Abstract
Typical metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) usually suffer from a limited visible light-trapping ability and easy recombination of charge carriers, hindering their photocatalytic applications. Acetylacetone (AA), leveraging its exceptional coordination capabilities, serves as a versatile and effective modifier for enhancing the photocatalytic activity of MOFs via a post-synthesis approach. The synthesis of diketone-anchored MOFs with AA can be achieved by first diazotizing the amino groups on the ligands of MOFs, followed by a condensation reaction between AA and the resulting azide. Gradient AA loadings ranging from 17% to 98% were obtained, showcasing the tunability of this approach. Interestingly, a sub-stoichiometric effect was exhibited between the AA loading and the visible photocatalytic performance of the modified photocatalyst. The singlet oxygen yields of MIL-125-AA-37% and MIL-125-AA-54% were about 1.3 times that of MIL-125-AA-17% and 3.0 times that of MIL-125-AA-98%. The improved photocatalytic activity could be attributed to the fact that the AA modification altered the electron density of the Ti metal center, leading to the creation of a significant amount of oxygen defects. This alteration resulted in a reduction in the recombination of charge carriers and thus a better charge separation. In short, AA modification provides a new strategy to maximize the visible photocatalytic performance of MOFs.
1. Introduction
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), formed by the interconnection of metal centers and polydentate organic ligands to create a topological structure [1,2], represent a promising category of photocatalysts with diverse applications in numerous scenarios, including CO2 conversion [3,4], hydrogen evolution [5,6,7], pollutant degradation [8,9,10,11], and algae or bacteria inhibition [12,13]. The versatility offered by their metal centers and organic ligands presents a plethora of opportunities for tailoring and customizing photocatalysts to suit specific needs and applications [14,15,16].
In comparison to the limited applicability of in situ synthesis, which is restricted to a specific subset of MOF candidates [17], post-synthetic modifications (PSMs) involve chemical transformations or exchanges based on pre-synthesized MOFs. This approach enables the functionalization of a wide range of MOFs and serves as a potent strategy for modifying MOFs [18,19]. Coordination or covalent modifications can introduce photoactive substances on metal centers or organic ligands, which helps avoid the difficulties in direct synthesis caused by the incompatibility and instability of the introduced functional groups, as well as the disruption of metal–organic skeletons [5].
Most of the reported MOFs are known to primarily absorb light in the ultraviolet region [11,20]. To extend their light absorption capabilities for enhanced photocatalytic applications, a common strategy involves introducing organic chromophore groups through PSM of ligands [21]. Among the various approaches, the PSM of organic ligands in MOFs utilizing amine groups has been extensively explored [22,23]. One notable example is the modification of NH2-MIL-125 via diazotization, followed by the attachment of methyl red as an organic dye functional group, resulting in the formation of MR-MIL-125 [22]. The presence of conjugated aromatic rings in the ligand enhances light absorption in the visible region, thereby leading to outstanding photocatalytic performance, such as in the selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde [22].
Beta-diketones, such as acetylacetone (AA), possess inherent photoactivity attributed to the presence of enol tautomer. The incorporation of AA into Zr-metallic MOFs, resulting in UiO-66-AA, has been shown to expand the light absorption spectrum, facilitating the efficient generation of singlet oxygen through charge transfer processes [23]. It was demonstrated that the oxygen vacancies introduced during AA modification were responsible for the enhanced energy transfer in MIL-125-AA [24]. Moreover, significant improvements in photocatalytic performance have been observed in Cr- and Al-centered MIL-101 after modification with AA [25]. However, it is still unclear whether the PSM of MOFs with AA is tunable. Additionally, the quantitative relationship between the AA loading and the photocatalytic performance remains inadequately understood.
In this study, MIL-125-AA-x% materials varying in the degree of AA modifications were synthesized using the PSM method. The research highlighted the non-stoichiometric impact of AA loading on the photocatalytic performance of the materials, which underscores the importance of achieving a delicate balance between the structure and the electronic properties via modification of the photocatalysts.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Structure of AA-Modified MOFs
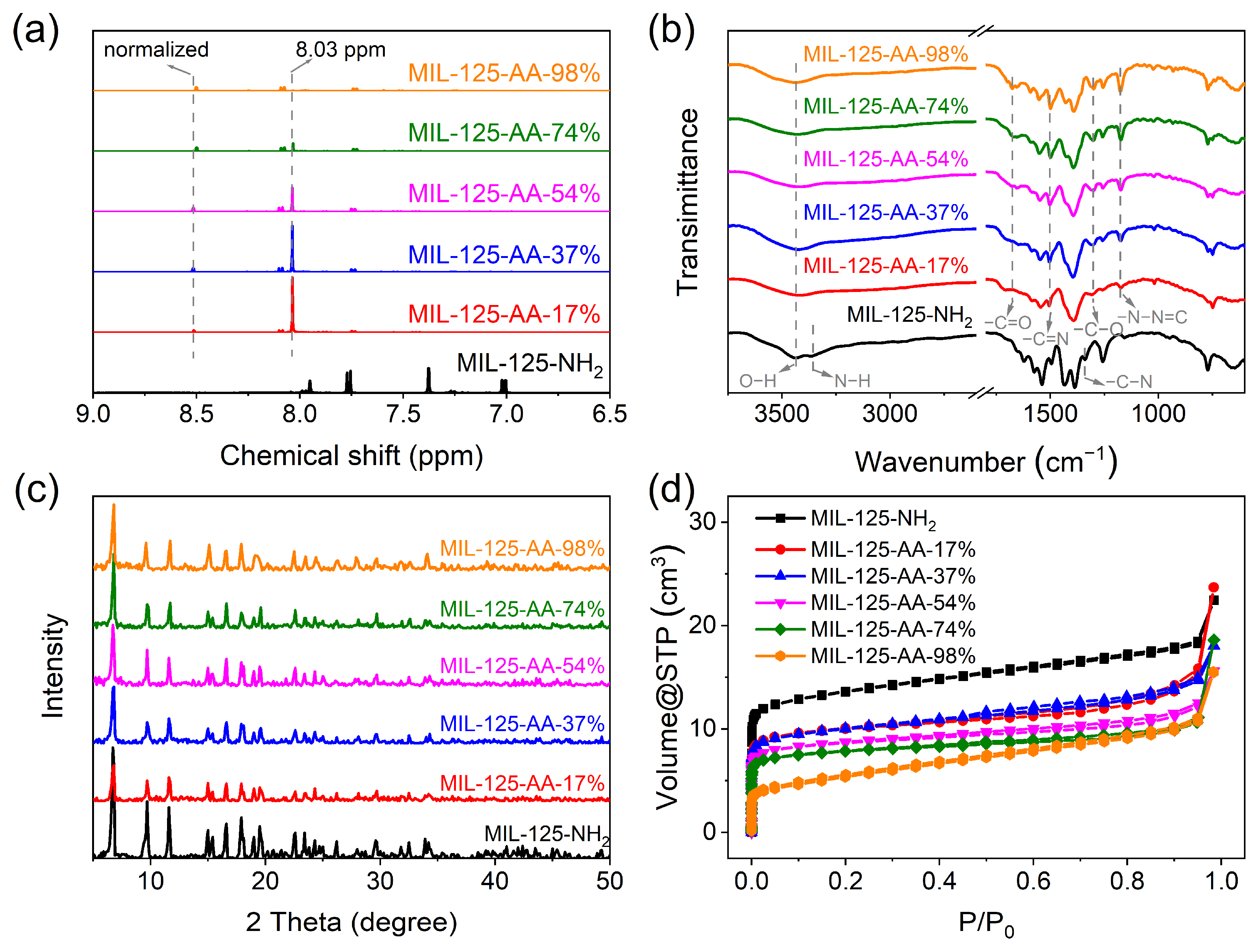
The tunable modification process of AA on MOFs is shown in Scheme S1. Starting from MIL-125-NH2, the BDC–NH2 ligand underwent a diazotization reaction to yield BDC–N=NH. Subsequently, a condensation reaction with AA led to the formation of the BDC-AA ligand. By adjusting the ratio of NH2 and AA, the extent of AA modification on the ligand could be precisely controlled, resulting in the synthesis of a material named MIL-125-AA-x%, where x% denoted the percentage of AA incorporated into the ligand. This attribution of the H atom was corroborated via the analysis of chemical shifts in the NMR H-spectrum, and the calculation of relative integral areas was employed to determine the actual loading of AA on the ligand. As shown in Figure 1a, the chemical shift at 8.03 ppm was identified as the three H on the benzene ring after ligand diazotization, as indicated by the MIL-125-N=NH profile (Figure S1), whereas the three distinct chemical shifts appearing at 8.52 ppm, 7.77 ppm, and 8.10 ppm in all the AA-modified MOFs corresponded to the H atoms at positions 1, 2, and 3 on the benzene ring of the ligand with AA modification [24]. Normalizing the peak area of the H atom at position 1, the precise loading amount of AA could be determined. The gradient loadings of AA in the five MOFs were quantified as 17%, 37%, 54%, 74%, and 98%, respectively, as detailed in Table S1.
