Radiation Increases Functional KCa3.1 Expression and Invasiveness in Glioblastoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Functional Expression of KCa3.1 Channels Increases in Irradiated Glioblastoma (GBM) Cells
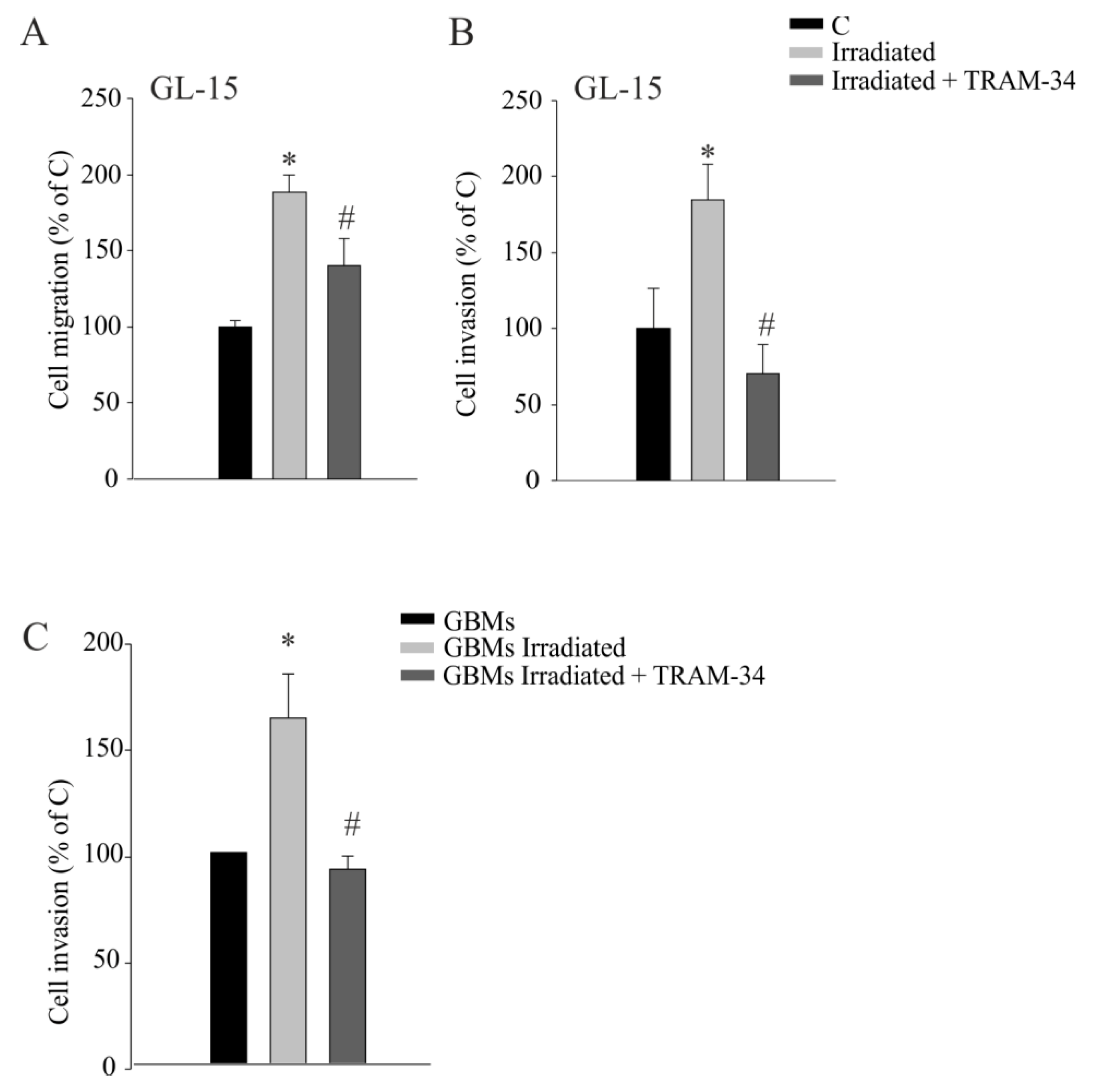
2.2. KCa3.1 Inhibition Decreases Radiation-Induced Cell Migration and Invasion
2.3. KCa3.1 Activity Is Involved in Radiation-Induced Transcription of Genes Related to GBM Cell Invasion
2.4. Radiation-Induced IL-4/IL-4R Expression is Dependent on KCa3.1 Channel Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Line Culture and Radiation Protocol
4.3. Primary Human GBM Cells
4.4. Migration and Invasion Assays
4.5. Electrophysiology
4.6. RNA Preparation and Analysis
4.7. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 world health organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, B.; Rosenthal, M.A. Survival comparison between glioblastoma multiforme and other incurable cancers. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; van den Bent, M.J.; Hegi, M.E. Optimal role of temozolomide in the treatment of malignant gliomas. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2005, 5, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, G.; Amelio, D.; Amichetti, M.; Salvati, M.; Muni, R.; Bozzao, A.; Lanzetta, G.; Scarpino, S.; Arcella, A.; Enrici, R.M. Patterns of failure and comparison of different target volume delineations in patients with glioblastoma treated with conformal radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 97, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, L.; Beaudry, C.; McDonough, W.S.; Hoelzinger, D.B.; Demuth, T.; Ross, K.R.; Berens, T.; Coons, S.W.; Watts, G.; Trent, J.M.; et al. Glioma cell motility is associated with reduced transcription of proapoptotic and proliferation genes: A cDNA microarray analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2001, 53, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joy, A.M.; Beaudry, C.E.; Tran, N.L.; Ponce, F.A.; Holz, D.R.; Demuth, T.; Berens, M.E. Migrating glioma cells activate the PI3-K pathway and display decreased susceptibility to apoptosis. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116 Pt 21, 4409–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Yu, C.F.; Hong, J.H.; Tsai, C.S.; Chiang, C.S. Radiation therapy-induced tumor invasiveness is associated with SDF-1-regulated macrophage mobilization and vasculogenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinle, M.; Palme, D.; Misovic, M.; Rudner, J.; Dittmann, K.; Lukowski, R.; Ruth, P.; Huber, S.M. Ionizing radiation induces migration of glioblastoma cells by activating BK K+ channels. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 101, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wank, M.; Schilling, D.; Reindl, J.; Meyer, B.; Gempt, J.; Motov, S.; Alexander, F.; Wilkens, J.J.; Schlegel, J.; Schmid, T.E.; et al. Evaluation of radiation-related invasion in primary patient-derived glioma cells and validation with established cell lines: Impact of different radiation qualities with differing LET. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 139, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagzag, D.; Esencay, M.; Mendez, O.; Yee, H.; Smirnova, I.; Huang, Y.; Chiriboga, L.; Lukyanov, E.; Liu, M.; Newcomb, E.W. Hypoxia- and vascular endothelial growth factor-induced stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha/CXCR4 expression in glioblastomas: One plausible explanation of Scherer’s structures. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Jan, L.Y. Targeting potassium channels in cancer. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 206, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edalat, L.; Stegen, B.; Klumpp, L.; Haehl, E.; Schilbach, K.; Lukowski, R.; Kuhnle, M.; Bernhardt, G.; Buschauer, A.; Zips, D.; et al. BK K+ channel blockade inhibits radiation-induced migration/brain infiltration of glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 14259–14278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, G.; Limatola, C.; Catalano, M. Functional Roles of the Ca2+-activated K+ Channel, KCa3.1, in Brain Tumors. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciaccaluga, M.; Fioretti, B.; Catacuzzeno, L.; Pagani, F.; Bertollini, C.; Rosito, M.; Catalano, M.; D’Alessandro, G.; Santoro, A.; Cantore, G.; et al. CXCL12-induced glioblastoma cell migration requires intermediate conductance Ca2+ -activated K+ channel activity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 299, C175–C184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciaccaluga, M.; D’Alessandro, G.; Pagani, F.; Ferrara, G.; Lopez, N.; Warr, T.; Gorello, P.; Porzia, A.; Mainiero, F.; Santoro, A.; et al. Functional cross talk between CXCR4 and PDGFR on glioblastoma cells is essential for migration. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.J.; Kummerlow, M.N.; Redmond, K.J.; Martinez-Gutierrez, J.C.; Usama, S.M.; Holdhoff, M.; Grossman, S.A.; Laterra, J.J.; Strowd, R.E.; Kleinberg, L.R. Re-irradiation for malignant glioma: Toward patient selection and defining treatment parameters for salvage. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 3, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankaitis, K.V.; Fingleton, B. Targeting IL4/IL4R for the treatment of epithelial cancer metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanshani, S.; Wulff, H.; Miller, M.J.; Rohm, H.; Neben, A.; Gutman, G.A.; Cahalan, M.D.; Chandy, K.G. Up-regulation of the IKCa1 potassium channel during T-cell activation. Molecular mechanism and functional consequences. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 37137–37149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R.; Lively, S.; Schlichter, L.C. IL-4 type 1 receptor signaling up-regulates KCNN4 expression, and increases the KCa3.1 current and its contribution to migration of alternative-activated microglia. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataga, K.I.; Stocker, J. Senicapoc (ICA-17043): A potential therapy for the prevention and treatment of hemolysis-associated complications in sickle cell anemia. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, G.; Catalano, M.; Sciaccaluga, M.; Chece, G.; Cipriani, R.; Rosito, M.; Grimaldi, A.; Lauro, C.; Cantore, G.; Santoro, A.; et al. KCa3.1 channels are involved in the infiltrative behavior of glioblastoma in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e773. [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi, A.; D’Alessandro, G.; Golia, M.T.; Grössinger, E.M.; Di Angelantonio, S.; Ragozzino, D.; Santoro, A.; Esposito, V.; Wulff, H.; Catalano, M.; et al. KCa3.1 inhibition switches the phenotype of glioma infiltrating microglia/ macrophages. