Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Contemporary Management and Patient Outcomes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Background
2. Preoperative Evaluation
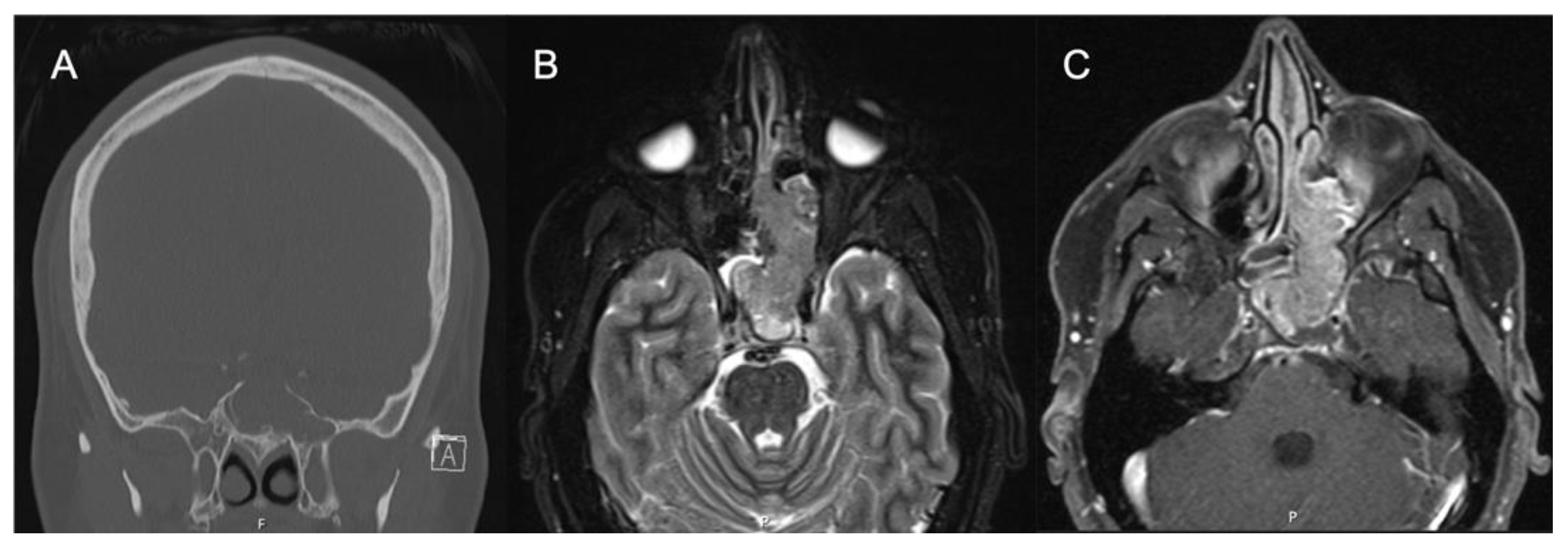
3. Imaging
4. Surgical Planning
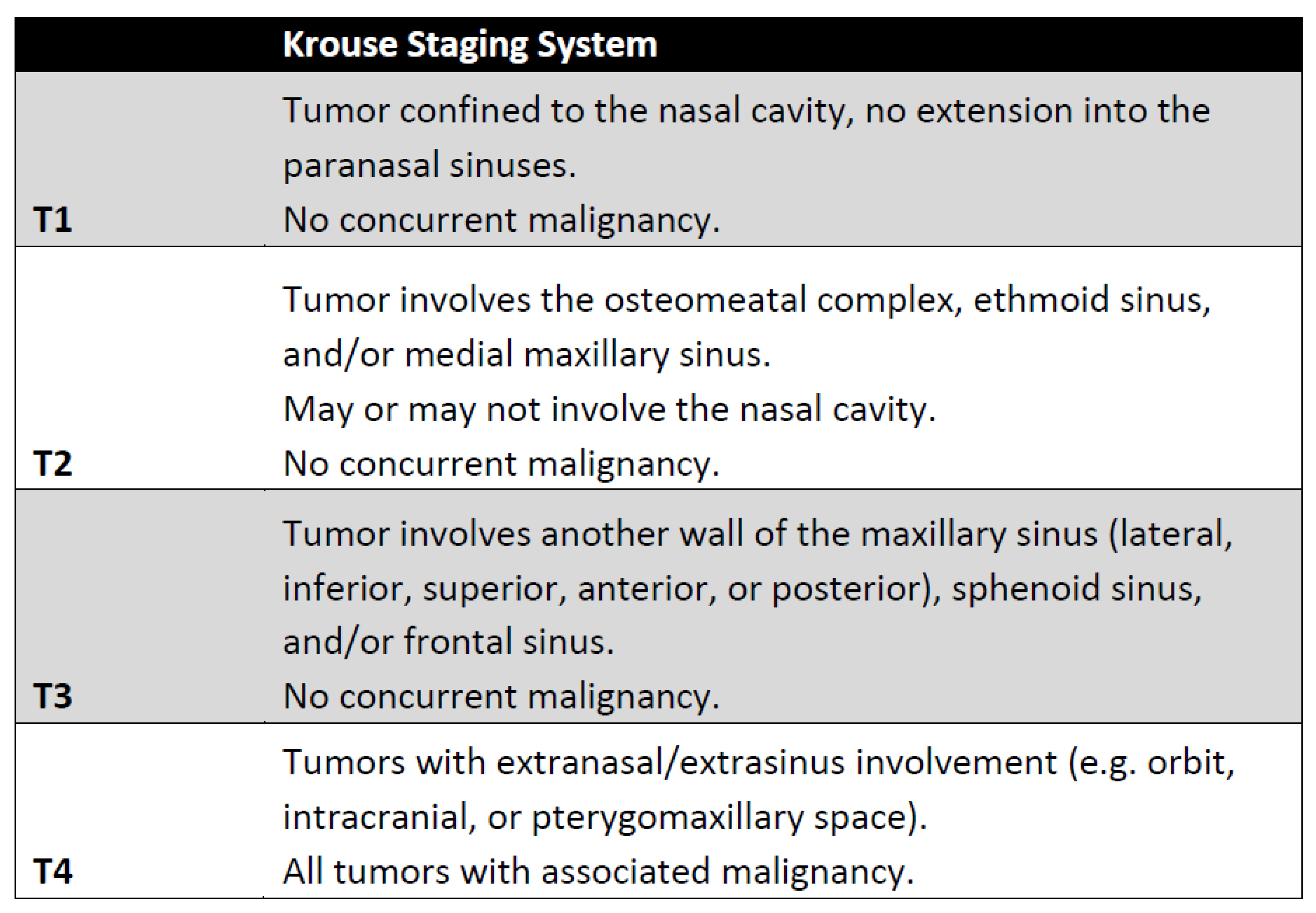
5. Staging
6. Pathology and Molecular Changes Associated with Malignant Degeneration
7. Surgical Management and Outcomes
7.1. Endoscopic versus Open Surgery for IP
7.2. Attachment-Oriented Surgery
7.3. Surgical Techniques and Outcomes
7.4. Management of IP-Associated Carcinoma In Situ
7.5. Management of IP-Degenerated Squamous Cell Carcinoma
7.6. Post-Surgical Surveillance
8. Adjuvant Therapy
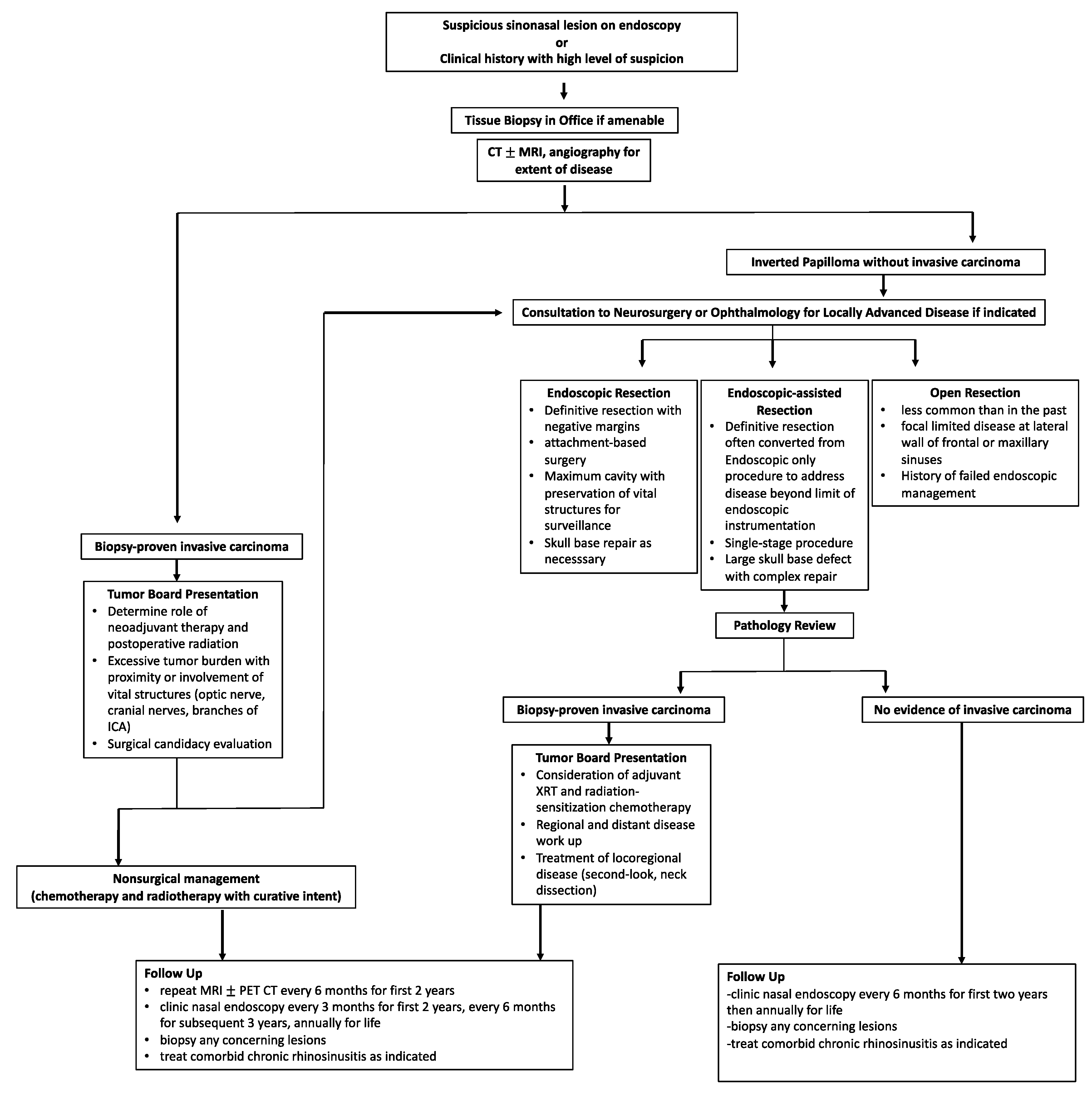
9. Treatment Algorithm
10. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lisan, Q.; Laccourreye, O.; Bonfils, P. Sinonasal inverted papilloma: From diagnosis to treatment. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2016, 133, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L. World Health Organization classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. Ear Nose Throat J. 2006, 85, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papagiannopoulos, P.; Tong, C.L.; Kuan, E.C.; Tajudeen, B.A.; Yver, C.M.; Kohanski, M.A.; Cohen, N.A.; Kennedy, D.W.; Palmer, J.N.; Adappa, N.D. Inverted papilloma is associated with greater radiographic inflammatory disease than other sinonasal malignancy. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlandi, R.R.; Rubin, A.; Terrell, J.E.; Anzai, Y.; Bugdaj, M.; Lanza, D.C. Sinus inflammation associated with contralateral inverted papilloma. Am. J. Rhinol. 2002, 16, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lawson, W.; Schlecht, N.F.; Brandwein-Gensler, M. The role of the human papillomavirus in the pathogenesis of Schneiderian inverted papillomas: An analytic overview of the evidence. Head Neck Pathol. 2008, 2, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, W.H.; Farzal, Z.; Kimple, A.J.; Ebert, C.S., Jr.; Senior, B.A.; Zanation, A.M.; Thorp, B.D. HPV in the malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papillomas: A meta-analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.P.; Suh, J.D.; Lee, J.T.; Wells, C.; Wang, M.B. Role of High-Risk HPV Detected by PCR in Malignant Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma: A Meta-Analysis. Laryngoscope 2021, 132, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udager, A.M.; Rolland, D.C.M.; McHugh, J.B.; Betz, B.L.; Murga-Zamalloa, C.; Carey, T.E.; Marentette, L.J.; Hermsen, M.A.; DuRoss, K.E.; Lim, M.S.; et al. High-Frequency Targetable EGFR Mutations in Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinomas Arising from Inverted Sinonasal Papilloma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2600–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, E.; Nishikawa, D.; Hanai, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Yatabe, Y. Sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma and EGFR mutations: A molecular footprint of a benign lesion. Histopathology 2018, 73, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnane, N.; Ottini, G.; Turri-Zanoni, M.; Furlan, D.; Battaglia, P.; Karligkiotis, A.; Albeni, C.; Cerutti, R.; Mura, E.; Chiaravalli, A.M.