Electrically Conductive Adhesive Based on Thermoplastic Hot Melt Copolyamide and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Composites Fabrication
2.3. Characterization Techniques
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure
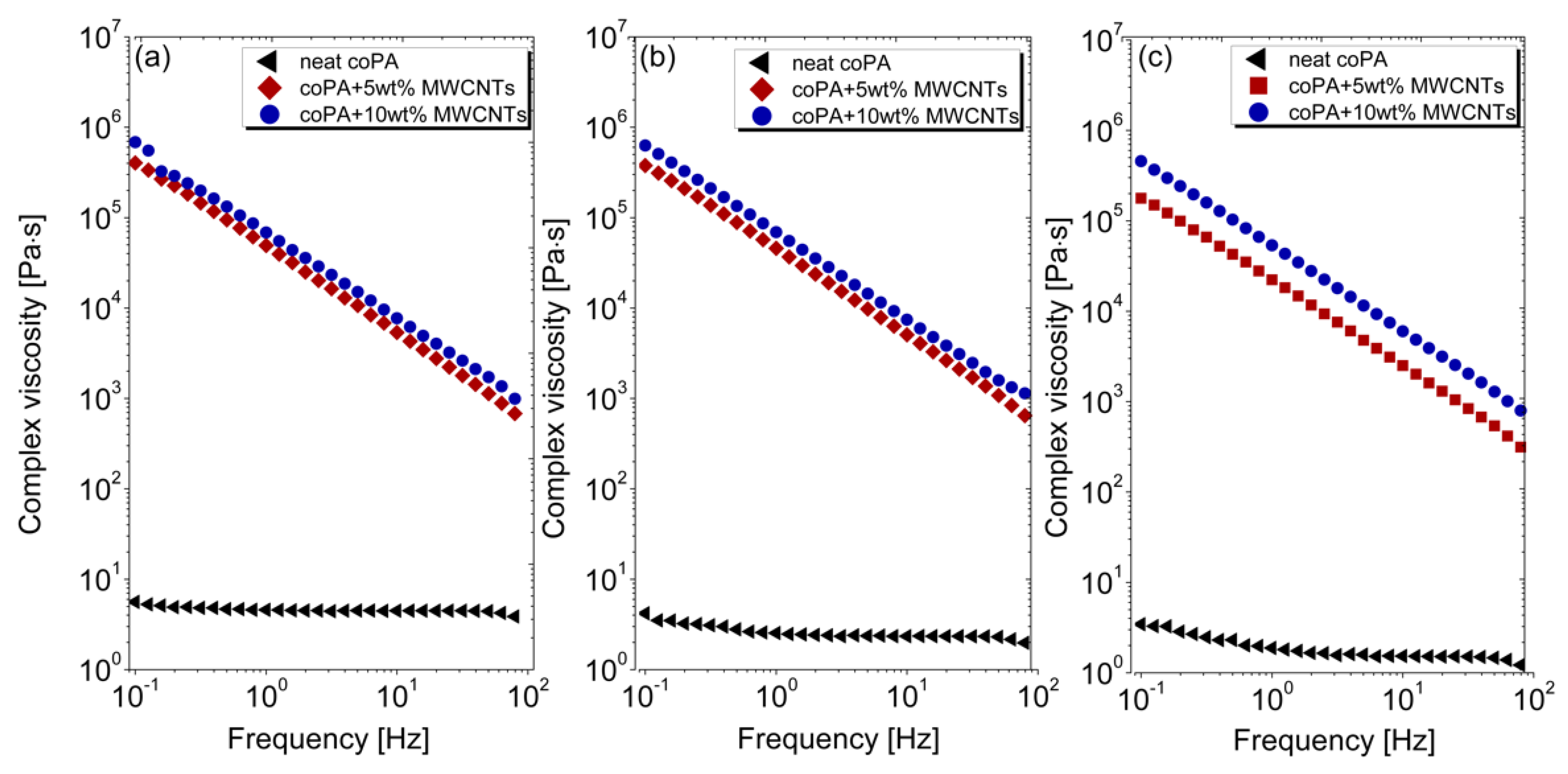
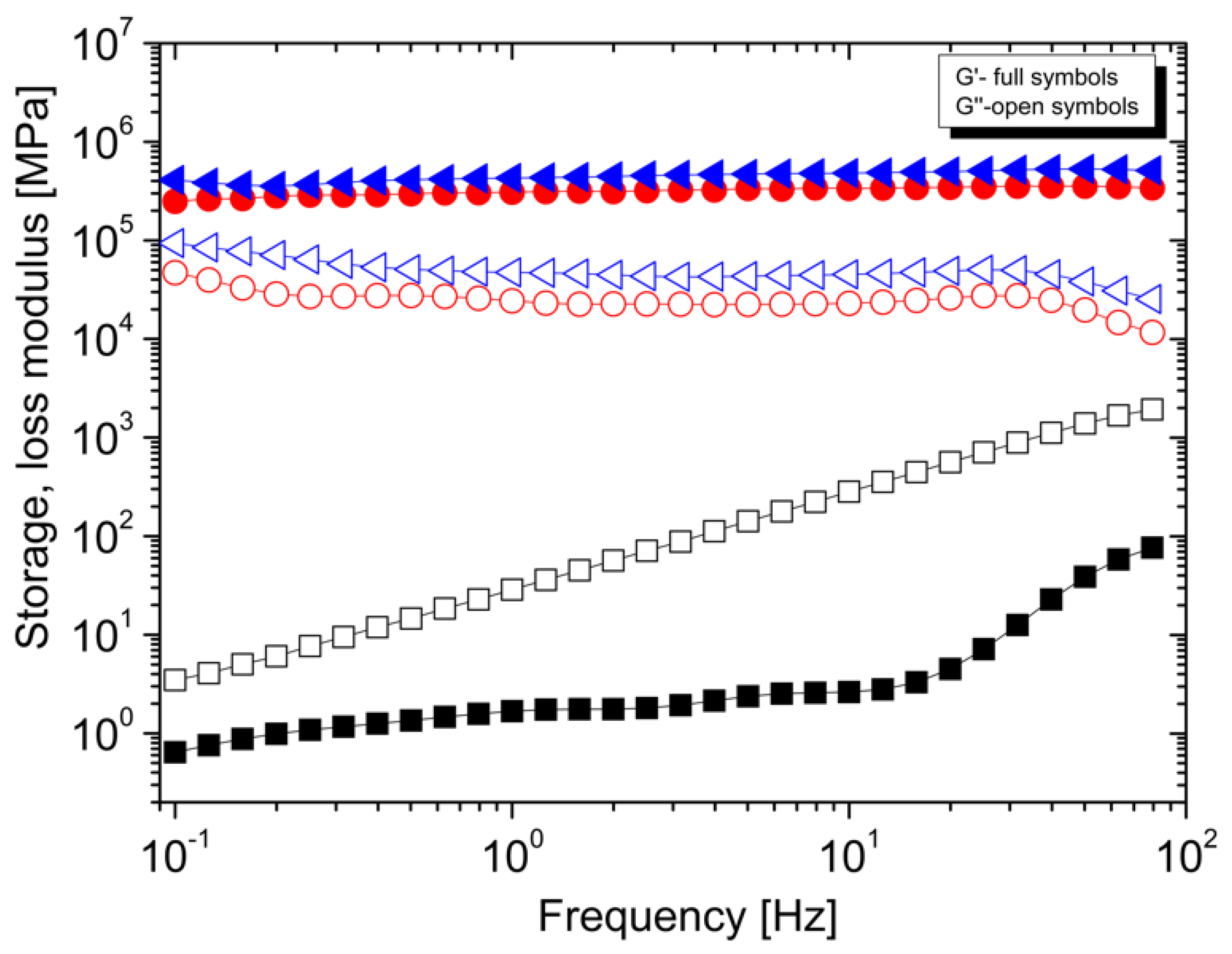
3.2. Rheological Properties
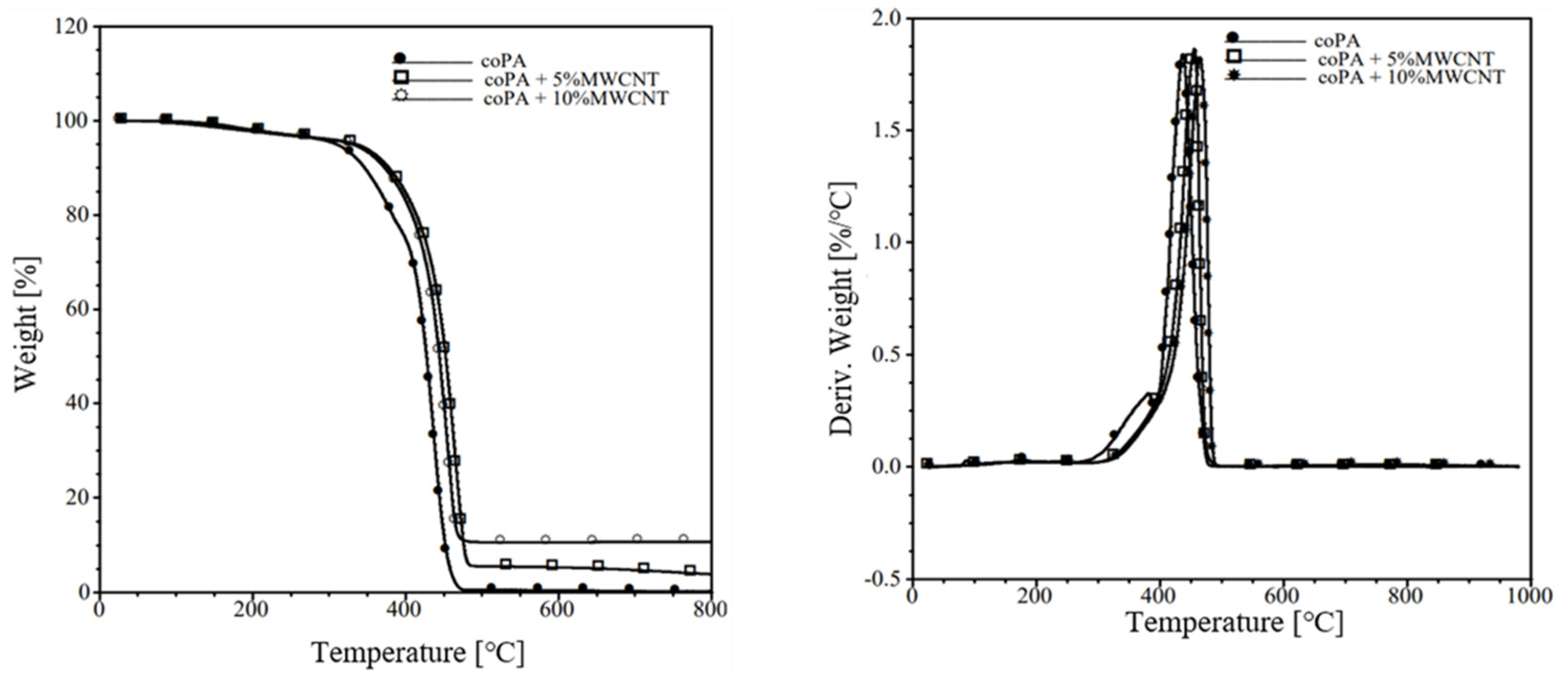
3.3. Thermal Properties
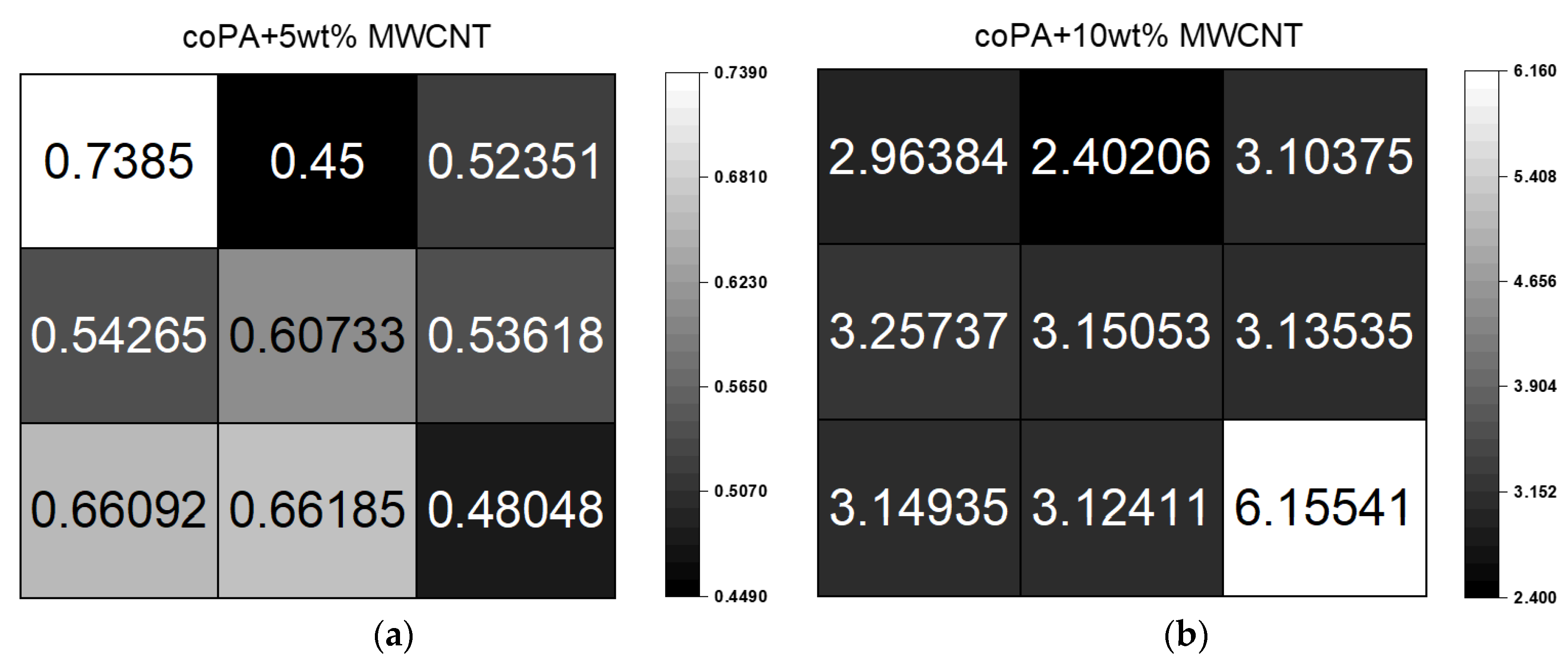
3.4. Electrical Properties
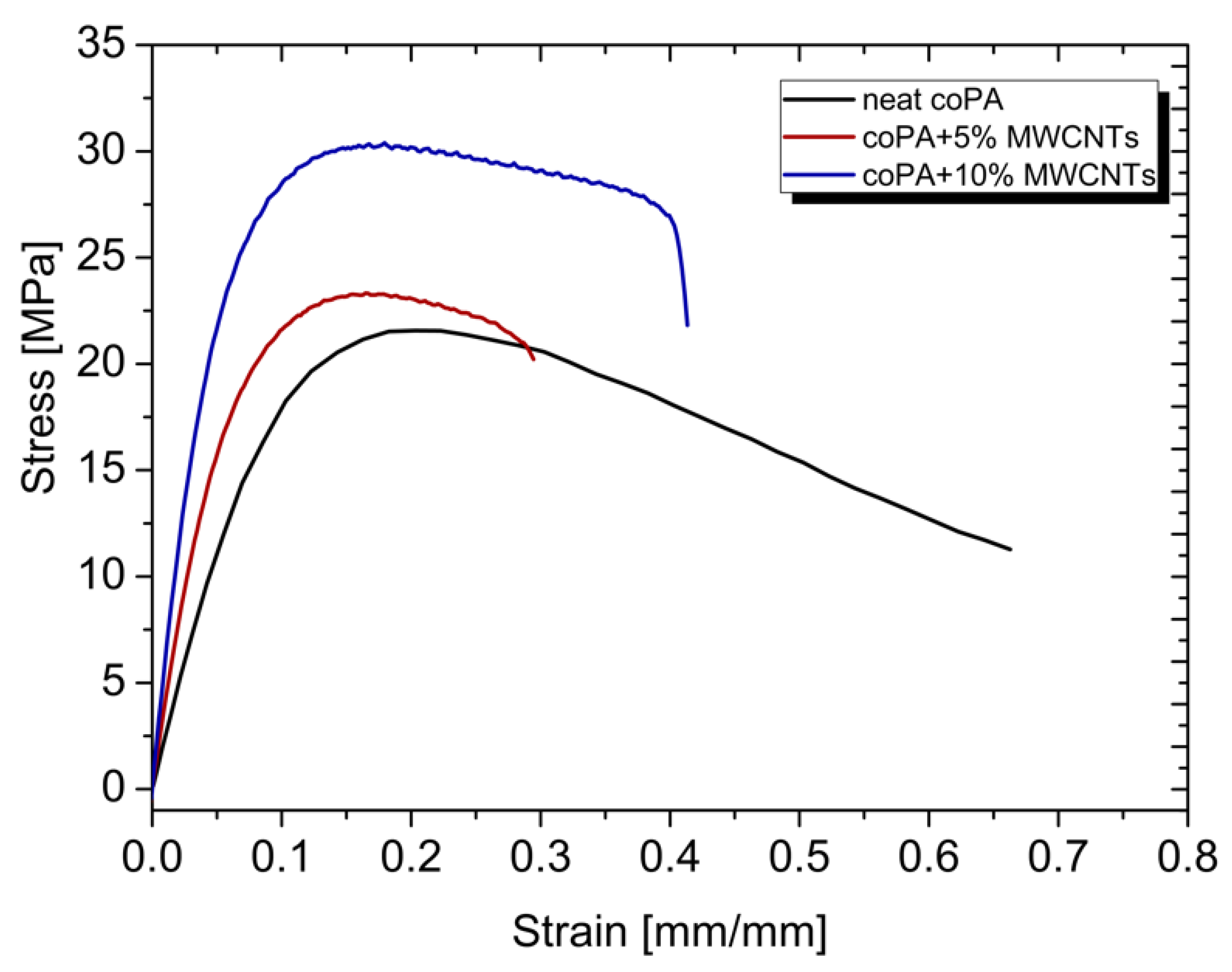
3.5. Mechanical Properties
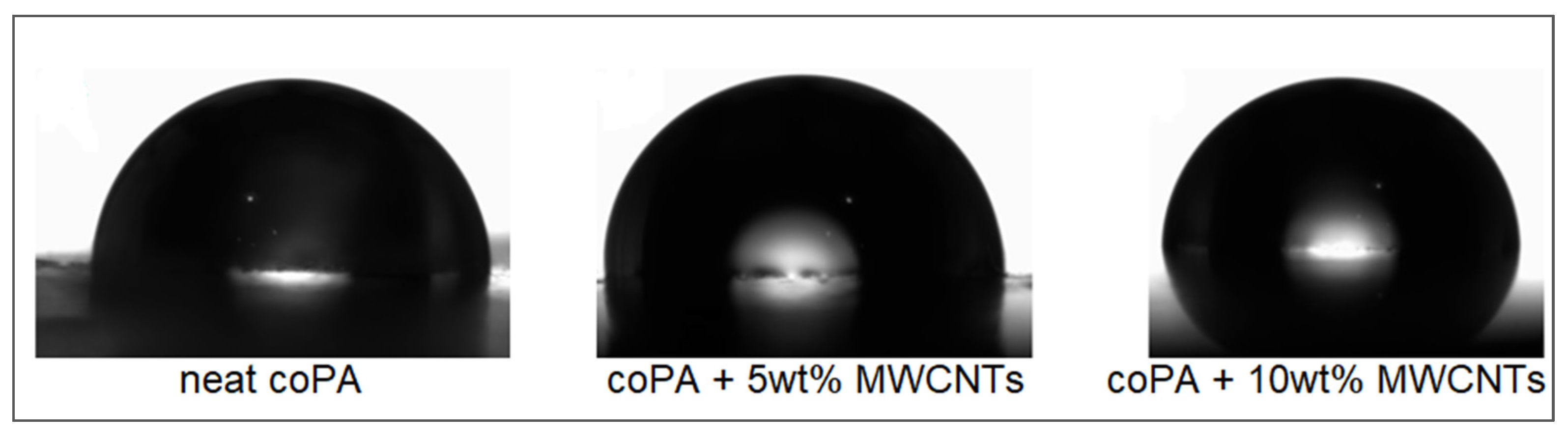
3.6. Contact Angle Measurements
3.7. Adhesive Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aradhana, R.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. A review on epoxy-based electrically conductive adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 99, 102596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nele, L.; Palmieri, B. Electromagnetic heating for adhesive melting in CFRTP joining: Study, analysis, and testing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 5317–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.P.; Xu, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Lu, J.; Dong, H. Recent advances on polymers and polymer nanocomposites for advanced electronic packaging applications. In Proceedings of the 2005 Conference on High Density Microsystem Design and Packaging and Component Failure