A Matter of Margins in Oral Cancer—How Close Is Enough?
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Risk Factors for Local, Regional, and Distant Recurrence
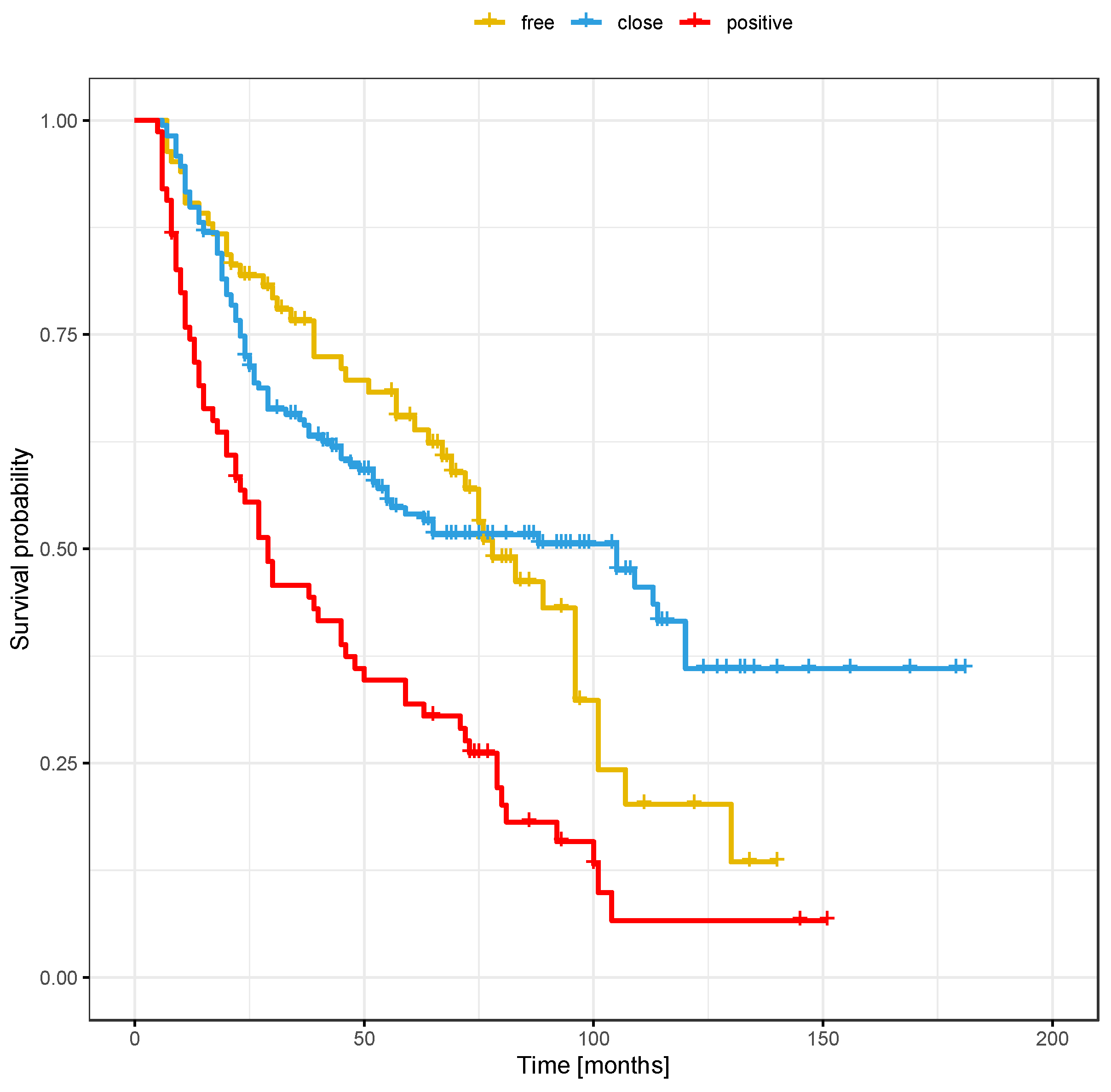
3.3. Local Recurrence
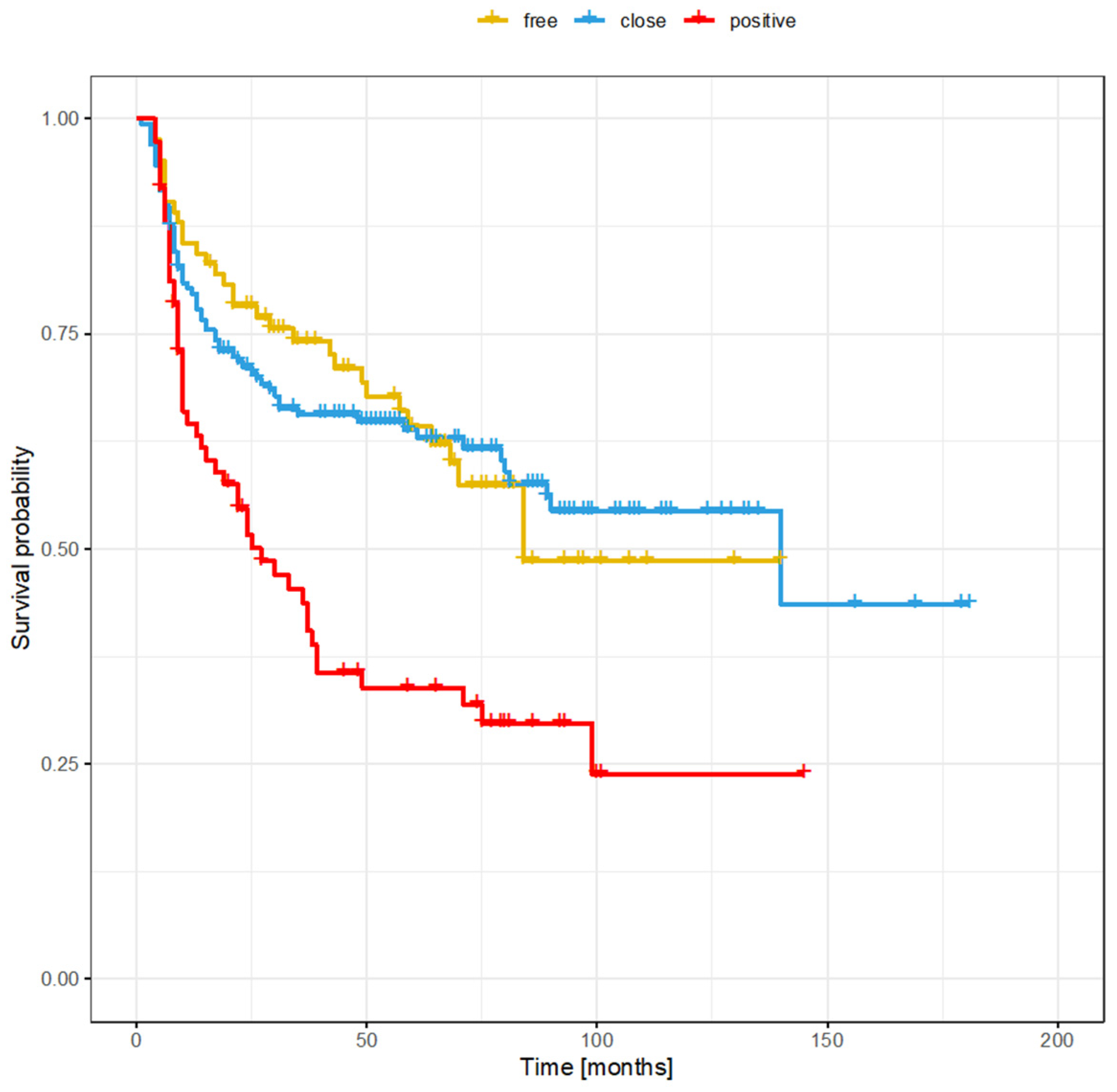
3.4. Regional Recurrence
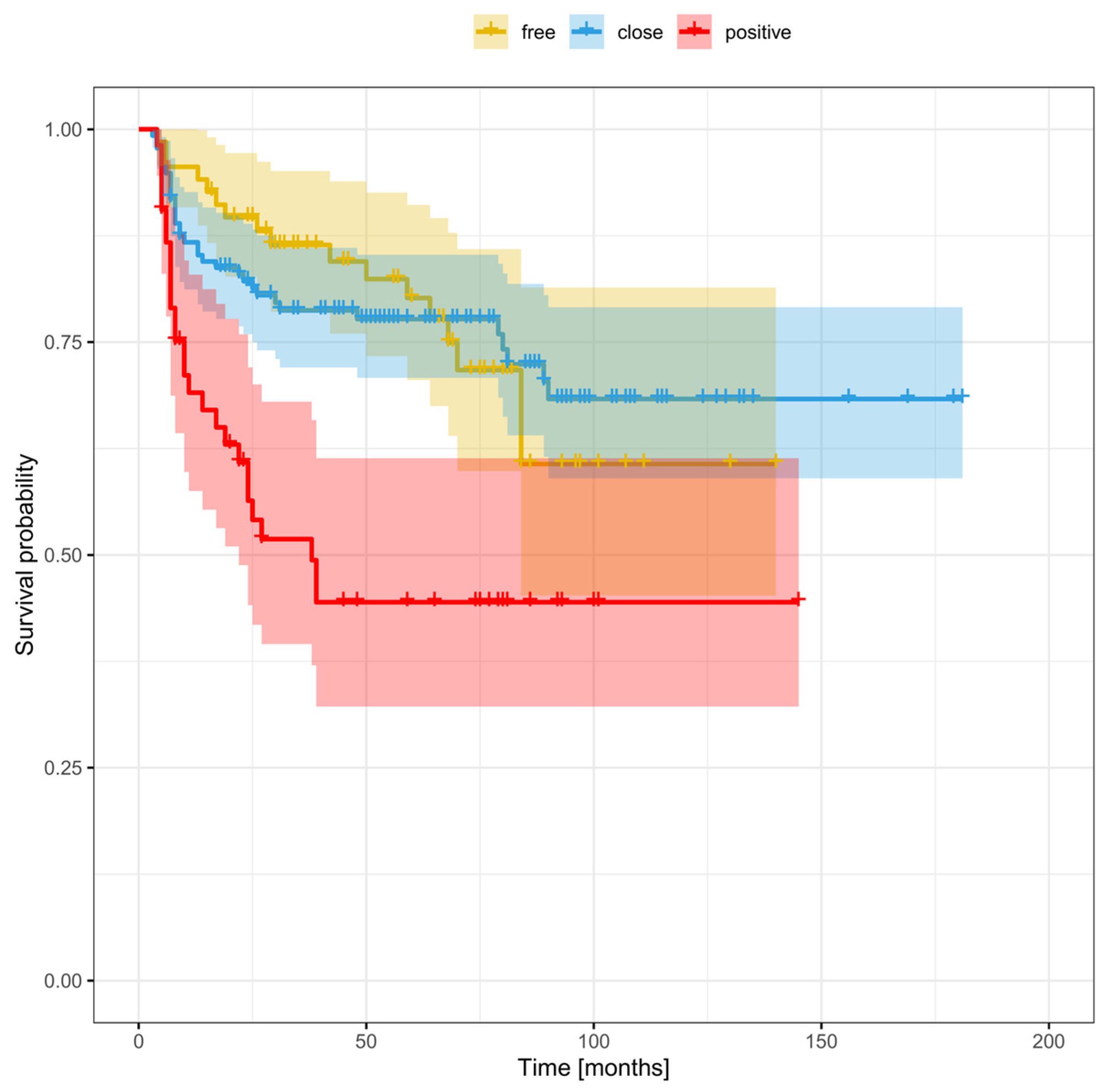
3.5. Distant Recurrence
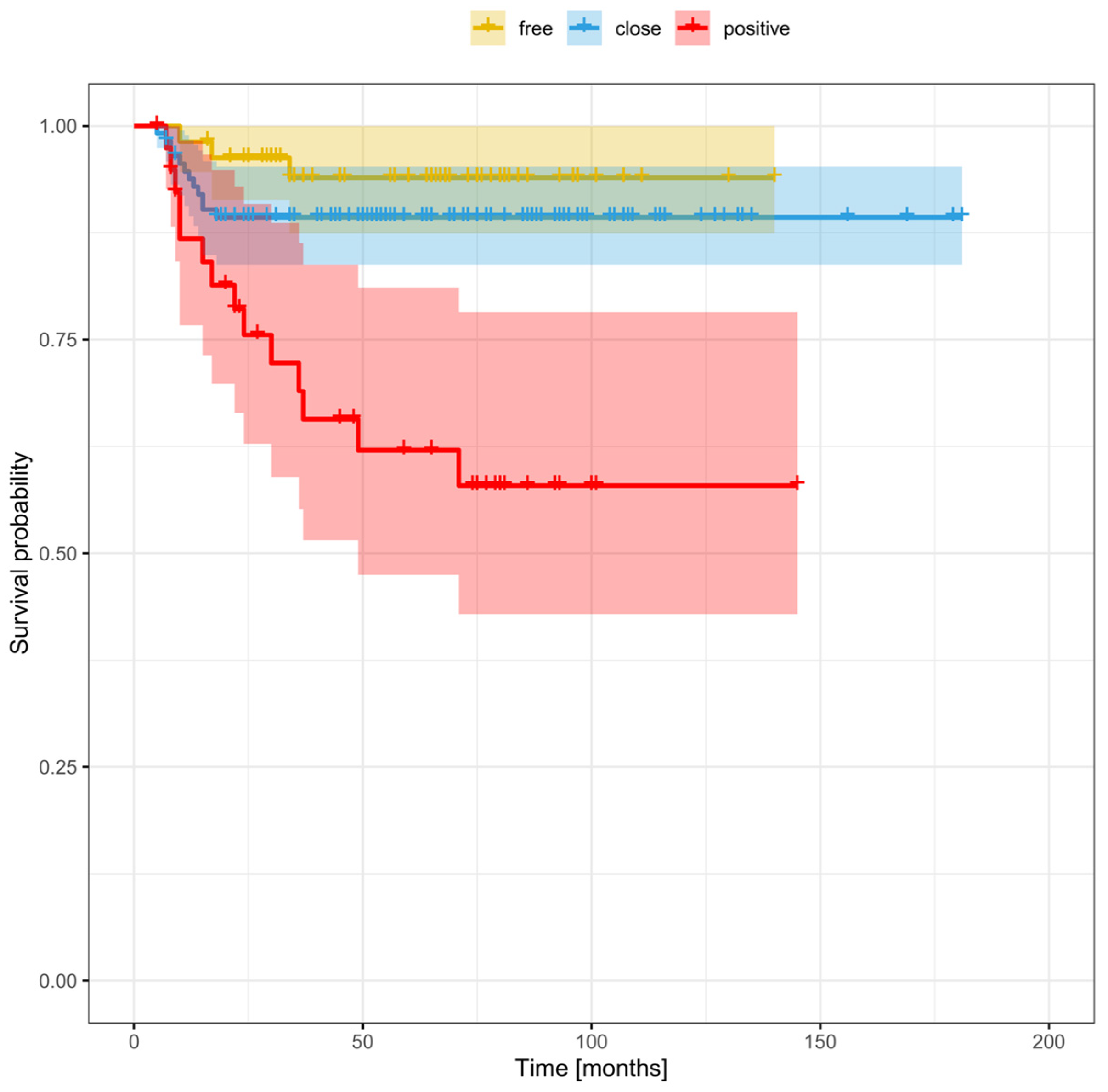
3.6. Risk Factors for Recurrence Based on Margin Status (Positive, Close, or Clear)
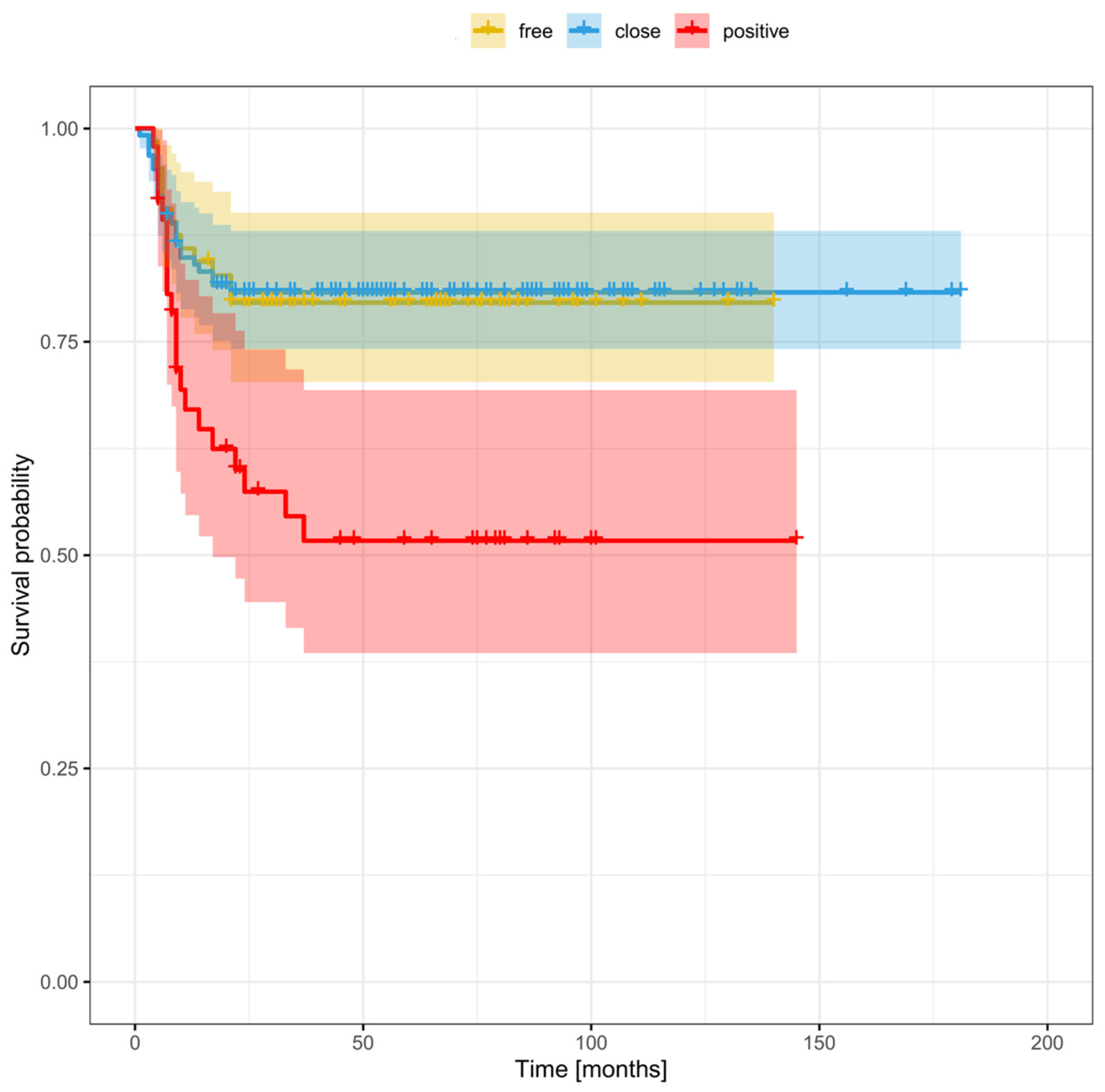
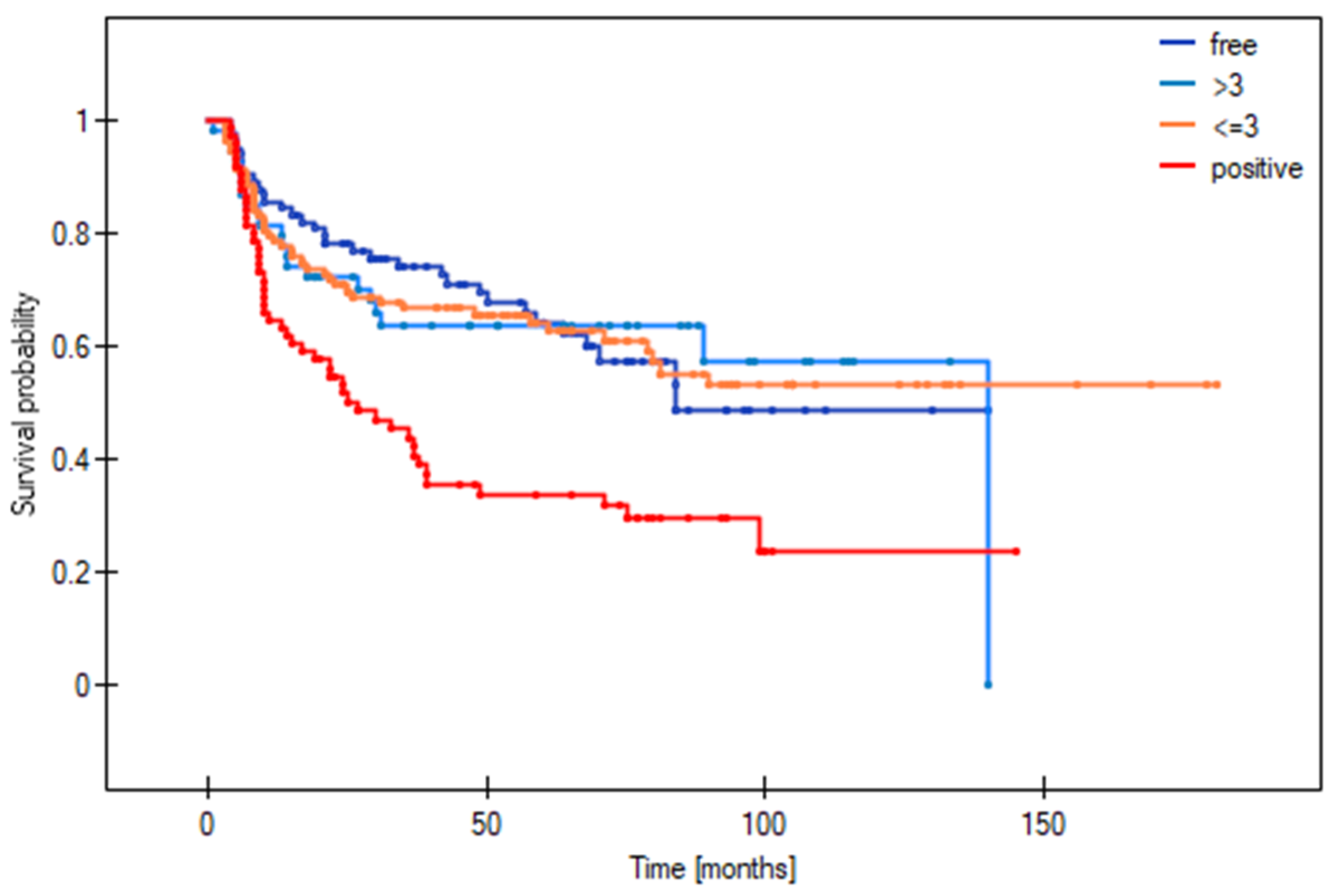
3.7. Cut-Off Point to Differentiate between Survival Outcomes in Patients with Close Margins
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chamoli, A.; Gosavi, A.S.; Shirwadkar, U.P.; Wangdale, K.V.; Behera, S.K.; Kurrey, N.K.; Kalia, K.; Mandoli, A. Overview of Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Risk Factors, Mechanisms, and Diagnostics. Oral Oncol. 2021, 121, 105451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Bray, F. Global Patterns and Trends in Cancers of the Lip, Tongue and Mouth. Oral Oncol. 2020, 102, 104551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanti, R.M.; O’Malley, B.W. Surgical Management of Oral Cancer. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 62, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, T.K.; Murphy, C.; Smith, A.B.; Kanatas, A.N.; Mitchell, D.A. Survival after Surgery for Oral Cancer: A 30-Year Experience. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 55, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, J.R.; Rowe, D.; Wiesenfeld, D.; McDowell, L.; Hall, K.A.; Nastri, A.; Iseli, T.A.; Wong, T. A Change in Surgical Margin: Do Wider Surgical Margins Lead to Decreased Rates of Local Recurrence in T1 and T2 Oral Tongue Cancer? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 52, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, R.W.H.; Koljenović, S.; Hardillo, J.A.; Ten Hove, I.; Meeuwis, C.A.; Sewnaik, A.; Dronkers, E.A.C.; Bakker Schut, T.C.; Langeveld, T.P.M.; Molenaar, J.; et al. Resection Margins in Oral Cancer Surgery: Room for Improvement. Head Neck 2016, 38, E2197–E2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolgar, J.A.; Triantafyllou, A. A Histopathological Appraisal of Surgical Margins in Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer Resection Specimens. Oral Oncol. 