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of HPV infection, EGFR exon 20 mutations and LINE1 hypomethylation as risk factors for malignant transformation of sinonasal-inverted papilloma to squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhai, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Hu, L.; Wang, D. Low prevalence of human papillomavirus infection in sinonasal inverted papilloma and oncocytic papilloma. Virchows Arch. 2020, 476, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udager, A.M.; McHugh, J.B.; Goudsmit, C.M.; Weigelin, H.C.; Lim, M.S.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S.J.; Betz, B.L.; Carey, T.E.; Brown, N.A. Human papillomavirus (HPV) and somatic EGFR mutations are essential, mutually exclusive oncogenic mechanisms for inverted sinonasal papillomas and associated sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, S.; Bradley, P.J.; Acharya, A.; Stacey, M.; Jones, N.S. Sinonasal inverted papillomas: Recurrence, and synchronous and metachronous malignancy. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2007, 121, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lesperance, M.M.; Esclamado, R.M. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope 1995, 105, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karligkiotis, A.; Lepera, D.; Volpi, L.; Turri-Zanoni, M.; Battaglia, P.; Lombardi, D.; Accorona, R.; Bignami, M.; Nicolai, P.; Castelnuovo, P. Survival outcomes after endoscopic resection for sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma arising on inverted papilloma. Head Neck 2016, 38, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anari, S.; Carrie, S. Sinonasal inverted papilloma: Narrative review. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2010, 124, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, T.; Atai, E.; Schubert, M.; Glanz, H. Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: Clinical data, surgical strategy and recurrence rates. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2000, 120, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minovi, A.; Kollert, M.; Draf, W.; Bockmühl, U. Inverted papilloma: Feasibility of endonasal surgery and long-term results of 87 cases. Rhinology 2006, 44, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Momeni, A.K.; Roberts, C.C.; Chew, F.S. Imaging of chronic and exotic sinonasal disease: Review. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, S35–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yousuf, K.; Wright, E.D. Site of attachment of inverted papilloma predicted by CT findings of osteitis. Am. J. Rhinol. 2007, 21, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Chung, S.K.; Dhong, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Bok, K.H. Focal hyperostosis on CT of sinonasal inverted papilloma as a predictor of tumor origin. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 618–621. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla, R.K.; Wright, E.D. Predicting the site of attachment of sinonasal inverted papilloma. Rhinology 2009, 47, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savy, L.; Lloyd, G.; Lund, V.J.; Howard, D. Optimum imaging for inverted papilloma. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2000, 114, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, T.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, S.K.; Dhong, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Yim, Y.J.; Kim, S.T.; Jeon, P.; Kim, K.H. Sinonasal inverted papilloma: Value of convoluted cerebriform pattern on MR imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 1556–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, C.H.; Tong, C.C.L.; Penta, M.; Patel, V.S.; Palmer, J.N.; Adappa, N.D.; Nayak, J.V.; Hwang, P.H.; Patel, Z.M. Imaging predictors for malignant transformation of inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, K.; Furuta, Y.; Oridate, N.; Nagahashi, T.; Homma, A.; Ryu, T.; Fukuda, S. Preoperative staging of sinonasal inverted papilloma by magnetic resonance imaging. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 1983–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasbekar, A.V.; Swords, C.; Attlmayr, B.; Kulkarni, T.; Swift, A.C. Sinonasal papilloma: What influences the decision to request a magnetic resonance imaging scan? J. Laryngol. Otol. 2018, 132, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, G.; Yu, W.; Yang, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Prediction of malignant sinonasal inverted papilloma transformation by preoperative computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Rhinology 2020, 58, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krouse, J.H. Development of a staging system for inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope 2000, 110, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kwon, S.H. Recurrence of sinonasal inverted papilloma following surgical approach: A meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisan, Q.; Moya-Plana, A.; Bonfils, P. Association of Krouse Classification for Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma With Recurrence: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Tsunemi, Y.; Kashiwagi, T.; Kuboki, A.; Yamakawa, S.; Konno, W.; Mori, A.; Iimura, J.; Tsukidate, T.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Comparison of Current Staging Systems for Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2021, 35, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, W.; Webb, D.; Al-Salihi, S.; Dadgostar, A.; Javer, A. Sinonasal inverted papilloma recurrence rates and evaluation of current staging systems. Rhinology 2018, 56, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre International de Recherche sur le Cancer. Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Re, M.; Gioacchini, F.M.; Bajraktari, A.; Tomasetti, M.; Kaleci, S.; Rubini, C.; Bertini, A.; Magliulo, G.; Pasquini, E. Malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma and related genetic alterations: A systematic review. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2017, 274, 2991–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Guo, W.; Wei, P.