Pancreatic Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities in Locoregional Therapies
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Pancreatic Cancer
2.1. Epidemiology
2.2. Risk Factors
2.2.1. Smoking (Tobacco)
2.2.2. Diabetes
2.2.3. Body-Mass Index (BMI)
2.2.4. Alcohol Consumption
2.2.5. Pancreatitis
2.2.6. Family History and Genetics
2.3. Types and Tissue Architecture of PC
2.4. Current Diagnostic Strategies
2.5. Current Therapeutic Strategies and Limitations
2.5.1. Surgery
2.5.2. Chemotherapy
2.5.3. Radiotherapy
2.5.4. Immunotherapy
2.5.5. Palliative Care and Pain Management
2.6. Recent Advances in Clinical Trials
2.6.1. K-RAS Derived Therapies
2.6.2. KRAS-LODER for PC
2.6.3. Combination Immunotherapies
| Intervention | Delivered Drug(s) | Pancreatic Cancer Stage | Phase | Trial Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-RAS-Targeting | siG12D-LODER with chemotherapy | Locally Advanced PC | Phase II | NCT01676259 |
| Decitabine 50 MG | KRAS-dependant refractory metastatic/recurrent Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase II | NCT05360264 | |
| Binimetinib Hydroxychloroquine | KRAS Mutant Metastatic PC | Phase I | NCT04132505 | |
| Mesenchymal Stromal Cells-derived Exosomes with KRAS G12D siRNA | Metastatic Pancreas Cancer with KrasG12D Mutation | Phase I | NCT03608631 | |
| mDC3/8-KRAS Vaccine | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma | Phase I | NCT03592888 | |
| Vemurafenib Sorafenib | Advanced KRAS G12D Mutated PC | Phase II | NCT05068752 | |
| NALRINOX combination (modified FOLFIRINOX) | Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma | Phase II | NCT04010552 | |
| ELI-002 2P | KRAS Mutated Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma | Phase I | NCT04853017 | |
| Binimetinib Palbociclib | Operable KRAS-Positive Lung, Colorectal, or PC | Phase I | NCT04870034 | |
| Immunotherapies Combinations | Mitazalimab FOLFIRINOX | Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma | Phase II | NCT04888312 |
| Cohort A: Nivolumab + Ipilimumab + Nab-paclitaxel + GEM Cohort B: Hydroxychloroquine + Ipilimumab + Nab-paclitaxel + GEM | Untreated Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase I | NCT04787991 | |
| Motixafortide, Cemiplimab, GEM, Nab-Paclitaxel | Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase II | NCT04543071 | |
| Nivolumab + Irreversible Electroporation | Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | NCT03080974 | ||
| Avelumab and Pepinemab | Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase I and II | NCT05102721 | |
| Cyclophosphamide GVAX PC Nivolumab Urelumab BMS-986253 | Resectable Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas | Phase II | NCT02451982 | |
| Nivolumab FOLFIRINOX | Borderline Resectable PC | Early Phase I | NCT03970252 | |
| Cyclophosphamide Nivolumab GVAX Pancreas Vaccine Stereotactic Body Radiation (SBRT) | Borderline Resectable PC | Phase II | NCT03161379 | |
| APX005M Nivolumab Nab-Paclitaxel GEM | Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase I and II | NCT03214250 | |
| Anetumab Ravtansine GEM Hydrochloride Ipilimumab Nivolumab | Metastatic and recurrent Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase I and II | NCT03816358 | |
| Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) Nivolumab Toll-Like Receptor 9 | Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase I | NCT04612530 | |
| Nivolumab, ipilimumab Stereotactic body radiation therapy Low dose irradiation | Stage IV PC | Phase I | NCT05088889 | |
| Pembrolizumab DEBIO1143 | Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas Adenocarcinoma of the Colon Adenocarcinoma of the Rectum | Phase I | NCT03871959 | |
| Cyclophosphamide GVAX PC vaccine Pembrolizumab Stereotactic Body Radiation (SBRT) | Locally Advanced PC | Phase II | NCT02648282 | |
| Stereotactic Body Radiation (SBRT) Nivolumab CCR2/CCR5 dual antagonist GVAX PC vaccine | Locally Advanced PC | Phase I and II | NCT03767582 | |
| Anti-SEMA4D, Monoclonal Antibody VX15/2503, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab | Resectable Pancreatic and Colorectal Cancer | Phase I | NCT03373188 | |
| Pembrolizumab Olaparib | Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase II | NCT05093231 | |
| Gene Mediated Cytotoxic Immunotherapy (GMCI™) (aglatimagene besadenovec + valacyclovir) + chemoradiation+ surgery | Advanced Non-Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase II | NCT02446093 | |
| Autologous Th-1 Dendritic Cell vaccine + chemotherapy | Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase I | NCT04157127 |
3. Locoregional Therapies
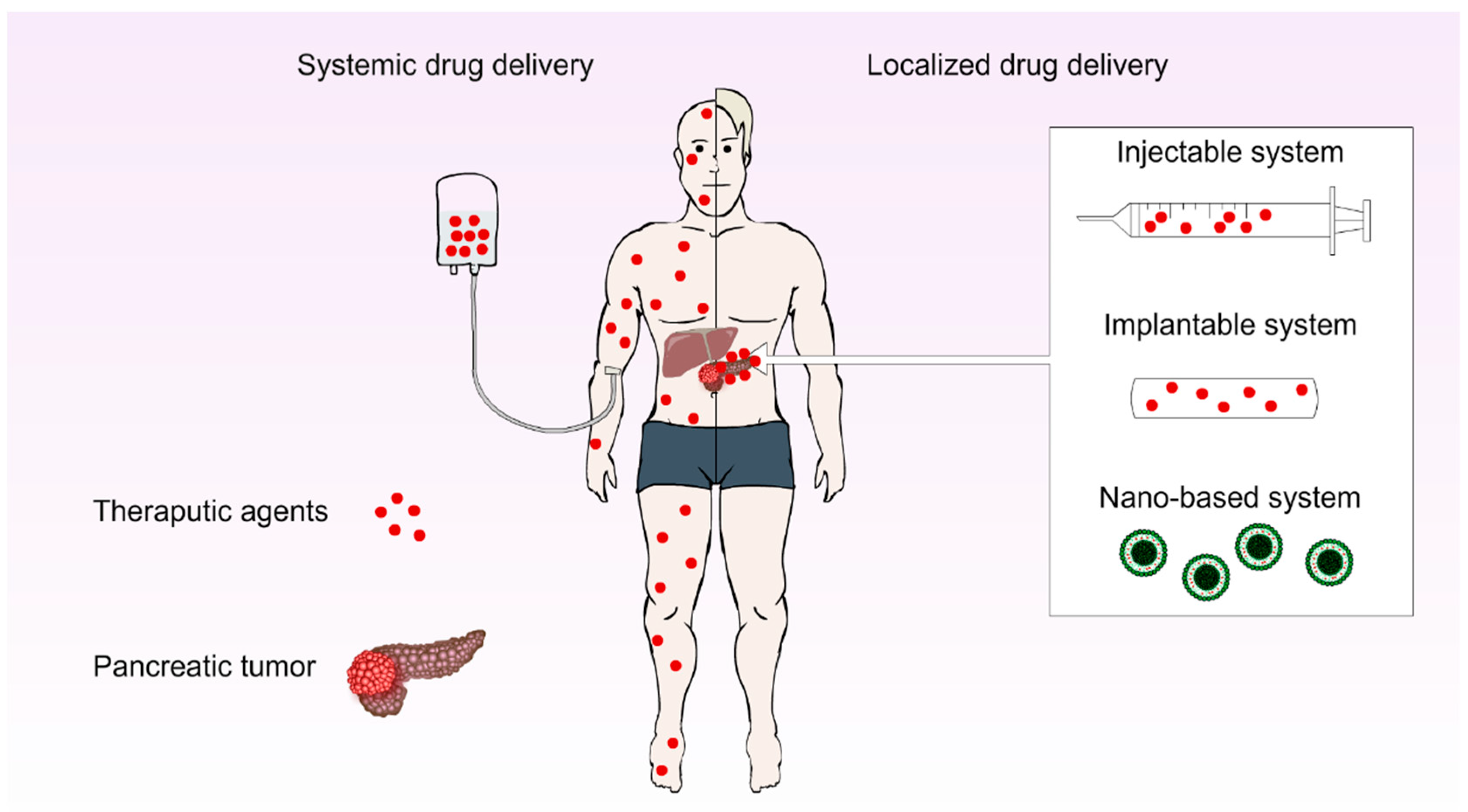
3.1. Localised Drug Delivery Systems (LDDs)
3.1.1. Injectable DDSs
Gel-Based Systems
Nanoparticle (NP)-Based Systems
Material-Free DDSs
3.1.2. Implantable DDSs
Casted Implants
Dip Coated Implants
Electrospun Fibrous Implants
3.2. Thermal/Energy Ablation Therapy
3.2.1. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
3.2.2. Microwave Ablation (MWA)
3.2.3. High Intensity Focused Ultrasound Ablation (HIFU)
3.2.4. Cryoablation
3.3. Irreversible Electroporation (IRE)
3.4. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) or Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR)
3.5. Intra-Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy or Transcatheter Arterial Infusion
3.6. Isolated Upper Abdominal Perfusion
3.7. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
4. Authors’ Opinion on the Future Perspectives of Locoregional Therapies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bengtsson, A.; Andersson, R.; Ansari, D. The actual 5-year survivors of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on real-world data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Partensky, C.; Bray, F. More deaths from pancreatic cancer than breast cancer in the EU by 2017. Acta. Oncol. 2016, 55, 1158–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michl, P.; Lohr, M.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Capurso, G.; Rebours, V.; Malats, N.; Ollivier, M.; Ricciardiello, L. UEG position paper on pancreatic cancer. Bringing pancreatic cancer to the 21st century: Prevent, detect, and treat the disease earlier and better. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teicher, B.A. Perspective: Opportunities in recalcitrant, rare and neglected tumours. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edition, S.; Edge, S.; Byrd, D. AJCC cancer staging manual. JAMA 2017, 304, 1726–1727. [Google Scholar]
- Khalaf, N.; El-Serag, H.B.; Abrams, H.R.; Thrift, A.P. Burden of pancreatic cancer: From epidemiology to practice. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunparmak, B.; Sahin, I.H. Pancreatic cancer microenvironment: A current dilemma. Clin. Trans. Med. 2019, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Pancreatic Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/pancreatic-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 5 June 2022).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Cancer Data in Australia; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Pancreatic Cancer: Statistics. Available online: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/pancreatic-cancer/statistics#:~:text=Incidence%20rates%20of%20pancreatic%20cancer,the%20United%20States%20this%20year (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Klein, A.P. Pancreatic cancer epidemiology: Understanding the role of lifestyle and inherited risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, S.; Gandini, S.; Maisonneuve, P.; Lowenfels, A.B. Tobacco and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A review and meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2008, 393, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Mitrou, P.N.; Reedy, J.; Graubard, B.I.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Schatzkin, A.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R. A Combined Healthy Lifestyle Score and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in a Large Cohort Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocci, E.; Kundu, P.; Wheeler, W.; Arslan, A.A.; Beane-Freeman, L.E.; Bracci, P.M.; Brennan, P.; Canzian, F.; Du, M.; Gallinger, S.; et al. Smoking Modifies Pancreatic Cancer Risk Loci on 2q21.3. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3134–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosetti, C.; Lucenteforte, E.; Silverman, D.T.; Petersen, G.; Bracci, P.M.; Ji, B.T.; Negri, E.; Li, D.; Risch, H.A.; Olson, S.H.; et al. Cigarette smoking and pancreatic cancer: An analysis from the International Pancreatic Cancer Case-Control Consortium (Panc4). Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.M.; Vrieling, A.; Lubin, J.H.; Kraft, P.; Mendelsohn, J.B.; Hartge, P.; Canzian, F.; Steplowski, E.; Arslan, A.A.; Gross, M.; et al. Cigarette Smoking and Pancreatic Cancer: A Pooled Analysis from the Pancreatic Cancer Cohort Consortium. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 170, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, Q.-W.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.-W.; Wang, L.-F.; Zou, D.