Neurotrophin Signaling in Medulloblastoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MB Biology
2.1. Molecular Subgroups of MB
2.2. MB Origins
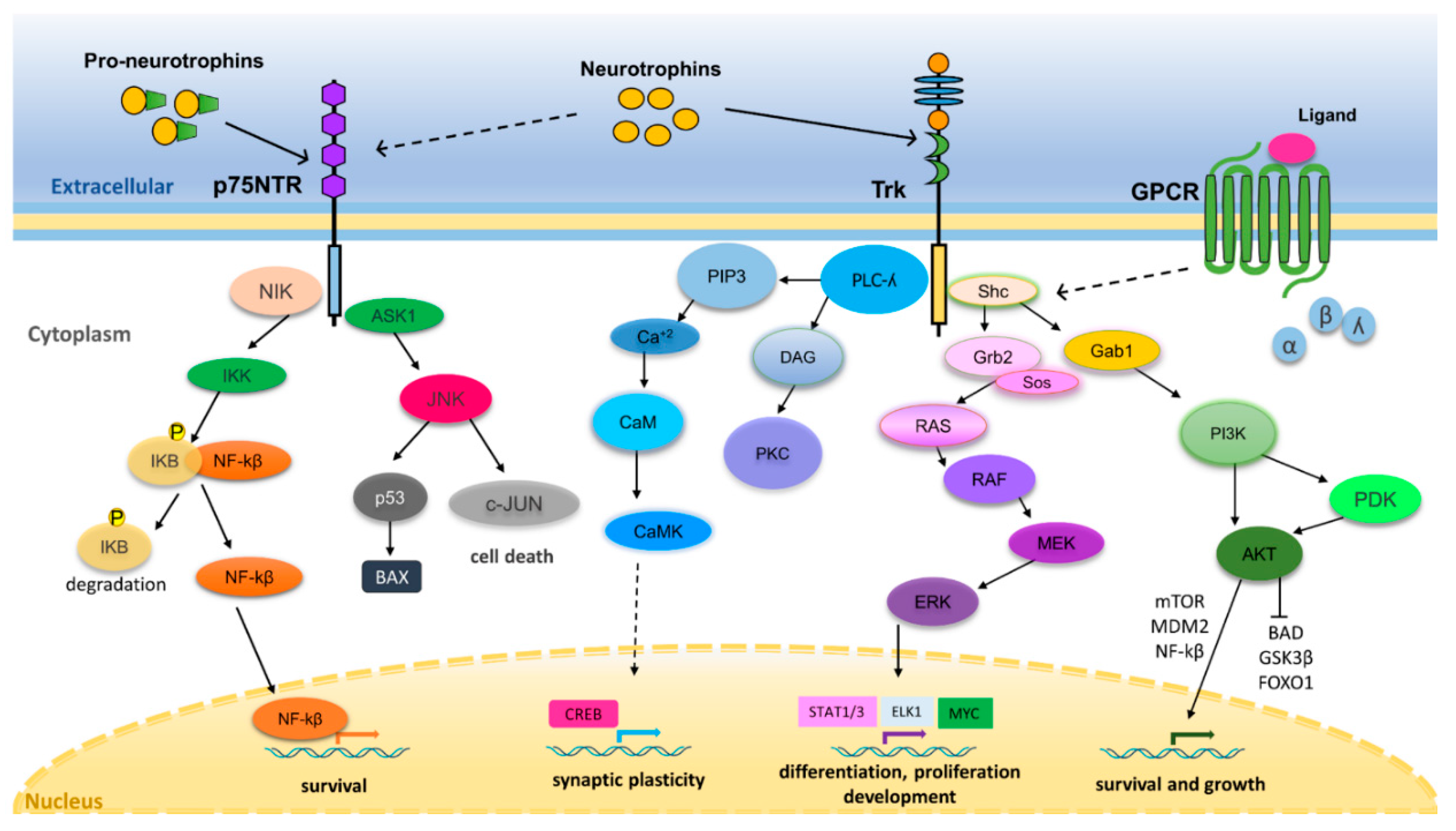
3. Neurotrophin Regulation of Nervous System Development and Function
4. Neurotrophin Signaling in Cancer
5. Neurotrophins and Their Receptors in MB
5.1. NGF and TrkA
5.2. BDNF and TrkB
5.3. NT3, NT4/5, and TrkC
5.4. p75NTR
5.5. Gene Expression Profile of Neurotrophins and Their Receptors in MB Primary Tumors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shawver, L.K.; Slamon, D.; Ullrich, A. Smart drugs: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Scholar, E.M. Role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmet, C.J.; Peeper, D.S. The neurotrophic receptor TrkB: A drug target in anti-cancer therapy? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, C.J.; Li, Z.; McKee, A.E. On Trk--the TrkB signal transduction pathway is an increasingly important target in cancer biology. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5962–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesler, R.; de Farias, C.B.; Abujamra, A.L.; Brunetto, A.L.; Schwartsmann, G. BDNF/TrkB signaling as an anti-tumor target. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2011, 11, 1473–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Caracciolo, V.; Russo, G.; Reiss, K.; Giordano, A. Medulloblastoma: From molecular pathology to therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northcott, P.A.; Robinson, G.W.; Kratz, C.P.; Mabbott, D.J.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Clifford, S.C.; Rutkowski, S.; Ellison, D.W.; Malkin, D.; Taylor, M.D.; et al. Medulloblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.D.; Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Remke, M.; Cho, Y.J.; Clifford, S.C.; Eberhart, C.G.; Parsons, D.W.; Rutkowski, S.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: The current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Pfister, S.M.; Taylor, M.D. The clinical implications of medulloblastoma subgroups. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Bouffet, E.; Bailey, S.; Clifford, S.C.; Doz, F.; Kool, M.; Dufour, C.; Vassal, G.; Milde, T.; et al. Risk stratification of childhood medulloblastoma in the molecular era: The current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northcott, P.A.; Buchhalter, I.; Morrissy, A.S.; Hovestadt, V.; Weischenfeldt, J.; Ehrenberger, T.; Gröbner, S.; Segura-Wang, M.; Zichner, T.; Rudneva, V.A.; et al. The whole-genome landscape of medulloblastoma subtypes. Nature 2017, 547, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, T.J.; Weeraratne, S.D.; Archer, T.C.; Pomeranz Krummel, D.A.; Auclair, D.; Bochicchio, J.; Carneiro, M.O.; Carter, S.L.; Cibulskis, K.; Erlich, R.L.; et al. Medulloblastoma exome sequencing uncovers subtype-specific somatic mutations. Nature 2012, 488, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Bueren, A.O.; Kortmann, R.D.; von Hoff, K.; Friedrich, C.; Mynarek, M.; Müller, K.; Goschzik, T.; Zur Mühlen, A.; Gerber, N.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; et al. Treatment of children and adolescents with metastatic medulloblastoma and prognostic relevance of clinical and biologic parameters. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4151–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northcott, P.A.; Shih, D.J.; Peacock, J.; Garzia, L.; Morrissy, A.S.; Zichner, T.; Stütz, A.M.; Korshunov, A.; Reimand, J.; Schumacher, S.E.; et al. Subgroup-specific structural variation across 1000 medulloblastoma genomes. Nature 2012, 488, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.M.G.; Remke, M.; Rampasek, L.; Peacock, J.; Shih, D.J.H.; Luu, B.; Garzia, L.; Torchia, J.; Nör, C.; Morrissy, A.S.; et al. Intertumoral heterogeneity within medulloblastoma subgroups. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 737–754.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissy, A.S.; Cavalli, F.M.G.; Remke, M.; Ramaswamy, V.; Shih, D.J.H.; Holgado, B.L.; Farooq, H.; Donovan, L.K.; Garzia, L.; Agnihotri, S.; et al. Spatial heterogeneity in medulloblastoma. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalbe, E.C.; Lindsey, J.C.; Nakjang, S.; Crosier, S.; Smith, A.J.; Hicks, D.; Rafiee, G.; Hill, R.M.; Iliasova, A.; Stone, T.; et al. Novel molecular subgroups for clinical classification and outcome prediction in childhood medulloblastoma: A cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Schwalbe, E.C.; Williamson, D.; Sill, M.; Hovestadt, V.; Mynarek, M.; Rutkowski, S.; Robinson, G.W.; Gajjar, A.; Cavalli, F.; et al. Second-generation molecular subgrouping of medulloblastoma: An international meta-analysis of Group 3 and Group 4 subtypes. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, R.J. Mapping cancer origins. Cell 2011, 145, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, G.M.; Carter, D.R.; Cheung, B.B.; Liu, T.; Mateos, M.K.; Meyerowitz, J.G. The prenatal origins of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, L.V.; Milenković, L.; Higgins, K.M.; Scott, M.P. Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants. Science 1997, 277, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.J.; Ellis, T.; Markant, S.L.; Read, T.A.; Kessler, J.D.; Bourboulas, M.; Schüller, U.; Machold, R.; Fishell, G.; Rowitch, D.H.; et al. Medulloblastoma can be initiated by deletion of Patched in lineage-restricted progenitors or stem cells. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladoiu, M.C.; El-Hamamy, I.; Donovan, L.K.; Farooq, H.; Holgado, B.L.; Sundaravadanam, Y.; Ramaswamy, V.; Hendrikse, L.D.; Kumar, S.; Mack, S.C.; et al. Childhood cerebellar tumours mirror conserved fetal transcriptional programs. Nature 2019, 572, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüller, U.; Heine, V.M.; Mao, J.; Kho, A.T.; Dillon, A.K.; Han, Y.G.; Huillard, E.; Sun, T.; Ligon, A.H.; Qian, Y.; et al. Acquisition of granule neuron precursor identity is a critical determinant of progenitor cell competence to form Shh-induced medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Du, F.; Yuelling, L.W.; Lin, T.; Muradimova, R.E.; Tricarico, R.; Wang, J.; Enikolopov, G.; Bellacosa, A.; Wechsler-Reya, R.J.; et al. A population of Nestin-expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvadurai, H.J.; Luis, E.; Desai, K.; Lan, X.; Vladoiu, M.C.; Whitley, O.; Galvin, C.; Vanner, R.J.; Lee, L.; Whetstone, H.; et al. Medulloblastoma arises from the persistence of a rare and transient Sox2+ granule neuron precursor. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawauchi, D.; Robinson, G.; Uziel, T.; Gibson, P.; Rehg, J.; Gao, C.; Finkelstein, D.; Qu, C.; Pounds, S.; Ellison, D.W.; et al. A mouse model of the most aggressive subgroup of human medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawauchi, D.; Ogg, R.J.; Liu, L.; Shih, D.J.H.; Finkelstein, D.; Murphy, B.L.; Rehg, J.E.; Korshunov, A.; Calabrese, C.; Zindy, F.; et al. Novel MYC-driven medulloblastoma models from multiple embryonic cerebellar cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5231–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Erkek, S.; Tong, Y.; Yin, L.; Federation, A.J.; Zapatka, M.; Haldipur, P.; Kawauchi, D.; Risch, T.; Warnatz, H.J.; et al. Active medulloblastoma enhancers reveal subgroup-specific cellular origins. Nature 2016, 530, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.; Tong, Y.; Robinson, G.; Thompson, M.C.; Currle, D.S.; Eden, C.; Kranenburg, T.A.; Hogg, T.; Poppleton, H.; Martin, J.; et al. Subtypes of medulloblastoma have distinct developmental origins. Nature 2010, 468, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.V. Neurotrophins and their receptors: A convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Trk receptors: Roles in neuronal signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 609–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Poo, M.M. Neurotrophin regulation of neural circuit development and function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bothwell, M. Recent advances in understanding neurotrophin signaling. F1000Research 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schecterson, L.C.; Bothwell, M. Neurotrophin receptors: Old friends with new partners. Dev. Neurobiol. 2010, 70, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Reynolds, B.A.; Weiss, S. BDNF enhances the differentiation but not the survival of CNS stem cell-derived neuronal precursors. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 5765–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K.; Turner, D.A. In Vitro survival and differentiation of neurons derived from epidermal growth factor-responsive postnatal hippocampal stem cells: Inducing effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Neurobiol. 1998, 35, 395–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoletopoulou, V.; Lickert, H.; Frade, J.M.; Rencurel, C.; Giallonardo, P.; Zhang, L.; Bibel, M.; Barde, Y.A. Neurotrophin receptors TrkA and TrkC cause neuronal death whereas TrkB does not. Nature 2010, 467, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibel, M.; Barde, Y.A. Neurotrophins: Key regulators of cell fate and cell shape in the vertebrate nervous system. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2919–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.M. The role of neurotrophins in the developing nervous system. J. Neurobiol. 1994, 25, 1334–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabelli, R.J.; Hohn, A.; Shatz, C.J. Inhibition of ocular dominance column formation by infusion of NT-4/5 or BDNF. Science 1995, 267, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowiański, P.; Lietzau, G.; Czuba, E.; Waśkow, M.; Steliga, A.; Moryś, J. BDNF: A key factor with multipotent impact on brain signaling and synaptic plasticity. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Zanca, D.; Hughes, S.H.; Barbacid, M. A human oncogene formed by the fusion of truncated tropomyosin and protein tyrosine kinase sequences. Nature 1986, 319, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardini, E.; Bosotti, R.; Borgia, A.L.; De Ponti, C.; Somaschini, A.; Cammarota, R.; Amboldi, N.; Raddrizzani, L.; Milani, A.; Magnaghi, P.; et al. The TPM3-NTRK1 rearrangement is a recurring event in colorectal carcinoma and is associated with tumor sensitivity to TRKA kinase inhibition. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatu, A.