5-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline-containing Electrospun Materials Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Carboxymethyl Cellulose and Their Cu2+ and Fe3+ Complexes with Diverse Biological Properties: Antibacterial, Antifungal and Anticancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the PVA/CMC and PVA/CMC/5A8Q Solutions and Electrospinning
2.3. Obtaining the Cu2+ (Fe3+) Complexes of cr(PVA/CMC)/5A8Q Mats and of 5A8Q
2.4. Characterization
2.5. In Vitro Release of 5A8Q (5A8Q,Cu2+ (Fe3+)) from the Fibrous Mats
2.6. Evaluation of the Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of the Fibrous Mats
2.7. MTT Cell Viability Assay
2.8. Detection of Cell Morphological Alterations by Fluorescence Microscopy
2.8.1. Acridine Orange/Ethidium Bromide Live–Death Staining
2.8.2. DAPI Staining
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
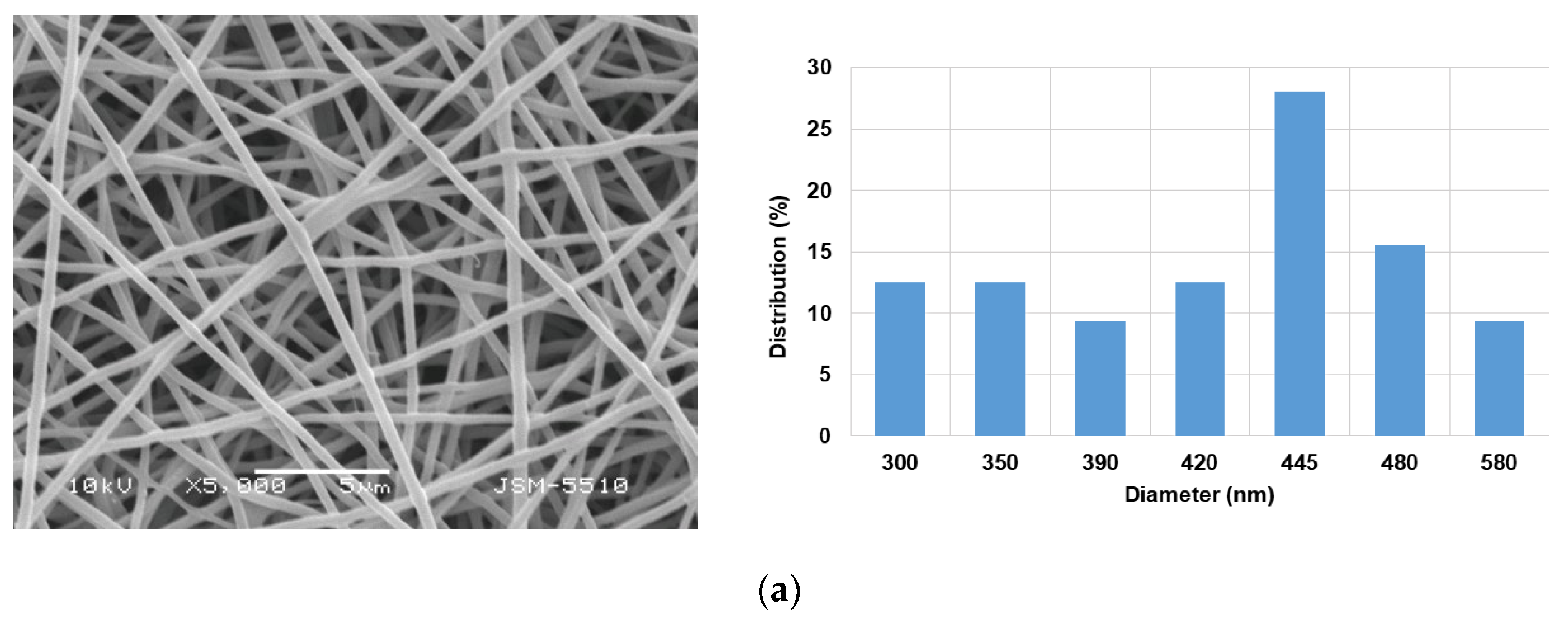
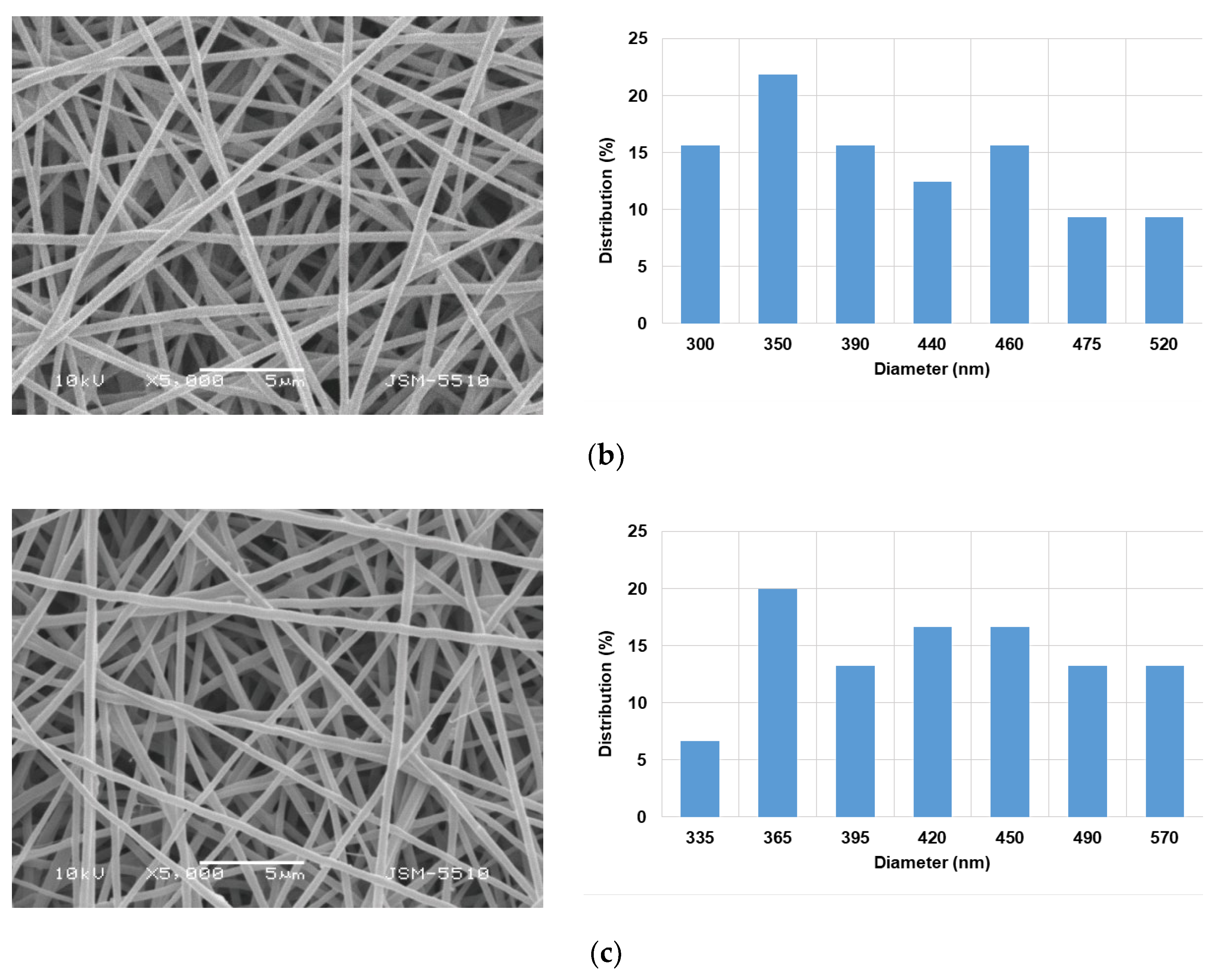
3.1. Morphology
3.2. ATR-FTIR Spectra of the Mats
3.3. Water Contact Angle Measurements
3.4. Thermal Analysis of the Mats
3.5. XPS Analysis of the Mats
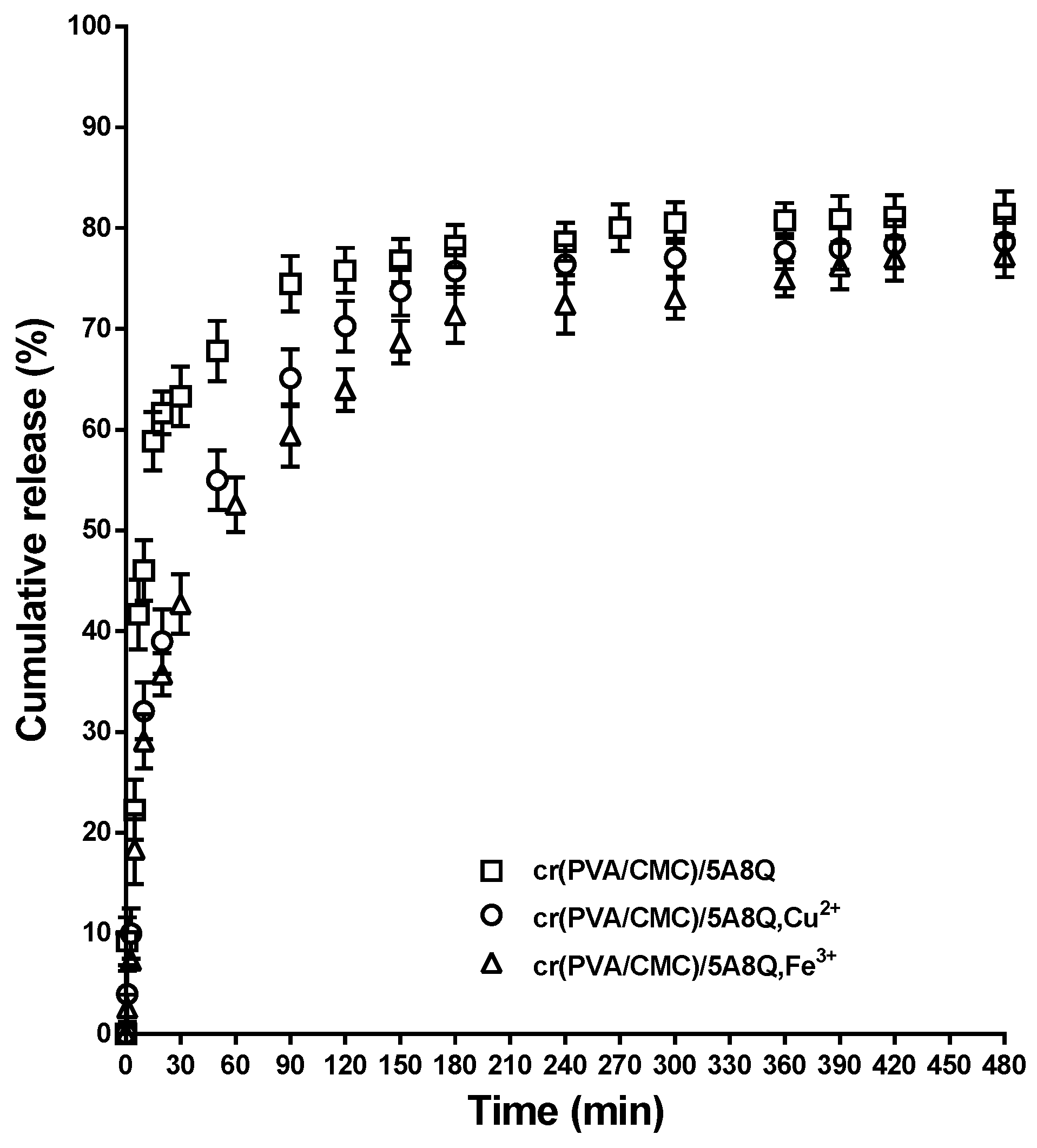
3.6. In Vitro 5A8Q and Its Complexes’ Release Studies
3.7. Assessment of the Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of the Mats
3.8. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of the Fibrous Mats towards HeLa and MCF-7 Cells and HaCaT Keratinocytes by MTT Assay
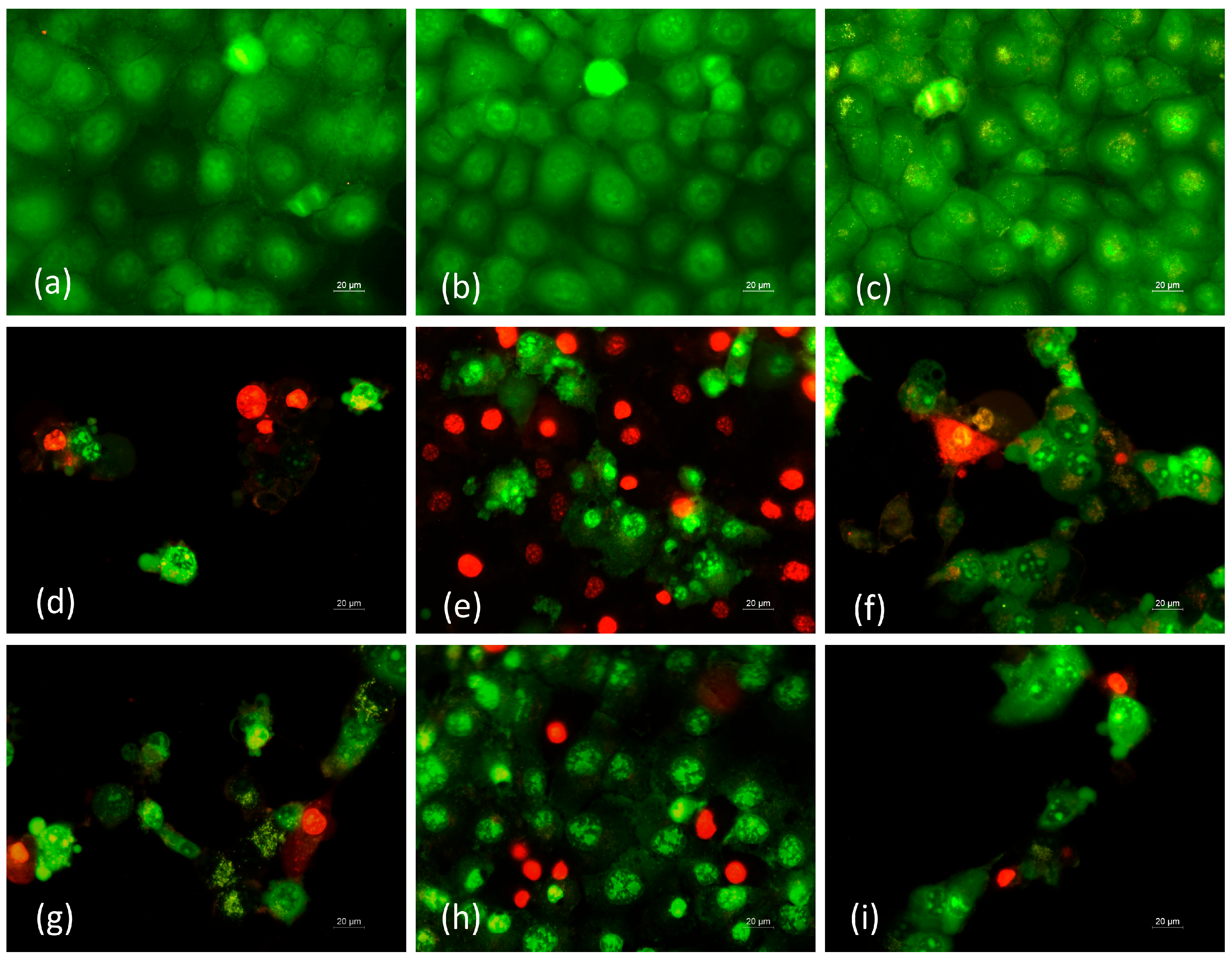
3.9. Fluorescence AO and EtBr Double Staining and DAPI Staining for Detection of Apoptosis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kriegel, C.; Arrechi, A.; Kit, K.; McClements, D.; Weiss, J. Fabrication, Functionalization, and Application of Electrospun Biopolymer Nanofibers. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zeng, L.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J. Fabrication of Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers with Diverse Morphologies. Molecules 2019, 24, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Yang, X.; Che, X.; Yang, M.; Zhai, G. Biomedical application and controlled drug release of electrospun fibrous materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odularu, A.T. Basic Principles of Electrospinning, Mechanisms, Nanofibre Production, and Anticancer Drug Delivery. J. Chem. Hindawi 2022, 2022, 9283325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulubayram, K.; Calamak, S.; Shahbazi, R.; Eroğlu, I. Nanofibers Based Antibacterial Drug Design, Delivery and Applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 1930–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luraghi, A.; Peri, F.; Moroni, L. Electrospinning for drug delivery applications: A review. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Hasan, M.S.; Nitai, A.S.; Nam, S.; Karmakar, A.K.; Ahsan, M.S.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Ahmed, M.B. Recent Developments of Carboxymethyl Cellulose. Polymers 2021, 13, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, T.; Pfeiffer, K. Studies on the synthesis and characterization of carboxymethylcellulose. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1999, 266, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maver, T.; Kurečič, M.; Pivec, T.; Maver, U.; Gradišnik, L.; Gašparič, P.; Kaker, B.; Bratuša, A.; Hribernik, S.; Kleinschek, K.S. Needleless electrospun carboxymethyl cellulose/polyethylene oxide mats with medicinal plant extracts for advanced wound care applications. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4487–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, T.; Muniyandy, S.; Chuah, L.H.; Janarthanan, P. Encapsulation of red palm oil in carboxymethyl sago cellulose beads by emulsification and vibration technology: Physicochemical characterization and in vitro digestion. J. Food Eng. 2018, 231, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshazly, E.H.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Zhang, S.; Ke, L.; Gong, R. Fabrication of folate-phytosterol-carboxymethyl cellulose nanoparticles derived from plant material as carrier of anticancer drug. Micro Nano Lett. 2019, 14, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Newehy, M.H.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Alotaiby, S.; El-Hamshary, H.; Moydeen, M.; Al-Deyab, S. Preparation of biocompatible system based on electrospun CMC/PVA nanofibers as controlled release carrier of diclofenac sodium. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2016, 53, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allafchian, A.; Hosseini, H.; Ghoreishi, S.M. Electrospinning of PVA-carboxymethyl cellulose nanofibers for flufenamic acid drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMerlis, C.C.; Schoneker, D.R. Review of the oral toxicity of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chu, C.; Hao, L.; She, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhai, L.; Jiang, S. Synthesis, antimicrobial, and