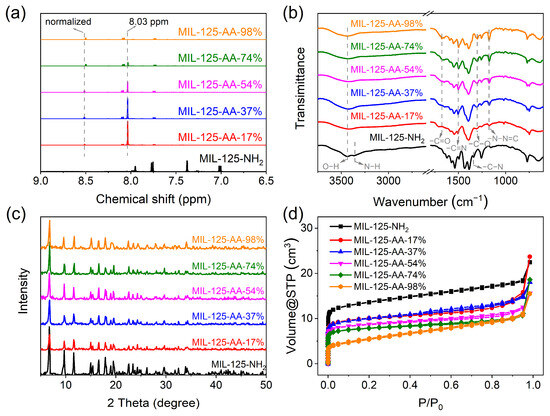
Figure 1.
Confirmation of the physicochemical structure of MIL-125-AA-x%. (a) H-NMR spectrum after digestion in DMSO-d6; (b) ATR-FTIR spectra; (c) XRD spectra; (d) nitrogen adsorption–desorption curves.
MIL-125-NH2 exhibited a prominent C-N stretching vibration signal at 1338 cm−1 in the IR spectrum (Figure 1b), which underwent attenuation in the MIL-125-AA-x% series of materials. This attenuation was accompanied by the emergence of stretching vibrations corresponding to the distinctive ligand structures of –C–O (1303 cm−1), –C=O (1676 cm−1), –C=N (1502 cm−1), and –N–N=C asymmetric stretching vibrations (1175 cm−1). Notably, the relative intensity of these signals exhibited a notable increase with higher values of x% [26]. The progressive changes in the relative intensities of the functional groups on the material surface served as a clear indicator of the successful attainment of gradient AA modification on the ligand. This observation underscores the systematic control and modulation of the material’s surface properties via the tailored incorporation of AA, leading to enhanced structural diversity and functionality in the MIL-125-AA-x% series.
The structural characteristics of the MOF materials following gradient AA modification were subjected to further scrutiny. Analysis of the XRD patterns (Figure 1c) pre- and post-AA modification revealed a high degree of similarity, suggesting that the original crystal structure of the MOFs remained largely unchanged even at elevated levels of AA modification (x% = 98%). This resilience indicated that the framework structure of the MOFs was robust and resistant to disruption by substantial AA incorporation [27,28]. As shown in Figure 1d and Figure S2 and Table S2, MIL-125-NH2 is a micro-mesoporous material with a large specific surface area (1478.00 m2 g−1) and pore volume (0.98 cm3 g−1). However, the introduction of AA induced notable alterations in the specific surface area of the material, with both the specific surface area and average pore volume of MIL-125-NH2 experiencing a discernible decrease after post-AA modification in the ligands. For example, the specific surface area and average pore volume of MIL-125-AA-17% was 592.70 m2 g−1 and 0.51 cm3 g−1, respectively. Moreover, this effect was more pronounced with higher levels of AA loading, indicating that the modification of ligands with AA resulted in the obstruction of the original voids within the material.
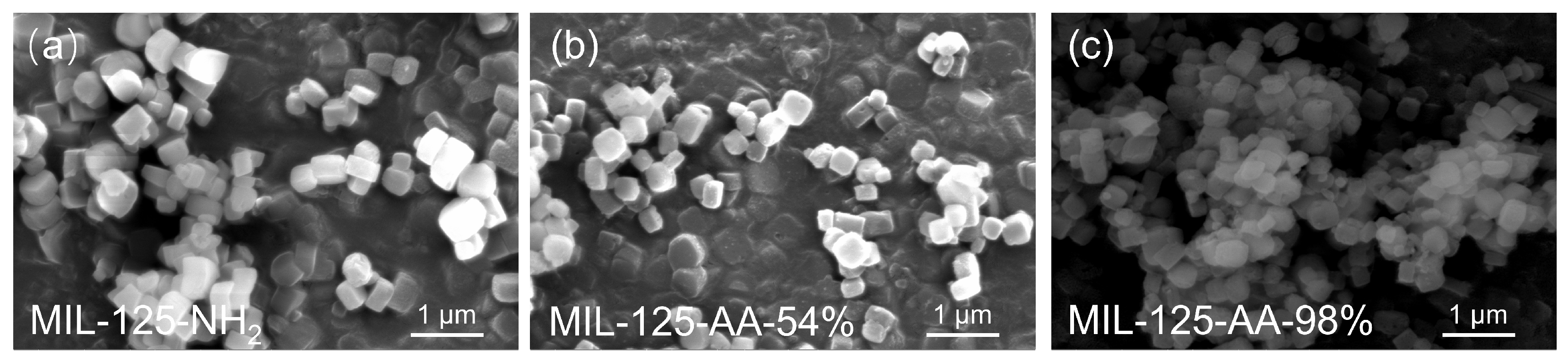
The microscopic morphology of the materials was observed by SEM, as shown in Figure 2. MIL-125-NH2 exhibits a typical tablet-like structure with a hundred-nanometer-scale diameter and retains its basic structure in the AA-modified materials. This was supported by the minor changes in the XRD patterns before and after AA modification. MIL-125-AA-54% retained a similar morphology to MIL-125-NH2 but with a slightly rougher surface due to pore structure clogging from AA modification. Conversely, MIL-125-AA-98% displayed a layered stacking outside the regular structure resulting from more significant AA modification, altering the morphology by filling and exposing the pore structure. Despite these variations, the overall impact of AA modification on the material’s morphology was minimal, with the original configuration largely maintained.
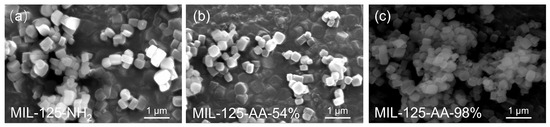
Figure 2.
