Characterization of Electrospinning Chitosan Nanofibers Used for Wound Dressing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Determination of the Molecular Weight
2.3. Determination of Degree of Deacetylation (DD)
2.4. The Preparation of Electrospinning Solutions
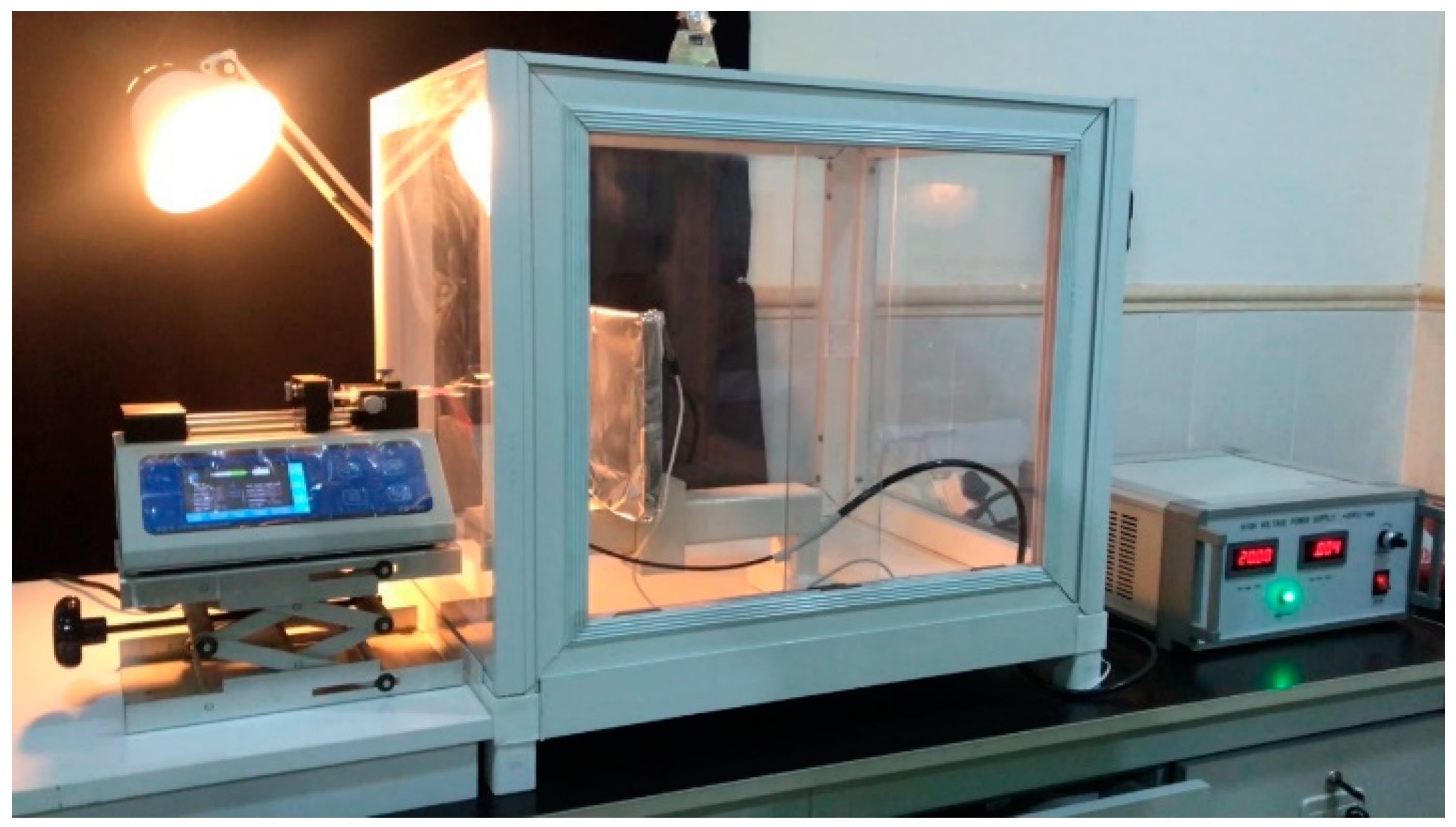
2.5. Electrospinning Process
2.6. Antibacterial Activity Method
2.7. Characterizations
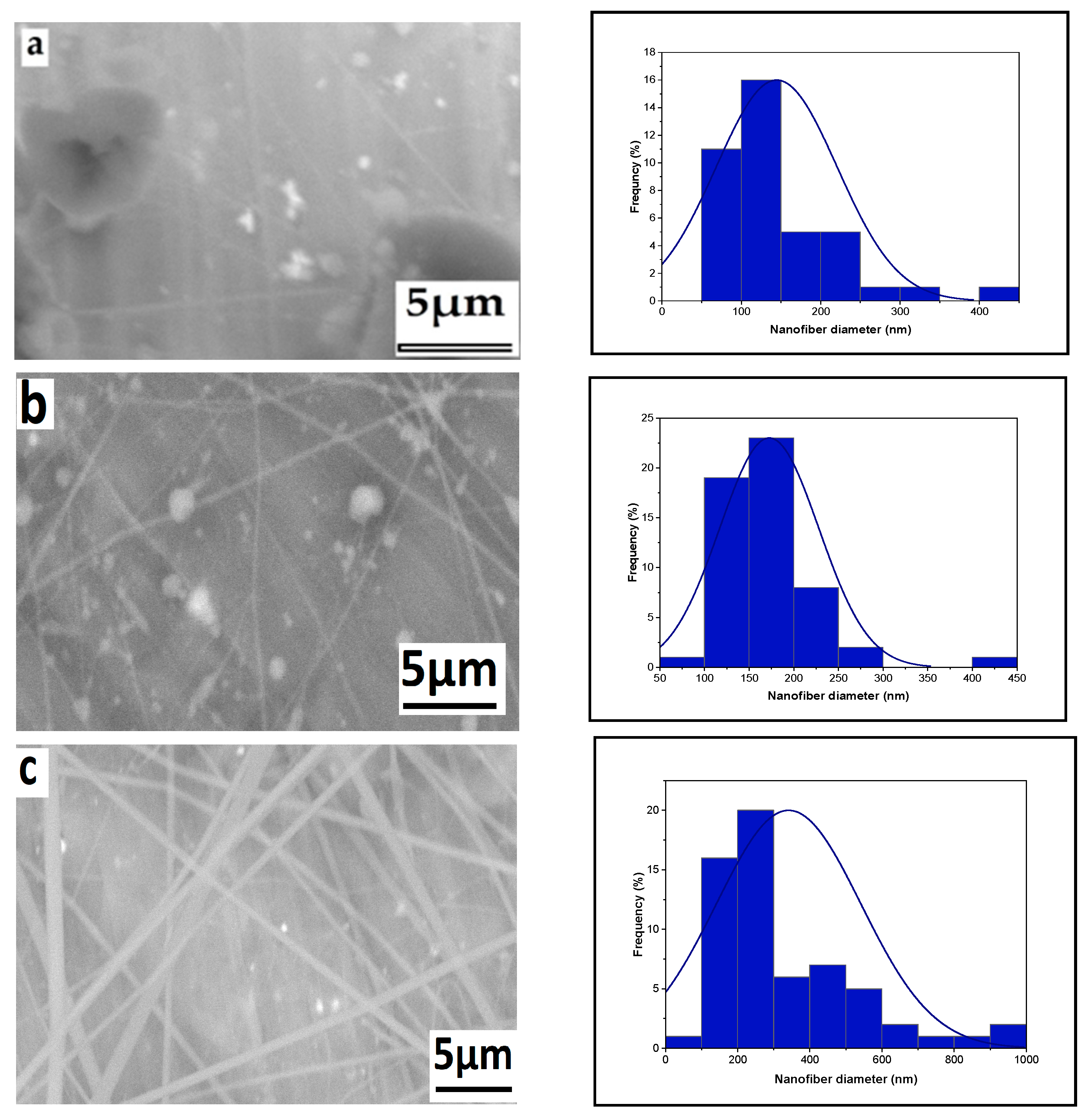
2.7.1. Scanning Electron Microscope
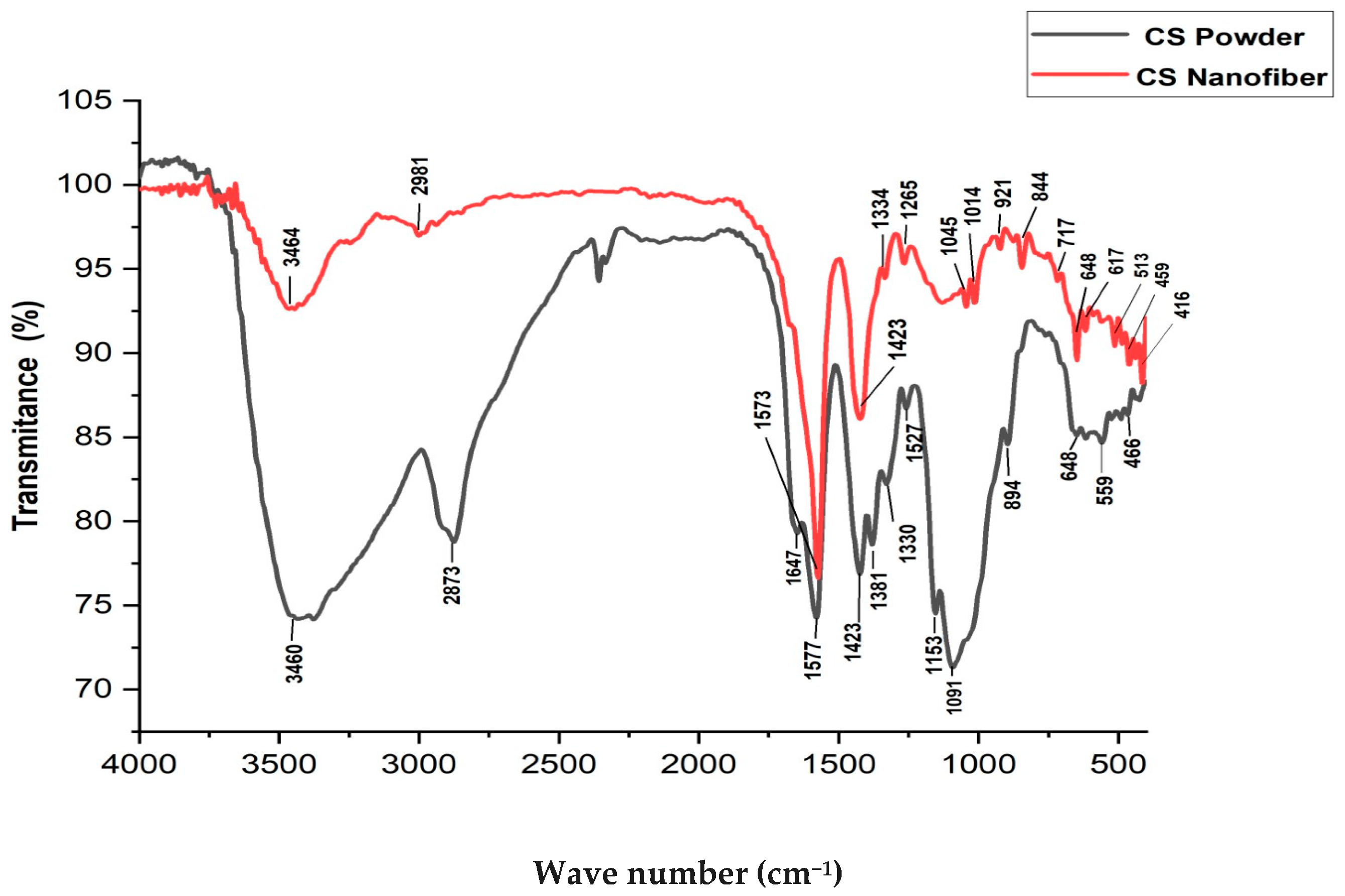
2.7.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)Spectroscopy
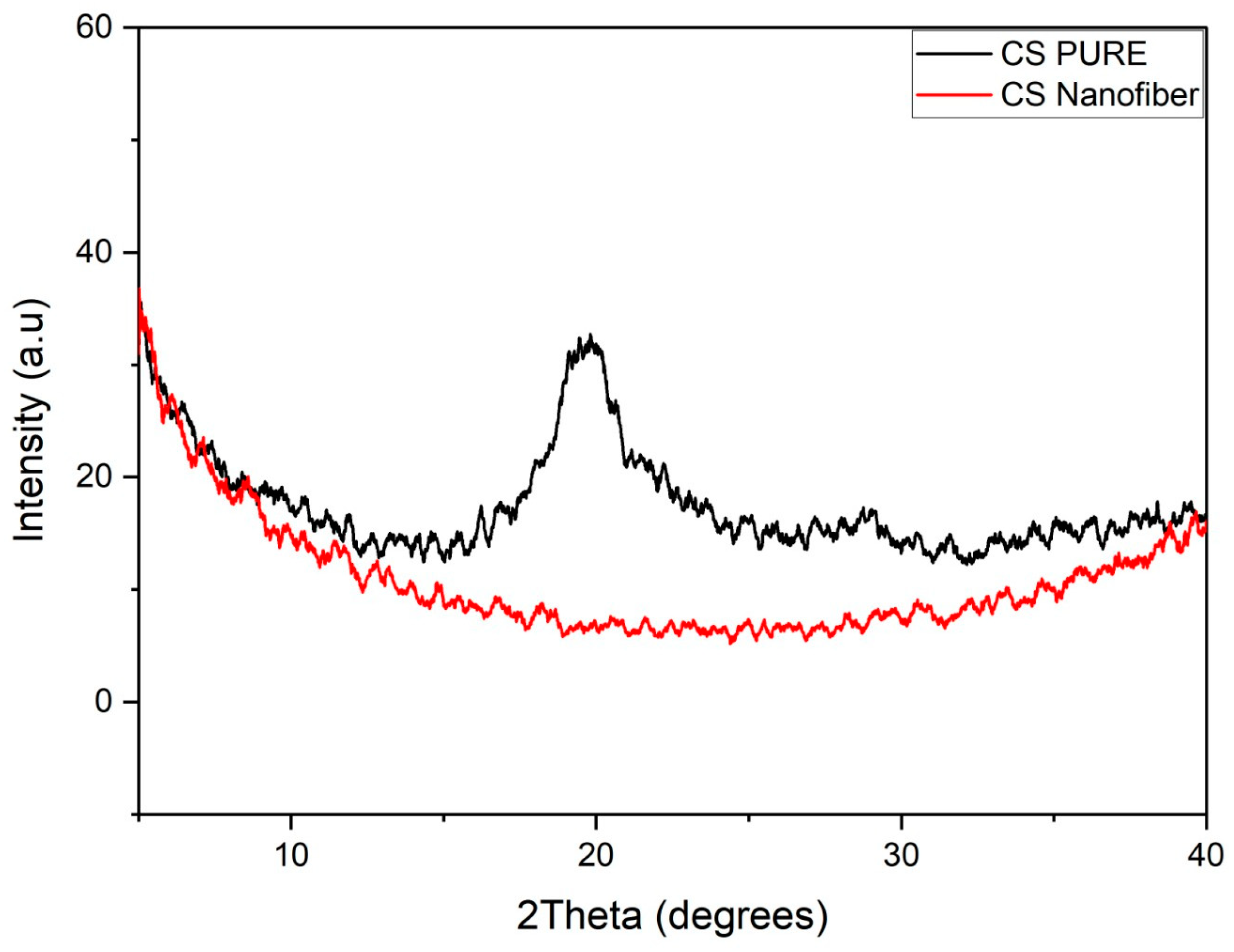
2.7.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Parameter Effects on Nanofiber Morphology
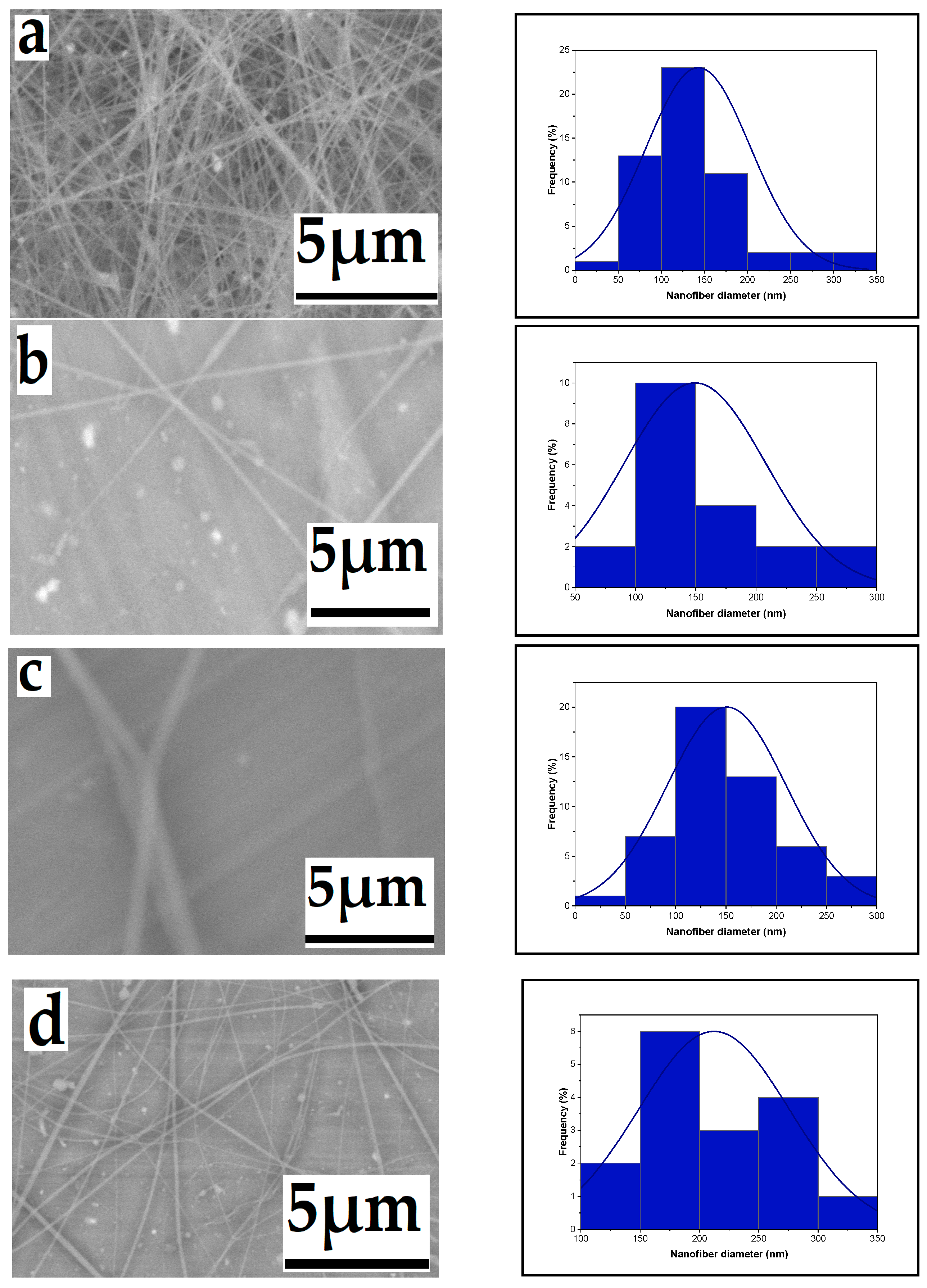
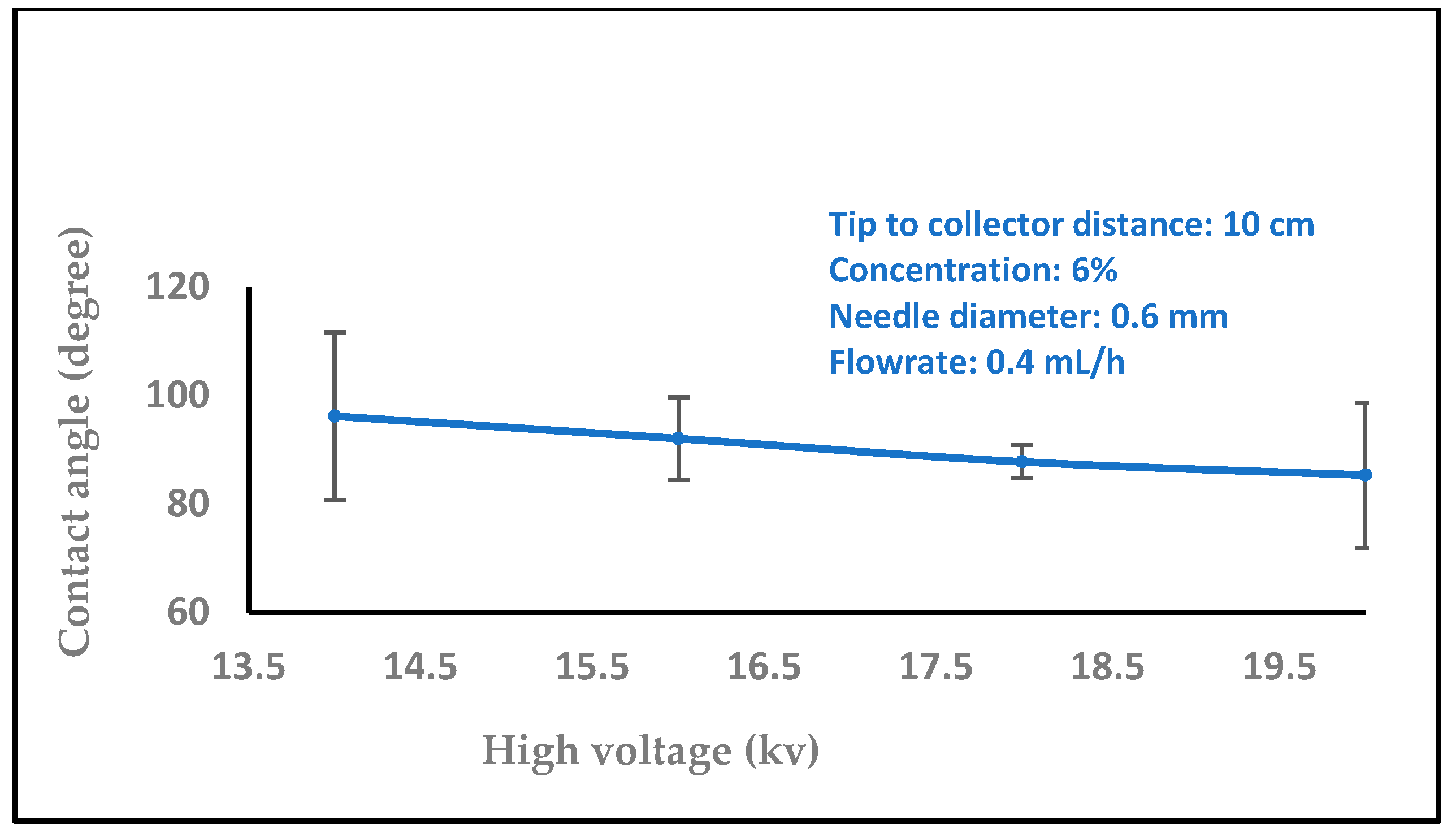
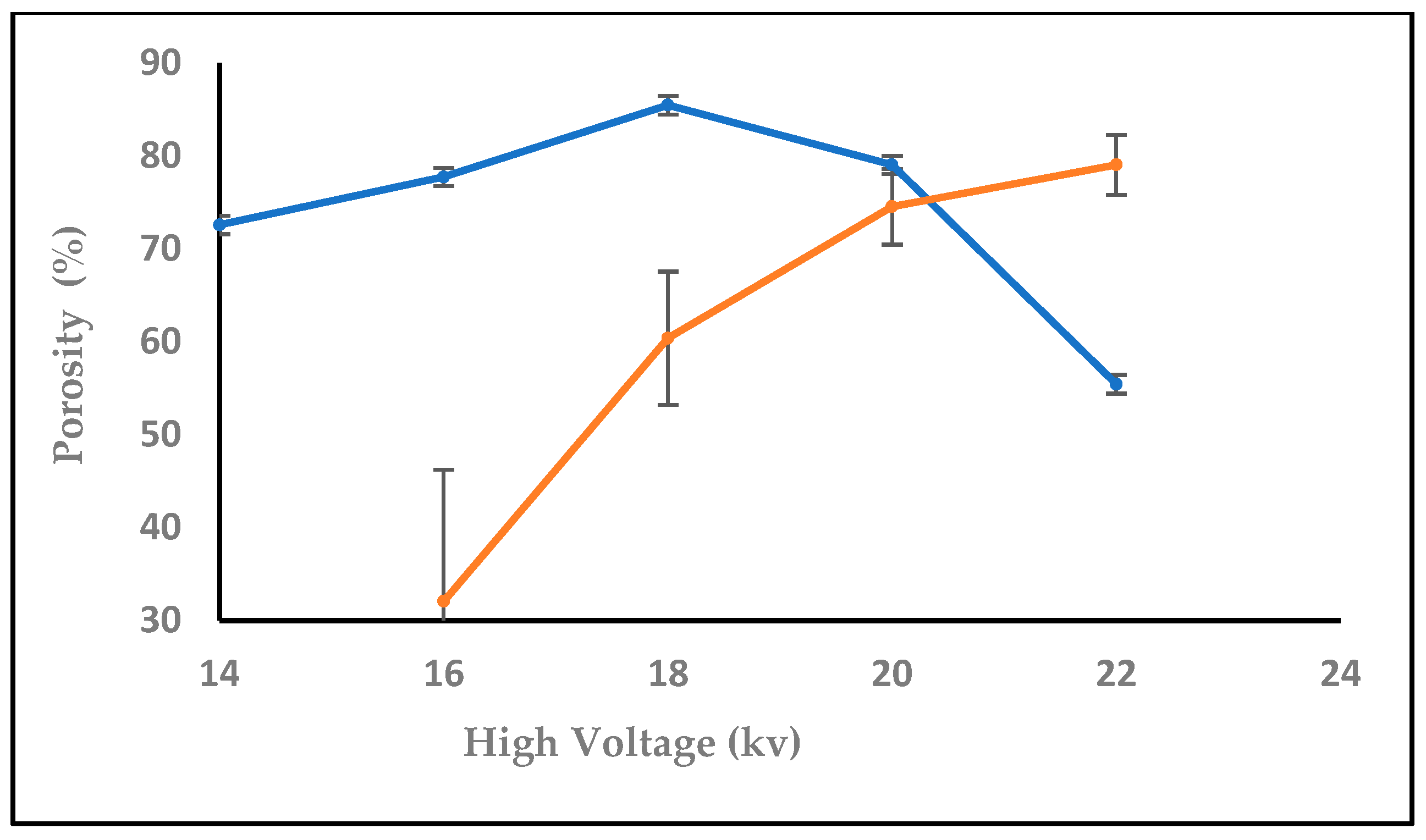
3.1.1. Effect of High Voltage
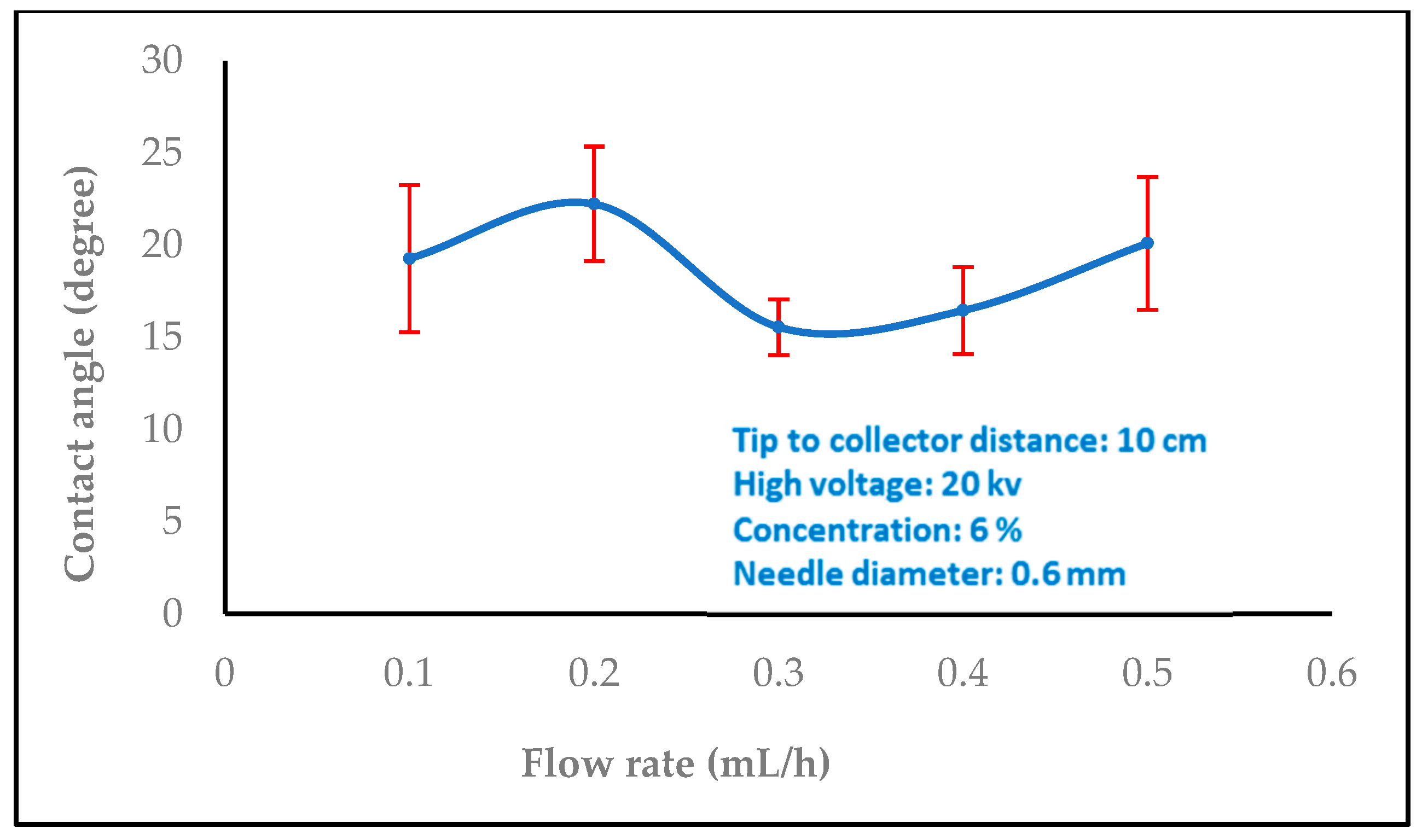
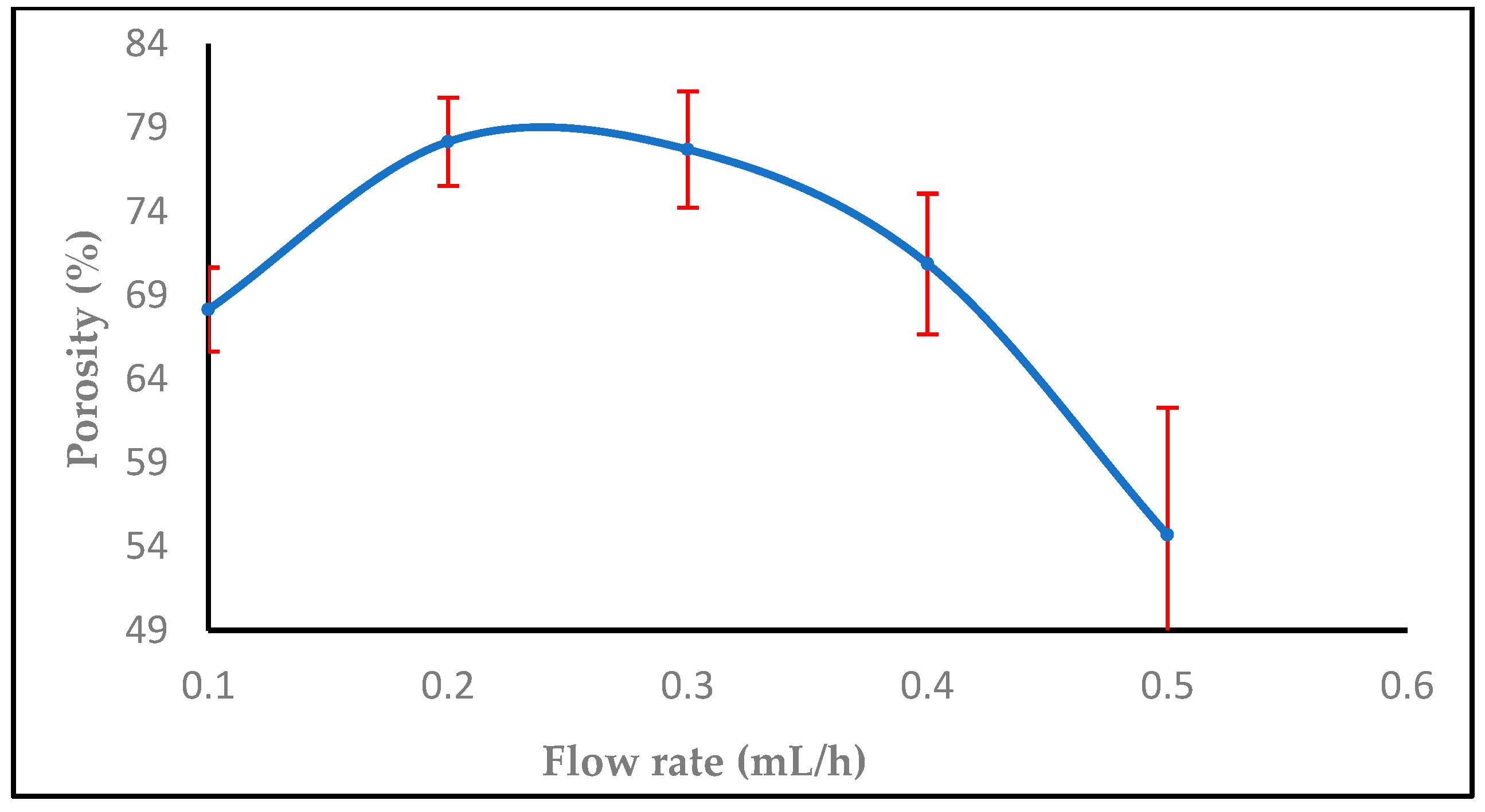
3.1.2. Effect of Flow Rate
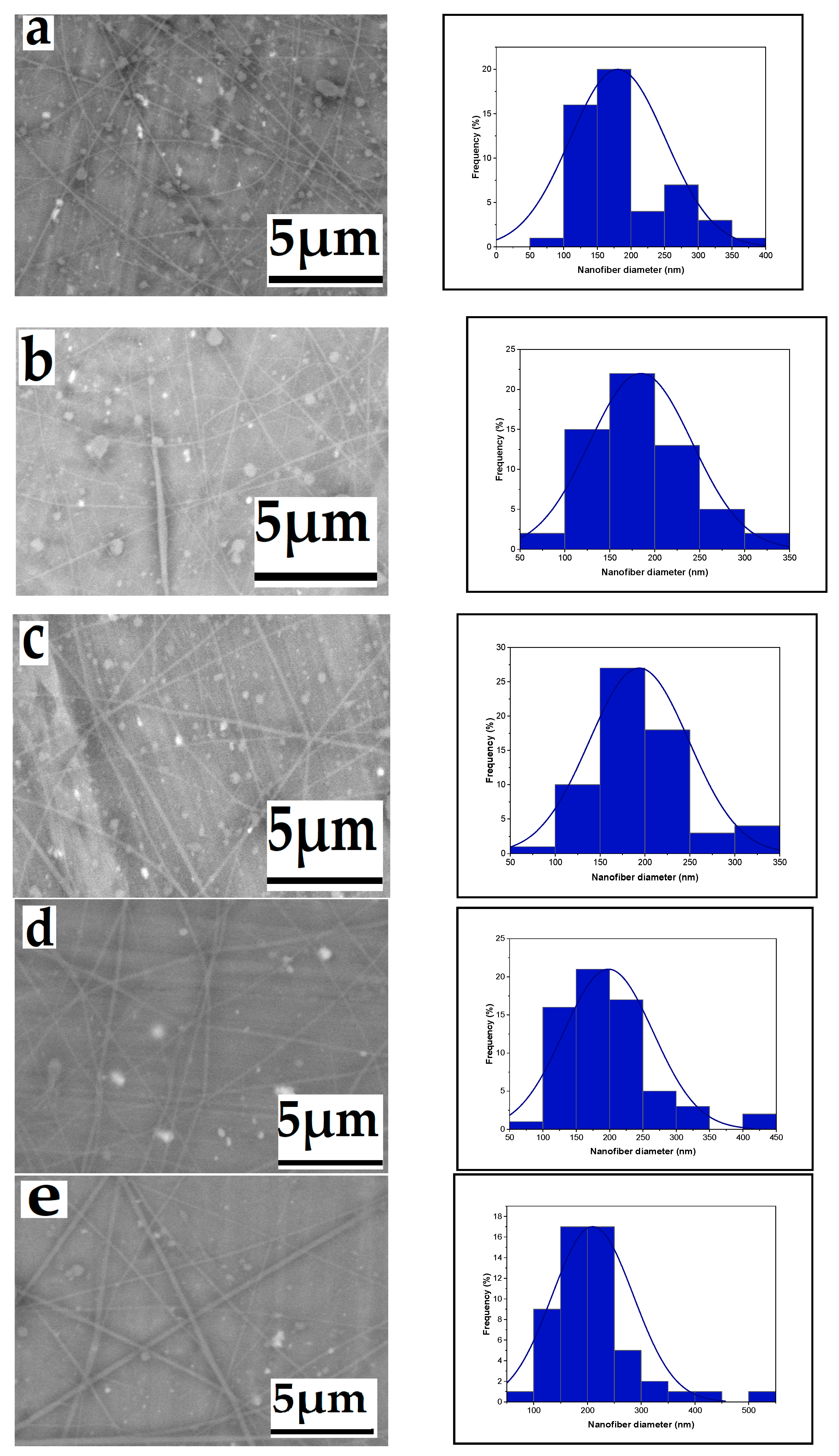
3.1.3. Effect of Tip-to-Target Distance
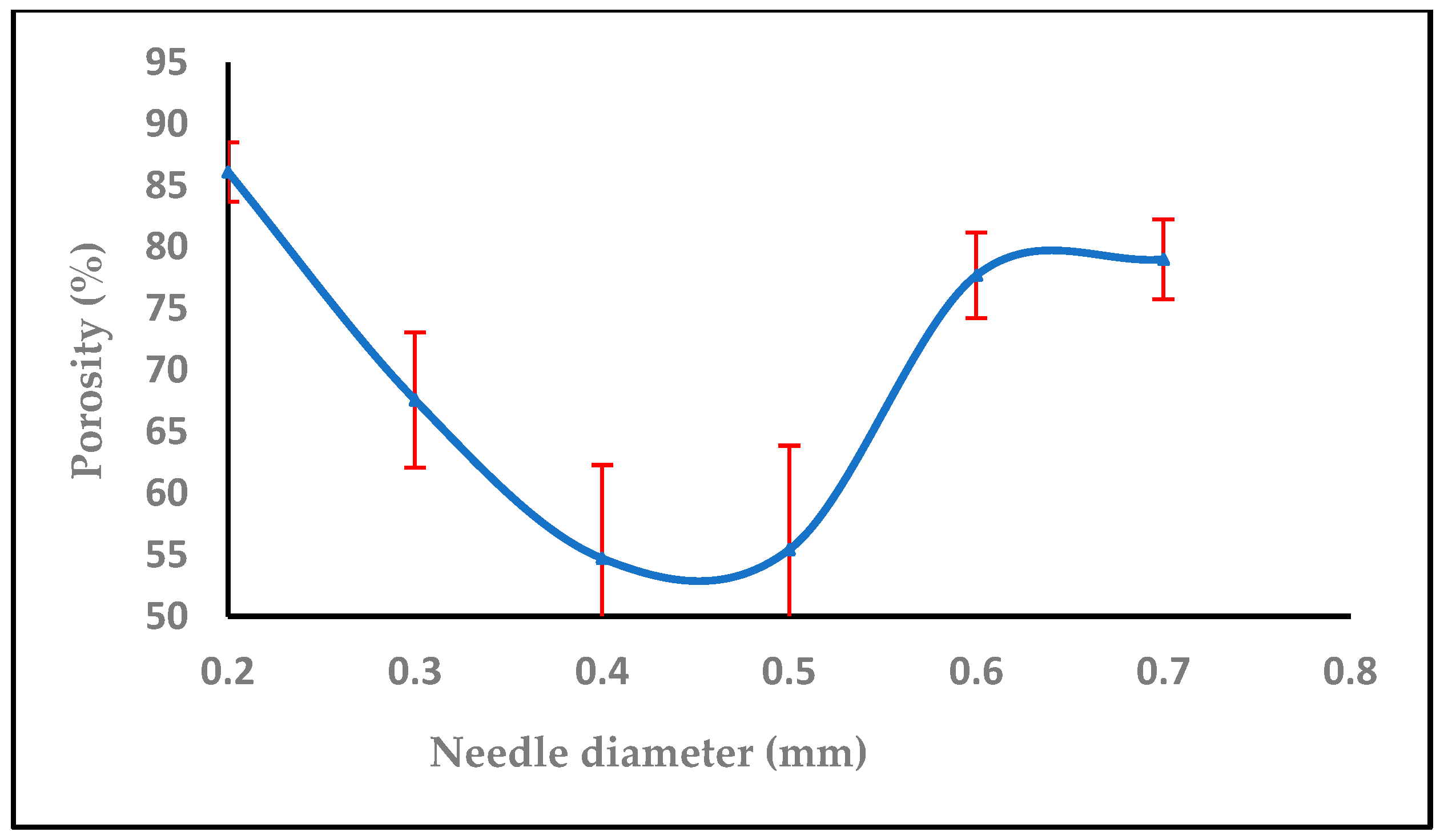
3.1.4. Effect of Needle Diameter
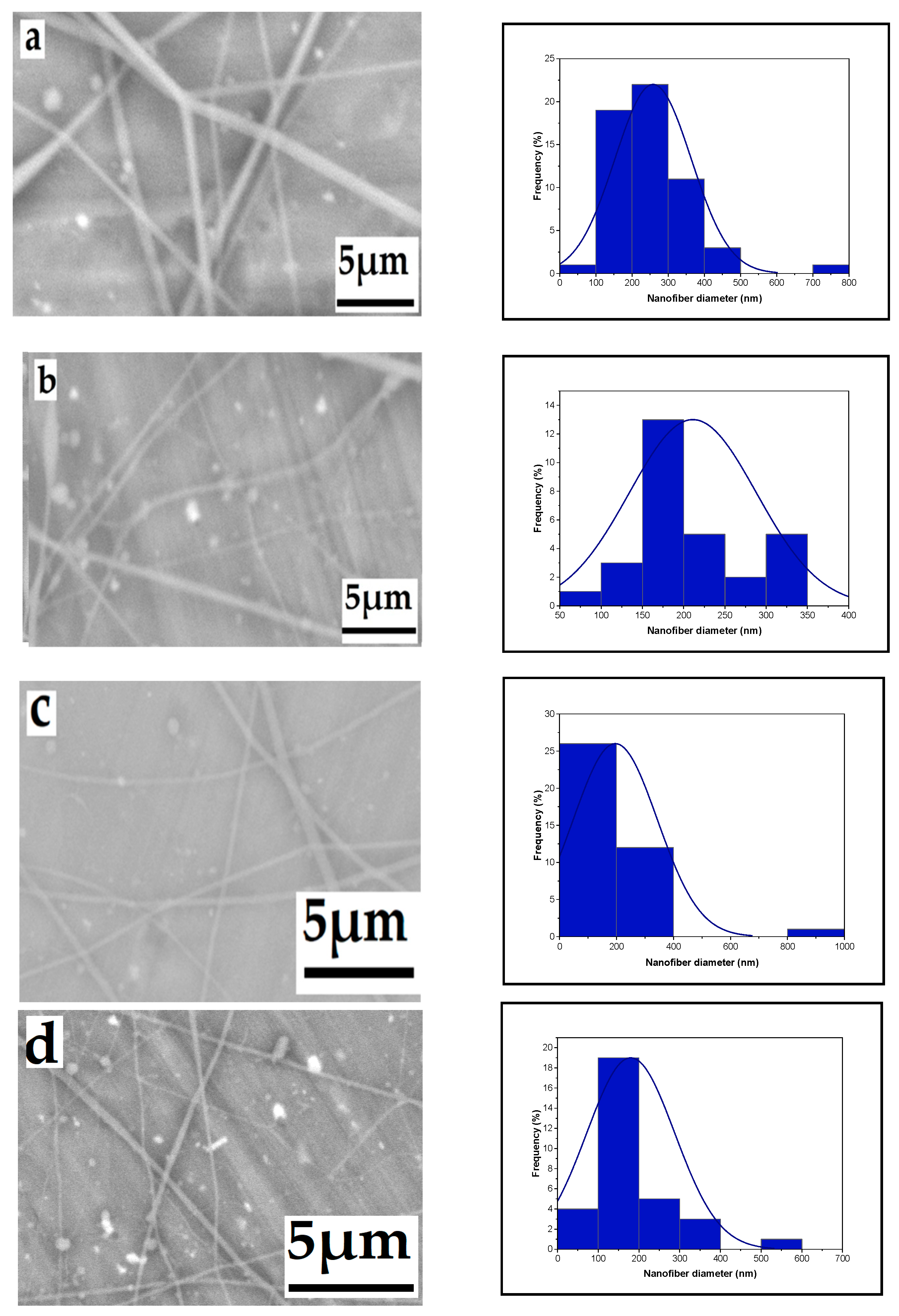
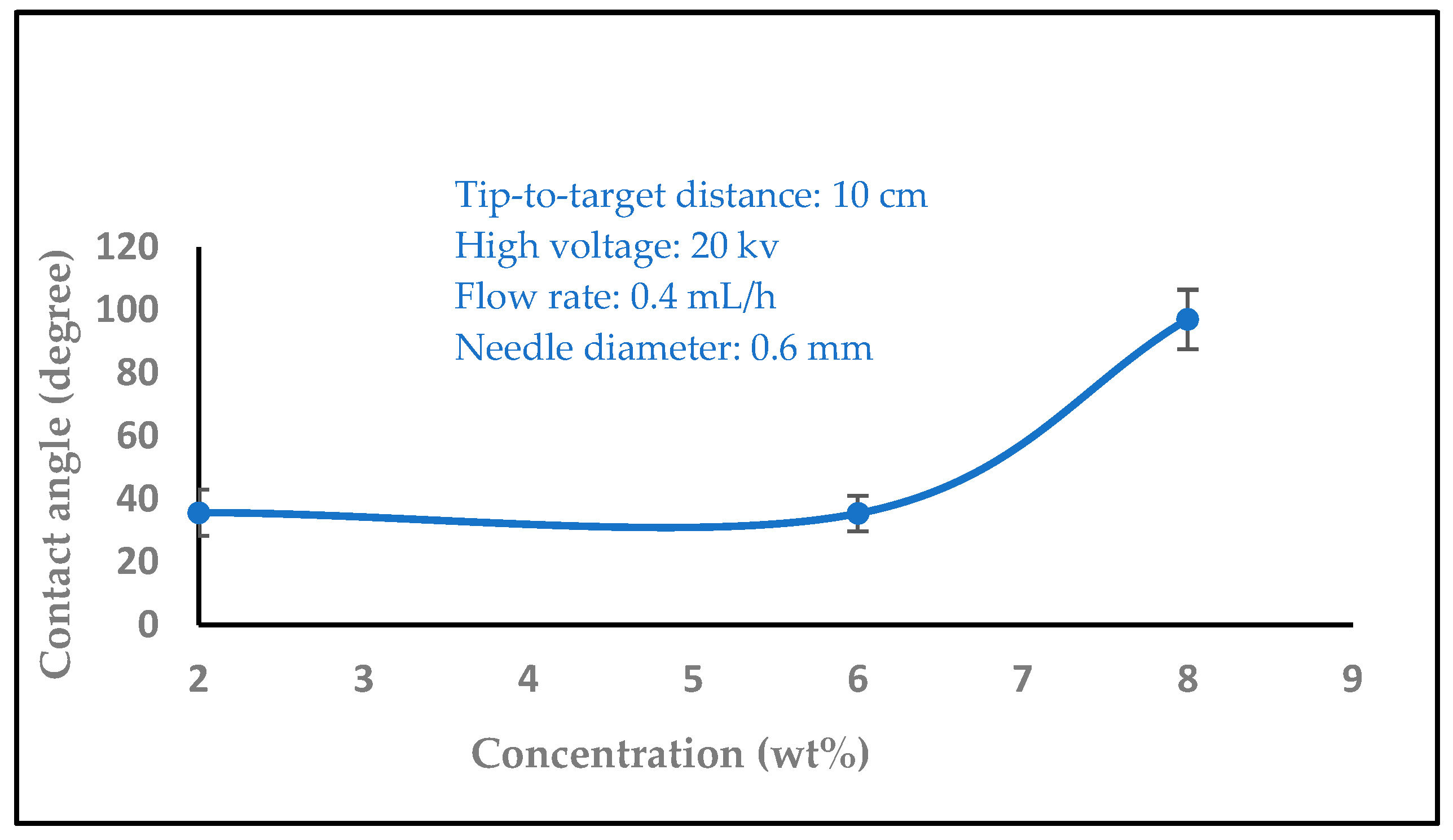
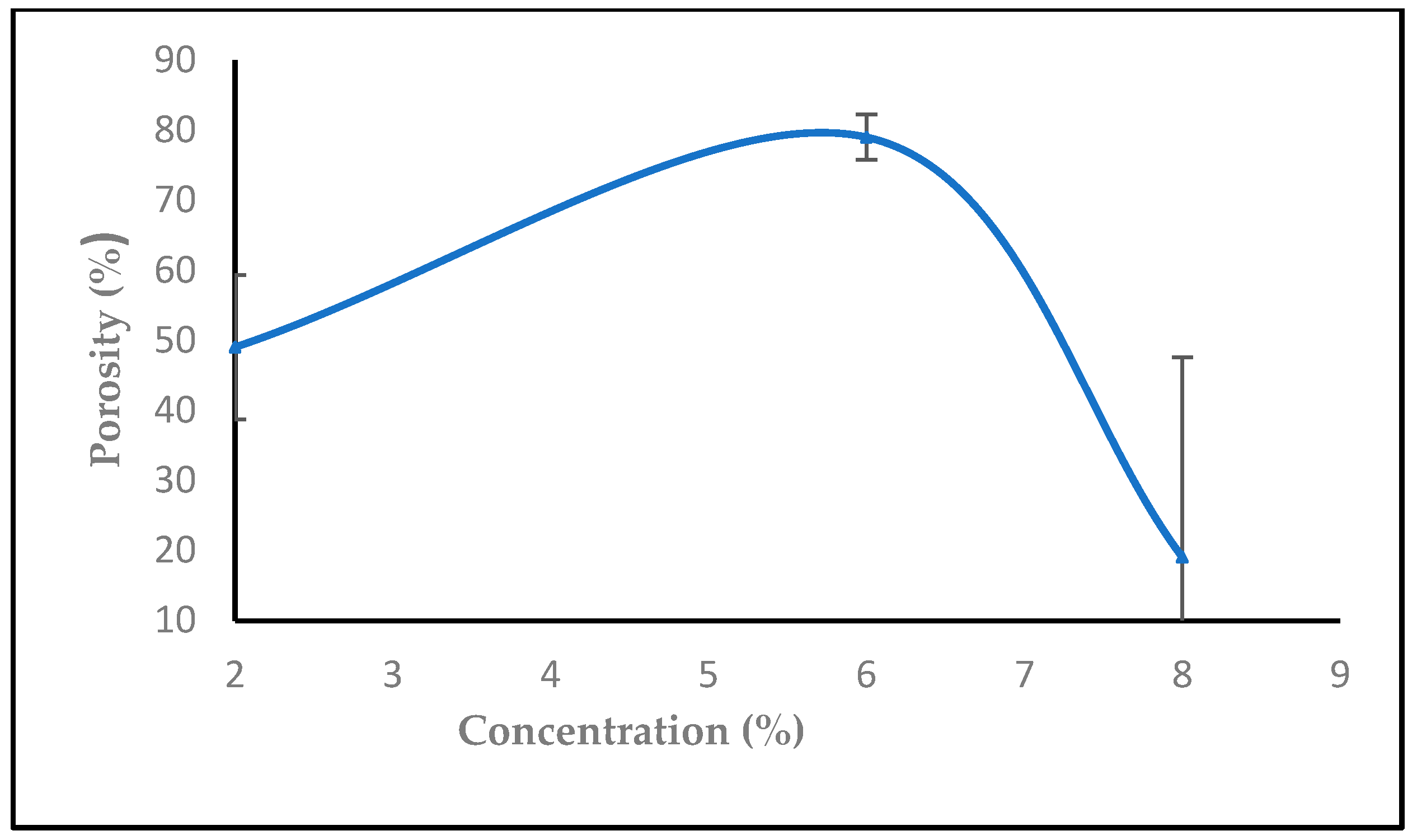
3.1.5. The Effect of Solution Concentration
3.1.6. Effect of High Voltage with Salt on Nanofiber Diameter
3.2. Water Contact Angle Measurement
3.3. Impact of Nanofiber Porosity
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.6. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, T.D.; Roh, S.; Nguyen, M.T.N.; Lee, J.S. Structural Control of Nanofibers According to Electrospinning Process Conditions and Their Applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Functional nanofibers for environmental applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5326–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.P.S.; Lim, C.T. Physical properties of a single polymeric nanofiber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 1603–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, F.T.; Mahammed, M.A. Investigation