2005, 41, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.D.; Oliver, D.A.; Varvares, M.A. Surgical Margin Determination in Head and Neck Oncology: Current Clinical Practice. The Results of an International American Head and Neck Society Member Survey. Head Neck 2005, 27, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machiels, J.-P.; René Leemans, C.; Golusinski, W.; Grau, C.; Licitra, L.; Gregoire, V. Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity, Larynx, Oropharynx and Hypopharynx: EHNS–ESMO–ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1462–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajwa, M.S.; Houghton, D.; Java, K.; Triantafyllou, A.; Khattak, O.; Bekiroglu, F.; Schache, A.G.; Brown, J.S.; McCaul, J.A.; Rogers, S.N.; et al. The Relevance of Surgical Margins in Clinically Early Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2020, 110, 104913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nason, R.W.; Binahmed, A.; Pathak, K.A.; Abdoh, A.A.; Sándor, G.K.B. What Is the Adequate Margin of Surgical Resection in Oral Cancer? Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2009, 107, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, J.; Hinther, A.; Matthews, T.W.; Nakoneshny, S.C.; Hart, R.; Dort, J.C.; Chandarana, S.P. The Impact of Close Surgical Margins on Recurrence in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2021, 50, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasche, K.K.; Buchakjian, M.R.; Pagedar, N.A.; Sperry, S.M. Definition of “Close Margin” in Oral Cancer Surgery and Association of Margin Distance With Local Recurrence Rate. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, D.K.; Migliacci, J.C.; Xu, B.; Katabi, N.; Montero, P.H.; Ganly, I.; Shah, J.P.; Wong, R.J.; Ghossein, R.A.; Patel, S.G. A Proposal to Redefine Close Surgical Margins in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Tongue. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, J.; Campanile, Y.; Warner, A.; Laxague, F.; Fnais, N.; Fung, K.; Mendez, A.; MacNeil, D.; Yoo, J.; Palma, D.; et al. Surgical Margins of the Oral Cavity: Is 5 Mm Really Necessary? J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2022, 51, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ch’ng, S.; Corbett-Burns, S.; Stanton, N.; Gao, K.; Shannon, K.; Clifford, A.; Gupta, R.; Clark, J.R. Close Margin Alone Does Not Warrant Postoperative Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer 2013, 119, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kligerman, M.P.; Moon, P.K.; Tusty, M.; Cloutier, J.M.; Ma, Y.; Holsinger, C.F.; Divi, V. Impact of Histologic Risk Factors on Recurrence Rates for Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2023, 132, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-H.; Kim, G.