release behaviors of tetracycline hydrochloride loaded poly(vInyl alcohol)/chitosan/ZrO2 nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Yoshimura, N.; Kobayashi, A.; Ito, T.; Hara, K.; Tahara, K. Emulsion-electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers as a solid dispersion system to improve solubility and control the release of probucol, a poorly water-soluble drug. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 67, 102953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S. 8-Hydroxyquinolines: A review of their metal chelating properties and medicinal applications. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 1157–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.; Luxami, V.; Paul, K. Insights of 8-hydroxyquinolines: A novel target in medicinal chemistry. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, N.; Paneva, D.; Mincheva, R.; Toncheva, A.; Manolova, N.; Dubois, P.; Rashkov, I. Poly (l-lactide) and poly (butylene succinate) immiscible blends: From electrospinning to biologically active materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 41, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasova, M.; Manolova, N.; Paneva, D.; Rashkov, I. Preparation of chitosan-containing nanofibres by electrospinning of chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) blend solutions. e-Polymers 2004, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincheva, R.; Manolova, N.; Paneva, D.; Rashkov, I. Preparation of polyelectrolyte-containing nanofibers by electrospinning in the presence of a non-ionogenic water-soluble polymer. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2005, 20, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Tsekova, P.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R.; Markova, N. Cellulose acetate-based electrospun materials with a variety of biological potentials: Antibacterial, antifungal and anticancer. Polymers 2021, 13, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Stoyanova, N.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Kukeva, R.; Stoyanova, R.; Toshkova, R.; Georgieva, A. Electrospun materials from polylactide and Schiff base derivative of Jeffamine ED® and 8-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxaldehyde and its complex with Cu2+: Preparation, antioxidant and antitumor activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Anastasova, I.