High Cell-Free DNA Integrity Is Associated with Poor Breast Cancer Survival
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients, Sample Material and Clinical Data
2.2. Isolation of Cell-Free DNA
2.3. Concentration and Fragmentation Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Cohort
3.2. High cfDConc Is Not Associated with Poor BC Survival
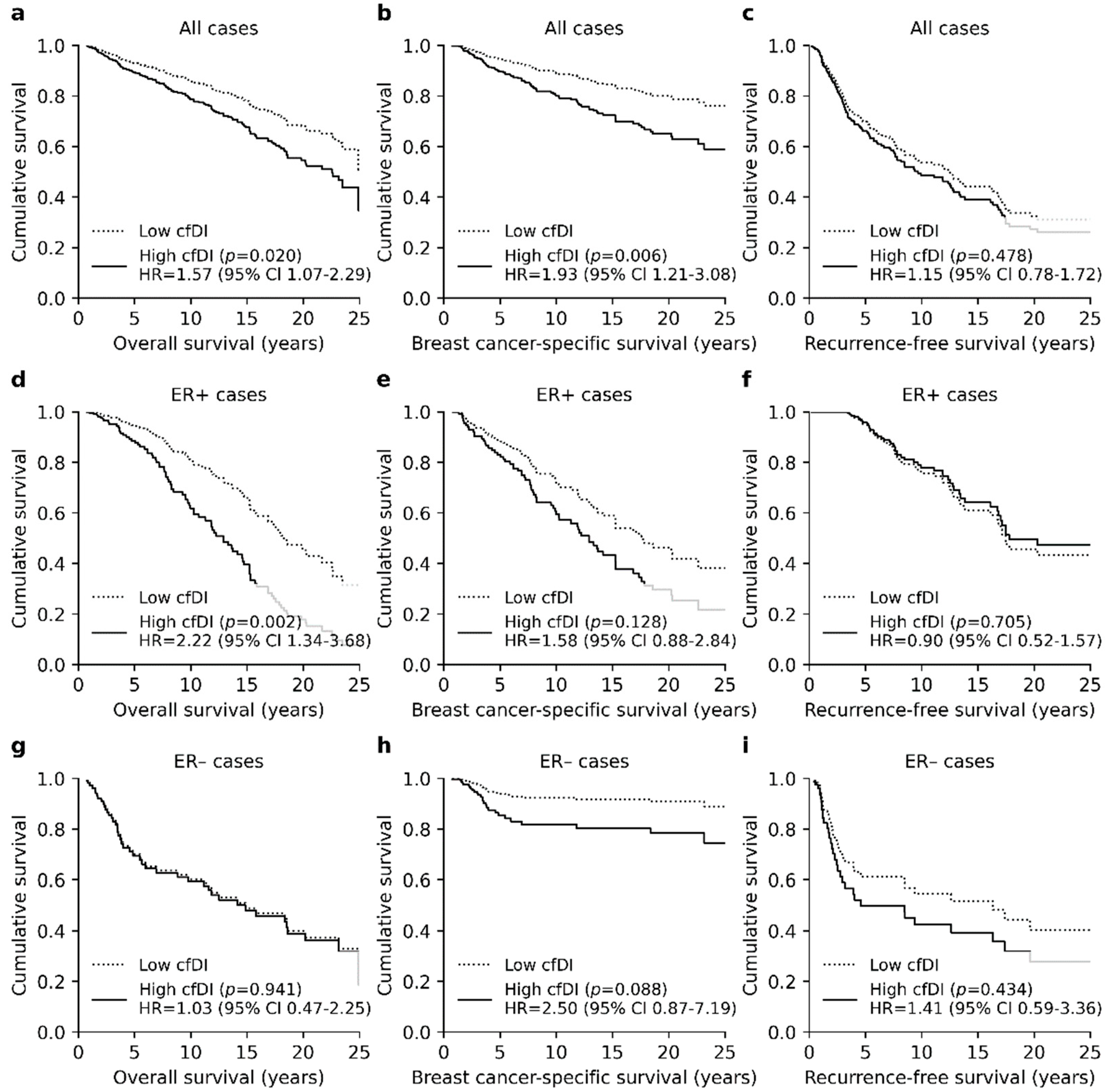
3.3. High Cfdi Is An Independent Prognostic Factor for Poor OS and BCSS
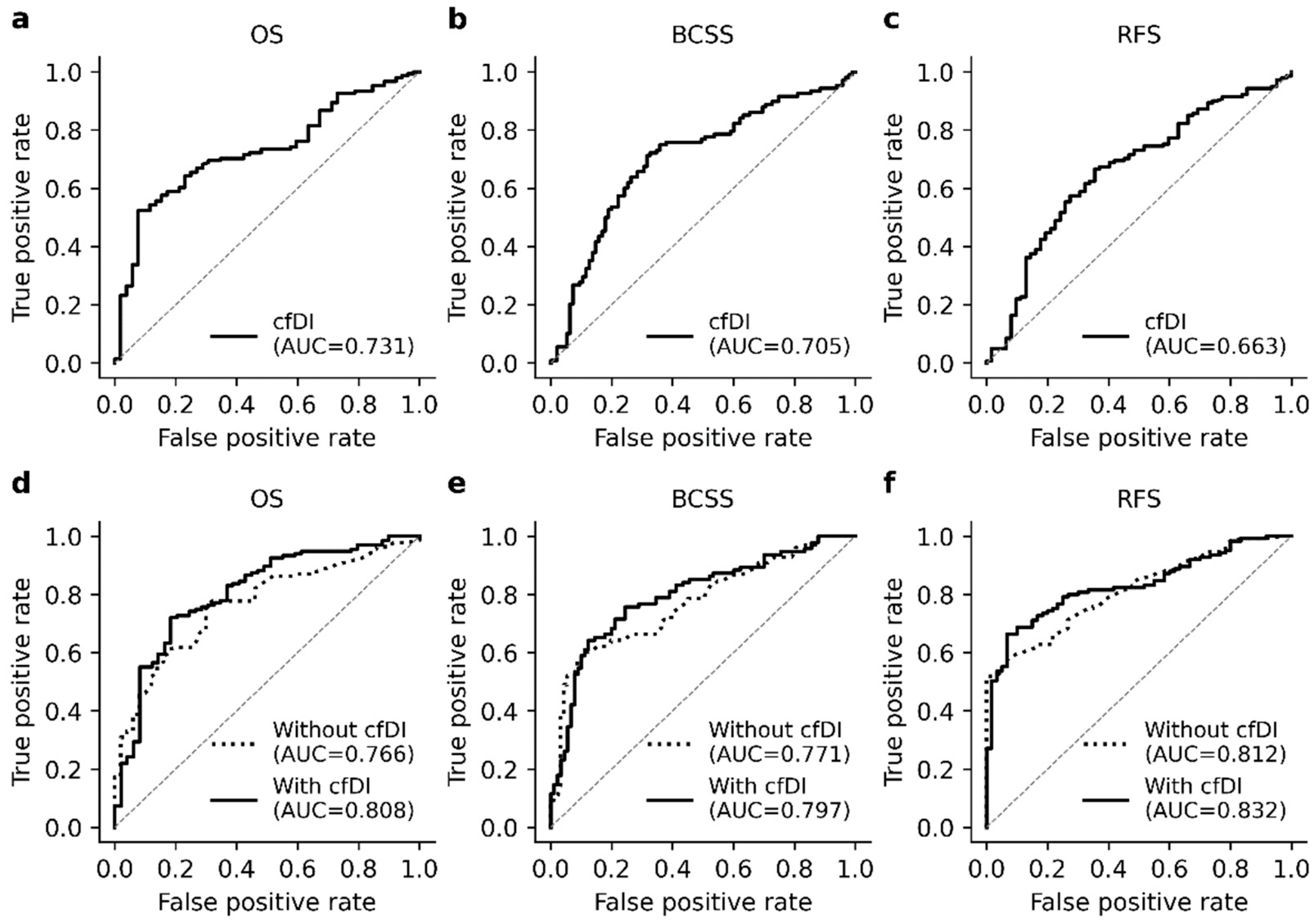
3.4. The cfDI Improves the Prediction Accuracy of Logistic Regression Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: Globocan Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemani, C.; Matsuda, T.; Di Carlo, V.; Harewood, R.; Matz, M.; Nikšić, M.; Bonaventure, A.; Valkov, M.; Johnson, C.J.; Estève, J.; et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–2014 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of individual records for 37,513,025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 2018, 391, 1023–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riggio, A.I.; Varley, K.E.; Welm, A.L. The lingering mysteries of metastatic recurrence in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Chu, C.; Gui, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Q. The prognostic value of circulating cell-free DNA in breast cancer. Medicine 2018, 97, e0197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Tong, Y.; Guo, X.; Feng, L.; Jiang, Z.; Ying, S.; Jia, J.; Fang, Y.; Yu, M.; Xia, H.; et al. Diagnostic Value of Concentration of Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jylhävä, J.; Lehtimäki, T.; Jula, A.; Moilanen, L.; Kesäniemi, Y.A.; Nieminen, M.S.; Kähönen, M.; Hurme, M. Circulating cell-free DNA is associated with cardiometabolic risk factors: The Health 2000 Survey. Atherosclerosis 2014, 233, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvvuri, B.; Lood, C. Cell-Free DNA as a Biomarker in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Kong, P.; Ma, G.