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Siena, S. NTRK gene fusions as novel targets of cancer therapy across multiple tumour types. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, A.M.; Lo, H.W. Inhibiting TRK proteins in clinical cancer therapy. Cancers 2018, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawara, A. Trk receptor tyrosine kinases: A bridge between cancer and neural development. Cancer Lett. 2001, 169, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, E.; Vanhecke, E.; Saule, P.; Mougel, A.; Page, A.; Romon, R.; Nurcombe, V.; Le Bourhis, X.; Hondermarck, H. Nerve growth factor is a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias, C.B.; Rosemberg, D.B.; Heinen, T.E.; Koehler-Santos, P.; Abujamra, A.L.; Kapczinski, F.; Brunetto, A.L.; Ashton-Prolla, P.; Meurer, L.; Reis Bogo, M.; et al. BDNF/TrkB content and interaction with gastrin-releasing peptide receptor blockade in colorectal cancer. Oncology 2010, 79, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, R.; Mnich, K.; Gorman, A.M. Nerve growth factor (NGF)-mediated regulation of p75(NTR) expression contributes to chemotherapeutic resistance in triple negative breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liang, Y.; He, Z.; An, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wu, J. Autocrine activity of BDNF induced by the STAT3 signaling pathway causes prolonged TrkB activation and promotes human non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Cruz-Morcillo, M.A.; Berger, J.; Sánchez-Prieto, R.; Saada, S.; Naves, T.; Guillaudeau, A.; Perraud, A.; Sindou, P.; Lacroix, A.; Descazeaud, A.; et al. p75 neurotrophin receptor and pro-BDNF promote cell survival and migration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34480–34497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Xing, Z.; Li, X.; Song, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Xing, Y. Tyrosine receptor kinase B silencing inhibits anoikis-resistance and improves anticancer efficiency of sorafenib in human renal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, M.; Onishi, H.; Ozono, K.; Yamasaki, A.; Imaizumi, A.; Kamakura, S.; Nakano, K.; Oda, Y.; Sumimoto, H.; Nakamura, M. Tropomyosin-related kinase B mediated signaling contributes to the induction of malignant phenotype of gallbladder cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 36211–36224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, L.; Zheng, J.; Geng, L.; Zhao, S. MiR-101 inhibits ovarian carcinogenesis by repressing the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 7, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, D.P.; Patel, P. BDNF: An oncogene or tumor suppressor? Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 3983–3990. [Google Scholar]
- de Moraes, J.K.; Wagner, V.P.; Fonseca, F.P.; Vargas, P.A.; de Farias, C.B.; Roesler, R.; Martins, M.D. Uncovering the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tyrosine kinase receptor B signaling in head and neck malignancies. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2018, 47, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Harada, T.; Ijichi, K.; Tanaka, K.; Liu, R.; Shibahara, D.; Kawano, Y.; Otsubo, K.; Yoneshima, Y.; Iwama, E.; et al. Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its receptor TrkB is associated with poor prognosis and a malignant phenotype in small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 120, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, G.; Valtorta, E.; Cerea, G.; Amatu, A.; Schirru, M.; Marrapese, G.; Fiorillo, V.; Recchimuzzo, P.; Cavenago, I.S.; Bonazzina, E.F.; et al. TRKA expression and NTRK1 gene copy number across solid tumours. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Ye, H.Q.; Ren, Q.C. Upregulation of the BDNF/TrKB pathway promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, as well as the migration and invasion of cervical cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.C.M.; Cartell, A.; de Farias, C.B.; Bakos, R.M.; Roesler, R.; Schwartsmann, G. Tropomyosin-related kinase receptor and neurotrophin expression in cutaneous melanoma is associated with a poor prognosis and decreased survival. Oncology 2019, 97, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.T.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.J.; Xi, Y.F.; Chen, L.H. Expression of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in astrocytomas. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Diaz, A.K.; Paugh, B.S.; Rankin, S.L.; Ju, B.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Qu, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. The genomic landscape of diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma and pediatric non-brainstem high-grade glioma. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmez, I.; Zhang, Y.; Manigat, L.; Benamar, M.; Brenneman, B.; Nakano, I.; Godlewski, J.; Bronisz, A.; Lee, J.; Abbas, T.; et al. Combined c-Met/Trk inhibition overcomes resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4360–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, K.V.; Alves, C.; Buendia, M.; Gil, M.S.; Thomaz, A.; Schwartsmann, G.; de Farias, C.B.; Roesler, R. Targeting tyrosine receptor kinase B in gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ni, J.; Xie, S.