The Role of Perirenal Adipose Tissue in Carcinogenesis—From Molecular Mechanism to Therapeutic Perspectives
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PRAT-Adapted Morphology in Cancer
3. Potential Mechanisms of Tumor Cell–PRAT Interrelationship
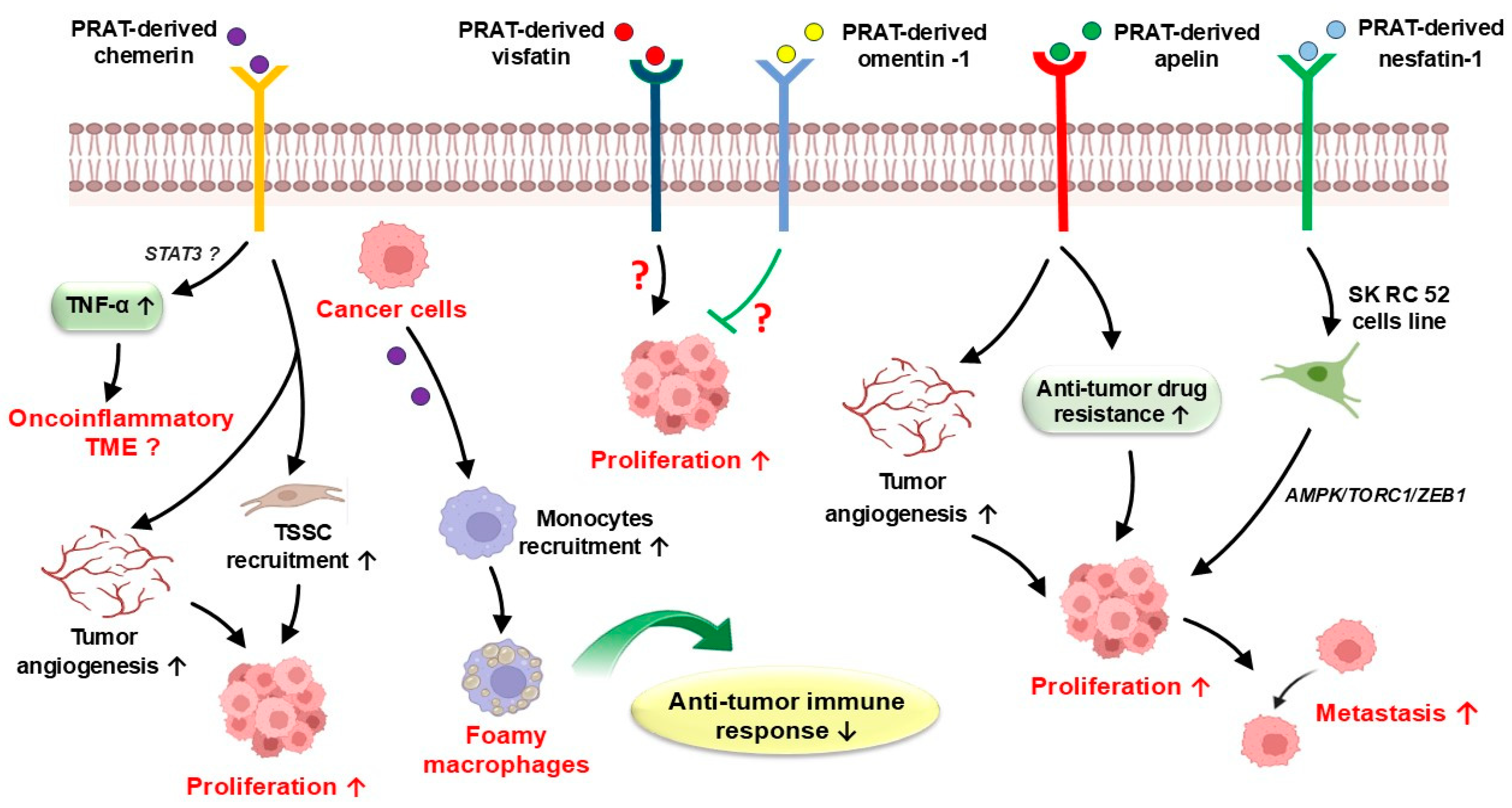
3.1. PRAT-Derived Adipokines in Cancer
3.2. PRAT-Induced Hypoxia and Inflammation in Cancer
3.3. PRAT-Derived Metabolic Dysfunctions in Cancer
4. PRAT’s Potential Value in RCC Prognosis
5. PRAT’s Potential Value in Gastric and Colorectal Cancer Prognosis
6. PRAT’s Potential Value in Prognosis of Other Cancers
7. PRAT-Targeted Therapeutic Perspectives in Cancer
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, D.; Ke, J. The relationship between perirenal fat thickness and reduced glomerular filtration rate in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 6076145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.J. The role of adipokines in tumor progression and its association with obesity. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoras, A.; Balan, R.A.; Caruntu, I.-D.; Giusca, S.E.; Lozneanu, L.; Avadanei, R.E.; Rusu, A.; Riscanu, L.A.; Amalinei, C. Perirenal adipose tissue—Current knowledge and future opportunities. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jespersen, N.Z.; Feizi, A.; Andersen, E.S.; Heywood, S.; Hattel, H.B.; Daugaard, S.; Peijs, L.; Bagi, P.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; Schultz, H.; et al. Heterogeneity in the perirenal region of humans suggests presence of dormant brown adipose tissue that contains brown fat precursor cells. Mol. Metab. 2019, 24, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazeli, S.A.; Nourollahi, S.; Alirezaei, A.; Mirhashemi, S.; Davarian, A.; Hosseini, I. Perirenal adipose tissue: Clinical implication and therapeutic interventions. Indian J. Nephrol. 2024, 34, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Xiao, M.; Li, X.; Cheng, L.; Cheng, W.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Y. Global gene expression profiling of perirenal brown adipose tissue whitening in goat kids reveals novel genes linked to adipose remodeling. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Mao, E.W.; Hou, N.N.; Liu, Y.P.; Han, F.; Sun, X.D. Novel insight into perirenal adipose tissue: A neglected adipose depot linking cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease. World J. Diabetes 2020, 11, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Ibáñez, C.; Xie, M. Perirenal adipose tissue contains a subpopulation of cold-inducible adipocytes derived from brown-to-white conversion. Elife 2024, 13, RP93151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosam, A.; Perry, R.J. Current mechanisms in obesity and tumor progression. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.; Haegeman, G.; Tsang, B.; Dhanasekaran, D.; Song, Y.S. Adipose stromal cells from visceral and subcutaneous fat facilitate migration of ovarian cancer cells via IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 49, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Shen, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, N.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; et al. The adiponectin-adipoR1 axis mediates tumor progression and tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Yoshimura, A.; Fukae, S.; Yoshida, T.; Kishikawa, H. Perirenal fat metastasis of prostate cancer. Urol. Case Rep. 2021, 39, 101778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, K.; Yoshida, N.; Iwatsuki, M.; Iwagami, S.; Nakamura, K.; Morita, K.; Ikeshima, S.; Horino, K.; Shimada, S.; Baba, H. Clinical impact of perirenal thickness on short-and long-term outcomes of gastric cancer after curative surgery. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2022, 6, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sönmez, M.R.; Aydın, İ.C.; Biçer, G.; Havan, N.; Sunar, A.O.; Ademoğlu, S.; Özduman, M.Ö.; Dinçer, M.; Polat, E.; Duman, M. Perirenal fat thickness as a risk factor for postoperative complications in elective colorectal cancer surgery. Medicine 2023, 102, e34072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, E.; Imada, K.; Abe, T.; Kinoshita, F.; Monji, K.; Shiota, M.; Takeuchi, A.; Inokuchi, J.; Tatsugami, K.; Eto, M. Thickness of perirenal fat predicts the growth pattern of renal cell carcinoma. Kidney Cancer 2020, 4, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, K.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Tian, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, l.; Zou, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Perirenal fat thickness significantly associated with prognosis of metastatic renal cell cancer patients receiving anti-vegf therapy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Chen, X.; Qi, P.; Ma, Z.; Han, D.; Zhang, X.; Shang, P. Research progress on the correlation between obesity and the occurrence and development of kidney cancer: A narrative review. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 5678–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocian-Jastrzebska, A.; Malczewska-Herman, A.; Kos-Kudła, B. Role of leptin and adiponectin in carcinogenesis. Cancers 2023, 15, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Sun, H.; Dong, K.; Hu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shao, Y.; Tang, H.; et al. The thermogenic activity of adjacent adipocytes fuels the progression of ccRCC and compromises anti-tumor therapeutic efficacy. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 2021–2039.