Microscopic morphology of (a) MIL-125-NH2; (b) MIL-125-AA-54%; (c) MIL-125-AA-98%.
The post-synthetic modification of MIL-125-NH2 with AA induced transformations in the surface functional groups of the material without compromising its crystal structure and microscopic morphology dramatically. This approach represented a favorable, stable, and controllable strategy for modifying MOFs. However, it was observed that while the introduction of polar functional groups via AA modification was advantageous for facilitating photochemical reactions, excessive levels of AA loading could lead to a significant reduction in specific surface area, which could be detrimental to photocatalytic performance [15]. Consequently, a comprehensive investigation into the photocatalytic properties of MIL-125-AA-x% with varying levels of AA loading in the ligand was deemed essential to fully understand and optimize their photocatalytic behavior.
2.2. Effect of AA Modification on Photocatalytic Performance of MOFs
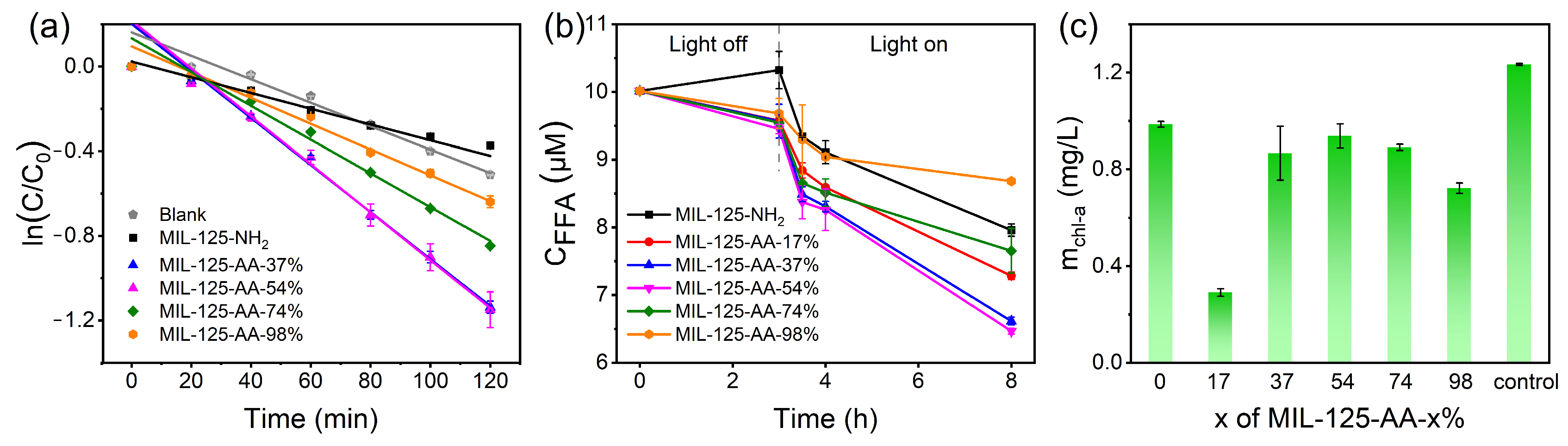
The assessment of the photocatalytic efficacy of the materials was conducted based on the decolorization ability of dye AO7, the consumption capacity of furfuryl alcohol (FFA), and the inhibitory effect on Microcystis aeruginosa. The results are depicted in Figure 3 and Table S3.
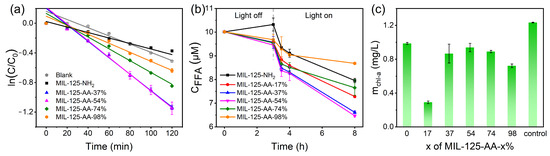
Figure 3.
Photocatalytic performance of MIL-125-AA-x% for different substrates. (a) AO7; (b) furfuryl alcohol (FFA); (c) Microcystis aeruginosa.
AO7, an azo dye with significant absorption in the visible region, is a common environmental pollutant in printing and dyeing wastewater, and its absorption spectrum is shown in Figure S3. In the context of photocatalytic degradation of AO7, all MIL-125-AA-x% materials with varying degrees of modification exhibited substantial enhancements compared to MIL-125-NH2. Notably, MIL-125-AA-54% and MIL-125-AA-37% showcased particularly commendable effects on AO7 degradation, in which the k1, AO7 was 3.0 times than that of MIL-125-NH2, surpassing the performance of other samples. To evaluate the photocatalyst performance with the other photocatalysts, the summary is shown in Table S4. The photocatalyst UiO-66-AA obtained by AA modification of Zr-centered MOFs in the literature exhibited k1, AO7 = 0.691 h−1 at a photocatalyst dosage of 1.0 g L−1 [23]. MIL-125-AA-54% in the present work achieved a similar degree of AO7 decolorization at a much smaller photocatalyst dosage (0.2 g L−1), which was precisely the significant advantage brought about by the optimization of the AA loadings. Compared with other MIL-125-NH2-based materials, the photocatalysts in this paper are more concise to synthesize with simple structures and have significant efficiency advantages when used for AO7 decolorization considering its reduction in photocatalyst dosage, demonstrating them as competitive candidates for photocatalyst [29,30]. Furthermore, as shown in Figures S4 and S5, MIL-125-AA-54% maintained a performance retention rate of 96.3% in the second cycle of use and did not cause more significant damage to the microscopic morphology than in MIL-125-NH2, demonstrating excellent cycling stability.
Previous studies have indicated that singlet oxygen serves as the primary active species in the MIL-125-AA photocatalytic system, underscoring the significance of this mechanism [24]. Therefore, the consumption capacity of furfuryl alcohol by the materials serves as a reflective indicator of their photocatalytic prowess. MIL-125-AA-54% and MIL-125-AA-37% demonstrated comparable and superior abilities in this regard, outshining the other AA-loaded materials. The consumption rate of furfuryl alcohol by these two materials exceeded that of MIL-125-AA-17% by 1.3 times and that of MIL-125-AA-98% by 3.0 times, highlighting their enhanced photocatalytic performance.
When these materials were used for cyanobacterial bloom control, the treated chlorophyll a content can indicate that all photocatalysts have an inhibitory effect on M. aeruginosa FACHB-905. MIL-125-AA-17% exhibited the lowest chlorophyll content after its treatment and achieved an inhibition ratio of 76.44%, indicating its optimal efficacy in algae inhibition.
All of the above photocatalytic experiments demonstrated that there was a non-stoichiometric effect between the AA loading and the photocatalytic performance. Similar findings have been reported in prior studies focusing on the impact of ligand amination levels in MOFs [31]. These observations prompted us to postulate that the mechanism by which AA modification influenced the performance of photocatalysts transcended mere structural and functional group alterations. By acknowledging the multifaceted nature of the interactions between AA modification and photocatalytic performance, we were able to unravel the intricate mechanisms governing the photocatalytic behavior of AA-modified materials and optimize their performance for diverse applications.
