Synthesis and Evaluation of High-Temperature-Resistant and Environmentally Friendly Polymer Filter Loss Additives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Inverse Micro-Lotion Polymerization Method
2.4. Principles and Advantages of Synthesis
2.5. Basic Performance Evaluation Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of Optimal Synthesis Conditions
3.1.1. Different Oil-to-Water Ratios and the Stability of Microemulsions
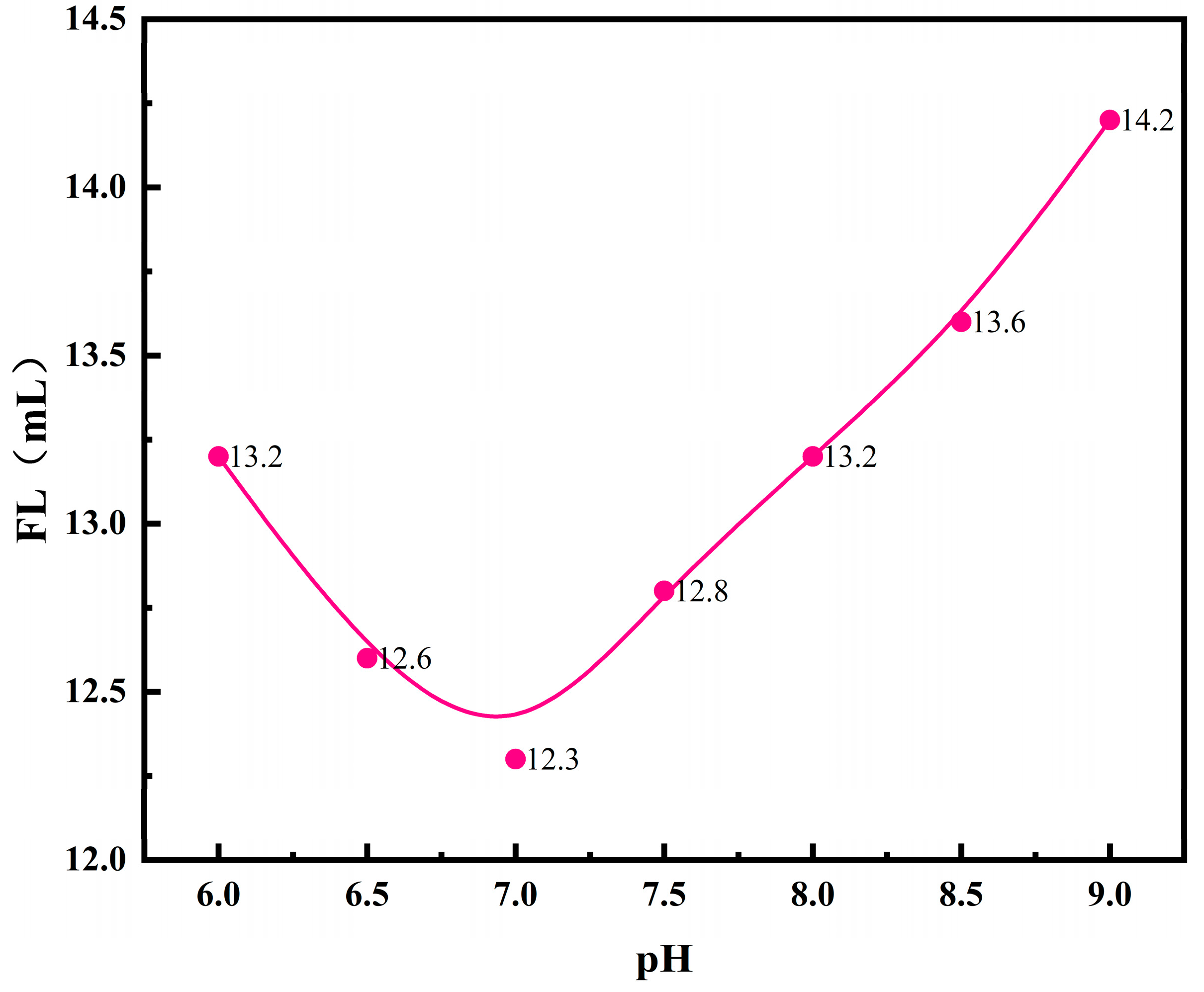
3.1.2. Reaction System pH and the Performance of Fluid Loss Additives
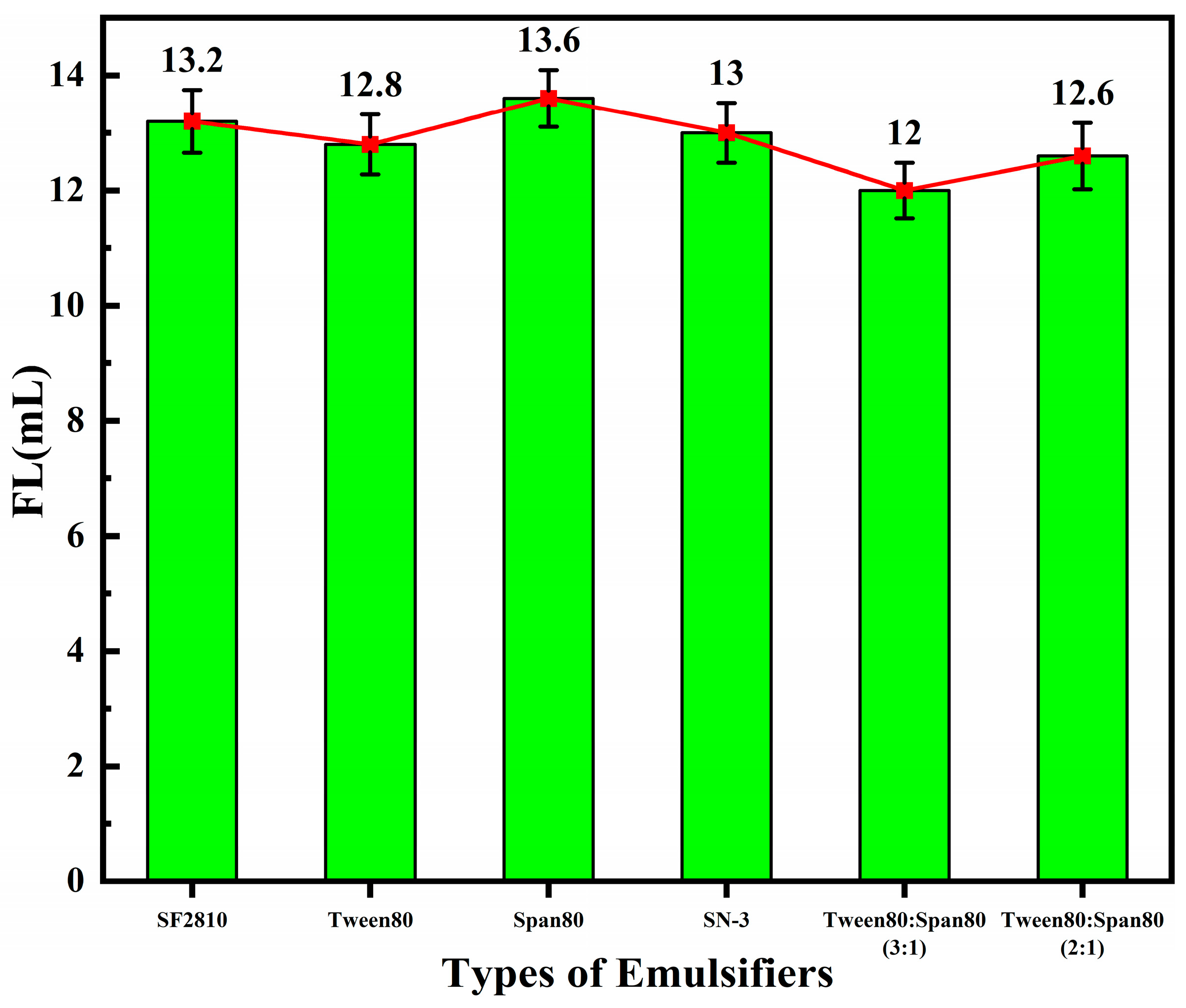
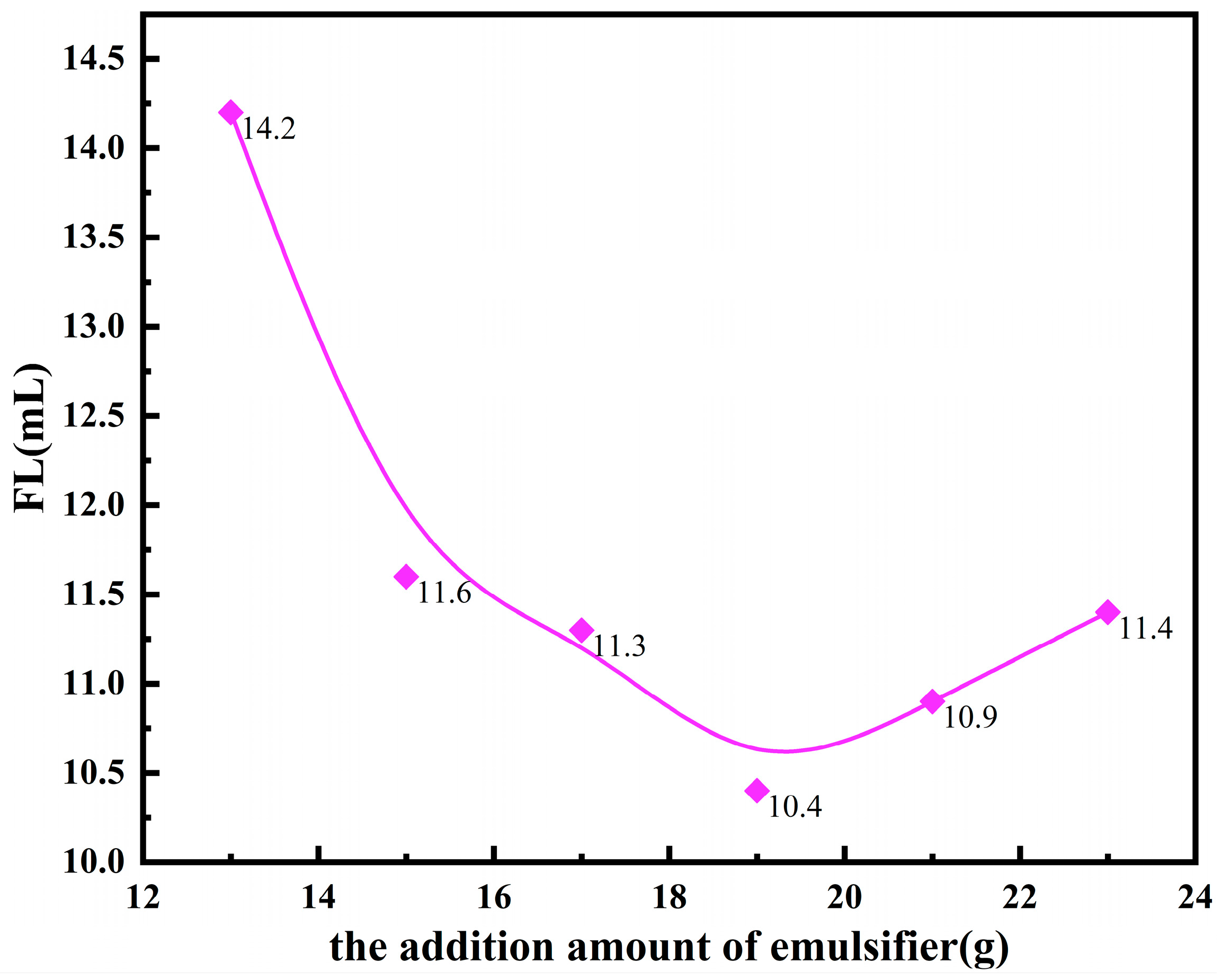
3.1.3. Emulsifiers and the Performance of Fluid Loss Additives
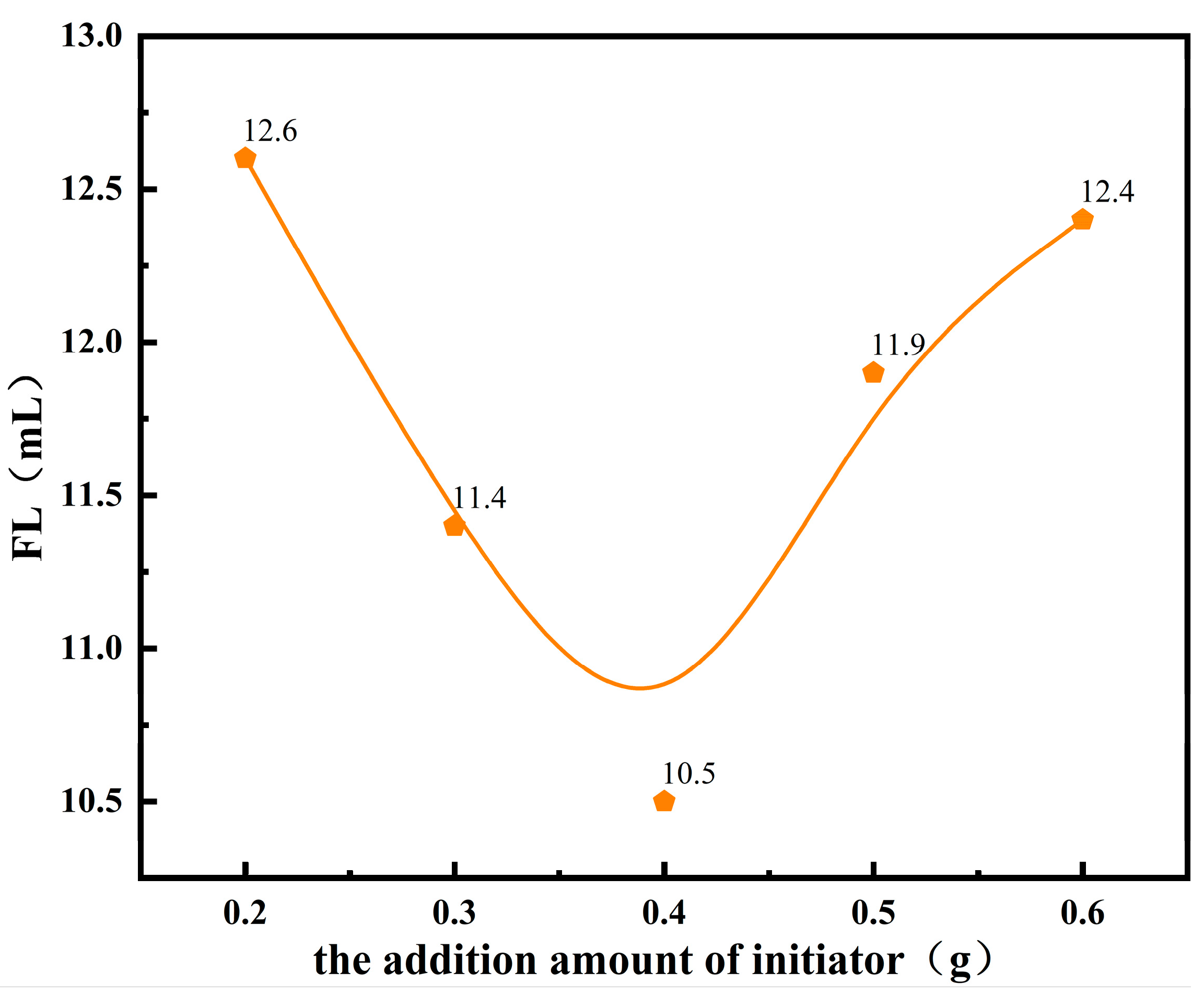
3.1.4. Initiator Dosage and the Performance of Fluid Loss Additives
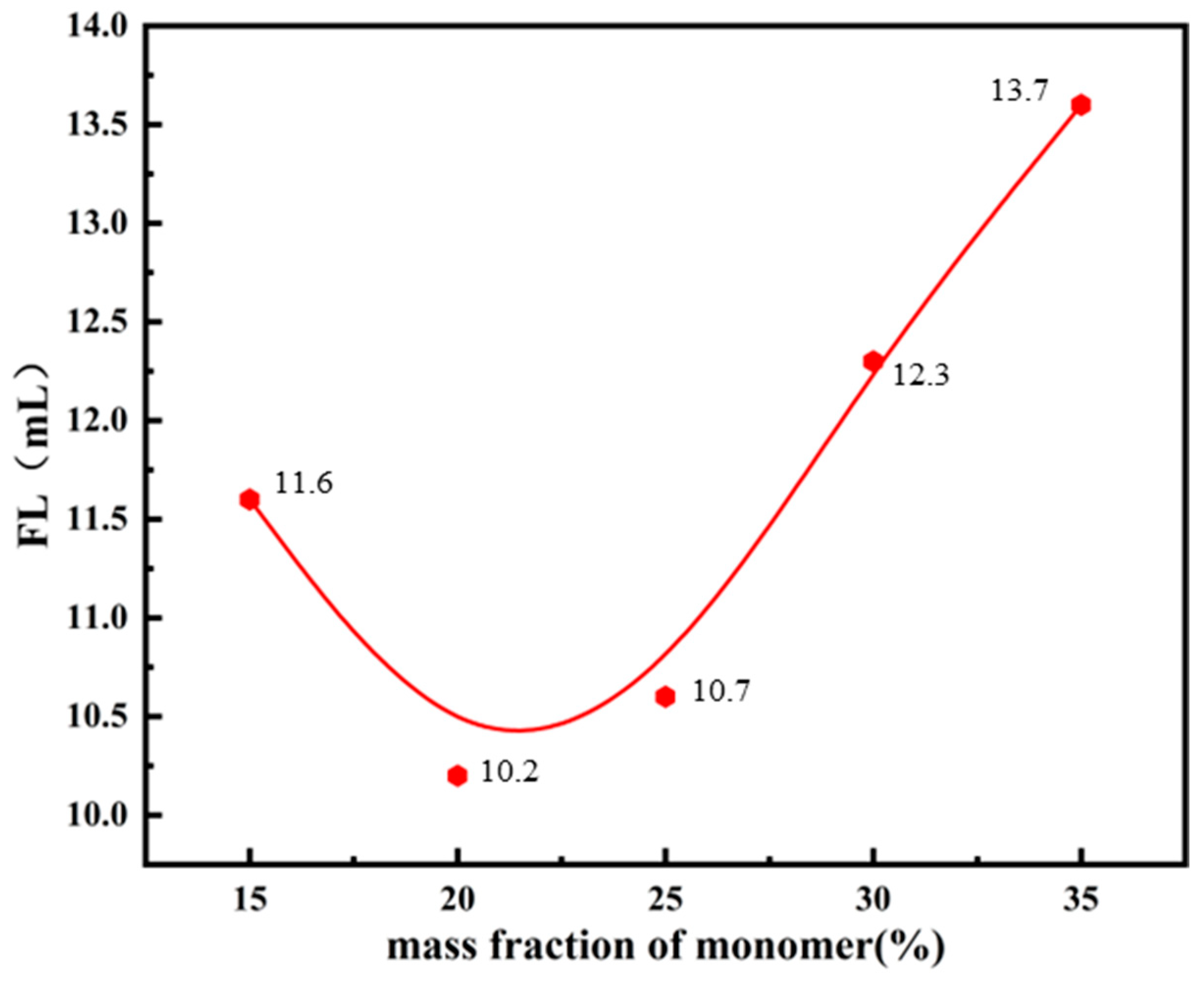
3.1.5. Monomer Mass Fraction and the Performance of Fluid Loss Additives
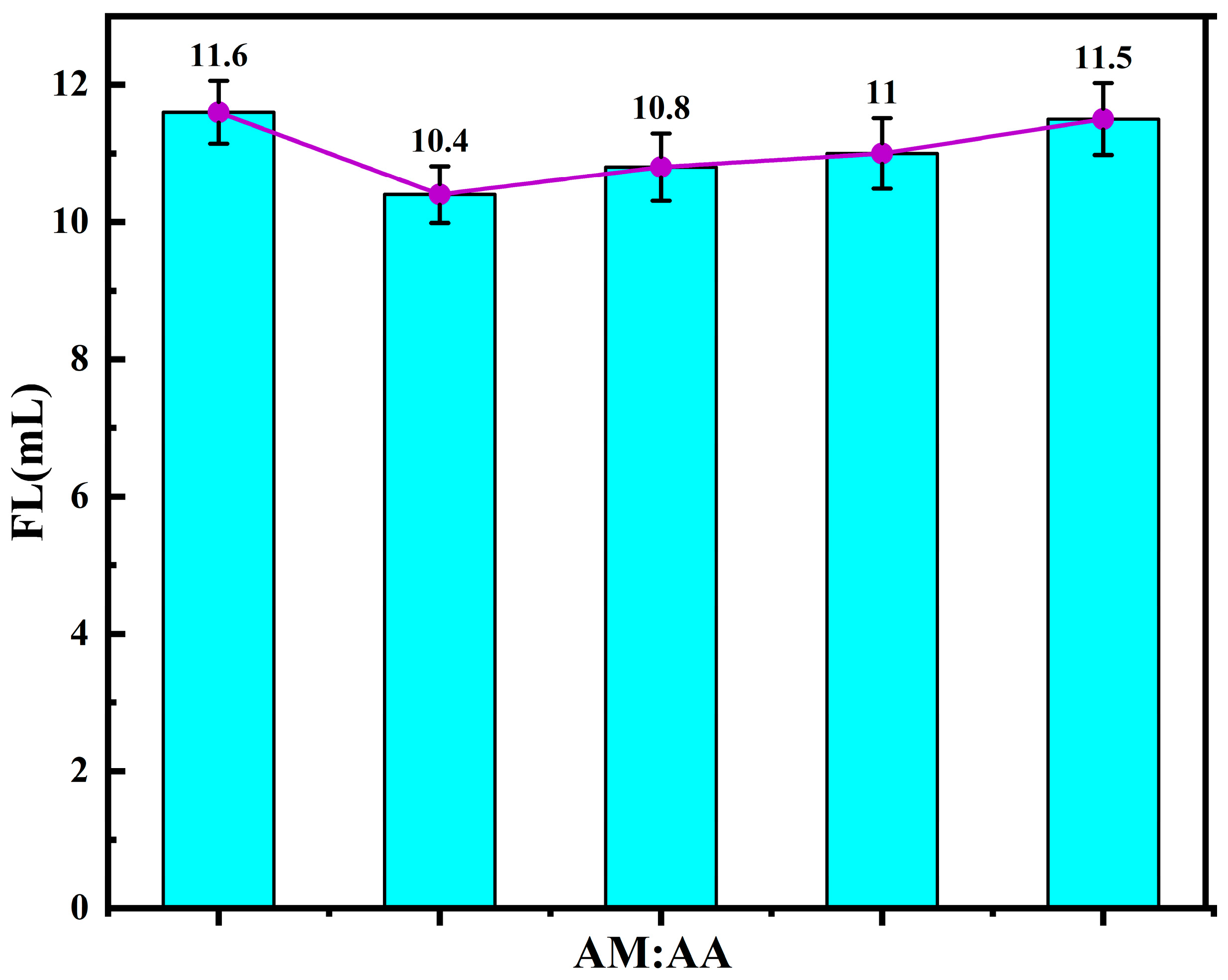
3.1.6. Monomer Molar Ratio and the Performance of Fluid Loss Additives
3.1.7. Reaction Time and the Performance of Fluid Loss Additives
3.1.8. Reaction Temperature and the Performance of Fluid Loss Additives