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Markova, N.; Kukeva, R.; Stoyanova, R.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R. Bio-based electrospun fibers from chitosan schiff base and polylactide and their Cu2+ and Fe3+ complexes: Preparation and antibacterial and anticancer activities. Polymers 2022, 14, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, V.; Lanza, V.; Milardi, D.; Viale, M.; Maric, I.; Sgarlata, C.; Vecchio, G. Amino- and chloro-8-hydroxyquinolines and their copper complexes as proteasome inhibitors and antiproliferative agents. Metallomics 2017, 9, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wood, T.E.; Sprangers, R.; Jansen, G.; Franke, N.E.; Mao, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Verbrugge, S.E.; Adomat, H.; et al. Effect of Noncompetitive Proteasome Inhibition on Bortezomib Resistance. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 1069–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdtrakulkiat, R.; Boonpangrak, S.; Sinthupoom, N.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Derivatives (halogen, nitro and amino) of 8-hydroxyquinoline with highly potent antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. BB Rep. 2016, 6, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ignatova, M.; Stoilova, O.; Manolova, N.; Markova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospun mats from styrene/maleic anhydride copolymers: Modification with amines and assessment of antimicrobial activity. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 944–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Taggart, J.E.; Zhang, X.; Benbrook, D.M.; Lind, S.E.; Ding, W.-Q. Nitroxoline (8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinoline) is more a potent anti-cancer agent than clioquinol (5-chloro-7-iodo-8-quinoline). Cancer Lett. 2011, 312, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ignatova, M.; Starbova, K.; Markova, N.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospun nano-fibre mats with antibacterial properties from quaternised chitosan and poly(vinyl alcohol). Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 2098–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, S.I.A.; Abdul, A.B.; Alzubairi, A.S.; Elhassan, M.M.; Mohan, S. In vitro ultramorphological assessment of apoptosis induced by zerumbone on (HeLa). J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 769568. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, L. Preparation and characterization of pH-responsive poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium carboxymethylcellulose nanofibers. Adv. Mat. Res. 2013, 796, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Guerrero, J.G.; Martínez-Rodríguez, M.A.; Garza-Navarro, M.A.; González-González, V.A.; Torres-Castro, A.; De La Rosa, J.R. Magnetic nanofibrous materials based on CMC/PVA polymeric blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, L.; Si, J.; Wang, Q.; Peng, X.; Chen, W. Electrospinning and crosslinking of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan composite nanofiber for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2017, 37, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Khil, M.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.U.; Jahng, K.Y. An improved hydrophilicity via electrospinning for enhanced cell attachment and proliferation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 78, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakane, K.; Yamashita, T.; Iwakura, K.; Suzuki, F. Properties and structure of poly(vinyl alcohol)/silica composites. J. Appl. Polym. 1999, 74, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sakhawy, M.; Tohamy, H.-A.S.; Salama, A.; Kamel, S. Thermal properties of carboxymethyl cellulose acetate butyrate. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2019, 53, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, M.; Matsushita, T.; Ikeda, S. X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy of copper (II) complexes with donor sets of O4, N2O4, N2O2, N4, N2S2, and S4. Anal. Sci. 1993, 9, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashid, S.; Shen, C.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Wen, Y.; Liu, J. Enhanced catalytic ability of chitosan–Cu–Fe bimetal complex for the removal of dyes in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 90731–90741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanparia, S.F.; Patel, T.S.; Sojitra, N.A.; Jagani, C.L.; Dixit, B.C.; Patel, P.S.; Dixit, R.B. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial study of novel 4-{[(8-Hydroxyquinolin-5-yl)methyl]amino}benzenesulfonamide and its oxinates. Acta Chim. Slov. 2010, 57, 600–667. [Google Scholar]
