Identification of miRNAs Present in Cell- and Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles—Possible Biomarkers of Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and EVs Isolation
2.2. Patients and EVs Isolation
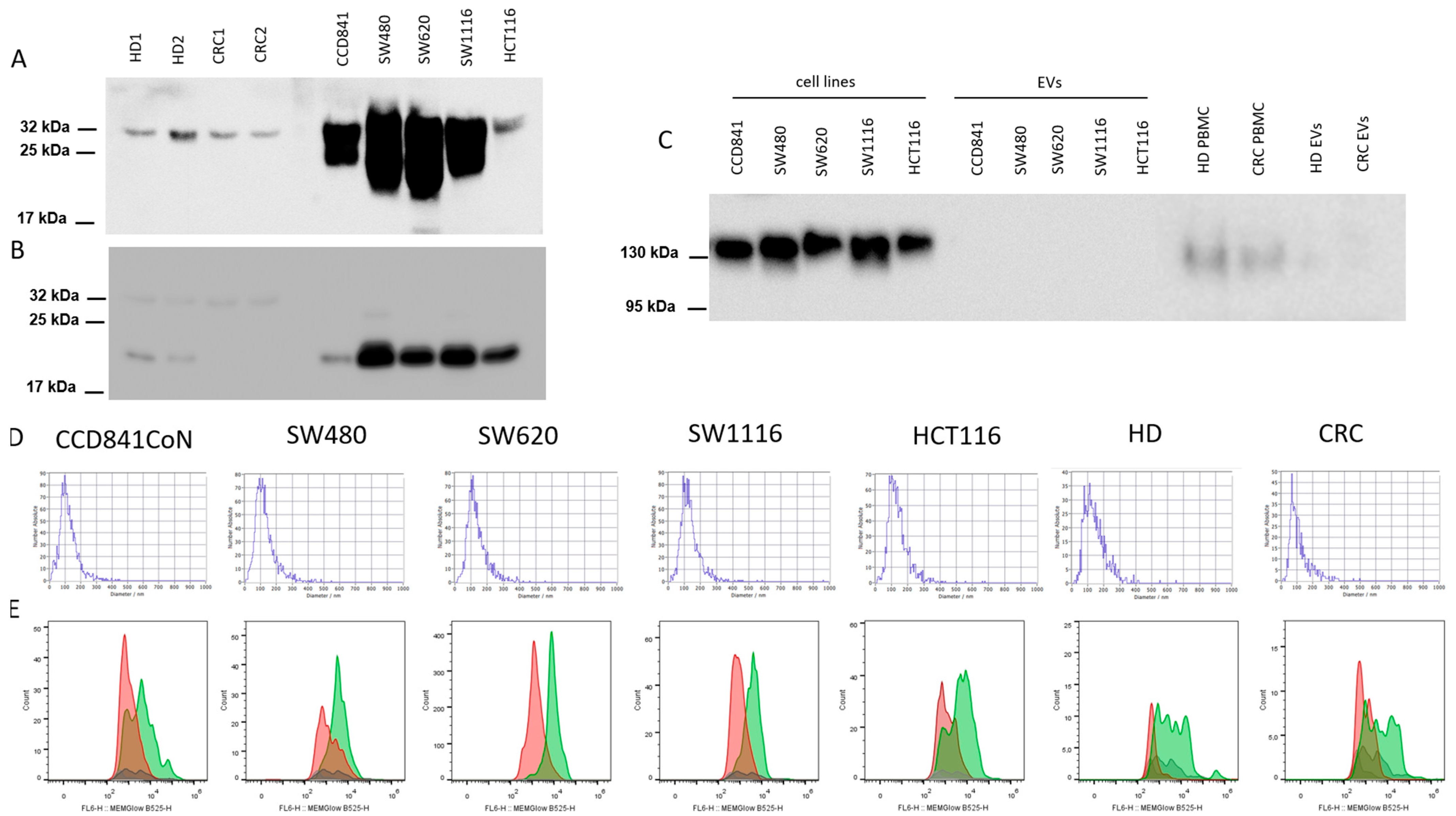