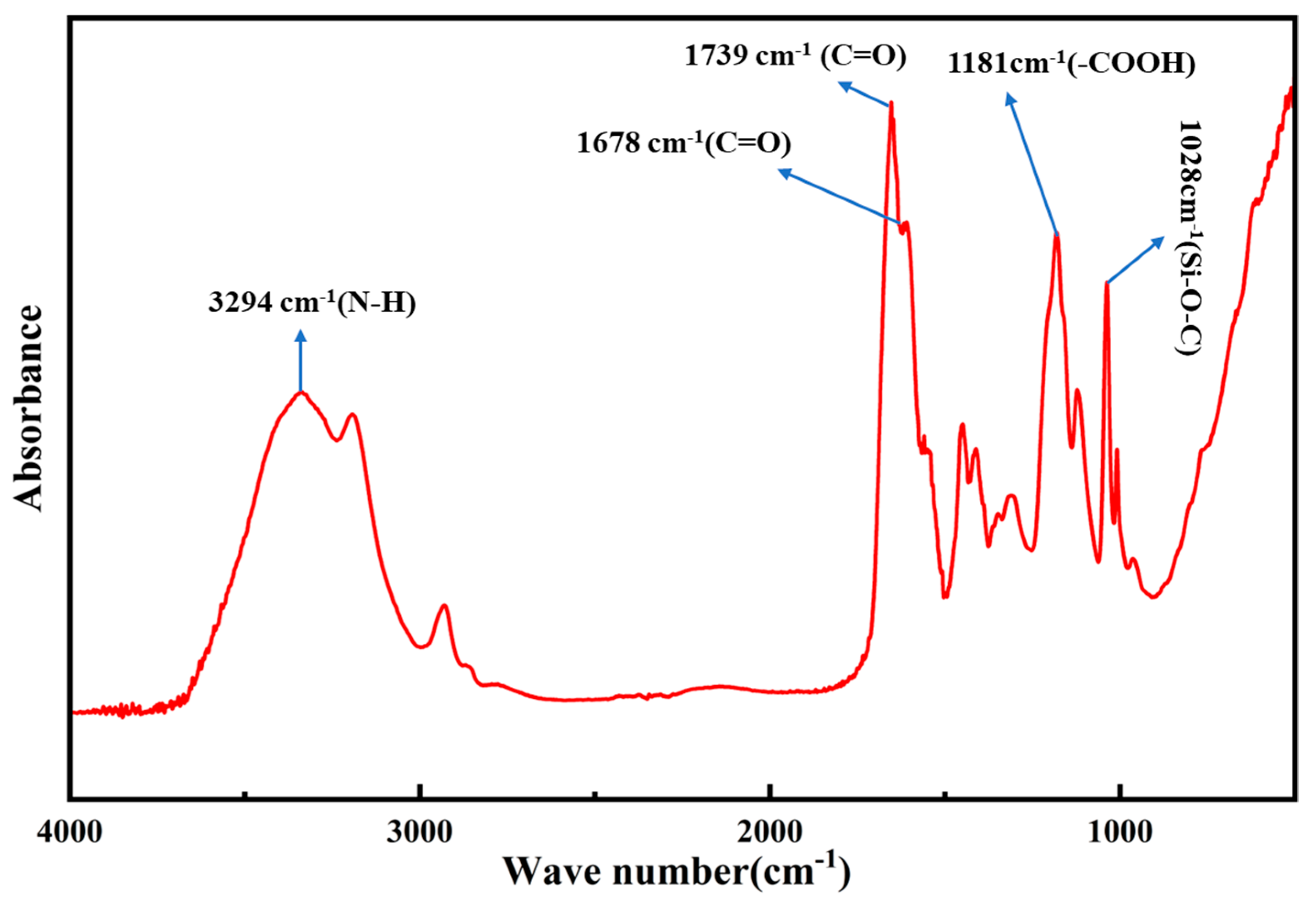
3.2. Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
3.3. Thermal Stability Analysis
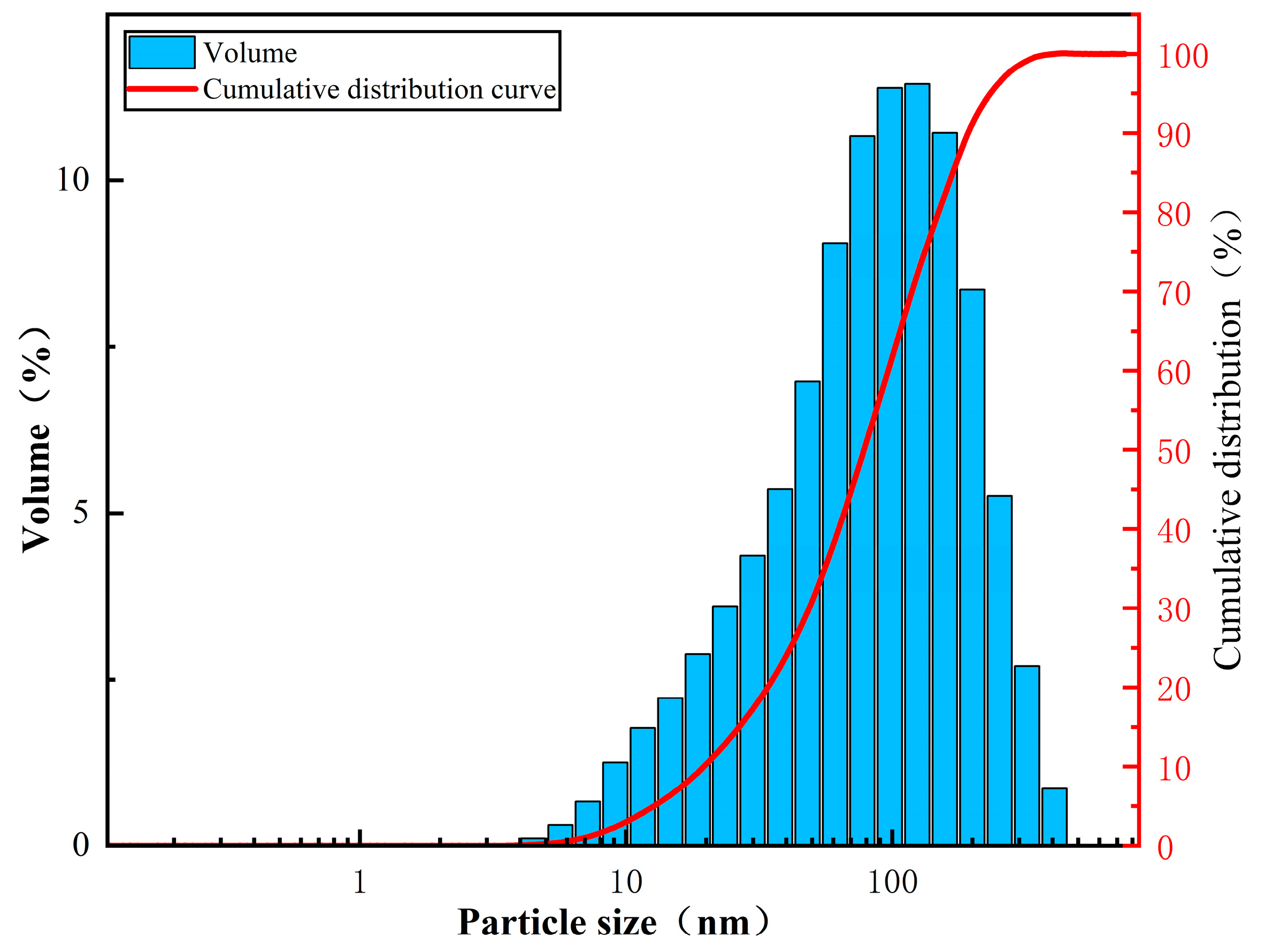
3.4. Particle Size Analysis
3.5. Analysis of Molecular Weight of Fluid Loss Additives
3.6. Fluid Loss Reduction Performance of Fluid Loss Additives
3.7. Evaluation of Biodegradability of Fluid Loss Additives
3.8. Evaluation of Biotoxicity of Fluid Loss Additives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, A.; Gao, S.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhai, R.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. A Review in Polymers for Fluid Loss Control in Drilling Operations. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2024, 225, 2300390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, C.; Ma, B.; Su, Z.; Wan, X.; Han, J.; Wu, G. An Overview of the Differential Carbonate Reservoir Characteristic and Exploitation Challenge in the Tarim Basin (NW China). Energies 2023, 16, 5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, B. Key oil accumulation periods of ultra-deep fault-controlled oil reservoir in northern