Abstract
Polydopamine (PDA), inspired by the adhesive mussel foot proteins, is widely applied in chemical, biological, medical, and material science due to its unique surface coating capability and abundant active sites. Energetic materials (EMs) play an essential role in both military and civilian fields as a chemical energy source. Recently, PDA was introduced into EMs for the modification of crystal phase stability and the interfacial bonding effect, and, as a result, to enhance the mechanical, thermal, and safety performances. This mini-review summarizes the representative works in PDA modified EMs from three perspectives. Before that, the self-polymerization mechanisms of dopamine and the methods accelerating this process are briefly presented for consideration of researchers in this field. The future directions and remaining issues of PDA in this field are also discussed at last in this mini-review.
1. Introduction
In 2007, Lee et al. proposed the surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings, which is inspired by the main component of adherent proteins in mussel, namely, dopamine [1,2]. Dopamine is able to form adhesive polydopamine (PDA) thin films on various material surfaces by oxidative self-polymerization in an alkaline aqueous medium. Fascinatingly, PDA films can also provide an important platform for secondary reactions since there are many reactive groups, such as catechol, amine, and imine, on its surface, which can serve as the starting points for covalent modification with desired molecules [3].
Due to its unique surface-coating capability and abundant active sites, unsurprisingly, PDA was rapidly applied in many fields across the chemical, biological, medical, and material sciences [4]. In barely more than a decade, the physicochemical properties of PDA were extensively studied, covering its biocompatibility and biodegradation, electrical conductivity, metal ions chelating and redox activities, and other potential properties. Among all these attractive features, its adhesive property and chemical reactivity are closely related, while they are also the basis of the vast majority of applications [5,6]. The adhesive properties of different mussel foot proteins with diverse compositions and contents of 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-L-alanine (DOPA, a derivative of PDA) were investigated, and it was concluded that possible interaction mechanisms between DOPA and substrates involve electrostatic, hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interactions, cation–π, π–π stacking, and metal complexation [7]. Further, the roughness of the PDA nanomembrane was also observed as a factor deciding its adhesion [8]. The abovementioned generalizable theories and trends were critical for PDA coating and surface functionalization in engineering practices.
Energetic materials (EMs) are very important power resources for civilian and military applications, covering explosives, propellants, and pyrotechnics, which release energy in the forms of combustion and explosion. PDA was introduced into EMs until very recently. Lin et al. fabricated a very compact PDA film on the surface of an explosive crystal, octogen (HMX), which not only improved the stability of the crystal phase, but also synergistically enhanced the mechanical, thermal, and safety performances of HMX-based polymer-bonded explosives (PBXs) [9]. Meanwhile, Yan’s group was interested in the control of the reactivity of metastable intermixed composites (MICs) by constructing a PDA interfacial layer between the nanoscale fuel and oxidizer [10], which resulted in an increased energy release and reduced sensitivity.
This review will summarize the recent progress of PDA surface modification for EMs. In the first section, the self-polymerization mechanisms and some methods to accelerate this polymerization process will be briefly discussed. The applications of PDA in EMs are presented in the main section, in terms of its functions including crystal transformation inhibition, interfacial bonding in composites, and related mechanical enhancement, as well as thermal stability and sensitivity modification. A straightforward summary of this review and some existing problems will be given in the last section. We hope this review will promote the application of PDA coating in EMs after solving some concerning issues.
2. Self-Polymerization Mechanisms and Catalytic Reactions of PDA
The self-polymerization of dopamine and deposition of PDA is a very facile but time-consuming process. A typical procedure may need 12 h including the dissolution and polymerization of the dopamine monomer (commercially, dopamine hydrochloride is typically used) in an alkaline aqueous solution (Tris-HCl buffer with pH 8.5 is typically used) without any sophisticated operations, presenting a significant color change from colorless to deep brown.
Although PDA can be facilely and mildly fabricated, its reaction mechanisms remain controversial due to the complex redox process and related intermediates during polymerization. The polymerization process was speculated as the oxidation of dopamine to dopamine-quinone, followed by intramolecular cyclization, oxidization, and rearrangement to form 5,6-dihydroxyindole (DHI) [11]. Furthermore, DHI and its oxide can eventually form a cross-linked polymer through the reverse dismutation reaction between catechol and o-quinone. Although the cyclized, nitrogenous species such as the indole- or indoline-type structures were also confirmed by other researchers, a distinct model was proposed that PDA was considered to be an aggregate of monomers cross-linked primarily via strong, noncovalent forces [12]. Hong et al. suggested that the formation of PDA is the combination of noncovalent self-assembly and covalent polymerization [13]. They identified a dual-path formation process, in which both paths form the oxidative product of dopamine, DHI, since a physical, self-assembled trimer of (dopamine)2/DHI was observed by HPLC. Instead, Alfieri et al. suggested that PDA’s polymerization mechanisms might have an alternative pathway besides the conventional DHI-oligomers as the essential intermediate [14]. Their experiments found that dissolved DHI cannot form PDA; rather, dopamine polymerization, on mechanism-based analysis, may arise by quinone-amine conjugation leading to polycyclic systems with extensive chain breakdown. It seems that the molecular mechanisms behind the polymerization and deposition of PDA are quite complicated and still unclear.