-J.; Kim, H.-B.; Shin, H.-I.; Kim, C.-S.; Nam, I.-C.; Cho, J.-H.; Joo, Y.-H.; Cho, K.-J.; Sun, D.-I.; et al. Close Surgical Margins in Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer: Do They Impact Prognosis? Cancers 2022, 14, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamman, J.; Howe, C.L.; Borgstrom, M.; Baker, A.; Wang, S.J.; Bearelly, S. Impact of Close Margins in Head and Neck Mucosal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, D.; Callanan, D.; O’Shea, R.; Jawad, H.; Feeley, L.; Sheahan, P. Impact of 3 Mm Margin on Risk of Recurrence and Survival in Oral Cancer. Oral Oncol. 2020, 110, 104883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: The 7th Edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual and the Future of TNM. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.-Y.; Lim, Y.C.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, J.W.; Jeong, H.M.; Choi, E.C. Predictive Factors of Isolated Distant Metastasis after Primary Definitive Surgery without Systemic Treatment for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2010, 46, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.C.; Bhayani, M.; Kuchta, K.; Galloway, T.; Fundakowski, C. Patterns of Distant Metastasis in Head and Neck Cancer at Presentation: Implications for Initial Evaluation. Oral Oncol. 2019, 88, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Kamp, M.F.; Muntinghe, F.O.W.; Iepsma, R.S.; Plaat, B.E.C.; Van Der Laan, B.F.A.M.; Algassab, A.; Steenbakkers, R.J.H.M.; Witjes, M.J.H.; Van Dijk, B.A.C.; De Bock, G.H.; et al. Predictors for Distant Metastasis in Head and Neck Cancer, with Emphasis on Age. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, R.N.; Efthymiou, V.; Goss, D.; Varvares, M.A. Margin Distance in Oral Tongue Cancer Surgery: A Systematic Review of Survival and Recurrence Outcomes. Oral Oncol. 2023, 147, 106609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.A.; Kanatas, A.; Murphy, C.; Chengot, P.; Smith, A.B.; Ong, T.K. Margins and Survival in Oral Cancer. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binahmed, A.; Nason, R.W.; Abdoh, A.A. The Clinical Significance of the Positive Surgical Margin in Oral Cancer. Oral Oncol. 2007, 43, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.; Bulosan, H.; Kida, C.C.; Bewley, A.F.; Abouyared, M.; Birkeland, A.C. Stratification of Surgical Margin Distances by the Millimeter on Local Recurrence in Oral Cavity Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Head Neck 2023, 45, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-C.; Leu, Y.-S.; Chiang, C.-J.; Ko, J.-Y.; Wang, C.-P.; Yang, T.-L.; Chen, T.-C.; Chen, C.-N.; Chen, H.-L.; Liao, C.-T.; et al. Adequate Surgical Margins for Oral Cancer: A Taiwan Cancer Registry National Database Analysis. Oral Oncol. 2021, 119, 105358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubair, F.; Farooq, S.; Wright, S.; Schipani, S.; McMahon, J. Patterns of Recurrence amongst Patients Undergoing Resection of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Curative Intent. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 60, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, D.K.; Valero, C.; McGill, M.R.; Montero, P.H.; Shah, J.P.; Wong, R.J.; Ganly, I.; Patel, S.G. Distant Metastasis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Does the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Act as a Surrogate of the Host Immune Status? Oral Oncol. 2022, 124, 105641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Mishra, A.; Singhvi, H.; Sharin, F.; Bal, M.; Laskar, S.G.; Prabhash, K.; Chaturvedi, P. Optimum Surgical Margins in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Tongue: Is the Current Definition Adequate? Oral Oncol. 2020, 111, 104938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Patients (n = 326) | % |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 210 | 64.4 |
| Female | 116 | 35.6 |
| Mean age, years (range) | 59.1 (23–97) | |
| Tobacco use | ||
| Never | 129 | 39.5 |
| Active | 197 | 60.5 |
| Alcohol use | ||
| Never/occasionally (less than 20 g of 100% alcohol per week) | 281 | 86.1 |
| Alcohol abuse | 45 | 13.9 |
| Location | ||
| Tongue | 155 | 47.5 |
| Floor of mouth | 111 | 34.0 |
| Buccal mucosa | 29 | 8.9 |
| Retromolar trigone | 8 | 2.5 |
| Mandibular gingiva | 21 | 6.5 |
| Maxillary gingiva | 2 | 0.6 |
| Grade | ||
| 1 | 67 | 20.5 |
| 2 | 208 | 63.8 |
| 3 | 51 | 15.7 |
| Clinical T stage | ||
| Early (T1/T2) | 258 | 79.1 |