- Anjaneyulu, Y.; Rao, R.P.; Swamy, R.Y.; Eknath, A.; Rao, K.N. In Vitro antimicrobial-activity studies on the mixed ligand complexes of Hg (II) with 8-hydroxyquinoline and salicylic acids. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 1982, 91, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, A.; Gibson, M.I.; Rubbo, S.D. The influence of chemical constitution on antibacterial activity. VI. The bactericidal action of 8-hydroxyquinoline (oxine). Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1953, 34, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pippi, B.; Lopes, W.; Reginatto, P.; Silva, F.K.; Joaquim, A.R.; Alves, R.J.; Silveira, G.P.; Vainstein, M.H.; Andrade, S.F.; Fuentefria, A.M. New insights into the mechanism of antifungal action of 8-hydroxyquinolines. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 27, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R.; Markova, N. 5-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline-containing Electrospun Materials Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Carboxymethyl Cellulose and Their Cu2+ and Fe3+ Complexes with Diverse Biological Properties: Antibacterial, Antifungal and Anticancer. Polymers 2023, 15, 3140. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143140
Ignatova M, Manolova N, Rashkov I, Georgieva A, Toshkova R, Markova N. 5-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline-containing Electrospun Materials Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Carboxymethyl Cellulose and Their Cu2+ and Fe3+ Complexes with Diverse Biological Properties: Antibacterial, Antifungal and Anticancer. Polymers. 2023; 15(14):3140. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143140
Chicago/Turabian StyleIgnatova, Milena, Nevena Manolova, Iliya Rashkov, Ani Georgieva, Reneta Toshkova, and Nadya Markova. 2023. "5-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline-containing Electrospun Materials Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Carboxymethyl Cellulose and Their Cu2+ and Fe3+ Complexes with Diverse Biological Properties: Antibacterial, Antifungal and Anticancer" Polymers 15, no. 14: 3140. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143140
APA StyleIgnatova, M., Manolova, N., Rashkov, I., Georgieva, A., Toshkova, R., & Markova, N. (2023). 5-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline-containing Electrospun Materials Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Carboxymethyl Cellulose and Their Cu2+ and Fe3+ Complexes with Diverse Biological Properties: Antibacterial, Antifungal and Anticancer. Polymers, 15(14), 3140. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143140







