Splenic Volume as a Surrogate Marker of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Efficacy in Metastatic Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
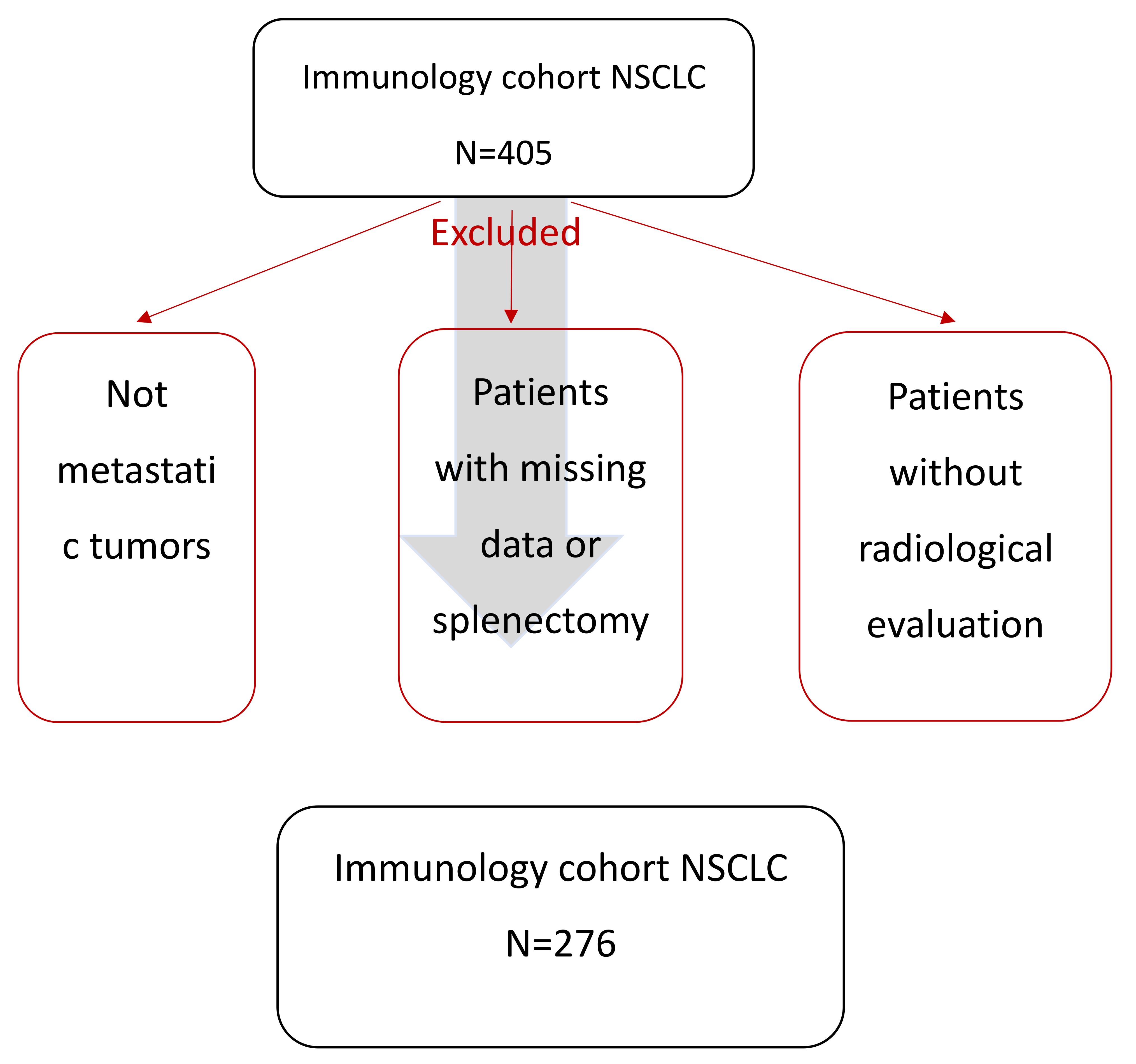
2.1. Study Population
2.2. PD-L1 Expression Analysis
2.3. Spleen Volume Estimation
2.4. LIPI Score Calculation
2.5. RNAseq Data
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Clinical Characteristics
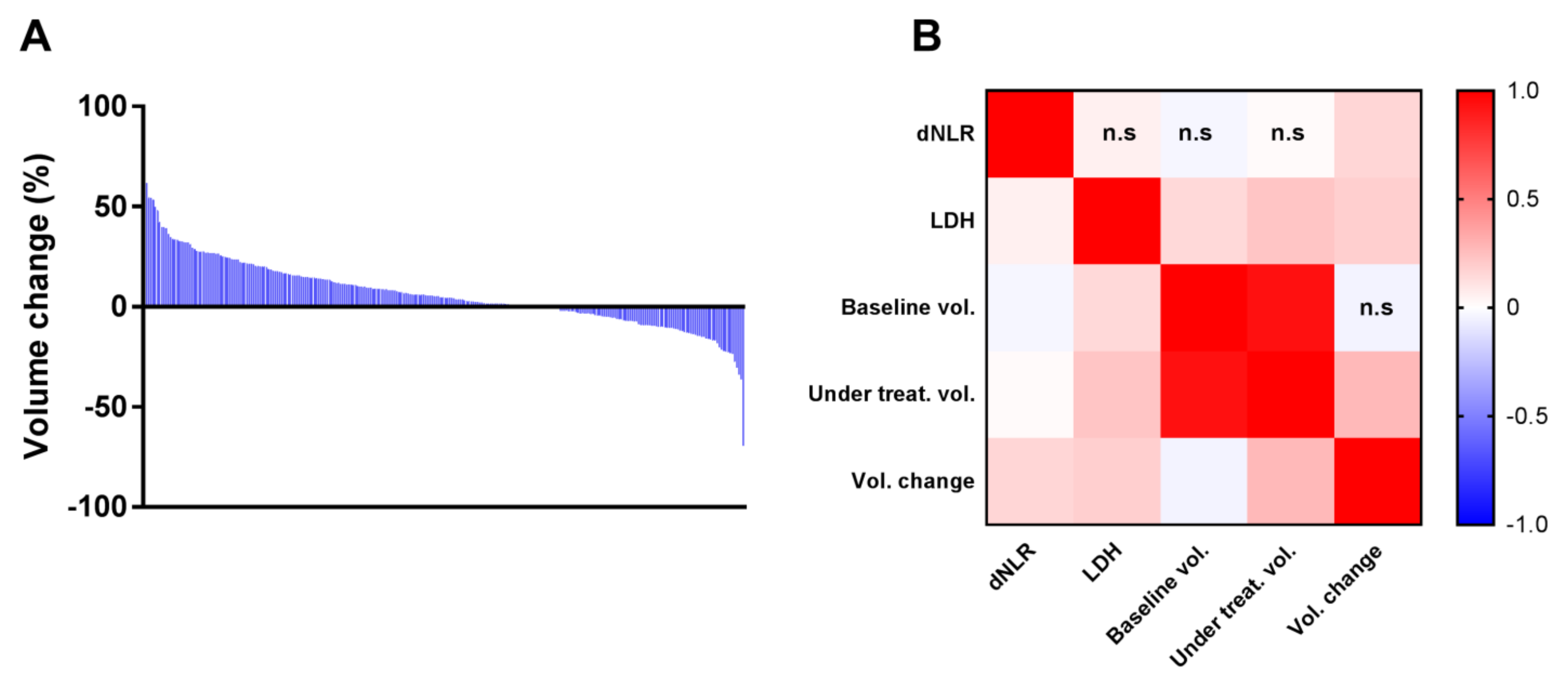
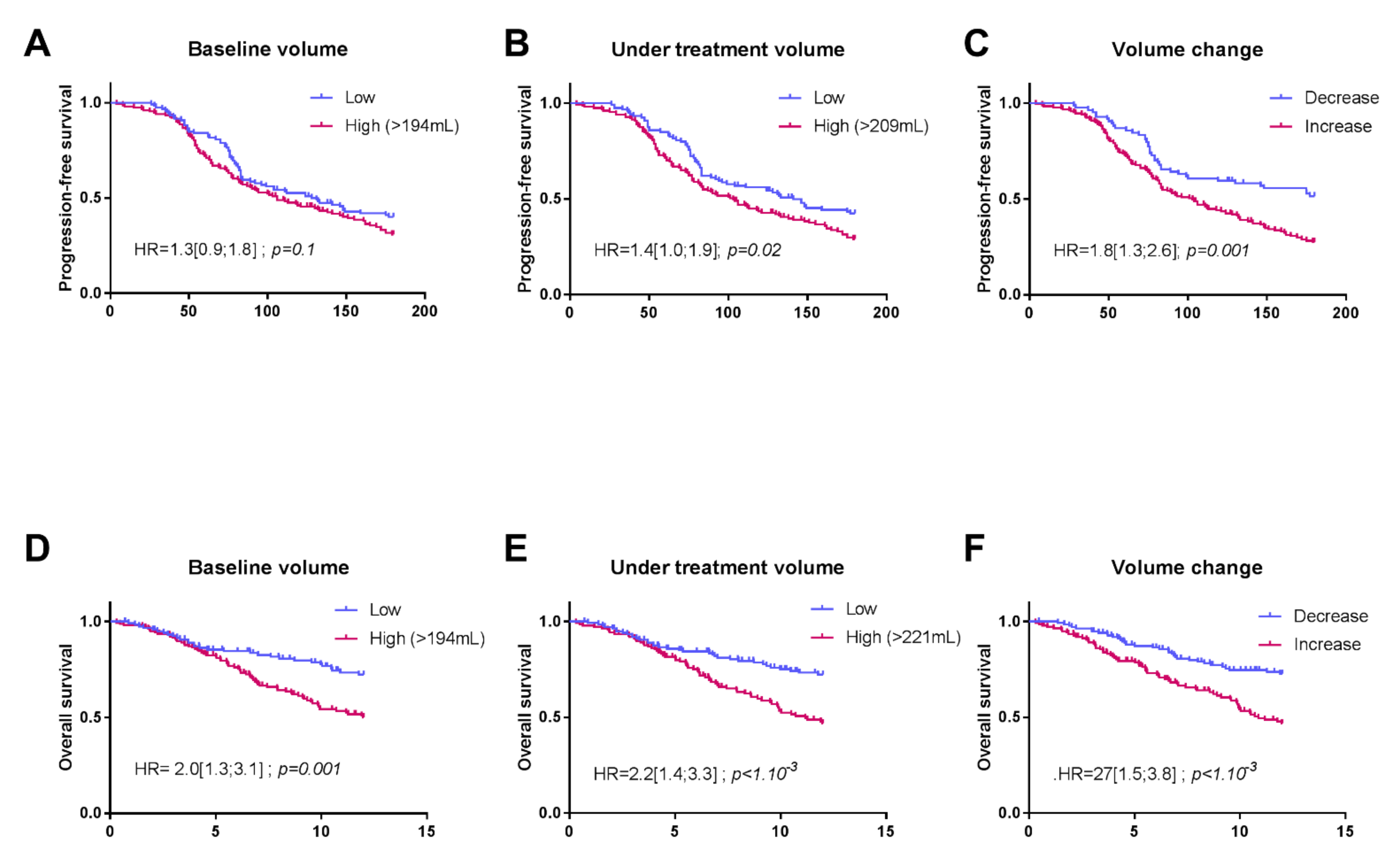
3.2. Associations between Splenic Volume and Progression-Free Survival (PFS) or Overall Survival (OS)
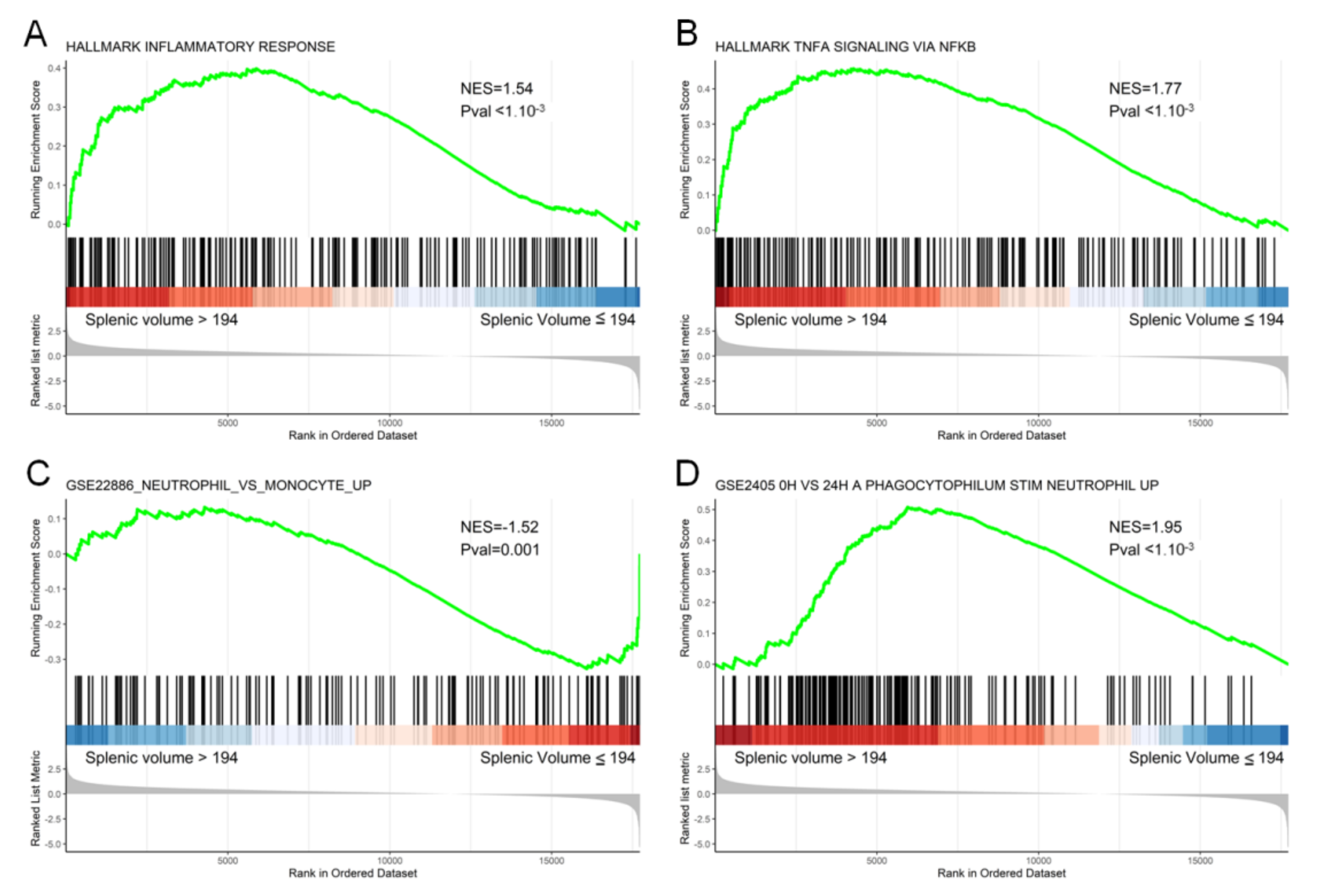
3.3. Transcriptomic and Histological Features Related to Splenic Volume
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bade, B.C.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Lung Cancer 2020: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Noguchi, M.; Nicholson, A.G.; Geisinger, K.R.; Yatabe, Y.; Beer, D.G.; Powell, C.A.; Riely, G.J.; Van Schil, P.E.; et al. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2011, 6, 244–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv192–iv237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, L.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Gadgeel, S.; Esteban, E.; Felip, E.; De Angelis, F.; Domine, M.; Clingan, P.; Hochmair, M.J.; Powell, S.F.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2078–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Ding, J.; Zhu, J.; Wei, H.; Zhao, K. Circulating and Tumor-Infiltrating Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Patients with Colorectal Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limagne, E.; Euvrard, R.; Thibaudin, M.; Rébé, C.; Derangère, V.; Chevriaux, A.; Boidot, R.; Végran, F.; Bonnefoy, N.; Vincent, J.; et al. Accumulation of MDSC and Th17 Cells in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Predicts the Efficacy of a FOLFOX-Bevacizumab Drug Treatment Regimen. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5241–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, Y.S.; Ammori, B.J.; Elkord, E. Increased Levels of Granulocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Peripheral Blood and Tumour Tissue of Pancreatic Cancer Patients. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 879897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trovato, R.; Fiore, A.; Sartori, S.; Canè, S.; Giugno, R.; Cascione, L.; Paiella, S.; Salvia, R.; De Sanctis, F.; Poffe, O.; et al. Immunosuppression by Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Carcinoma Is Orchestrated by STAT3. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabitass, R.F.; Annels, N.E.; Stocken, D.D.; Pandha, H.A.; Middleton, G.W. Elevated Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Pancreatic, Esophageal and Gastric Cancer Are an Independent Prognostic Factor and Are Associated with Significant Elevation of the Th2 Cytokine Interleukin-13. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2011, 60, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, R.; Wang, B.; Lian, J.; Yao, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, C.; Fang, L.; Guan, X.; Shi, J.; et al. Blocking IL-17A Enhances Tumor Response to Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Microsatellite Stable Colorectal Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghonim, M.A.; Ibba, S.V.; Tarhuni, A.F.; Errami, Y.; Luu, H.H.; Dean, M.J.; El-Bahrawy, A.H.; Wyczechowska, D.; Benslimane, I.A.; Del Valle, L.; et al. Targeting PARP-1 with Metronomic Therapy Modulates MDSC Suppressive Function and Enhances Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Colon Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronte, V.; Pittet, M.J. The Spleen in Local and Systemic Regulation of Immunity. Immunity 2013, 39, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnink, A.; Richard, C.; Truntzer, C.; Vincent, J.; Bengrine, L.; Vienot, A.; Borg, C.; Ghiringhelli, F. Baseline Splenic Volume as a Surrogate Marker of FOLFIRINOX Efficacy in Advanced Pancreatic Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 25617–25629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niogret, J.; Limagne, E.; Thibaudin, M.; Blanc, J.; Bertaut, A.; Le Malicot, K.; Rinaldi, Y.; Caroli-Bosc, F.