| Advanced (T3/T4) | 68 | 20.9 |
| Clinical N stage | ||
| N0 | 187 | 57.3 |
| N+ | 139 | 42.7 |
| Tumour stage | ||
| Early (I/II) | 156 | 47.8 |
| Advanced (III/IV) | 170 | 52.2 |
| PNI | 40 | 12.2 |
| LVI | 27 | 8.2 |
| ENE | 57 | 17.4 |
| Margins | ||
| Positive (<1 mm) | 83 | 25.5 |
| Close (1–5 mm) | 168 | 51.5 |
| Clear (>5 mm) | 75 | 23% |
| Adjuvant treatment | ||
| Radiotherapy | 263 | 80.6 |
| Chemoradiotherapy | 85 | 26 |
| Recurrence | 147 | 45.1 |
| Local | 53 | 16.2 |
| Regional | 33 | 10.1 |
| Locoregional | 17 | 5.2 |
| Distant | 21 | 6.4 |
| Locoregional + distant | 8 | 2.4 |
| Second primary tumour | 15 | 4.6 |
| Risk Factor | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Local recurrence | ||||
| Grade (3 vs. 1 + 2) | 1.71 (0.97–3.01) | 0.0671 | 0.9 (0.5–1.63) | 0.7265 |
| T stage (advanced vs. early) | 1.75 (1.07–2.87) | 0.0260 | 1.3 (0.77–2.2) | 0.3343 |
| Nodal disease (N+ vs. N0) | 3.54 (2.23–5.64) | <0.0001 | 3.39 (1.9–6.03) | <0.0001 |
| Stage (advanced vs. early) | 3.32 (2.02–5.44) | <0.0001 | 3.37 (1.84–6.16) | 0.0001 |
| PNI | 2.09 (1.15–3.79) | 0.0156 | 1.5 (0.79–2.85) | 0.2207 |
| LVI | 2.94 (1.55–5.59) | 0.0001 | 1.9 (0.93–3.88) | 0.0774 |
| ENE | 1.91 (1.11–3.27) | 0.0189 | 1.41 (0.78–2.53) | 0.2514 |
| Adjuvant treatment | 0.64 (0.34–1.21) | 0.1654 | 1.78 (0.8–4.0) | 0.1605 |
| Margins | ||||
| positive | 2.75 (1.5–5.06) | 0.0011 | 2.02 (1.02–4.01) | 0.0446 |
| close | 1.02 (0.57–1.83) | 0.9464 | 0.96 (0.51–1.81) | 0.9071 |
| clear | ref | ref | ref | ref |
| Smoking status (active vs. never) | 0.58 (0.37–0.91) | 0.017 | 0.67 (0.41–1.08) | 0.0997 |
| Alcohol abuse | 1.25 (0.68–2.32) | 0.4704 | 1.14 (0.57–2.27) | 0.7065 |
| Regional recurrence | ||||
| Grade (3 vs. 1 + 2) | 2.16 (1.21–3.85) | 0.0088 | 1.11 (0.59–2.09) | 0.7439 |
| T stage (advanced vs. early) | 1.5 (0.83–2.07) | 0.1776 | 1.05 (0.59–2.09) | 0.8948 |
| Nodal disease (N+ vs. N0) | 3.66 (2.14–6.26) | <0.0001 | 3.85 (1.84–8.04) | 0.0003 |
| Stage (advanced vs. early) | 3.6 (2.02–6.42) | <0.0001 | 3.93 (1.89–8.18) | 0.0003 |
| PNI | 3.58 (2.03–6.31) | <0.0001 | 2.74 (1.47–5.13) | 0.0016 |
| LVI | 3.67 (1.94–6.94) | 0.0001 | 1.99 (0.99–3.99) | 0.0052 |
| ENE | 2.82 (1.63–4.89) | 0.0002 | 2.1 (1.11–3.98) | 0.0228 |
| Adjuvant treatment | 0.87 (0.45–1.68) | 0.678 | 2.9 (0.89–4.28) | 0.0876 |
| Margins | ||||
| positive | 2.56 (1.28–5.12) | 0.0078 | 1.91 (0.85–4.32) | 0.118 |
| close | 0.96 (0.49–1.88) | 0.898 | 0.89 (0.42–1.88) | 0.7593 |