of the impact of different parameters on the morphology of electrospun polyurethane nanofibers. Sci. J. Univ. Zakho 2024, 12, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatemadi, A.; Daraee, H.; Zarghami, N.; Melat Yar, H.; Akbarzadeh, A. Nanofiber: Synthesis and biomedical applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Kwon, O.-H.; Jang, J. Electrospinning of chitosan dissolved in concentrated acetic acid solution. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohman, M.M.; Shin, M.; Rutledge, G.; Brenner, M.P. Electrospinning and electrically forced jets. II. Applications. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhljar, L.É.; Ambrus, R. Electrospinning of potential medical devices (wound dressings, tissue engineering scaffolds, face masks) and their regulatory approach. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, D.; Getachew, E.; Mondal, A.K. Study on the Physicochemical Properties of Chitosan and their Applications in the Biomedical Sector. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 2023, 5025341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konop, M. Biomaterials in Skin Wound Healing and Tissue Regenerations—An Overview. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezvani Ghomi, E.; Khalili, S.; Nouri Khorasani, S.; Esmaeely Neisiany, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Wound dressings: Current advances and future directions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, K.; Zhang, L.; Han, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ling, J.; Wang, Y. Degradable tough chitosan dressing for skin wound recovery. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, J.; Brandl, F.P.; Goepferich, A.M. Hydrogel wound dressings for bioactive treatment of acute and chronic wounds. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, A.Y.; Pereira, A.V.; Lipinski, L.C.; Oliveira, M.R.P. Evaluation of wound healing effect of alginate films containin g Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) gel. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 32, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Hou, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, J. Assessment of biological properties of recombinant collagen-hyaluronic acid composite scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, M.; Al-Homidan, I.; Ebeid, T.; Abou-Emera, O.; Mostafa, M.; Abd El-Razik, M.; Shehab-El-Deen, M.; Abdel Ghani, S.; Fathi, M. Effect of silver nanoparticle administration on productive performance, blood parameters, antioxidative status, and silver residues in growing rabbits under hot climate. Animals 2019, 9, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levengood, S.L.; Erickson, A.E.; Chang, F.; Zhang, M. Chitosan–poly (caprolactone) nanofibers for skin repair. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 1822–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biranje, S.S.; Madiwale, P.V.; Patankar, K.C.; Chhabra, R.; Dandekar-Jain, P.; Adivarekar, R. V Hemostasis and anti-necrotic activity of wound-healing dressing containing chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasa, M.T.; Ramanamurthy, K.V.; Arun Bhupathi, P. Electrospun Nanofibrous Wound Dressings: A Review on Chitosan Composite Nanofibers As Potential Wound Dressings. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2023, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.P.A.; Luong, A.H.; Lin, W.-C. Characterizations of Centrifugal Electrospun Polyvinyl alcohol/Sodium alginate/Tamanu oil/Silver nanoparticles Wound Dressing. IEEE Trans. Nanobioscience 2024, 23, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benčina, M.; Mavrič, T.; Junkar, I.; Bajt, A.; Krajnović, A.; Lakota, K.; Žigon, P.; Sodin-Šemrl, S.; Kralj-Iglič, V.; Iglič, A. The importance of antibacterial surfaces in biomedical applications. In Advances in Biomembranes and Lipid Self-Assembly; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 28, pp. 115–165. ISBN 2451-9634. [Google Scholar]