2.3. Characterization of EVs
2.4. Western Blotting (WB)
2.5. Total RNA Isolation
2.6. MicroRNA Next-Generation-Sequencing
2.7. qRT-PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of EVs
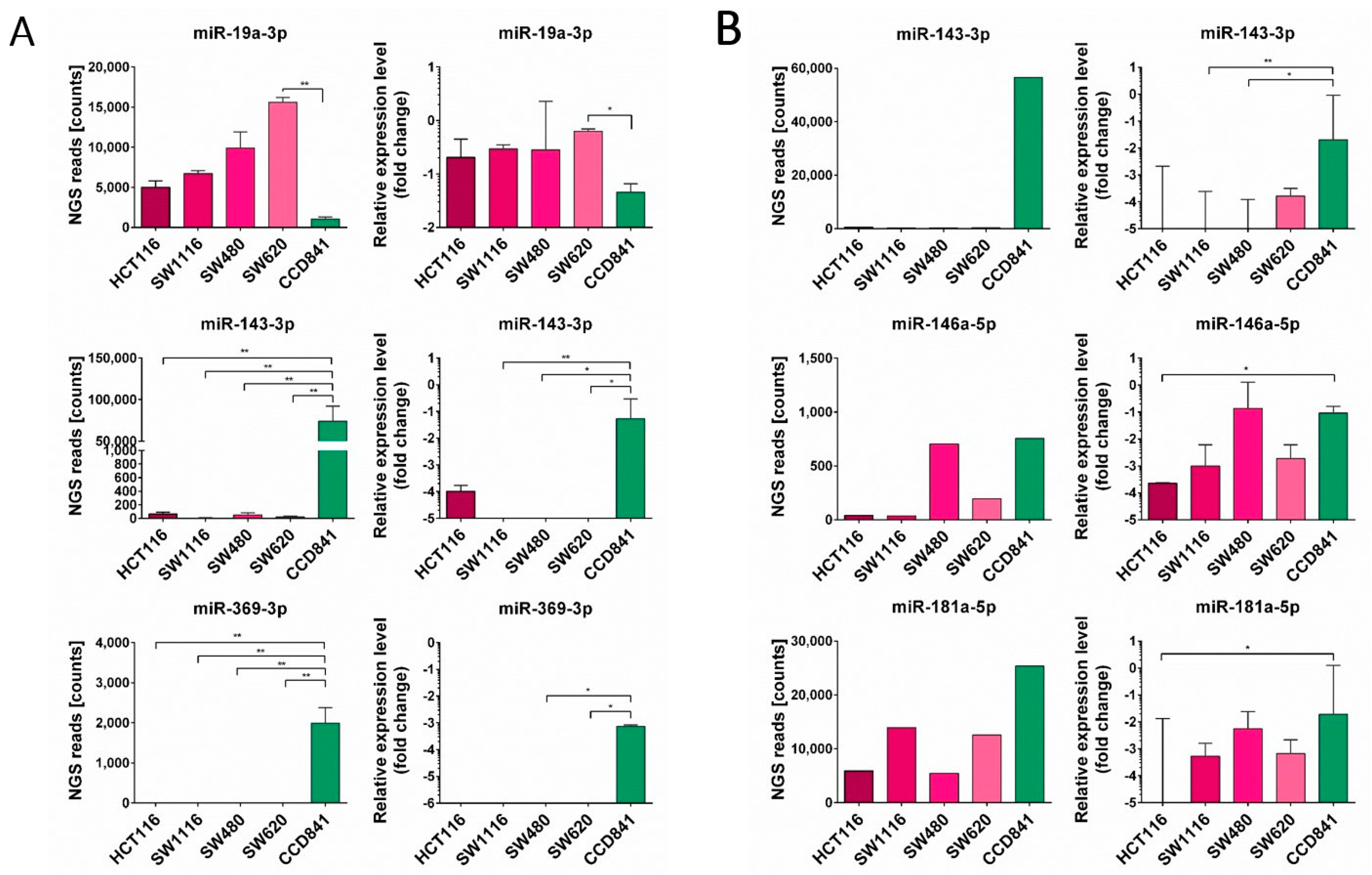