Analysis, HDP’05, Shanghai, China, 27–29 June 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latko-Durałek, P.; Kozera, R.; Macutkevič, J.; Dydek, K.; Boczkowska, A. Relationship between Viscosity, Microstructure and Electrical Conductivity in Copolyamide Hot Melt Adhesives Containing Carbon Nanotubes. Materials 2020, 13, 4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshankhah, H.; Mohammad-Rezaei, R.; Massoumi, B.; Abbasian, M.; Rezaei, A.; Samadian, H.; Jaymand, M. Conducting polymer-based electrically conductive adhesive materials: Design, fabrication, properties, and applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 10947–10961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, M.J.; Li, Y.; Moon, K.S.; Paik, K.W.; Wong, C.P. Review of recent advances in electrically conductive adhesive materials and technologies in electronic packaging. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2008, 22, 1593–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantena, K.; Li, J.; Lumpp, J.K. Electrically conductive carbon nanotube adhesives on lead free printed circuit board surface finishes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 1–8 March 2008; pp. 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alig, I.; Lellinger, D.; Engel, M.; Skipa, T.; Pötschke, P. Destruction and formation of a conductive carbon nanotube network in polymer melts: In-line experiments. Polymer 2008, 49, 1902–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Lin, Y.; Song, M.; Gui, C.; Leesirisan, S. Enhancing the electrical conductivity of polymer composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Cheng, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, Q.; Yao, Y. Electrically conductive adhesives based on thermoplastic polyurethane filled with silver flakes and carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 129, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xie, Q.; Wu, G. Research on electrically conductive acrylate resin filled with silver nanoparticles plating multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Rezaei, R.; Massoumi, B.; Abbasian, M.; Eskandani, M.; Jaymand, M. Electrically conductive adhesive based on novolac-grafted polyaniline: Synthesis and characterization. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 2821–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.W.; Kowalczyk, A.; Li, D.S.; Fan, Q. High performance electrically conductive adhesives from functional epoxy, micron silver flakes, micron silver spheres and acidified single wall carbon nanotube for electronic package. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 44, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, M.G.; Lavenya, K.; Kirubashini, K.A.; Ajeesh, G.; Bhowmik, S.; Epaarachchi, J.A.; Yuan, X. Electrically conductive nano adhesive bonding: Futuristic approach for satellites and electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Aircr. Spacecr. Sci. 2017, 4, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bouzidi, L.; Narine, S.S. Current Research and Development Status and Prospect of Hot-Melt Adhesives: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 7524–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, E.M. Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants; McGraw Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, C.W. Hot Melt Adhesives; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Liu, S.; Huang, Y.; Sang, L. Investigation of joining of continuous glass fibre reinforced polypropylene laminates via fusion bonding and hotmelt adhesive film. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 100, 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latko-Durałek, P.; Dydek, K.; Bolimowski, P.; Golonko, E.; Duralek, P.; Kozera, R.; Boczkowska, A. Nonwoven fabrics with carbon nanotubes used as interleaves in CFRP. 13th International Conference on Textile Composites. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 406, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, G.; Gharehaghaji, A.A. Improving adhesion of electrospun nanofiber mats to supporting substrate by using adhesive bonding. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2018, 86, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Landa, M.; Muñoz, M.E.; Santamaría, A. Tackiness of an electrically conducting polyurethanenanotube nanocomposite. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2010, 30, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehnert, F.; Pötschke, P.; Jansen, I. Hotmelts with improved properties by integration of carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 62, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latko-Durałek, P.; Mcnally, T.; Macutkevic, J.; Kay, C.; Boczkowska, A. Hot-melt adhesives based on co-polyamide and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, T.; Krishnamoorti, R. Rheology of polymer carbon nanotubes composites. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, M.R. Rheology of polymer–carbon nanotube composites melts. In Polymer–Carbon Nanotube Composites Preparation, Properties and Applications; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 428–481. ISBN 978-1-84569-761-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, N.; Islam, M.; Hameed, A.; Saeed, S. Polyamide 6/multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanocomposites with modified morphology and thermal properties. Polymers 2013, 5, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Landa, M.; Muñoz, M.E.; Santamaría, A. Thermal and viscoelastic features of new nanocomposites based on a hot-melt adhesive polyurethane and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Nicolais, L. Glass transition temperature in nylons. Polymer 1976, 17, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.L.; Mai, Y.W.; Zhou, X.P. Dispersion and alignment of carbon nanotubes in polymer matrix: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 49, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, M.; Canales, J.; Fernández, M.; Muñoz, M.E.; Santamaría, A. Effect of MWCNTs and graphene on the crystallization of polyurethane based nanocomposites, analyzed via calorimetry, rheology and AFM microscopy. Polym. Test. 2014, 35, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socher, R.; Krause, B.; Boldt, R.; Hermasch, S.; Wursche, R.; Pötschke, P. Melt mixed nano composites of PA12 with MWNTs: Influence of MWNT and matrix properties on macrodispersion and electrical properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakošov, D.; Bakošov, A. Testing of Rubber Composites Reinforced with Carbon Nanotubes. Polymers 2022, 14, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Takatani, R.; Sato, Y.; Maeda, S. Moisture-sensitive smart hot-melt adhesive from polyamide 6. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Cui, H.W.; Lu, X.Z.; Fan, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Ye, L.; Liu, J. Development and characterisation of nanofiber films with high adhesion. In Proceedings of the Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Florida, FL, USA, 21 May–3 June 2011; pp. 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutar, Y.; Naïmi, S.; Mezlini, S.; Da Silva, L.F.M.; Hamdaoui, M.; Ben Sik Ali, M. Effect of adhesive thickness and surface roughness on the shear strength of aluminium one-component polyurethane adhesive single-lap joints for automotive applications. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 1913–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
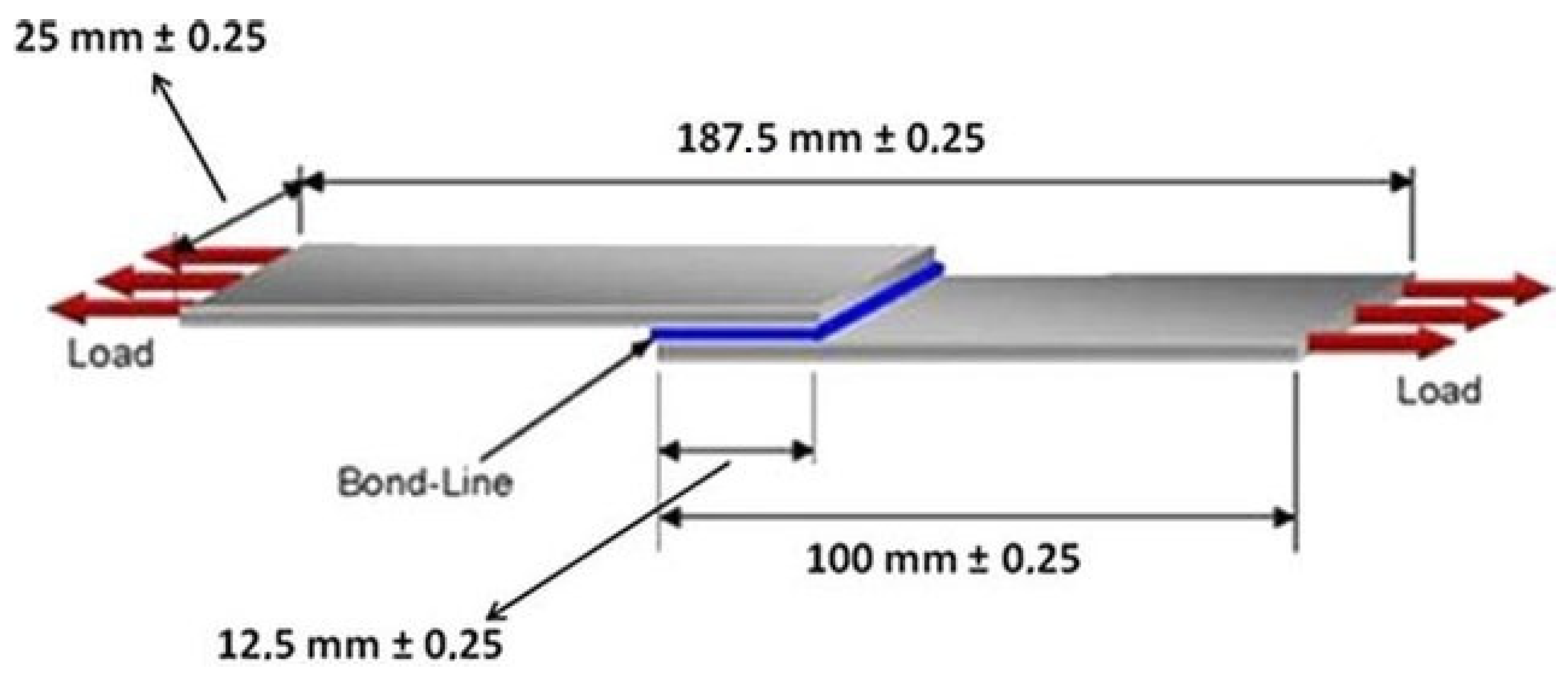




| MWCNTs Content | Barrel Temperature (°C) | Mould Temperature (°C) | Injection Pressure (bar) | Injection Time (s) | Post Pressure (bar) | Post Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 110 | 35 | 650 | 3 | 400 | 6 |
| 5 wt% | 150 | 35 | 800 | 5 | 700 | 10 |
| 10 wt% | 150 | 35 | 800 | 5 | 700 | 10 |
| TGA | DSC | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | T5% (°C) | T10% (°C) | Td (°C) | 1st Heating | 2nd Heating | Cooling | |||||
| Tg (°C) | Tm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Tg (°C) | Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Tc (°C) | ||||
| coPA | 310 | 346 | 437 | 17 48 | 101 | 18 | 17 | 103 | 76 | 27 | - |
| coPA + 5 wt% MWCNT | 336 | 378 | 465 | 18 63 | 101 | 13 | 28 | 103 | - | 17 | 74 |
| coPA + 10 wt% MWCNT | 330 | 373 | 456 | 19 66 | 100 | 10 | 30 | 101 | - | 15 | 74 |
| Tensile Test | Hardness Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Hardness (°ShD) |
| coPA | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 17.7 ± 1.81 | 55.9 ± 21.8 | 54 |
| coPA + 5 wt% MWCNT | 0.41 ± 0.02 | 22.9 ± 0.61 | 36.7 ± 11.2 | 60 |
| coPA + 10 wt% MWCNT | 0.66 ± 0.03 | 30.4 ± 0.73 | 28.6 ± 4.28 | 65 |
| Material | Lap Shear Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|
| coPA | 8.4 ± 0.51 |
| coPA + 5 wt% MWCNT | 5.4 ± 0.68 |
| coPA + 10 wt% MWCNT | 4.8 ± 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latko-Durałek, P.; Misiak, M.; Boczkowska, A. Electrically Conductive Adhesive Based on Thermoplastic Hot Melt Copolyamide and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Polymers 2022, 14, 4371. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204371
Latko-Durałek P, Misiak M, Boczkowska A. Electrically Conductive Adhesive Based on Thermoplastic Hot Melt Copolyamide and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Polymers. 2022; 14(20):4371. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204371
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatko-Durałek, Paulina, Michał Misiak, and Anna Boczkowska. 2022. "Electrically Conductive Adhesive Based on Thermoplastic Hot Melt Copolyamide and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes" Polymers 14, no. 20: 4371. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204371
APA StyleLatko-Durałek, P., Misiak, M., & Boczkowska, A. (2022). Electrically Conductive Adhesive Based on Thermoplastic Hot Melt Copolyamide and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Polymers, 14(20), 4371. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204371