2.3. Effect of AA Modification on the Photovoltaic Properties of MOFs
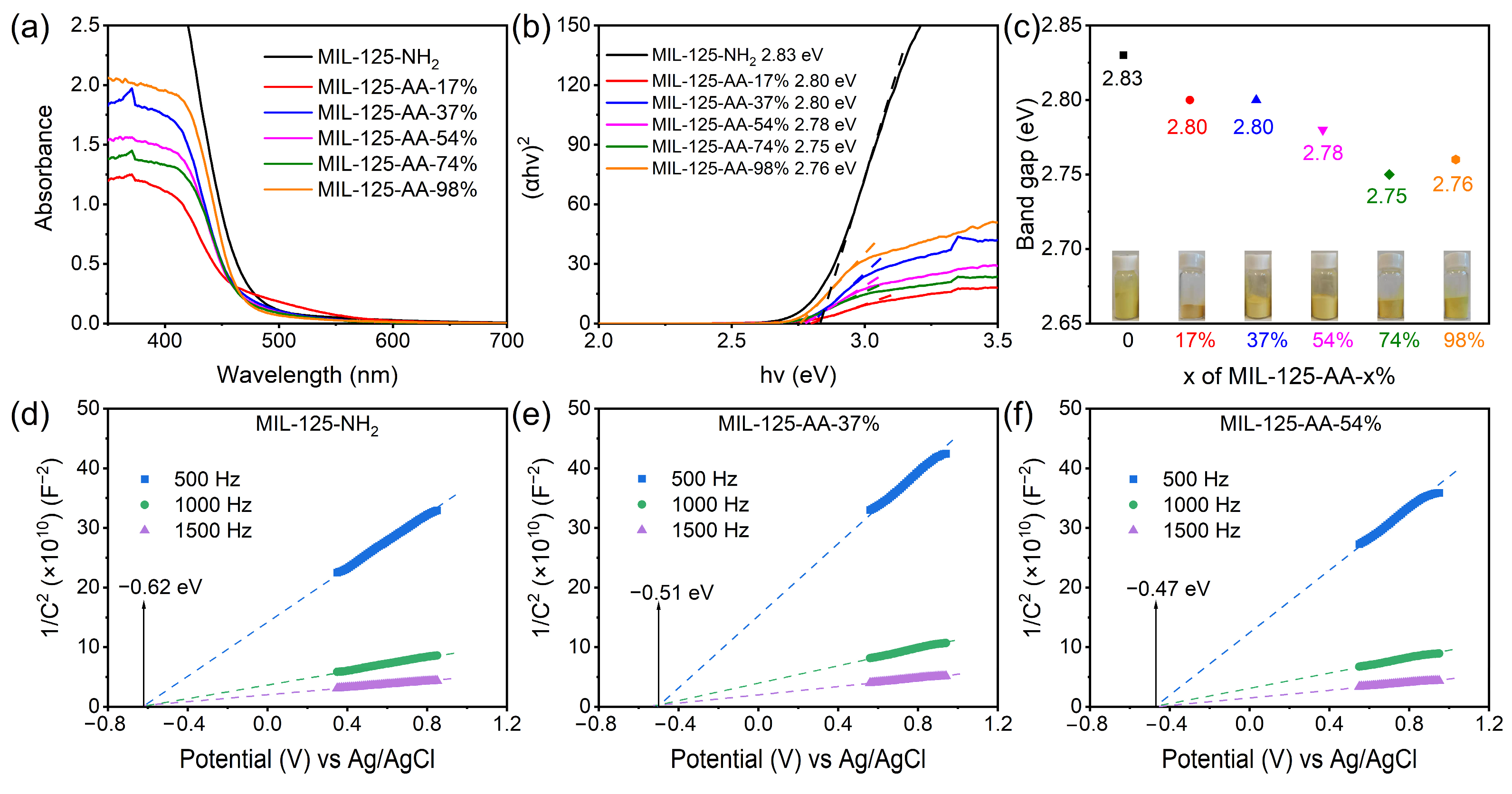
The assessment of the visible light absorption capability of MIL-125-AA-x% using UV-DRS (Figure 4) unveiled that the incorporation of AA acting as a photosensitive modifying group and modifying MIL-125-NH2 at varying loading levels facilitated the shift of the absorption edge towards longer wavelengths within the visible light spectrum. This led to a significant enhancement in its light absorption efficiency. Notably, MIL-125-AA-17% exhibited a distinct additional absorption band extending beyond 480 nm. The photosensitivity of AA was attributed to the presence of its enol tautomeric form [32]. The application of existing modification techniques preserved the α-hydrogen of AA, enabling it to exist in the enol form upon attachment to the ligand, thereby substantially bolstering the material’s light absorption capacity in the visible light range. Further examination of the material’s band gap utilizing the Tauk plot equation revealed that the band gap of MIL-125-AA-x% narrowed compared to MIL-125-NH2 to some extent. This narrowing of the band gap may serve as one of the factors contributing to the enhanced photocatalytic performance of the material following modification with AA.
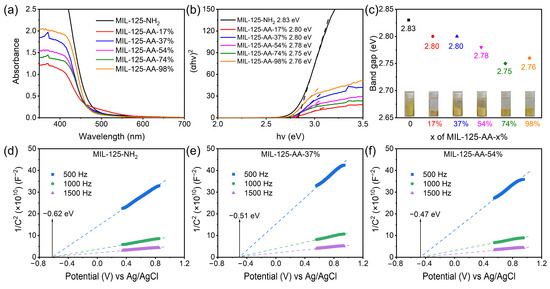
Figure 4.
Band structure of MIL-125-AA-x%. (a) UV–visible diffuse reflectance spectrum; (b) Tauc-plot; (c) Band gap; (d–f) Mott–Schottky curve of MIL-125-NH2, MIL-125-AA-37%, and MIL-125-AA-54%. (The dotted line was used to determine the intersection of the fitted line with the horizontal coordinate).
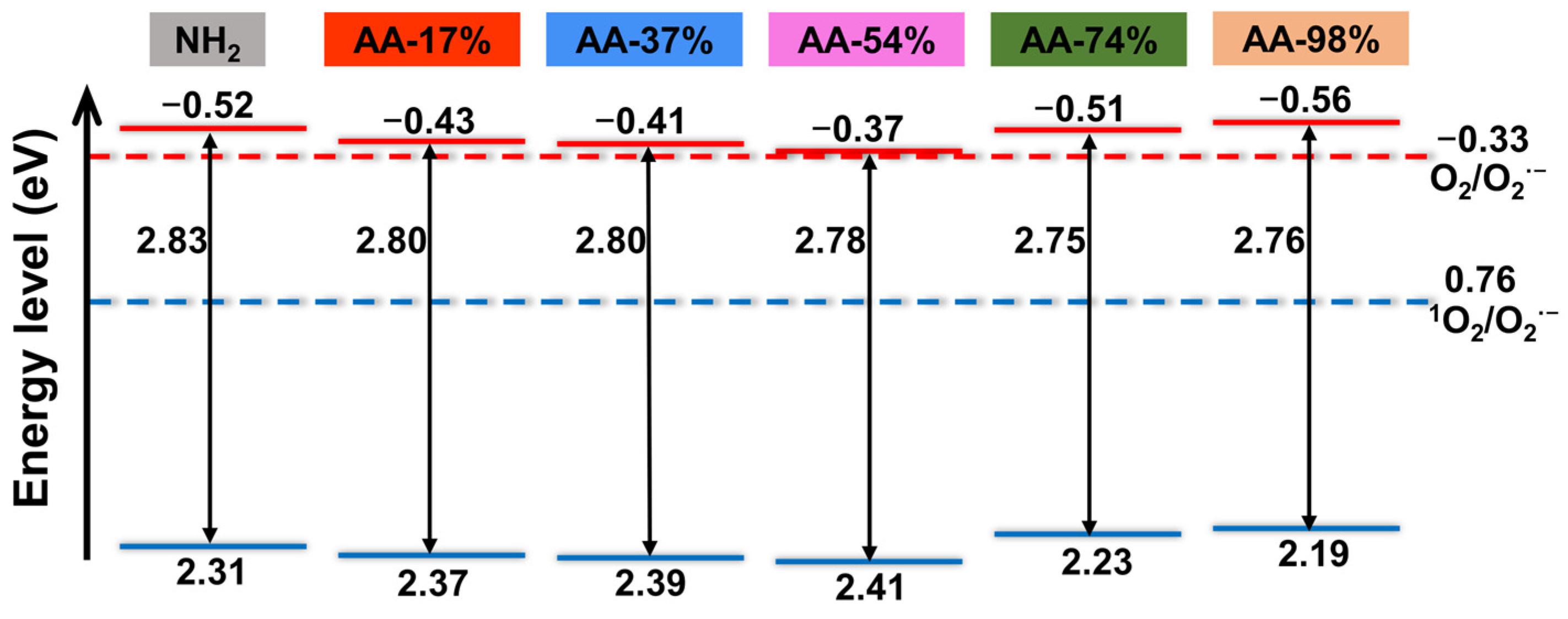
MIL-125-NH2 was identified as a typical n-type semiconductor [33], and the Mott–Schottky curve of MIL-125-AA-x% exhibited similarities to it, leading to further exploration of its flat band potential. In n-type semiconductors, the potential at the bottom of the conduction band is typically 0.1 eV lower than the flat band potential [34]. Analysis of Figure 4 and Figure S6 revealed that with the exception of MIL-125-AA-98%, the conduction band bottoms of MIL-125-AA-x% materials with varying AA modifications were all positioned higher than that of MIL-125-NH2 (−0.52 V vs. NHE). Notably, the most significant enhancements were observed in MIL-125-AA-54% (−0.37 V vs. NHE) and MIL-125-AA-37% (−0.41 V vs. NHE). When considering this in conjunction with the band gap [35], the material’s band structure of MIL-125-Xs (Xs represents the NH2 ligand or AA-x% ligand) is illustrated in Figure 4.