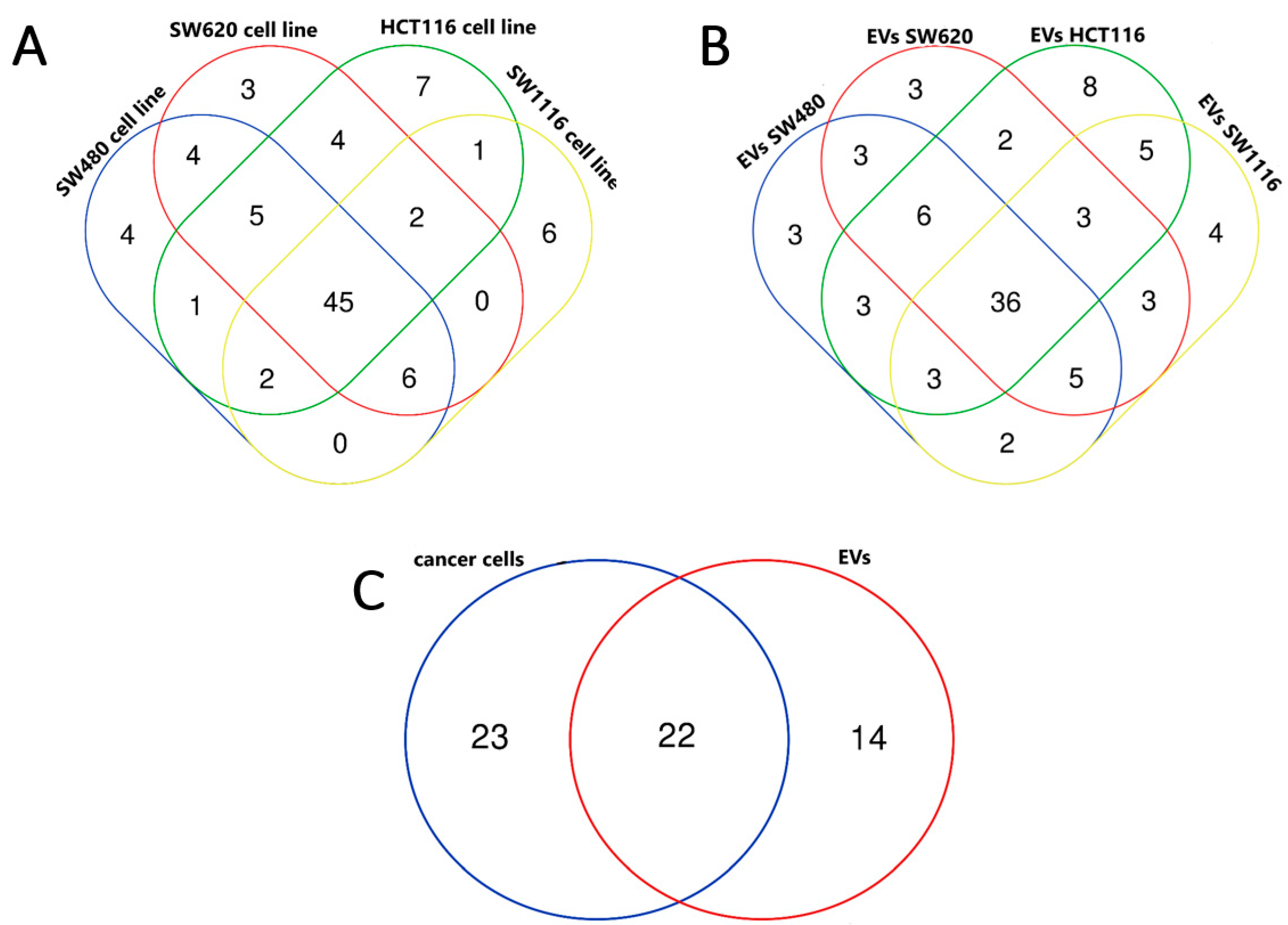
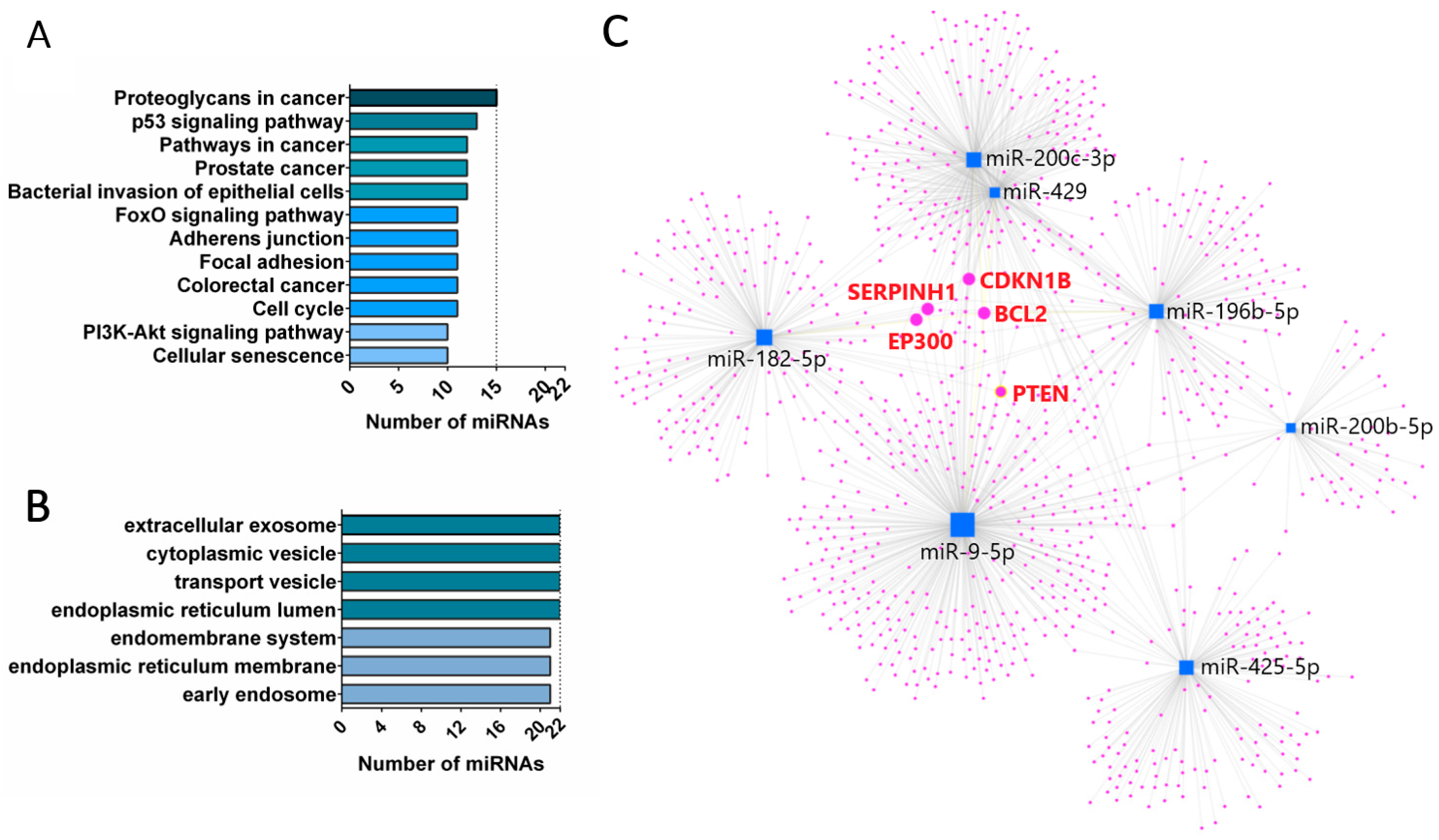
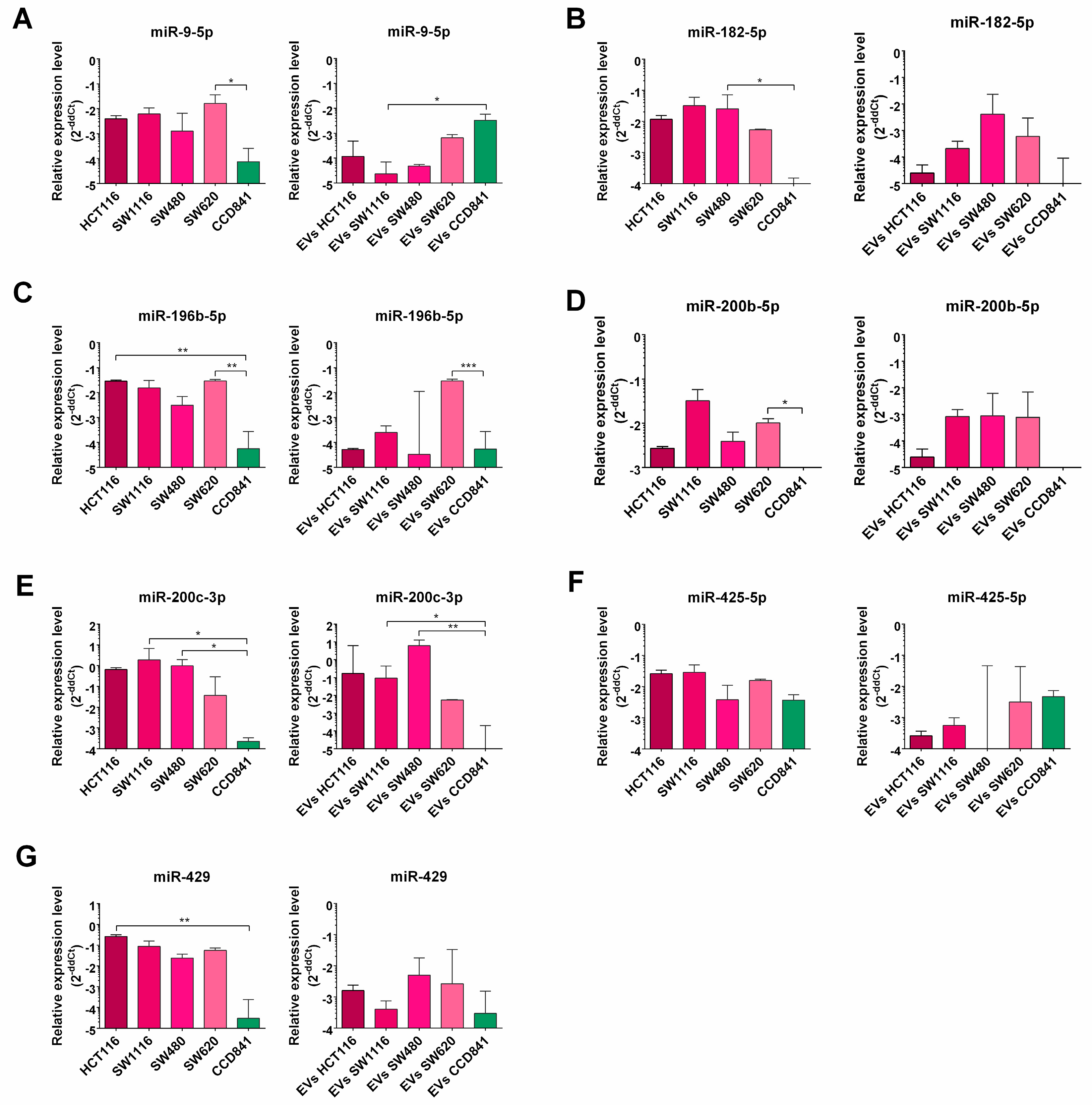
3.2. miRNA Enrichment in Tumor Cell Lines and EVs Derived from Them
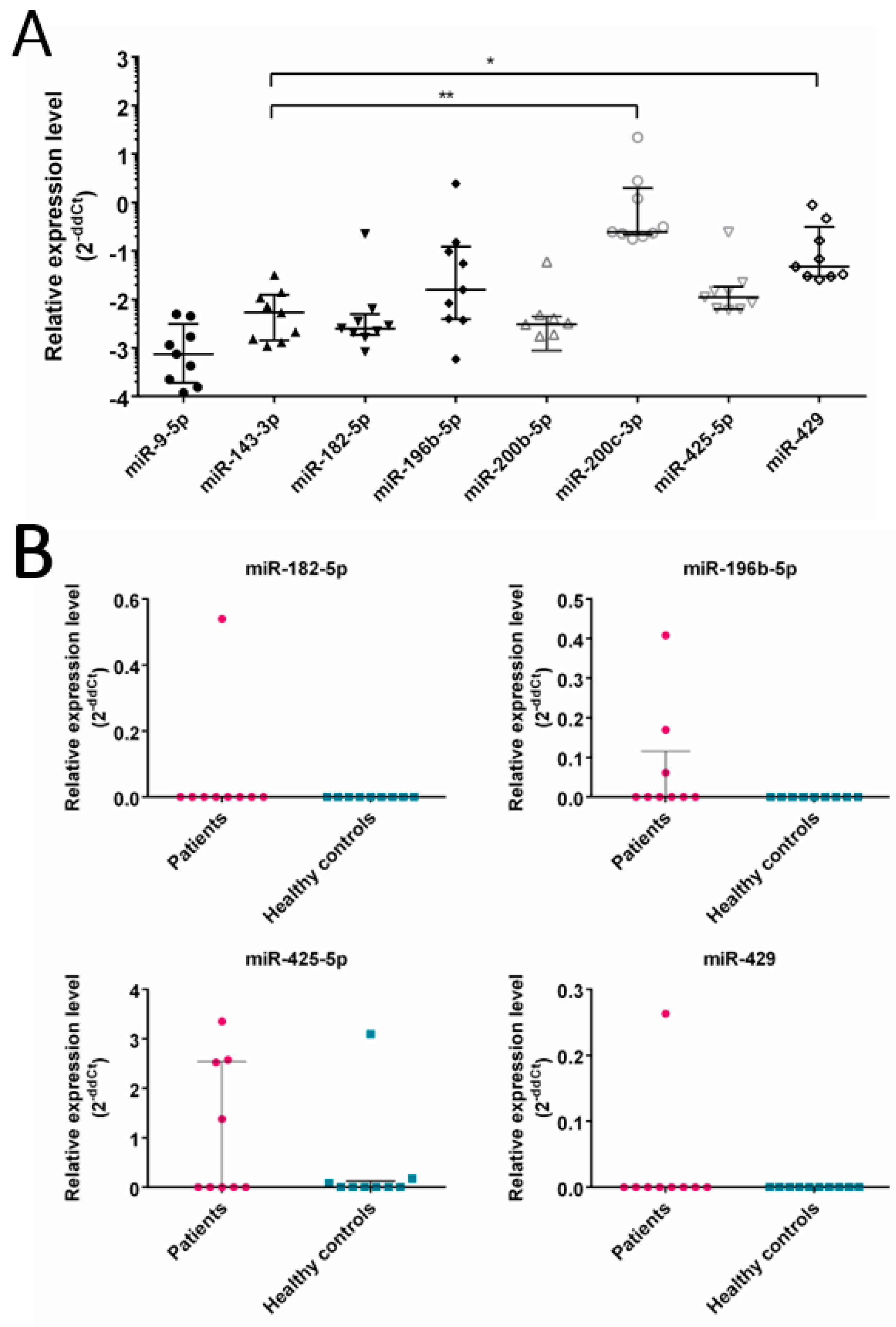
3.3. Expression of Selected miRNA in CRC Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (i)
- similarities in miRNA expression profile between CRC cell lines (SW480, SW620, SW1116 and HCT116), tumor EVs and patients’ tumor.
- (ii)
- a set of miRs are differentially expressed in CRC cell lines when compared with normal epithelial cell line (CCD841CoN).
- (iii)
- CRC-related miRNAs are efficiently loaded into EVs derived from tested cell lines.
- (iv)
- Several CRC related miRNAs are detected in EVs isolated from CRC patients’ plasma.