-X.; Audemar, F.; Nguyen, S.; et al. Baseline Splenic Volume as a Prognostic Biomarker of FOLFIRI Efficacy and a Surrogate Marker of MDSC Accumulation in Metastatic Colorectal Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours: Revised RECIST Guideline (Version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prassopoulos, P.; Daskalogiannaki, M.; Raissaki, M.; Hatjidakis, A.; Gourtsoyiannis, N. Determination of Normal Splenic Volume on Computed Tomography in Relation to Age, Gender and Body Habitus. Eur. Radiol. 1997, 7, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, P.F.; Ascierto, P.A.; Pigozzo, J.; Del Vecchio, M.; Maio, M.; Antonini Cappellini, G.C.; Guidoboni, M.; Queirolo, P.; Savoia, P.; Mandalà, M.; et al. Baseline Neutrophils and Derived Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio: Prognostic Relevance in Metastatic Melanoma Patients Receiving Ipilimumab. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2016, 27, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-Optimal Probabilistic RNA-Seq Quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausen, B.; Schumacher, M. Maximally Selected Rank Statistics. Biometrics 1992, 48, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Interpreting Genome-Wide Expression Profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. ClusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes among Gene Clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Du, P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, W. Prognostic Role of Pretreatment Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Advanced Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 66 Cohort Studies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 58, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Dai, G. Significance of Baseline and Change in Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting Prognosis: A Retrospective Analysis in