One part is for certain, though; oxidation plays a decisive role in PDA formation, which provides meaningful inspiration for accelerating this process. Several methods were excogitated to overcome the drawback of the low polymerization rate, for instance, UV irradiation, electrochemical actuation, and oxidant promotion [15,16,17,18,19]. Among all this research, Zhang et al. used CuSO4/H2O2 to induce the polymerization of dopamine and accelerate the deposition rate of PDA [20,21]. Their works obtained a uniform PDA thin film with a thickness of 30 nm in 0.7 h, which is a considerably rapid deposition rate compared to other works, as shown in Table 1. Another attempt to achieve rapid PDA formation included the rising reaction temperature from the perspective of kinetics, which fabricated a PDA film in 0.5 h and obtained similar properties as those polymerized by the conventional method in 24 h [22], but the surface of the PDA obtained by this method was relatively rough due to the shambolic deposition of PDA nanoparticles under vigorous stirring. Interestingly, the self-polymerization of dopamine normally occurs in alkaline conditions; however, some researchers also explored the possibility of PDA formation in an acidic environment [23,24], on the basis of understanding the relevance of oxidation.

Table 1.
Thickness and deposition rate of PDA coatings with different methods.
Understanding the potential mechanisms of accelerating the polymerization and deposition rates of PDA is purposeful to engineering practices, not limited to EMs. However, given that most of EMs having oxidability, PDA formation on the surface of EMs seems to be rational and logical. For example, Ammonium perchlorate (AP), which is a commonly used oxidant in composite solid propellants, was employed to induce polymerization of dopamine in Wei et al.’s work [18]. Further, Lin et al. also realized the limitation of the low polymerization rate and inaccurate kinetic control of PDA in EMs, and they investigated the kinetics of PDA formation under different conditions, including concentrations of dopamine and oxygen, as well as environment temperatures, when studying the PDA coating on an insensitive high explosive 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene (TATB) [25].
3. Applications of PDA in Energetic Materials
The applications of PDA in EMs mainly include the compact coating and surface functionalization, which are able to improve the stability of crystals, the reactivity of composites, as well as the mechanical, thermal, and safety properties, respectively.
3.1. Surface Modification of Energetic Crystals
Gong’s group firstly introduce PDA coating into the field of EMs when they modified the crystal phase stability of a polymorphic high explosive, 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetraazacyclooctane (HMX), as shown in Figure 1. In the referenced work, the crystal transformation temperature of HMX (from β to δ phase) was improved by 28 °C with PDA of 0.5 wt.%, and mechanical sensitivity was also reduced after thermal damage compared with raw HMX [26]. Their following work also investigated the kinetics of the polymorphic transition of PDA-coated HMX and probed the possible inhibition mechanisms basing on the density functional theory calculation [27], which suggested that PDA coating significantly decreased the polymorphic transition rate, especially for the nucleation process.
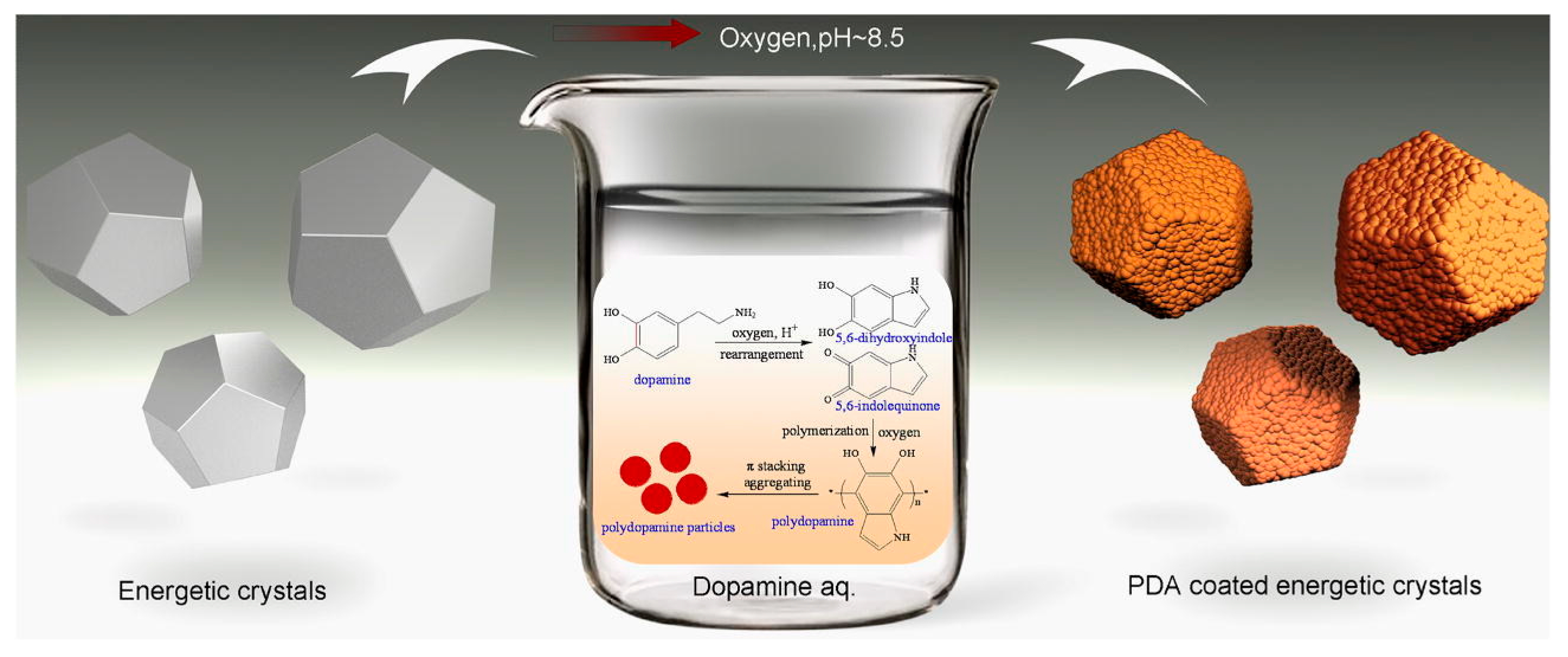
Figure 1.
