Zinc Finger Proteins: Functions and Mechanisms in Colon Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Zinc Finger Proteins
3. ZFPs and Their Role in Colon Cancer Patient Outcomes
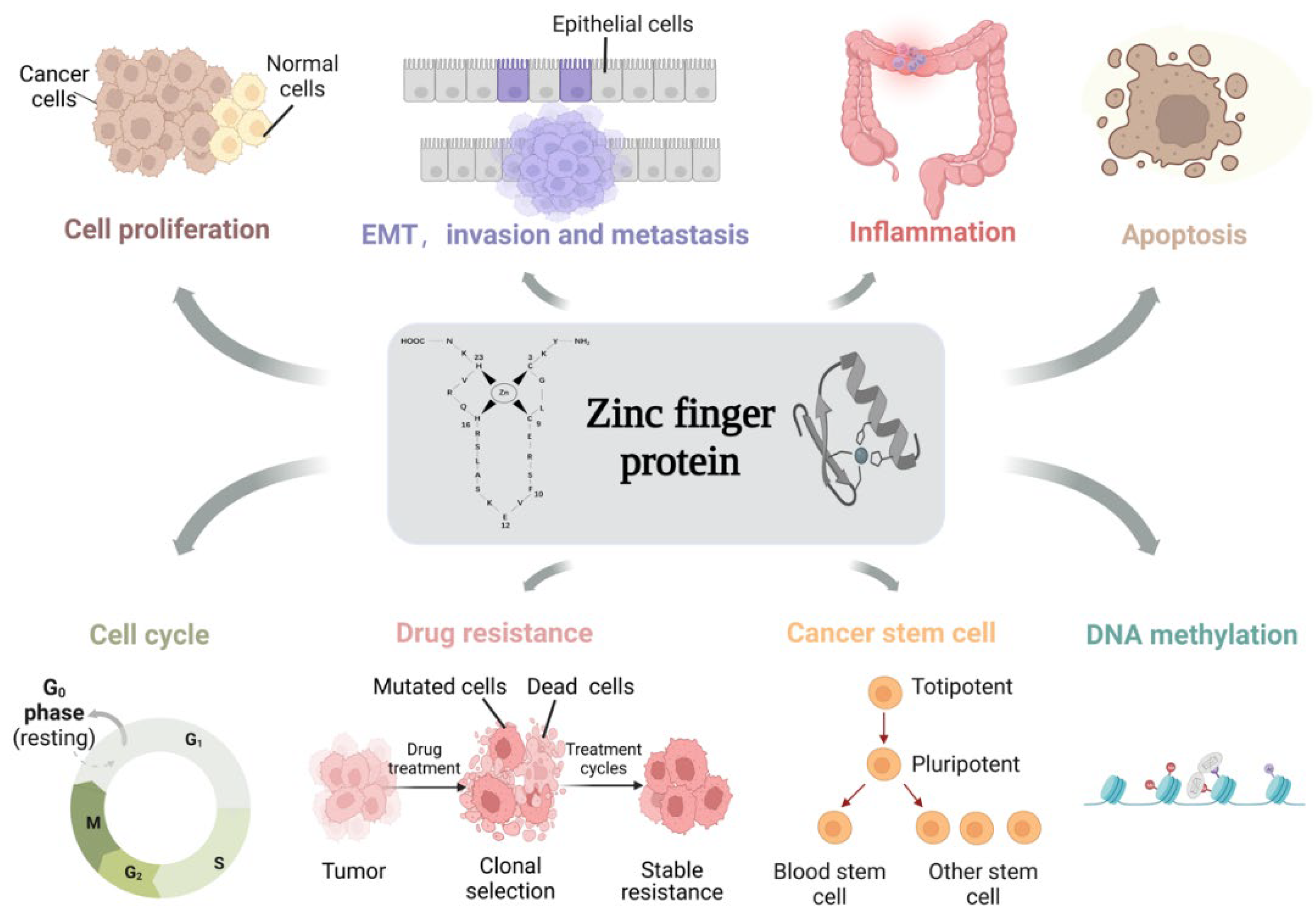
4. Biological Functions of ZFPs in Colon Cancer
4.1. ZFPs Regulate Cell Proliferation
4.2. ZFPs Regulate EMT and Promote Invasion and Metastasis
4.3. ZFPs Regulate Inflammation
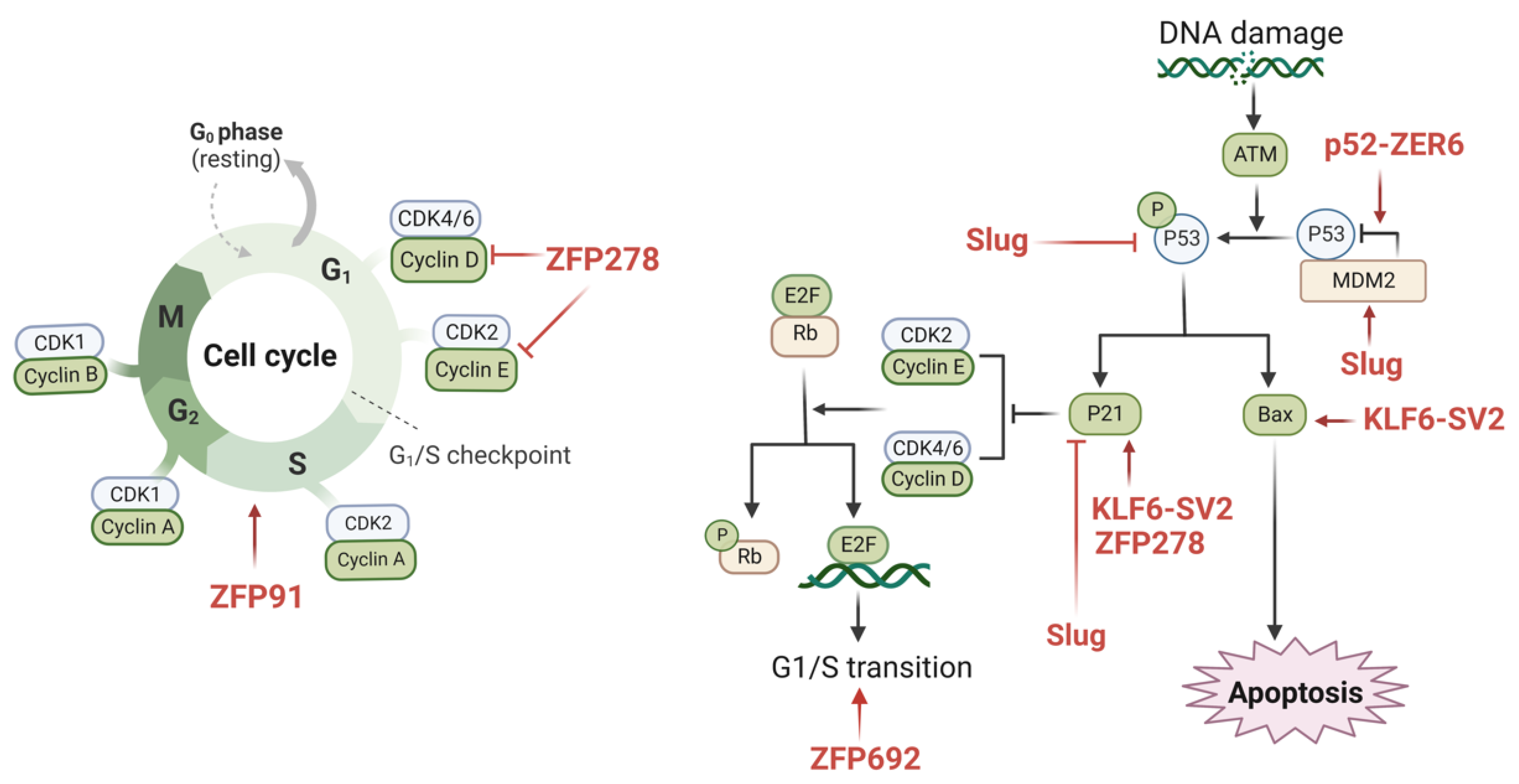
4.4. ZFPs Regulate Apoptosis
4.5. ZFPs Regulate Cell Cycle
4.6. ZFPs Regulate Drug Resistance
4.7. ZFPs Regulate Cancer Stem Cell
4.8. ZFPs Regulate DNA Methylation
5. MZF1: A Double-Edged Sword in Colon Cancer
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MZF1 | Myeloid zinc finger 1 |
| Axl | AXL receptor tyrosine kinase |
| SP1 | sp1 transcription factor |
| Gas6 | growth arrest specific 6 |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells |
| RAC | Rac family small GTPase |
| SRC | SRC proto-oncogene, non-receptor tyrosine kinase |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| GRB2 | Growth Factor Receptor-bound Protein 2 |
| SOS | SOS Ras/Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor |
| GDP | Guanosine 5′-diphosphate |
| GTP | Guanosine 5′-triphosphate |
| Raf | Rheumatoid Arthritis Factor |
| MEK | MAPK/ERK kinase |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| p55PIK | p55 Phosphatidylinositol kinases |
| GF | growth factor |
| RTK | receptor Tyrosine Kinase |
| PIP2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| PIP3 | Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate |
| AKT | Alpha-serine/Threonine Kinase |
| GSK3B | glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
| BCD | beta-cyclodextrin |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase |
| RAC | Rac family small GTPase 1 |
| c-myc | cellular MYC proto-oncogene |
| MINA53 | MYC-induced nuclear antigen |
| ID2 | Inhibitor of DNA binding 2 |
| BCL2 | BCL2 Apoptosis Regulator |
| PTMA | Prothymosin alpha |
| FTO | fat mass and obesity-associated protein |
| DR5 | death receptor 5 |
| TRAIL | TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand |
| FADD | Fas-associated via death domain |
| CDK1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
| CDK2 | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| CDK4/6 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 |
| E2F | E2F transcription factor |
| Rb | Retinoblastoma Protein |
| Bax | BCL2-associated X, apoptosis regulator |
| ATM | ATM serine/threonine kinase |
| MDM2 | MDM2 proto-oncogene |
| ZFP91 | Zinc finger protein 91, atypical E3 ubiquitin ligase |
| ZFP278 | Zinc finger protein 278 |
| ZFP691 | Zinc finger protein 691 |
| Slug | Zinc finger protein SNAI2 |
| KLF6-SV2 | Krüppel-like factor 6- SV2 variant |
| P52-ZER6 | p52 isoforms-zinc-finger estrogen receptor interaction clone 6 |
| KAP1 | KRAB-associated protein-1 |
| CYTOR | Cytoskeleton Regulator RNA |
References
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, W.; Lan, X.L.; Zeng, Z.C.; Liang, Y.S.; Yan, Y.R.; Song, F.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Zhu, X.H.; Liao, W.J.; et al. CAFs secreted exosomes promote metastasis and chemotherapy resistance by enhancing cell stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, P. Colon Cancer: What Do the Stages Mean? Available online: https://www.everydayhealth.com/colon-cancer/stages-what-they-mean-survival/ (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Hedayat-Evrigh, N.; Khalkhali-Evrigh, R.; Bakhtiarizadeh, M.R. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of Variants in Domestic and Wild Bactrian Camels Using Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. Int. J. Genom. 