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.; Xia, T.; Xie, H.; Zhou, W.; Wang, S. Characterization of the release and biological significance of cell-free DNA from breast cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 43180–43191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabuschnig, S.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Holdenrieder, S.; Rodriguez, I.R.; Schliep, K.P.; Schwendenwein, D.; Ungerer, V.; Sensen, C.W. Putative Origins of Cell-Free DNA in Humans: A Review of Active and Passive Nucleic Acid Release Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Bristow, R.E.; Kassauei, K.; Cheng, C.-C.; Roden, R.; Sokoll, L.J.; Chan, D.W.; Shih, I.-M. Increased plasma DNA integrity in cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3966–3968. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Umetani, N.; Giuliano, A.E.; Hiramatsu, S.H.; Amersi, F.; Nakagawa, T.; Martino, S.; Hoon, D.S. Prediction of Breast Tumor Progression by Integrity of Free Circulating DNA in Serum. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligezer, U.; Eralp, Y.; Akisik, E.E.; Akisik, E.Z.; Saip, P.; Topuz, E.; Dalay, N. Size distribution of circulating cell-free DNA in sera of breast cancer patients in the course of adjuvant chemotherapy. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.M.; Teama, S.; Fawzy, A.; El Deftar, M. Plasma DNA integrity index as a potential molecular diagnostic marker for breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 37, 7565–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, T.; Li, R. Clinical value of plasma cfDNA concentration and integrity in breast cancer patients. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2019, 65, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorano, E.; Regan, M.M.; Viale, G.; Mastropasqua, M.G.; Colleoni, M.; Castiglione-Gertsch, M.; Price, K.N.; Gelber, R.D.; Goldhirsch, A.; Coates, A.S. Prognostic and predictive impact of central necrosis and fibrosis in early breast cancer: Results from two International Breast Cancer Study Group randomized trials of chemoendocrine adjuvant therapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 121, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jahr, S.; Hentze, H.; Englisch, S.; Hardt, D.; Fackelmayer, F.O.; Hesch, R.D.; Knippers, R. DNA