Advanced Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezquita, L.; Auclin, E.; Ferrara, R.; Charrier, M.; Remon, J.; Planchard, D.; Ponce, S.; Ares, L.P.; Leroy, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; et al. Association of the Lung Immune Prognostic Index with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Outcomes in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weide, B.; Martens, A.; Hassel, J.C.; Berking, C.; Postow, M.A.; Bisschop, K.; Simeone, E.; Mangana, J.; Schilling, B.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; et al. Baseline Biomarkers for Outcome of Melanoma Patients Treated with Pembrolizumab. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5487–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, S.J.; Kothari, S.; Aggarwal, C.; Bauml, J.M.; Alley, E.W.; Evans, T.L.; Kosteva, J.A.; Ciunci, C.A.; Gabriel, P.E.; Thompson, J.C.; et al. Pretreatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Marker of Outcomes in Nivolumab-Treated Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2017, 106, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrilovich, D.I. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Patel, S.; Tcyganov, E.; Gabrilovich, D.I. The Nature of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xing, Y.-F.; Lei, A.-H.; Xiao, Q.; Lin, Z.-H.; Hong, Y.-F.; Wu, X.-Y.; Zhou, J. Neutrophil Count Is Associated with Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cell Level and Presents Prognostic Value of for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24380–24388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, S.M.; Syed Khaja, A.S.; El Salhat, H.; Faour, I.; Kanbar, J.; Quadri, A.A.; Albashir, M.; Elkord, E. Myeloid Cells in Circulation and Tumor Microenvironment of Breast Cancer Patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2017, 66, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, K.R.; Kapoor, P.; Spongberg, E.; Tobin, R.P.; Gao, D.; Borges, V.F.; McCarter, M.D. Immunosuppressive Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Are Increased in Splenocytes from Cancer Patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2017, 66, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, T.J.; Greeneltch, K.M.; Reid, J.E.; Liewehr, D.J.; Steinberg, S.M.; Liu, K.; Abrams, S.I. Interferon Regulatory Factor-8 Modulates the Development of Tumour-Induced CD11b+Gr-1+ Myeloid Cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 3939–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.; Wang, A.; He, M.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, S. Increased Circulating Lin(-/Low) CD33(+) HLA-DR(-) Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2014, 44, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | All Patients (N = 276) |
|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Male | 193 (69.9) |
| Female | 83 (30.1) |
| Age at diagnosis, years, median (IQR) | 65.4 (13.3) |
| n (%) | |
| ≤60 | 86 (31.2) |
| >60 | 190 (68.8) |
| Smoking status, n (%) | |
| Never smoker | 17 (6.2) |
| Current or former smoker | 235 (85.1) |
| NA | 24 (8.9) |
| Histological type, n (%) | |
| Non-squamous Squamous | 170 (61.6) 82 (29.7) |
| Other | 24 (8.7) |
| WHO performance status, n (%) | |
| 0 | 80 (29) |
| >0 | 184 (66.7) |
| NA | 12 (4.3) |
| Cerebral metastasis, n (%) | 70 (25.4) |
| Liver metastasis, n (%) | 66 (23.9) |
| Bone metastasis, n (%) | 116 (42) |
| Lymph node metastasis, n (%) | 206(74.6) |
| Pleuro-peritoneal metastasis, n (%) | 169 (61.2) |
| Line of ICI, n (%) | |
| 1 | 94 (34) |
| >1 | 182 (66) |
| Type of ICI, n (%) | |
| Anti PD-L1 | 34 (12.3) |
| Anti PD-1 | 218 (79) |
| Anti CTLA4 | 1 (0.4) |
| Anti PD-L1 + anti CTLA4 | 4 (1.4) |
| Anti PD-1 + anti CTLA4 | 9 (3.3) |
| Other association | 10 (3.6) |
| PD-L1 status (cutoff at 1%), n (%) | |
| Negative tumors | 66 (23.9) |
| Positive tumors—Strong expressors | 146 (52.9) –75 |
| NA | 64 (23.2) |
| LDH, median (IQR) | 217 (86.8) |
| dNLR, median (IQR) | 2.3 (1.6) |
| LIPI score, n (%) | |
| 0 | 98 (35.5) |
| >0 | 132 (47.8) |
| NA | 46 (16.7) |
| OS (months) (95% IC) | 16.1 (13.2; 18.7) |
| PFS (months) (95% IC) | 3.7 (3.1; 4.9) |
| Variables | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Volume | Volume during Treatment | Volume Change | ||