2020, 2020, 2430846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, R.A.; Li, H.; Tummala, R.; Maul, R.; Sinha, S. Identification of Basonuclin2, a DNA-binding zinc-finger protein expressed in germ tissues and skin keratinocytes. Genomics 2004, 83, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doran, B.; Gherbesi, N.; Hendricks, G.; Flavell, R.A.; Davis, R.J.; Gangwani, L. Deficiency of the zinc finger protein ZPR1 causes neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7471–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.S.; ZeRuth, G.; Lichti-Kaiser, K.; Vasanth, S.; Yin, Z.; Kim, Y.S.; Jetten, A.M. Gli-similar (Glis) Krüppel-like zinc finger proteins: Insights into their physiological functions and critical roles in neonatal diabetes and cystic renal disease. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhie, S.K.; Yao, L.; Luo, Z.; Witt, H.; Schreiner, S.; Guo, Y.; Perez, A.A.; Farnham, P.J. ZFX acts as a transcriptional activator in multiple types of human tumors by binding downstream of transcription start sites at the majority of CpG island promoters. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Graves, D.T. FOXO transcription factors: Their clinical significance and regulation. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 925350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beerli, R.R.; Barbas, C.F., 3rd. Engineering polydactyl zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayer, K.J.; Kulshreshtha, S.; Segal, D.J. The protein-binding potential of C2H2 zinc finger domains. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 51, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, J.; Mackay, J.P. Beyond DNA: Zinc finger domains as RNA-binding modules. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 649, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Chen, Y.; Han, D.; Lei, Z.; Chu, X. Role of the zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing transcription factors in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 816–836. [Google Scholar]
- Vrana, K.E.; Churchill, M.E.; Tullius, T.D.; Brown, D.D. Mapping functional regions of transcription factor TFIIIA. Mol. Cell Biol. 1988, 8, 1684–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, G.; Feng, L.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Bai, J.; He, L.; Gu, S.; Zhao, X. A bioinformatics analysis of zinc finger protein family reveals potential oncogenic biomarkers in breast cancer. Gene 2022, 828, 146471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragantini, B.; Tiotiu, D.; Rothé, B.; Saliou, J.M.; Marty, H.; Cianférani, S.; Charpentier, B.; Quinternet, M.; Manival, X. Functional and Structural Insights of the Zinc-Finger HIT protein family members Involved in Box C/D snoRNP Biogenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 2488–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassandri, M.; Smirnov, A.; Novelli, F.; Pitolli, C.; Agostini, M.; Malewicz, M.; Melino, G.; Raschellà, G. Zinc-finger proteins in health and disease. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jen, J.; Wang, Y.C. Zinc finger proteins in cancer progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Peng, H.; Schultz, D.C.; Lopez-Guisa, J.M.; Rauscher, F.J., 3rd; Marmorstein, R. Structure-function studies of the BTB/POZ transcriptional repression domain from the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger oncoprotein. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5275–5282. [Google Scholar]
- Del Rizzo, P.A.; Trievel, R.C. Substrate and product specificities of SET domain methyltransferases. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Q.; Wang, K.; Yan, D.W.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Li, M.X.; Wang, X.W.; Liu, J.; Peng, Z.H.; Li, G.X.; et al. Ciz1 is a novel predictor of survival in human colon cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2014, 239, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Zheng, L.Q.; Pan, L.J.; Guo, J.X.; Yang, G.S. ZNF217 is overexpressed and enhances cell migration and invasion in colorectal carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 2459–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.J.; Bu, P.L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.T.; Li, Q.Y.; Liu, J.T.; Dong, H.C.; Ren, X.Q. ZNF281 Regulates Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Colorectal Cancer through Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 52, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; Boyd, D.D. Unbiased screening for transcriptional targets of ZKSCAN3 identifies integrin beta 4 and vascular endothelial growth factor as downstream targets. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 35295–35304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, Y.; Ren, S.; Ai, L.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Piao, D. ZNF692 promotes colon adenocarcinoma cell growth and metastasis by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otsuka, R.; Akutsu, Y.; Sakata, H.; Hanari, N.; Murakami, K.; Kano, M.; Toyozumi, T.; Takahashi, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Sekino, N.; et al. ZNF750 Expression Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncology 2018, 94, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Yang, S.S.; Vo, M.T.; Cho, W.J.; Lee, B.J.; Leem, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Cha, H.J.; Park, J.W. Tristetraprolin down-regulates IL-23 expression in colon cancer cells. Mol. Cells 2013, 36, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panneerselvam, J.; Madka, V.; Rai, R.; Morris, K.T.; Houchen, C.W.; Chandrakesan, P.; Rao, C.V. Inflammatory Mediators and Gut Microbial Toxins Drive Colon Tumorigenesis by IL-23 Dependent Mechanism. Cancers 2021, 13, 5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.J.; Lee, H.H.; Chae, S.W.; Cho, W.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Choi, H.J.; Choi, D.H.; Jung, S.W.; Min, Y.J.; Lee, B.J.; et al. Tristetraprolin downregulates the expression of both VEGF and COX-2 in human colon cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 2011, 58, 790–795. [Google Scholar]
- Montorsi, L.; Guizzetti, F.; Alecci, C.; Caporali, A.; Martello, A.; Atene, C.G.; Parenti, S.; Pizzini, S.; Zanovello, P.; Bortoluzzi, S.; et al. Loss of ZFP36 expression in colorectal cancer correlates to wnt/ ß-catenin activity and enhances epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through upregulation of ZEB1, SOX9 and MACC1. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59144–59157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Ge, X.; Liao, W.; Cao, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, B.; Du, J. ZFP36 promotes VDR mRNA degradation to facilitate cell death in oral and colonic epithelial cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Tilló, E.; de Barrios, O.; Siles, L.; Amendola, P.G.; Darling, D.S.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Castells, A.; Postigo, A. ZEB1 Promotes invasiveness of colorectal carcinoma cells through the opposing regulation of uPA and PAI-1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, D.; Luo, Y.; Qin, S.; Yu, M.; Mu, Y.; Ye, G.; Yang, N.; Cong, Z.; Chen, J.; Qin, J.; et al. Metallopanstimulin-1 (MPS-1) mediates the promotion effect of leptin on colorectal cancer through activation of JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tinguely, P.; Dal, G.; Bottai, M.; Nilsson, H.; Freedman, J.; Engstrand, J. Microwave ablation versus resection for colorectal cancer liver metastases—A propensity score analysis from a population-based nationwide registry. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Meng, W.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Qin, C.Y. Comparison of overall survival in patients with unresectable hepatic metastases with or without transarterial chemoembolization: A Propensity Score Matching Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.J.; Zhou, T.; Tian, H.P.; Liu, Z.L.; Xia, S.S. High expression of ZEB1 correlates with liver metastasis and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, H.; Li, J.; Xie, M.; Lei, R.; Hu, B. Comprehensive analysis of metastasis-related genes reveals a gene signature predicting the survival of colon cancer patients. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paek, A.R.; Lee, C.H.; You, H.J. A role of zinc-finger protein 143 for cancer cell migration and invasion through ZEB1 and E-cadherin in colon cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog 2014, 53 (Suppl. 