fragments in the blood plasma of cancer patients: Quantitations and evidence for their origin from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Xu, W. Fast Implementation of DeLong’s Algorithm for Comparing the Areas under Correlated Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Vishnubhatla, S.; Raina, V.; Sharma, S.; Gogia, A.; Deo, S.S.V.; Mathur, S.R.; Shukla, N.K. Circulating cell-free DNA and its integrity as a prognostic marker for breast cancer. Springerplus 2015, 4, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madhavan, D.; Wallwiener, M.; Bents, K.; Zucknick, M.; Nees, J.; Schott, S.; Cuk, K.; Riethdorf, S.; Trumpp, A.; Pantel, K.; et al. Plasma DNA integrity as a biomarker for primary and metastatic breast cancer and potential marker for early diagnosis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Holland-Letz, T.; Wallwiener, M.; Surowy, H.; Cuk, K.; Schott, S.; Trumpp, A.; Pantel, K.; Sohn, C.; Schneeweiss, A.; et al. Circulating free DNA integrity and concentration as independent prognostic markers in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 169, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustanovich, A.; Schwartz, R.; Peretz, T.; Grinshpun, A. Life and death of circulating cell-free DNA. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rostami, A.; Lambie, M.; Yu, C.W.; Stambolic, V.; Waldron, J.N.; Bratman, S.V. Senescence, Necrosis, and Apoptosis Govern Circulating Cell-free DNA Release Kinetics. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.A.; Yeung, S.-W.; Lui, W.-B.; Rainer, T.; Lo, Y.D. Effects of Preanalytical Factors on the Molecular Size of Cell-Free DNA in Blood. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variable | Grouping | Total | ER+ | ER− |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis | ≤39 years | 25 (12.3%) | 15 (10.9%) | 10 (15.2%) |
| 40–49 years | 47 (23.0%) | 30 (21.7%) | 17 (25.8%) | |
| 50–59 years | 56 (27.5%) | 36 (26.1%) | 20 (30.3%) | |
| 60–69 years | 37 (18.1%) | 27 (19.6%) | 10 (15.2%) | |
| ≥70 years | 39 (19.1%) | 30 (21.7%) | 9 (13.6%) | |
