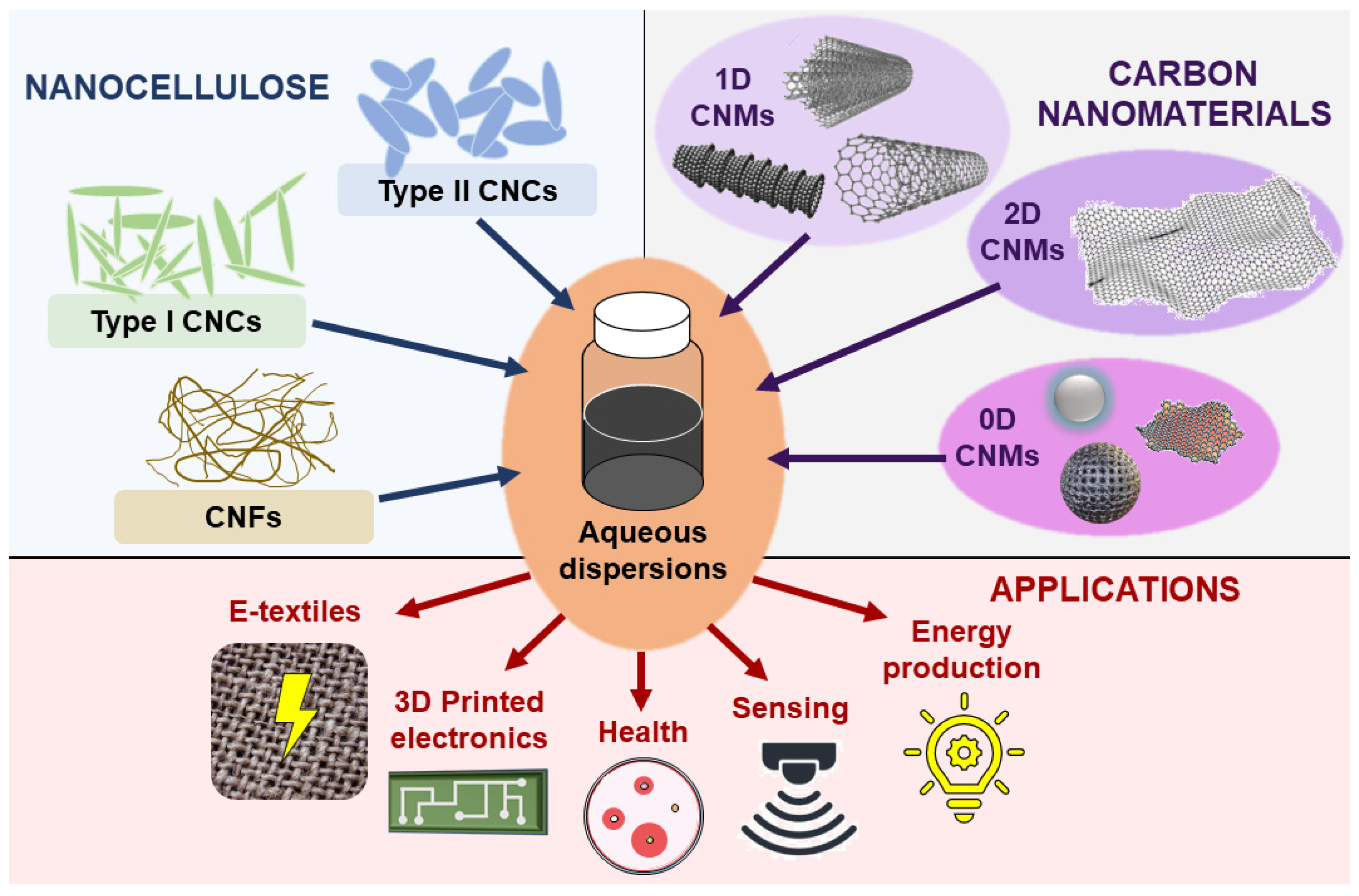
Nanocellulose: The Ultimate Green Aqueous Dispersant for Nanomaterials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
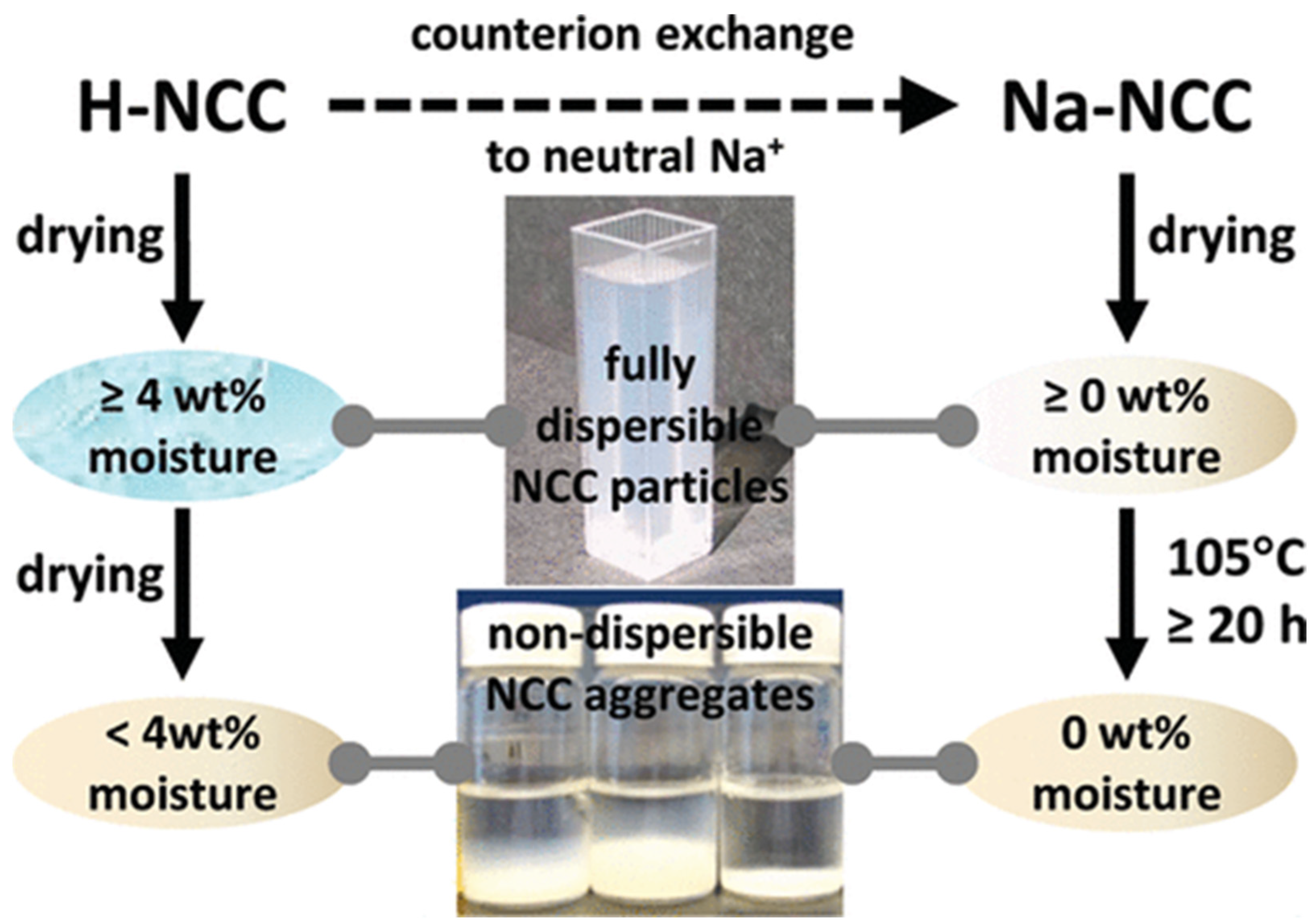
2. Nanocellulose-Water Interactions and Their Implications for Its Aqueous Colloidal Properties
3. Carbon Nanomaterials Aqueous Dispersions via Nanocellulose
4. Other Nanomaterials Dispersed via Nanocellulose
5. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Sullivan, A.C. Cellulose: The Structure Slowly Unravels. Cellulose 1997, 4, 173–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Heublein, B.; Fink, H.-P.; Bohn, A. Cellulose: Fascinating Biopolymer and Sustainable Raw Material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3358–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargarzadeh, H.; Mariano, M.; Gopakumar, D.; Ahmad, I.; Thomas, S.; Dufresne, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, N. Advances in Cellulose Nanomaterials. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2151–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esa, F.; Tasirin, S.M.; Rahman, N.A. Overview of Bacterial Cellulose Production and Application. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2014, 2, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Kramer, F.; Moritz, S.; Lindström, T.; Ankerfors, M.; Gray, D.; Dorris, A. Nanocelluloses: A New Family of Nature-Based Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5438–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, V.; Fuentes, L.; Berdejo, D.; González-Domínguez, J.M.; Maser, W.K.; Benito, A.M. Oil-in-Water Pickering Emulsions Stabilized with Nanostructured Biopolymers: A Venue for Templating Bacterial Cellulose. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, V.; Torrubia, J.; Blanco, D.; García-Bordeje, E.; Maser, W.K.; Benito, A.M.; González-Domínguez, J.M. Optimizing Bacterial Cellulose Production Towards Materials for Water Remediation. In Nanoscience and Nanotechnology in Security and Protection against CBRN Threats; NATO Science for Peace and Security Series B: Physics and Biophysics Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 391–403. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Heng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zou, H.; Liang, M. Robust and Flexible Cellulose Nanofiber/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Film for High-Performance Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 17152–17160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Domínguez, J.M.; Ansón-Casaos, A.; Grasa, L.; Abenia, L.; Salvador, A.; Colom, E.; Mesonero, J.E.; García-Bordejé, J.E.; Benito, A.M.; Maser, W.K. Unique Properties and Behavior of Nonmercerized Type-II Cellulose Nanocrystals as Carbon Nanotube Biocompatible Dispersants. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3147–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, C.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Figueiredo, F.M.L.; Freire, C.S.R. Nanocellulose-Based Materials as Components of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2019, 7, 20045–20074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.; Ching, Y.; Chuah, C.; Julai, S.; Liou, N.