1), E161–E168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.A.; Fitzgerald, J.; Fitzgerald, S.; Kenny, D.; Kay, E.W.; O’Kennedy, R.; Kijanka, G.S. Diagnostic potential of zinc finger protein-specific autoantibodies and associated linear B-cell epitopes in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, A.T.; Sharma, M.; Holtz, A.E.; Wu, C.; Sun, Z.; Weigel, R.J. A novel zinc finger transcription factor with two isoforms that are differentially repressed by estrogen receptor-alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9326–9334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Colon, D.; Shi, J.; Napier, D.; Rychahou, P.; Lu, W.; Lee, E.Y.; Weiss, H.L.; et al. Regulation of the potential marker for intestinal cells, Bmi1, by β-catenin and the zinc finger protein KLF4: Implications for colon cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3760–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, T.; Wang, C.; Lai, D.; Wu, S.; et al. GTSE1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by attenuating of KLF4 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Lab. Investig. 2022, 102, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; He, H.; Qiu, F.; Qian, H. Expression and Prognosis Value of the KLF Family Members in Colorectal Cancer. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 6571272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Mi, C.; Wang, K.S.; Lee, J.J.; Jin, X. Zinc finger protein 91 (ZFP91) activates HIF-1α via NF-κB/p65 to promote proliferation and tumorigenesis of colon cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36551–36562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ma, J.; Jin, X. Zinc finger protein 91 positively regulates the production of IL-1β in macrophages by activation of MAPKs and non-canonical caspase-8 inflammasome. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 4338–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pierdomenico, M.; Palone, F.; Cesi, V.; Vitali, R.; Mancuso, A.B.; Cucchiara, S.; Oliva, S.; Aloi, M.; Stronati, L. Transcription Factor ZNF281: A Novel Player in Intestinal Inflammation and Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschke, L.; Jopek, K.; Szyszka, M.; Tyczewska, M.; Malendowicz, L.K.; Rucinski, M. ZFP91 zinc finger protein expression pattern in normal tissues and cancers. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 3599–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Li, M.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Jin, H.L.; Zuo, H.X.; Ma, J.; Jin, X. Convallatoxin inhibits IL-1β production by suppressing zinc finger protein 91 (ZFP91)-mediated pro-IL-1β ubiquitination and caspase-8 inflammasome activity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 1887–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xue, X.; Taylor, M.; Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Nagaoka, K.; Hao, C.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Shah, Y.M. Hypoxia-inducible factor/MAZ-dependent induction of caveolin-1 regulates colon permeability through suppression of occludin, leading to hypoxia-induced inflammation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 3013–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.Q.; Guo, F.F.; Sun, D.F.; Wang, Y.C.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.L.; Hong, J.; Fang, J.Y. Downregulation of ZNF278 arrests the cell cycle and decreases the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells via inhibition of the ERK/MAPK pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 3685–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.M.; Zhang, F.; Tao, W.P.; Ye, J.J.; Ge, W. Twist mediates an aggressive phenotype in human colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Rai, B.; Qi, F.; Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, B. Influence of the Twist gene on the invasion and metastasis of colon cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, U.; Park, J.K.; Um, H.D. Slug promotes p53 and p21 protein degradation by inducing Mdm2 expression in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Tilló, E.; Lázaro, A.; Torrent, R.