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Luu, V.; Sun, Y.; Bandopadhayay, P.; Beroukhim, R.; Roberts, T.M.; Stiles, C.D.; Segal, R.A.; et al. Tyrosine receptor kinase B is a drug target in astrocytomas. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinet, S.; Bessette, B.; Vedrenne, N.; Lacroix, A.; Richard, L.; Jauberteau, M.O.; Battu, S.; Lalloué, F. TrkB-containing exosomes promote the transfer of glioblastoma aggressiveness to YKL-40-inactivated glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 50349–50364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maris, J.M.; Hogarty, M.D.; Bagatell, R.; Cohn, S.L. Neuroblastoma. Lancet 2007, 369, 2106–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawara, A.; Arima-Nakagawara, M.; Scavarda, N.J.; Azar, C.G.; Cantor, A.B.; Brodeur, G.M. Association between high levels of expression of the TRK gene and favorable outcome in human neuroblastoma. N. Eng. J. Med. 1993, 328, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawara, A.; Arima-Nakagawara, M.; Azar, C.G.; Scavarda, N.J.; Brodeur, G.M. Clinical significance of expression of neurotrophic factors and their receptors in neuroblastoma. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1994, 385, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Scala, S.; Wosikowski, K.; Giannakakou, P.; Valle, P.; Biedler, J.L.; Spengler, B.A.; Lucarelli, E.; Bates, S.E.; Thiele, C.J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects neuroblastoma cells from vinblastine toxicity. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 3737–3742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaboin, J.; Kim, C.J.; Kaplan, D.R.; Thiele, C.J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of TrkB protects neuroblastoma cells from chemotherapy-induced apoptosis via phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase pathway. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6756–6763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Woo, C.W.; Thiele, C.J. Downregulation of Bim by brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of TrkB protects neuroblastoma cells from paclitaxel but not etoposide or cisplatin-induced cell death. Cell Death Diff. 2007, 14, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Wada, R.K.; Yamashiro, J.M.; Kaplan, D.R.; Thiele, C.J. Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and p145TrkB affects survival, differentiation, and invasiveness of human neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Z.; Gu, X.; Dong, Y.; Tan, F.; Liu, Z.; Thiele, C.J.; Li, Z. PI3K and MAPK pathways mediate the BDNF/TrkB-increased metastasis in neuroblastoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 16227–16236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogenmann, E.; Peterson, S.; Maekawa, K.; Matsushima, H. Regulation of NGF responsiveness in human neuroblastoma. Oncogene 1998, 17, 2367–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bunone, G.; Mariotti, A.; Compagni, A.; Morandi, E.; Della Valle, G. Induction of apoptosis by p75 neurotrophin receptor in human neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene 1997, 14, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eggert, A.; Sieverts, H.; Ikegaki, N.; Brodeur, G.M. p75 mediated apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells is inhibited by expression of TrkA. Med. Pediatr Oncol. 2000, 35, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshan, V.; Ashton, J.; Schor, N.F. p75NTR: An enhancer of fenretinide toxicity in neuroblastoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ho, R.; Minturn, J.E.; Simpson, A.M.; Iyer, R.; Light, J.E.; Evans, A.E.; Brodeur, G.M. The effect of P75 on Trk receptors in neuroblastomas. Cancer Lett. 2011, 305, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Levetzow, C.; Jiang, X.; Gwye, Y.; von Levetzow, G.; Hung, L.; Cooper, A.; Hsu, J.H.; Lawlor, E.R. Modeling initiation of Ewing sarcoma in human neural crest cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinen, T.E.; dos Santos, R.P.; da Rocha, A.; dos Santos, M.P.; Lopez, P.L.; Silva Filho, M.A.; Souza, B.K.; Rivero, L.F.; Becker, R.G.; Gregianin, L.J. Trk inhibition reduces cell proliferation and potentiates the effects of chemotherapeutic agents in Ewing sarcoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34860–34880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewitt, J.; Ochoa, V.; Urschitz, J.; Elston, M.; Moisyadi, S.; Nishi, R. Constitutively active TrkB confers an aggressive transformed phenotype to a neural crest-derived cell line. Oncogene 2014, 33, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nobusawa, S.; Hirato, J.; Yokoo, H. Molecular genetics of ependymomas and pediatric diffuse gliomas: A short review. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2014, 31, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassaletta, A.; Zapotocky, M.; Bouffet, E.; Hawkins, C.; Tabori, U. An integrative molecular and genomic analysis of pediatric hemispheric low-grade gliomas: An update. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanan, M.I.; Underhill, D.A.; Eisenstat, D.D. Targeting epigenetic pathways in the treatment of pediatric diffuse (high grade) gliomas. Neurotherapeutics 2017, 14, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T.; Hutter, B.; Jäger, N.; Korshunov, A.; Kool, M.; Warnatz, H.J.; Zichner, T.; Lambert, S.R.; Ryzhova, M.; Quang, D.A.; et al. Recurrent somatic alterations of FGFR1 and NTRK2 in pilocytic astrocytoma. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, H.; Monje, M. Neuronal activity in ontogeny and oncology. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagel, C.; Treszl, A.; Fehlert, J.; Harder, J.; von Haxthausen, F.; Kern, M.; von Bueren, A.O.; Kordes, U. Supra- and infratentorial pediatric ependymomas differ significantly in NeuN, p75 and GFAP expression. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 112, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaretti, A.; Aloe, L.; Antonelli, A.; Ruggiero, A.; Piastra, M.; Riccardi, R.; Tamburrini, G.; Di Rocco, C. Neurotrophic factor expression in childhood low-grade astrocytomas and ependymomas. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2004, 20, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portich, J.P.; Gil, M.S.; dos Santos, R.P.; Goulart, B.K.; Ferreira, M.B.; Loss, J.F.; Gregianin, L.J.; Brunetto, A.L.; Brunetto, A.T.; Roesler, R.; et al. Low brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels are associated with active disease and poor prognosis in childhood acute leukemia. Cancer Biomark. 2016, 17, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, Y.; Molina, R.P., Jr.; Rorke, L.B.; Kaplan, D.R.; Radeke, M.; Feinstein, S.C.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Neurotrophins and neuronal versus glial differentiation in medulloblastomas and other pediatric brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol. 1998, 95, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washiyama, K.; Muragaki, Y.; Rorke, L.B.; Lee, V.M.; Feinstein, S.C.; Radeke, M.J.; Blumberg, D.; Kaplan, D.R.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Neurotrophin and neurotrophin receptor proteins in medulloblastomas and other primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the pediatric central nervous system. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 148, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eberhart, C.G.; Kaufman, W.E.; Tihan, T.; Burger, P.C. Apoptosis, neuronal maturation, and neurotrophin expression within medulloblastoma nodules. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, T.; Watanabe, T.; Katayama, Y.; Kurihara, J.; Yoshino, A.; Nishimoto, H.; Kishimoto, H. TrkA expression is associated with an elevated level of apoptosis in classic medulloblastomas. Neuropathology 2006, 26, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokunai, T.; Sawa, H.; Tamaki, N. Functional analysis of trk proto-oncogene product in medulloblastoma cells. Neurol. Med. Chir. 1996, 36, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harel, L.; Costa, B.; Tcherpakov, M.; Zapatka, M.; Oberthuer, A.; Hansford, L.M.; Vojvodic, M.; Levy, Z.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lee, F.S.; et al. CCM2 mediates death signaling by the TrkA receptor tyrosine kinase. Neuron 2009, 63, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, L.; Costa, B.; Fainzilber, M. On the death Trk. Dev. Neurobiol. 2010, 70, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsetos, C.D.; Del Valle, L.; Legido, A.; de Chadarévian, J.P.; Perentes, E.; Mörk, S.J. On the neuronal/neuroblastic nature of medulloblastomas: A tribute to Pio del Rio Hortega and Moises Polak. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 105, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muragaki, Y.; Chou, T.T.; Kaplan, D.R.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Nerve growth factor induces apoptosis in human medulloblastoma cell lines that express TrkA receptors. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. A novel apoptotic pathway induced by nerve growth factor-mediated TrkA activation in medulloblastoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent induction of gadd45 expression in nerve growth factor-induced apoptosis in medulloblastomas. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 41120–41127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, A.; Lenzi, L.; Nakagawara, A.; Osaki, T.; Chiaretti, A.; Aloe, L. Tumor suppressor proteins are differentially affected in human ependymoblastoma and medulloblastoma cells exposed to nerve growth factor. Cancer Investig. 2007, 25, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valderrama, X.; Rapin, N.; Verge, V.M.; Misra, V. Zhangfei induces the expression of the nerve growth factor receptor, trkA, in medulloblastoma cells and causes their differentiation or apoptosis. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 91, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnarchuk, T.W.; Napper, S.; Rapin, N.; Misra, V. Mechanism for the induction of cell death in ONS-76 medulloblastoma cells by Zhangfei/CREB-ZF. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 109, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; MacDonald, J.I.; Hryciw, T.; Meakin, S.O. Nerve growth factor activation of the TrkA receptor induces cell death, by macropinocytosis, in medulloblastoma Daoy cells. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 882–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; MacDonald, J.I.; Talebian, A.; Leuenberger, J.; Seah, C.; Pasternak, S.H.; Michnick, S.W.; Meakin, S.O. Unravelling the mechanism of TrkA-induced cell death by macropinocytosis in medulloblastoma Daoy cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 2596–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Kean, M.J.; Ast, V.; Knight, J.D.; Mett, A.; Levy, Z.; Ceccarelli, D.F.; Badillo, B.G.; Eils, R.; König, R.; et al. STK25 protein mediates TrkA and CCM2 protein-dependent death in pediatric tumor cells of neural origin. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29285–29289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.L.; de Farias, C.B.; Abujamra, A.L.; Kapczinski, F.; Schwartsmann, G.; Brunetto, A.L.; Roesler, R. BDNF and PDE4, but not the GRPR, regulate viability of human medulloblastoma cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2010, 40, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, A.; Jaeger, M.; Buendia, M.; Bambini-Junior, V.; Gregianin, L.J.; Brunetto, A.L.; Brunetto, A.T.; de Farias, C.B.; Roesler, R. BDNF/TrkB signaling as a potential novel target in pediatric brain tumors: Anticancer activity of selective TrkB inhibition in medulloblastoma cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 59, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, A.; de Vargas Pinheiro, K.; Souza, B.K.; Gregianin, L.; Brunetto, A.L.; Brunetto, A.T.; de Farias, C.B.; Jaeger, M.D.C.; Ramaswamy, V.; Nör, C.; et al. Antitumor activities and cellular changes induced by TrkB inhibition in medulloblastoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nör, C.; de Farias, C.B.; Abujamra, A.L.; Schwartsmann, G.; Brunetto, A.L.; Roesler, R. The histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate in combination with brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces the viability of DAOY human medulloblastoma cells. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2011, 27, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, D.P.; Coyle, B.; Walker, D.A.; Grabowska, A.M. In vitro models of medulloblastoma: Choosing the right tool for the job. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 236, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ommeren, R.; Garzia, L.; Holgado, B.L.; Ramaswamy, V.; Taylor, M.D. The molecular biology of medulloblastoma metastasis. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincenti, A.P.; Ríos, A.S.; Paratcha, G.; Ledda, F. Mechanisms that modulate and diversify BDNF functions: Implications for hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnappah-Kang, N.D.; Mrak, R.E.; Paulsen, D.B.; Marchetti, D. Heparanase expression and TrkC/p75NTR ratios in human medulloblastoma. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2006, 23, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, R.A.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Kwon, Y.K.; Stiles, C.D.; Pomeroy, S.L. Expression of the neurotrophin receptor TrkC is linked to a favorable outcome in medulloblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12867–12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotzer, M.A.; Janss, A.J.; Fung, K.; Biegel, J.A.; Sutton, L.N.; Rorke, L.B.; Zhao, H.; Cnaan, A.; Phillips, P.C.; Lee, V.M.; et al. TrkC expression predicts good clinical outcome in primitive neuroectodermal brain tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotzer, M.A.; Hogarty, M.D.; Janss, A.J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Eggert, A.; Sutton, L.N.; Rorke, L.B.; Brodeur, G.M.; Phillips, P.C. MYC messenger RNA expression predicts survival outcome in childhood primitive neuroectodermal tumor/medulloblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 2425–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowski, S.; von Bueren, A.; von Hoff, K.; Hartmann, W.; Shalaby, T.; Deinlein, F.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Soerensen, N.; Emser, A.; Bode, U.; et al. Prognostic relevance of clinical and biological risk factors in childhood medulloblastoma: Results of patients treated in the prospective multicenter trial HIT’91. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2651–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, C.; Shalaby, T.; Oehler, C.; Pruschy, M.; Seifert, B.; Picard, D.; Remke, M.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Kortmann, R.D.; Rutkowski, S.; et al. Tropomyosin receptor kinase C (TrkC) expression in medulloblastoma: Relation to the molecular subgroups and impact on treatment response. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomeroy, S.L.; Sutton, M.E.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Segal, R.A. Neurotrophins in cerebellar granule cell development and medulloblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 1997, 35, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Ho, M.; Ma, J.; Parkes, R.K.; Mainprize, T.G.; Ueda, S.; McLaughlin, J.; Bouffet, E.; Rutka, J.T.; Hawkins, C.E. A clinicobiological model predicting survival in medulloblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7613–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajjar, A.; Hernan, R.; Kocak, M.; Fuller, C.; Lee, Y.; McKinnon, P.J.; Wallace, D.; Lau, C.; Chintagumpala, M.; Ashley, D.M. Clinical, histopathologic, and molecular markers of prognosis: Toward a new disease risk stratification system for medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Sutton, M.E.; Lu, D.J.; Cho, T.A.