Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Lorlatinib and Alectinib for ALK-Rearrangement Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Asian and Non-Asian Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
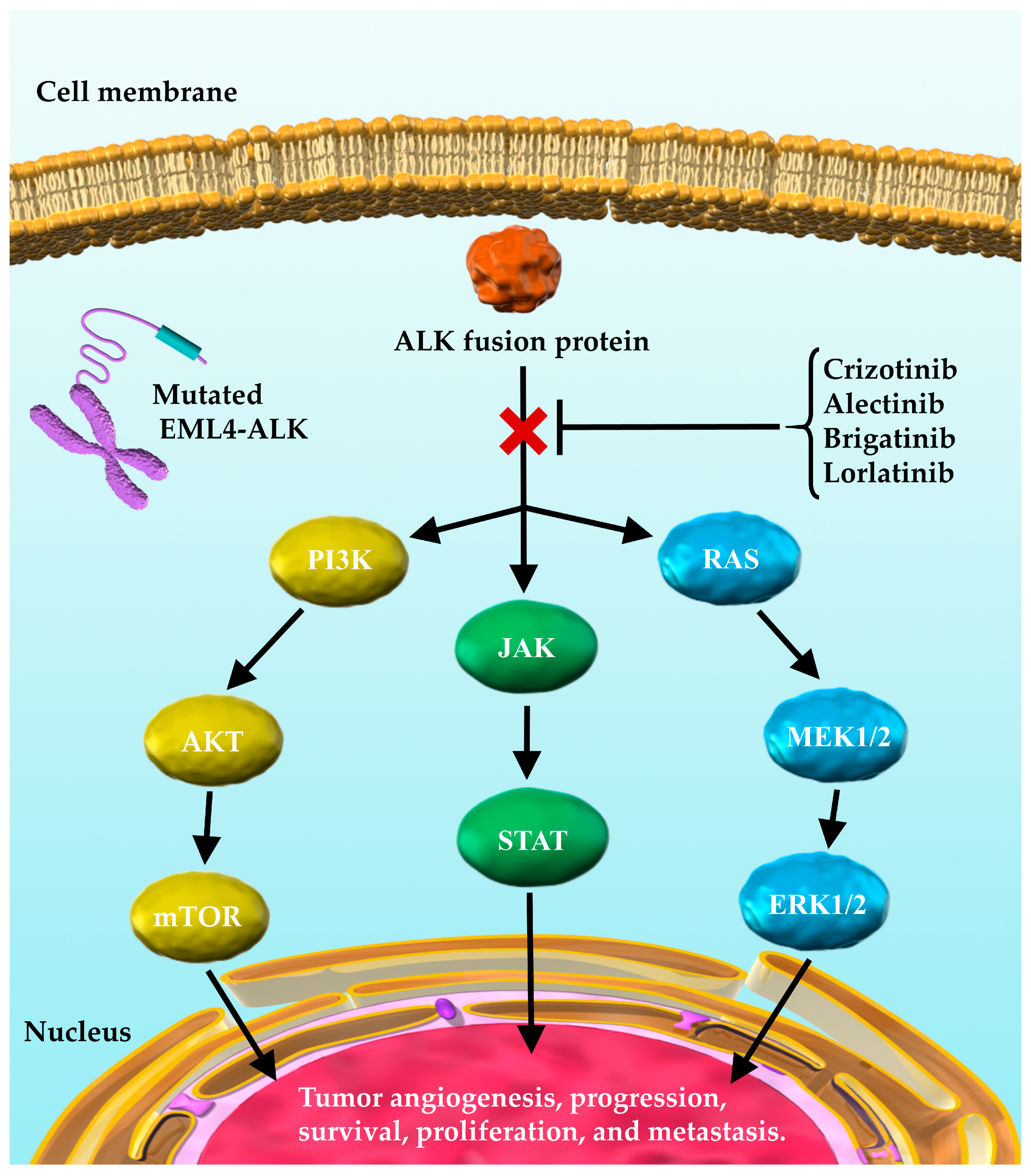
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review
2.2. Quality Evaluation
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria (Predefined PICOS)
2.3.1. Patients
2.3.2. Interventions and Comparisons
2.3.3. Outcomes
2.3.4. Study Design
2.4. Statistical Analysis Method of Network Meta-Analysis
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
2.6. Assessment for Between-Study Heterogeneity
2.7. Ethical Aspects
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Review
3.2. Primary Efficacy Endpoint: PFS
3.3. Subgroup Analysis for the Primary Efficacy Endpoint (PFS) in the Non-Asian and Asian Subgroups
3.3.1. Subgroup Analysis for the Primary Efficacy Endpoint (PFS) in the Non-Asian Subgroup
3.3.2. Subgroup Analysis for the Primary Efficacy Endpoint (PFS) in the Asian Subgroup
3.4. Subgroup Analysis for the Primary Efficacy Endpoint (PFS) in the Subgroups with and without CNS Metastases
3.4.1. Subgroup Analysis for the Primary Efficacy Endpoint (PFS) in the Subgroups with CNS Metastasis
3.4.2. Subgroup Analysis for the Primary Efficacy Endpoint (PFS) in the Subgroup without CNS Metastasis
3.5. Subgroup Analysis by PS for PFS
3.6. Primary Efficacy Endpoint: OS
3.7. Secondary Efficacy Endpoint: Proportions of Objective Response (ObRs)
3.8. Primary Safety Endpoint: Incidence of G3-AEs
3.9. Secondary Safety Endpoints: Incidence of AG-AEs, AG-SAEs, and G3-SAEs
3.10. Secondary Safety Endpoints: Incidence of AG-Nausea, G3-Nausea, AG-Diarrhea, and G3-Diarrhea
3.11. Secondary Safety Endpoints: Incidence of AG-AST, G3-AST, AG-ALT, and G3-ALT
3.12. Secondary Safety Endpoinst: Incidence of AG-Pneumonitis and G3-Pneumonitis
3.13. Bias Assessment
3.14. Sensitivity Analysis
3.15. Assessment of Between-Study Heterogeneity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Search Strategies in PubMed (Searched on 6 May 2021)
| Search | Query | Results |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | (“Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer” OR “Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma” OR “Non Small Cell Lung Carcinoma” OR “Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma” OR “Non small Cell Lung Cancer” OR “Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinomas” OR “NSCLC”) | 82,152 |
| #2 | (“crizotinib”[ALL] OR (“crizotinib”[Supplementary Concept] OR “PF-02341066”[ALL] OR “PF 02341066”[ALL] OR “PF02341066”[ALL] OR “xalkori”[ALL] OR “ceritinib”[ALL] OR “ceritinib”[Supplementary Concept] OR “LDK-378”[ALL] OR “LDK 378”[ALL] OR “LDK378”[ALL] OR “zykadia”[ALL]) OR “alectinib”[ALL] OR (“alectinib”[Supplementary Concept] OR “CH-5424802”[ALL] OR “CH 5424802”[ALL] OR “CH5424802”[ALL] OR “RO-5424802”[ALL] OR “RO 5424802”[ALL] “RO5424802”[ALL] OR “alecensa”[ALL]) OR “brigatinib”[ALL] OR (“brigatinib”[Supplementary Concept] OR “AP-26113”[ALL] OR “AP 26113”[ALL] OR “AP26113”[ALL] OR “alunbrig”[ALL]) OR “lorlatinib”[ALL] OR (“lorlatinib” [Supplementary Concept] OR “PF-06463922”[ALL] OR “PF 06463922”[ALL] OR “PF06463922”[ALL] OR “lorbrena”[ALL]) OR “cisplatin”[ALL] OR “cisplatin”[Supplementary Concept] OR “CDDP”[ALL] OR “carboplatin”[ALL] OR “carboplatin”[Supplementary Concept] OR “CBDCA”[ALL] OR “Platinum”[ALL]) | 129,332 |
| #3 | (“anaplastic lymphoma kinase” OR “ALK inhibitor” OR “ALK“ OR “ALKI”) | 11,907 |
| #4 | (“Randomized Controlled trial”[Title/Abstract] OR “Controlled clinical trial”[Title/Abstract] OR “Randomized”[Title/Abstract] OR “Placebo”[Title/Abstract] OR “Randomly”[Title/Abstract] OR “Trial”[Title/Abstract] OR “Drug Therapy”[Title/Abstract] OR ”Groups”[Title/Abstract]) | 3,149,296 |
| #5 | #1 AND #2 AND #3 AND #4 | 361 |
References