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Vaquero, E.C.; Castells, A.; Engel, P.; Postigo, A. ZEB1 represses E-cadherin and induces an EMT by recruiting the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling protein BRG1. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3490–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Tang, B.; Hu, C.J.; Xiao, Y.F.; Xie, R.; Yong, X.; Wu, Y.Y.; Dong, H.; Yang, S.M. An hTERT/ZEB1 complex directly regulates E-cadherin to promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindner, P.; Paul, S.; Eckstein, M.; Hampel, C.; Muenzner, J.K.; Erlenbach-Wuensch, K.; Ahmed, H.P.; Mahadevan, V.; Brabletz, T.; Hartmann, A.; et al. EMT transcription factor ZEB1 alters the epigenetic landscape of colorectal cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peinado, H.; Ballestar, E.; Esteller, M.; Cano, A. Snail mediates E-cadherin repression by the recruitment of the Sin3A/histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)/HDAC2 complex. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, C.; Wu, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Rychahou, P.G.; Evers, B.M.; Zhou, B.P. G9a interacts with Snail and is critical for Snail-mediated E-cadherin repression in human breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1469–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, Z.T.; Cai, M.Y.; Wang, X.G.; Kong, L.L.; Mai, S.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Liao, Y.J.; Zheng, F.; Zhu, W.; et al. EZH2 supports nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell aggressiveness by forming a co-repressor complex with HDAC1/HDAC2 and Snail to inhibit E-cadherin. Oncogene 2012, 31, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Chai, K.; Ying, X.; Zhou, B.P. The Role of Snail in EMT and Tumorigenesis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin-Kleiner, I. BORIS in human cancers—A review. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.P.; Chen, J.; He, M.; Ching, A.K.; Lau, C.; Lai, P.B.; To, K.F.; Wong, N. Overexpression of ZFX confers self-renewal and chemoresistance properties in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Yan, L.; Su, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, S.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y. Zinc-finger protein X-linked is a novel predictor of prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 3150–3157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, K.; Zhang, M.; Chu, Q.; Gan, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, W. The Role of p-STAT3 as a Prognostic and Clinicopathological Marker in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Zhang, X.; Lv, X. Zinc finger protein 750(ZNF750), negatively regulated by miR-17-5p, inhibits proliferation, motility and invasion of colonic cancer cells. J. Gene Med. 2020, 22, e3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wong, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, C.; Zhai, J.; Wang, G.; Wei, H.; Zhang, X.; He, H.H.; et al. ZNF545 loss promotes ribosome biogenesis and protein translation to initiate colorectal tumorigenesis in mice. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6590–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, N.; Garriga, G. Asymmetric cell division: From A to Z. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3625–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Chen, W. Gambogic acid is a novel anti-cancer agent that inhibits cell proliferation, angiogenesis and metastasis. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sáez, J.F.; de la Torre, C.; Pincheira, J.; Giménez-Martín, G. Cell proliferation and cancer. Histol. Histopathol. 1998, 13, 1197–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koury, J.; Lucero, M.; Cato, C.; Chang, L.; Geiger, J.; Henry, D.; Hernandez, J.; Hung, F.; Kaur, P.; Teskey, G.; et al. Immunotherapies: Exploiting the Immune System for Cancer Treatment. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 9585614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wu, S.; Li, W.; Herkilini, A.; Miyagishi, M.; Zhao, H.; Kasim, V. Zinc-finger protein p52-ZER6 accelerates colorectal cancer cell proliferation and tumour progression through promoting p53 ubiquitination. EBioMedicine 2019, 48, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semenza, G.L. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, T.; Prince, T.; Wegiel, B.; Calderwood, S.K. Role and Regulation of Myeloid Zinc Finger Protein 1 in Cancer. J. Cell Biochem. 2015, 116, 2146–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mudduluru, G.; Vajkoczy, P.; Allgayer, H. Myeloid zinc finger 1 induces migration, invasion, and in vivo metastasis through Axl gene expression in solid cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, D.; Chijiwa, T.; Matsuyama, M.; Mukai, M.; Matsuo, E.I.; Nishimura, O.; Kawai, K.; Suemizu, H.; Hiraoka, N.; Nakagohri, T.; et al. Zinc finger protein 185 is a liver metastasis-associated factor in colon cancer patients. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, H.; Fang, J. Zinc finger protein 278, a potential oncogene in human colorectal cancer. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe, S.; Abdelrahim, M. Sp transcription factor family and its role in cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2438–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, D.D.; Zheng, J.Y.; Wu, Y.A. Expression of KLF6-SV2 in colorectal cancer and its impact on proliferation and apoptosis. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 27, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vu, T.; Datta, P.K. Regulation of EMT in Colorectal Cancer: A Culprit in Metastasis. Cancers 2017, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herranz, N.; Pasini, D.; Díaz, V.M.; Francí, C.; Gutierrez, A.; Dave, N.; Escrivà, M.; Hernandez-Muñoz, I.; Di Croce, L.; Helin, K.; et al. Polycomb complex 2 is required for E-cadherin repression by the Snail1 transcription factor. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 4772–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.; Ponn, A.; Hu, X.; Law, B.K.; Lu, J. Requirement of the histone demethylase LSD1 in Snai1-mediated transcriptional repression during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4896–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, L.E.; Sanduja, S.; Bemis-Standoli, K.; Pena, E.A.; Price, R.L.; Dixon, D.A. The mRNA binding proteins HuR and tristetraprolin regulate cyclooxygenase 2 expression during colon carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Postigo, A.A.; Dean, D.C. ZEB represses transcription through interaction with the corepressor CtBP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6683–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Postigo, A.A.; Depp, J.L.; Taylor, J.J.; Kroll, K.L. Regulation of Smad signaling through a differential recruitment of coactivators and corepressors by ZEB proteins. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahashi, M.; Abe, M.; Sakimura, K.; Takabe, K.; Wakai, T. The role of sphingosine-1-phosphate in inflammation and cancer progression. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3671–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, X.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Anderson, E.; Taylor, M.; Zimmermann, E.M.; Spence, J.R.; Huang, S.; Greenson, J.K.; Shah, Y.M. Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 activates the inflammatory response in the intestinal epithelium to promote colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Triner, D.; Castillo, C.; Hakim, J.B.; Xue, X.; Greenson, J.K.; Nuñez, G.; Chen, G.Y.; Colacino, J.A.; Shah, Y.M. Myc-Associated Zinc Finger Protein Regulates the Proinflammatory Response in Colitis and Colon Cancer via STAT3 Signaling. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 38, e00386-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Liang, P.; Geng, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Cheng, S.H.; Ying, J.; Su, X.; Ng, K.M.; Ng, M.H.; et al. A novel 19q13 nucleolar zinc finger protein suppresses tumor cell growth through inhibiting ribosome biogenesis and inducing apoptosis but is frequently silenced in multiple carcinomas. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Jing, Y.M.; Lou, H.Z.; Lou, Q.A. Effect and mechanism of long non-coding RNA ZEB2-AS1 in the occurrence and development of colon cancer. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 8109–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Huang, L.; Nguyen, P.; Bisht, K.S.; Bar-Sela, G.; Ho, A.S.; Bradbury, C.M.; Yu, W.; Cui, H.; Lee, S.; et al. DNA methyltransferase 1 and 3B activate BAG-1 expression via recruitment of CTCFL/BORIS and modulation of promoter histone methylation. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2726–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, P.; Cui, H.; Bisht, K.S.; Sun, L.; Patel, K.; Lee, R.S.; Kugoh, H.; Oshimura, M.; Feinberg, A.P.; Gius, D. CTCFL/BORIS is a methylation-independent DNA-binding protein that preferentially binds to the paternal H19 differentially methylated region. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5546–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, L.; Lin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lian, J. ZNF750 facilitates carcinogenesis via promoting the expression of long non-coding RNA CYTOR and influences pharmacotherapy response in colon adenocarcinoma. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2022, 23, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.G.; Jones, H.; Eggert, U.S. Membrane and organelle dynamics during cell division. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.X.; Greene, L.A. Neuronal apoptosis at the G1/S cell cycle checkpoint. Cell Tissue Res. 2001, 305, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhou, M.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, B. Roquin1 inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cells by inducing G1/S cell cycle arrest via selectively destabilizing the mRNAs of cell cycle-promoting genes. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Li, Z.; Gao, C.Y.; Cho, C.H. Mechanisms of drug resistance in colon cancer and its therapeutic strategies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6876–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, B.; Ning, F.; Wang, H.S.; Cai, S.H.; Du, J. Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype and cancer stem cell-like properties in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells through AKT/β-catenin/Snail signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 723, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.T.; Guzman, M.L.; Noble, M. Cancer stem cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.; Sidransky, D. DNA methylation markers in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, W.J.; Guanzon, D.; Ma, C.; Liew, Y.J.; Duesing, K.R.; Fung, K.Y.C.; Ross, J.P. DNA Methylation Cancer Biomarkers: Translation to the Clinic. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, D.M.; Bundgaard Clemmensen, K.K.; Kallunki, T. Zinc Finger Transcription Factor MZF1-A Specific Regulator of Cancer Invasion. Cells 2020, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edelstein, L.C.; Collins, T. The SCAN domain family of zinc finger transcription factors. Gene 2005, 359, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Jin, Y.; Luo, X.; Xia, X.; Gong, J.; Hu, J. p55PIK transcriptionally activated by MZF1 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 868131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Wang, S. Kinase GSK3β functions as a suppressor in colorectal carcinoma through the FTO-mediated MZF1/c-Myc axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 2655–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horinaka, M.; Yoshida, T.; Tomosugi, M.; Yasuda, S.; Sowa, Y.; Sakai, T. Myeloid zinc finger 1 mediates sulindac sulfide-induced upregulation of death receptor 5 of human colon cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ZFPs | Aliases | Expression | Biological Functions | Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZNF143 | pHZ-1, SBF, STAF | ↓ | EMT, invasion and metastasis | ZEB1, CDH1 | [38] |