- Beigmoradi, R.; Samimi, A.; Mohebbi-Kalhori, D. Controllability of the hydrophilic or hydrophobic behavior of the modified polysulfone electrospun nanofiber mats. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.O.; Son, W.K.; Cho, D.; Youk, J.H.; Park, W.H. Preparation of porous ultra-fine fibres via selective thermal degradation of electrospun polyetherimide/poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) fibres. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 86, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarresi Chahardehi, A.; Barati, M.; Navaderi, M.; Velashjerdi, Z.; Zare, I.; Mostafavi, E. Antibacterial and Antiviral Functional Materials: Design Strategies, Classifications, Mechanisms, Advantages, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. In Antibacterial and Antiviral Functional Materials, Volume 1; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; pp. 1–32. ISBN 1947-5918. [Google Scholar]
- Alprol, A.E.; Mansour, A.T.; Abdelwahab, A.M.; Ashour, M. Advances in green synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles by marine algae for wastewater treatment by adsorption and photocatalysis techniques. Catalysts 2023, 13, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Duan, X.-P.; Li, Y.-M.; Yang, D.-P.; Long, Y.-Z. Electrospun nanofibers for wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladhari, S.; Vu, N.-N.; Boisvert, C.; Saidi, A.; Nguyen-Tri, P. Recent Development of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)-based Materials for Antibacterial applications: A review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 1398–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmana, M.; Mahmood, S.; Hilles, A.R.; Rahman, A.; Bin Arifin, M.A.; Ahmed, S. A review on chitosan and chitosan-based bionanocomposites: Promising material for combatting global issues and its applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 832–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, Z.; Meral, R.; Özogul, F.; Yilmaz, M.T. Importance of electrospun chitosan-based nanoscale materials for seafood products safety. In Handbook of Chitin and Chitosan; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 195–223. [Google Scholar]
