A Comparative Investigation of the Reliability of Biodegradable Components Produced through Additive Manufacturing Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material Characteristics
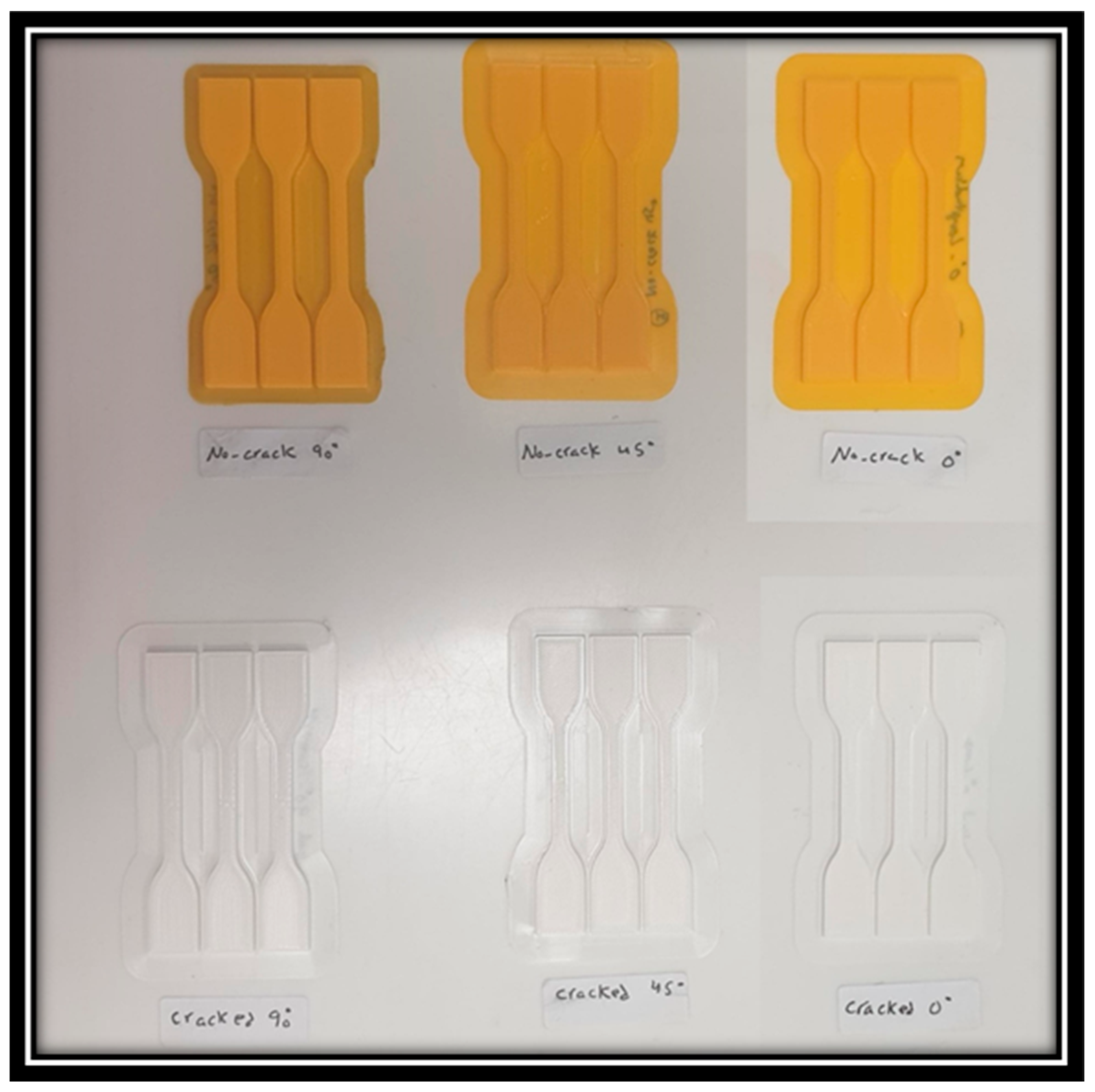
- The 3D-printed undamaged specimens: These specimens were created without any defects and played the role of a reference point for comparison with the other types of samples.
- The 3D-printed flawed specimens: In this group, all specimens were intentionally introduced with a centrally located through-thickness flaw, possessing an aspect ratio of one to half, employing 3D printing technology. This precise flaw geometry was consistently incorporated into each of these specimens.
Investigation Hypothesis
- Consistent Layer Adhesion Properties: Varied printing parameters do not compromise the consistent layer adhesion properties, ensuring robust structural integrity.
- Fixed Printing Temperature and Print Speed: Maintaining a fixed printing temperature and speed contributes to standardized material deposition, enhancing print quality and structural uniformity.
- Uniform Infill Density Over the Samples: Ensuring uniform infill density across printed samples results in consistent mechanical properties, mitigating structural variations within the printed objects.
- Uniform Filament Material Properties: Homogeneous filament material properties contribute to predictable and reproducible mechanical behavior across the printed samples.
- Printed Samples are Defect-Free: Precise quality control measures during the 3D printing process eliminate defects, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of printed components.
- Dimensional Stability: Controlled printing conditions lead to dimensional stability, minimizing distortions and deviations in the final printed objects.
- 7.
- Linear Elastic Analysis: The linear elastic analysis assumption represents the deformation behavior of FDM 3D-printed structures under applied loads.
- 8.
- Isotropic Properties: Treating the material as isotropic simplifies the analysis without compromising the accuracy of predicting structural responses.
- 9.
- Layers Overlapped at 0.01 mm: Overlapping layers at a specific distance ensures a realistic representation of the FDM printing process and its impact on structural integrity.
- 10.
- Adhesion Characteristic is Neglected: Neglecting adhesion characteristics in FEA does not significantly affect the accuracy of predicting stress and strain distributions in FDM printed components.
- 11.
- Analysis Performed at the Max Experimental Load: Conducting FEA at the maximum experimental load provides insights into the structural performance of printed objects under extreme conditions.
- 12.
- Consistent Mesh Density Over Samples: Maintaining a consistent mesh density across samples ensures a reliable and comparable analysis of structural behavior.
- 13.
- Samples Aligned with the Vertical Axis: Aligning samples with the vertical axis of the 3D printing machine results in consistent material properties and structural characteristics.
- 14.
- Average Values Considered: Utilizing average values from tested samples accurately represents the typical mechanical behavior of FDM 3D-printed components.
- 15.
- No Stress Concentration Caused by Machine Jaws: The experimental setup minimizes stress concentrations induced by machine jaws, providing accurate representations of material behavior.
- 16.
- Samples Tested at Room Temperature: Conducting tests at room temperature eliminates temperature-induced variations, offering a standardized assessment of material properties.
- 17.
- Constant Testing Speed: Maintaining a constant testing speed ensures consistent loading conditions, facilitating accurate comparisons of mechanical properties.
- 18.