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, M.; Bruna, F.A.; Romeo, L.R.; Contador, D.; Moya-Morales, D.L.; Santiano, F.; Zyla, L.; Gomez, S.; Lopez-Fontana, C.L.; Calvo, J.C.; et al. Renal peritumoral adipose tissue undergoes a browning process and stimulates the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in human renal cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Mahmud, I.; Thakur, V.; Tan, S.K.; Isom, D.; Lombard, D.; Gonzalgo, M.; Kryvenko, O.; Lorenzi, P.; Tcheuyap, V.; et al. GPR1 and CMKLR1 control lipid metabolism to support development of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 2141–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboud, A.; Wettersten, H.I.; Weiss, R.H. Inhibition of PPARα induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and synergizes with glycolysis inhibition in kidney cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.L.; Bayeh, L.; Scheuermann, T.H.; Longgood, J.; Key, J.; Naidoo, J.; Melito, L.; Shokri, C.; Frantz, D.; Bruick, R.; et al. Development of inhibitors of the PAS-B domain of the HIF-2α transcription factor. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Henau, O.; Degroot, G.N.; Imbault, V.; Robert, V.; De Poorter, C.; McHeik, S.; Galés, C.; Parmentier, M.; Springael, J.Y. Signaling properties of chemerin receptors CMKLR1, GPR1 and CCRL2. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, M.; Maruyama, R.; Kawabata, Y.; Tajima, Y.; Takenaga, K. Antidiabetic adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon suppresses tumour growth of pancreatic cancer by inducing RIPK1/ERK-dependent necroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Gonçalves, V.; Lameirinhas, A.; Macedo-Silva, C.; Lobo, J.; Dias, P.; Ferreira, V.; Henrique, R.; Carmen Jerónimo, C. Lactate increases renal cell carcinoma aggressiveness through sirtuin 1-dependent epithelial mesenchymal transition axis regulation. Cells 2020, 9, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Cortegana, C.; López-Saavedra, A.; Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Pérez-Pérez, A.; Castiñeiras, J.; Virizuela-Echaburu, J.A.; de la Cruz-Merino, L.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Leptin, both bad and good actor in cancer. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Ding, G. Increased UCP1 expression in the perirenal adipose tissue of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1972–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitkus, J.A.; Celi, F.S. The role of adipose tissue in cancer-associated cachexia. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, A. The role of tumor microenvironment cells in colorectal cancer (CRC) cachexia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preza-Fernandes, J.; Passos, P.; Mendes-Ferreira, M.; Rodrigues, A.; Gouveia, A.; Fraga, A.; Medeiros, R. A hint for the obesity paradox and the link between obesity, perirenal adipose tissue and renal cell carcinoma progression. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19956. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Sun, S.; Yuan, J.; Sun, S. Cancer-associated adipocytes as immunomodulators in cancer. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Iacono, M.L.; Modica, C.; Porcelli, G.; Brancato, O.R.; Muratore, G.; Bianca, P.; Gaggianesi, M.; Turdo, A.; Veschi, V.; Todaro, M.; et al. Targeting of the peritumoral adipose tissue microenvironment as an innovative antitumor therapeutic strategy. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoras, A.; Amalinei, C. Multi-faceted role of cancer-associated adipocytes in colorectal cancer. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.H.; Chun, S.Y.; Lee, J.N.; Chung, J.-W.; Yoon, B.H.; Kim, H.T.; Kwon, T.G.; Ha, Y.-S.; Kim, B.S. Perirenal adipose tissue from healthy donor: Characteristics and promise as potential therapeutic cell source. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, W.; Liu, H.; Qin, C.; Tang, X.; Xu, T. Perirenal fat as a new independent prognostic factor in patients with surgically treated clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2022, 20, e75–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Coletta, A.M.; Allen, P.K.; Parikh, A.M.; Cox-Mattin, M.; Meyer, L.A.; Sun, C.C.; Basen-Engquist, K.M.; Lu, K.H.; Klopp, A.H. Perirenal adiposity is associated with lower progression-free survival from ovarian cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2018, 28, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Eto, K.; Ida, S.; Ohashi, T.; Kumagai, K.; Nunobe, S.; Ohashi, M.; Sano, T.; Hiki, N. Perirenal fat thickness as a predictor of postoperative complications after laparoscopic distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer. BJS Open 2020, 4, 865–872. [Google Scholar]
- Delahunt, B.; Eble, J.N.; Samaratunga, H.; Thunders, M.; Yaxley, J.W.; Egevad, L. Staging of renal cell carcinoma: Current progress and potential advances. Pathology 2021, 53, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, N.M.; Gucalp, A.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Hudis, C.A. Obesity and cancer mechanisms: Tumor microenvironment and inflammation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinapayan, S.M.; Kuppusamy, S.; Yap, N.Y.; Perumal, K.; Gobe, G.; Rajandram, R. Potential value of visfatin, omentin-1, nesfatin-1 and apelin in renal cell carcinoma (rcc): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Torroella-Kouri, M.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Oncogenic role and therapeutic target of leptin signaling in breast cancer and cancer stem cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1825, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amalinei, C.; Grigoras, A.; Lozneanu, L.; Caruntu, I.-D.; Giusca, S.-E.; Balan, R.A. The interplay between tumour microenvironment components in malignant melanoma. Medicina 2022, 58, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.L.; Yeh, Y.M.; Liu, T.T.; Lin, W.M.; Yang, T.