Deep Learning Based Automated Orthotopic Lung Tumor Segmentation in Whole-Body Mouse CT-Scans
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Experimental and Imaging Procedures
2.1.1. Animals
2.1.2. Tumor Model
2.1.3. Experimental Protocol
2.1.4. Animal Imaging
2.1.5. Manual Segmentation
2.2. Automatic Image Segmentation
2.2.1. Deep Learning Algorithm
2.2.2. µCBCT to Mass Density Conversion
3. Results
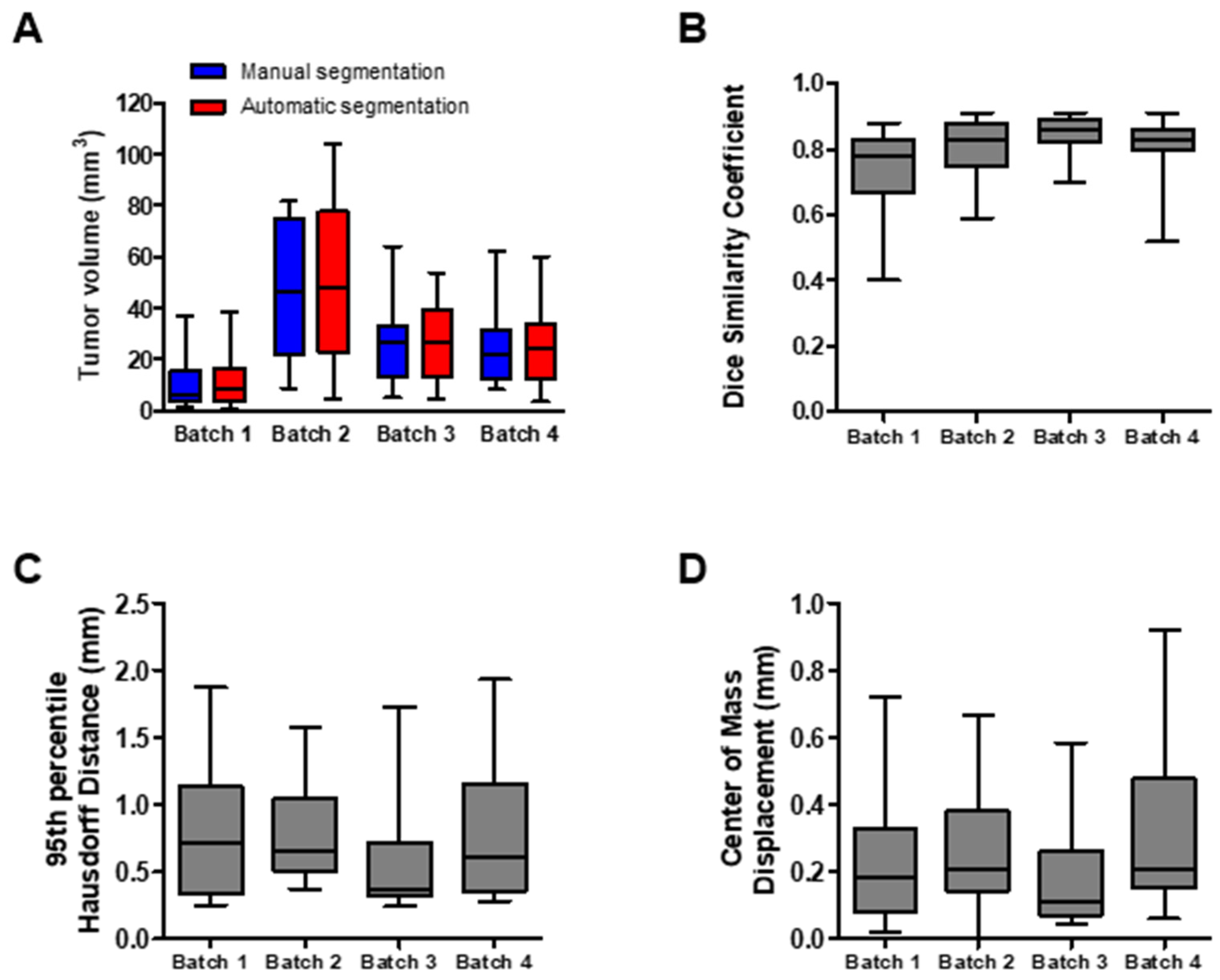
3.1. Quantitative Evaluation of the Segmentation Performance
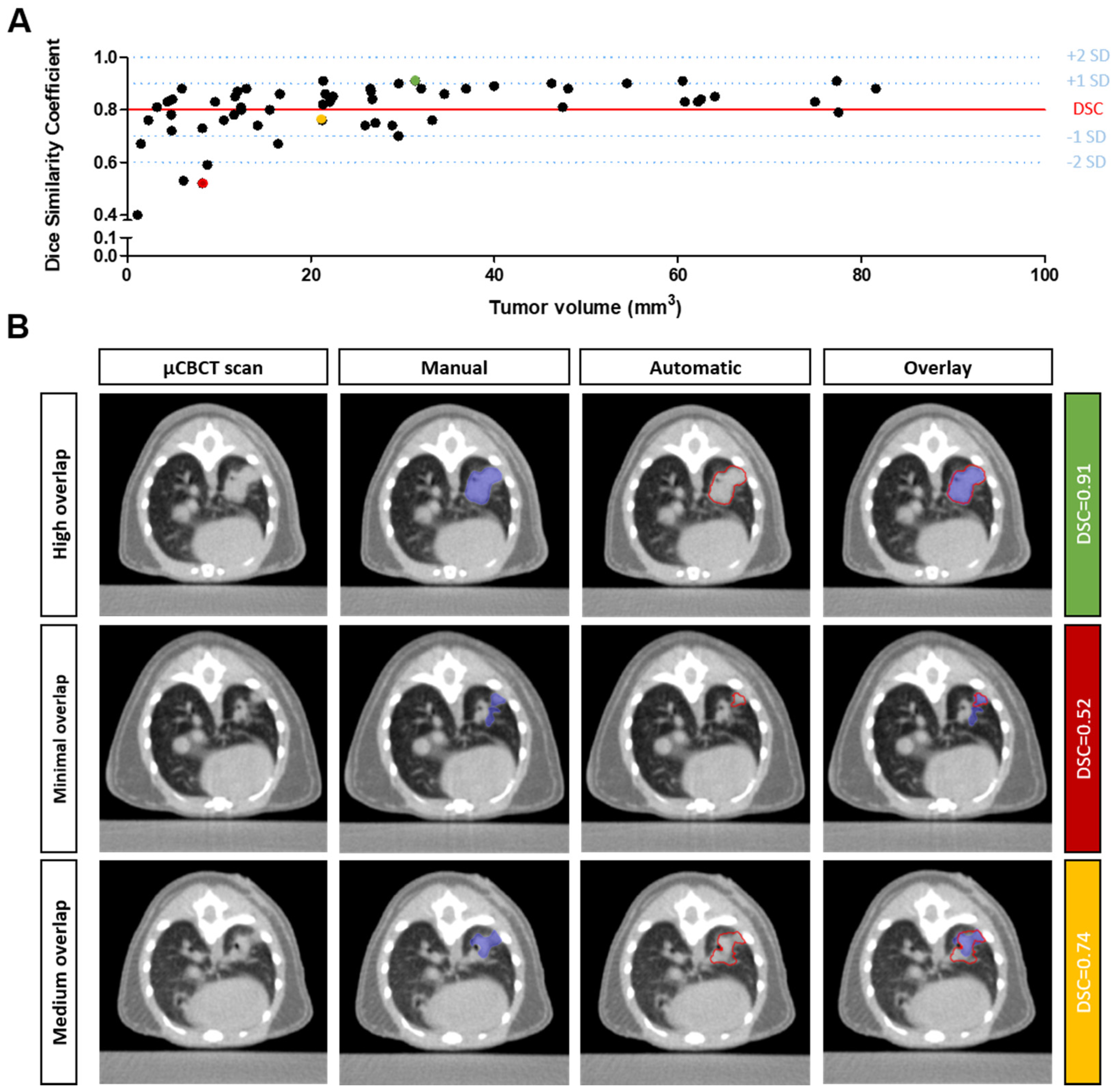
3.2. Qualitative Evaluation of the Segmentation Performance
3.3. Assessment of Subjectivity and Bias in Human Interpretation
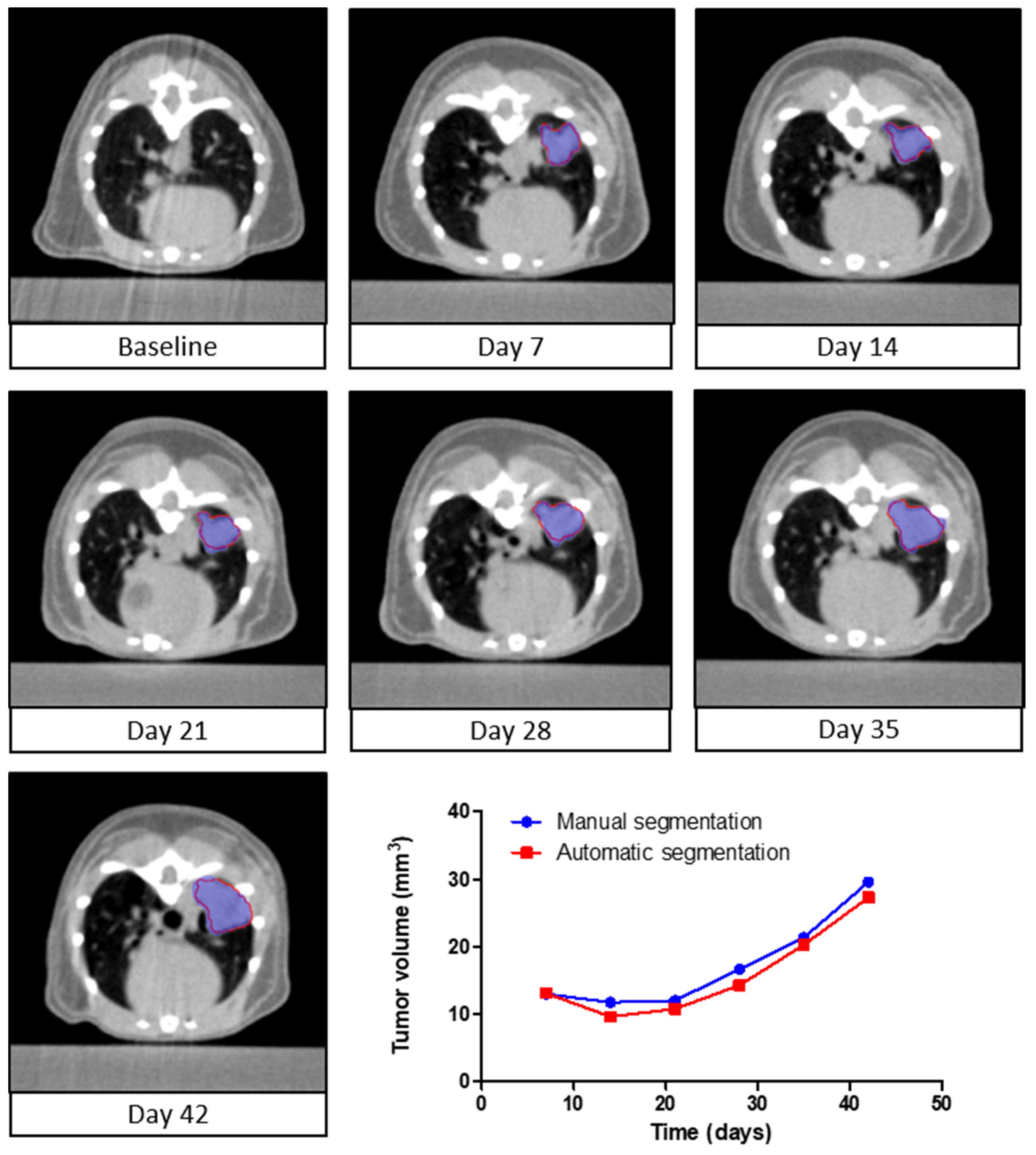
3.4. Longitudinal Assessment of Tumor Volume
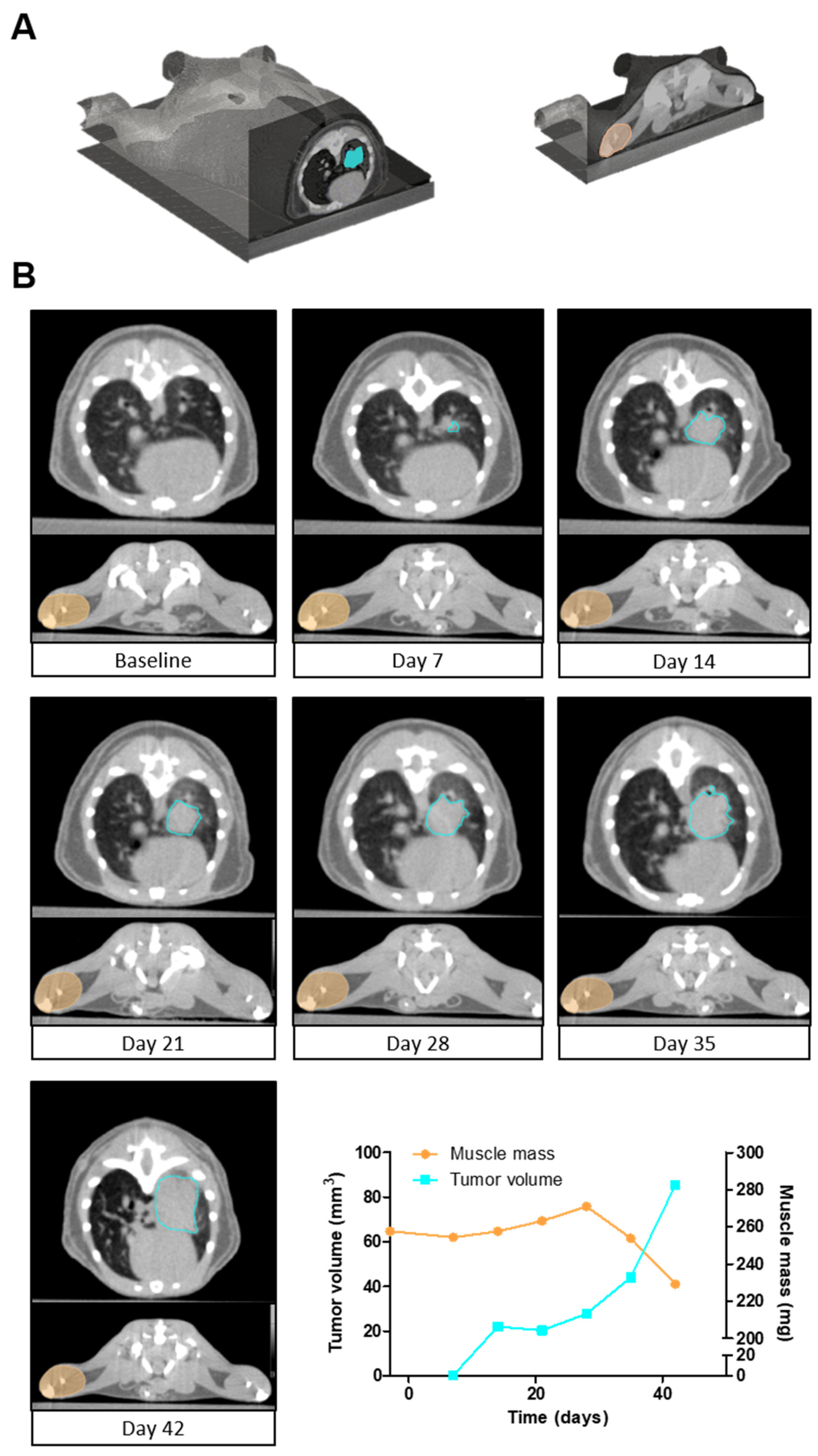
3.5. Simultaneous Quantification of Tumor Volume and Muscle Mass
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, M.S.; Holcomb, R.; Muscaritoli, M.; von Haehling, S.; Haverkamp, W.; Jatoi, A.; Morley, J.E.; Strasser, F.; Landmesser, U.; Coats, A.J.S. Orphan disease status of cancer cachexia in the USA and in the European Union: A systematic review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewys, W.D.; Begg, C.; Lavin, P.T.; Band, P.R.; Bennett, J.M.; Bertino, J.R.; Cohen, M.H.; Douglass, H.O.; Engstrom, P.F.; Ezdinli, E.Z. Prognostic effect of weight loss prior tochemotherapy in cancer patients. Am. J. Med. 1980, 69, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.J.; Ashley, S.; Norton, A.; Priest, K.; Waters, J.S.; Eisen, T.; Smith, I.E.; O’Brien, M.E. Do patients with weight loss have a worse outcome when undergoing chemotherapy for lung cancers? Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 1905–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M.; Naito, T.; Kenmotsu, H.; Taira, T.; Wakuda, K.; Oyakawa, T.; Hisamatsu, Y.; Tokito, T.; Imai, H.; Akamatsu, H. Prognostic impact of cancer cachexia in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2015, 23, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.P.; Merlino, G.; Van Dyke, T. Preclinical mouse cancer models: A maze of opportunities and challenges. Cell 2015, 163, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koontz, B.F.; Verhaegen, F.; De Ruysscher, D. Tumour and normal tissue radiobiology in mouse models: How close are mice to mini-humans? Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Junttila, M.R.; de Sauvage, F.J. Influence of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response. Nature 2013, 501, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordant, P.; Loriot, Y.; Lahon, B.; Castier, Y.; Lesèche, G.; Soria, J.-C.; Vozenin, M.-C.; Decraene, C.; Deutsch, E. Bioluminescent Orthotopic Mouse Models of Human Localized Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Feasibility and Identification of Circulating Tumour Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Justilien, V.; Fields, A.P. Utility and applications of orthotopic models of human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) for the evaluation of novel and emerging cancer therapeutics. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2013, 62, 14.27.11–14.27.17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iglesias, V.S.; Van Hoof, S.J.; Vaniqui, A.; Schyns, L.E.; Lieuwes, N.; Yaromina, A.; Spiegelberg, L.; Groot, A.J.; Verhaegen, F.; Theys, J. An orthotopic non-small cell lung cancer model for image-guided small animal radiotherapy platforms. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, T.; Murakami, K.; Doki, Y.; Sugiyama, S.; Misaki, T.; Yamada, Y.; Saiki, I. Solitary lung tumors and their spontaneous metastasis in athymic nude mice orthotopically implanted with human non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Han, Y.-A.; Yang, H.-S.; Song, J.-A.; Yang, Y.-S.; Kwon, S.; Kang, M.-S.; Lee, K.; Heo, J.-D.; Cho, K.