| clear | ref | ref | ||
| Smoking status (active vs. never) | 0.53 (0.32–0.88) | 0.0151 | 0.54 (0.32–0.93) | 0.025 |
| Alcohol abuse | 1.02 (0.48–2.16) | 0.9531 | 0.66 (0.27–1.61) | 0.363 |
| Distant recurrence | ||||
| Grade (3 vs. 1 + 2) | 1.19 (0.41–3.43) | 0.7451 | 0.62 (0.21–1.82) | 0.381 |
| T stage (advanced vs. early) | 0.95 (0.36–2.49) | 0.9178 | 0.52 (0.19–1.39) | 0.1902 |
| Nodal disease (N+ vs. N0) | 5.94 (2.62–13.44) | <0.0001 | 4.01 (1.63–9.89) | 0.0025 |
| Stage (advanced vs. early) | 3.79 (1.68–8.56) | 0.0014 | 2.26 (0.94–5.42) | 0.0687 |
| PNI | 1.31 (0.4–4.34) | 0.6537 | 0.63 (0.16–2.4) | 0.4933 |
| LVI | 4.74 (1.93–11.66) | 0.0007 | 5.65 (1.78–17.95) | 0.0033 |
| ENE | 3.46 (1.61–7.46) | 0.0015 | 2.19 (0.92–5.23) | 0.076 |
| Adjuvant treatment | 0.13 (0.02–0.97) | 0.0471 | 0.52 (0.06–4.64) | 0.5561 |
| Margins | ||||
| Positive | 7.53 (2.16–26.22) | 0.0015 | 5.6 (1.41–22.19) | 0.0142 |
| Close | 1.99 (0.56–7.04) | 0.2874 | 1.05 (0.27–4.05) | 0.9491 |
| Clear | ref | Ref | ||
| Smoking status (active vs. never) | 1.1 (0.5–2.43) | 0.8046 | 1.15 (0.51–2.62) | 0.7374 |
| Alcohol abuse | 1.75 (0.71–4.31) | 0.2218 | 1.09 (0.41–2.9) | 0.8699 |
| Clinical or Tumour-Related Factors | Positive Margins (n = 83) | Close Margins (n = 168) | Clear Margins (n = 75) | Positive vs. Close | Positive vs. Clear | Clear vs. Close |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | p Value | |||||
| Active smoker | 42 (56) | 106 (63.1) | 49 (59.1) | 0.6998 | 0.6998 | 0.6998 |
| Advanced T stage | 25 (33.3) | 33 (19.6) | 10 (12.1) | 0.0311 | 0.0039 | 0.133 |
| Nodal disease | 45 (60) | 72 (42.9) | 22 (26.5) | 0.0135 | 0.0001 | 0.0135 |
| Advanced disease | 50 (67.6) | 92 (54.8) | 27 (32.5) | 0.0623 | 0.0014 | <0.0001 |
| PNI | 13 (17.3) | 20 (11.9) | 7 (8.4) | 0.3808 | 0.1438 | 0.4037 |
| LVI | 8 (10.7) | 16 (9.5) | 3 (3.6) | 0.7827 | 0.1438 | 0.1438 |
| ENE | 22 (29.3) | 29 (17.3) | 6 (7.3) | 0.0334 | 0.001 | 0.0334 |
| Adjuvant treatment | 74 (98.7) | 141 (83.9) | 48 (57.8) | 0.0009 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Positive Surgical Margins | ||||||
| Local Recurrence | Regional Recurrence | Distant Recurrence | ||||
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Advanced T stage | 1.67 (0.79–3.68) | 0.1758 | 1.8 (0.76–4.28) | 0.1844 | 0.76 (0.21–2.72) | 0.4326 |
| Nodal disease | 2.45 (1.07–5.64) | 0.0346 | 3.54 (1.28–9.78) | 0.0147 | 2.53 (0.84–7.61) | 0.0992 |