- Nasim, F.; Sabath, B.F.; Eapen, G.A. Lung cancer. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duma, N.; Santana-Davila, R.; Molina, J.R. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Aisner, D.L.; Wood, D.E.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; Dilling, T.J.; Dobelbower, M.; et al. NCCN guidelines insights: Non-small cell lung cancer, Version 5.2018. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Jemal, A. Lung cancer statistics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 893, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, I.; Planchard, D. ALK Inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: The latest evidence and developments. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 8, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, J.; Pareek, V.; Liu, H.; Cheng, H. Emerging treatment for ALK-positive lung cancer. Exp. Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2016, 21, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.I.; Shirai, K. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) signaling in lung cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 893, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, L.; Solomon, B. New treatment options for ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2015, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducray, S.P.; Natarajan, K.; Garland, G.D.; Turner, S.D.; Egger, G. The transcriptional roles of ALK fusion proteins in tumorigenesis. Cancers 2019, 11, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aubry, A.; Galiacy, S.; Allouche, M. Targeting ALK in cancer: Therapeutic potential of proapoptotic peptides. Cancers 2019, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamaoka, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ohba, M.; Ohmori, T. Receptor tyrosine kinase-targeted cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rybarczyk-Kasiuchnicz, A.; Ramlau, R.; Stencel, K. Treatment of brain metastases of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.C.; Itchins, M.; Khasraw, M. Brain metastases in lung cancers with emerging targetable fusion drivers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griesinger, F.; Roeper, J.; Pöttgen, C.; Willborn, K.C.; Eberhardt, W.E.E. Brain metastases in ALK-positive NSCLC—Time to adjust current treatment algorithms. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 35181–35194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, I.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Palmer, J.D.; Mehra, R.; Lu, B. Targeting brain metastases in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e510–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.; Dhillon, S. Alectinib: A review in advanced, ALK-positive NSCLC. Drugs 2018, 78, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A. Alectinib for ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Exp. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 9, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeage, K. Alectinib: A review of its use in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Drugs 2015, 75, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Nokihara, H.; Kondo, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Azuma, K.; Seto, T.; Takiguchi, Y.; Nishio, M.; Yoshioka, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, H.; Ninomiya, K.; Kenmotsu, H.; Morise, M.; Daga, H.; Goto, Y.; Kozuki, T.; Miura, S.; Sasaki, T.; Tamiya, A.; et al. The Japanese Lung Cancer Society guideline for non-small cell lung cancer, stage IV. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 24, 731–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isozaki, H.; Ichihara, E.; Takigawa, N.; Ohashi, K.; Ochi, N.; Yasugi, M.; Ninomiya, T.; Yamane, H.; Hotta, K.; Sakai, K.; et al. Non-small cell lung cancer cells acquire resistance to the ALK inhibitor alectinib by activating alternative receptor tyrosine kinases. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1506–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syed, Y.Y. Lorlatinib: First global approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Darsa, H.; Abdel-Rahman, O.; Sangha, R. Pharmacological and clinical properties of lorlatinib in the treatment of ALK-rearranged advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Exp. Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, J.R.; Soo, R.A. Lorlatinib for the Treatment of ALK-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Exp. Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2020, 20, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.; Milner-Watts, C.; Perna, M.; Janzic, U.; Vidal, N.; Kaudeer, N.; Ahmed, M.; McDonald, F.; Locke, I.; Minchom, A.; et al. Systemic treatment of brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 132, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.Y.; Friboulet, L.; Kodack, D.P.; Engstrom, L.D.; Li, Q.; West, M.; Tang, R.W.; Wang, H.; Tsaparikos, K.; Wang, J.; et al. PF-06463922, an ALK/ROS1 inhibitor, overcomes resistance to first and second generation ALK inhibitors in preclinical models. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, T.W.; Richardson, P.F.; Bailey, S.; Brooun, A.; Burke, B.J.; Collins, M.R.; Cui, J.J.; Deal, J.G.; Deng, Y.L.; Dinh, D.; et al. Discovery of (10R)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2h-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo [4,3-h][2,5,11]-benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile (PF-06463922), a macrocyclic inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) with preclinical brain exposure and broad-spectrum potency against ALK-resistant mutations. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4720–4744. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-line lorlatinib or crizotinib in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, I.R. Network meta-analysis. STATA J. 2015, 15, 951–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornell, J.E. The PRISMA extension for network meta-analysis: Bringing clarity and guidance to the reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 797–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, A.; Higgins, J.P.; Geddes, J.R.; Salanti, G. Conceptual and technical challenges in network meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jansen, J.P.; Crawford, B.; Bergman, G.; Stam, W. Bayesian meta-analysis of multiple treatment comparisons: An introduction to mixed treatment comparisons. Value Health 2008, 11, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, G.; Ades, A.E. Combination of direct and indirect evidence in mixed treatment comparisons. Stat. Med. 2004, 23, 3105–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumley, T. Network meta-analysis for indirect treatment comparisons. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonin, F.S.; Rotta, I.; Mendes, A.M.; Pontarolo, R. Network meta-analysis: A technique to gather evidence from direct and indirect comparisons. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 15, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ades, A.E.; Cliffe, S. Markov chain Monte Carlo estimation of a multiparameter decision model: Consistency of evidence and the accurate assessment of uncertainty. Med. Decis. Mak. 2002, 22, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials [CENTRAL]. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/ (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Embase. Available online: https://www.embase.com/login (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- SCOPUS. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/home.uri (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.; Flemyng, E. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, J.P.; Fleurence, R.; Devine, B.; Itzler, R.; Barrett, A.; Hawkins, N.; Lee, K.; Boersma, C.; Annemans, L.; Cappelleri, J.C. Interpreting indirect treatment comparisons and network meta-analysis for health-care decision making: Report of the ISPOR task force on indirect treatment comparisons good research practices: Part 1. Value Health 2011, 14, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoaglin, D.C.; Hawkins, N.; Jansen, J.P.; Scott, D.A.; Itzler, R.