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alifieris, C.; Trafalis, D.T. Glioblastoma multiforme: Pathogenesis and treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 152, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillamo, J.S.; Lisovoski, F.; Christov, C.; Le Guérinel, C.; Defer, G.L.; Peschanski, M.; Lefrançois, T. Migration pathways of human glioblastoma cells xenografted into the immunosuppressed rat brain. J. Neurooncol. 2001, 52, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilalta, M.; Rafat, M.; Graves, E.E. Effects of radiation on metastasis and tumor cell migration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2999–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trog, D.; Yeghiazaryan, K.; Fountoulakis, M.; Friedlein, A.; Moenkemann, H.; Haertel, N.; Schueller, H.; Breipohl, W.; Schild, H.; Leppert, D. Pro-invasive gene regulating effect of irradiation and combined temozolomide-radiation treatment on surviving human malignant glioma cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 542, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild-Bode, C.; Weller, M.; Rimner, A.; Dichgans, J.; Wick, W. Sublethal irradiation promotes migration and invasiveness of glioma cells. Implications for radiotherapy of human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2744–2750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, C.A.; Nguyen, H.P.T.; Morokoff, A.P.; Luwor, R.B.; Paradiso, L.; Kaye, A.H.; Mantamadiotis, T.; Stylli, S.S. Inhibition of Radiation and Temozolomide-Induced Invadopodia Activity in Glioma Cells Using FDA-Approved Drugs. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Whitehead, C.A.; Paradiso, L.; Kaye, A.H.; Morokoff, A.P.; Luwor, R.B.; Stylli, S.S. Enhancement of invadopodia activity in glioma cells by sublethal doses of irradiation and temozolomide. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegen, B.; Butz, L.; Klumpp, L.; Zips, D.; Dittmann, K.; Ruth, P.; Huber, S.M. Ca2+−Activated IK K+ Channel Blockade Radiosensitizes Glioblastoma. Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabai, G.; Frank, B.; Mohle, R.; Weller, M.; Wick, W. Irradiation and hypoxia promote homing of haematopoietic progenitor cells towards gliomas by TGF-b-dependent HIF-1a-mediated induction of CXCL12. Brain 2006, 129, 2426–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.N.; Zamler, D.; Baker, G.J.; Kadiyala, P.; Erdreich-Epstein, A.; DeCarvalho, A.C.; Mikkelsen, T.; Castro, M.G.; Lowenstein, P.R. CXCR4 increases in-vivo glioma perivascular invasion, and reduces radiation induced apoptosis: A genetic knockdown study. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83701–83719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinou, M.; Giannopoulou, E.; Malatara, G.; Argyriou, A.A.; Kalofonos, H.P.; Kardamakis, D. Ionizing radiation affects epidermal growth factor receptor signalling and metalloproteinase secretion in glioma cells. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2011, 8, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Misek, S.A.; Chen, J.; Schroeder, L.; Rattanasinchai, C.; Sample, A.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Gallo, K.A. EGFR Signals through a DOCK180-MLK3 Axis to Drive Glioblastoma Cell Invasion. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badiga, A.V.; Chetty, C.; Kesanakurti, D.; Are, D.; Gujrati, M.; Klopfenstein, J.D.; Dinh, D.H.; Rao, J.S. MMP-2 siRNA inhibits radiation-enhanced invasiveness in glioma cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nottingham, L.K.; Yan, C.H.; Yang, X.; Si, H.; Coupar, J.; Bian, Y.; Cheng, T.F.; Allen, C.; Arun, P.; Gius, D.; et al. Aberrant IKKα and IKKβ cooperatively activate NF-κB and induce EGFR/AP1 signaling to promote survival and migration of head and neck cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Luo, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Hua, L.; Wang, H.W.; Chen, W.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, D.; et al. MiR-622 suppresses proliferation, invasion and migration by directly targeting activating transcription factor 2 in glioma cells. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 121, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Fajol, A.; Tu, X.; Ren, B.; Shi, S. miR-204 suppresses the development and progression of human glioblastoma by targeting ATF2 binding promoters of genes related to invasion. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 70058–70065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, M.M.; Sathyan, P.; Singh, S.K.; Zinn, P.O.; Marisetty, A.L.; Liang, S.; Gumin, J.; El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Suki, D.; Colman, H.; et al. REST regulates oncogenic properties of glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, M.H.; Lee, W.J.; Yang, Y.C.; Li, Y.L.; Chen, B.R.; Cheng, T.Y.; Yang, P.W.; Wang, M.Y.; Jan, Y.H.; Lin, Y.K.; et al. KSRP suppresses cell invasion and metastasis through miR-23a-mediated EGR3 mRNA degradation in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2017, 1860, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, A.; Bingham, A.J.; Li, J.; Kumar, B.; Sukumar, P.; Munsch, C.; Buckley, N.J.; Neylon, C.B.; Porter, K.E.; Beech, D.J.; et al. Downregulated REST transcription factor is a switch enabling critical potassium channel expression and cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.S.; Choi, Y.E.; Hwang, S.J.; Han, Y.H.; Park, M.J.; Bae, I.H. IL-4, a direct target of miR-340/429, is involved in radiation-induced aggressive tumor behavior in human carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 86836–86856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.U.; Xiao, J.; Ni, H.T.; Cho, K.H.; Spellman, S.R.; Low, W.C.; Hall, W.A. Changes in expression of transferrin, insulin-like growth factor 1, and interleukin 4 receptors after irradiation of cells of primary malignant brain tumor cell lines. Radiat. Res. 2003, 160, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreansky, S.; He, B.; van Cott, J.; McGhee, J.; Markert, J.M.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Roizman, B.; Whitley, R.J. Treatment of intracranial gliomas in immunocompetent mice using herpes simplex viruses that express murine interleukins. Gene Ther. 1998, 5, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, J.; Kuwashima, N.; Hatano, M.; Nishimura, F.; Dusak, J.E.; Storkus, W.J.; Okada, H. IL-4-transfected tumor cell vaccines activate tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells and promote type-1 immunity. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 7194–7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulzewsky, F.; Pelz, A.; Feng, X.; Synowitz, M.; Markovic, D.; Langmann, T.; Holtman, I.R.; Wang, X.; Eggen, B.J.; Boddeke, H.W.; et al. Glioma-associated microglia/macrophages display an expression profile different from M1 and M2 polarization and highly express Gpnmb and Spp1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambardzumyan, D.; Gutmann, D.H.; Kettenmann, H. The role of microglia and macrophages in glioma maintenance and progression. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisakis, A.; Piperi, C.; Themistocleous, M.S.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Boviatsis, E.I.; Sakas, D.E.; Patsouris, E.; Lea, R.W.; Kalofoutis, A. Comparative analysis of peripheral and localised cytokine secretion in glioblastoma patients. Cytokine 2007, 39, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepore, F.; D’Alessandro, G.; Fabrizio, A.; Santoro, A.; Esposito, V.; Limatola, C.; Trettel, F. CXCL16/CXCR6 axis drives microglia/macrophages phenotype in physiological conditions and plays a crucial role in glioma. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, G.; Grimaldi, A.; Chece, G.; Porzia, A.; Esposito, V.; Santoro, A.; Salvati, M.; Mainiero, F.; Ragozzino, D.; Di Angelantonio, S.; et al. KCa3.1 channel inhibition sensitizes glioma sto temozolomide treatment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30781–30796. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| AP-1 | Forward: 5′-AGAGGAAGCGCATGAGGAAC-3′ Reverse: 5′-CACCTGTTCCCTGAGCATGT-3′ |
| ATF2 | Forward: 5′-GGCCAATTGTCCCTGTACCA-3′ Reverse: 5′-ACCATGGTGACTGGTCGAAC-3′ |
| CXCL12 | Forward: 5′-AGCCAACGTCAAGCATCTCA-3′ Reverse: 5′-GTGGGTCTAGCGGAAAGTCC-3′ |
| CXCR4 | Forward: 5′-CCCTCCTGCTGACTATTCCC-3′ Reverse: 5′-TAAGGCCAACCATGATGTG-3′ |
| EGR3 | Forward: 5′-AGTTTGCTAAACCAACTGCC-3′ Reverse: 5′-TTGGTCAGACCGATGTCCAT-3′ |
| GAPDH | Forward: 5′-CCCCTTCATTGACCTCAACTAC-3′ Reverse: 5′-GATGACAAGCTTCCCGTTCTC-3′ |
| IL-4 | Forward: 5′-GACTCTGTGCACCGAGTTGA-3′ Reverse: 5′-TCAGGAATCGGATCAGCTGC-3′ |
| IL-4R | Forward: 5′-ATGAAGGTCTTGCAGGAGCC-3′ Reverse: 5′-ACGTCATCCATGAGCAGGTG-3′ |
| KCNN4 | Forward: 5′-GGCTGAAACACCGGAAGCTC-3′ Reverse: 5′-CAGCTCTGTCAGGGCATCCA-3′ |
| MMP2 | Forward: 5′-AGATCTTCTTCTTCAAGGACCGGTT-3′ Reverse: 5′-ACAGCCTTCTCCTCCTGTGG-3′ |
| MMP9 | Forward: 5′-AACTACGACCGGGACAAG-3′ Reverse: 5′-TCCGCGGCCCTCGCTGGTAC-3′ |
| MMP12 | Forward: 5′-AGGAATCGGGCCTAAAATTG-3′ Reverse: 5′-TGCTTTTCAGTGTTTTGGTGA-3′ |
| REST | Forward: 5′-GTTAGAACTCATACAGGAGAA-3′ Reverse: 5′-AACTGCACTGATCACATTTAA-3′ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Alessandro, G.; Monaco, L.; Catacuzzeno, L.; Antonangeli, F.; Santoro, A.; Esposito, V.; Franciolini, F.; Wulff, H.; Limatola, C. Radiation Increases Functional KCa3.1 Expression and Invasiveness in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030279
D’Alessandro G, Monaco L, Catacuzzeno L, Antonangeli F, Santoro A, Esposito V, Franciolini F, Wulff H, Limatola C. Radiation Increases Functional KCa3.1 Expression and Invasiveness in Glioblastoma. Cancers. 2019; 11(3):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030279
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Alessandro, Giuseppina, Lucia Monaco, Luigi Catacuzzeno, Fabrizio Antonangeli, Antonio Santoro, Vincenzo Esposito, Fabio Franciolini, Heike Wulff, and Cristina Limatola. 2019. "Radiation Increases Functional KCa3.1 Expression and Invasiveness in Glioblastoma" Cancers 11, no. 3: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030279
APA StyleD’Alessandro, G., Monaco, L., Catacuzzeno, L., Antonangeli, F., Santoro, A., Esposito, V., Franciolini, F., Wulff, H., & Limatola, C. (2019). Radiation Increases Functional KCa3.1 Expression and Invasiveness in Glioblastoma. Cancers, 11(3), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030279