-H. The Incidence Rate and Severity of Orthotopic Lung Cancer in an Animal Model Depends on the Number of A549 Cells and Transplantation Period. Lab. Anim. Res. 2010, 26, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prescott, M.J.; Lidster, K. Improving quality of science through better animal welfare: The NC3Rs strategy. Lab. Anim. 2017, 46, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clerck, N.M.; Meurrens, K.; Weiler, H.; Van Dyck, D.; Van Houtte, G.; Terpstra, P.; Postnov, A.A. High-resolution X-ray microtomography for the detection of lung tumors in living mice. Neoplasia 2004, 6, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavanaugh, D.; Johnson, E.; Price, R.E.; Kurie, J.; Travis, E.L.; Cody, D.D. In Vivo Respiratory-Gated Micro-CT Imaging in Small-Animal Oncology Models. Mol. Imaging 2004, 3, 15353500200403184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, D.D.; Nelson, C.L.; Bradley, W.M.; Wislez, M.; Juroske, D.; Price, R.E.; Zhou, X.; Bekele, B.N.; Kurie, J.M. Murine lung tumor measurement using respiratory-gated micro-computed tomography. Investig. Radiol. 2005, 40, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines, B.B.; Bettano, K.A.; Chenard, M.; Sevilla, R.S.; Ware, C.; Angagaw, M.H.; Winkelmann, C.T.; Tong, C.; Reilly, J.F.; Sur, C. A quantitative volumetric micro-computed tomography method to analyze lung tumors in genetically engineered mouse models. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fushiki, H.; Kanoh-Azuma, T.; Katoh, M.; Kawabata, K.; Jiang, J.; Tsuchiya, N.; Satow, A.; Tamai, Y.; Hayakawa, Y. Quantification of mouse pulmonary cancer models by microcomputed tomography imaging. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, D.G.; Grimm, J.; Guimaraes, A.R.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Perez, B.A.; Santiago, P.M.; Anthony, N.K.; Forbes, T.; Doppke, K.; Weissleder, R. Imaging primary lung cancers in mice to study radiation biology. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namati, E.; Thiesse, J.; Sieren, J.C.; Ross, A.; Hoffman, E.A.; McLennan, G. Longitudinal assessment of lung cancer progression in the mouse using in vivo micro-CT imaging. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 4793–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodt, T.; von Falck, C.; Dettmer, S.; Hueper, K.; Halter, R.; Hoy, L.; Luepke, M.; Borlak, J.; Wacker, F. Lung tumour growth kinetics in SPC-c-Raf-1-BB transgenic mice assessed by longitudinal in-vivo micro-CT quantification. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rudyanto, R.D.; Bastarrika, G.; de Biurrun, G.; Agorreta, J.; Montuenga, L.M.; Ortiz-de-Solorzano, C.; Muñoz-Barrutia, A. Individual nodule tracking in micro-CT images of a longitudinal lung cancer mouse model. Med. Image Anal. 2013, 17, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiker, M.; Milles, J.; Dijkstra, J.; Henning, T.D.; Weber, A.W.; Que, I.; Kaijzel, E.L.; Löwik, C.W.; Reiber, J.H.; Lelieveldt, B.P. Atlas-based whole-body segmentation of mice from low-contrast Micro-CT data. Med. Image Anal. 2010, 14, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heyden, B.; Podesta, M.; Eekers, D.B.; Vaniqui, A.; Almeida, I.P.; Schyns, L.E.; Van Hoof, S.J.; Verhaegen, F. Automatic multiatlas based organ at risk segmentation in mice. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heyden, B.; van de Worp, W.R.; van Helvoort, A.; Theys, J.; Schols, A.M.; Langen, R.C.; Verhaegen, F. Automated CT-derived skeletal muscle mass determination in lower hind limbs of mice using a 3D U-Net deep learning network. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 128, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoppe, O.; Pan, C.; Coronel, J.; Mai, H.; Rong, Z.; Todorov, M.I.; Müskes, A.; Navarro, F.; Li, H.; Ertürk, A. Deep learning-enabled multi-organ segmentation in whole-body mouse scans. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, D.L.; Lin, W.; Creighton, C.J.; Rizvi, Z.H.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J.; Thilaganathan, N.; Du, L.; Zhang, Y.; Pertsemlidis, A. Contextual extracellular cues promote tumor cell EMT and metastasis by regulating miR-200 family expression. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verhaegen, F.; Dubois, L.; Gianolini, S.; Hill, M.A.; Karger, C.P.; Lauber, K.; Prise, K.M.; Sarrut, D.; Thorwarth, D.; Vanhove, C. ESTRO ACROP: Technology for precision small animal radiotherapy research: Optimal use and challenges. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.M.; Coffey, C.W.; DeWerd, L.A.; Liu, C.; Nath, R.; Seltzer, S.M.; Seuntjens, J.P. AAPM protocol for 40-300 kV x-ray beam dosimetry in radiotherapy and radiobiology. Med. Phys. 2001, 28, 868–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaniqui, A.; Schyns, L.E.J.R.; Almeida, I.P.; Van Der Heyden, B.; Podesta, M.; Verhaegen, F. The effect of different image reconstruction techniques on pre-clinical quantitative imaging and dual-energy CT. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Transactions on Petri Nets and Other Models of Concurrency XV; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.-A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Veeraraghavan, H.; Armato III, S.G.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.S.; Kalpathy-Kramer, J.; van Elmpt, W.; Dekker, A.; Han, X.; Feng, X. Autosegmentation for thoracic radiation treatment planning: A grand challenge at AAPM 2017. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 4568–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, T.-W.; Tsai, Y.-L.; Su, S.-F. Automatic detect lung node with deep learning in segmentation and imbalance data labeling. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Vibashan, V.S.; Jose, V.J.M.; Wijethilake, N.; Utkarsh, U.; Ren, H. Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Prediction Using 3D Attention UNet. In Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 262–272. [Google Scholar]