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Male | 1.5 (1.0; 2.4) p = 0.06 | 0.8 (0.4; 1.5); p = 0.6 | 1.0 (0.5; 1.8); p = 0.9 | 0.9 (0.5; 1.7); p = 0.8 |
| Age at diagnosis, years, median (IQR) | -- | -- | -- | |
| ≤60 | 1 | |||
| >60 | 0.9 (0.6; 1.4); p = 0.7 | |||
| Smoking status | -- | -- | -- | |
| Never smoker | 1 | |||
| Current or former smoker | 1.8 (0.7; 4.9); p = 0.2 | |||
| Histological type | ||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Epidermoid | 1.4 (0.9; 2.1); p = 0.1 | 2.1 (1.1.1); p = 0.03 | 2.1 (1.1; 4.0); p = 0.02 | 1.6 (0.8; 3.1); p = 0.2 |
| Other | 1.4 (0.4; 0.7); p = 0.4 | 0.7 (0.2; 3.4); p = 0.7 | 0.73 (0.1; 3.3); p = 0.7 | 0.7 (0.1; 2.9); p = 0.6 |
| WHO performance status | ||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| >0 | 2.8 (1.7; 4.8); p < 1.10−3 | 1.8 (0.9; 3.5); p = 0.07 | 1.8 (0.9; 3.4); p = 0.09 | 1.7 (0.9; 3.4); p = 0.1 |
| Cerebral metastasis | 1.4 (0.9; 2.2); p = 0.1 | 1.3 (0.7; 2.6); p = 0.4 | 1.3 (0.66; 2.7); p = 0.42 | 1.2 (0.6; 2.3); p = 0.6 |
| Liver metastasis | 2.6 (1.7; 3.9); p < 1.10−3 | 2.9 (1.7; 5.1); p < 0.001 | 2.5 (1.5; 4.4); p = 0.001 | 2.2 (1.3; 3.9); p = 0.004 |
| Bone metastasis | 1.7 (1.1; 2.5); p = 0.01 | 2.1 (1.2; 3.7); p = 0.01 | 1.83 (1.0; 3.3); p = 0.05 | 1.9 (1.0; 3.6); p = 0.04 |
| Lymph node metastasis | 1.3 (0.8; 2.1); p = 0.3 | -- | -- | -- |
| Pleuro-peritoneal metastasis | 1.3 (0.9; 2.0); p = 0.2 | 1.2 (0.7; 2.2); p = 0.5 | 1.3 (0.7; 2.3); p = 0.4 | 1.4 (0.8; 2.4); p = 0.3 |
| Line of ICI | ||||
| 1 | 1 | |||
| >1 | 0.1 (0.04; 0.4); p < 1.10−3 | 0.2 (0.04; 0.7); p = 0.01 | 0.2 (0.04; 0.7); p = 0.01 | 0.2(0.04; 0.7); p = 0.01 |
| PD-L1 status (cut-off at 1%) | ||||
| Negative tumors | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Positive tumors | 0.6 (0.4; 1.0); p = 0.09 | 0.7 (0.4; 1.13); p = 0.1 | 0.7 (0.37; 1.20); p = 0.2 | 0.5 (0.3; 0.9); p = 0.03 |
| LDH | 1 (1; 1); p = 0.003 | -- | -- | -- |
| dNLR | 1.2 (1.1; 1.3); p < 1.10−3 | -- | -- | -- |
| LIPI score | ||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| >0 | 2.0 (1.3; 3.1); p = 0.003 | 1.4 (0.8; 2.5); p = 0.2 | 1.4 (0.8; 2.4); p = 0.3 | 1.3 (0.8; 2.3); p = 0.3 |