- Korniienko, V.; Husak, Y.; Radwan-Pragłowska, J.; Holubnycha, V.; Samokhin, Y.; Yanovska, A.; Varava, J.; Diedkova, K.; Janus, Ł.; Pogorielov, M. Impact of electrospinning parameters and post-treatment method on antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of chitosan nanofibers. Molecules 2022, 27, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norzita, Y.; Norhashidah, T.; Maznah, M. Determination of viscosity-average molecular weight of chitosan using intrinsic viscosity measurement. J. Nucl. Relat. Technol. 2013, 10, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Brugnerotto, J.; Lizardi, J.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Argüelles-Monal, W.; Desbrieres, J.; Rinaudo, M. An infrared investigation in relation with chitin and chitosan characterization. Polymer 2001, 42, 3569–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vårum, K.M.; Antohonsen, M.W.; Grasdalen, H.; Smidsrød, O. Determination of the degree of N-acetylation and the distribution of N-acetyl groups in partially N-deacetylated chitins (chitosans) by high-field nmr spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 1991, 211, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabur, A.R.; Abass, L.K.; MuhiAldain, S.M. Effects of High Voltage and Flow Rate Parameters on Nanofibers Diameter Synthesis by Electrospinning. J. Phys. Sci. Appl. 2016, 6, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A.E.; Atibeni, R.A.; Sassi, K.M.; Sakal, S.A. The Effect of Flow Rate and Needle Diameter on the Formation of Poly (ethylene-Terephthalate) Nanofiber. Int. Sci. Technol. J. 2021, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.-P.; Si, N.; Xu, L.; Liu, H.-Y. Effect of flow rate on diameter of electrospun nanoporous fibers. Therm. Sci. 2014, 18, 1447–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabur, A.R.; Abbas, L.K.; Muhi Aldain, S.M. Effects of ambient temperature and needle to collector distance on PVA nanofibers diameter obtained from electrospinning technique. Eng. Technol. J. 2017, 35, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabur, A.R.; Abbas, L.K.; Muhi Aldain, S.M. The effects of operating parameters on the morphology of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofibres. J. kerbala Univ. 2012, 8, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Ang, B.C.; Andriyana, A.; Afifi, A.M. A review on fabrication of nanofibers via electrospinning and their applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrostat. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunahel, B.M.; Azman, N.Z.N.; Jamil, M. Effect of needle diameter on the morphological structure of electrospun n-Bi2O3/epoxy-PVA nanofiber mats. Int. J. Chem. Mater. Eng. 2018, 12, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, S.S.S.; Foong, K.M.; Halif, N.A.; Yahud, S. Effect of solution concentration and applied voltage on electrospun polyacrylonitrile fibers. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 701, p. 12018. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Wang, Y.; Farkas, B.; Nagy, Z.K.; Molnar, K. Analysis and prediction of the diameter and orientation of AC electrospun nanofibers by response surface methodology. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Padhye, R.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Truong, Y.B.; Arnold, L. Effect of viscosity and electrical conductivity on the morphology and fiber diameter in melt electrospinning of polypropylene. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MPUKUTA, O.; Dincer, K.; Özaytekin, İ. Effect of Dynamic Viscosity on Nanofiber Diameters and Electrical Conductivity of Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers Doped Nano-Cu Particles. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Appl. 2020, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.I.; Sultana, N. Characterization, drug loading and antibacterial activity of nanohydroxyapatite/polycaprolactone (nHA/PCL) electrospun membrane. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.; Ng, S. Effect of membrane properties on contact angle. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, S.; Sant, S.; Nichol, J.W.; Khabiry, M.; Traversa, E.; Khademhosseini, A. Controlling the porosity of fibrous scaffolds by modulating the fiber diameter and packing density. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 96, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizaki, K.; Komarneni, S.; Nanko, M. Porous Materials: Process Technology and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 4, ISBN 1461558115. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lin, T.; Fang, J.; Yao, G.; Zhao, H.; Dodson, M.; Wang, X. In vivo wound healing and antibacterial performances of electrospun nanofibre membranes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 94, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabetzadeh, N.; Gharehaghaji, A.A. How porous nanofibers have enhanced the engineering of advanced materials: A review. J. Text. Polym. 2017, 5, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, F.A.A.; Haider, S.; Al-Masry, W.A.; Al-Zeghaye, Y. Fabrication of chitosan nanofibres membrane and its treatment. Coll. Eng. King Saud Univ. 2013, 1–4. Available online: https://www.jeaconf.org/UploadedFiles/Document/a2a3a6d5-6810-4b3e-93a0-09140c4740c4.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Szymańska, E.; Wojasiński, M.; Czarnomysy, R.; Dębowska, R.; Łopianiak, I.; Adasiewicz, K.; Ciach, T.; Winnicka, K. Chitosan-enriched solution blow spun poly (ethylene oxide) nanofibers with poly (dimethylsiloxane) hydrophobic outer layer for skin healing and regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Chitosan bicomponent nanofibers and nanoporous fibers. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koosha, M.; Mirzadeh, H. Electrospinning, mechanical properties, and cell behavior study of chitosan/PVA nanofibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, D.; Sahl, H. Chitosan and its antimicrobial potential–a critical literature survey. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L. Comparison of Disk Diffusion, Agar Dilution, and Broth Microdiultion for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Five Chitosans; Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2011; ISBN 9798819307564. [Google Scholar]