-W.; Yuan, Y.-Z. Cigarette Smoking and Mortality in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pancreas 2019, 48, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, D.K.; Korc, M.; Petersen, G.M.; Eibl, G.; Li, D.; Rickels, M.R.; Chari, S.T.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Diabetes, Pancreatogenic Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menini, S.; Iacobini, C.; Vitale, M.; Pesce, C.; Pugliese, G. Diabetes and Pancreatic Cancer—A Dangerous Liaison Relying on Carbonyl Stress. Cancers 2021, 13, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, Obesity, and Mortality from Cancer in a Prospectively Studied Cohort of U.S. Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Morris, J.S.; Liu, J.; Hassan, M.M.; Day, R.S.; Bondy, M.L.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Body Mass Index and Risk, Age of Onset, and Survival in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA 2009, 301, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, E.J.; Newton, C.C.; Patel, A.V.; Stevens, V.L.; Islami, F.; Flanders, W.D.; Gapstur, S.M. The Association Between Body Mass Index and Pancreatic Cancer: Variation by Age at Body Mass Index Assessment. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 189, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Gou, Y.-W.; Jin, W.-W.; Xiao, M.; Fang, H.-Y. Association between alcohol intake and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A dose–response meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, P.A.; Conwell, D.L. Chronic Pancreatitis: Managing a Difficult Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.; Lowenfels, A.B. The epidemiology of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froeling, F.E.M.; Casolino, R.; Pea, A.; Biankin, A.V.; Chang, D.K. Molecular Subtyping and Precision Medicine for Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberle, L.; Esposito, I. Pathology of pancreatic cancer. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of Pancreatic Cancer: Global Trends, Etiology and Risk Factors. World. J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partelli, S.; Mazza, M.; Andreasi, V.; Muffatti, F.; Crippa, S.; Tamburrino, D.; Falconi, M. Management of small asymptomatic nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: Limitations to apply guidelines into real life. Surgery 2019, 166, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Yang, G.; Zhou, W.; Qiu, J.; Chen, G.; Luo, W.; Zhao, F.; You, L.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, T.; et al. Targeting hypoxic tumour microenvironment in pancreatic cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Radhakrishnan, P. Tumour-stromal crosstalk in pancreatic cancer and tissue fibrosis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neesse, A.; Bauer, C.A.; Öhlund, D.; Lauth, M.; Buchholz, M.; Michl, P.; Tuveson, D.A.; Gress, T.M. Stromal biology and therapy in pancreatic cancer: Ready for clinical translation? Gut 2019, 68, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zhou, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; You, L.; Guo, J. Stroma-Targeting Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer: One Coin With Two Sides? Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 576399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Ebeling, M.C.; Chauhan, N.; Thompson, P.A.; Gara, R.K.; Ganju, A.; Yallapu, M.M.; Behrman, S.W.; Zhao, H.; Zafar, N.; et al. Ormeloxifene Suppresses Desmoplasia and Enhances Sensitivity of Gemcitabine in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2292–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olive, K.P.; Jacobetz, M.A.; Davidson, C.J.; Gopinathan, A.; McIntyre, D.; Honess, D.; Madhu, B.; Goldgraben, M.A.; Caldwell, M.E.; Allard, D.; et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Science 2009, 324, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, L.; Walsh, N.; Larkin, A.; Ballot, J.; Ooi, W.S.; Gullo, G.; O’Connor, R.; Clynes, M.; Crown, J.; Kennedy, S. MDR1/P-glycoprotein and MRP-1 drug efflux pumps in pancreatic carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moffat, G.T.; Epstein, A.S.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic cancer-A disease in need: Optimizing and integrating supportive care. Cancer 2019, 125, 3927–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Could a Diabetes Diagnosis Help Detect Pancreatic Cancer Early? Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/cancer-currents-blog/2021/pancreatic-cancer-diabetes-early-detection (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Herreros-Villanueva, M.; Bujanda, L. Non-invasive biomarkers in pancreatic cancer diagnosis: What we need versus what we have. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swords, D.S.; Firpo, M.A.; Scaife, C.L.; Mulvihill, S.J. Biomarkers in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Current perspectives. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 7459–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, S.A.; Luecke, L.B.; Kahlert, C.; Fernandez, A.F.; Gammon, S.T.; Kaye, J.; LeBleu, V.S.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Weitz, J.; Rahbari, N.; et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 523, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Bai, B. The Expression, Regulation, and Biomarker Potential of Glypican-1 in Cancer. Front Oncol. 2019, 9, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, E.; Ren, N.; Shi, X.; Zhang, R.; Yu, H.; Yu, F.; Qin, S.; Xue, J. Extracellular vesicle biomarkers for pancreatic cancer diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, R.; Wang, C.; Qiu, J.; Ren, B.; You, L. Early screening and diagnosis strategies of pancreatic cancer: A comprehensive review. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1257–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LIU, Z.-w.; ZHAO, Y.-p. The discussion on the issues related to NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology for pancreatic adenocarcinoma (V2011). J. Clin. Hepatol. 2011, 27, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar]
- National Cancer Institute. Advances in Pancreatic Cancer Research. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/pancreatic/research (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Esposito, I.; Kleeff, J.; Bergmann, F.; Reiser, C.; Herpel, E.; Friess, H.; Schirmacher, P.; Buchler, M.W. Most pancreatic cancer resections are R1 resections. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principe, D.R.; Underwood, P.W.; Korc, M.; Trevino, J.G.; Munshi, H.G.; Rana, A. The Current Treatment Paradigm for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Barriers to Therapeutic Efficacy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 688377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalski, C.W.; Weitz, J.; Buchler, M.W. Surgery insight: Surgical management of pancreatic cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2007, 4, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.; Jeong, H.; Cheon, J.; Chon, H.J.; Ryu, H.; Kim, I.H.; Kang, M.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Kim, K.P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of second-line nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine after progression on FOLFIRINOX for unresectable or metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Multicenter retrospective analysis. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920923424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, T.; Desseigne, F.; Ychou, M.; Bouche, O.; Guimbaud, R.; Becouarn, Y.; Adenis, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; de la Fouchardiere, C.; et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.; Krisnawan, V.E.; Herzog, B.H.; Zuo, C.; Breden, M.A.; Knolhoff, B.L.; Hogg, G.D.; Tang, J.P.; Baer, J.M.; Mpoy, C.; et al. Dendritic Cell Paucity Leads to Dysfunctional Immune Surveillance in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 289–307.e289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindler, H.L. A New Direction for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment: FOLFIRINOX in Context. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2012, 32, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology. Testing the Use of the Usual Chemotherapy before and after Surgery for Removable Pancreatic Cancer; Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- de Jong, E.J.M.; Janssen, Q.P.; Simons, T.F.A.; Besselink, M.G.; Bonsing, B.A.; Bouwense, S.A.W.; Geurts, S.M.E.; Homs, M.Y.V.; de Meijer, V.E.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.G.; et al. Real-world evidence of adjuvant gemcitabine plus capecitabine vs. gemcitabine monotherapy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, L.; Schwarz, L.; Bachet, J.B. Adjuvant chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer: State of the art and future perspectives. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2020, 32, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasi, A.; McGinnis, T.; Naik, G.; Handa, S.; Williams, G.; Paluri, R. Efficacy and tolerability of the combination of nano-liposomal irinotecan and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin in advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Post-approval clinic experience. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbrenner, D.S. Olaparib Approved for Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. Am. J. Nurs. 2020, 120, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehlsen, A.D.; Goodman, K.A. Controversies in radiotherapy for pancreas cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 123, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versteijne, E.; van Dam, J.L.; Suker, M.; Janssen, Q.P.; Groothuis, K.; Akkermans-Vogelaar, J.M.; Besselink, M.G.; Bonsing, B.A.; Buijsen, J.; Busch, O.R.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Versus Upfront Surgery for Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: Long-Term Results of the Dutch Randomized PREOPANC Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolny-Rokicka, E.; Sutkowski, K.; Grządziel, A.; Dorsz, Ż.; Tukiendorf, A.; Lipiński, J.; Wydmański, J. Tolerance and efficacy of palliative radiotherapy for advanced pancreatic cancer: A retrospective analysis of single-institutional experiences. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 4, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bari, B.; Porta, L.; Mazzola, R.; Alongi, F.; Wagner, A.D.; Schafer, M.; Bourhis, J.; Ozsahin, M. Hypofractionated radiotherapy in pancreatic cancer: Lessons from the past in the era of stereotactic body radiation therapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 103, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Durham, J.N.; Smith, K.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Aulakh, L.K.; Lu, S.; Kemberling, H.; Wilt, C.; Luber, B.S.; et al. Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumours to PD-1 blockade. Science 2017, 357, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Almhanna, K. Pancreatic cancer and immune checkpoint inhibitors-still a long way to go. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robatel, S.; Schenk, M. Current Limitations and Novel Perspectives in Pancreatic Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perinel, J.; Adham, M. Palliative therapy in pancreatic cancer-palliative surgery. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouma, D.J.; Busch, O.R.; Van Gulik, T.M. Pancreatic carcinoma: Palliative surgical and endoscopic treatment. HPB 2006, 8, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, Z.; Reddy, D.N. Endoscopic Palliation for Biliary and Pancreatic Malignancies: Recent Advances. Clin. Endosc. 2019, 52, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscail, L.; Bournet, B.; Cordelier, P. Role of oncogenic KRAS in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Li, B.T.; Dy, G.K.; Price, T.J.; Falchook, G.S.; Wolf, J.; Italiano, A.; Schuler, M.; Borghaei, H.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Sotorasib for Lung Cancers with KRAS p.G12C Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Meythaler, J.G.; Garcia-Mayea, Y.; Mir, C.; Kondoh, H.; ME, L.L. Autophagy Takes Center Stage as a Possible Cancer Hallmark. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 586069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadrashid, D.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Derakhshani, A.; Leone, P.; Silvestris, N.; Racanelli, V.; Solimando, A.G.; Baradaran, B. Pancreatic Cancer Signaling Pathways, Genetic Alterations, and Tumour Microenvironment: The Barriers Affecting the Method of Treatment. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Khvalevsky, E.Z.; Hubert, A.; Gabai, R.M.; Hen, N.; Segal, A.; Domb, A.; Harari, G.; David, E.B.; Raskin, S.; et al. RNAi therapy targeting KRAS in combination with chemotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24560–24570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Chen, L.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhan, X. Application of natural killer cells in pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.L.; Yan, J.; Wang, Z.; Ruan, H.; Chen, Q.; Gunadhi, V.; Bell, R.B.; Gu, Z. Advances in drug delivery for post-surgical cancer treatment. Biomaterials 2019, 219, 119182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquib, M.; Juthi, A.Z.; Farooq, M.A.; Ali, M.G.; Janabi, A.H.W.; Bavi, S.; Banerjee, P.; Bhosale, R.; Bavi, R.; Wang, B. Advances in local and systemic drug delivery systems for post-surgical cancer treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 8507–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Herrero, E.; Fernandez-Medarde, A. Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanikas, M.; Esempidis, A.; Chasan, Z.T.; Deftereou, T.; Antonopoulou, M.; Bozali, F.; Amarantidis, K.; Man, Y.G. Pancreatic Cancer from Molecular Pathways to Treatment Opinion. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, L.; Coll, C.; Erthal, L.C.S.; De la Torre, C.; Serrano, D.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Santos-Martínez, M.J.; Ruiz-Hernández, E. Drug Delivery Nanosystems for the Localized Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Materials 2018, 11, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashby, L.S.; Smith, K.A.; Stea, B. Gliadel wafer implantation combined with standard radiotherapy and concurrent followed by adjuvant temozolomide for treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: A systematic literature review. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bota, D.A.; Desjardins, A.; Quinn, J.A.; Affronti, M.L.; Friedman, H.S. Interstitial chemotherapy with biodegradable BCNU (Gliadel) wafers in the treatment of malignant gliomas. Ther. Clin. Risk. Manag. 2007, 3, 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Brem, H.; Tamargo, R.J.; Olivi, A.; Pinn, M.; Weingart, J.D.; Wharam, M.; Epstein, J.I. Biodegradable polymers for controlled delivery of chemotherapy with and without radiation therapy in the monkey brain. J. Neurosurg. 1994, 80, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, A.B.; Saltzman, W.M. Pharmacokinetics of the carmustine implant. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 41, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGirt, M.J.; Than, K.D.; Weingart, J.D.; Chaichana, K.L.; Attenello, F.J.; Olivi, A.; Laterra, J.; Kleinberg, L.R.; Grossman, S.A.; Brem, H.; et al. Gliadel (BCNU) wafer plus concomitant temozolomide therapy after primary resection of glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 110, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.-Z.; Wang, Z.-F.; Lan, T.; Huang, W.-H.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Ma, C.; Li, Z.-Q. Carmustine as a Supplementary Therapeutic Option for Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliadel. Intra-Operative Carmustine Wafer (GLIADEL®) Included in National Treatment Guidelines. Available online: https://www.gliadel.com/hcp/treatment-guide.php (accessed on 9 June 2022).
- Eisai. License Agreement for GLIADEL® WAFER in Japan Signed; Eisai Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhari, A.; Anand Subramony, J. Engineered in-situ depot-forming hydrogels for intratumoural drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, M.; Nazari, B.; Miller, D.W. Injectable hydrogel-based drug delivery systems for local cancer therapy. Drug. Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
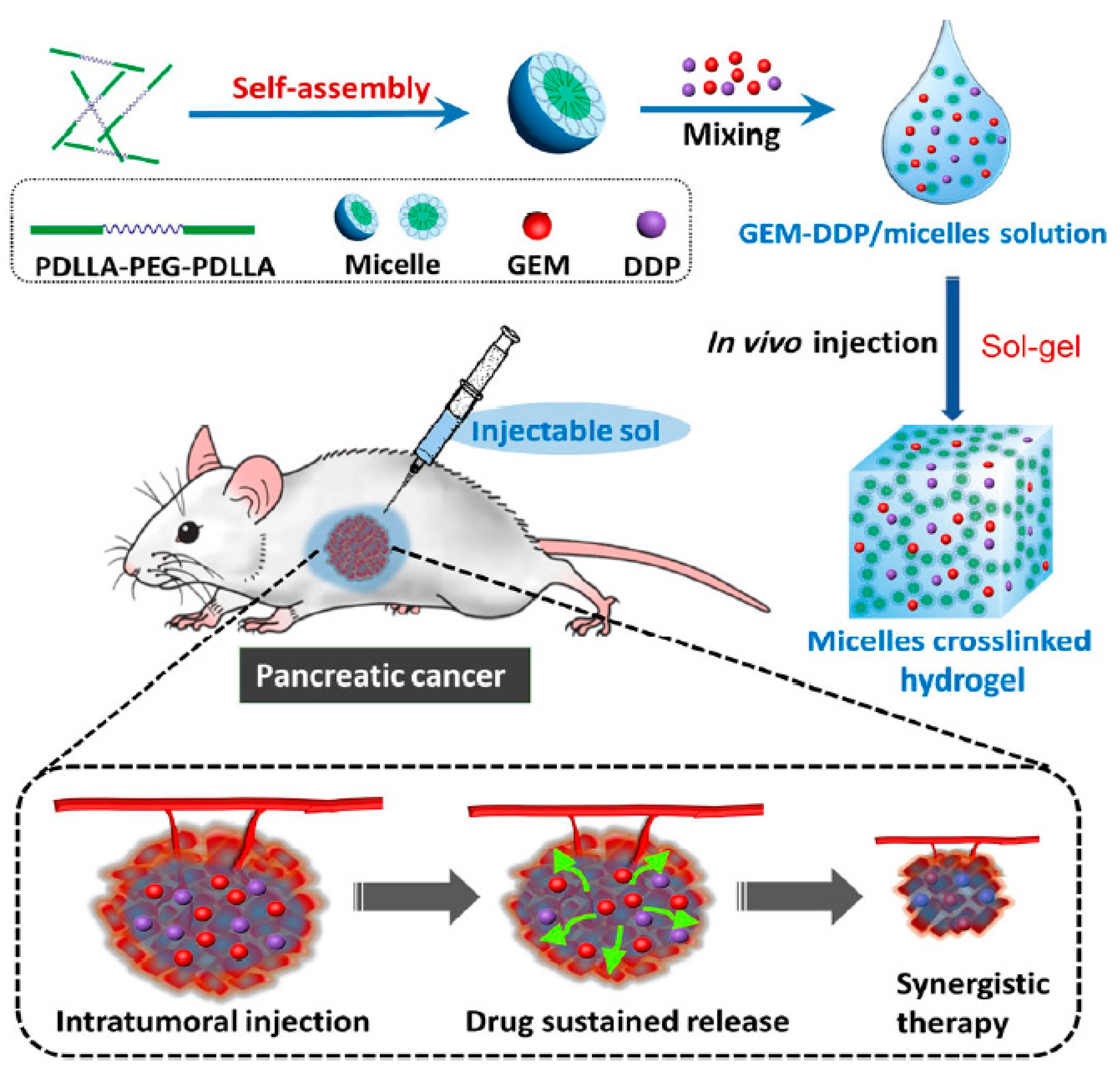
- Shi, K.; Xue, B.; Jia, Y.; Yuan, L.; Han, R.; Yang, F.; Peng, J.; Qian, Z. Sustained co-delivery of gemcitabine and cis-platinum via biodegradable thermo-sensitive hydrogel for synergistic combination therapy of pancreatic cancer. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranquillo, E.; Bollino, F. Surface Modifications for Implants Lifetime extension: An Overview of Sol-Gel Coatings. Coatings 2020, 10, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.; Ajazuddin; Khan, J.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels for biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supper, S.; Anton, N.; Seidel, N.; Riemenschnitter, M.; Curdy, C.; Vandamme, T. Thermosensitive chitosan/glycerophosphate-based hydrogel and its derivatives in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, V.H.G.; Lee, E.; Maeng, J.H.; Thambi, T.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, D.; Lee, D.S. Pancreatic cancer therapy using an injectable nanobiohybrid hydrogel. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 41644–41655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, S. Thermosensitive Hydrogel System with Paclitaxel Liposomes Used in Localized Drug Delivery System for In Situ Treatment of Tumour: Better Antitumour Efficacy and Lower Toxicity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.M.; Hickey, S.M.; Song, Y.; Plush, S.E.; Garg, S. Novel Tamoxifen Nanoformulations for Improving Breast Cancer Treatment: Old Wine in New Bottles. Molecules 2020, 25, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.M.; Sweetman, M.J.; Song, Y.; Plush, S.E.; Garg, S. Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Delivery Systems for Doxorubicin: Drug Loading and Release. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.M.; Sweetman, M.J.; Hickey, S.M.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Plush, S.E.; Garg, S. Concept Design, Development and Preliminary Physical and Chemical Characterization of Tamoxifen-Guided-Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Molecules 2021, 26, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, P.; Hall, J.B.; McLeland, C.B.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Nanoparticle interaction with plasma proteins as it relates to particle biodistribution, biocompatibility and therapeutic efficacy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, F.F.; Zhang, X.H. Strategies for Preparing Albumin-based Nanoparticles for Multifunctional Bioimaging and Drug Delivery. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3667–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorani, M.; Azarpira, N.; Karimian, K.; Heli, H. Erlotinib-loaded albumin nanoparticles: A novel injectable form of erlotinib and its in vivo efficacy against pancreatic adenocarcinoma ASPC-1 and PANC-1 cell lines. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basel, M.T.; Balivada, S.; Wang, H.; Shrestha, T.B.; Seo, G.M.; Pyle, M.; Abayaweera, G.; Dani, R.; Koper, O.B.; Tamura, M.; et al. Cell-delivered magnetic nanoparticles caused hyperthermia-mediated increased survival in a murine pancreatic cancer model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
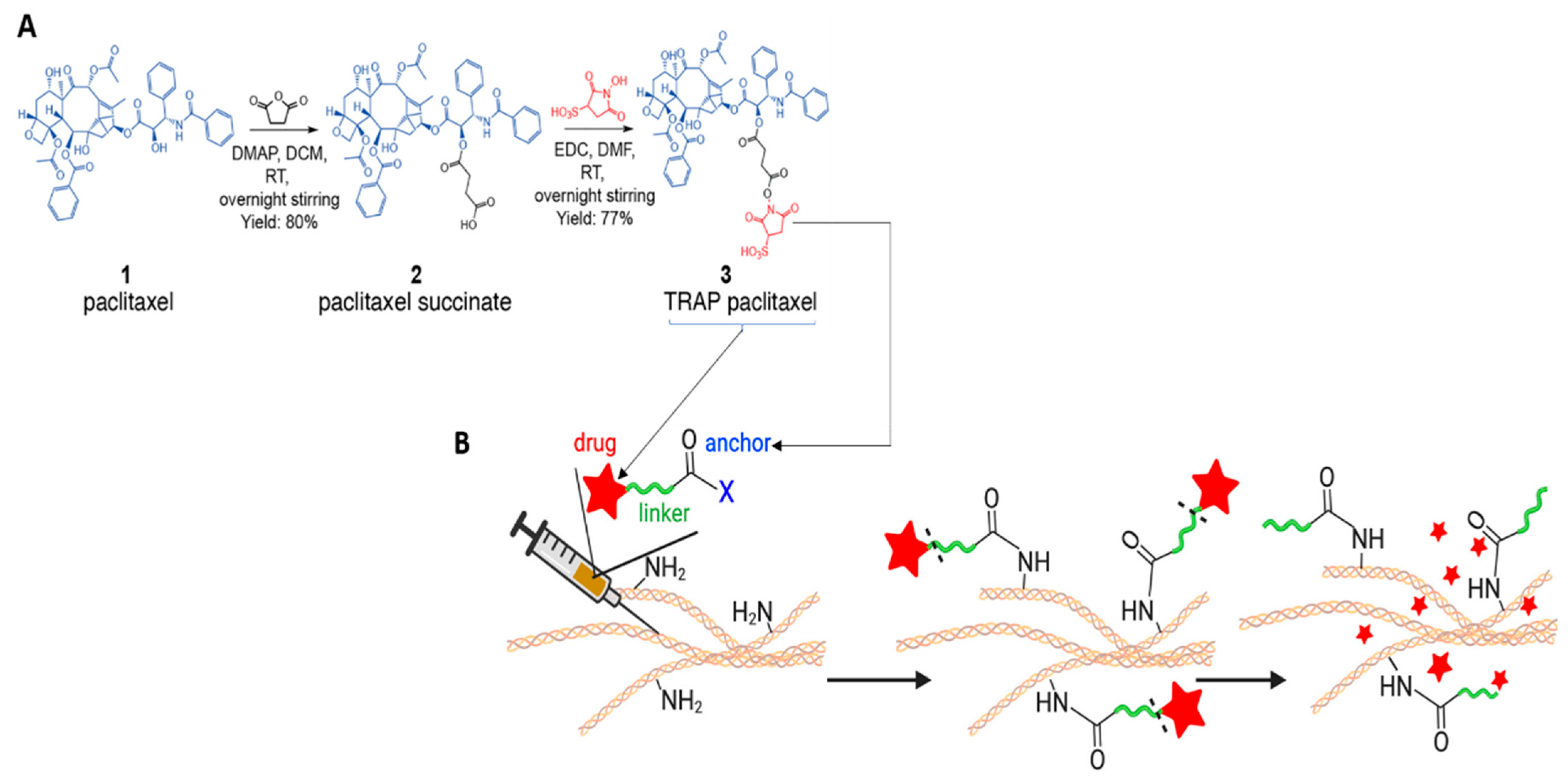
- Pandit, S.; Palvai, S.; Massaro, N.P.; Pierce, J.G.; Brudno, Y. Tissue-reactive drugs enable materials-free local depots. J. Control. Release 2022, 343, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, K.; Kohno, M.; Horibe, T.; Kawakami, K. Local drug delivery to a human pancreatic tumour via a newly designed multiple injectable needle. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okino, H.; Maeyama, R.; Manabe, T.; Matsuda, T.; Tanaka, M. Trans-tissue, sustained release of gemcitabine from photocured gelatin gel inhibits the growth of heterotopic human pancreatic tumour in nude mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 5786–5793. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Pillai, J. Chapter 13—Implantable drug delivery systems: An overview. In Nanostructures for the Engineering of Cells, Tissues and Organs; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 473–511. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, S.A.; Dominguez-Robles, J.; Donnelly, R.F.; Larraneta, E. Implantable Polymeric Drug Delivery Devices: Classification, Manufacture, Materials, and Clinical Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebian, S.; Foroughi, J.; Wade, S.J.; Vine, K.L.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Mehrali, M.; Conde, J.; Wallace, G.G. Biopolymers for Antitumour Implantable Drug Delivery Systems: Recent Advances and Future Outlook. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Park, S. Gemcitabine release behavior of polyurethane matrixes designed for local anti-cancer drug delivery via stent. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.I.; Fang, S.; Baek, Y.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Na, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, D.K. Local Delivery of Gemcitabine Inhibits Pancreatic and Cholangiocarcinoma Tumour Growth by Promoting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.-A.; Nam, S.W. Application of sol-gel techniques in fabrication of fuel cells. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Rhee, H.-K., Nam, I.-S., Park, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 159, pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kakaei, K.; Esrafili, M.D.; Ehsani, A. (Eds.) Chapter 8—Graphene and Anticorrosive Properties. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 27, pp. 303–337. [Google Scholar]
- Neacşu, I.A.; Nicoară, A.I.; Vasile, O.R.; Vasile, B.Ş. Chapter 9—Inorganic micro- and nanostructured implants for tissue engineering. In Nanobiomaterials in Hard Tissue Engineering; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 271–295. [Google Scholar]
- Hesselbach, J.; Böttcher, A.-C.; Kampen, I.; Garnweitner, G.; Schilde, C.; Kwade, A. Process and Formulation Strategies to Improve Adhesion of Nanoparticulate Coatings on Stainless Steel. Coatings 2018, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, J.D.; Jajja, M.R.N.; Schorzman, A.N.; Keeler, A.W.; Luft, J.C.; Zamboni, W.C.; DeSimone, J.M.; Yeh, J.J. Iontophoretic device delivery for the localized treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2200–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, J.D.; Jajja, M.R.N.; O’Neill, A.T.; Schorzman, A.N.; Keeler, A.W.; Luft, J.C.; Zamboni, W.C.; DeSimone, J.M.; Yeh, J.J. Impact of formulation on the iontophoretic delivery of the FOLFIRINOX regimen for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indolfi, L.; Ligorio, M.; Ting, D.T.; Xega, K.; Tzafriri, A.R.; Bersani, F.; Aceto, N.; Thapar, V.; Fuchs, B.C.; Deshpande, V.; et al. A tunable delivery platform to provide local chemotherapy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Biomaterials 2016, 93, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, S.; Misra, M. Electrospun polymeric nanofibers: New horizons in drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 107, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Bechelany, M.; Kalkura, N.S.; Miele, P.; Bohatier, C.P.; Balme, S. Chapter 20—Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery in Regenerative Medicine. In Applications of Targeted Nano Drugs and Delivery Systems; Mohapatra, S.S., Ranjan, S., Dasgupta, N., Mishra, R.K., Thomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 595–625. [Google Scholar]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kocbek, P.; Kristl, J. Critical attributes of nanofibers: Preparation, drug loading, and tissue regeneration. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Aigner, A.; Czubayko, F.; Kissel, T.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers by electrospinning as a protein delivery system and the retardation of enzyme release by additional polymer coatings. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
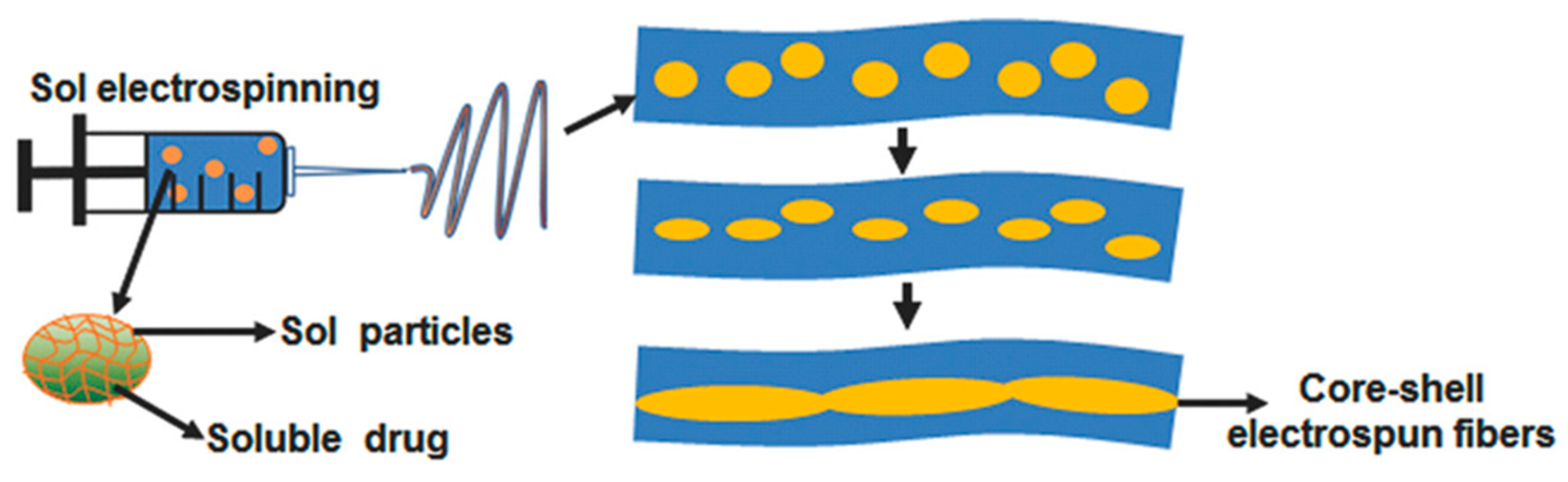
- Xia, G.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, R.; Wang, H.; Song, Z.; Deng, L.; Huang, X.; Santos, H.A.; Cui, W. Localized Controlled Delivery of Gemcitabine via Microsol Electrospun Fibers to Prevent Pancreatic Cancer Recurrence. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1800593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakura, K.; Sasai, M.; Mino, T.; Uyama, H. Non-Woven Sheet Containing Gemcitabine: Controlled Release Complex for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Q.; Shen, B.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Jin, J.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Li, H. Drug-eluting scaffold to deliver chemotherapeutic medication for management of pancreatic cancer after surgery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, S.J.; Sahin, Z.; Piper, A.K.; Talebian, S.; Aghmesheh, M.; Foroughi, J.; Wallace, G.G.; Moulton, S.E.; Vine, K.L. Dual Delivery of Gemcitabine and Paclitaxel by Wet-Spun Coaxial Fibers Induces Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cell Death, Reduces Tumour Volume, and Sensitizes Cells to Radiation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, e2001115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, N.; Takanohashi, M.; Chen, L.; Uto, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Ebara, M. A Diels-Alder polymer platform for thermally enhanced drug release toward efficient local cancer chemotherapy. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2021, 22, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, S.J.; Zuzic, A.; Foroughi, J.; Talebian, S.; Aghmesheh, M.; Moulton, S.E.; Vine, K.L. Preparation and in vitro assessment of wet-spun gemcitabine-loaded polymeric fibers: Towards localized drug delivery for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, E.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, C.M.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.; Shim, I.K. Synergistic effect of a drug loaded electrospun patch and systemic chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer xenograft. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.L. Actual role of radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 17, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.F.; Dupuy, D.E. Thermal ablation of tumours: Biological mechanisms and advances in therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, K.; Akhter, J.; Chua, T.C.; Shehata, M.; Alzahrani, N.; Al-Alem, I.; Morris, D.L. Heat sink effect on tumour ablation characteristics as observed in monopolar radiofrequency, bipolar radiofrequency, and microwave, using ex vivo calf liver model. Medicine 2015, 94, e580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.S.; Lee, F.T., Jr.; Mahvi, D.M. Hepatic microwave ablation with multiple antennae results in synergistically larger zones of coagulation necrosis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 10, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; Crocetti, L. Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Cancer. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 10, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, S.C.; Thistlethwaite, P.A.; Sewell, P.E.; Vance, R.B. Lung Cancer and Radiofrequency Ablation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 17, 927–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medicine, J.H. Radiofrequency Ablation. Available online: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/radiofrequency-ablation#:~:text=Radiofrequency%20ablation%2C%20or%20RFA%2C%20is,chronic%20back%20and%20neck%20pain (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Teng, L.S.; Jin, K.T.; Han, N.; Cao, J. Radiofrequency ablation, heat shock protein 70 and potential anti-tumour immunity in hepatic and pancreatic cancers: A minireview. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2010, 9, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsui, Y.; Nakagawa, A.; Kamiyama, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Kubo, N.; Nakase, Y. Selective thermocoagulation of unresectable pancreatic cancers by using radiofrequency capacitive heating. Pancreas 2000, 20, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollapudi, L.A.; Tyberg, A. EUS-RFA of the pancreas: Where are we and future directions. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Huang, M.; Liao, J.; Lin, S.; Yu, P.; Yang, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, S.; Xu, L.; Peng, Z.; et al. Insufficient Radiofrequency Ablation Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis Through N6-Methyladenosine mRNA Methylation-Dependent Mechanism. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1339–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pei, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B. Incomplete radiofrequency ablation provokes colorectal cancer liver metastases through heat shock response by PKCα/Fra-1 pathway. Cancer Biol. Med. 2019, 16, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Yousaf, M.N.; Ehsan, H.; Muneeb, A.; Wahab, A.; Sana, M.K.; Neupane, K.; Chaudhary, F.S. Role of Radiofrequency Ablation in the Management of Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaccini, M.; Di Leo, M.; Iannone, A.; von den Hoff, D.; Fugazza, A.; Galtieri, P.A.; Pellegatta, G.; Maselli, R.; Anderloni, A.; Colombo, M.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided ablation of solid pancreatic lesions: A systematic review of early outcomes with pooled analysis. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Seo, D.W.; Song, T.J.; Park, D.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, M.H. Clinical outcomes of EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation for unresectable pancreatic cancer: A prospective observational study. Endosc. Ultrasound. 2022, 11, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, M.; Barbi, E.; Girelli, R.; Martone, E.; Gallotti, A.; Salvia, R.; Martini, P.T.; Bassi, C.; Pederzoli, P.; Mucelli, R.P. Radiofrequency ablation of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: An overview. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzawi, T.; Chaiyapo, A.; Kongkam, P.; Ridtitid, W.; Rerknimitr, R. Elastography of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma following EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation (with video). Arab J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 21, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Ning, Z.Y.; Wang, P.; Zhuang, L.P.; Xu, L.T.; Zhu, Z.F.; Sheng, J.; Shen, Y.H.; Hua, Y.Q.; Meng, Z.Q. Combined ablation-chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for pancreatic cancer with liver metastasis: A propensity score matching study. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, I.; Paiella, S.; Barbi, E.; Bianco, R.; Boz, G.; Butturini, G.; Cantore, M.; Cardarelli, N.; Mirko, D.; Fiorentini, G.; et al. Open radiofrequency ablation as upfront treatment for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Requiem from a randomized controlled trial. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walma, M.S.; Rombouts, S.J.; Brada, L.J.H.; Borel Rinkes, I.H.; Bosscha, K.; Bruijnen, R.C.; Busch, O.R.; Creemers, G.J.; Daams, F.; van Dam, R.M.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation and chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for locally advanced pancreatic cancer (PELICAN): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2021, 22, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gala, K.B.; Shetty, N.S.; Patel, P.; Kulkarni, S.S. Microwave ablation: How we do it? Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2020, 30, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubner, M.G.; Brace, C.L.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Lee, F.T., Jr. Microwave tumour ablation: Mechanism of action, clinical results, and devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, S192–S203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietti Violi, N.; Duran, R.; Guiu, B.; Cercueil, J.P.; Aube, C.; Digklia, A.; Pache, I.; Deltenre, P.; Knebel, J.F.; Denys, A. Efficacy of microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: A randomised controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulou, L.S.; Botsa, E.; Thanou, I.; Ziakas, P.D.; Thanos, L. Percutaneous microwave ablation vs. radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Di Maso, M.; Muscatiello, N. Microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Hyperth. 2016, 32, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.J.; Panahi, B.; Albrecht, M.H.; Naguib, N.N.N.; Nour-Eldin, N.-E.A.; Gruber-Rouh, T.; Thompson, Z.M.; Basten, L.M. Microwave ablation of pancreatic tumours. Minim. Invasive Allied Technol. 2018, 27, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofuni, A.; Asai, Y.; Mukai, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Itoi, T. High-intensity focused ultrasound therapy for pancreatic cancer. J. Med. Ultrason. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haen, S.P.; Pereira, P.L.; Salih, H.R.; Rammensee, H.G.; Gouttefangeas, C. More than just tumour destruction: Immunomodulation by thermal ablation of cancer. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2011, 2011, 160250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-F. High intensity focused ultrasound in clinical tumour ablation. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 2, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergadi, M.P.; Magouliotis, D.E.; Rountas, C.; Vlychou, M.; Athanasiou, T.; Symeonidis, D.; Pappa, P.A.; Zacharoulis, D. A meta-analysis evaluating the role of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) as a fourth treatment modality for patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofuni, A.; Asai, Y.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tanaka, R.; Tonozuka, R.; Honjo, M.; Mukai, S.; Nagai, K.; Yamamoto, K.; et al. Novel therapeutic method for unresectable pancreatic cancer—The impact of the long-term research in therapeutic effect of high-intensity focused ultrasound (Hifu) therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4845–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shen, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y. The efficacy of a new high-intensity focused ultrasound therapy for metastatic pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.; Stanislavova, N.; Yotsov, T.; Zhou, K. Recurrent pancreatic cancer patient treated by chemotherapy and focused ultrasound surgery. A case report. Med. Ultrason. 2020, 22, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, M.; Feradova, H.; Gonzalez-Carmona, M.A.; Conrad, R.; Tonguc, T.; Thudium, M.; Becher, M.U.; Kun, Z.; Gorchev, G.; Tomov, S.; et al. Improving quality of life in pancreatic cancer patients following high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) in two European centers. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 5818–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolotina, L.V.; Moskvicheva, L.I.; Kornietskaya, A.L.; Sidorov, D.V.; Grishin, N.A.; Lozhkin, M.V.; Kaprin, A.D. Preliminary evaluation of the effectiveness of hifu-therapy in patients with pancreatic cancer. Sib. J. Oncol. 