CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Delta (C/EBP?): A Previously Unrecognized Tumor Suppressor that Limits the Oncogenic Potential of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CEBPD mRNA Expression Is Decreased in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Tissue
2.2. C/EBPδ Protein Levels Are Decreased in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma but Not in Ampullary Carcinoma or Intrapancreatic Cholangiocarcinoma
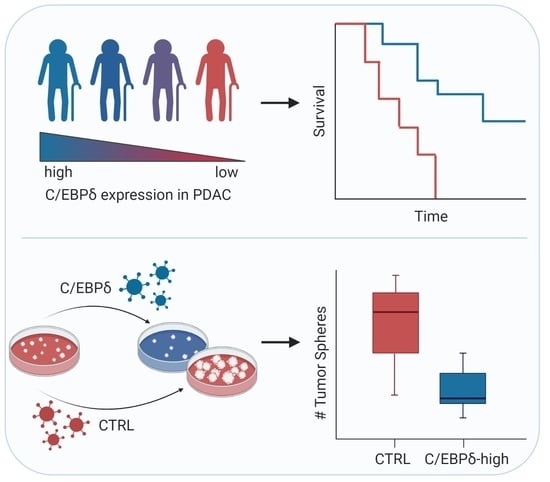
2.3. C/EBPδ Protein Expression Is Associated with Regional Lymph Node Involvement and Correlates with Overall Survival in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
2.4. C/EBPδ Modulates Oncogenesis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells
2.4.1. C/EBPδ Over-Expression Reduces Proliferation of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells
2.4.2. A Tet-on System Reveals Dose-Dependent Effects of C/EBPδ on Proliferation and Clonogenicity
2.4.3. Silencing C/EBPδ Enhances Proliferation of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mining of Publicly Available RNA Microarray Datasets
4.2. Tissue Microarray (TMA)
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Quantification of C/EBPδ Protein Levels
4.5. Cell Lines and Cell Culture Reagents
4.6. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis and RT-qPCR
4.7. Gene Transfection and Transduction
4.8. Fluorescent Activated Cell Sorting
4.9. Clonogenic Assay
4.10. Western Blot
4.11. Proliferation Assay
4.12. Soft Agar Tumor Sphere Formation Assay
4.13. Knock-down of C/EBPδ in CAPAN-2 Cells
4.14. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stark, A.P.; Sacks, G.D.; Rochefort, M.M.; Donahue, T.R.; Reber, H.A.; Tomslinson, J.S.; Dawson, D.W.; Eibl, G.; Hines, O.J. Long-term Survival in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Surgery 2016, 159, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, W.; Maitra, A.; Ying, H. Recent insights into the biology of pancreatic cancer. EBioMedicine 2020, 53, e102655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, M. Pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, D.P.; Hong, T.S.; Bardeesy, N. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, E.S.; Jaffee, E.; Azad, N.S. Current and emerging therapies for patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A bright future. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e135–e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenes, H.R.; Chiorean, E.G.; Dewitt, J.; Schmidt, M.; Loehrer, P. Locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Current therapeutic approach. Oncologist 2006, 11, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibi, A.; Adamian, Y.; Kelber, J.A. Cellular and molecular aspects of pancreatic cancer. Acta. Histochem. 2016, 118, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, D.H.; Bekaii-Saab, T. Ampullary cancer: An overview. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2014, 34, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeny, P.C. Computed tomography in the diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma and pancreatic carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 1999, 10, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hrad, V.; Abebe, Y.; Ali, S.H.; Velgersdyk, J.; Al Hallak, M.; Imam, M. Risk and Surveillance of Cancers in Primary Biliary Tract Disease. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, e3432640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cicenas, J.; Kvederaviciute, K.; Meskinyte, I.; Meskinyte-Kausiliene, E.; Skeberdyte, A. KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, SMAD4, BRCA1, and BRCA2 Mutations in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ying, H.; Elpek, K.G.; Vinjamoori, A.; Zimmerman, S.M.; Chu, G.C.; Yan, H.; Fletcher-Sananikone, E.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. PTEN is a major tumor suppressor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and regulates an NF-kB-cytokine network. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramji, D.P.; Foka, P. CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: Structure, function and regulation. Biochem. J. 2002, 365, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivko, G.S.; DeWille, J.W. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta (C/EBP delta) regulation and expression in human mammary epithelial cells: I. “Loss of function” alterations in the C/EBP delta growth inhibitory pathway in breast cancer cell lines. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 93, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, S.A.; Sarkar, T.R.; Balamurugan, K.; Sharan, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dowdy, S.F.; Huang, A.M.; Sterneck, E. C/EBPdelta targets cyclin D1 for proteasome-mediated degradation via induction of CDC27/APC3 expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9210–9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gery, S.; Tanosaki, S.; Hofmann, W.K.; Koppel, A.; Koeffler, H.P. C/EBPdelta expression in a BCR-ABL-positive cell line induces growth arrest and myeloid differentiation. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.C.; Li, C.F.; Ko, C.Y.; Pan, M.H.; Chen, P.J.; Tseng, J.T.; Wu, W.C.; Chang, W.C.; Huang, A.M.; Sterneck, E.; et al. CEBPD reverses RB/E2F1-mediated gene repression and participates in HMDB-induced apoptosis of cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5770–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Rourke, J.; Yuan, R.; DeWille, J. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-delta (C/EBP-delta) is induced in growth-arrested mouse mammary epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 6291–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thangaraju, M.; Rudelius, M.; Bierie, B.; Raffeld, M.; Sharan, S.; Hennighausen, L.; Huang, A.M.; Sterneck, E. C/EBPdelta is a crucial regulator of pro-apoptotic gene expression during mammary gland involution. Development 2005, 132, 4675–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza-Villanueva, D.; Balamurugan, K.; Ali, H.R.; Kim, S.R.; Sharan, S.; Johnson, R.C.; Merchant, A.S.; Caldas, C.; Landberg, G.; Sterneck, E. The C/EBPδ protein is stabilized by estrogen receptor α activity, inhibits SNAI2 expression and associates with good prognosis in breast cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6166–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmieri, C.; Monteverde, M.; Lattanzio, L.; Gojis, O.; Rudraraju, B.; Fortunato, M.; Syed, N.; Thompson, A.; Garrone, O.; Merlano, M.; et al. Site-specific CpG methylation in the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta (CEBPδ) CpG island in breast cancer is associated with metastatic relapse. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, D.; Sivko, G.S.; DeWille, J.W. Promoter methylation reduces C/EBPdelta (CEBPD) gene expression in the SUM-52PE human breast cancer cell line and in primary breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 95, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowamber, R.; Chehade, R.; Bitar, M.; Dodds, L.V.; Milea, A.; Slomovitz, B.; Shaw, P.A.; George, S.H.L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta (C/EBPδ) demonstrates a dichotomous role in tumor initiation and promotion of epithelial carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, C.Y.; Hsu, H.C.; Shen, M.R.; Chang, W.C.; Wang, J.M. Epigenetic silencing of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta activity by YY1/polycomb group/DNA methyltransferase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30919–33032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agrawal, S.; Hofmann, W.K.; Tidow, N.; Ehrich, M.; Van den Boom, D.; Koschmieder, S.; Berdel, W.E.; Serve, H.; Müller-Tidow, C. The C/EBPdelta tumor suppressor is silenced by hypermethylation in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2007, 109, 3895–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Tsai, H.H.; Ko, C.Y.; Pan, Y.C.; Yen, C.J.; Lai, H.Y.; Yuh, C.H.; Wu, W.C.; Wang, J.M. HMDB and 5-AzadC Combination Reverses Tumor Suppressor CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Delta to Strengthen the Death of Liver Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Cao, W.; Ma, B.; Li, M.; Chen, K.; Sideras, K.; Duitman, J.W.; Sprengers, D.; Khe Tran, T.C.; Ijzermans, J.N.M.; et al. Action and clinical significance of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.A.; Gutman, D.A.; Chisolm, C.; Appin, C.; Kong, J.; Rong, Y.; Kurc, T.; Van Meir, E.G.; Saltz, J.H.; Moreno, C.S.; et al. The tumor microenvironment strongly impacts master transcriptional regulators and gene expression class of glioblastoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 2108–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balamurugan, K.; Wang, J.; Tsai, H.; Sharan, S.; Anver, A.; Leighty, R.; Sterneck, E. The tumour suppressor C/EBPδ inhibits FBXW7 expression and promotes mammary tumour metastasis. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 4106–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.H.; Wu, W.J.; Wang, W.J.; Huang, H.Y.; Li, W.M.; Yeh, B.W.; Wu, T.F.; Shiue, Y.L.; Sheu, J.J.; Wang, J.M.; et al. CEBPD amplification and overexpression in urothelial carcinoma: A driver of tumor metastasis indicating adverse prognosis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31069–31084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.R.; Li, C.F.; Hung, L.Y.; Huang, A.M.; Tseng, J.T.; Tsou, J.H.; Wang, J.M. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta mediates tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced Aurora kinase C transcription and promotes genomic instability. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 28662–28670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Schetter, A.; He, P.; Funamizu, N.; Gaedcke, J.; Ghadimi, B.M.; Ried, T.; Hassan, R.; Yfantis, H.G.; Lee, D.H.; et al. DPEP1 inhibits tumor cell invasiveness, enhances chemosensitivity and predicts clinical outcome in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, H.; Li, L.; Fridley, B.L.; Jenkins, G.D.; Kalari, K.R.; Lingle, W.; Petersen, G.; Lou, Z.; Wang, L. FKBP51 affects cancer cell response to chemotherapy by negatively regulating Akt. Cancer Cell. 2009, 16, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben-Porath, I.; Thomson, M.W.; Carey, V.J.; Ge, R.; Bell, G.W.; Regev, A.; Weinberg, R.A. An embryonic stem cell-like gene expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human tumors. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, D.Y.; Villanueva, A.; Hoshida, Y.; Peix, J.; Nevell, P.; Minguez, B.; LeBlanc, A.C.; Donovan, D.J.; Thung, S.N.; Sole, M.; et al. Focal Gains of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A and Molecular Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6779–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Chang, T.; Wang, T.; Hsu, T.; Chi, J.; Hsiao, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, J. Hepatoma-derived growth factor supports the antiapoptosis and profibrosis of pancreatic stellate cells. Cancer Lett. 2019, 457, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, L.; Herlea, V.; Dima, S.O.; Dumitrascu, T.; Popescu, I. Combined gene expression analysis of whole-tissue and microdissected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma identifies genes specifically overexpressed in tumor epithelia. Hepato Gastroenterol. 2008, 55, 2016–2027. [Google Scholar]
- Grimont, A.; Pinho, A.V.; Cowley, M.J.; Augereau, C.; Mawson, A.; Giry-Laterriere, M.; Van den Steen, G.; Waddell, N.; Pajic, M.; Sempoux, C.; et al. SOX9 regulates ERBB signalling in pancreatic cancer development. Gut 2015, 64, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raphael, B.J.; Aguirre, A.J. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated Genomic Characterization of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2017, 32, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; He, P.; Wang, J.; Schetter, A.; Tang, W.; Funamizu, N.; Yanaga, K.; Uwagawa, T.; Satoskar, A.R.; Gaedcke, J.; et al. A Novel MIF Signaling Pathway Drives the Malignant Character of Pancreatic Cancer by Targeting NR3C2. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3838–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dijk, F.; Veenstra, V.L.; Soer, E.C.; Dings, M.P.G.; Zhao, L.; Halfwerk, J.B.; Hooijer, G.K.; Damhofer, H.; Marzano, M.; Steins, A.; et al. Unsupervised class discovery in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma reveals cell-intrinsic mesenchymal features and high concordance between existing classification systems. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmordgoli, M.; Martinez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Hoon, K.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Trevino, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.w.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, e2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Chang, J.T.; Andrechek, E.R.; Matsumura, N.; Baba, T.; Yao, G.; Kim, J.W.; Gatza, M.; Murphy, S.; Nevins, J.R. Anchorage-independent cell growth signature identifies tumors with metastatic potential. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2790–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maupin, K.A.; Sinha, A.; Eugster, E.; Miller, J.; Ross, J.; Paulino, V.; Keshamouni, V.G.; Tran, N.; Berens, M.; Webb, C.; et al. Glycogene expression alterations associated with pancreatic cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition in complementary model systems. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R2: Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform. Available online: http://r2.amc.nl (accessed on 5 August 2020).
- Balamurugan, K.; Sterneck, E. The many faces of C/EBPδ and their relevance for inflammation and cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Dis. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broad Institute; Firehose Broad GDAC; PAAD. Available online: https://gdac.broadinstitute.org/ (accessed on 3 December 2019).