-S. Preparation and Characterization of Polyvinyl Alcohol-Chitosan Composite Films Reinforced with Cellulose Nanofiber. Materials 2016, 9, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang Molino, B.; Wang, X.; Cheng, F.; Xu, W.; Molino, P.; Bacher, M.; Su, D.; Rosenau, T.; Willför, S.; et al. 3D Printing of Nanocellulose Hydrogel Scaffolds with Tunable Mechanical Strength towards Wound Healing Application. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 7066–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Davoudpour, Y.; Islam, M.N.; Mustapha, A.; Sudesh, K.; Dungani, R.; Jawaid, M. Production and Modification of Nanofibrillated Cellulose Using Various Mechanical Processes: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y. Extraction and Comparison of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Lemon (Citrus limon) Seeds Using Sulfuric Acid Hydrolysis and Oxidation Methods. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Qi, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, K. Selective Isolation Methods for Cellulose and Chitin Nanocrystals. Chempluschem 2020, 85, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Mo, L.; Li, J. A Comparative Study on the Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Nanocrystals with Various Polymorphs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flauzino Neto, W.P.; Putaux, J.L.; Mariano, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Otaguro, H.; Pasquini, D.; Dufresne, A. Comprehensive Morphological and Structural Investigation of Cellulose I and II Nanocrystals Prepared by Sulphuric Acid Hydrolysis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 76017–76027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, V.; Álvarez Sánchez, M.Á.; Güemes, L.; Martínez-Barón, C.; Baúlde, S.; Criado, A.; González-Domínguez, J.M.; Maser, W.K.; Benito, A.M. Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystals: Controlling the Crystalline Type by One-Pot Acid Hydrolysis. ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Takabe, K.; Xu, F. Nanocrystals of Cellulose Allomorphs Have Different Adsorption of Cellulase and Subsequent Degradation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 112, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinquefield, S.; Ciesielski, P.N.; Li, K.; Gardner, D.J.; Ozcan, S. Nanocellulose Dewatering and Drying: Current State and Future Perspectives. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 9601–9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, W.; Xiao, H. Dispersion Properties of Nanocellulose: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hsieh, Y. Lo Aqueous Exfoliated Graphene by Amphiphilic Nanocellulose and Its Application in Moisture-Responsive Foldable Actuators. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 11719–11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solhi, L.; Guccini, V.; Heise, K.; Solala, I.; Niinivaara, E.; Xu, W.; Mihhels, K.; Kröger, M.; Meng, Z.; Wohlert, J.; et al. Understanding Nanocellulose–Water Interactions: Turning a Detriment into an Asset. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 1925–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benselfelt, T.; Kummer, N.; Nordenström, M.; Fall, A.B.; Nyström, G.; Wågberg, L. The Colloidal Properties of Nanocellulose. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202201955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curvello, R.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Garnier, G. Engineering Nanocellulose Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 267, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, L.; Derakhshandeh, M.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G.; Hamad, W.Y.; MacLachlan, M.J. Hydrothermal Gelation of Aqueous Cellulose Nanocrystal Suspensions. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suenaga, S.; Osada, M. Hydrothermal Gelation of Pure Cellulose Nanofiber Dispersions. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.; Bouchard, J.; Berry, R. Dispersibility in Water of Dried Nanocrystalline Cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Luo, J.; Bakhtiary Davijani, A.A.; Chien, A.T.; Wang, P.H.; Liu, H.C.; Kumar, S. Individually Dispersed Wood-Based Cellulose Nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5768–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santmarti, A.; Tammelin, T.; Lee, K.Y. Prevention of Interfibril Hornification by Replacing Water in Nanocellulose Gel with Low Molecular Weight Liquid Poly(Ethylene Glycol). Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.Z.; Guan, Q.F.; Xia, J.; Ling, Z.C.; He, Z.Z.; Han, Z.M.; Yang, H.-B.; Gu, P.; Zhu, Y.B.; Yu, S.H.; et al. Strengthening and Toughening Hierarchical Nanocellulose via Humidity-Mediated Interface. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yao, Q.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, H. Processing Nanocellulose to Bulk Materials: A Review. Cellulose 2019, 26, 7585–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jović, D.; Jaćević, V.; Kuča, K.; Borišev, I.; Mrdjanovic, J.; Petrovic, D.; Seke, M.; Djordjevic, A. The Puzzling Potential of Carbon Nanomaterials: General Properties, Application, and Toxicity. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, V.; Souza Filho, A.G.; Barros, E.B.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Physical Properties of Low-Dimensional Sp2-Based Carbon Nanostructures. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2016, 88, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Pint, C.L.; Islam, A.E.; Weatherup, R.S.; Hofmann, S.; Meshot, E.R.; Wu, F.; Zhou, C.; Dee, N.; Amama, P.B.; et al. Carbon Nanotubes and Related Nanomaterials: Critical Advances and Challenges for Synthesis toward Mainstream Commercial Applications. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11756–11784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Terentjev, E.M. Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes: Mixing, Sonication, Stabilization, and Composite Properties. Polymers 2012, 4, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiry, D.; Roubeau, O. Stoichiometric Control of Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes Functionalization. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4385–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, V.; Paleo, A.J.; González-Domínguez, J.M.; Muñoz, E.; Krause, B.; Pötschke, P.; Maser, W.K.; Benito, A.M. The Aqueous Processing of Carbon Nanofibers via Cellulose Nanocrystals as a Green Path towards E-Textiles with n-Type Thermoelectric Behaviour. Carbon 2024, 217, 118640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, C.; Moreau, C.; Bizot, H.; Cathala, B.; Chauvet, O. Cellulose Nanocrystals Mediated Dispersion of Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWNTs) and Elaboration of SWNTs /Cellulose Nanocrystals Multilayered Thin Films. MRS Proc. 2011, 1362, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, H.; Saito, T.; Kitaoka, T.; Nogi, M.; Suganuma, K.; Isogai, A. Transparent, Conductive, and Printable Composites Consisting of TEMPO-Oxidized Nanocellulose and Carbon Nanotube. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, C.; Moreau, C.; Bertoncini, P.; Bizot, H.; Chauvet, O.; Cathala, B. Cellulose Nanocrystal-Assisted Dispersion of Luminescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Layer-by-Layer Assembled Hybrid Thin Films. Langmuir 2012, 28, 12463–12471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougel, J.B.; Adda, C.; Bertoncini, P.; Capron, I.; Cathala, B.; Chauvet, O. Highly Efficient and Predictable Noncovalent Dispersion of Single-Walled and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by Cellulose Nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 22694–22701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougel, J.B.; Bertoncini, P.; Cathala, B.; Chauvet, O.; Capron, I. Macroporous Hybrid Pickering Foams Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Cellulose Nanocrystals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 544, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Domínguez, J.M.; Grasa, L.; Frontiñán-Rubio, J.; Abás, E.; Domínguez-Alfaro, A.; Mesonero, J.E.; Criado, A.; Ansón-Casaos, A. Intrinsic and Selective Activity of Functionalized Carbon Nanotube/Nanocellulose Platforms against Colon Cancer Cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 212, 112363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dortez, S.; Sierra, T.; Álvarez-Sánchez, M.Á.; González-Domínguez, J.M.; Benito, A.M.; Maser, W.K.; Crevillen, A.G.; Escarpa, A. Effect of Nanocellulose Polymorphism on Electrochemical Analytical Performance in Hybrid Nanocomposites with Non-Oxidized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Chen, T.; Hou, K.; Ma, W.; Tebyetekerwa, M.; Cheng, Y.; Weng, W.; Zhu, M. Robust, Hydrophilic Graphene/Cellulose Nanocrystal Fiber-Based Electrode with High Capacitive Performance and Conductivity. Carbon 2018, 127, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Domínguez, J.M.; Baigorri, A.; Álvarez-Sánchez, M.Á.; Colom, E.; Villacampa, B.; Ansón-Casaos, A.; García-Bordejé, E.; Benito, A.M.; Maser, W.K. Waterborne Graphene- and Nanocellulose-Based Inks for Functional Conductive Films and 3D Structures. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Caldas, M.X.; Andrei, C.M.; Evans, S.; de Lannoy, C.F. The Role of Cellulose Nanocrystals in Stabilizing Iron Nanoparticles. Cellulose 2020, 27, 8709–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Barón, C.M.; González-Domínguez, J.M.; Hernández-Ferrer, J.; Calvo, V.; Ansón-Casaos, A.; Villacampa, B.; Maser, W.K.; Benito, A.M. Towards sustainable TiO2 photoelectrodes based on cellulose nanocrystals as a processing adjuvant. RSC Sustain. 