The successful introduce of dopamine chemistry in an energetic system as reported firstly: compact core–shell structure for every single energetic crystal with highly enhanced thermal stability. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [26]. 2017, Elsevier.
2,4,6,8,10,12-Hexanitro-2,4,6,8,10,12-Hexaazaisowurtzitane (HNIW, CL-20) is the most powerful military explosive and has promising application prospects. However, there are four crystal phases for CL-20 at ambient temperature, including α, β, γ and ε phases, which can transfer into other phases under certain conditions. Accordingly, Jiao’s group fabricated a stable core–shell CL-20/PDA structure by the conventional PDA formation method, which not only increases the ε-CL-20 crystal transformation temperature by about 30 °C, but also significantly improves the mechanical sensitivity and thermal stability [28]. PDA-coated graphene oxide was used to dope ε-CL-20 in situ during its crystallization in Huang’s work [29]. The obtained CL-20 has a polygon shape with a smooth surface and relatively small size, as well as an improved polymorphic transition temperature up to 19 °C, and with some special dopants, a completely new crystal phase was even observed except in the four reported phases.
Lin extended the application of PDA from HMX to TATB for modifying its irreversible thermal expansion and mechanical properties by constructing a microcapsule [30,31]; due to the highly cross-linked and dense PDA shell with 1.5 wt.%, the irreversible expansion strain at room temperature dropped from 0.520% to 0.376%, and the tensile strength and toughness of TATB/PDA composites were 73% and 219% higher, respectively, than that of pristine TATB. Thenceforward, the mechanical enhancement of EMs by PDA and mechanisms behind this effect attracted more research interest.
3.2. Interfacial Bonding and Mechanical Enhancement of Energetic Composites
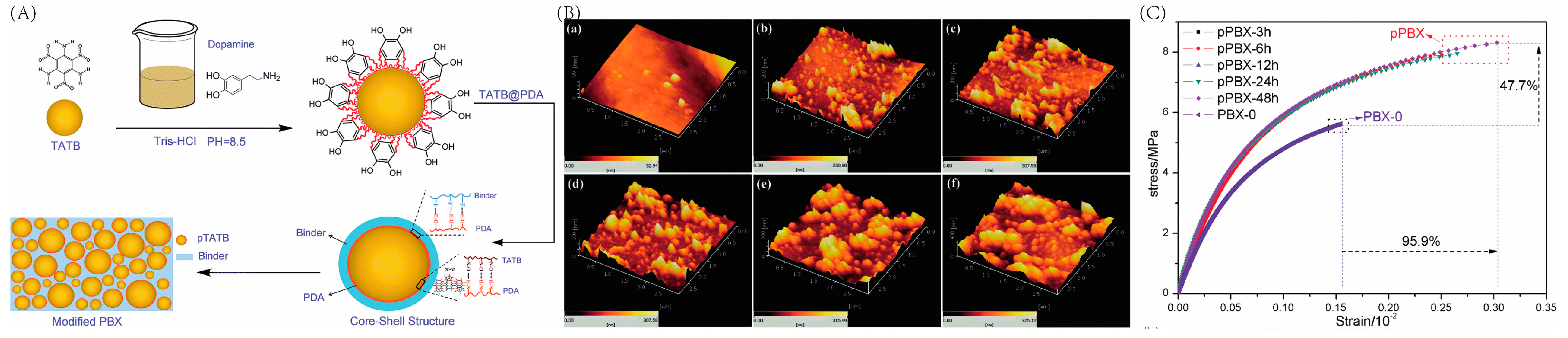
He’s group fabricated a dense PDA film with a thickness of 56 nm by adjusting the reaction time, pH value, and temperature, and used PDA-coated TATB as the solid filler of a polymer-bonded explosive (PBX) [32]. The abovementioned PBX exhibited significantly improved tensile and compression strength or strain and creep resistance, due to the strong interfacial interaction between crystalline particles and binders with PDA as the interlayer, as shown in Figure 2. Moreover, they proposed a new model combining the chemical “interactional bonding” and physical “interlocking block” at the interface to explain the enhancement of mechanical properties which are demonstrated as hydrogen bonds and π–π interactions between the PDA and polymer binder, and increased roughness on the crystal surface, respectively.