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Goritchenko, L.; Kaufman, J.R.; Lam, K.K.; Billet, A.L.; Tarbell, N.J. Activation of neurotrophin-3 receptor TrkC induces apoptosis in medulloblastomas. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Shinwari, Z.; Al-Hindi, H.; Al-Shail, E.; Khafaga, Y.; Al-Kofide, A.; El-Kum, N.; Aboussekhra, A. Response of medulloblastoma cells to vincristine and lomustine: Role of TRKC, CTNNB1 and STK15. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 1721–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.Y.; Nelson, A.L.; Algon, S.A.; Graves, O.; Sturla, L.M.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Rowitch, D.H.; Segal, R.A.; Pomeroy, S.L. Medulloblastoma tumorigenesis diverges from cerebellar granule cell differentiation in patched heterozygous mice. Dev. Biol. 2003, 263, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnappah-Kang, N.D.; Kaiser, A.J.; Blust, B.E.; Mrak, R.E.; Marchetti, D. Heparanase, TrkC and p75NTR: Their functional involvement in human medulloblastoma cell invasion. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 27, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber-Olipitz, M.; Ströbel, T.; Chen, W.Q.; Grotzer, M.A.; Quehenberger, F.; Slavc, I.; Lubec, G. Synthesis, chaperoning, and metabolism of proteins are regulated by NT-3/TrkC signaling in the medulloblastoma cell line DAOY. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 1932–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber-Olipitz, M.; Ströbel, T.; Kang, S.U.; John, J.P.; Grotzer, M.A.; Slavc, I.; Lubec, G. Neurotrophin 3/TrkC-regulated proteins in the human medulloblastoma cell line DAOY. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, E.; De Smaele, E.; Po, A.; Di Marcotullio, L.; Tosi, E.; Espinola, M.S.; Di Rocco, C.; Riccardi, R.; Giangaspero, F.; Farcomeni, A.; et al. MicroRNA profiling in human medulloblastoma. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühren, J.; Christoph, A.H.; Buslei, R.; Albrecht, S.; Wiestler, O.D.; Pietsch, T. Expression of the neurotrophin receptor p75NTR in medulloblastomas is correlated with distinct histological and clinical features: Evidence for a medulloblastoma subtype derived from the external granule cell layer. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 59, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, M.; Eberhart, C.G.; Collins, R.; Tihan, T. Expression of p75NTR in fetal brain and medulloblastomas: Evidence of a precursor cell marker and its persistence in neoplasia. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 92, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, D.; Mrak, R.E.; Paulsen, D.D.; Sinnappah-Kang, N.D. Neurotrophin receptors and heparanase: A functional axis in human medulloblastoma invasion. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 26, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Küchler, J.; Hartmann, W.; Waha, A.; Koch, A.; Endl, E.; Wurst, P.; Kindler, D.; Mikeska, T.; Waha, A.; Goodyer, C.G.; et al. p75(NTR) induces apoptosis in medulloblastoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Xin, P. Inhibition of neurotrophin receptor p75 intramembrane proteolysis by gamma-secretase inhibitor reduces medulloblastoma spinal metastasis. Biochem. Biophy. Res. Commun. 2010, 403, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, L.C.; McClelland, R.; Aiken, C.; Bridges, M.; Liang, L.; Wang, X.; Di Curzio, D.; Del Bigio, M.R.; Taylor, M.D.; Werbowetski-Ogilvie, T.E. Deconstruction of medulloblastoma cellular heterogeneity reveals differences between the most highly invasive and self-renewing phenotypes. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Aiken, C.; McClelland, R.; Morrison, L.C.; Tatari, N.; Remke, M.; Ramaswamy, V.; Issaivanan, M.; Ryken, T.; Del Bigio, M.R.; et al. Characterization of novel biomarkers in selecting for subtype specific medulloblastoma phenotypes. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38881–38900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Morrison, L.C.; Tatari, N.; Stromecki, M.; Fresnoza, A.; Porter, C.J.; Del Bigio, M.R.; Hawkins, C.; Chan, J.A.; Ryken, T.C.; et al. CD271+ cells are diagnostic and prognostic and exhibit elevated MAPK activity in SHH medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4745–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, R.B.; Hevezi, P.; Lee, J.; Willhite, D.; Lechner, S.M.; Foster, A.C.; Zlotnik, A. Gene expression analyses reveal molecular relationships among 20 regions of the human CNS. Neurogenetics 2006, 7, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawn, S.; Krishna, N.; Pisklakova, A.; Qu, X.; Fenstermacher, D.A.; Fournier, M.; Vrionis, F.D.; Tran, N.; Chan, J.A.; Kenchappa, R.S.; et al. Neurotrophin signaling via TrkB and TrkC receptors promotes the growth of brain tumor-initiating cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 3814–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frattinic, V.; Trifonov, V.; Chan, J.M.; Castano, A.; Lia, M.; Abate, F.; Keir, S.T.; Ji, A.X.; Zoppoli, P.; Niola, F.; et al. The integrated landscape of driver genomic alterations in glioblastoma. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, Y.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, Y.E.; An, J.; Cho, G.H.; Ko, Y.H.; Joo, K.M.; Nam, D.H. NTRK1 fusion in glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishnavi, A.; Le, A.T.; Doebele, R.C. TRKing down an old oncogene in a new era of targeted therapy. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, L. Development of small-molecule tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK) inhibitors for NTRK fusion cancers. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyhárt, O.; Győrffy, B. Molecular stratifications, biomarker candidates and new therapeutic options in current medulloblastoma treatment approaches. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of larotrectinib in TRK fusion-positive cancers in adults and children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.S.; Wong, M.; Mayoh, C.; Kumar, A.; Tsoli, M.; Mould, E.; Tyrrell, V.; Khuong-Quang, D.A.; Pinese, M.; Gayevskiy, V.; et al. Brief report: Potent clinical and radiological response to larotrectinib in TRK fusion-driven high-grade glioma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Receptor | TrkA | TrkB | TrkC | Truncated TrkC | p75NTR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of alteration | Expression and activation by NGF [100] | Expression and activation by BDNF [93] | Inhibition [110,111] | Overexpression and NT-3 activation [117] | Overexpression [131] | Expression [137] | Inhibition [136] |
| Main functional effect | ↑Cell death (apoptosis [101] or micropinocytosis [106]) ↓Proliferation and ↑differentiation [94] | ↓Cell viability [109] BDNF+ HDACi ↓ Cell viability [112] | ↓Cell viability, proliferation and survival [110] ↑Apoptosis and differentiation↓ Subcutaneous tumor growth in nude mice [111] | ↑Apoptosis and differentiation [125] | ↑Proliferation Targeted by miR-9 and miR-125a to inhibit cell proliferation [131] | Marker for SHH progenitor/stem cells [137] | ↓Migration, proliferation and spinal metastasis [136] |
| Clinical evidence | Apoptotic index and neuronal differentiation [95] | Unknown | Unknown | Higher overall survival [118] Favorable outcome [120] High expression in SHH MB [121] | Unknown | Potential diagnostic and prognostic marker for SHH group [138,139] | Unknown |
| Marker | Subgroups | p-Value (High vs Low Gene Expression Levels) | Hazard Ratio | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTRK1 | All | 0.0727 | 0.7512 | 0.55 to 1.02 |
| WNT | 0.2113 | 0.1654 | 0.009 to 2.77 | |
| SHH | 0.0195 | 2.142 | 1.13 to 4.05 | |
| Group3 | 0.0728 | 0.5038 | 0.28 to 0.89 | |
| Group4 | 0.8478 | 1.046 | 0.65 to 1.66 | |
| NTRK2 | All | 0.7805 | 1.045 | 0.76 to 1.42 |
| WNT | 0.0531 | 0.1022 | 0.01 to 1.03 | |
| SHH | 0.0328 | 2.014 | 1.06 to 3.81 | |
| Group3 | 0.7083 | 0.987 | 0.55 to 1.75 | |
| Group4 | 0.254 | 1.321 | 0.80 to 2.16 | |
| NTRK3 | All | <0.0001 | 0.5242 | 0.38 to 0.71 |
| WNT | 0.0574 | 0.1067 | 0.01 to 1.07 | |
| SHH | 0.4931 | 0.8012 | 0.42 to 1.51 | |
| Group3 | 0.1206 | 0.6388 | 0.35 to 1.13 | |
| Group4 | 0.0097 | 0.5352 | 0.33 to 0.85 | |
| NGF | All | 0.0784 | 0.743 | 0.55 to 0.99 |
| WNT | 0.9105 | 0.8902 | 0.08 to 9.41 | |
| SHH | 0.8937 | 1.044 | 0.55 to 1.97 | |
| Group3 | 0.5987 | 0.8576 | 0.48 to 1.52 | |
| Group4 | 0.2205 | 0.7505 | 0.47 to 1.19 | |
| BDNF | All | 0.0104 | 1.503 | 1.10 to 2.05 |
| WNT | 0.1552 | 0.08509 | 0.008 to 0.86 | |
| SHH | 0.7331 | 0.8956 | 0.47 to 1.69 | |
| Group3 | 0.7175 | 1.111 | 0.62 to 1.97 | |
| Group4 | 0.1912 | 1.377 | 0.83 to 2.26 | |
| NT-3 | All | 0.5943 | 1.088 | 0.79 to 1.48 |
| WNT | 0.9406 | 0.9141 | 0.08 to 9.74 | |
| SHH | 0.6472 | 0.8559 | 0.44 to 1.66 | |
| Group3 | 0.1234 | 1.571 | 0.88 to 2.78 | |
| Group4 | 0.0135 | 0.5557 | 0.34 to 0.88 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomaz, A.; Jaeger, M.; Brunetto, A.L.; Brunetto, A.T.; Gregianin, L.; de Farias, C.B.; Ramaswamy, V.; Nör, C.; Taylor, M.D.; Roesler, R. Neurotrophin Signaling in Medulloblastoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092542
Thomaz A, Jaeger M, Brunetto AL, Brunetto AT, Gregianin L, de Farias CB, Ramaswamy V, Nör C, Taylor MD, Roesler R. Neurotrophin Signaling in Medulloblastoma. Cancers. 2020; 12(9):2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092542
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomaz, Amanda, Mariane Jaeger, Algemir L. Brunetto, André T. Brunetto, Lauro Gregianin, Caroline Brunetto de Farias, Vijay Ramaswamy, Carolina Nör, Michael D. Taylor, and Rafael Roesler. 2020. "Neurotrophin Signaling in Medulloblastoma" Cancers 12, no. 9: 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092542
APA StyleThomaz, A., Jaeger, M., Brunetto, A. L., Brunetto, A. T., Gregianin, L., de Farias, C. B., Ramaswamy, V., Nör, C., Taylor, M. D., & Roesler, R. (2020). Neurotrophin Signaling in Medulloblastoma. Cancers, 12(9), 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092542