- Warfield, S.K.; Zou, K.H.; Wells, W.M. Validation of image segmentation by estimating rater bias and variance. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 2006, 9 Pt 2, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joskowicz, L.; Cohen, D.; Caplan, N.; Sosna, J. Inter-observer variability of manual contour delineation of structures in CT. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akselrod-Ballin, A.; Dafni, H.; Addadi, Y.; Biton, I.; Avni, R.; Brenner, Y.; Neeman, M. Multimodal Correlative Preclinical Whole Body Imaging and Segmentation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Han, Y.; Chen, Z.; Hu, R.; Chatziioannou, A.F.; Zhang, B. Prediction of major torso organs in low-contrast micro-CT images of mice using a two-stage deeply supervised fully convolutional network. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 245014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, I.P.; Vaniqui, A.; Schyns, L.E.; Van Der Heyden, B.; Cooley, J.; Zwart, T.; Langenegger, A.; Verhaegen, F. Exploring the feasibility of a clinical proton beam with an adaptive aperture for pre-clinical research. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoof, S.J.; Verde, J.B.; Verhaegen, F. Dose painting by dynamic irradiation delivery on an image-guided small animal radiotherapy platform. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Hanneke, S.; Carbonell, J. A theory of transfer learning with applications to active learning. Mach. Learn. 2013, 90, 161–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Segmented Tumor Volume | Quantitative Performance Metrics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation (R2) * | Agreement ** | DSC | 95HD (mm) | ΔCOM (mm) | |
| Annotator 1 vs. Annotator 2 | 0.79 (p < 0.001) | No (p = 0.005) | 0.76 ± 0.13 | 0.84 ± 0.63 | 0.51 ± 0.41 |