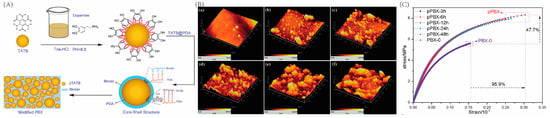
Figure 2.
(A) Preparation of core-shell structured pTATB and the supposed interaction between PDA, TATB, and the fluoropolymer. (B) Topographical AFM images of PDA films deposited on the TATB crystal for (a) 0 h, (b) 3 h, (c) 6 h, (d) 12 h, (e) 24 h, (f) 48 h. (C) Stress-strain curves of PBX composites prepared from the abovementioned TATB. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [32]. 2012, Royal Society of Chemistry.
According to He’s model, Lin designed and fabricated PDA-coated HMX, TATB, and 2,6-diamino-3,5-dinitropyrazine-1-oxide (LLM-105), and used these modified explosive crystals in PBXs [33,34]. The compressive and tensile strength of coated LLM-105-based PBX could be improved by 27–52% and 47–100%, respectively. Furthermore, PBXs containing coated HMX and TATB also exhibited higher strength, stronger toughness, higher creep resistance, and higher microstructural thermal stability simultaneously, compared to PBXs containing pristine explosive crystals. This research group also adopted theoretical calculations to explain the accounts for mechanical enhancement, which combines the van der Waals forces, π–π interaction, and hydrogen bonds, as well as surface roughness. Since the complex interfacial interaction cannot be experimentally observed, molecular dynamic simulation and quantitative analysis were widely used to demonstrate related mechanisms. Zeng and Lin [35,36] used different theoretical calculation methods to study the interfacial strength and contributing factors, and obtained the consistent conclusion that PDA can form a strong interfacial interaction with energetic crystals and crosslink with a polymeric matrix via abundant hydrogen bonds.
Another attempt to improve the mechanical properties is by grafting polymer binders onto explosive crystals directly through the abundant functional groups on PDA. Zeng et al. grafted three polymers including glycidyl azide polymer (GAP), polyethylene glycol (PEG), and polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMEG) onto TATB via PDA, and PBXs prepared by these grafted explosive crystals showed remarkably increased mechanical properties; in particular, the PTMEG-grafted TATB exhibited excellent wettability of two phases [37]. Further, they grafted two hyperbranched polyesters (HBPs) onto TATB via hydroxyl groups on PDA [38]. PBXs using modified TATB showed improved storage modulus, creep resistance properties, and higher wettability, and tensile and compressive strength were increased significantly by 26.5% and 19.8%, respectively, due to the strong interfacial reinforcement of HBPs. This “grafting-from” route was popularized to tailor mechanical properties of other energetic polymeric composites by multilevel core–shell strategies [39], which resulted in a high-efficiency mechanical enhancement, including tensile and compressive strength and creep resistance.
3.3. Thermal, Sensitivity, and Safety Modification
Except for the mechanical enhancement of PBXs prepared from PDA-coated explosive crystals, the influences of PDA on the thermal, sensitivity, and safety properties of EMs also raised attention right from the start. Zhu et al. noticed that the friction and impact sensitivities of HMX@PDA particles were 30% and 50% lower, respectively, than those of HMX, along with displaying better wettability [40]. Another extension for reducing the sensitivities by PDA is constructing a “core–dual-shell (CDS)” structure with a completely inert material or an explosive exhibiting relatively lower sensitivity. Regarding HMX as a sensitive explosive, Lin et al. used TATB nanoparticles as the inner shell and PDA as the outer shell to fabricate an HMX@TATB@PDA CDS microstructure via a facile ultrasonic method and a simple immersion method, respectively [41]. Consistent with their previous works, PDA coating resulted in the increased β-δ phase transition temperature of HMX from 197.0 to 212.8 °C, and the impact sensitivity was 50% lower than that of the physical mixture without deteriorating its explosion performance; these properties were also combined with improved mechanical strength and roughness, storage modulus, and creep resistance. Instead of TATB, they also used high-melting-point paraffin wax (HPW) as the inner shell for CDS, which demonstrated a 117% increase in impact energy than that using conventional wax due to the high melting enthalpy of HPW and the associated optimization molding process, and a stronger interfacial interaction [42].