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Lin, T.C. Leptin is associated with poor clinical outcomes and promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.J.; LeRoith, D. Obesity and diabetes: The increased risk of cancer and cancer-related mortality. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Xu, X.; Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Leptin-mediated regulation of MT1-MMP localization is KIF1B dependent and enhances gastric cancer cell invasion. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Cleary, M.P. The potential role of leptin in tumor invasion and metastasis. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2017, 38, 80–97. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, P.; Xi, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xu, P. Linking obesity with colorectal cancer: Epidemiology and mechanistic insights. Cancers 2020, 12, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski-Bergner, S.; Kielstein, H. Adipokines regulate the expression of tumor-relevant microRNAs. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumminia, A.; Vinciguerra, F.; Parisi, M.; Graziano, M.; Sciacca, L.; Baratta, R.; Frittitta, L. Adipose tissue, obesity and adiponectin: Role in endocrine cancer risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Jin, W.; Wang, J. The bifurcated role of adiponectin in colorectal cancer. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 11952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Zazzo, E.; Polito, R.; Bartollino, S.; Nigro, E.; Porcile, C.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A.; Moncharmont, B. Adiponectin as link factor between adipose tissue and cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spyridopoulos, T.N.; Petridou, E.T.; Skalkidou, A.; Dessypris, N.; Chrousos, G.P.; Mantzoros, C.S. Low adiponectin levels are associated with renal cell carcinoma: A case-control study. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Martino, M.; Leitner, C.V.; Hofbauer, S.L.; Lucca, I.; Haitel, A.; Shariat, S.; Klatte, T. Serum adiponectin predicts cancer-specific survival of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. Focus. 2016, 2, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinthus, J.H.; Kleinmann, N.; Tisdale, B.; Chatterjee, S.; Lu, J.-P.; Gillis, A.; Hamlet, T.; Singh, G.; Farrokhyar, F.; Kapoor, A. Lower plasma adiponectin levels are associated with larger tumor size and metastasis in clear-cell carcinoma of the kidney. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruna, F.A.; Romeo, L.R.; Campo-Verde-Arbocco, F.; Contador, D.; Gómez, S.; Santiano, F.; Sasso, C.V.; Zyla, L.; López-Fontana, C.; Calvo, J.C.; et al. Human renal adipose tissue from normal and tumor kidney: Its influence on renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 5454–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, H.; Aksnes, T.; Åkra, S.; Eggesbø, H.B.; Byrkjeland, R.; Seljeflot, I.; Opstad, T.B. Abdominal adipose tissue associates with adiponectin and TNFα in middle-aged healthy men. Front. Endocrinol 2022, 13, 874977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Lan, X.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, X.; Xie, X. The role of perirenal adipose tissue deposition in chronic kidney disease progression: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Life Sci. 2024, 352, 122866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo-Verde-Arbocco, F.; López-Laur, J.; Romeo, L.; Giorlando, N.; Bruna, F.; Contador, D.; López-Fontana, G.; Santiano, F.; Sasso, C.; Zyla, L.; et al. Human renal adipose tissue induces the invasion and progression of renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 94223–94234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, A.; Sumitomo, M.; Asakuma, J.; Asano, T.; Zheng, R.; Asano, T.; Nanus, D.M.; Hayakawa, M. Leptin promotes invasiveness of murine renal cancer cells via extracellular signal-regulated kinases and rho dependent pathway. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 1636–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbard, L.W.; Garlatti, M.; Young, L.J.; Cardiff, R.D.; Oshima, R.G.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin supports angiogenesis and adiponectin association with the vasculature in a mouse mammary tumor model. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denzel, M.S.; Hebbard, L.W.; Shostak, G.; Shapiro, L.; Cardiff, R.D.; Ranscht, B. Adiponectin deficiency limits tumor vascularization in the MMTV-PyV-mT mouse model of mammary cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3256–3264. [Google Scholar]
- Zorena, K.; Jachimowicz-Duda, O.; Ślęzak, D.; Robakowska, M.; Mrugacz, M. Adipokines and obesity. Potential link to metabolic’ disorders and chronic complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adya, R.; Tan, B.K.; Chen, J.; Randeva, H.S. Protective actions of globular and full-length adiponectin on human endothelial cells: Novel insights into adiponectin-induced angiogenesis. J. Vasc. Res. 2012, 49, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nigro, E.; Mallardo, M.; Polito, R.; Scialò, F.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A. Adiponectin and leptin exert antagonizing effects on huvec tube formation and migration modulating the expression of CXCL1, VEGF, MMP-2 and MMP-9. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralski, K.; Jackson, A.; McKeown, B.; Sinal, C. More than an adipokine: The complex roles of chemerin signaling in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treeck, O.; Buechler, C.; Ortmann, O. Chemerin and cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3750. [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk, K.M.; Nilsson, H.; Allaoui, R.; Lindgren, D.; Arvidsson, M.; Leandersson, K.; Johansson, M.E. Papillary renal cell carcinoma-derived chemerin, IL-8, and CXCL16 promote monocyte recruitment and differentiation into foam-cell macrophages. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.T.; Mahmud, I.; Fontanesi, F.; Puchowicz, M.; Neumann, C.; Griswold, A.; Patel, R.; Dispagna, M.; Ahmed, H.; Gonzalgo, M.; et al. Obesity-dependent adipokine chemerin suppresses fatty acid oxidation to confer ferroptosis resistance. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2072–2093. [Google Scholar]