| Tumor stage | I | 81 (39.7%) | 59 (42.8%) | 22 (33.3%) |
| II | 98 (48.0%) | 66 (47.8%) | 32 (48.5%) | |
| II | 25 (12.3%) | 12 (9.4%) | 12 (18.2%) | |
| Tumor grade | I | 36 (17.6%) | 34 (24.6%) | 2 (3.0%) |
| II | 97 (47.5%) | 78 (56.5%) | 19 (28.8%) | |
| II | 70 (43.3%) | 25 (18.1%) | 45 (68.2%) | |
| Nodal status | N0 | 115 (56.4%) | 80 (58.0%) | 35 (53.0%) |
| N1 | 79 (38.7%) | 53 (38.4%) | 26 (39.4%) | |
| N2 | 10 (4.9%) | 5 (3.6%) | 5 (7.6%) | |
| PR status | Negative | 95 (46.6%) | 34 (24.6%) | 61 (92.4%) |
| Positive | 109 (53.4%) | 104 (75.4%) | 5 (7.6%) | |
| HER2 status | Negative | 173 (84.8%) | 122 (88.4%) | 51 (77.3%) |
| Positive | 17 (8.3%) | 4 (2.9%) | 13 (19.7%) | |
| Missing | 14 (6.9%) | 12 (8.7%) | 2 (3.0%) | |
| Chemotherapy | Yes | 43 (21.1%) | 21 (15.2%) | 22 (33.3%) |
| No | 161 (78.9%) | 117 (84.8%) | 44 (66.7%) | |
| Hormonal therapy | Yes | 51 (25.0%) | 40 (29.0%) | 11 (16.7%) |
| No | 153 (75.0%) | 98 (71.0%) | 55 (83.3%) | |
| Radiotherapy | Yes | 129 (63.2%) | 86 (62.3%) | 43 (65.2%) |
| No | 75 (36.8%) | 52 (37.7%) | 23 (34.8%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamminaho, M.; Kujala, J.; Peltonen, H.; Tengström, M.; Kosma, V.-M.; Mannermaa, A. High Cell-Free DNA Integrity Is Associated with Poor Breast Cancer Survival. Cancers 2021, 13, 4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184679
Lamminaho M, Kujala J, Peltonen H, Tengström M, Kosma V-M, Mannermaa A. High Cell-Free DNA Integrity Is Associated with Poor Breast Cancer Survival. Cancers. 2021; 13(18):4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184679
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamminaho, Maria, Jouni Kujala, Hanna Peltonen, Maria Tengström, Veli-Matti Kosma, and Arto Mannermaa. 2021. "High Cell-Free DNA Integrity Is Associated with Poor Breast Cancer Survival" Cancers 13, no. 18: 4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184679
APA StyleLamminaho, M., Kujala, J., Peltonen, H., Tengström, M., Kosma, V.-M., & Mannermaa, A. (2021). High Cell-Free DNA Integrity Is Associated with Poor Breast Cancer Survival. Cancers, 13(18), 4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184679