Tarim Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2022, 49, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, S.; Al-Shargabi, M.; Wood, D.A.; Rukavishnikov, V.S.; Minaev, K.M. Synthetic polymers: A review of applications in drilling fluids. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 475–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Luo, X.; Yu, X.; Han, W.; Luo, Y. Synthesis and performance evaluation of a micron-size silica-reinforced polymer microsphere as a fluid loss agents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 130, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hameedi, A.T.T.; Alkinani, H.H.; Dunn-Norman, S.; Al-Alwani, M.A.; Alshammari, A.F.; Alkhamis, M.M.; Alkhamis, M.M.; Al-Bazzaz, W.H. Experimental investigation of environmentally friendly drilling fluid additives (mandarin peels powder) to substitute the conventional chemicals used in water-based drilling fluid. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodja, M.; Debih, H.; Lebtahi, H.; Amish, M.B. New HTHP fluid loss control agent for oil-based drilling fluid from pharmaceutical waste. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 8, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, R.F. Evaluation of drilling-fluid filter-loss additives under dynamic conditions. J. Pet. Technol. 1963, 15, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, J.; Lv, K.; Ji, Y.; Ji, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Shi, S.; Huang, X.; et al. A zwitterionic copolymer as fluid loss reducer for water-based drilling fluids in high temperature and high salinity conditions. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 222, 111200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lin, L.; Luo, P.; Li, X.; Ren, W.; Yi, T. Polymer-laponite composites as filtrate reducer for high temperature and salt resistant drilling fluid: Characterization and performance evaluation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 688, 133679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Du, W.; Dong, H.; Gao, S.; Qu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, H. Synthesis and mechanism study of an environmentally friendly filtrate reducing agent from humic acid and organic silicon. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e54994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okon, A.N.; Akpabio, J.U.; Tugwell, K.W. Evaluating the locally sourced materials as fluid loss control additives in water-based drilling fluid. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaimon, A.A.; Akintola, S.A.; Mohd Johari MA, B.; Isehunwa, S.O. Evaluation of drilling muds enhanced with modified starch for HPHT well applications. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. 2021, 11, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Sun, X.; Feng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Song, H.; Zhu, K.; Yang, S. Application in oil field drilling with temperature-resistant natural modified filtrate reducer: A review. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2023, 59, 146–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Li, M.C.; Lv, K.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Shen, H.; Dai, L.; Lalji, S.M. Cellulose derivatives as environmentally-friendly additives in water-based drilling fluids: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 342, 122355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hameedi, A.T.T.; Alkinani, H.H.; Dunn-Norman, S.; Al-Alwani, M.A.; Al-Bazzaz, W.H.; Alshammari, A.F.; Albazzaz, H.W.; Mutar, R.A. Experimental investigation of bio-enhancer drilling fluid additive: Can palm tree leaves be utilized as a supportive eco-friendly additive in water-based drilling fluid system? J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Sharma, N.; Bhattacharya, M.; Raina, A.; Gusain, M.M.; Sharma, K. Evaluation of environment friendly micro-ionized litchi leaves powder (LLP) as a fluid loss control agent in water-based drilling fluid. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. 2021, 11, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Lin, L. Effect of molecular flexibility on the rheological and filtration properties of synthetic polymers used as fluid loss additives in water-based drilling fluid. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8608–8619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad MS, K.; Mansouri, A.; Goodarznia, I. Experimental Study on using Nano-Gilsonite in Water-Based Drilling Fluids as a High-Performance Filtration Control Agent and Stuck Pipe Reducer in High-Pressure High-Temperature Wells. Int. J. Pet. Geosci. Eng. Exp. 2021, 2021, IJPGE-2105092112325. [Google Scholar]