2024; accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian, A.; Lindström, S.B.; Pettersson, T.; Hamedi, M.M.; Wågberg, L. Understanding the Dispersive Action of Nanocellulose for Carbon Nanomaterials. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeng, F.; Denneulin, A.; Neuman, C.; Bras, J. Charge Density Modification of Carboxylated Cellulose Nanocrystals for Stable Silver Nanoparticles Suspension Preparation. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Crespiera, S.; Pepió-Tàrrega, B.; González-Gil, R.M.; Cecilia-Morillo, F.; Palmer, J.; Escobar, A.M.; Beneitez-álvarez, S.; Abitbol, T.; Fall, A.; Aulin, C.; et al. Use of Nanocellulose to Produce Water-Based Conductive Inks with Ag NPs for Printed Electronics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Castrillo, M.; Reguera, J.; Lizundia, E. Aqueous Cellulose Nanocrystal-Colloidal Au Inks for 2D Printed Photothermia. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 1468–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Huang, R.; Chai, S.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q. Completely Green Approach for the Preparation of Strong and Highly Conductive Graphene Composite Film by Using Nanocellulose as Dispersing Agent and Mechanical Compression. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9102–9113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Y.; Ray, U.; Zhu, S.; Dai, J.; Chen, C.; Fu, K.; Jang, S.H.; Henderson, D.; et al. Cellulose-Nanofiber-Enabled 3D Printing of a CarbonNanotube Microfiber Network. Small Methods 2017, 1, 1700222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Li, M.C.; Liu, C.; Wu, Q.; Mei, C. 3D Printed Ti3C2Tx MXene/Cellulose Nanofiber Architectures for Solid-State Supercapacitors: Ink Rheology, 3D Printability, and Electrochemical Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2109593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Ning, D.; Ma, Q.; Geng, B.; Liu, J.; Lu, Z. Highly Water-Dispersed Composite of Cellulose Nanofibers and Boron Nitride Nanosheets. Cellulose 2022, 29, 9657–9670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, R.; Liu, W.; Fang, Z.; Wang, L. A New Photoelectric Ink Based on Nanocellulose/CdS Quantum Dots for Screen-Printing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.E.P.; Bernardes, J.S.; Loh, W. Stabilizing Both Oil Droplets and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Aqueous Dispersion with Nanofibrillated Cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 302, 120354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamedi, M.M.; Hajian, A.; Fall, A.B.; Hkansson, K.; Salajkova, M.; Lundell, F.; Wgberg, L.; Berglund, L.A. Highly Conducting, Strong Nanocomposites Based on Nanocellulose-Assisted Aqueous Dispersions of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmenko, V.; Karabulut, E.; Pernevik, E.; Enoksson, P.; Gatenholm, P. Tailor-Made Conductive Inks from Cellulose Nanofibrils for 3D Printing of Neural Guidelines. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Peng, L.; Fang, Z.; Lin, X.; Sun, C.; Qiu, X. Dispersing Boron Nitride Nanosheets with Carboxymethylated Cellulose Nanofibrils for Strong and Thermally Conductive Nanocomposite Films with Improved Water-Resistance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 321, 121250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Wang, J.; Kang, W.; Cui, M.; Wang, X.; Foo, C.Y.; Chee, K.J.; Lee, P.S. Highly Stretchable Piezoresistive Graphene-Nanocellulose Nanopaper for Strain Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Wu, M. Cellulose Nanofiber Assisted Dispersion of Hydrophobic SiO2 Nanoparticles in Water and Its Superhydrophobic Coating. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 290, 119504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paleo, A.J.; Vieira, E.M.F.; Wan, K.; Bondarchuk, O.; Cerqueira, M.F.; Bilotti, E.; Melle-Franco, M.; Rocha, A.M. Vapor grown carbon nanofibre based cotton fabrics with negative thermoelectric power. Cellulose 2020, 27, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, W.H.; Md Bahri, N.F.; Abdul Majid, Z. Preparation, Marriage Chemistry and Applications of Graphene Quantum Dots–Nanocellulose Composite: A Brief Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprea, M.; Panaitescu, M.D. Nanocellulose Hybrids with Metal Oxides Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wu, W.; Xiao, H. Methods and Applications of Nanocellulose Loaded with Inorganic Nanomaterials: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Nanocellulose | Synthesis Method | Dispersed Nanomaterial | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNCs | Acid hydrolysis | SWCNTs | [9,39,41,42,43,44,45] |
| MWCNTs | [42,43] | ||
| Carbon nanofibers | [38] | ||
| rGO | [46] | ||
| GO and MWCNTs | [47] | ||
| nZVI | [48] | ||
| TiO2 NPs | [49] | ||
| TEMPO Oxidation + Acid hydrolysis | SWCNTs | [50] | |
| MWCNTs | |||
| rGO | |||
| TEMPO oxidation | Ag NPs | [51,52] | |
| Transition metal catalyzed oxidation | Au NPs | [53] | |
| CNFs | TEMPO oxidation | Graphene | [22] |
| Graphene nanosheets | [54] | ||
| SWCNTs | [40,50,55] | ||
| MWCNTs | [8,50] | ||
| rGO | [50] | ||
| MXene | [56] | ||
| BNNS | [57] | ||
| CdS dots | [58] | ||
| TiO2 NPs | [59] | ||
| Acid treatment + mechanical disintegration | SWCNTs | [60] | |
| Carboxymethylation | SWCNTs | [61] | |
| BNNS | [62] | ||
| Ag NPs | [52] | ||
| Mechanical disintegration | Crumpled graphene | [63] | |
| Unavailable information | SiO2 NPs | [64] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calvo, V.; Martínez-Barón, C.; Fuentes, L.; Maser, W.K.; Benito, A.M.; González-Domínguez, J.M. Nanocellulose: The Ultimate Green Aqueous Dispersant for Nanomaterials. Polymers 2024, 16, 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121664
Calvo V, Martínez-Barón C, Fuentes L, Maser WK, Benito AM, González-Domínguez JM. Nanocellulose: The Ultimate Green Aqueous Dispersant for Nanomaterials. Polymers. 2024; 16(12):1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121664
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalvo, Víctor, Carlos Martínez-Barón, Laura Fuentes, Wolfgang K. Maser, Ana M. Benito, and José M. González-Domínguez. 2024. "Nanocellulose: The Ultimate Green Aqueous Dispersant for Nanomaterials" Polymers 16, no. 12: 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121664
APA StyleCalvo, V., Martínez-Barón, C., Fuentes, L., Maser, W. K., Benito, A. M., & González-Domínguez, J. M. (2024). Nanocellulose: The Ultimate Green Aqueous Dispersant for Nanomaterials. Polymers, 16(12), 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121664