- No Impact of 3D Printing Extrusion Process on Material Properties: The 3D printing extrusion process does not compromise the intrinsic material properties, allowing for the reliable evaluation of printed components.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Work
3.2. Mathematic Model of the Intact 3D-Printed Samples
3.3. Mathematical Model of the Defective 3D-Printed Samples
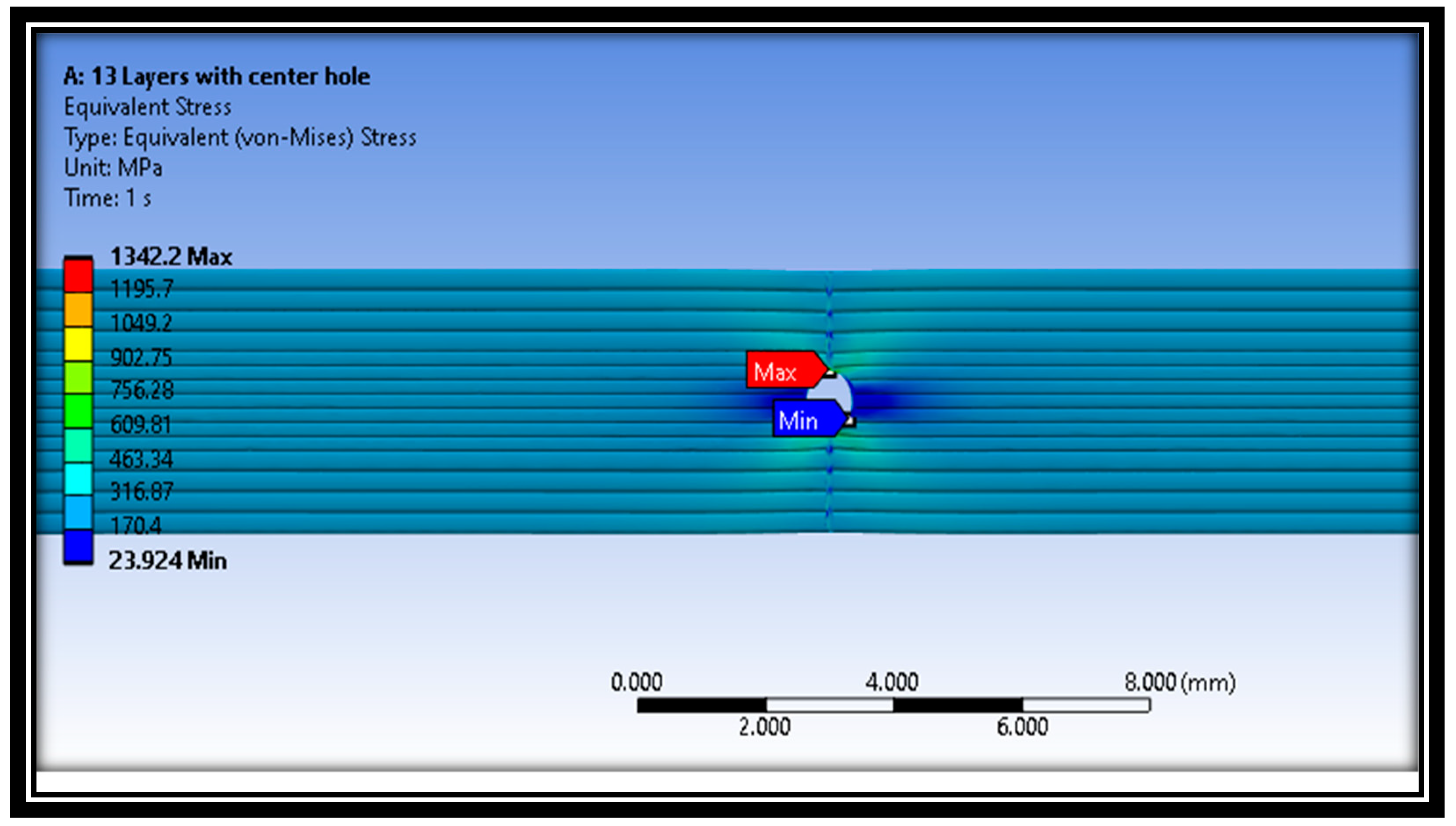
3.4. Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
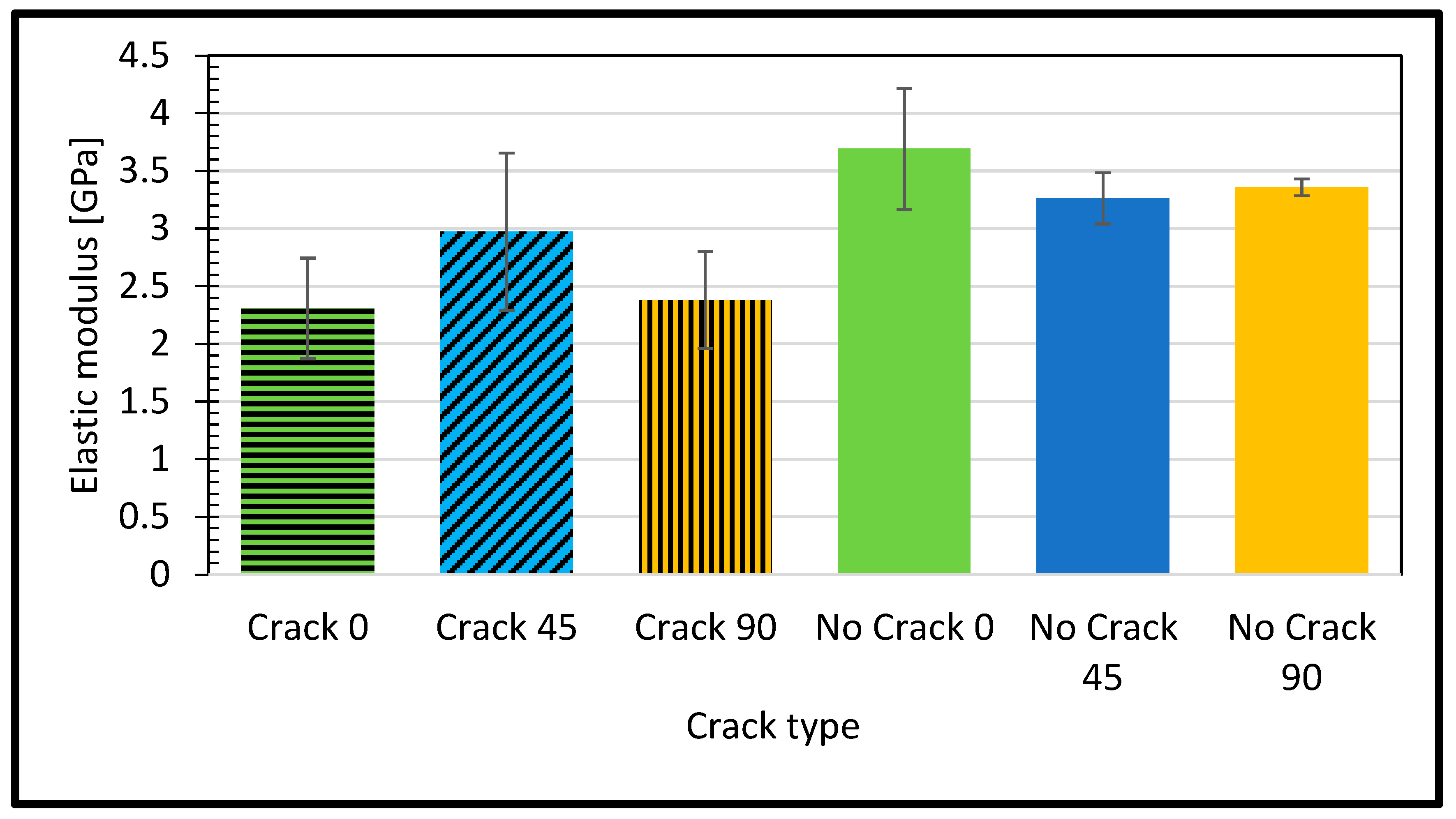
- The defective sample stiffness (modulus of elasticity) demonstrated lower levels than the corresponding intact ones. The lowest stiffness is at the raster angle of 90 degrees, and the highest value is at 0 degrees, the longitudinal raster. This is because the longitudinal raster will support the sample resistance to the load contrary to the transverse one.