| Advanced disease | 3.01 (1.14–7.97) | 0.0268 | 3.16 (1.06–9.43) | 0.0395 | 1.57 (0.53–4.71) | 0.4174 |
| PNI | 2.36 (0.88–6.32) | 0.0868 | 3.02 (1.15–7.89) | 0.0245 | 0.99 (0.13–7.64) | 0.9943 |
| LVI | 3.33 (1.1–10.07) | 0.0335 | 4.05 (1.43–1.48) | 0.0084 | - | - |
| ENE | 2.53 (1.12–5.72) | 0.0261 | 4.41 (1.82–10.71) | 0.001 | 3.06 (0.93–10.04) | 0.0648 |
| Adjuvant treatment | - | 0.9337 | - | 0.9795 | - | 0.9825 |
| Smoking status | 1.44 (0.67–3.09) | 0.3487 | 2.8 (1.02–7.69) | 0.0466 | 3.93 (1.09–14.23) | 0.0341 |
| Close Surgical Margins | ||||||
| Local Recurrence | Regional Recurrence | Distant Recurrence | ||||
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Advanced T stage | 1.67 (0.78–3.58) | 0.1879 | 1.19 (0.45–3.2) | 0.7239 | 0.92 (0.2–4.21) | 0.9912 |
| Nodal disease | 3.42 (1.69–6.94) | 0.0006 | 3.7 (1.58–8.66) | 0.0025 | 9.16 (2.01–41.82) | 0.0043 |
| Advanced disease | 2.83 (1.35–5.92) | 0.0059 | 5.75 (1.96–16.83) | 0.0014 | 5.74 (1.26–26.21) | 0.024 |
| PNI | 2.11 (0.87–5.1) | 0.0994 | 4.66 (2.03–10.7) | 0.0003 | 1.06 (0.14–8.18) | 0.9585 |
| LVI | 2.71 (1.12–6.58) | 0.0272 | 3.64 (1.44–9.19) | 0.0063 | - | - |
| ENE | 1.44 (0.63–3.31) | 0.3912 | 2.0 (0.83–4.82) | 0.1235 | 3.66 (1.16–11.53) | 0.027 |
| Adjuvant treatment | 1.63 (0.71–3.75) | 0.2482 | 2.1 (0.83–5.3) | 0.1156 | - | 0.9795 |
| Smoking status | 0.4 (0.2–0.81) | 0.01 | 0.24 (0.1–0.56) | 0.001 | 0.81 (0.24–2.68) | 0.7268 |
| Clear Surgical Margins | ||||||
| Local Recurrence | Regional Recurrence | Distant Recurrence | ||||
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Advanced T stage | 1.01 (0.23–4.42) | 0.9933 | 0.57 (0.07–4.36) | 0.586 | - | 0.9843 |
| Nodal disease | 4.08 (1.57–10.61) | 0.004 | 2.95 (0.96–9.04) | 0.0587 | 9.96 (0.9–110.25) | 0.061 |
| Advanced disease | 3.94 (1.48–10.48) | 0.0059 | 1.93 (0.63–5.91) | 0.2493 | 5.97 (0.54–65.85) | 0.1447 |
| PNI | 1.4 (0.32–6.2) | 0.6551 | 2.19 (0.49–9.9) | 0.307 | 5.56 (0.5–61.62) | 0.1621 |
| LVI | 5.87 (0.73–47.41) | 0.0965 | 3.3 (0.43–25.56) | 0.2524) | - | - |
| ENE | 0.82 (0.11–6.24) | 0.8501 | 2.35 (0.52–10.62) | 0.2675 | 5.43 (0.49–60.24) | 0.1678 |
| Adjuvant treatment | 0.37 (0.12–1.12) | 0.0792 | 0.69 (0.22–2.1) | 0.5077 | 0.5 (0.05–5.33) | 0.5717 |
| Smoking status | 0.66 (0.25–1.71) | 0.3942 | 0.29 (0.09–0.95) | 0.0415 | 0.3 (0.03–3.31) | 0.326 |
| Margin Status | 5-Year DFS | 5-Year OS |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | 33.8% | 31.8% |