This CDS-sensitivity-reducing route also derives from those microstructures regarding PDA as an inner shell utilizing its adhesion effect. Amorphous TiO2 was used to reduce the impact and electrostatic discharge sensitivities of RDX (hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine); however, uniform deposition of TiO2 as a shell to the RDX crystals surfaces was a great challenge. Wang et al. employed PDA as a bio-adhesive agent coated on the surface of RDX to enhance the interfacial adhesion between RDX and amorphous TiO2, which improved the impact energy and electrostatic discharge energy by about 200.0% and 514.3% in the samples with optimal PDA and TiO2 contents, respectively, compared with pristine RDX [43].
It was also found that this explosive@PDA@TiO2 structure has the effect of enhancing the thermal decomposition of HMX. In Zhu’s work, TiO2 nanoparticles were anchored on the surface of HMX by PDA coating, which decreased the decomposition onset temperature and peak temperature by about 60 °C and 35 °C, respectively [44]. However, PDA itself contributes to improving the thermal stability of EMs in many cases. Yu et al. coated LLM-105 with PDA and investigated its thermal decomposition behaviors in different heating conditions [45]. They found that PDA can hardly affect the thermal stability of LLM-105 under non-adiabatic conditions but remarkably intensified under adiabatic conditions. They proposed an inference that the amount of heat released by PDA decomposition and the heat-exchange rate between the sample and environment are the key to this effect, and it was confirmed by the Comsol numerical simulation in their work. Meanwhile, He’s group constructed a multidimensional filler structure composed of 2D graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs), 0D AgNPs, and a bioinspired interfacial PDA layer on TATB, and PBXs were prepared from the referred-to TATB [46]. The thermal conductivity of PBXs was dramatically enhanced due to the stable 2D GNPs and 0D AgNPs anchored by PDA, which served as thermally conductive “bridges” to link the components and facilitate the heat transfer across the interfaces. Their previous work adopted carbon nanofillers, including multiwalled carbon nanotubes, graphene, and graphene nanoplates, into the surface of TATB via PDA anchoring, and the prepared PBXs exhibited improved thermal conductivity, as well as creep resistance and tensile and compression strength [47].
3.4. Reactivity and Energetic Performances Tailoring
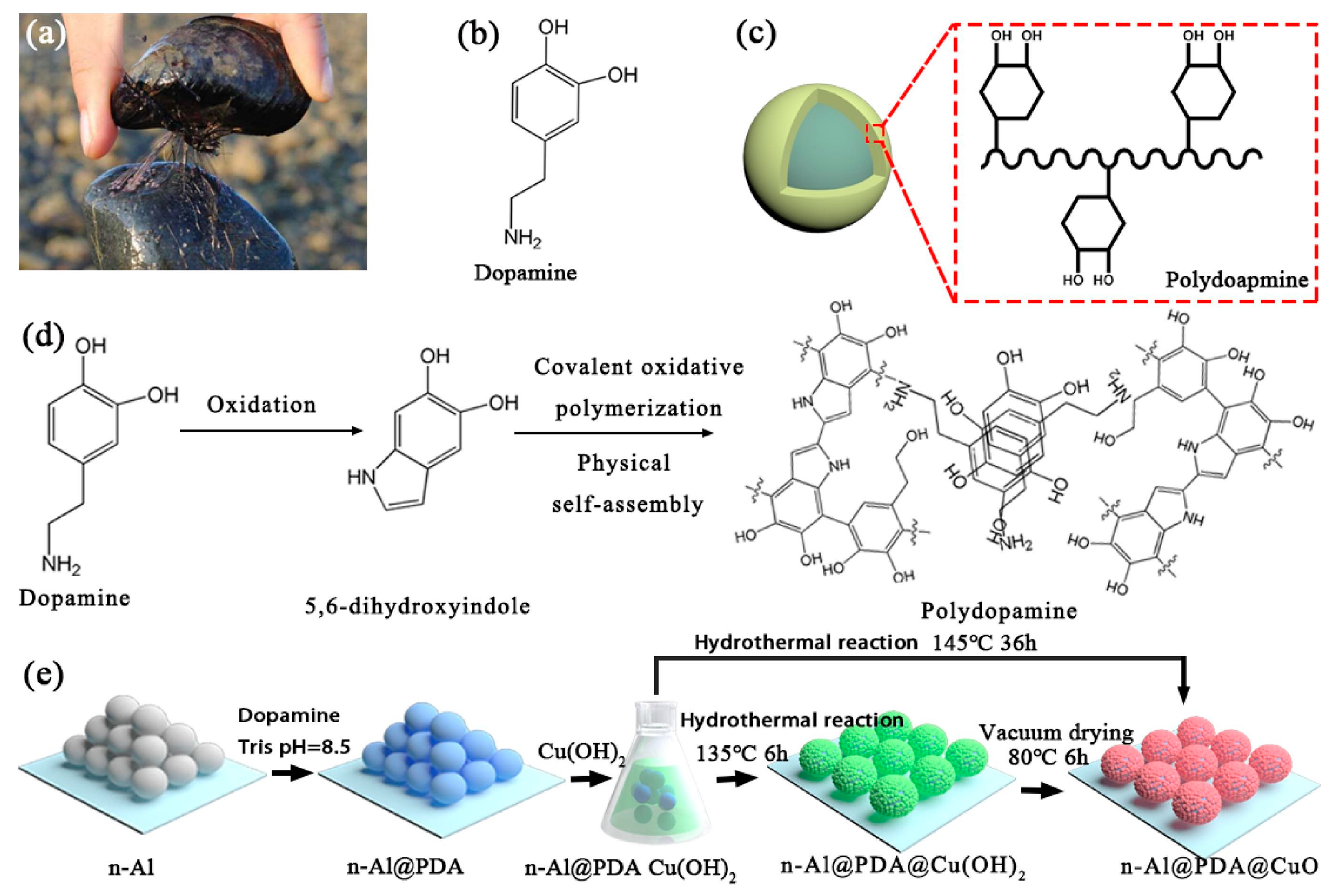
Due to the impact of coating and its stable anchoring effect, a dramatic influence, reactivity and energetic performances tailoring of PDA was also observed during its applications in EMs. Yan’s group focused on the performances tailoring of MICs by adopting PDA as a binding layer [10,48,49]. In the early stage of their research, PDA was used to coat aluminum nanoparticles (nAl) and poly(tetrafluoroethylene) for preparing MICs, which exhibiting increased energy release and reduced sensitivity, and more importantly tunable reactivity by controlling the thickness of PDA coating. After understanding the anchoring effect of PDA, they further constructed nAl@PDA@oxidizers MICs by the direction of PDA on the heterogeneous nucleation and growth of Cu(OH)2 and CuO after nAl functionalization, as shown in Figure 3. The abovementioned MICs