 78. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, B.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M.; Place, A.R. Ichthyotoxicity of four species of gymnodinioid dinoflagellates (Kareniaceae, Dinophyta) and purified karlotoxins to larval sheepshead minnow. Harmful Algae 2011, 9, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimany, E.; Place, A.R.; Jutson, M.; Pipe, R.K. The effects of feeding Karlodinium veneficum (PLY # 103; Gymnodinium veneficum Ballantine) to the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecker, D.K.; Adolf, J.E.; Place, A.R.; Glibert, P.M.; Meritt, D.W. Effects of the dinoflagellates Karlodinium veneficum and Prorocentrum minimum on early life history stages of the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Talapatra, S.; Katz, J.; Tester, P.A.; Waggett, R.J.; Place, A.R. Algal toxins alter copepod feeding behavior. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waggett, R.J.; Tester, P.A.; Place, A.R. Anti-grazing properties of the toxic dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum during predator–prey interactions with the copepod Acartia tonsa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 366, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Adolf, J.E.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A.R.; Coats, D.W. The interplay between host toxins and parasitism by Amoebophrya. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, A.R.; Bai, X.; Kim, S.; Sengco, M.R.; Coats, D.W.; Larsen, D.B.J.; Ge, H.; Balech, M.L.; Inoue, H.; Balech, F.; et al. Dinoflagellate host-parasite sterol profile dictate karlotoxin sensitivity. J. Phycol. 2009, 385, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wagoner, R.M.; Deeds, J.R.; Satake, M.; Ribeiro, A.A.; Place, A.R.; Wright, J.L.C. Isolation and characterization of karlotoxin 1, a new amphipathic toxin from Karlodinium veneficum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 6457–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeds, J.R.; Hoesch, R.E.; Place, A.R.; Kao, J.P.Y. The cytotoxic mechanism of karlotoxin 2 (KmTx 2) from Karlodinium veneficum (Dinophyceae). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 159, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, A.L.; Oh, J.; Place, A.R.; Hamann, M.T. Stereochemical studies of the karlotoxin class using NMR spectroscopy and DP4 chemical-shift analysis: Insights into their mechanism of action. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15705–15710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Inoue, K. The mechanism of the action of Prymnesium toxin on membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 1974, 352, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, J.D.; Wisecaver, J.H.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Kulis, D.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Bhattacharya, D.; Plumley, F.G.; Erdner, D.L. Evolution of saxitoxin synthesis in cyanobacteria and dinoflagellates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 30, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusick, K.D.; Sayler, G.S. An overview on the marine neurotoxin, saxitoxin: Genetics, moleculartargets, methods of detection and ecological functions. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 991–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, T.; Jenkinson, I.R. Notes on Alexandrium population dynamics. J. Plankton Res. 1997, 19, 551–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U. Kill and eat your predator: A winning strategy of the planktonic flagellate Prymnesium parvum. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 32, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, T.; Poulsen, L.K.; Moldrup, M.; Daugbjerg, N.; Hansen, P.J. Marine microalgae attack and feed on metazoans. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, W.W.; Hackett, J.D.; Ferrière, R. Eco-evolutionary feedbacks between private and public goods: Evidence from toxic algal blooms. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, P.R.; Pavia, H.; Toth, G. Formation of harmful algal blooms cannot be explained by allelopathic interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11177–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breier, R.E.; Lalescu, C.C.; Waas, D.; Wilczek, M.; Mazza, M.G. Emergence of phytoplankton patchiness at small scales in mild turbulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12112–12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, W.M.; Climent, E.; Barry, M.; De Lillo, F.; Boffetta, G.; Cencini, M.; Stocker, R. Turbulence drives microscale patches of motile phytoplankton. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.D.; Secchi, E.; Rusconi, R.; Stocker, R. Not just going with the flow: The effects of fluid flow on bacteria and plankton. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 35, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basterretxea, G.; Font-Muñoz, J.S.; Tuval, I. Phytoplankton orientation in a turbulent ocean: A microscale perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, X.; Zheng, T.; Hong, H. An efficient method to obtain axenic cultures of Alexandrium tamarense-a PSP-producing dinoflagellate. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 69, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaberc-porekar, V.; Menart, V. Perspectives of immobilized-metal affinity chromatography. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2001, 49, 335–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.L.; Stauber, J.L.; Wilson, M.R.; Jolley, D.F. The use of immobilised metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) to compare expression of copper-binding proteins in control and copper-exposed marine microalgae. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).