- A similar conclusion to the previous point has been reached regarding the ultimate tensile strength of the defective sample, where all samples showed less resistance to failure than the intact ones. Furthermore, the highest tensile strength is indicated by the longitudinal raster. The lowest resistance to the failure is at the transverse raster, i.e., 90 degrees.
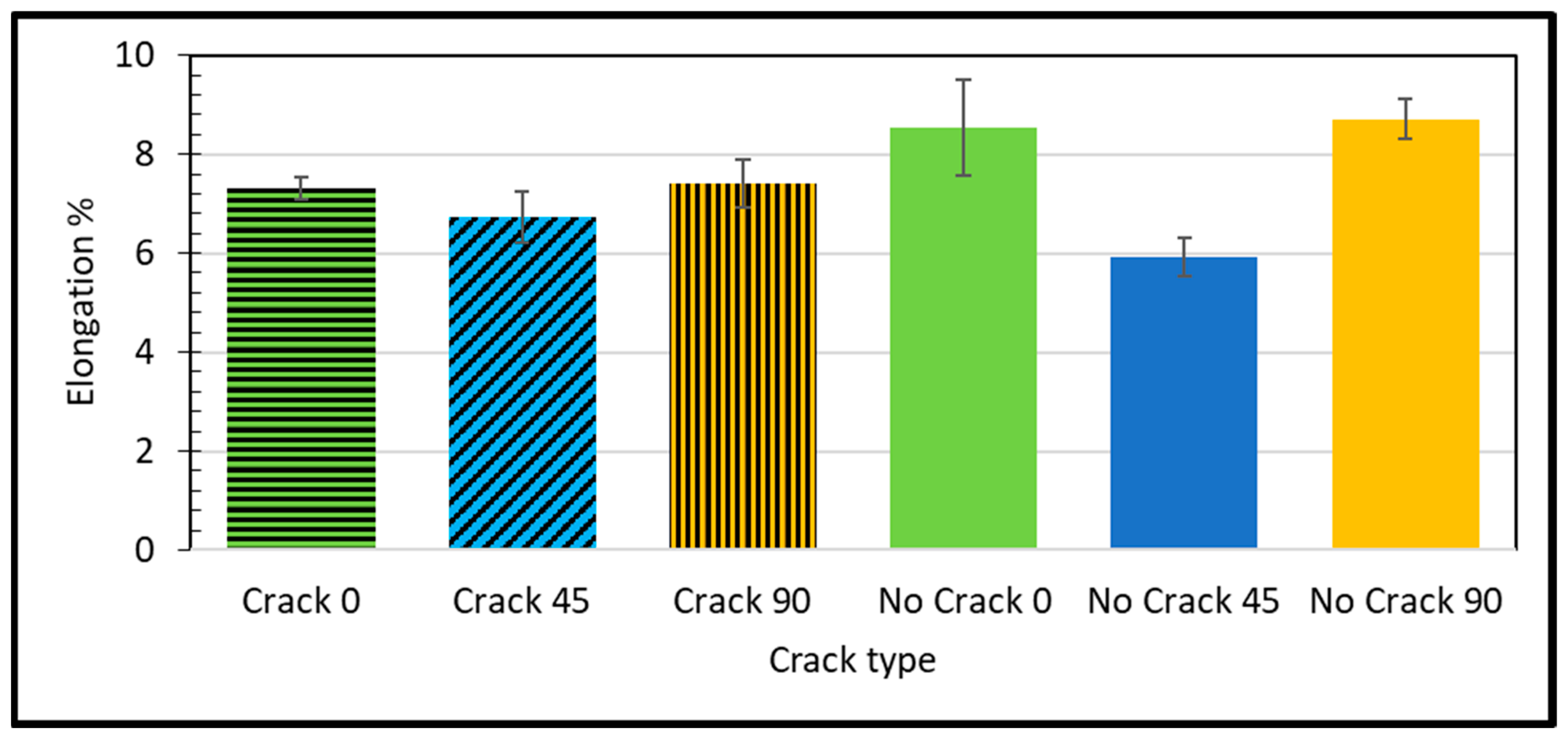
- The elongation for the defective samples is lower than the intact ones, which is normal. In addition, it has been observed that the longitudinal raster offers the lowest elongation due to having the highest stiffness in this direction, whereas the transverse raster accommodates the most elevated extension due to the insufficient stiffness.