2021, 20, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erinjeri, J.P.; Clark, T.W. Cryoablation: Mechanism of action and devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, S187–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.C.; van Hillegersberg, R.; Schoots, I.G.; Levi, M.; Beek, J.F.; Crezee, H.; van Gulik, T.M. Cryoablation induces greater inflammatory and coagulative responses than radiofrequency ablation or laser induced thermotherapy in a rat liver model. Surgery 2010, 147, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Brace, C.L.; Lee, F.T., Jr.; Goldberg, S.N. Principles of and advances in percutaneous ablation. Radiology 2011, 258, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Niu, L.; Korpan, N.N.; Sumida, S.; Xiao, Y.; Li, J.; Sutedja, B.; Lu, Y.; Zuo, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Cryosurgery of Pancreatic Cancer: A Consensus Statement from the China Cooperative Group of Cryosurgery on Pancreatic Cancer, International Society of Cryosurgery, and Asian Society of Cryosurgery. Pancreas 2017, 46, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Mohan, P.; Amin, A.; Garcia-Buitrago, M.; Rodriguez, J.; Peaden, R. Liquid Nitrogen-Based Cryoablation in In Vivo Porcine Tissue: A Pilot Study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 3069–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Qian, Z. Laparoscopic ultrasonography-guided cryoablation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A preliminary report. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2022, 40, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sheng, S.; Zhang, K.; Liu, T. Pain Analysis in Patients with Pancreatic Carcinoma: Irreversible Electroporation versus Cryoablation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2543026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Chen, J.; He, L.; Liao, M.; Yuan, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, J.; Zuo, J.; Xu, K. Combination treatment with comprehensive cryoablation and immunotherapy in metastatic pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2013, 42, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.G.; Hao, J.H.; Gao, S.; Gao, C.T.; Tang, Y.; Liu, J.C. The outcome of cryoablation in treating advanced pancreatic cancer: A comparison with palliative bypass surgery alone. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baust, J.M.; Santucci, K.L.; Van Buskirk, R.G.; Raijman, I.; Fisher, W.E.; Baust, J.G.; Snyder, K.K. An In Vitro Investigation into Cryoablation and Adjunctive Cryoablation/Chemotherapy Combination Therapy for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer Using the PANC-1 Cell Line. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, K.W.; Baust, J.M.; Snyder, K.K.; Baust, J.G.; Van Buskirk, R.G. Characterization of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Thermal Response to Heat Ablation or Cryoablation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat 2017, 16, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G. Irreversible Electroporation. Semin. Interv. 2015, 32, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, G.T.; Padula, C.A.; Stauffer, J.A.; Toskich, B.B. Intraoperative Irreversible Electroporation in Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Guide for the Interventional Radiologist. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 36, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, K.R.; Cheung, W.; Ellis, S.J.; Federman, D.; Kavnoudias, H.; Loader-Oliver, D.; Roberts, S.; Evans, P.; Ball, C.; Haydon, A. Investigation of the safety of irreversible electroporation in humans. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 22, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmer, F.E.F.; Geboers, B.; Ruarus, A.H.; Schouten, E.A.C.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; Puijk, R.S.; de Vries, J.J.J.; Meijerink, M.R.; Scheffer, H.J. Irreversible Electroporation for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 23, 100675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silk, M.; Tahour, D.; Srimathveeravalli, G.; Solomon, S.B.; Thornton, R.H. The state of irreversible electroporation in interventional oncology. Semin. Inter. Radiol. 2014, 31, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, S. T-cell activation and immune memory enhancement induced by irreversible electroporation in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, H.J.; Stam, A.G.M.; Geboers, B.; Vroomen, L.; Ruarus, A.; de Bruijn, B.; van den Tol, M.P.; Kazemier, G.; Meijerink, M.R.; de Gruijl, T.D. Irreversible electroporation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer transiently alleviates immune suppression and creates a window for antitumour T cell activation. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, 1652532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, F.; Li, S. The role of irreversible electroporation in promoting M1 macrophage polarization via regulating the HMGB1-RAGE-MAPK axis in pancreatic cancer. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1897295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Irreversible Electroporation Plus Anti-PD-1 Antibody versus Irreversible Electroporation Alone for Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 4795–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Zhang, X.; Liang, S.; Luo, H.; Alnaggar, M.; Liu, A.; Yin, Z.; Chen, J.; Niu, L.; Jiang, Y. Irreversible electroporation plus allogenic Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells enhances antitumour effect for locally advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Sun, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, S. Survival Comparison of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Followed by Irreversible Electroporation Versus Conversional Resection for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 622318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, D.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Moris, D.; Dimitrokallis, N.; Papamichael, D.; Kountourakis, P.; Astras, G.; Davakis, S.; Papalampros, A.; Schizas, D.; et al. Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) Combined with Chemotherapy Increases Survival in Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer (LAPC). Am. J. Clin. Oncol. Cancer Clin. Trials 2021, 44, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudno-Rudzinska, J.; Kielan, W.; Guzinski, M.; Plochocki, M.; Antonczyk, A.; Kulbacka, J. New therapeutic strategy: Personalization of pancreatic cancer treatment-irreversible electroporation (IRE), electrochemotherapy (ECT) and calcium electroporation (CaEP)—A pilot preclinical study. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 38, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Lin, X.; Li, S. Comparison of Survival Between Irreversible Electroporation Followed by Chemotherapy and Chemotherapy Alone for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruarus, A.H.; Vroomen, L.G.P.H.; Geboers, B.; van Veldhuisen, E.; Puijk, R.S.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; Besselink, M.G.; Zonderhuis, B.M.; Kazemier, G.; de Gruijl, T.D.; et al. Percutaneous irreversible electroporation in locally advanced and recurrent pancreatic cancer (PANFIRE-2): A multicenter, prospective, single-arm, phase II study. Radiology 2020, 294, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ng, H.; Smith, A.M.; Wah, T.M. Severe duodenal thickening post image guided Irreversible Electroporation of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer mimicking duodenal infarction: A case report. Radiol. Case Rep. 2020, 15, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flak, R.V.; Malmberg, M.M.; Stender, M.T.; Hauberg, A.; Thorlacius-Ussing, O. Irreversible electroporation of pancreatic cancer—Effect on quality of life and pain perception. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woeste, M.R.; Wilson, K.D.; Kruse, E.J.; Weiss, M.J.; Christein, J.D.; White, R.R.; Martin, R.C.G., 2nd. Optimizing Patient Selection for Irreversible Electroporation of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: Analyses of Survival. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 817220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinic, M. Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/sbrt/pyc-20446794 (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Wu, G.; Baine, M.J.; Zhao, N.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Lin, C. Lymphocyte-sparing effect of stereotactic body radiation therapy compared to conventional fractionated radiation therapy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, M.; Gogineni, E.; Herman, J.; Saif, M.W. New Potential Options for SBRT in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Med. J. 2021, 4, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, A.; Rodrigues, D.; Ferreira, B.C. Comparison of Different Radiotherapy Techniques for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Tumours. In IFMBE Proceedings; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1283–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Arcelli, A.; Buwenge, M.; Macchia, G.; Bertini, F.; Guido, A.; Deodato, F.; Cilla, S.; Scotti, V.; Rosetto, M.E.; Djan, I.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy vs. conventionally fractionated chemoradiation in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A multicenter case-control study (PAULA-1). Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 7879–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.S.; Rosati, L.M.; Hu, C.; Fu, W.; Sehgal, S.; Hacker-Prietz, A.