- (v)
- Our results extend the previously described profile of CRC-related miRNAs and may become a step toward identifying CRC biomarkers.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Wagle, N.S.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Xu, P. Global Colorectal Cancer Burden in 2020 and Projections to 2040. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Xin, L.; Ma, Y.F.; Hu, L.H.; Li, Z.S. Colonoscopy Reduces Colorectal Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Patients With Non-Malignant Findings: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Hurley, J.; Roberts, D.; Chakrabortty, S.K.; Enderle, D.; Noerholm, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J.K. Exosome-Based Liquid Biopsies in Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papareddy, P.; Tapken, I.; Kroh, K.; Varma Bhongir, R.K.; Rahman, M.; Baumgarten, M.; Cim, E.I.; Györffy, L.; Smeds, E.; Neumann, A.; et al. The Role of Extracellular Vesicle Fusion with Target Cells in Triggering Systemic Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francavilla, A.; Turoczi, S.; Tarallo, S.; Vodicka, P.; Pardini, B.; Naccarati, A. Exosomal MicroRNAs and Other Non-Coding RNAs as Colorectal Cancer Biomarkers: A Review. Mutagenesis 2020, 35, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmin, F.; Ladoire, S.; Mignot, G.; Vincent, J.; Bruchard, M.; Remy-Martin, J.-P.; Boireau, W.; Rouleau, A.; Simon, B.; Lanneau, D.; et al. Membrane-Associated Hsp72 from Tumor-Derived Exosomes Mediates STAT3-Dependent Immunosuppressive Function of Mouse and Human Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baj-Krzyworzeka, M.; Szatanek, R.; Węglarczyk, K.; Baran, J.; Urbanowicz, B.; Brański, P.; Ratajczak, M.Z.; Zembala, M. Tumour-Derived Microvesicles Carry Several Surface Determinants and MRNA of Tumour Cells and Transfer Some of These Determinants to Monocytes. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2006, 55, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, S.; Moeinafshar, A.; Rezaei, N. The Multifaceted Role of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) in Colorectal Cancer: Metastasis, Immune Suppression, Therapy Resistance, and Autophagy Crosstalk. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Poliakov, A.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Z.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Shah, S.V.; Wang, G.-J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Induction of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells by Tumor Exosomes. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2621–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, A.; Rani, S. MiRNA Biogenesis and Regulation of Diseases: An Updated Overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2595, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Di, K.; Fan, B.; Wu, J.; Gu, X.; Sun, Y.; Khan, A.; Li, P.; Li, Z. MicroRNAs in Extracellular Vesicles: Sorting Mechanisms, Diagnostic Value, Isolation, and Detection Technology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 948959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, M.; Iinuma, H.; Yagi, T.; Matsuda, K.; Hashiguchi, Y. Circulating Exosomal MicroRNA-21 as a Biomarker in Each Tumor Stage of Colorectal Cancer. Oncology 2017, 92, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.H.; Tian, D.; Yang, Z.C.; Li, J.L. Exosomal MiR-21 Promotes Proliferation, Invasion and Therapy Resistance of Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells through Its Target PDCD4. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ba, Y.; Ma, L.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Characterization of MicroRNAs in Serum: A Novel Class of Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Cancer and Other Diseases. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, D.; Ni, S.; Peng, Z.; Sheng, W.; Du, X. Plasma MicroRNAs Are Promising Novel Biomarkers for Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata-Kawata, H.; Izumiya, M.; Kurioka, D.; Honma, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Furuta, K.; Gunji, T.; Ohta, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sonoda, H.; et al. Circulating Exosomal MicroRNAs as Biomarkers of Colon Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yan, F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, F.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X. Circulating Exosomal MiR-125a-3p as a Novel Biomarker for Early-Stage Colon Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Huang, X.; Woodcock, M.; Du, M.; Dittmar, R.; Wang, Y.; Tsai, S.; Kohli, M.; Boardman, L.; Patel, T.; et al. Plasma Extracellular RNA Profiles in Healthy and Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xu, R.; Rai, A.; Suwakulsiri, W.; Izumikawa, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Greening, D.W.; Takahashi, N.; Simpson, R.J. Distinct Shed Microvesicle and Exosome MicroRNA Signatures Reveal Diagnostic Markers for Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamina, K.; Diendorfer, A.B.; Skalicky, S.; Weigl, M.; Pultar, M.; Krammer, T.L.; Fournier, C.A.; Schofield, A.L.; Otto, C.; Smith, A.T.; et al. A MicroRNA Next-Generation-Sequencing Discovery Assay (MiND) for Genome-Scale Analysis and Absolute Quantitation of Circulating MicroRNA Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews Simon Babraham Bioinformatics. FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize Analysis Results for Multiple Tools and Samples in a Single Report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and Memory-Efficient Alignment of Short DNA Sequences to the Human Genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedländer, M.R.; MacKowiak, S.D.