- Buechler, C.; Feder, S.; Haberl, E.M.; Aslanidis, C. Chemerin isoforms and activity in obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlee, S.D.; Ernst, M.C.; Muruganandan, S.; Sinal, C.J.; Goralski, K.B. Serum chemerin levels vary with time of day and are modified by obesity and tumor necrosis factor-α. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 2590–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.C. The role of visfatin in cancer proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis, drug resistance and clinical prognosis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3481–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.P.; Zou, J.; Xu, Z.Q.; Ruan, J.; Yang, S.D.; Yin, Y.; Mu, H.J. Association of leptin, visfatin, apelin, resistin and adiponectin with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamada, Y.; Arai, T.; Sugawara, S.; Okato, A.; Kato, M.; Kojima, S.; Yamazaki, K.; Naya, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Impact of novel oncogenic pathways regulated by antitumor miR-451a in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulatos, G.S.; Antonakos, G.; Karampela, I.; Psallida, S.; Stratigou, T.; Vallianou, N.; Lekka, A.; Marinou, I.; Vogiatzakis, E.; Kokoris, S.; et al. Circulating omentin-1 as a biomarker at the intersection of postmenopausal breast cancer occurrence and cardiometabolic risk: An observational cross-sectional study. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocka, M.B.; Pietraszek-Gremplewicz, K.; Nowak, D. The role of apelin in cardiovascular diseases, obesity and cancer. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Dai, B.; Xu, J.; Ye, D. High NUCB2 expression level represents an independent negative prognostic factor in Chinese cohorts of non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 35244–35254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, W.; Qi, K.; Zhou, J.; Gu, M.; Wang, Z. A novel function of NUCB2 in promoting the development and invasion of renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2425–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Niu, W.B.; Dou, P.H.; Ni, S.B.; Yu, Y.P.; Cai, L.C.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, C.; Luo, Z.G. Nucleobindin-2 enhances the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 3653–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Rysz, J.; Ławiński, J.; Franczyk, B. Renal Cell Cancer and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, H.M.; Underkofler, C.M.; Kern, P.A.; Erickson, C.; Bredbeck, B.; Rasouli, N. Adipose tissue hypoxia, inflammation, and fibrosis in obese insulin-sensitive and obese insulin-resistant subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoud, S.; AlZaim, I.; Al-Dhaheri, Y.; Eid, A.; El-Yazbi, A. Perirenal adipose tissue inflammation: Novel insights linking metabolic dysfunction to renal diseases. Front. Endocrinol 2021, 12, 707126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raval, R.R.; Lau, K.W.; Tran, M.G.; Sowter, H.; Mandriota, S.; Li, J.L.; Pugh, C.; Maxwell, P.; Harris, A.; Ratcliffe, P. Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in von Hippel-Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 5675–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challapalli, A.; Carroll, L.; Aboagye, E.O. Molecular mechanisms of hypoxia in cancer. Clin. Transl. Imaging. 2017, 5, 225–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefflin, R.; Harlander, S.; Schäfer, S.; Metzger, P.; Kuo, F.; Schönenberger, D.; Adlesic, M.; Peighambari, A.; Seidel, P.; Chen, C.Y.; et al. HIF-1α and HIF-2α differently regulate tumour development and inflammation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma in mice. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatte, T.; Seligson, D.B.; Riggs, S.B.; Leppert, J.T.; Berkman, M.K.; Kleid, M.D.; Yu, H.; Kabbinavar, F.F.; Pantuck, A.J.; Belldegrun, A.S. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 7388–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudas, L.J.; Fu, L.; Minton, D.R.; Mongan, N.P.; Nanus, D.M. The role of HIF1α in renal cell carcinoma tumorigenesis. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurilio, G.; Piva, F.; Santoni, M.; Cimadamore, A.; Sorgentoni, G.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Cheng, L.; Battelli, N.; Nolè, F.; Montironi, R. The role of obesity in renal cell carcinoma patients: Clinical-pathological implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incio, J.; Tam, J.; Rahbari, N.N.; Suboj, P.; McManus, D.T.; Chin, S.M.; Vardam, T.D.; Batista, A.; Babykutty, S.; Jung, K.; et al. PlGF/VEGFR-1 signaling promotes macrophage polarization and accelerated tumor progression in obesity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2993–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Yang, Q.; Cao, J.; Xie, N.; Liu, K.; Shou, P.; Qian, F.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Local proliferation initiates macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue during obesity. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.S.; Jung, D.Y.; Morel, C.; Lakhani, S.A.; Kim, J.K.; Flavell, R.A.; Davis, R.J. JNK expression by macrophages promotes obesity-induced insulin resistance and inflammation. Science 2013, 339, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riscal, R.; Skuli, N.; Simon, C. Even cancer cells watch their cholesterol! Mol. Cell. 2019, 76, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heravi, G.; Yazdanpanah, O.; Podgorski, I.; Matherly, L.; Liu, W. Lipid metabolism reprogramming in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022, 41, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Temkin, S.; Hawkridge, A.; Guo, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.Y.; Fang, X. Fatty acid oxidation: An emerging facet of metabolic transformation in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 435, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, K.M.; Kenny, H.A.; Penicka, C.V.; Ladanyi, A.; Buell-Gutbrod, R.; Zillhardt, M.R.; Romero, I.; Carey, M.; Mills, G.; Hotamisligil, G.; et al. Adipocytes promote ovarian cancer metastasis and provide energy for rapid tumor growth. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloribi-Djefaflia, S.; Vasseur, S.; Guillaumond, F. Lipid metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, H.; Abe, M.; Yang, Y.; Cui, D.; Seki, T.; Nakamura, M.; Hosaka, K.; Lim, S.; Wu, J.; He, X.; et al. Cancer lipid metabolism confers antiangiogenic drug resistance. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Quiles, M.; Broekema, M.F.; Kalkhoven, E. PPARgamma in metabolism, immunity, and cancer: Unified and diverse mechanisms of action. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 624112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmari, I.; Töröcsik, D.; Agostini, M.; Nagy, T.; Gurnell, M.; Barta, E.; Chatterjee, K.; Nagy, L. PPARg regulates the function of human dendritic cells primarily by altering lipid metabolism. Blood 2007, 110, 3271–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuaranta-Monroy, I.; Kiss, M.; Simandi, Z.; Nagy, L. Genomewide effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in macrophages and dendritic cells—Revealing complexity through systems biology. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2015, 45, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, S.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: A key link between lipid metabolism and cancer progression. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, T.; Liu, M.; He, Q.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Ni, D.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Gu, Y.; et al. PPARG negatively modulates Six2 in tumor formation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, Z.; Han, C.; Ruan, N.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Xia, Q.; Wu, G. A new prognostic risk model based on PPAR pathway-related genes in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. PPAR Res. 2020, 22, 6937475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecorino, L. Molecular Biology of Cancer: Mechanisms, Targets, and Therapeutics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Qannita, R.A.; Alalami, A.I.; Harb, A.A.; Aleidi, S.M.; Taneera, J.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; El-Huneidi, W.; Saleh, M.A.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Semreen, M.H.; et al. Targeting hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) in cancer: Emerging therapeutic strategies and pathway regulation. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, R.; Wills, J.; Roby, K.F.; Be’ne’zech, C.; Stimson, R.H.; Wabitsch, M.; Pollard, J.W.; Finch, A.; Michailidou, Z. Hypoxia-driven metabolic reprogramming of adipocytes fuels cancer cell proliferation. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 989523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Zhang, L.; BrettMorris, A.; Aguila, B.; Kerner, J.; Hoppel, C.; Puchowicz, M.; Serra, D.; Herrero, L.; Rini, B.; et al. HIF drives lipid deposition and cancer in ccRCC via repression of fatty acid metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; DeBerardinis, R. Mechanisms and implications of metabolic heterogeneity in cancer. Cell Metabol. 2019, 30, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Zhao, X.; Gu, P.; Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Guo, Q.; Long, Q.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Adipocyte-derived lactate is a signalling metabolite that potentiates adipose macrophage inflammation via targeting PHD2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Singh, M.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, V.; Rani, R. Intervention on lactate in cancer: A promising approach for the development of cancer therapeutics. Adv. Cancer Biol. Metastasis 2022, 5, 10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmann, B.M. Hypoxiainducible factor in cancer: From pathway regulation to therapeutic opportunity. BMJ Oncol. 2024, 3, e000154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Xing, J. High perirenal fat thickness predicts a poor progression-free survival in patients with localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Ba, X.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, J.; Kuang, X.; Xie, H.; Gong, P.; Shi, Y.; et al. Association between CT-based adipose variables, preoperative blood biochemical indicators and pathological T stage of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, P.; Singh, G.; Patel, T.; Dave, R. The WHO 2022 classification of renal neoplasms (5th edition): Salient updates. Cureus 2024, 16, e58470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Yao, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Sun, L.; Zhang, G. Construction of a model for predicting the risk of pT3 based on perioperative characteristics in cT1 renal cell carcinoma: A retrospective study at a single institution. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2024, 22, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Velet, L.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, F. The difference in prognosis between renal sinus fat and perinephric fat invasion for pT3a renal cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stühler, V.; Rausch, S.; Kroll, K.; Scharpf, M.; Stenz, A.; Bedke, J. The prognostic value of fat invasion and tumor expansion in the hilar veins in pT3a renal cell carcinoma. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 3367–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X. Multiple patterns of perirenal fat invasion are associated with a poorer prognosis compared with isolated invasion: A proposal for a revision of T3aN0M0 TNM staging system. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresowik, T.P.; Johnson, M.T.; Joudi, F.N. Combined renal sinus fat and perinephric fat renal cell carcinoma invasion has a worse prognosis than either alone. J. Urol. 2010, 184, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.H.; Lyon, T.D.; Lohse, C.M.; Cheville, J.C.; Leibovich, B.C.; Boorjian, S.A.; Thompson, H. Prognostic evaluation of perinephric fat, renal sinus fat, and renal vein invasion for patients with pathological stage T3a clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.H.; Leibovich, B.C.; Cheville, J.C.; Webster, W.S.; Lohse, C.M.; Kwon, E.D.; Frank, I.; Zincke, H.; Blute, M.L. Is renal sinus fat invasion the same as perinephric fat invasion for pT3a renal cell carcinoma? J. Urol. 2005, 174, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margulis, V.; Tamboli, P.; Matin, S.F.; Meisner, M.; Swanson, D.A.; Wood, C.G. Location of extrarenal tumor extension does not impact survival of patients with pT3a renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2007, 178, 1878–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, S.A.; Gonzalez, J.R.; Benson, M.C.; McKiernan, J. Invasion of renal sinus fat is not an independent predictor of survival in pT3a renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2009, 103, 1622–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faiella, E.; Vergantino, E.; Vaccarino, F.; Bruno, A.; Perillo, G.; Grasso, R.F.; Zobel, B.B.; Santucci, D. A review of the paradigmatic role of adipose tissue in renal cancer: Fat measurement and tumor behavior features. Cancers 2024, 16, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.G.; Jeong, I.G.; Kwak, C.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, E. Reevaluation of renal cell carcinoma and perirenal fat invasion only. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-P.; Lin, D.-C.; Huang, W.-M.; Chen, M.; Chen, Y.-H. Comparison of perinephric fat measurements between malignant and benign renal tumours. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 3000605221125086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, S.; Aufderklamm, S.; Todenhofer, T.; Kruck, S.; Schuster, K.; Rausch, S.; Othman, A.; Notohamiprodjo, M.; Nikolaou, K.; Schwentner, C.; et al. Prediction of postoperative risks in laparascoping partial nephrectomy using RENAL, Mayo adhesive probability and renal pelvic score. Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Thiel, D.D.; Davidiuk, A.J.; Meschia, C.; Serie, D.; Custer, K.; Petrou, S.P.; Parker, A.S. Mayo adhesive probability score is associated with localized renal cell carcinoma progression-free survival. Urology 2015, 89, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, A.P.; Fram, E.B.; Sankin, A.; Kovac, E.; Srivastava, A.; DiVito, J.; Stern, J.M. A comparison of perinephric fat surface area and Mayo Adhesive Probability score in predicting malignancy in T1 renal masses. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2018, 36, 499.e17–499.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, M.; Liao, Z.; He, K.; Qu, W.; Li, J.; Kamel, I.; Chu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Incremental value of automatically segmented perirenal adipose tissue for pathological grading of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A multicenter cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 4221–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.M.; Feng, L.Y.; Liu, C.C.; Huang, W.P.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, P.Y.; Gao, J.B. Can visceral fat parameters based on computed tomography be used to predict occult peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer? World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 2310–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomassen, I.; van Gestel, Y.R.; van Ramshorst, B.; Luyer, M.; Bosscha, K.; Nienhuijs, S.W.; Lemmens, V.; de Hingh, I. Peritoneal carcinomatosis of gastric origin: A populationbased study on incidence, survival and risk factors. Int. J. Canc. 2014, 134, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsueh, S. Lymphatic tumor emboli of perirenal fat in patient with nephrotic syndrome receiving renal biopsy, ultimately revealed gastric adenocarcinoma with membranous glomerulonephritis. Ren. Fail. 2001, 23, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wua, T.; Lub, Y.X.; Wanga, J.X.; Yua, F.H.; Yang, M.Z.; Huang, Y.J.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, S.L.; Huang, L.; et al. Obesity promotes gastric cancer metastasis via diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2-dependent lipid droplets accumulation and redox. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Volonte, F.; Buchs, N.C.; Gayet-Ageron, A.; Pugin, F.; Gervaz, P.; Ris, F.; Morel, P. Perirenal fat surface area as a risk factor for morbidity after elective colorectal surgery. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 2014, 57, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- der Hagopian, O.; Dahlberg, M.; Heinius, G.; Nordberg, J.; Gustafsson, J.; Nordenvall, C.; Sandblom, G.; Farahnak, P.; Everhov, A.H. Perirenal fat surface area as a risk factor for perioperative difficulties and 30-day postoperative complications in elective colon cancer surgery. Color. Dis. 2018, 20, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.A.; Scavizzi, M.; Ministrini, S.; De Vuono, S.; Pucci, G.; Lupattelli, G. Morbid obesity and hypertension: The role of perirenal fat. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2018, 20, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckberg, S.E.; Dahlberg, M.J.A.; der Hagopian, O.S.; Farahnak, P.; Sandblom, G.; Nordenvall, C.; Everhov, A. Perirenal fat surface area and oncologic outcome in elective colon cancer surgery. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 2021, 64, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamid, A.; Ashkenazi, I.; Shapira-Rootman, M.; Olsha, O.; Alfici, R.; Bekhor, E.Y.; Abo-Mouch, I.; Zeina, A.R. Impact of increased visceral fat measured by CT on colon adenocarcinoma stage. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2017, 48, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakopoulou, E.V.; Lempesis, I.; Trakas, N.; Sklapani, P.; He, Y.; Spandidos, D. Lung cancer and obesity: A contentious relationship (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2024, 52, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervochon, R.; Bobbio, A.; Guinet, C.; Mansuet-Lupo, A.; Rabbat, A.; Regnard, J.F.; Roche, N.; Damotte, D.; Iannelli, A.; Alifano, M. Body mass index and total psoas area affect outcomes in patients undergoing pneumonectomy for cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbi, J.; Patnaik, S.; Pabla, S.; Zollo, R.; Smith, R.; Sass, S.; Srinivasan, A.; Petrucci, C.; Seager, R.; Conroy, J.; et al. Visceral obesity promotes lung cancer progression—Towards resolution of the obesity paradox in lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, Q.; Shen, T.; Welsh, E.; Teer, J.; Cai, J.; Cress, D.; Wu, J. Overexpression of major CDKN3 transcripts is associated with poor survival in lung adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattenmuller, J.; Wochner, R.; Muley, T.; Steins, M.; Hummler, S.; Teucher, B.; Wiskemann, J.; Kauczor, H.U.; Wielpütz, M.O.; Heussel, C.P. Prognostic impact of CT-quantified muscle and fat distribution before and after first-line-chemotherapy in lung cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabla, S.; Conroy, J.M.; Nesline, M.K.; Glenn, S.; Papanicolau-Sengos, A.; Burgher, B.; Hagen, J.; Giamo, V.; Andreas, J.; Lenzo, F.; et al. Proliferative potential and resistance to immune checkpoint blockade in lung cancer patients. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, T.I.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.J.; Yoon, D.K.; Cho, J.H.; Koh, S.K. Lung cancer metastasizing to ipsilateral renal cell carcinoma and contralateral perirenal space. BJU Int. 1999, 83, 512–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbur, A.C.; Turk, J.N.; Capek, V. Perirenal metastases from lung cancer: CT diagnosis. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1992, 16, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, D.L.; Heinze, S.B.; Dowling, R.J. Unusual presentation of perirenal lung metastases. Australas. Radiol. 2006, 50, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başara, I.; Altay, C.; Seçil, M. Unusual perirenal metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma. J. Urol. Surg. 2015, 3, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza, I.A.; Holgado, P.; Mingorance, D.; de Alda, A.L. Renal metastasis from lung cancer. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 7, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Villoldo, G.; Paleta, C.; Domenecchini, E.; Vaccaro, F.; Chacon, R.; Villaronga, A. Retroperitoneoscopic resection of metastatic melanoma in perirenal fat. Urology 2009, 74, S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandekar, K.R.; Satapathy, S.; Panaiyadiyan, S.; Kumar, R. Perirenal Fascia—An Uncommon Site of Metastases in Prostate Cancer Detected on 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 57, 254–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Abarzua-Catalan, L.; Trigo, C.; Delpiano, A.; Sanhueza, C.; García, K.; Ibañez, C.; Hor-mazábal, K.; Diaz, D.; Brañes, J.; et al. Leptin stimulates migration and invasion and maintains cancer stem-like properties in ovarian cancer cells: An explanation for poor outcomes in obese women. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21100–21119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquila, I.; Ricci, P.; Oliverio, A.; Gratteri, S. Role of the body mass index in the genesis of ascites in ovarian cancer: A forensic case and review of the literature. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 11, e226491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.F.; Czerniak, A.S.; Weiß, T.; Schoeder, C.T.; Wolf, P.; Seitz, O.; Meiler, J.; Beck-Sickinger, A. Ligand-binding and -scavenging of the chemerin receptor GPR1. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6265–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monjaras-Avila, C.U.; Lorenzo-Leal, A.C.; Luque-Badillo, A.C.; D’Costa, N.; Chavez-Munoz, C.; Bach, H. The Tumor immune microenvironment in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golijanin, B.; Malshy, K.; Khaleel, S.; Lagos, G.; Amin, A.; Cheng, L.; Golijanin, D.; Mega, A. Evolution of the HIF targeted therapy in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 121, 102645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuermann, T.H.; Li, Q.; Ma, H.W.; Key, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, R.; Garcia, J.; Naidoo, J.; Longgood, J.; Frantz, D.; et al. Allosteric inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor-2 with small molecules. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, E.M.; Rizzi, J.P.; Han, G.; Wehn, P.M.; Cao, Z.; Du, X.; Cheng, T.; Czerwinski, R.M.; Dixon, D.D.; Goggin, B.S.; et al. A small-molecule antagonist of HIF2α is efficacious in preclinical models of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5491–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, K.D.; Infante, J.R.; Lam, E.T.; Figlin, R.; Rini, B.; Brugarolas, J.; Zojwalla, N.; Lowe, A.; Wang, K.; Wallace, E.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation trial of PT2385, a first-in-class hypoxia-inducible factor-2α antagonist in patients with previously treated advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, H.E.; Tariq, Z.; Housden, B.E.; Jennings, R.; Stransky, L.; Perrimon, N.; Signoretti, S.; Kaelin, W., Jr. HIF-independent synthetic lethality between CDK4/6 inhibition and VHL loss across species. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaay0482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Nie, B.; Nie, T.; Hui, X.; Gao, X.; Lin, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, X.; Yuan, R.; et al. Visualization and quantification of browning using a Ucp1-2A-luciferase knock-in mouse model. Diabetes 2017, 66, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Qiu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Z.; Li, S.; Reyad-Ul Ferdous, M.; et al. Screening of FDA-approved drugs identifies sutent as a modulator of UCP1 expression in brown adipose tissue. EbioMedicine 2018, 37, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, H.; Song, Y.; Lee, H.-W. Emphasis on adipocyte transformation: Anti-inflammatory agents to prevent the development of cancer-associated adipocytes. Cancers 2023, 15, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.M.; Schwartz, K.; Pollak, M.; Graubard, B.I.; Li, Z.; Ruterbusch, J.; Rothman, N.; Davis, F.; Wacholder, S.; Colt, J.; et al. Serum leptin and adiponectin levels and risk of renal cell carcinoma. Obesity 2013, 21, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinmann, N.; Duivenvoorden, W.C.; Hopmans, S.N.; Beatty, L.K.; Qiao, S.; Gallino, D.; Lhotak, S.; Daya, D.; Paschos, A.; Austin, R.C.; et al. Underactivation of the adiponectin-adiponectin receptor 1 axis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Implications for progression. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2014, 31, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otvos, L., Jr.; Haspinger, E.; La Russa, F.; Maspero, F.; Graziano, P.; Kovalszky, I.; Lovas, S.; Nama, K.; Hoffmann, R.; Knappe, D.; et al. Design and development of a peptide-based adiponectin receptor agonist for cancer treatment. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelaria, P.; Rampoldi, A.; Harbuzariu, A.; Gonzalez-Perez, R. Leptin signaling and cancer chemoresistance: Perspectives. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 8, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsey, C.C.; Harbuzariu, A.; Daley-Brown, D.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Oncogenic role of leptin and Notch interleukin-1 leptin crosstalk outcome in cancer. World J. Methodol. 2016, 6, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, T.; Harbuzariu, A.; Lanier, V.; Lipsey, C.C.; Kirlin, W.; Yang, L.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Nanoparticle-linked antagonist for leptin signaling inhibition in breast cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 8, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Jiang, L.; Guo, W.; Shao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. The association between leptin level and breast cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Y.; Pan, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Luo, X.; Chen, L. The association between obesity related adipokines and risk of breast cancer: A meta analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75389–75399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgharzadeh, F.; Memarzia, A.; Alikhani, V.; Beigoli, S.; Boskabady, M.H. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: Key regulators of tumor progression and growth. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 47, 102039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigoraș, A.; Amalinei, C. The Role of Perirenal Adipose Tissue in Carcinogenesis—From Molecular Mechanism to Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers 2025, 17, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071077
Grigoraș A, Amalinei C. The Role of Perirenal Adipose Tissue in Carcinogenesis—From Molecular Mechanism to Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071077
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigoraș, Adriana, and Cornelia Amalinei. 2025. "The Role of Perirenal Adipose Tissue in Carcinogenesis—From Molecular Mechanism to Therapeutic Perspectives" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071077
APA StyleGrigoraș, A., & Amalinei, C. (2025). The Role of Perirenal Adipose Tissue in Carcinogenesis—From Molecular Mechanism to Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers, 17(7), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071077