| Baseline volume | ||||
| ≤194 mL >194 mL | 1 | 1 | -- | -- |
| 2.0 (1.3; 3.1); p = 0.001 | 2.6 (1.4; 4.9); p = 0.002 | |||
| Volume during treatment | ||||
| ≤221 mL >221 mL | 1 | -- | 1 | -- |
| 2.2 (1.45; 3.3); p < 1.10−3 | 1.2 (0.7; 2.1); p = 0.4 | |||
| Volume change | ||||
| ≤4 >4 | 1 | -- | -- | 1 |
| 2.10 (1.1–3.8); p = 0.01 | ||||
| 2.27 (1.5; 3.8); p < 1.10−3 | ||||
| Variables | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Volume | Volume during Treatment | Volume Change | ||
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Male | 1.5 (1.1; 2.1); p = 0.03 | 1.0 (0.7; 1.6); p = 0.9 | 1.0 (0.7; 1.6); p = 0.9 | 1.1 (0.7; 1.6); p = 0.7 |
| Age at diagnosis, years, median (IQR) | -- | -- | -- | |
| ≤60 | 1 | |||
| >60 | 0.9 (0.7; 1.2); p = 0.5 | |||
| Smoking status | -- | -- | -- | |
| Never smoker | 1 | |||
| Current or former smoker | 0.7 (0.4; 1.3); p = 0.3 | |||
| Histological type | -- | -- | -- | |
| Adenocarcinoma Epidermoïd | 1 1.2 (0.9; 1.6); p = 0.4 | |||
| Other | 0.8 (0.5; 1.5); p = 0.5 | |||
| WHO performance status | -- | -- | -- | |
| 0 | 1 | |||
| >0 | 1.2 (0.84; 1.6); p = 0.3 | |||
| Cerebral metastasis | 1.2 (0.9; 1.7); p = 0.3 | -- | -- | -- |
| Liver metastasis, | 2.1 (17; 2.9); p < 1.10−3 | 1.9 (1.2; 2.80); p = 0.003 | 1.8 (1.2; 2.8); p = 0.003 | 1.8 (1.2; 2.7); p = 0.005 |
| Bone metastasis | 1.5 (1.1; 2.0); p = 0.01 | 1.5 (1.1; 2.2); p = 0.02 | 1.53 (1.1; 2.2); p = 0.02 | 1.51 (1.0; 2.2); p = 0.03 |
| Lymph node metastasis | 1.1 (0.8; 1.6); p = 0.7 | -- | -- | -- |
| Pleuro-peritoneal metastasis | 1.2 (0.9; 1.7); p = 0.04 | 1.38 (0.9; 2.0); p = 0.1 | 1.35 (0.9; 2.0); p = 0.1 | 1.36 (0.9; 2.0); p = 0.1 |
| Line of ICI | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| >1 | 0.06 (0.02; 0.2); p < 1.10−3 | 0 0.06 (0.02; 0.2); p < 0.001 | 0.06 (0.02; 0.2); p < 0.001 | 0.06 (0.02; 0.20); p < 0.001 |
| PD-L1 status (cut-off at 1%) | ||||
| Negative tumors | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Positive tumors | 0.7 (0.5; 0.9); p = 0.03 | 0.6 (0.4; 0.9); p = 0.01 | 0.6 (0.4; 0.9); p = 0.01 | 0.6 (0.4; 0.9); p = 0.01 |