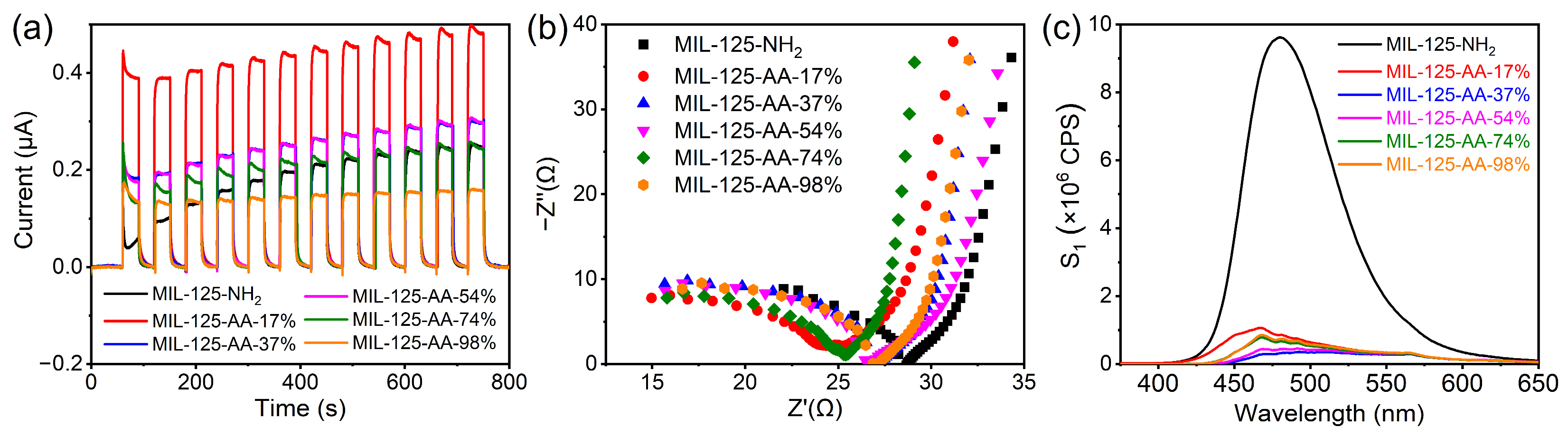
The photocurrent spectrum of the materials is depicted in Figure 5, where all MIL-125-AA-x% materials exhibited enhanced visible light response compared to MIL-125-NH2, with the exception of MIL-125-AA-98%. Among them, MIL-125-AA-17% demonstrated the most remarkable performance, followed by MIL-125-AA-37% and MIL-125-AA-54%, which exhibited similar enhancements. This observation suggests that an optimal proportion of AA modification could facilitate swift carrier separation under visible light [36], a crucial factor contributing to the material’s enhanced photocatalytic performance. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) semicircle diameters of all MIL-125-AA-x% materials were observed to be smaller than that of MIL-125-NH2, with MIL-125-AA-17% displaying the smallest diameter. This phenomenon indicates that AA modification could effectively diminish the interfacial charge transfer resistance within the materials, thereby enhancing carrier separation efficiency [37]. This finding aligns with the conclusion drawn from the photocurrent analysis, further underscoring the positive impact of AA modification on the material’s photocatalytic performance.
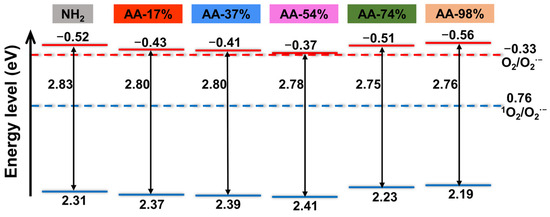
Figure 5.
Band structure of MIL-125-AA-x%.
As the fluorescence emission spectrum and fluorescence lifetime spectrum shown in Figure 6c and Figure S7, in contrast to MIL-125-NH2, MIL-125-AA-x% materials exhibited a notable decrease in fluorescence emission intensity and an increase in the average fluorescence lifetime, offering compelling evidence that AA modification plays a pivotal role in diminishing carrier recombination [36,38]. Notably, MIL-125-AA-37% and MIL-125-AA-54% demonstrated the least amount of carrier recombination in conjunction with their heightened photocurrent response, underscoring their exceptional capacity for efficient carrier separation. This phenomenon elucidates why these two materials excel in the decolorization of AO7 and the generation of singlet oxygen.
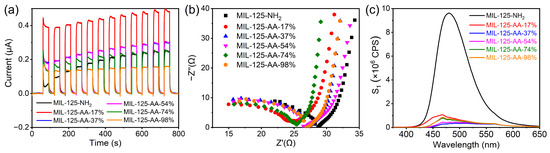
Figure 6.
Photoelectric properties and fluorescence response of MIL-125-AA-x%. (a) Photocurrent; (b) electrochemical impedance spectrum; (c) fluorescence emission spectrum.
2.4. Mechanisms of How Tunable AA Modification Boosted the Photocatalytic Performance of MOFs
In Table 1, the elements present in MIL-125-Xs are C, O, Ti, and N, as determined via XPS wide-spectrum scanning (Figure S8). By analyzing the elemental ratios, it was anticipated that the theoretical C content in the material would increase with the addition of AA modification to the ligand. However, the overall XPS spectrum results revealed a reduction in the relative carbon content on the surfaces of MIL-125-AA-17% and MIL-125-AA-54% materials, suggesting that the introduction of a lower amount of AA on the ligand exposed the metal center Ti more prominently on the material surface. With an increase in AA modification to 98%, the influence of AA as a surface modifier in elevating the C and O content became apparent, indicating that the excess AA did not occupy the material’s pores but instead became exposed on the surface. This observation aligns with the fact that MIL-125-AA-98% did not exhibit a significant decrease in specific surface area and pore volume but did show a notable increase in surface functional groups compared to the materials with slightly lower AA content.