- Taher, F.S.T.; Othman, H.E. Molecular identification and genotyping of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (mrsa) in different clinical samples. Sci. J. Univ. Zakho 2024, 12, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliszewska, I.; Czapka, T. Electrospun polymer nanofibers with antimicrobial activity. Polymers 2022, 14, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Windbergs, M. Functional electrospun fibers for the treatment of human skin wounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 119, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, M.; Jin, T.Z.; Arabi, S.A.; He, Q.; Ismail, B.B.; Hu, Y.; Liu, D. Antimicrobial and UV Blocking Properties of Composite Chitosan Films with Curcumin Grafted Cellulose Nanofiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



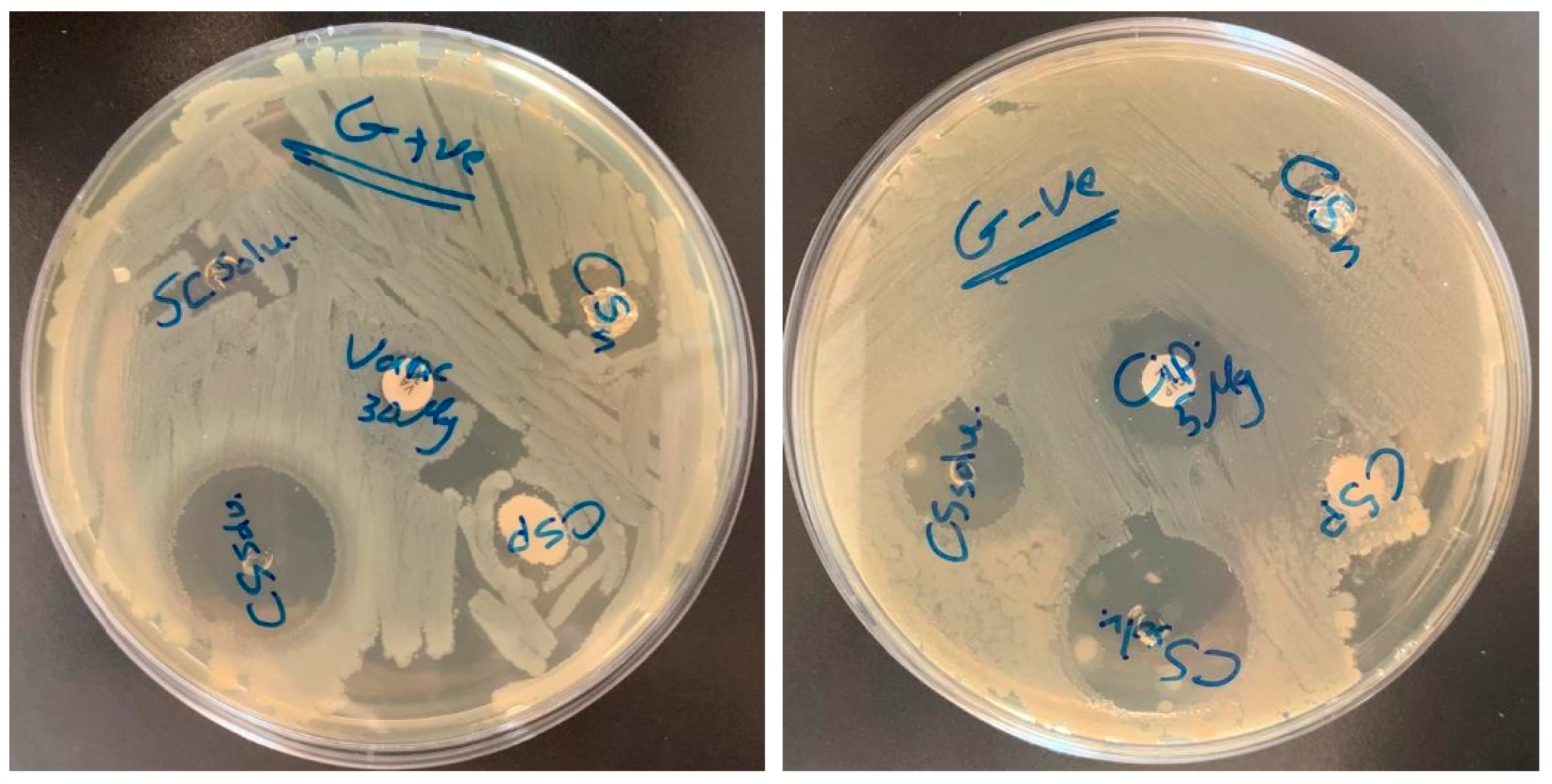
| Material | S. areous | E. coli | |
|---|---|---|---|
| chitosan powder (CSP) | 8 mm | chitosan powder (CSP) | 7 mm |
| chitosan nanofiber (CSN) | 18 mm | chitosan nanofiber (CSN) | 11 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.H.; Mahammed, M.A.; Yasin, S.A. Characterization of Electrospinning Chitosan Nanofibers Used for Wound Dressing. Polymers 2024, 16, 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16141984
Ali SH, Mahammed MA, Yasin SA. Characterization of Electrospinning Chitosan Nanofibers Used for Wound Dressing. Polymers. 2024; 16(14):1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16141984
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Shahla H., Manaf A. Mahammed, and Suhad A. Yasin. 2024. "Characterization of Electrospinning Chitosan Nanofibers Used for Wound Dressing" Polymers 16, no. 14: 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16141984
APA StyleAli, S. H., Mahammed, M. A., & Yasin, S. A. (2024). Characterization of Electrospinning Chitosan Nanofibers Used for Wound Dressing. Polymers, 16(14), 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16141984