showed an improved initial reaction temperature, enhanced energy release, lower combustion temperature, and higher combustion efficiency compared with conventional MICs. The nAl functionalization provided more possibilities for constructing MICs containing different ingredients and tailoring their energy release processes. The results from similar works from Yan’s group include introducing energetic metal–organic frameworks (MOF), which can decompose to metal oxide as oxidizers in conventional nanothermites and release extra energy during decomposition into MICs. These MICs undergo self-sustainable combustion with multilevel energy releases with lower ignition temperatures.
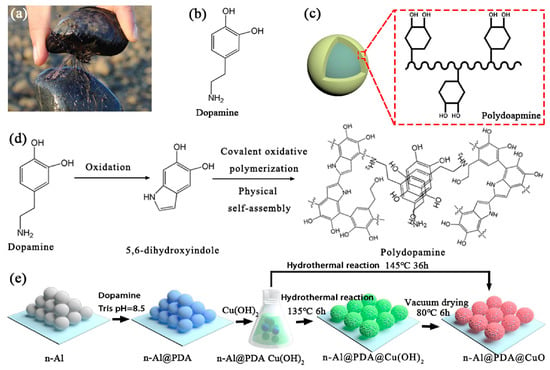
Figure 3.
(a) A picture of a mussel, showing the strong adhesive of the byssus. (b) The molecular structure of dopamine. (c) The structure of polydopamine film binding on the particle surface. (d) The polymerization of dopamine. (e) Schematic description of the fabrication of n-Al@PDA@CuO MICs constructed by dopamine-nucleated crystal growth. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [48]. 2019, Elsevier.
Wang’s group also attempted to improve the energetic performance through PDA when preparing CL-20-based energetic film by employing 3D micro-jet printing [50]. PDA was utilized as a linking bridge to induce the in situ self-assembly of CL-20-based polymeric composites. They suggested that PDA enhanced the physical entanglement between the binders and energetic crystal, and resulted in an improved detonation performance, elastic modulus, and deposition density.
4. Conclusions
To summarize, PDA plays an essential role in the crystal phase stability, thermal stability, and mechanical sensitivity of modified EMs, and its binding effect also provides more possibilities for mechanical enhancement, reactivity tailoring, and substances anchoring via secondary functionalization. This review firstly introduced possible self-polymerization mechanisms of dopamine and listed some representative methods to accelerate this process for inspiring researchers in the field of EMs, based on the fact that current accelerating methods in EMs still remain in adjusting concentrations of dopamine and oxygen, and reaction temperatures. Then we amply demonstrated the applications of PDA in EMs in terms of its effects, including surface modification of single energetic crystals; interfacial bonding and mechanical enhancement of energetic composites; thermal, sensitivity, and safety modification; as well as reactivity and energetic performances tailoring.
5. Future Directions
Although the applications of PDA in EMs are on the rise, some issues remain unaddressed in this field, which may be considered as future directions, or more appropriately, need to be solved. These are as follows:
- The content of PDA, which is significant to the energetic performances of EMs, is very hard to measure due to its insolubility. Since the current method only can characterize the thickness of PDA film, converting thickness to content seems to be necessary.
- Low polymerization and deposition rates of PDA on EMs limit its applications. PDA formation processes are affected by many factors including temperature, pH value, oxidizing catalysts, and so on. Optimal processing conditions are worth exploring, especially for EMs with high sensitivity, reactivity, or oxidability.