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. MiRDeep2 Accurately Identifies Known and Hundreds of Novel MicroRNA Genes in Seven Animal Clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Barrell, D.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Cummins, C.; Gall, A.; Girón, C.G.; et al. Ensembl 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D754–D761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Grocock, R.J.; van Dongen, S.; Bateman, A.; Enright, A.J. MiRBase: MicroRNA Sequences, Targets and Gene Nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D140–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tastsoglou, S.; Skoufos, G.; Miliotis, M.; Karagkouni, D.; Koutsoukos, I.; Karavangeli, A.; Kardaras, F.S.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-MiRPath v4.0: Expanding Target-Based MiRNA Functional Analysis in Cell-Type and Tissue Contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W154–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Zhou, G.; Soufan, O.; Xia, J. MiRNet 2.0: Network-Based Visual Analytics for MiRNA Functional Analysis and Systems Biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W244–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corté, H.; Manceau, G.; Blons, H.; Laurent-Puig, P. MicroRNA and Colorectal Cancer. Dig. Liver Dis. 2012, 44, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Sevignani, C.; Dumitru, C.D.; Hyslop, T.; Noch, E.; Yendamuri, S.; Shimizu, M.; Rattan, S.; Bullrich, F.; Negrini, M.; et al. Human MicroRNA Genes Are Frequently Located at Fragile Sites and Genomic Regions Involved in Cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Joseph, T.C.; Chan, E.C.; Chao, Y.K.; Yeh, T.S.; Chen, J.S.; Cheng, A.J. MiR-196, an Emerging Cancer Biomarker for Digestive Tract Cancers. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellizar, A.; Refuerzo, V.; Ramos, J.D.; Albano, P.M. Expression of Specific MicroRNAs in Tissue and Plasma in Colorectal Cancer. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2022, 57, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourdavoud, P.; Pakzad, B.; Mosallaei, M.; Saadatian, Z.; Esmaeilzadeh, E.; Alimolaie, A.; Shaygannejad, A. MiR-196: Emerging of a New Potential Therapeutic Target and Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 9913–9920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lin, B.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, K.; et al. Exosomal MiR-196b-5p Is a Potential Diagnostic Marker for Colorectal Cancer with Metachronous Liver Metastasis. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambal, S.; Shah, M.; Mihelich, B.; Nonn, L. The MicroRNA-183 Cluster: The Family That Plays Together Stays Together. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 7173–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, L.; Wen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, W.; et al. Up-Regulation of MiR-182 Expression in Colorectal Cancer Tissues and Its Prognostic Value. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2013, 28, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, K.N.; Xiong, B. MiR-182-5p Inhibited Proliferation and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer by Targeting MTDH. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, T.; Hu, X.; Chen, X.X.; Zeng, K.; Sun, L.; Wang, S. Elevated Circulating MiR-182 Acts as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Early Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.J.; Carter, J.V.; Burton, J.F.; Oxford, B.G.; Schmidt, M.N.; Hallion, J.C.; Galandiuk, S. The Role of the MiR-200 Family in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 2501–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhou, B.; Zhan, L.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, X. The Quantitative Analysis by Stem-Loop Real-Time PCR Revealed the MicroRNA-34a, MicroRNA-155 and MicroRNA-200c Overexpression in Human Colorectal Cancer. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 3113–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toiyama, Y.; Hur, K.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Serum MiR-200c Is a Novel Prognostic and Metastasis-Predictive Biomarker in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2014, 259, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santasusagna, S.; Moreno, I.S.; Navarro, A.; Muñoz, C. Prognostic Impact of MiR-200 Family Members in Plasma and Exosomes from Tumor-Draining versus Peripheral Veins of Colon Cancer Patients. Oncology 2018, 95, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, L.; Capobianco, I.; Magrì, C.; Marafini, I.; Petito, V.; Scaldaferri, F. MicroRNAs as Innovative Biomarkers for Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Prediction of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, T.; Jaygal, G.; Woo, J.; Kim, C.J.; Baek, M.J.; Jeong, D. Downregulation of MiR-9 Correlates with Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Gao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Yue, L.; Cao, Y. PAK4, a Target of MiR-9-5p, Promotes Cell Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sun, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, H.; Kang, S.; Alkhanjaf, A.A.M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D. MiR-9 Maintains Cell Migration and Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Targeting Repressor Element-1 Silencing Transcription Factor (REST). Sci. Adv. Mater. 2022, 14, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandrés, E.; Cubedo, E.; Agirre, X.; Malumbres, R.; Zárate, R.; Ramirez, N.; Abajo, A.; Navarro, A.; Moreno, I.; Monzó, M.; et al. Identification by Real-Time PCR of 13 Mature MicroRNAs Differentially Expressed in Colorectal Cancer and Non-Tumoral Tissues. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y. MiR-425-5p Promoting Colorectal Carcinoma Progression by Regulating Its Target Gene PTEN to Change Activity of the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 14, 144–153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, X.; Shan, X.; Qi, L.W.; Wu, L.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. A Panel of MicroRNA Signature in Serum for Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, T.; Sugimachi, K.; Iinuma, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Kurashige, J.; Sawada, G.; Ueda, M.; Uchi, R.; Ueo, H.; Takano, Y.; et al. Exosomal MicroRNA in Serum Is a Novel Biomarker of Recurrence in Human Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Sharples, R.A.; Scicluna, B.J.; Hill, A.F. Exosomes Provide a Protective and Enriched Source of MiRNA for Biomarker Profiling Compared to Intracellular and Cell-Free Blood. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 23743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Lin, J.J.; Yang, X.F.; Gou, D.M.; Fu, L.W.; Li, F.R.; Yu, X.F. A Panel of Three Plasma MicroRNAs for Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 60, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsen, T.A.; Aae, T.F.; Brinchmann, J.E. Robust Profiling of MicroRNAs and IsomiRs in Human Plasma Exosomes across 46 Individuals. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparello, J.; Papi, C.; Allegretti, M.; Giordani, E.; Carboni, F.; Zazza, S.; Pescarmona, E.; Romania, P.; Giacomini, P.; Scapoli, C.; et al. A Distinctive MicroRNA (MiRNA) Signature in the Blood of Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Patients at Surgery. Cancers 2020, 12, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Granados-López, A.J.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, H. In Vitro Study of MiRNA-369-3p Targeting TCF4 Regulating the Malignant Biological Behavior of Colon Cancer Cells. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 14, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahadi, A. The Significance of MicroRNA Deregulation in Colorectal Cancer Development and the Clinical Uses as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Agent. Noncoding RNA Res. 2020, 5, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, M.; Winter, E.; Stotz, M.; Eberhard, K.; Samonigg, H.; Lax, S.; Hoefler, G. Down-Regulation of KRAS-Interacting MiRNA-143 Predicts Poor Prognosis but Not Response to EGFR-Targeted Agents in Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.K.; Zhao, M.; Yang, M.; Zhong, J.L.; Gu, Y.Y.; Peng, H.; Che, Y.Q.; Huang, C.Z. Identification of a Circulating MicroRNA Signature for Colorectal Cancer Detection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Upregulated | Downregulated |
|---|---|
| miR-7-5p, miR-7-1-3p, miR-9-5p, miR-10a-3p, miR-16-2-3p, miR-17-3p, miR-17-5p, miR-19a-3p, miR-19b-3p, miR-20a-5p, miR-21-3p, miR-25-5p, miR-27a-5p, miR-33b-5p, miR-93-5p, miR-95-3p, miR-96-5p, miR-101-3p, miR-135b-5p, miR-182-5p, miR-183-5p, miR-196a-5p, miR-196b-5p, miR-200a-3p, miR-200a-5p, miR-200b-3p, miR-200b-5p, miR-200c-3p, miR-203a-3p, miR-362-3p, miR-378a-3p, miR-378a-5p, miR-378c, miR-425-5p, miR-429, miR-500a-3p, miR-502-3p, miR-532-5p, miR-577, miR-584-5p, miR-660-5p, miR-1247-5p, miR-1304-3p, miR-12135, miR-12136 | miR-127-3p, miR-134-5p, miR-136-3p, miR-143-3p, miR-143-5p, miR-143-5p, miR-154-3p, miR-199a-3p, miR-199a-5p, miR-199b-3p, miR-214-3p, miR-323b-3p, miR-337-5p, miR-369-3p, miR-369-5p, miR-370-3p, miR-382-3p, miR-382-5p, miR-409-3p, miR-409-5p, miR-410-3p, miR-431-5p, miR-432-5p, miR-433-3p, miR-485-3p, miR-490-3p, miR-490-5p, miR-543, miR-665 |
| Patient | Gender | Age | Localization | Grade | Astler Coller Classification | TNM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 74 | sigmoid colon | G2 | B2 | pT3N0 |
| 2 | F | 36 | ascending colon | G1 | B2 | pT3N0 |
| 3 | M | 67 | rectum | G2 | C2 | pT3N1a |
| 4 | M | 77 | descending colon | G3 | C2 | PT3N1b |
| 5 | F | 54 | rectum | G1 | A | pT1N0 |
| 6 | F | 72 | rectum | G1 | A | pT1N0 |
| 7 | M | 75 | descending colon | G2 | C2 | pT3N1b |
| 8 | M | 69 | sigmoid colon | G1 | B2 | pT3N0 |
| 9 | M | 60 | rectum | G1 | A | pTis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lenart, M.; Siemińska, I.; Szatanek, R.; Mordel, A.; Szczepanik, A.; Rubinkiewicz, M.; Siedlar, M.; Baj-Krzyworzeka, M. Identification of miRNAs Present in Cell- and Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles—Possible Biomarkers of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16132464
Lenart M, Siemińska I, Szatanek R, Mordel A, Szczepanik A, Rubinkiewicz M, Siedlar M, Baj-Krzyworzeka M. Identification of miRNAs Present in Cell- and Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles—Possible Biomarkers of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(13):2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16132464
Chicago/Turabian StyleLenart, Marzena, Izabela Siemińska, Rafał Szatanek, Anna Mordel, Antoni Szczepanik, Mateusz Rubinkiewicz, Maciej Siedlar, and Monika Baj-Krzyworzeka. 2024. "Identification of miRNAs Present in Cell- and Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles—Possible Biomarkers of Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 13: 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16132464
APA StyleLenart, M., Siemińska, I., Szatanek, R., Mordel, A., Szczepanik, A., Rubinkiewicz, M., Siedlar, M., & Baj-Krzyworzeka, M. (2024). Identification of miRNAs Present in Cell- and Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles—Possible Biomarkers of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 16(13), 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16132464