- DeWille, J.W.; Sanford, D.C. C/EBPdelta is a downstream mediator of IL-6 induced growth inhibition of prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2005, 63, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.H.; Lai, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Li, C.F.; Huang, H.S.; Liu, H.S.; Tsai, Y.S.; Wang, J.M. Metformin promotes apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma through the CEBPD-induced autopathy pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13832–13845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, C.Y.; Chang, W.C.; Wang, J.M. Biological roles of CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein delta during inflammation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valls Serón, M.; Duitman, J.; Geldhoff, M.; Engelen-Lee, J.; Havik, S.R.; Brouwer, M.C.; Van de Beek, D.; Spek, C.A. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein δ (C/EBPδ) aggravates inflammation and bacterial dissemination during pneumococcal meningitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duitman, J.; Schouten, M.; Groot, A.P.; Daalhuisen, J.B.; Florquin, S.; Van der Poll, T.; Spek, C.A. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein δ facilitates bacterial dissemination during pneumococcal pneumonia in a platelet-activating factor receptor-dependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9113–9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duitman, J.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; Groot, A.P.; Ruela, R.R.; Van der Poll, T.; Florquin, S.; Spek, C.A. CCAAT-Enhancer-Binding Protein delta (C/EBPδ) protects against Klebsiella-pneumoniae-induced pulmonary infection; potential role for macrophage migration. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 1826–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duitmann, J.; Cong, L.; Moog, S.; Jaillet, M.; Castier, Y.; Cazes, A.; Borensztaijn, K.S.; Crestani, B.; Speck, C.A. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta (C/EBPδ) deficiency does not affect bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 3, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brzozowska, B.; Galecki, M.; Tartas, A.; Ginter, J.; Kazmierczak, U.; Lundholm, L. Freeware tool for analysing numbers and sizes of cell colonies. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2019, 58, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| N-Status | C/EBPδ Expression | |
|---|---|---|
| Low | High | |
| (N = 47) | (N = 20) | |
| N0 | 7 | 8 |
| N1 | 40 | 12 |
| Fisher’s exact test | p = 0.029 | |
| Median survival (months) | 16.9 | 22.2 |
| Characteristic | PDAC (N = 67) | AC (N = 42) | IP CCA (N = 20) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | |
| Median age (range) (years) | 63 (47–83) | 66.5 (48–78) | 64.5 (49–82) | |||
| Sex (M/F) | (49/18) | (73.2/26.8) | (28/14) | (66.7/33.3) | (12/8) | (60/40) |
| Surgery | ||||||
| PPPD | 59 | 88.1 | 39 | 92.9 | 18 | 90 |
| Whipple–Kausch | 8 | 11.9 | 3 | 7.1 | 2 | 10 |
| Radicality | ||||||
| R0 (≤1mm) | 32 | 47.8 | 38 | 90.5 | 15 | 75 |
| R1 (<1mm) | 27 | 40.3 | 4 | 9.5 | 5 | 25 |
| Dubious | 8 | 11.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Diameter post-op (cm) | ||||||
| 1–2 | 1 | 1.5 | N/A | N/A | ||
| 2–4 | 34 | 50.7 | N/A | N/A | ||
| 4–6 | 17 | 25.4 | N/A | N/A | ||
| N/A | 15 | 22.4 | ||||
| N-stage | ||||||
| N0 | 15 | 22.4 | 27 | 64.3 | 8 | 40 |
| N1 | 52 | 77.6 | 15 | 35.7 | 12 | 60 |
| Grading | ||||||
| Well differentiated | 2 | 3 | N/A | N/A | ||
| Moderately differentiated | 18 | 26.9 | N/A | N/A | ||
| Poorly differentiated | 21 | 31.3 | N/A | N/A | ||
| N/A | 26 | 38.8 | ||||
| Survival | ||||||
| Median (range) (months) | 18.33 (1.58–88.9) | 49.92 (6.6–127.38) | 24.36 (1.97–103.36) | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hartl, L.; Duitman, J.; Aberson, H.L.; Chen, K.; Dijk, F.; Roelofs, J.J.T.H.; Dings, M.P.G.; Hooijer, G.K.J.; Hernanda, P.Y.; Pan, Q.; et al. CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Delta (C/EBP?): A Previously Unrecognized Tumor Suppressor that Limits the Oncogenic Potential of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092546
Hartl L, Duitman J, Aberson HL, Chen K, Dijk F, Roelofs JJTH, Dings MPG, Hooijer GKJ, Hernanda PY, Pan Q, et al. CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Delta (C/EBP?): A Previously Unrecognized Tumor Suppressor that Limits the Oncogenic Potential of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells. Cancers. 2020; 12(9):2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092546
Chicago/Turabian StyleHartl, Leonie, JanWillem Duitman, Hella L. Aberson, Kan Chen, Frederike Dijk, Joris J.T.H. Roelofs, Mark P.G. Dings, Gerrit K.J. Hooijer, Pratika Y. Hernanda, Qiunwei Pan, and et al. 2020. "CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Delta (C/EBP?): A Previously Unrecognized Tumor Suppressor that Limits the Oncogenic Potential of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells" Cancers 12, no. 9: 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092546
APA StyleHartl, L., Duitman, J., Aberson, H. L., Chen, K., Dijk, F., Roelofs, J. J. T. H., Dings, M. P. G., Hooijer, G. K. J., Hernanda, P. Y., Pan, Q., Busch, O. R., Besselink, M. G. H., Boerman, T., Peppelenbosch, M. P., Bijlsma, M. F., & Spek, C. A. (2020). CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Delta (C/EBP?): A Previously Unrecognized Tumor Suppressor that Limits the Oncogenic Potential of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells. Cancers, 12(9), 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092546