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Boersma, C.; Thompson, D.; Larholt, K.M.; Diaz, M.; et al. Conducting indirect-treatment-comparison and network-meta-analysis studies: Report of the ISPOR task force on indirect treatment comparisons good research practices: Part 2. Value Health 2011, 14, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dias, S.; Welton, N.J.; Sutton, A.J.; Caldwell, D.M.; Lu, G.; Ades, A.E. Evidence synthesis for decision making 4: Inconsistency in networks of evidence based on randomized controlled trials. Med. Decis. Mak. 2013, 33, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dias, S.; Sutton, A.J.; Welton, N.J.; Ades, A.E. Evidence synthesis for decision making 3: Heterogeneity—subgroups, meta-regression, bias, and bias-adjustment. Med. Decis. Mak. 2013, 33, 618–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, S.; Sutton, A.J.; Ades, A.E.; Welton, N.J. Evidence synthesis for decision making 2: A generalized linear modeling framework for pairwise and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Med. Decis. Mak. 2013, 33, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salanti, G.; Ades, A.E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: An overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, S.P.; Roberts, G.O. Convergence assessment techniques for Markov chain Monte Carlo. Stat. Comput. 1998, 8, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.P.; Gelman, A. General methods for monitoring convergence of iterative simulations. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1998, 7, 434–455. [Google Scholar]
- Chootrakool, H.; Shi, J.Q.; Yue, R. Meta-analysis and sensitivity analysis for multi-arm trials with selection bias. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copas, J.; Shi, J.Q. Meta-analysis, funnel plots and sensitivity analysis. Biostatistics 2000, 1, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.L.; Lu, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shi, Y.K.; Sriuranpong, V.; Ho, J.C.M.; Ong, C.K.; Tsai, C.M.; Chung, C.H.; et al. Results of PROFILE 1029, a phase III comparison of first-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in east asian patients with ALK-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.; Kim, S.W.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, J.J.; Cheng, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Bu, L.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated Asian patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ALESIA): A randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.J.; et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.J.; Yang, J.C.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Hochmair, M.J.; Li, J.Y.; Chang, G.C.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Brigatinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Akimoto, K.; Sato, H.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Homma, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohmori, T.; et al. Brigatinib and alectinib for ALK rearrangement-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer with or without central nervous system metastasis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabari, J.K.; Santini, F.C.; Schram, A.M.; Bergagnini, I.; Chen, R.; Mrad, C.; Lai, W.V.; Arbour, K.C.; Drilon, A. The activity, safety, and evolving role of brigatinib in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancers. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.W.; Tiseo, M.; Ahn, M.J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Hansen, K.H.; Kim, S.W.; Huber, R.M.; West, H.L.; Groen, H.J.M.; Hochmair, M.J.; et al. Brigatinib in patients with crizotinib-refractory anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: A randomized, multicenter phase II trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2490–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, M.; Christopoulos, P. Therapeutic sequencing in ALK(+) NSCLC. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrona, A.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Jassem, J. Management of brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer in the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 71, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Soo, R.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Chiari, R.; Bearz, A.; Lin, C.C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a global phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, D. Lung cancer: First-in-man phase I trial with lorlatinib. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okada, K.; Araki, M.; Sakashita, T.; Ma, B.; Kanada, R.; Yanagitani, N.; Horiike, A.; Koike, S.; Oh-Hara, T.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Prediction of ALK mutations mediating ALK-TKIs resistance and drug re-purposing to overcome the resistance. EBioMedicine 2019, 41, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.J.; Zhu, V.W.; Yoda, S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Schrock, A.B.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Jessop, N.A.; Jiang, G.Y.; Le, L.P.; Gowen, K.; et al. Impact of EML4-ALK variant on resistance mechanisms and clinical outcomes in ALK-positive lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, T.; Myung, S.K.; Pham, T.T.; Park, B. Efficacy of crizotinib, ceritinib, and alectinib in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer treatment: A meta-analysis of clinical trials. Cancers 2020, 12, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.C.; Lee, Y.L.; Li, C.Y. Which should be used first for ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Chemotherapy or targeted therapy? A meta-analysis of five randomized trials. Medicina 2019, 55, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.; Fong, T.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, J.; Luo, P. The efficacy and safety of ALK inhibitors in the treatment of ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 4993–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.H.; Chen, H.L.; Chang, H.M.; Tsai, Y.C.; Wu, K.L.; Chen, I.H.; Chen, K.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, C.L.; et al. Systematic review and network meta-analysis of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors for treatment-naïve ALK-positive lung cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Bai, Z.; Hsieh, S.C.; Kelly, S.E.; Chen, L.; Skidmore, B.; Yousef, S.; Zheng, C.; Stewart, D.J.; Wells, G.A. ALK inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, H.; Lu, Y.; Hao, W.; Han, L. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: A meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Song, J.; Teng, L.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Li, B. Comparison of lorlatinib, alectinib and brigatinib in ALK inhibitor-naive/untreated ALK-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Chemother. 2021, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gristina, V.; La Mantia, M.; Iacono, F.; Galvano, A.; Russo, A.; Bazan, V. The emerging therapeutic landscape of ALK inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ando, K.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohmori, T.; Sagara, H. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Lorlatinib and Alectinib for ALK-Rearrangement Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Asian and Non-Asian Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 3704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153704
Ando K, Manabe R, Kishino Y, Kusumoto S, Yamaoka T, Tanaka A, Ohmori T, Sagara H. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Lorlatinib and Alectinib for ALK-Rearrangement Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Asian and Non-Asian Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2021; 13(15):3704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153704
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndo, Koichi, Ryo Manabe, Yasunari Kishino, Sojiro Kusumoto, Toshimitsu Yamaoka, Akihiko Tanaka, Tohru Ohmori, and Hironori Sagara. 2021. "Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Lorlatinib and Alectinib for ALK-Rearrangement Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Asian and Non-Asian Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis" Cancers 13, no. 15: 3704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153704
APA StyleAndo, K., Manabe, R., Kishino, Y., Kusumoto, S., Yamaoka, T., Tanaka, A., Ohmori, T., & Sagara, H. (2021). Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Lorlatinib and Alectinib for ALK-Rearrangement Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Asian and Non-Asian Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 13(15), 3704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153704