Table 1.
Elemental composition and oxygen atom attribution in MIL-125-AA-x%.
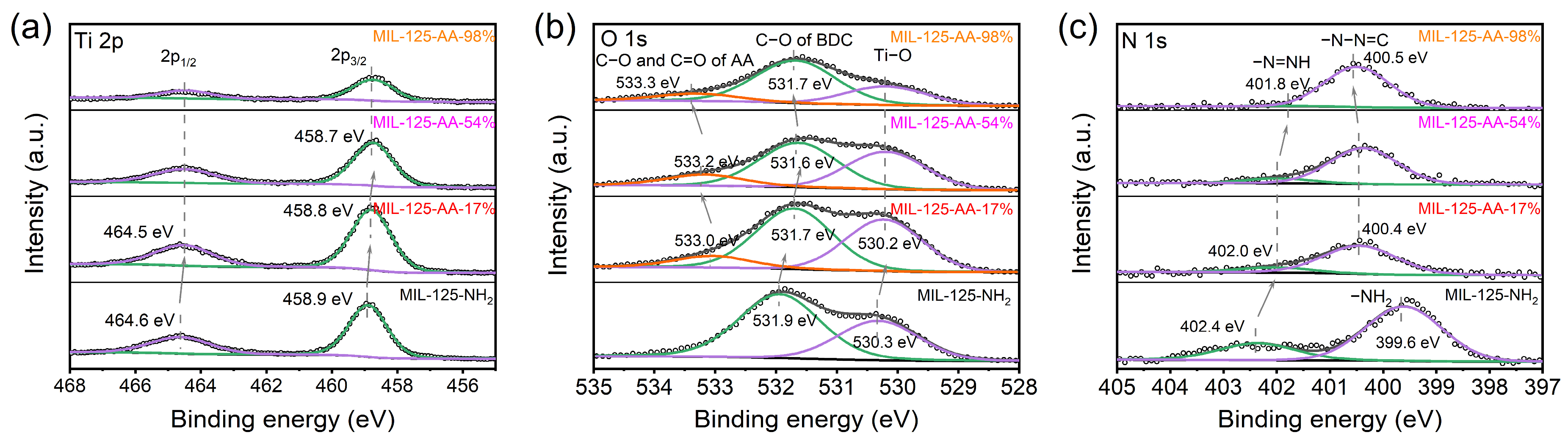
The Ti 2p binding energy exhibited a notable shift towards lower energy levels following AA modification in the material, as illustrated in Figure 7a. Specifically, the Ti 2p1/2 binding energy was 464.6 eV in MIL-125-NH2 and 464.5 eV in materials with 17% or higher AA modification. Similarly, the Ti 2p3/2 binding energy decreased from 458.9 eV in MIL-125-NH2 to 458.8 eV in MIL-125-AA-17% and further to 458.7 eV in MIL-125-AA-54%, indicating that AA modification led to a reduction in the electron cloud density surrounding the Ti metal center. This phenomenon suggested the presence of coordinatively unsaturated Ti3+ ions within the Ti-oxo clusters, hinting at the existence of oxygen vacancies within the material [39,40].
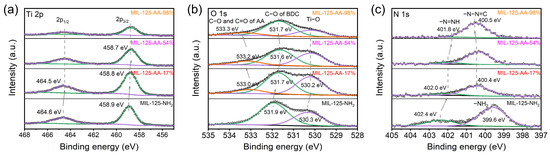
Figure 7.
XPS spectra of MIL-125-AA-x%. (a) Ti 2p spectrum; (b) O 1s; (c) N 1s.
Deconvolution of the O1s spectra peaks provided insight into the chemical environment of oxygen atoms, revealing their specific positions (Figure 7b). In MIL-125-NH2, peaks corresponding to Ti–O and C–O in BDC were detected at binding energies of 530.3 eV and 531.9 eV, respectively. Following AA modification in MIL-125-AA-17%, these peaks shifted to 530.2 eV and 531.7 eV, accompanied by additional peaks corresponding to C–O and C=O in AA at 533.0 eV.
Analyzing the allocation of oxygen atoms, as depicted in Table 1, it was observed that in MIL-125-AA-17% and MIL-125-AA-54%, despite significant differences in AA loading, the proportions of oxygen atoms assigned to the Ti-oxo cluster and the BDC were nearly identical. This finding suggests that across a wide range of AA loadings, the incorporation of AA may potentially result in a more balanced distribution of oxygen atoms between the metal center and ligands [6]. Considering the presence of oxygen vacancies within the Ti-oxo clusters, it was plausible to infer that a relatively stable state existed in the level of oxygen vacancies.
With the AA loading escalating to 54% and 98%, peaks associated with Ti–O and C–O in BDC exhibited a shift towards lower binding energies, whereas peaks linked to oxygen atoms in AA shifted towards higher binding energies. Given that Ti-oxo clusters contribute to the top of the conduction band and ligands contribute to the bottom of the valence band [41], this transition elucidates the reduction in the bandgap of the material subsequent to AA modification.
Further analysis of N1s spectra confirmed the successful AA modification accomplished via diazonium coupling. Peaks attributed to –N=NH and –N–N=C exhibited shifts towards lower and higher binding energies, respectively, as the AA loading increased from 17% to 54% and 98%. This observation implies that the extent of AA modification impacts the conjugate stabilization state of the keto functional group with the diazonium functional group.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
All chemicals were analytically pure and were used without further purification.
3.2. Synthesis of MIL-125-Xs
MIL-125-NH2 was prepared using a solvothermal method as described in the literature [22,42].
The attachment of AA to the ligand was designed with reference to the method in the literature [23]. The preset gradients of AA modification were 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100%, and the actual adjusted ratios of NaNO2 and AA were 0.2:1, 0.3:1, 0.6:1, 1:1, and 20:1, respectively. Taking NaNO2: AA = 0.3:1 as an example, the synthesis method was as follows: At 0 °C, NaNO2 solution (0.077 g, 1.11 mmol, 0.3 equivalents) in H2O (1.25 mL) was added dropwise to a solution of MIL-125-NH2 (1.020 g, 3.7 mmol amine, 1.0 equivalent amine), acetic acid (5.00 mL), and 12 M HCl (0.85 mL), followed by stirring for 1 h at 0 °C. The resulting solution was then transferred to a solution of pentane-2,4-dione (0.76 mL, 2.0 equivalents) and sodium acetate (0.905 g, 11.05 mmol, 3.0 equivalents) in ethanol (3.50 mL) and H2O (2.00 mL) to form a precipitate, which was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. The precipitate was collected by filtration, washed 5 times with H2O, followed by washing 3 times with a mixed solution of H2O/ethanol in a volume ratio of 1:1, and dried under vacuum overnight.
3.3. Characterization
3.3.1. Structural Characterization of MIL-125-Xs
H-NMR spectra were recorded using a Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer (DRX 500, Bruker Germany, Berlin, Germany) to quantify the actual amount of AA modification on the ligand.
The bonding structure on the surface of the materials was characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy using a Nicolet iS5 FTIR spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Co., Waltham, MA, USA) in single attenuation total reflectance (ATR) mode.