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L. Putative biomarkers of malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma into squamous cell carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffman, Y.; Bublik, D.R.; Pilpel, Y.; Oren, M. miR-661 downregulates both Mdm2 and Mdm4 to activate p53. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.W.; Jeong, H.J.; Choi, M.; Karbowski, M.; Choi, C. Optic atrophy 3 as a protein of the mitochondrial outer membrane induces mitochondrial fragmentation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, D.; Thomas, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Fernández-del, C.C.; Bauer, T.W.; Williams, M.; Warshaw, A.L.; Thayer, S.P.; Kelly, K.A. Plectin-1 as a novel biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puiffe, M.L.; Le Page, C.; Filali-Mouhim, A.; Zietarska, M.; Ouellet, V.; Tonin, P.N.; Chevrette, M.; Provencher, D.M.; Mes-Masson, A.M. Characterization of ovarian cancer ascites on cell invasion, proliferation, spheroid formation, and gene expression in an in vitro model of epithelial ovarian cancer. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakizaki, T.; Hatakeyama, H.; Nakamaru, Y.; Takagi, D.; Mizumachi, T.; Sakashita, T.; Kano, S.; Homma, A.; Fukuda, S. Role of microRNA-296-3p in the malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stambolic, V.; MacPherson, D.; Sas, D.; Lin, Y.; Snow, B.; Jang, Y.; Benchimol, S.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of PTEN transcription by p53. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, A.A.; D’Almeida Costa, F.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Guimarães, A.P.; Chinen, L.T.; Lopes, C.A.; de Lima, V.C. Low PTEN expression is associated with worse overall survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with chemotherapy and cetuximab. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 20, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasukawa, S.; Kano, S.; Hatakeyama, H.; Nakamaru, Y.; Takagi, D.; Mizumachi, T.; Suzuki, M.; Suzuki, T.; Nakazono, A.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Genetic mutation analysis of the malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma by targeted amplicon sequencing. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 23, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maisch, S.; Mueller, S.K.; Traxdorf, M.; Weyerer, V.; Stoehr, R.; Iro, H.; Hartmann, A.; Agaimy, A. Sinonasal papillomas: A single centre experience on 137 cases with emphasis on malignant transformation and EGFR/KRAS status in “carcinoma ex papilloma”. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 46, 151504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchi, R.; Jiromaru, R.; Yasumatsu, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Hongo, T.; Manako, T.; Sato, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Wakasaki, T.; Matsuo, M.; et al. Genomic Sequencing of Cancer-related Genes in Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Coexisting Inverted Papilloma. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Sun, X. Overexpression of FoxM1 in Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma and Associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2019, 33, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabal, V.N.; Menendez, M.; Vivanco, B.; Potes-Ares, S.; Riobello, C.; Suarez-Fernandez, L.; Garcia-Marin, R.; Blanco-Lorenzo, V.; Lopez, F.; Alvarez-Marcos, C.; et al. EGFR mutation and HPV infection in sinonasal inverted papilloma and squamous cell carcinoma. Rhinology 2020, 58, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outzen, K.E.; Grøntveld, A.; Jørgensen, K.; Clausen, P.P.; Ladefoged, C. Inverted papilloma: Incidence and late results of surgical treatment. Rhinology 1996, 34, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Mortuaire, G.; Arzul, E.; Darras, J.A.; Chevalier, D. Surgical management of sinonasal inverted papillomas through endoscopic approach. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2007, 264, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets, J.M.; Hwang, P.H. Endoscopic resection of sinonasal inverted papilloma: A meta-analysis. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2006, 134, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.; Thamboo, A.; Choby, G.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, B.; Hwang, P.H. Outcomes of sinonasal inverted papilloma resection by surgical approach: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudakos, J.K.; Blioskas, S.; Nikolaou, A.; Vlachtsis, K.; Karkos, P.; Markou, K.D. Endoscopic Resection of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2018, 32, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodworth, B.A.; Bhargave, G.A.; Palmer, J.N.; Chiu, A.G.; Cohen, N.A.; Lanza, D.C.; Bolger, W.E.; Kennedy, D.W. Clinical outcomes of endoscopic and endoscopic-assisted resection of inverted papillomas: A 15-year experience. Am. J. Rhinol. 2007, 21, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.J.; Huang, S.F.; Huang, C.C. Tailored endoscopic surgery for the treatment of sinonasal inverted papilloma. Head Neck 2004, 26, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglani, A.; Hoxworth, J.M.; Zarka, M.A.; Lal, D. Use of intraoperative negative margins reduces inverted papilloma recurrence. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2018, 32, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.A.; Palmer, J.N.; Chiu, A.G.; O’Malley, B.W., Jr.; Woodworth, B.A.; Kennedy, D.W. Endoscopic closure of CSF rhinorrhea: 193 cases over 21 years. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2009, 140, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.C.L.; Patel, N.N.; Maina, I.W.; Triantafillou, V.; Yan, C.H.; Kuan, E.C.; Kohanski, M.A.; Papagiannopoulos, P.; Workman, A.D.; Cohen, N.A.; et al. Inverted papilloma with multifocal attachment is associated with increased recurrence. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrabec, D.P. The inverted Schneiderian papilloma: A clinical and pathological study. Laryngoscope 1975, 85, 186–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Yoo, F.; Wang, M.; Vengerovich, G.; Suh, J.D. Modified endoscopic Denker approach in management of inverted papilloma of the anterior maxillary sinus. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, I.W.; Tong, C.C.L.; Baranov, E.; Patel, N.N.; Triantafillou, V.; Kuan, E.C.; Kohanski, M.A.; Papagiannopoulos, P.; Yan, C.H.; Workman, A.D.; et al. Clinical Implications of Carcinoma In Situ in Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, D.Y., Jr.; Chhabra, N.; Metson, R.; Holbrook, E.H.; Gray, S.T. Surgical risk factors for recurrence of inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Lu, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Hu, L.; Wang, D. Squamous cell carcinoma associated with inverted papilloma: Recurrence and prognostic factors. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.H.; Newman, J.G.; Kennedy, D.W.; Palmer, J.N.; Adappa, N.D. Clinical outcomes of sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas based on tumor etiology. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017, 7, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Hong, S.L.; Lee, C.H.; Jin, H.R.; Kang, J.M.; Lee, B.J.; Moon, I.J.; Chung, S.K.; Rha, K.S.; Cho, S.H.; et al. Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: A Korean multicenter study. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.X.; Liu, G. Malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma: A retrospective analysis of 32 cases. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 2637–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuan, E.C.; Frederick, J.W.; Palma Diaz, M.F.; Lim, D.W.; Suh, J.D. Complete response of skull base inverted papilloma to chemotherapy: Case report. Allergy Rhinol. (Provid. R.I.) 2017, 8, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adriaensen, G.F.; Lim, K.H.; Georgalas, C.; Reinartz, S.M.; Fokkens, W.J. Challenges in the Management of Inverted Papilloma: A Review of 72 Revision Cases. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Molecular Change |
|---|
| Hypermethylated Genes |
| OPA3 |
| MIR661 |
| PLEC |
| MicroRNA |
| miR-296-3p |
| Transcription Factor |
| FoxM1 |
| Gene Mutations |
| KRAS |
| APC |
| STK11 |
| EGFR |
| KMT2D |
| CDKN2A |
| TP53 |
| PDE4DIP |
| NF1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eide, J.G.; Welch, K.C.; Adappa, N.D.; Palmer, J.N.; Tong, C.C.L. Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Contemporary Management and Patient Outcomes. Cancers 2022, 14, 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092195
Eide JG, Welch KC, Adappa ND, Palmer JN, Tong CCL. Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Contemporary Management and Patient Outcomes. Cancers. 2022; 14(9):2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092195
Chicago/Turabian StyleEide, Jacob G., Kevin C. Welch, Nithin D. Adappa, James N. Palmer, and Charles C. L. Tong. 2022. "Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Contemporary Management and Patient Outcomes" Cancers 14, no. 9: 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092195
APA StyleEide, J. G., Welch, K. C., Adappa, N. D., Palmer, J. N., & Tong, C. C. L. (2022). Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Contemporary Management and Patient Outcomes. Cancers, 14(9), 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092195