- The binding effect or secondary functionalization of PDA could be further extended to combine substances with high surface tension to fabricate CDS microstructures which originally cannot bond stably.
- With rapid development of EMs, the applications of PDA in the next-generation EMs such as N5 salts, polyCO, and other high-nitrogen compounds should raise attention for stabilization and sensitivity reduction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.J. and Y.O.; validation, S.D.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Q.; writing—review and editing, D.L.; supervision, Y.O.; funding acquisition, Y.O.; resources, J.P. and P.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22005031) and the Autonomous Research Program of SKLEST (Grant No. QNKT22-13).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, H.; Lee, B.P.; Messersmith, P.B. A reversible wet/dry adhesive inspired by mussels and geckos. Nature 2007, 448, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, H.; Hanks, T.W. Polydopamine: A bioinspired adhesive and surface modification platform. Polym. Int. 2022, 71, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanze, K.S.; Lee, H.; Messersmith, P.B. Ten years of polydopamine: Current status and future directions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7521–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L.H. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Ramimoghadam, D.; Mirabedini, A. The use of polydopamine coatings for timber protection against the fire: A critical review and feasibility analysis. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 175, 107359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Danner, E.; Waite, J.H.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Zeng, H.; Hwang, D.S. Adhesion of mussel foot proteins to different substrate surfaces. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, I.S.; Tang, G.; Chiang, P.J.; Bettinge, C.J. Texture-dependent adhesion in polydopamine nanomembrane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7681–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Gong, F.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, C.; Li, J.; Guo, S. Core-shell structured HMX@polydopamine energetic microspheres: Synergistically enhanced mechanical, thermal, and safety performances. Polymers 2019, 11, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Liu, P.; Gong, F.; Tao, B.; Gu, J.; Yang, Z.; Yan, Q.L. Tuning the reactivity of metastable intermixed composite n-Al/PTFE by polydopamine interfacial control. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 32849–32858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczak, T. Preparation and characterization of the dopamine film electrochemically deposited on a gold template and its applications for dopamine sensing in aqueous solution. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5725–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W. Elucidating the structure of poly(dopamine). Langmuir 2012, 28, 6428–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Na, Y.S.; Choi, S.; Song, I.T.; Kim, W.Y.; Lee, H. Non-covalent self-assembly and covalent polymerization co-contribute to polydopamine formation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4711–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, M.L.; Micillo, R.; Panzella, L.; Crescenzi, O.; Oscurato, S.L.; Maddalena, P.; Napolitano, A.; Ball, V.; d’Ischia, M. Structural basis of polydopamine film formation: Probing 5,6-dihydroxyindole-based eumelanin type units and the porphyrin issue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7670–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Frenkel, N.; Welle, A.; Heissler, S.; Nefedov, A.; Grunze, M.; Levkin, P.A. UV-triggered dopamine polymerization: Control of polymerization, surface coating and photopatterning. Adv. Mater. 2014, 47, 8029–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Zhang, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhong, Q.Z.; Yang, X.; Xu, Z.K. Mussel-inspired coatings directed and accelerated by an electric field. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; McCloskey, B.D.; Choi, T.H.; Lee, C.; Kim, M.J.; Freeman, B.D.; Park, H.B. Oxygen concentration control of dopamine-induced high uniformity surface coating chemistry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, F.L.; Li, J.; Li, B.J.; Zhao, C.S. Oxidant induced dopamine polymerization for multifunctional coatings. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 1430–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, Q. Oxidant-induced high-efficient mussel-inspired modification on PVDF membrane with superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity characteristics for oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 8297–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ou, Y.; Lei, W.X.; Wan, L.S.; Ji, J.; Xu, Z.K. CuSO4/H2O2-Induced rapid deposition of polydopamine coatings with high uniformity and enhanced stability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3054–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.N.; Du, Y.; Ma, M.Q.; Xu, Z.K. CuSO4/H2O2-Triggered polydopamine/poly(sulfobetainemethacrylate) coatings for antifouling membrane surfaces. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Deng, Y.; Lyu, B.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H.; Lyu, Y.; Wei, S. Rapidly-deposited polydopamine coating via high temperature and vigorous stirring: Formation, characterization and biofunctional evaluation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Fan, H.; Wang, L.; Jin, Z. Oxidative self-polymerization of dopamine in an acidic environment. Langmuir 2015, 31, 11671–11677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzio, F.; Barthes, J.; Bour, J.; Michel, M.; Bertani, P.; Hemmerle, J.; d’Ischia, M.; Ball, V. Oxidant control of polydopamine surface chemistry in acids: A mechanism-based entry to superhydrophilic-superoleophobic coatings. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 4697–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Liu, S.; Qian, W.; Gong, F.; Zhao, X.; Pan, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, S. Controllable tuning of energetic crystals by bioinspired polydopamine. Energetic Mater. Front. 2020, 1, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X. Mussel-inspired coating of energetic crystals: A compact core-shell structure with highly enhanced thermal stability. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Yang, Z.; Qian, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; Lin, C.; Zeng, C.; Yan, Q. Kinetics for inhibited polymorphic transition of HMX crystal after strong surface confinement. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 11011–11019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiao, Q.; Zhao, W.; Guo, X.; Li, D.; Sun, X. Enhanced crystal stabilities of ε-CL-20 via core-shell structured energetic composites. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Xue, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Xu, K.; Yan, Q.L. Stabilization of ε-CL-20 crystals by a minor interfacial doping of polydopamine-coated graphene oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, H.; Gong, F.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Guo, S. Tailoring the irreversible thermal expansion of 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene crystals by bioinspired polydopamine coating. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 137, 48695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Gong, F.; Yang, Z.; Pan, L.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Guo, S. Bio-inspired fabrication of core@shell structured TATB/polydopamine microparticles via in situ polymerization with tunable mechanical properties. Polym. Test. 2018, 68, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Yang, Z.; Pan, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Yan, Q.L. Bioinspired interfacial reinforcement of polymer based energetic composites with a high loading of solid explosive crystals. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 13499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wen, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, Z.; Gong, F.; Zhao, X.; Hao, S.; Pan, L.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; et al. Tuning the mechanical performance efficiently of various LLM-105 based PBXs via bioinspired interfacial reinforcement of polydopamine modification. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2020, 186, 107824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Gong, F.; Qian, W.; Huang, X.; Tu, X.; Sun, G.; Bai, L.; Wen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, J. Tunable interfacial interaction intensity: Construction of a bio-inspired interface between polydopamine and energetic crystals. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 211, 108816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.C.; Gong, F.Y.; Lin, C.M.; He, G.S.; Pan, L.P.; Li, Y.B.; Hao, S.L.; Yang, Z.J. Bioinspired energetic composites with enhanced interfacial, thermal and mechanical performance by “grafting to” way. Energetic Mater. Front. 2021, 2, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Yang, X.; He, G.; Wen, Y.; Qian, W.; Liu, R.; Liu, S.; Gong, F.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, C.; et al. Mussel-inspired interfacial reinforcement of thermoplastic polyurethane based energetic composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 232, 109875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, C.; He, G.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Gong, F. Enhanced interfacial and mechanical properties of PBX composites via surface modification on energetic crystals. Polymers 2019, 11, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Lin, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; He, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Gong, F.; Yang, Z. Grafting hyperbranched polyester on the energetic crystals: Enhanced mechanical properties in highly-loaded polymer based composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 184, 107842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Li, X.; Bai, L.; Meng, L.; Dai, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, C.; Yang, Z.; Yang, G. Multilevel core-shell strategies for improving mechanical properties of energetic polymeric composites by the “grafting-from” route. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2020, 191, 107967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Xiao, C.; Li, S.; Luo, G. Bioinspired fabrication of insensitive HMX particles with polydopamine coating. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 2016, 41, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Huang, B.; Gong, F.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, S. Core@double-shell structured energetic composites with reduced sensitivity and enhanced mechanical properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 30341–30351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Zeng, C.; Wen, Y.; Gong, F.; He, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Guo, S. Litchi-like core-shell HMX@HPW@PDA microparticles for polymer-bonded energetic composites with low sensitivity and high mechanical properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 4002–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, Q.; Xu, B.; Chen, F.; Liao, X. Bio-inspired synthesis of RDX@polydopamine@TiO2 double layer core-shell energetic composites with reduced impact and electrostatic discharge sensitivities. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 567, 150729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Xiao, C.; Xie, X.; Zheng, B.H.; Li, S.B.; Luo, G. Thermal decomposition enhancement of HMX by bonding with TiO2 Nanoparticles. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2019, 44, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Q.; Sui, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, J. Influence of polydopamine coating on the thermal stability of 2,6-diamino-3,5-dinitropyrazine-1-oxide explosive under different heating conditions. Thermochim. Acta 2020, 686, 178530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Tian, X.; Dai, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S. Bioinspired interfacial engineering of polymer based energetic composites towards superior thermal conductivity via reducing thermal resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 493, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Liu, J.; Gong, F.; Lin, C.; Yang, Z. Bioinspired mechanical and thermal conductivity reinforcement of highly explosive-filled polymer composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 107, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Tao, B.; Yang, Z.; Yang, G.; Guo, X.; Liu, P.J.; Yan, Q.L. Mussel-inspired polydopamine-directed crystal growth of core-shell n-Al@PDA@CuO metastable intermixed composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Ao, W.; Yang, G.; Yang, Z.; Yan, Q.L. Metastable Energetic Nanocomposites of MOF-activated aluminum featured with multi-level energy releases. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Kong, S.; Liao, D.J.; An, C.W.; Ye, B.Y.; Wang, J.Y. Fabrication and characterization of mussel-inspired layer-by-layer assembled CL-20-based energetic films via micro-jet printing. Def. Technol. 2022, 18, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).