The crystal structure of MIL-125-Xs was analyzed by X’TRA (ARL Co., Lugano, Switzerland) X-ray diffractometer (XRD) at room temperature.
The pore and surface structures of MIL-125-Xs were analyzed using nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms recorded at −196 °C on an ASiQ instrument (Quantachrome Co., Boynton Beach, FL, USA).
The microscope morphology of MIL-125-Xs was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) measurement using an Ultra 55 microscope (Carl Zeiss AG, Jena, Germany). For pretreatment, the samples were dusted on an adhesive conductive carbon belt and coated with 10 nm Au.
3.3.2. Optical Properties of MIL-125-Xs
The UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra (UV-vis DRS) of MIL-125-Xs were tested on a UV-vis spectrophotometer (UV 2700, Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan). Subsequently, the bandgap energy (Eg) was calculated based on the Tauc equation using the Kubelka–Munk model. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra and fluorescence lifetime spectra of MIL-125-Xs were detected using a fluorescence spectrometer (FluoroMax-4, HORIBA Scientific Co., Kyoto, Japan).
3.3.3. Electrochemical Characterization of MIL-125-Xs
Photocurrent curves, Mott–Schottky curves, and electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) of the MIL-125-Xs materials were obtained in a three-electrode cell system using an electrochemical constant potential instrument (CHI600E, CH Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). A platinum sheet was used as the counter electrode, an Ag/AgCl electrode (3.0 M KCl) was used as the reference electrode, and the electrolyte solution was 0.2 M Na2SO4. The working electrode was obtained by coating a certain amount of MIL-125-Xs slurry on a fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) glass (0.25 cm2) and drying it naturally at room temperature.
3.4. Photocatalytic Performance
Experiments were conducted to evaluate the photocatalytic performance of the materials by using AO7, furfuryl alcohol (FFA), and Microcystis aeruginosa as substrates.
The treatment effect experiments on AO7 and furfuryl alcohol were performed using a PLS-SXE300D photoreactor equipped with a white light disc (Beijing Perfect Light Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) to provide the reaction conditions for the photoreactions. In each experiment, 10 mg of MIL-125-Xs was added to 50 mL of the AO7 solution at an initial concentration of 0.1 mM of (C0). The pH of the solution was adjusted to 4.5 with HCl. Before the photocatalytic reaction started, the suspension was stirred for 3 h in darkness to achieve adsorption–desorption equilibrium. At specific time intervals, a certain amount of the suspension was removed and filtered through a 0.22 μm membrane to remove the catalyst. For the stability test, the materials were collected by filtration after being used for the first time, and a new AO7 solution was added for the second cycle. The concentration of AO7 at different reaction times was determined by measuring the absorbance value at 484 nm using a UV–visible spectrophotometer (UV-2700, Shimadzu Co., Japan). The initial concentration of FFA was 10 μM and reached adsorption saturation before the start of the light reaction. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC, Ultimate 3000, Dionex Co., Ltd., Sunnyvale, CA, USA) was used to determine the concentration of FFA at specific moments.
The inhibition effect experiment on Microcystis aeruginosa (FACHB-905) was conducted using a heterogeneous photocatalytic reactor equipped with a 500 W xenon lamp. The Microcystis aeruginosa used in this study was collected at the logarithmic phase, and the algal solution was adjusted to OD680 = 0.2 before the reaction, which corresponds to a cell density of 3 × 106 cells/mL. A portion of 50 mL of the algal solution and 20 mg of MIL-125-Xs were added to tubes for irradiation. After irradiation, the cells were filtered, enriched, and then soaked overnight in 95% ethanol at 4 °C. The content of chlorophyll a was calculated with Equation (1).
mChl-a (mg/L) = 13.95 × OD665 − 6.88 × OD649
The inhibition ratio was calculated based on the content of chlorophyll a of the control sample and treatment samples.
Inhibition ratio (100%) = (mChl-a, control − mChl-a, treatment)/mChl-a, control
4. Conclusions
A series of MIL-125-AA-x% materials were synthesized using the PSM strategy, which showcases a progressive impact on the chemical stoichiometry of surface functional groups and the specific surface area but a non-stoichiometric effect on catalytic performance under visible light. MIL-125-AA-37% and MIL-125-AA-54% demonstrated superior performance in the generation of singlet oxygen, whereas MIL-125-AA-17% excelled in algal inhibition. Upon analysis of their band structures and photoelectric effects, it was revealed that all levels of AA modification could reduce the band gap, but only those with the appropriate amount of AA could achieve an improved photocatalytic performance. The match between the level of defection and the generation of singlet oxygen stemmed from the appropriately distributed oxygen vacancies within the Ti-oxo clusters and ligands. The results demonstrate that PSM with AA provides a highly tunable approach for the modification of MOFs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal14060367/s1. Scheme S1: The synthesis route from MIL-125-NH2 to MIL-125-AA; Figure S1: H-NMR spectrum of the product after azidation of MIL-125-NH2; Figure S2: Pore size distribution of MIL-125-Xs; Figure S3: The absorption profile of 0.1 mM AO7 (pH 4.5); Figure S4: Stability test of MIL-125-AA-54% in cycle run of photocatalytic degradation of AO7 (0.1 mM, pH 4.5) under visible-light irradiation; Figure S5: Microscopic morphology of (a) MIL-125-NH2; (b) MIL-125-AA-54% after used for photocatalysis; Figure S6: Mott–Schottky curve of (a) MIL-125-AA-17% (b) MIL-125-AA-74% (c) MIL-125-AA-98%; Figure S7: Fluorescence lifetime spectrum of MIL-125-AA-x% at the emission wavelength of 570 nm; Figure S8: XPS wide-scan spectrum of several MIL-125-AA-x% materials; Table S1: Confirmation of H attribution and relative integral area in the H-NMR spectrum of MIL-125-AA-x%; Table S2: The specific surface area, pore volume, and average pore diameter of MIL-125-Xs based on the BET test; Table S3: Photocatalytic performance of MIL-125-AA-x% for different substrates; Table S4: Summary of AO7 decolorization efficiencies over various catalysts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z.; methodology, K.W.; validation, K.W. and J.Y.; formal analysis, K.W., J.Y., H.Z. and S.W.; investigation, K.W.; resources, S.Z.; data curation, K.W.; writing—original draft preparation, K.W.; writing—review and editing, S.Z., J.Y. and S.W.; visualization, K.W. and H.Z.; supervision, S.Z.; project administration, S.Z.; funding acquisition, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22176087 and 22336002).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Hong Chen of Southern University of Science and Technology for the help in characterization of the materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Figueroa-Quintero, L.; Villalgordo-Hernández, D.; Delgado-Marín, J.J.; Narciso, J.; Velisoju, V.K.; Castaño, P.; Gascón, J.; Ramos-Fernández, E.V. Post-Synthetic Surface Modification of Metal–Organic Frameworks and Their Potential Applications. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2201413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljammal, N.; Jabbour, C.; Chaemchuen, S.; Juzsakova, T.; Verpoort, F. Flexibility in Metal–Organic Frameworks: A Basic Understanding. Catalysts 2019, 9, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, T.K.; De, D.; Bharadwaj, P.K. Metal–organic frameworks for the chemical fixation of CO2 into cyclic carbonates. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 408, 213173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Tan, X.; Zheng, L.; Tan, D.; Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, F.; et al. Improved photocatalytic performance of metal–organic frameworks for CO2 conversion by ligand modification. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 7637–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Y.; Pan, D.L.; Chen, H.; Bu, X.B.; Gao, Y.X.; Gao, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, G.S.; Wang, G.; Cao, S.L.; et al. A Methylthio-Functionalized-MOF Photocatalyst with High Performance for Visible-Light-Driven H2 Evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9864–9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Xiao, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q. Rich oxygen vacancies, mesoporous TiO2 derived from MIL-125 for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 9704–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Li, W.; Sun, Y. Metal–Organic Frameworks and Their Derivatives for Photocatalytic Water Splitting. Inorganics 2017, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Dong, H.; Chen, X.; Leng, L.; Wu, Z.; Peng, L. In situ synthesis of In2S3@MIL-125(Ti) core–shell microparticle for the removal of tetracycline from wastewater by integrated adsorption and visible-light-driven photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 186, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Huang, R.; Wang, X.; Ying, S.; Yan, G.; Wu, L. Functionalized MIL-68(In) for the photocatalytic treatment of Cr(VI)-containing simulation wastewater: Electronic effects of ligand substitution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 464, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.