| ZNF146 | OZF | ↑ | - | - | [39] |
| ZNF398 | KIAA1339, P51, P71, p52-ZER6 | ↑ | Tumorigenesis, cell proliferation and cell cycle | p53 | [40] |
| KLF4 | EZF, GKLF | ↓ | Cell proliferation | Bmi1 | [41,42,43] |
| ZFP91 | PZF, ZNF757, HPF7, HTF10 | ↑ | Tumorigenesis, cell proliferation and inflammation | NF-κB/p65, HIF-1α, IL-1β | [44,45,46,47,48] |
| MAZ | Pur-1, ZF87, Zif87, ZNF801 | ↑ | Inflammation | HIF-2a, Tnfa, Cxcl1, STAT3 | [49] |
| ZNF185 | SCELL | ↑ | Cell proliferation and liver metastasis | - | [36,37] |
| PATZ1 | dJ400N23, MAZR, PATZ, RIAZ, ZSG ZBTB19, ZNF278, | ↑ | Potential proto-oncogene, cell proliferation and cell cycle | MAPK/ERK pathway | [50] |
| Twist | - | ↑ | Cancer stem cell and EMT, invasion and metastasis | Fibronectin, Vimentin, Snail, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, | [51,52] |
| Slug | - | ↑ | Cell cycle | Mdm2, P53, P21 | [53] |
| ZEB1 | AREB6, Zfhep, BZP, FECD6, NIL-2-A, ZEB, TCF8, Zfhx1a, PPCD3 | ↑ | liver metastasis, DNA methylation, EMT, invasion and metastasis | CTBP, BRG1, uPA, PAI-1 E-cadherin, HDAC1, DNMT1 | [30,32,36,38,54,55,56] |
| Snail | SNAI1 | ↑ | - | E-cadherin, G9a, LSD1, HDACs, SUV39H1 inhibitor, PRC2 | [57,58,59,60] |
| ZEB2 | KIAA0569, SIP-1, SIP1, ZFHX1B | ↑ | EMT, invasion and metastasis | CTBP, E-cadherin | [54,60] |
| ZEB2-AS1 | ↑ | Cell proliferation, apoptosis, EMT, invasion and metastasis | β-Catenin | [61] | |
| CIZ1 | LSFR1, ZNF356 | ↑ | EMT, invasion and metastasis | - | [21] |
| ZFX | ZNF92 | ↑ | Cell proliferation, cancer stem cell, EMT, invasion and metastasis | MAPK/ERK, PI3K/Akt, STAT3 pathway | [8,62,63] |
| RPS27 | MPS-1, MPS1, S27 | ↑ | EMT, invasion and metastasis | JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway | [33] |
| ZNF511 | MGC30006, ZFP511 | ↑ | - | - | [39] |
| ZNF217 | ZABC1 | ↑ | Oncogene, liver metastasis, EMT, invasion and metastasis | E-cadherin | [22] |
| ZNF70 | Cos17, MGC48959 | ↑ | Inflammation | NLRP3, IL-1β, inflammasome, STAT3 | [64] |
| ZFP36 | G0S24, NUP475, RNF162A, TIS11, TTP | ↓ | Cell proliferation, EMT, invasion and metastasis | IL-23, VDR, COX-2, VEGF, SOX9, MACC1, N-cadherin, ZEB1, Vimentin, E-cadherin, ZO-1 | [30,31] |
| KLF12 | AP-2rep, AP2REP, HSPC122 | ↑ | Tumorigenesis and cell proliferation | - | [16] |
| KLF6-SV2 | ZFP9 | ↓ | Cell proliferation and cell cycle | Bax, p21 | [18] |
| MZF1 | MZF1A, MZF1B, ZFP98, ZSCAN6, ZNF42, | ↑ | Cell proliferation, apoptosis, EMT, invasion and metastasis | Axl, p55PIK, DR5, FADD Caspases | [17] |
| ZKSCAN3 | ZF47, ZFP47, ZNF306, ZNF309, ZSCAN35 | ↑ | EMT, invasion and metastasis | Integrin β4 and VEGF | [19] |
| ZNF692 | AREBP, FLJ20531 | ↑ | Cell proliferation, EMT, invasion and metastasis | CDK2, cyclin D1, Mmp-9, p27Kip1 | [20] |
| ZNF750 | FLJ13841 | ↑ | Cell proliferation, cell apoptosis, EMT, invasion and metastasis | CYTOR | [65] |
| ZNF545 | ZFP82, KIAA1948, MGC45380 | ↓ | Apoptosis | KAP1 | [66] |
| ZNF281 | ZBP-99 | ↑ | EMT, invasion and metastasis | IL-8, IL-1β, IL-17, IL-23,SNAIL, α-SMA Slug, TIMP-1, Vimentin, fibronectin, α-SMA | [4] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Sima, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, H. Zinc Finger Proteins: Functions and Mechanisms in Colon Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215242
Liu S, Sima X, Liu X, Chen H. Zinc Finger Proteins: Functions and Mechanisms in Colon Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215242
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shujie, Xiaonan Sima, Xingzhu Liu, and Hongping Chen. 2022. "Zinc Finger Proteins: Functions and Mechanisms in Colon Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215242
APA StyleLiu, S., Sima, X., Liu, X., & Chen, H. (2022). Zinc Finger Proteins: Functions and Mechanisms in Colon Cancer. Cancers, 14(21), 5242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215242