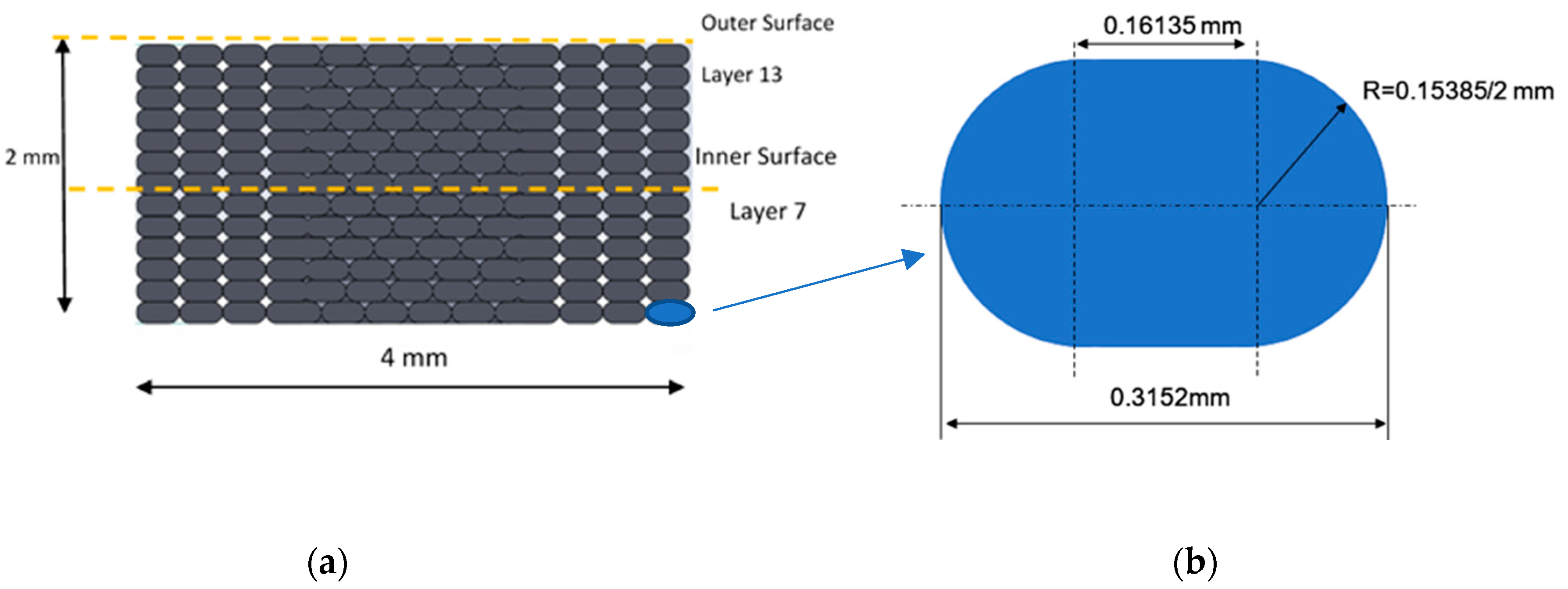
- The stresses at the outer layer (layer 13), demonstrated higher levels than the inner layer, i.e., layer 7, since the outer layer is not supported by one side, whereas the inner layer is supported by material from both sides.
- The maximum principal stresses, max shear stresses, and Von Mises stresses for the defective samples are higher than the analogous values for the intact samples. This indicates the complication of the case and that the raster angle plays a significant role in the failure’s contribution.
- The sample always shows the highest stress at the longitudinal raster, and this will lead to quick failure.
4. Conclusions
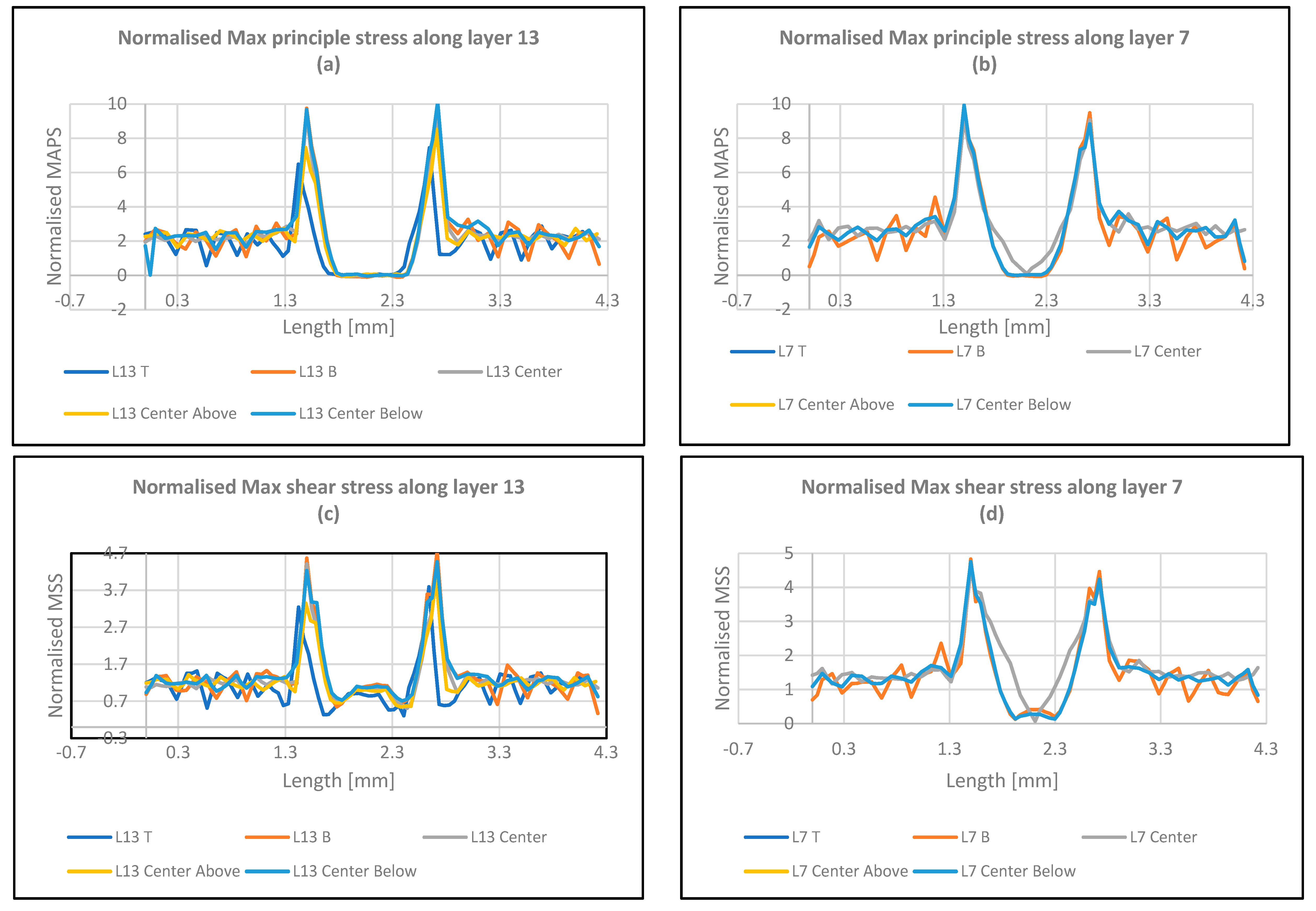
- As demonstrated graphically, stress distribution remains consistent throughout inner layers in scenarios with uniform layers and no voids. The absence of voids typically leads to initial fractures occurring at the terminal regions of the cross-sectional profile.
- In situations devoid of voids, maximum principal stresses surpass both shear and Von Mises stresses. Specifically, the 45-degree raster pattern exhibits the highest stress levels compared to the 0- and 90-degree raster patterns in void-free cases.
- Stress concentration in cases involving voids primarily occurs at locations x = 1.5 and 2.75, corresponding to the terminus of the void.
- In configurations with voids, the 90-degree raster pattern demonstrates the highest stress values compared to the 0- and 45-degree raster patterns.
- Maximum principal stresses hold a significant dominance over both shear and Von Mises stresses in samples without voids. This emphasizes their primary role in shaping stress distributions in void-free configurations.