| LDH | 1.0 (1.0; 1.0); p < 1.10−3 | -- | -- | -- |
| dNLR | 1.1 (1.0; 1.2); p = 0.4 | -- | -- | -- |
| LIPI score | -- | |||
| 0 | 1 | -- | -- | |
| >0 | 1.0 (0.7; 1.4); p = 0.9 | |||
| Baseline volume | ||||
| ≤194 mL >194 mL | 1 | -- | -- | |
| 1.3 (0.9; 1.8); p = 0.1 | 1.2 (0.9; 1.8); p = 0.2 | |||
| Volume during treatment | -- | -- | ||
| ≤209 mL >209 mL | 1 | |||
| 1.45 (1.0; 2.1); p = 0.05 | ||||
| 1.4 (1.0; 1.9); p = 0.02 | ||||
| Volume change | -- | -- | ||
| ≤0 >0 | 1 | |||
| 1.8 (1.3; 2.6); p = 0.001 | 1.3 (0.8; 2.1); p = 0.2 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galland, L.; Lecuelle, J.; Favier, L.; Fraisse, C.; Lagrange, A.; Kaderbhai, C.; Truntzer, C.; Ghiringhelli, F. Splenic Volume as a Surrogate Marker of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Efficacy in Metastatic Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123020
Galland L, Lecuelle J, Favier L, Fraisse C, Lagrange A, Kaderbhai C, Truntzer C, Ghiringhelli F. Splenic Volume as a Surrogate Marker of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Efficacy in Metastatic Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(12):3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123020
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalland, Loïck, Julie Lecuelle, Laure Favier, Cléa Fraisse, Aurélie Lagrange, Courèche Kaderbhai, Caroline Truntzer, and François Ghiringhelli. 2021. "Splenic Volume as a Surrogate Marker of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Efficacy in Metastatic Non Small Cell Lung Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 12: 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123020
APA StyleGalland, L., Lecuelle, J., Favier, L., Fraisse, C., Lagrange, A., Kaderbhai, C., Truntzer, C., & Ghiringhelli, F. (2021). Splenic Volume as a Surrogate Marker of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Efficacy in Metastatic Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers, 13(12), 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123020