| Deep margin ≤3 mm | 52.6% | 41.7% |
| Deep margin >3 mm | 80.2% | 71.3% |
| Clear | 64.2% | 65.4% |
| Deep margin ≤ 3 mm | ||
| p value * | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | ||
| >3 mm vs. clear | 0.66 (0.42–1.03) | 0.54 (0.37–0.8) |
| ≤3 mm vs. clear | 1.38 (0.9–2.13) | 1.26 (0.87–1.84) |
| positive vs. clear | 2.17 (1.34–3.52) | 2.15 (1.39–3.31) |
| ≤3 mm vs. >3 mm | 2.1 (1.35–3.28) | 2.32 (1.59–3.39) |
| positive vs. >3 mm | 3.31 (2.02–5.41) | 3.94 (2.55–6.1) |
| positive vs. ≤3 mm | 1.57 (0.98–2.53) | 1.7 (1.11–2.61) |
| Local Recurrence Risk | Regional Recurrence Risk | Distant Recurrence Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deep margin ≤ 3 | |||
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | |||
| p-value * | <0.0001 | 0.0007 | <0.0001 |
| >3 mm vs. clear | 0.58 (0.32–1.05) | 0.52 (0.26–1.06) | 1.04 (0.39–2.82) |
| ≤3 mm vs. clear | 1.41 (0.79–2.54) | 1.33 (0.67–2.62) | 2.84 (1.08–7.48) |
| Positive vs. clear | 2.74 (1.37–5.45) | 2.55 (1.17–5.57) | 7.51 (2.45–23.04) |
| ≤3 vs. >3 mm | 2.45 (1.35–4.46) | 2.55 (1.26–5.14) | 2.72 (1.02–7.24) |
| Positive vs. >3 mm | 4.74 (2.36–9.55) | 4.9 (2.2–10.89) | 7.19 (2.32–22.27) |
| Positive vs. ≤3 mm | 1.93 (0.98–3.83) | 1.92 (0.89–4.17) | 2.64 (0.87–8.02) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szewczyk, M.; Pazdrowski, J.; Pieńkowski, P.; Wojtera, B.; Więckowska, B.; Golusiński, P.; Golusiński, W. A Matter of Margins in Oral Cancer—How Close Is Enough? Cancers 2024, 16, 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081488
Szewczyk M, Pazdrowski J, Pieńkowski P, Wojtera B, Więckowska B, Golusiński P, Golusiński W. A Matter of Margins in Oral Cancer—How Close Is Enough? Cancers. 2024; 16(8):1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081488
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzewczyk, Mateusz, Jakub Pazdrowski, Piotr Pieńkowski, Bartosz Wojtera, Barbara Więckowska, Paweł Golusiński, and Wojciech Golusiński. 2024. "A Matter of Margins in Oral Cancer—How Close Is Enough?" Cancers 16, no. 8: 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081488
APA StyleSzewczyk, M., Pazdrowski, J., Pieńkowski, P., Wojtera, B., Więckowska, B., Golusiński, P., & Golusiński, W. (2024). A Matter of Margins in Oral Cancer—How Close Is Enough? Cancers, 16(8), 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081488