- For void-free cases, stress magnitudes vary based on the orientation of the load, particularly notable with the 45-degree raster pattern. Compared to the 0- and 90-degree raster configurations, the utilization of 45-degree raster results in the highest stress magnitudes, highlighting the significant influence of load orientation on stress patterns.
- Stress concentrations reach their peak at specific spatial coordinates, notably at x = 1.5 and 2.75, corresponding to the extremities of the voids. These locations emerge as focal points of heightened stress concentration within configurations that include voids.
- Cracks typically initiate precisely at the extremities of the cross-section. This observation suggests a trend toward end-point fracture initiation in configurations devoid of voids. This is when with no voids exist within the cross-sectional geometry.
- The analysis thoroughly examines stress distribution and fracture behavior across various structural configurations. It demonstrates how stress patterns vary depending on void presence and load orientation. In void-free scenarios, maximum principal stresses are pivotal in determining structural integrity. The identification of stress concentration zones, particularly at void termini, offers valuable insights into potential failure points. Additionally, the observation that cracking initiates at cross-sectional ends highlights a significant trend in fracture behavior, suggesting localized stress accumulation. These findings underscore the importance of considering structural characteristics and load orientations in engineering analysis and design processes. Understanding stress distributions and fracture mechanisms enables engineers to make informed decisions, enhancing material and structural performance and durability.
- In the experimental tensile test, we observed that the highest values for elastic modulus, ultimate strength, and elongation were recorded for the “No Crack 0” configuration. Conversely, the lowest values for elastic modulus, ultimate strength, and elongation were observed for the “No Crack 0”, “Crack 90”, and “No Crack 45” configurations, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, M.A.; Yeoh, C.K.; Teh, P.L.; Rahim, N.A.; Song, C.C.; Mansor, N.S.S. Effect of infill density and raster angle on the mechanical properties of PLA. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2080, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, G.H. Structural topology optimization of layout and raster angle for additive manufacturing technology with the shadow density filter. Comput. Struct. 2021, 256, 106637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Guessasma, S.; Li, J. Numerical prediction of orthotropic elastic properties of 3D-printed materials using micro-CT and representative. Acta Mech. 2020, 516, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, H.; Laoutid, F.; Mehrpouya, M.; Saeb, M.R.; Dubois, P. Flame retardant polymer materials: An update and the future for 3D printing developments. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 144, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Anido, R.L. Finite element modeling of 3D-printed part with cellular internal structure using homogenized properties. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 4, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordelier, T.J.; Thies, P.R.; Turner, L.; Johanning, L. Optimising the FDM additive manufacturing process to achieve maximum tensile strength: A state-of-the-art review. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2019, 25, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, K.B.; Metwalli, K.M. A review of fused deposition modelling for 3D printing of smart polymeric materials and composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 156, 110591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hassan, A.; Ahmed, W.; Zaneldin, E. Investigating the Impact of Inclusions on the Behavior of 3D-Printed Composite Sandwich Beams. Buildings 2022, 12, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Traxel, K.D.; Bose, S. Nature-inspired materials and structures using 3D Printing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 145, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonabadi, H.; Chen, Y.; Yadav, A.; Bull, S. Investigation of the effect of raster angle, build orientation, and infill density on the elastic response of 3D printed parts using finite element microstructural modeling and homogenization techniques. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 118, 1485–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyweert, P.; Nicolas, V.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A. 3D printing of carbon-based materials: A review. Carbon 2021, 183, 449–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Dong, E.; Kang, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Li, D. Effects of raster angle and material components on mechanical properties of polyether-ether-ketone/calcium silicate scaffolds. Polymers 2021, 13, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Roozbahani, H.; Alizadeh, M.; Handroos, H. 3D Printing of Plant-Derived Compounds and a Proposed Nozzle Design for the More Effective 3D FDM Printing. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 57107–57119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaneldin, E.; Ahmed, W.; Mansour, A.; El Hassan, A. Dimensional stability of 3d printed objects made from plastic waste using fdm: Potential construction applications. Buildings 2021, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaei, H.R.; El Magri, A.; Rastak, M.A.; Vanaei, S.; Vaudreuil, S.; Tcharkhtchi, A. Numerical–Experimental Analysis toward the Strain Rate Sensitivity of 3D-Printed Nylon Reinforced by Short Carbon Fiber. Materials 2022, 15, 8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenkovic, S.; Slavkovic, V.; Fragassa, C.; Grujovic, N.; Palic, N.; Zivic, F. Effect of the raster orientation on strength of the continuous fiber reinforced PVDF/PLA composites, fabricated by hand-layup and fused deposition modeling. Compos. Struct. 2021, 270, 114063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Geng, P.; Li, G.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. Influence of layer thickness and raster angle on the mechanical properties of 3D-printed PEEK and a comparative mechanical study between PEEK and ABS. Materials 2015, 8, 5834–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, H.; Hussain, G.; Sulaiman, M.; Hassan, M.; Ali, A.; Muhammad, R.; Wei, H.; Shehbaz, T.; Aamir, M.; Altaf, K. Effect of Raster Angle and Infill Pattern on the In-Plane and Edgewise Flexural Properties of Fused Filament Fabricated Acrylonitrile–Butadiene–Styrene. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foltut, D.; Valean, E.; Dzitac, V.; Marsavina, L. The influence of temperature on the mechanical properties of 3D printed and injection molded ABS. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 78, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Ponnusamy, S.; Nallamilli, M.S.R. The influence of process parameters on the impact resistance of 3D printed PLA specimens under water-absorption and heat-treated conditions. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2021, 27, 1108–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakır, A.A.; Atik, R.; Özerinç, S. Mechanical properties of thermoplastic parts produced by fused deposition modeling: A review. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2021, 27, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouassil, S.E.; El Magri, A.; Vanaei, H.R.; Vaudreuil, S. Investigating the effect of printing conditions and annealing on the porosity and tensile behavior of 3D-printed polyetherimide material in Z-direction. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Mulholland, T.; Osswald, T.A. Effects of raster angle on the mechanical properties of PLA and Al/PLA composite part produced by fused deposition modeling. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 2122–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Rizvi, G.M.; Bellehumeur, C.T.; Gu, P. Effect of processing conditions on the bonding quality of FDM polymer filaments. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2008, 14, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.C.; Tandon, G.P.; Bradford, R.L.; Koerner, H.; Baur, J.W. Process-structure-property effects on ABS bond strength in fused filament fabrication. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 19, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloyaydi, B.; Sivasankaran, S.; Mustafa, A. Investigation of infill-patterns on mechanical response of 3D printed poly-lactic-acid. Polym. Test. 2020, 87, 106557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeykoon, C.; Sri-Amphorn, P.; Fernando, A. Optimization of fused deposition modeling parameters for improved PLA and ABS 3D printed structures. Int. J. Light. Mater. Manuf. 2020, 3, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qi, S.; Zhang, D.; Su, Y.; Wang, D. The role of poly (ethylene glycol) on crystallization, interlayer bond and mechanical performance of polylactide parts fabricated by fused filament fabrication. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolszczak, P.; Lygas, K.; Paszko, M.; Wach, R.A. Heat distribution in material during fused deposition modelling. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozó, É.; Ervasti, H.; Halonen, N.; Shokouh, S.H.H.; Tolvanen, J.; Pitkanen, O.; Järvinen, T.; Pálvölgyi, P.S.; Szamosvölgyi, Á.; Sápi, A.; et al. Bioplastics and Carbon-Based Sustainable Materials, Components, and Devices: Toward Green Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 49301–49312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Patil, R.S.; Patil, M.; John, J. Addressing the Sustainability Conundrums and Challenges within the Polymer Value Chain. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftekar, S.F.; Aabid, A.; Amir, A.; Baig, M. Advancements and Limitations in 3D Printing Materials and Technologies: A Critical Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Siraj, S.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H. 3D Printing PLA Waste to Produce Ceramic Based Particulate Reinforced Composite Using Abundant Silica-Sand: Mechanical Properties Characterization. Polymers 2020, 12, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakan, B.G. Effects of raster angle on tensile and surface roughness properties of various FDM filaments. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 3347–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mazrouei, N.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; Ahmed, W. Characterization and Sustainability Potential of Recycling 3D-Printed Nylon Composite Wastes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W. Finite Element Analysis of Composite Materials Reinforced with Flawed Nano-Particles. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 13th International Conference Nanomaterials: Applications & Properties (NAP), Bratislava, Slovakia, 10–15 September 2023; pp. NEE19-1–NEE19-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarni, M. The influence of raster angle and moisture content on the mechanical properties of pla parts produced by fused deposition modeling. Polymers 2021, 13, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Xie, J.; Yang, J.; Zhuo, C.; Fu, J.; Zhao, P. Research on the fused deposition modeling of polyether ether ketone. Polymers 2021, 13, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ultimaker PLA Data Sheet. PLA. Available online: https://ultimaker.com/materials/s-series-pla/ (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- ASTM D638; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Arifvianto, B.; Wirawan, Y.B.; Salim, U.A.; Suyitno, S.; Mahardika, M. Effects of extruder temperatures and raster orientations on mechanical properties of the FFF-processed polylactic-acid (PLA) material. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2021, 27, 1761–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, J.A.; Alves, J.L.; Caldas, G.; Gouveia, B.P.; Santana, L.; Belinha, J. Influence of 3D printing process parameters on the mechanical properties and mass of PLA parts and predictive models. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2021, 27, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocher, J.; Wioland, J.B.; Panesar, A.S. Additive manufacturing with fibre-reinforcement—Design guidelines and investigation into the influence of infill patterns. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 1241–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadimu, S.O.; Kourousis, K.I. Shrinkage behaviour of material extrusion steel 316L: Influence of primary 3D printing parameters. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




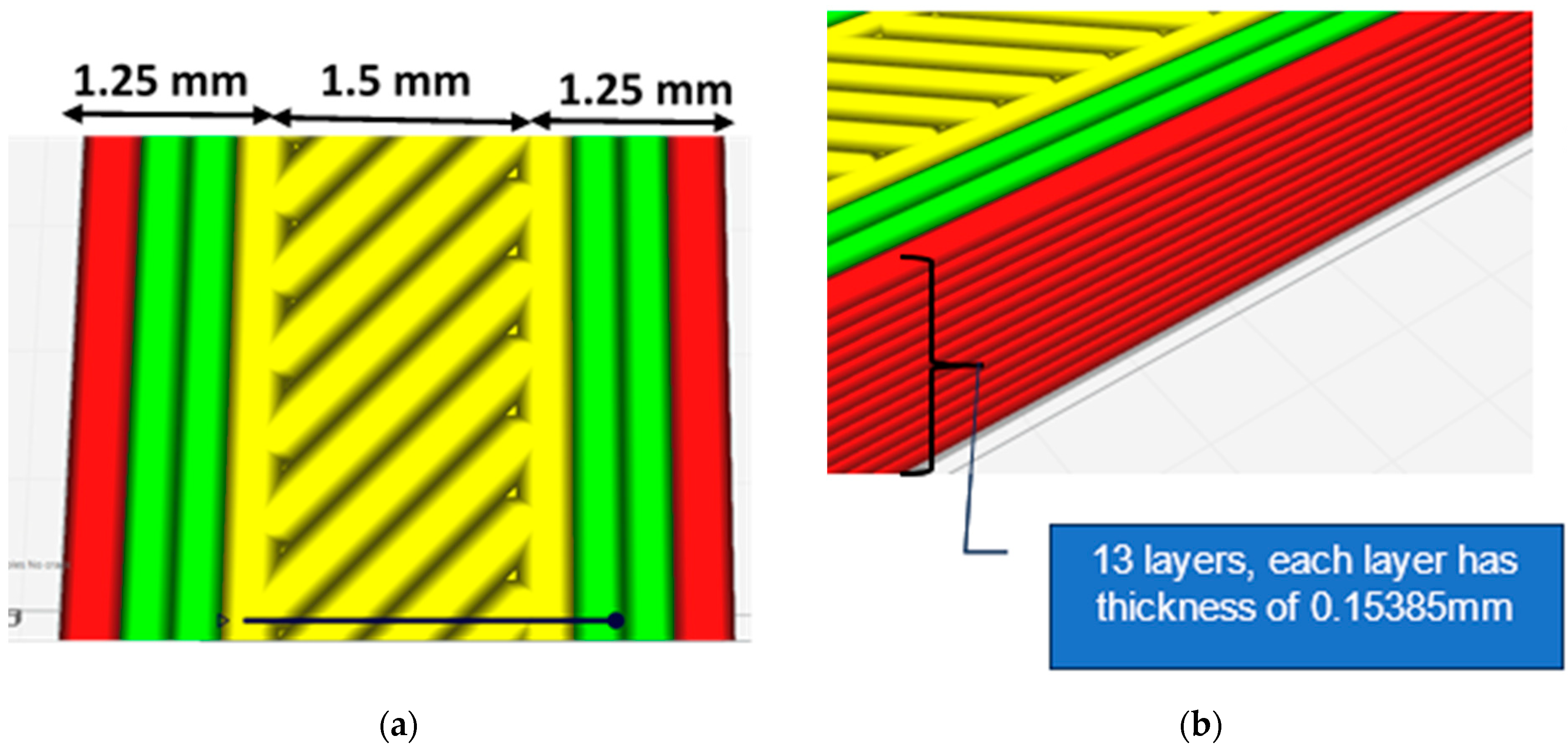

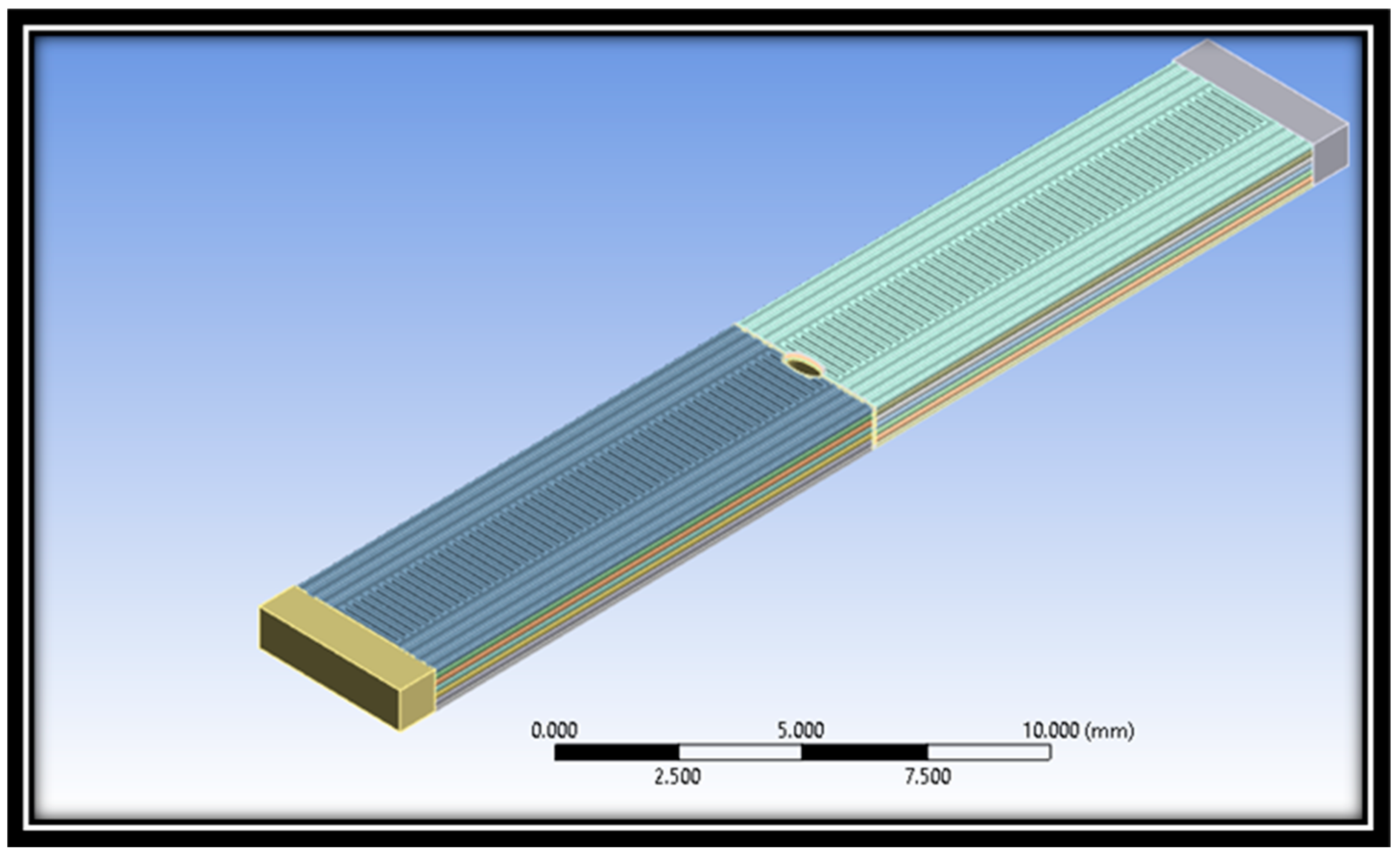
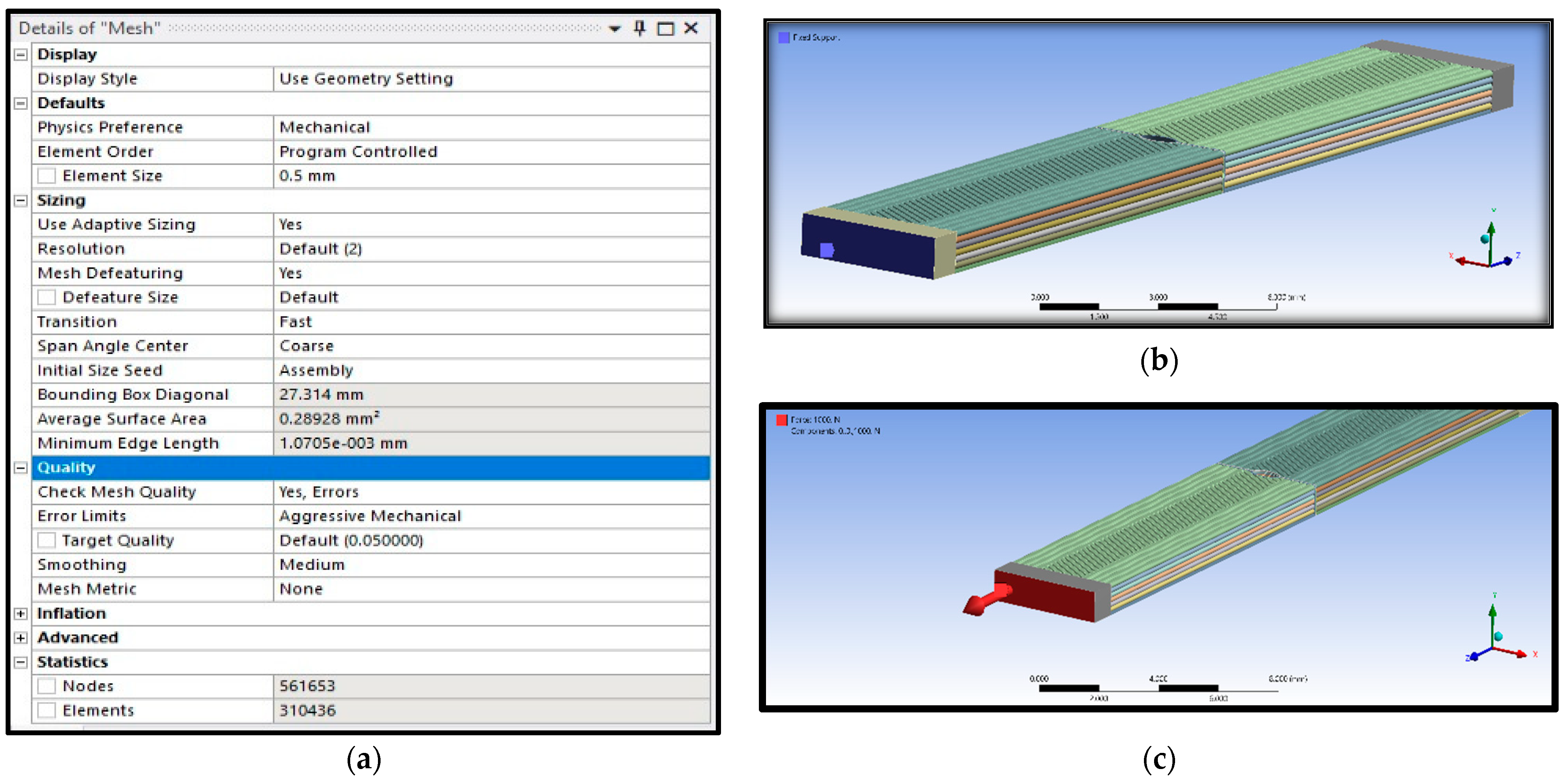
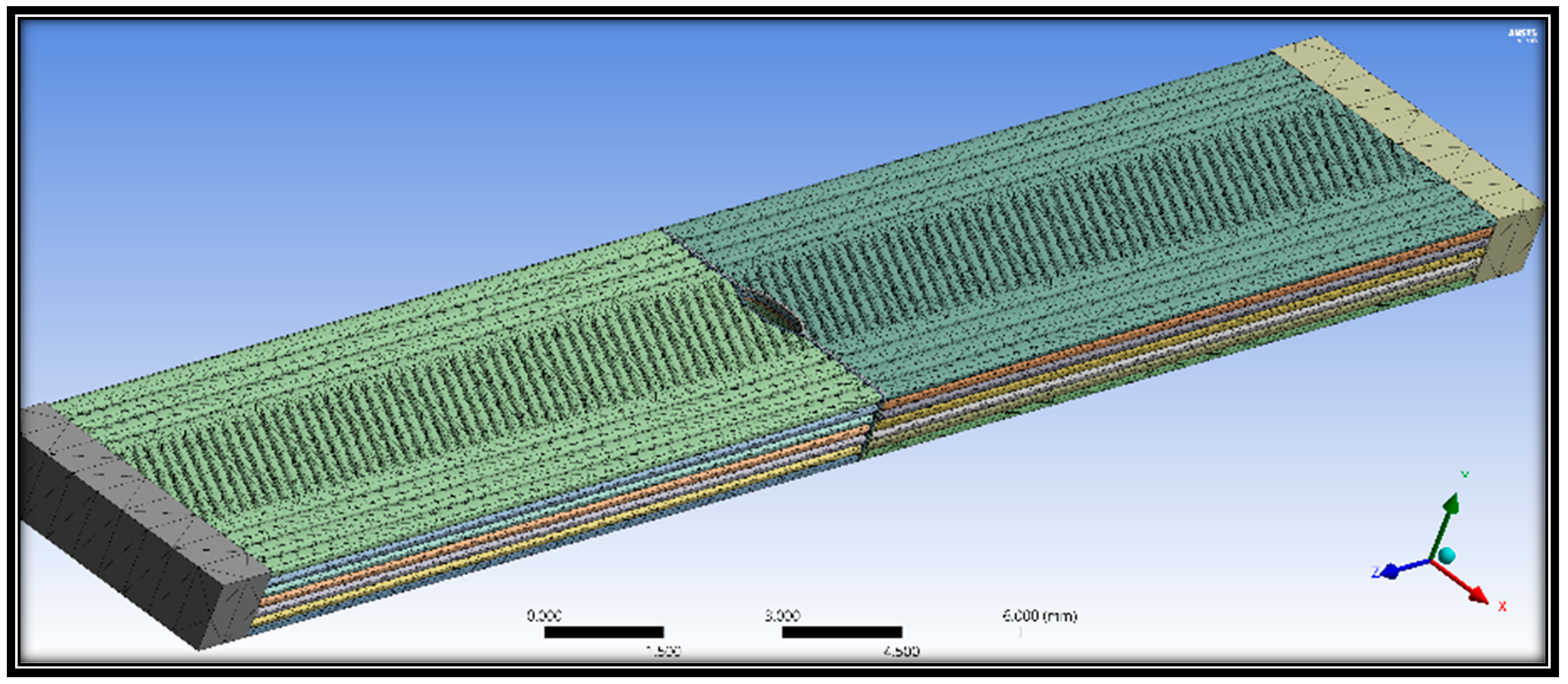



| Considered Properties | Experimental Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Tensile Modulus | 2.35 GPa |
| Yield Strength | 50 MPa |
| Strength at Break | 46 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 5.3% |
| Parameters Used | Settings |
|---|---|
| Printing speed | 1.167 mm/s |
| Temperature of the printing | 205 °C |
| Temperature of the printing bed | 65 °C |
| Height of the printed layer | 0.2 mm |
| Thickness of the wall | 1 mm |
| Thickness of the top layer | 1 mm |
| Thickness of the bottom layer | 1 mm |
| Scheme 0. | Abbreviation | Number of Elements | Number of Nodes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intact raster angel 0 | Intact R0 | 350,908 | 618,796 |
| Intact raster angel 45 | Intact R45 | 348,205 | 611,695 |
| Intact raster angel 90 | Intact R90 | 256,805 | 452,647 |
| Crack raster angel 0 | Crack R0 | 360,480 | 641,234 |
| Crack raster angel 45 | Crack R45 | 354,160 | 630,487 |
| Crack raster angel 90 | Crack R90 | 266,220 | 480,370 |
| Experimental | Modulus of Elasticity (E) | Tensile Strength (TS) | Elongation (EL%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intact R0 | 1.14 | 1.23 | 0.76 |
| Intact R45 | 1.03 | 1.16 | 1.09 |
| Intact R90 | 1.00 | 1.06 | 1.12 |
| Crack R0 | 0.90 | 1.09 | 0.87 |
| Crack R45 | 0.73 | 0.97 | 0.94 |
| Crack R90 | 0.71 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| Inner Surface (Layer 7) | Outer Surface (Layer 13) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEA | Max Principal | Max Shear | Von Misses | Max Principal | Max Shear | Von Misses |
| Intact R0 | 3.9 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 5 | 1.8 | 3.9 |
| Intact R45 | 4.3 | 1.34 | 2.37 | 5.8 | 2.1 | 3.95 |
| Intact R90 | 4.8 | 1.4 | 2.5 | 6.5 | 2.3 | 4 |
| Crack R0 | 9.8 | 4.7 | 8.3 | 9.4 | 4.3 | 8.2 |
| Crack R45 | 9.9 | 4.8 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 4.8 | 8.9 |
| Crack R90 | 12.6 | 6.0 | 10.6 | 12.1 | 5.7 | 10.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
ElHassan, A.; Ahmed, W.; Zaneldin, E. A Comparative Investigation of the Reliability of Biodegradable Components Produced through Additive Manufacturing Technology. Polymers 2024, 16, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050615
ElHassan A, Ahmed W, Zaneldin E. A Comparative Investigation of the Reliability of Biodegradable Components Produced through Additive Manufacturing Technology. Polymers. 2024; 16(5):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050615
Chicago/Turabian StyleElHassan, Amged, Waleed Ahmed, and Essam Zaneldin. 2024. "A Comparative Investigation of the Reliability of Biodegradable Components Produced through Additive Manufacturing Technology" Polymers 16, no. 5: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050615
APA StyleElHassan, A., Ahmed, W., & Zaneldin, E. (2024). A Comparative Investigation of the Reliability of Biodegradable Components Produced through Additive Manufacturing Technology. Polymers, 16(5), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050615