-W.; Liu, J.-M.; Zhao, N.; Li, C.-Y.; Wang, Z.-H.; Wang, S. Benzothiadiazole functionalized Co-doped MIL-53-NH2 with electron deficient units for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A and ofloxacin under visible light. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 122011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedia, J.; Muelas-Ramos, V.; Peñas-Garzón, M.; Gómez-Avilés, A.; Rodríguez, J.; Belver, C. A Review on the Synthesis and Characterization of Metal Organic Frameworks for Photocatalytic Water Purification. Catalysts 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, A.; Wang, C.; Ding, P. Inactivation of harmful algae using photocatalysts: Mechanisms and performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhi, S.; Wang, X.; Sun, J. Visible-light-driven heterostructured g-C3N4/Bi-TiO2 floating photocatalyst with enhanced charge carrier separation for photocatalytic inactivation of Microcystis aeruginosa. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syzgantseva, M.A.; Ireland, C.P.; Ebrahim, F.M.; Smit, B.; Syzgantseva, O.A. Metal Substitution as the Method of Modifying Electronic Structure of Metal–Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6271–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, S.A.; Kwon, E.E.; Qasim, M.; Kim, K.-H.; Kim, T.; Kukkar, D.; Dou, X.; Ali, I. Metal-organic framework as a photocatalyst: Progress in modulation strategies and environmental/energy applications. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2020, 81, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, B.; Chen, L. First-Principles Study of Microporous Magnets M-MOF-74 (M = Ni, Co, Fe, Mn): The Role of Metal Centers. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 9356–9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhao, D. Post-synthetic modification of metal-organic framework-based membranes for enhanced molecular separations. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 491, 215259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Hao, M.; Wang, D.; Li, Z. Post-synthetic modifications (PSM) on metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) for visible-light-initiated photocatalysis. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 13201–13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Natarajan, S.; Mani, P.; Pankajakshan, A. Post-Synthetic Modification of Metal–Organic Frameworks Toward Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2006291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Yao, J. Modified metal-organic frameworks as photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 231, 317–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, B.; Wang, S. Porphyrin-Based Metal-Organic Framework Materials: Design, Construction, and Application in the Field of Photocatalysis. Molecules 2024, 29, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasalevich, M.A.; Goesten, M.G.; Savenije, T.J.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Enhancing optical absorption of metal–organic frameworks for improved visible light photocatalysis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10575–10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fang, W.; Ma, J. Intraligand charge transfer boosts visible-light-driven generation of singlet oxygen by metal-organic frameworks. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 273, 119087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, W.; Jin, J.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, S. Oxygen-vacancy-mediated energy transfer for singlet oxygen generation by diketone-anchored MIL-125. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 292, 120197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, K.; Huang, W.; Yang, J.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, S. A joint mechanism for singlet oxygen generation by diketone-anchored MIL-101: Exciton-mediated energy transfer and photosensitization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 626, 118360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Qi, S.; Cao, Y.; Shen, L.; Au, C.; Jiang, L. Morphology evolution of acetic acid-modulated MIL-53(Fe) for efficient selective oxidation of H2S. Chin. J. Catal. 2021, 42, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Bao, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z. A post-synthetic modified NH2-MIL-125 (Ti) catalyst for boosting photochemical Cr (VI) reduction. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 172, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, A.; Fu, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.-C. Enhanced photo-Fenton activity and stability for sulfamethoxazole degradation by FeS2@TiO2 heterojunction derived from MIL-125. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, B.; Cai, J.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, L. Fabrication of NH2-MIL-125(Ti) nanodots on carbon fiber/MoS2-based weavable photocatalysts for boosting the adsorption and photocatalytic performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 611, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Cheng, M. Graphite oxide as an electronic conductor modified ZIF-8/NH2-MIL-125(Ti) hybrid material used as a photocatalyst for removal of organic dyes under visible light irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 68691–68700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, M.B.; Wang, X.; Ellezam, L.; Ersen, O.; Fontecave, M.; Sanchez, C.; Rozes, L.; Mellot-Draznieks, C. Maximizing the Photocatalytic Activity of Metal–Organic Frameworks with Aminated-Functionalized Linkers: Substoichiometric Effects in MIL-125-NH2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8222–8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, H.; Tratnyek, P.G. Advanced redox processes for sustainable water treatment. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Mubarak, N.S.; Foo, K.Y.; Schneider, R.; Abdelhameed, R.M.; Sabar, S. The chemistry of MIL-125 based materials: Structure, synthesis, modification strategies and photocatalytic applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Wang, S.; Ding, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, X. Amine-functionalized zirconium metal–organic framework as efficient visible-light photocatalyst for aerobic organic transformations. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 11656–11658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, T.; Sun, X. Trace to the Source: Self-Tuning of MOF Photocatalysts. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2300086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Quan, X.; Yu, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S. Nanoscale lightning rod effect in 3D carbon nitride nanoneedle: Enhanced charge collection and separation for efficient photocatalysis. J. Catal. 2019, 375, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Zha, Z.; Li, Y.; Geng, X.; Yang, J.; Cui, S.; Yang, J. Visible-light-driven MIL-53(Fe)/BiOCl composite assisted by persulfate: Photocatalytic performance and mechanism. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 380, 111862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Fan, Y.; Quan, X.; Yu, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S. Energy-transfer-mediated oxygen activation in carbonyl functionalized carbon nitride nanosheets for high-efficient photocatalytic water disinfection and organic pollutants degradation. Water Res. 2020, 177, 115798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X.; Xing, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, T.; Gao, S.; Lu, S.; Chen, G.; Asiri, A.M.; et al. Identifying the Origin of Ti3+ Activity toward Enhanced Electrocatalytic N2 Reduction over TiO2 Nanoparticles Modulated by Mixed-Valent Copper. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, X.-S.; Philo, D.; Ichihara, F.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Qiu, T.; Wang, S.; Ye, J. Toward visible-light-assisted photocatalytic nitrogen fixation: A titanium metal organic framework with functionalized ligands. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 267, 118686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobov, N.; Goesten, M.G.; Gascon, J. Metal–Organic Frameworks: Molecules or Semiconductors in Photocatalysis? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 26038–26052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-M.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Dao, X.-Y.; Wang, S.-Q.; Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Sun, W.-Y. Crystallographic facet heterojunction of MIL-125-NH2(Ti) for carbon dioxide photoreduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 298, 120524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).