| Annotator 1 vs. Annotator 3 | 0.88 (p < 0.001) | No (p = 0.011) | 0.76 ± 0.13 | 0.82 ± 0.55 | 0.41 ± 0.54 |
| Annotator 2 vs. Annotator 3 | 0.77 (p < 0.001) | Yes (p = 0.251) | 0.75 ± 0.13 | 0.66 ± 0.47 | 0.39 ± 0.36 |
| Annotator 1 vs. Deep learning | 0.93 (p < 0.001) | Yes (p = 0.365) | 0.81 ± 0.09 | 0.78 ± 0.53 | 0.30 ± 0.23 |
| Annotator 2 vs. Deep learning | 0.87 (p < 0.001) | No (p = 0.001) | 0.74 ± 0.12 | 0.82 ± 0.41 | 0.51 ± 0.37 |
| Annotator 3 vs. Deep learning | 0.92 (p < 0.001) | No (p = 0.007) | 0.76 ± 0.10 | 0.77 ± 0.39 | 0.45 ± 0.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van de Worp, W.R.P.H.; van der Heyden, B.; Lappas, G.; van Helvoort, A.; Theys, J.; Schols, A.M.W.J.; Verhaegen, F.; Langen, R.C.J. Deep Learning Based Automated Orthotopic Lung Tumor Segmentation in Whole-Body Mouse CT-Scans. Cancers 2021, 13, 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184585
van de Worp WRPH, van der Heyden B, Lappas G, van Helvoort A, Theys J, Schols AMWJ, Verhaegen F, Langen RCJ. Deep Learning Based Automated Orthotopic Lung Tumor Segmentation in Whole-Body Mouse CT-Scans. Cancers. 2021; 13(18):4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184585
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan de Worp, Wouter R. P. H., Brent van der Heyden, Georgios Lappas, Ardy van Helvoort, Jan Theys, Annemie M. W. J. Schols, Frank Verhaegen, and Ramon C. J. Langen. 2021. "Deep Learning Based Automated Orthotopic Lung Tumor Segmentation in Whole-Body Mouse CT-Scans" Cancers 13, no. 18: 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184585
APA Stylevan de Worp, W. R. P. H., van der Heyden, B., Lappas, G., van Helvoort, A., Theys, J., Schols, A. M. W. J., Verhaegen, F., & Langen, R. C. J. (2021). Deep Learning Based Automated Orthotopic Lung Tumor Segmentation in Whole-Body Mouse CT-Scans. Cancers, 13(18), 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184585