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Weiss, M.J.; Burkhart, R.A.; Hruban, R.H.; et al. Neoadjuvant Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy After Upfront Chemotherapy Improves Pathologic Outcomes Compared with Chemotherapy Alone for Patients With Borderline Resectable or Locally Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Without Increasing Perioperative Toxicity. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, E.C.; Benjamin, K.T.; Formenti, S.C. Generating antitumour immunity by targeted radiation therapy: Role of dose and fractionation. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 3, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, B.N.; Qiu, H.; Drage, M.G.; Chen, C.; Mathew, J.S.; Garrett-Larsen, J.; Ye, J.; Uccello, T.P.; Murphy, J.D.; Belt, B.A.; et al. Modulation of the Human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Immune Microenvironment by Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cao, F.; Xie, H.; Ju, X.; Cao, Y.; Qing, S.; Jia, Z.; Gu, L.; Fang, F.; et al. Re-Irradiation with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for In-Field Recurrence of Pancreatic Cancer After Prior Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: Analysis of 24 Consecutive Cases. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 729490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W.; Ju, X.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, L.; Ye, Y.; Jin, G.; Zhang, H. Stereotactic body radiotherapy plus pembrolizumab and trametinib versus stereotactic body radiotherapy plus gemcitabine for locally recurrent pancreatic cancer after surgical resection: An open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, e105–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.M.; Johansen, J.S.; Theile, S.; Hjaltelin, J.X.; Novitski, S.I.; Brunak, S.; Hasselby, J.P.; Willemoe, G.L.; Lorentzen, T.; Madsen, K.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study of Nivolumab With or Without Ipilimumab Combined with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Refractory Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer (CheckPAC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 27, JCO2102511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teriaca, M.A.; Loi, M.; Suker, M.; Eskens, F.; van Eijck, C.H.J.; Nuyttens, J.J. A phase II study of stereotactic radiotherapy after FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC-1 trial): Long-term outcome. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 155, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, B.; Zhang, X.; Tsauo, J.; Zhao, H.; Gong, T.; Li, J.; Li, X. Transcatheter arterial infusion for pancreatic cancer: A 10-year National Cancer Center experience in 115 patients and literature review. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 2801–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, T.; Okino, H.; Maeyama, R.; Mizumoto, K.; Nagai, E.; Tanaka, M.; Matsuda, T. Novel strategic therapeutic approaches for prevention of local recurrence of pancreatic cancer after resection: Trans-tissue, sustained local drug-delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Sakaguchi, H.; Anai, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Morimoto, K.; Nishiofuku, H.; Kichikawa, K. Catheter position for adequate intra-arterial chemotherapy for advanced pancreatic cancer: Evaluation with CT during arterial injection of contrast material. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2004, 15, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Sakaguchi, H.; Sho, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Nishiofuku, H.; Nakajima, Y.; Kichikawa, K. A Novel Interventional Radiology Technique for Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy Against Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 192, W168–W177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E. Industry news update covering September 2021. Ther. Deliv. 2021, 13, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RenovoRx. RenovoRx Receives New 510(k) Clearance for Its RenovoCath® Delivery System Designed for Targeted Treatment of Solid Tumours. RenovoRx. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/renovorx-receives-new-510k-clearance-for-its-renovocath-delivery-system-designed-for-targeted-treatment-of-solid-tumors-301369829.html (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Rosemurgy, A.S.; Ross, S.B.; Vitulli, P.L.; Malek, R.; Li, J.; Agah, R. Safety Study of Targeted and Localized Intra-Arterial Delivery of Gemcitabine in Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. J. Pancreat. Cancer 2017, 3, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Gemcitabine-Based Regional Intra-Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Medicine 2016, 95, e3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasada, T.; Denno, R.; Tanaka, T.; Kanai, M.; Mizukami, Y.; Kohno, S.; Takabayashi, A. Intra-arterial infusion chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin in advanced pancreatic cancer: A feasibility study. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. Cancer Clin. Trials 2008, 31, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Luo, J. Endovascular implantation of iodine-125 seed strand combined and stent placement for locally advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with vascular invasion: A prospective single-arm pilot study. J. Contemp. Brachyther. 2020, 12, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.Y.; Tan, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Li, X.Q. Prognostic value of glypican-1 for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer following regional intra-arterial chemotherapy. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingpank, J.F. Chapter 102—Isolated hepatic perfusion for extensive liver cancer. In Blumgart’s Surgery of the Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas, 2-Volume Set, 6th ed.; Jarnagin, W.R., Ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 1514–1519.e1511. [Google Scholar]
- Broman, K.K.; Zager, J.S. Intra-arterial perfusion-based therapies for regionally metastatic cutaneous and uveal melanoma. Melanoma Manag. 2019, 6, MMT26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aigner, K.R.; Gailhofer, S.; Selak, E.; Aigner, K. Intra-arterial infusion chemotherapy versus isolated upper abdominal perfusion for advanced pancreatic cancer: A retrospective cohort study on 454 patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 2855–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigner, K.R.; Gailhofer, S.; Selak, E.; Aigner, K. Survival and quality of life after isolated upper abdominal perfusion with chemofiltration (UAP-F) for stage III and IV pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beane, J.D.; Griffin, K.F.; Levy, E.B.; Pandalai, P.; Wood, B.; Abi-Jaoudeh, N.; Beresnev, T.; Shutack, Y.; Webb, C.C.; Avital, I.; et al. Duodenal ischemia and upper GI bleeding are dose-limiting toxicities of 24-h continuous intra-arterial pancreatic perfusion of gemcitabine following vascular isolation of the pancreatic head: Early results from the Regional Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer (RECLAP) study. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Valle, S.J.; Alzahrani, N.A.; Liauw, W.; Sugarbaker, P.H.; Bhatt, A.; Morris, D.L. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) Methodology, Drugs and Bidirectional Chemotherapy. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 7, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tentes, A.-A.K. Hyperthermic intra-operative intraperitoneal chemotherapy as an adjuvant to pancreatic cancer resection. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2021, 12, S91–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, T.J.; Mohamed, S.A.; Albrecht, M.H.; Gruber-Roh, T.; Lin, H.; Nour Eldin, N.E.A.; Bednarova, I.; Naguib, N.N.; Panahi, B. Transarterial chemoembolization in pancreatic adenocarcinoma with liver metastases: MR-based tumour response evaluation, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) patterns, and survival rates. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Hua, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhuang, L.; Feng, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Shen, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine in the treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer by transcatheter arterial chemotherapy: A retrospective study. China Oncol. 2020, 30, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, Y.; Pereira, S.P.; Pogue, B.; Maytin, E.V.; Hasan, T.; Linn, B.; Mangels-Dick, T.; Wang, K.K. EUS-guided verteporfin photodynamic therapy for pancreatic cancer. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramu, V.; Gautam, S.; Kondaiah, P.; Chakravarty, A.R. Diplatinum (II) Catecholate of Photoactive Boron-Dipyrromethene for Lysosome-Targeted Photodynamic Therapy in Red Light. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 9067–9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Liu, J.; Guan, R.; Jin, C.; Ji, L.; Chao, H. Endoplasmic reticulum targeted cyclometalated iridium(iii) complexes as efficient photodynamic therapy photosensitizers. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 6408–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk-Mahapatra, R.; Gollnick, S.O. Photodynamic therapy and immunity: An update. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfsen, H.C. Photodynamic therapy for pancreatic cancer: Let’s get serious. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 67, 961–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-P.; Yen, C.-J.; Wu, B.-S.; Wong, T.-W. Recent Advances in Photodynamic Therapy for Deep-Seated Tumours with the Aid of Nanomedicine. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, E.S.; Balaji, U.; Mannakee, B.; Vail, P.; Eslinger, C.; Moxom, C.; Mansour, J.; Witkiewicz, A.K. Pancreatic cancer cell lines as patient-derived avatars: Genetic characterisation and functional utility. Gut 2018, 67, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, G.R.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.; Kim, M.S. Advances in Injectable In Situ-Forming Hydrogels for Intratumoural Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfo, R.; Tavakoli, S.; Junnuthula, V.; Williams, D.S.; Urtti, A.; van Hest, J.C.M. Exploring the Impact of Morphology on the Properties of Biodegradable Nanoparticles and Their Diffusion in Complex Biological Medium. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Kang, K.S.; Hong, J.M.; Pati, R.G.; Park, M.N.; Shim, I.K.; Lee, C.M.; Kim, S.C.; Cho, D.W. A 3D-printed local drug delivery patch for pancreatic cancer growth suppression. J. Control. Release 2016, 238, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebian, S.; Shim, I.K.; Foroughi, J.; Orive, G.; Vine, K.L.; Kim, S.C.; Wallace, G.G. 3D-Printed Coaxial Hydrogel Patches with Mussel-Inspired Elements for Prolonged Release of Gemcitabine. Polymers 2021, 13, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, V.; Grassi, R.; Fusco, R.; Setola, S.V.; Palaia, R.; Belli, A.; Miele, V.; Brunese, L.; Grassi, R.; Petrillo, A.; et al. Assessment of Ablation Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer: The Radiologist’s Challenge. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 560952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ierardi, A.M.; Lucchina, N.; Bacuzzi, A.; Marco, D.C.; Bracchi, E.; Cocozza, E.; Dionigi, G.; Tsetis, D.; Floridi, C.; Carrafiello, G. Percutaneous ablation therapies of inoperable pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Incorporative Drugs | Type | Polymer | Production Method | Drug Release | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEM Montmorillonite (MTT) NPs | Nanobiohybrid hydrogel | PDLLAPEG-PDLLA, PLEL | Sol-gel of GEM-loaded-MTT NPs | 40% after 12 h | [96] |
| PTX | Thermosensitive hydrogel | Poloxamer 407 and Poloxamer 188 | Sol-gel | 120 h | [97] |
| GEM Cis platinum (DDP) | Thermosensitive hydrogel | PDLLAPEG-PDLLA, PLEL | Sol-gel | >10 days | [91] |
| GEM | Adhesive matrix | Styrenated gelatin | - | >80% after 6 h | [108] |
| PTX | Material free DDS | N/A | TRAP depots | 32% at 96 h (neutral pH) 60% at 96 h (acidic pH) | [106] |
| Ethanol | Material free DDS | N/A | Multiple injectable needle (MIN) | N/A | [107] |
| Incorporative Drugs | Type | Polymer | Production Method | Drug Release | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEM | Membrane | Polyurethane | Solvent casting | Up to 16 days | [112] |
| GEM | Membrane | Polyurethane | Solvent casting | - | [113] |
| PTX | Polymeric drug-embedding matrix | Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) | Dip-Coating | Up to 60 days | [120] |
| FOLFIRINOX Combination | Implantable Iontophoretic Device | Polyurethane | Dip coating | - | [118,119] |
| GEM | Nano-fibre film | Poly (furfuryl methacrylate) | Spin coating | 1 h with heat | [129] |
| GEM | Fibrous Scaffolds | Polylactic acid and Hyaluronic acid | Electrospinning | >3 weeks | [125] |
| GEM | Non-woven sheets | Poly (L-lactic acid) (PLLA) | Electrospinning | 30 days | [126] |
| GEM | Spun fibres | Alginate or chitosan | Coaxial wet spinning | 5–15 days | [130] |
| GEM and PTX | Patch | Polycaprolactone shell and alginate core | Electrospinning | 21 days | [128] |
| 5-FU | Spun Fibres | PLLA | Electrospinning | 30 days | [131] |
| FOLFIRINOX Drugs Combination | Electrospun scaffold | Polyglycolide-co-trimethylene carbonate (PGA-TMC) and porcine gelatin A | Electrospinning | 3 weeks | [127] |
| Intervention | Combined Therapy | PC Stage | Trial Phase | Trial Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) | Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Phase II | NCT04990609 |
| - | PCs | Not Applicable | NCT03218345 | |
| - | Pain relief in PC | Phase IV | NCT04809935 | |
| - | Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours | Not Applicable | NCT04520932 | |
| - | Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms | Not Applicable | NCT03834701 | |
| High-intensity focused ultrasound ablation (HIFU) | FOLFIRINOX regimen | Non-resectable PC | Not Applicable | NCT05262452 |
| biliary stent | Pancreatic Carcinoma Biliary Obstruction | Not Applicable | NCT03962478 | |
| - | PDAC | Not Applicable | NCT04298242 | |
| Microwave ablation | Durvalumab 50 MG/ML Tremelimumab GEM | Unresectable Locally Advanced PC | Phase II | NCT04156087 |
| First-line or second-line chemotherapy | PC Oligohepatic Metastasis | Phase II | NCT04677192 | |
| Cryoablation | - | PC | Phase I | NCT01335945 |
| Irreversible electroporation (IRE) | NK Immunotherapy | Advanced PC | Phase I and II | NCT02718859 |
| - | Locally advanced PC | - | NCT02841436 | |
| chemotherapy | Unresectable Locally Advanced PC | - | NCT04093141 | |
| GEM | Locally Advanced PC | NCT02981719 | ||
| - | Unresectable PC | NCT02041936 | ||
| Nivolumab Toll-Like Receptor 9 | Metastatic PC | Phase I | NCT04612530 | |
| Nivolumab | Metastatic PC | Phase II | NCT04212026 | |
| - | Locally Advanced PC | - | NCT04276857 | |
| - | PC | - | NCT05170802 | |
| Pembrolizumab | Metastatic PC | Phase II | NCT04835402 | |
| GEM FOLFIRINOX | Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase I | NCT03484299 | |
| - | Inoperable Hepatic and Pancreatic Malignancy | - | NCT02822716 | |
| Modified FOLFIRINOX Regimen | Stage III PC | Phase III | NCT03899636 | |
| - | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma | - | NCT03257150 | |
| Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) | Anti-programmed Cell Death Protein 1(Anti-PD-1) | Late Stage or Recurrent PC Patients | Phase I | NCT03716596 |
| GEM-based doublets | Advanced PC | Not applicable | NCT02416609 | |
| Modified FOLFIRINOX | Non-metastatic Unresectable Pancreatic | Phase II | NCT03991962 | |
| GEM nab-paclitaxel | Localised PC | Phase II | NCT03492671 | |
| - | Resectable PC | Not applicable | NCT05043857 | |
| Defactinib | Advanced Pancreas Adenocarcinoma | Phase II | NCT04331041 | |
| With or without modified FOLFIRINOX | Locally Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | NCT04986930 | ||
| - | Pain control for Metastatic PC | Phase II | NCT05114213 | |
| Modified FOLFIRINOX GEM + Nab-paclitaxel GEM + Capecitabine | High Risk and Locally Advanced PC | Phase II | ||
| Capecitabine Fluorouracil Zoledronic Acid | Locally Advanced PC | Phase II | NCT03073785 | |
| Durvalumab | Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase I and II | NCT03245541 | |
| Nano-smart AGuIX® | Advanced and unresectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Phase I and II | NCT04789486 | |
| Neoadjuvant GEM plus nab-paclitaxel Neoadjuvant GEM plus nab-paclitaxel with SBRT Neoadjuvant S-1 plus nab-paclitaxel with SBRT | Borderline Resectable PC | Phase II | NCT03777462 | |
| Drug GC4711 | borderline resectable and nonresectable PC | Phase IIb | NCT04698915 | |
| Nivolumab CCR2/CCR5 dual antagonist GVAX | Locally Advanced Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma | Phase I and II | NCT03767582 | |
| Intra-arterial infusion | GEM nab-paclitaxel using RenovoCath™ | Locally Advanced PC | Phase III | NCT03257033 |
| GEM Oxaliplatin | Locally Advanced PC | Phase II | NCT02635971 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bazeed, A.Y.; Day, C.M.; Garg, S. Pancreatic Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities in Locoregional Therapies. Cancers 2022, 14, 4257. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174257
Bazeed AY, Day CM, Garg S. Pancreatic Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities in Locoregional Therapies. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4257. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174257
Chicago/Turabian StyleBazeed, Alaa Y., Candace M. Day, and Sanjay Garg. 2022. "Pancreatic Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities in Locoregional Therapies" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4257. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174257
APA StyleBazeed, A. Y., Day, C. M., & Garg, S. (2022). Pancreatic Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities in Locoregional Therapies. Cancers, 14(17), 4257. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174257