- Davoodi, S.; Al-Shargabi, M.; Wood, D.A.; Minaev, K.M.; Rukavishnikov, V.S. Modified-starch applications as fluid-loss reducers in water-based drilling fluids: A review of recent advances. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 434, 140430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Lan, J.; Xu, N.; Sun, J.; Meng, L. Synthesis and properties of a high-performance environment-friendly micro–nano filtration reducer. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 43204–43212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Gao, X.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, W.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Li, S. Minimization of Ultra-High Temperature Filtration Loss for Water-Based Drilling Fluid with ß-Cyclodextrin Polymer Microspheres. In Proceedings of the SPE Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference, Sanabis, Bahrain, 28 November–1 December 2021; p. D031S032R001. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Xu, W. Synthesis and performance study of amphoteric ion fluid loss additive SSS/AM/FA/DMDAAC. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemeyer, C.; Plank, J. Working mechanism of a high temperature (200 °C) synthetic cement retarder and its interaction with an AMPS®-based fluid loss polymer in oil well cement. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 4772–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Pu, X.; Wang, X. Synthesis, characterization, and performance evaluation of the AM/AMPS/DMDAAC/SSS quadripolymer as a fluid loss additive for water-based drilling fluid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Lin, D.; Li, A.; Deng, L.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. Synergistic effects of covalent crosslinking and hydrophobic association on enhancing thermal and salt resistance of polymeric filtrate reducer. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 407, 125204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Pang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, B.; An, Y. Experimental study on the polymer/graphene oxide composite as a fluid loss agent for water-based drilling fluids. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9750–9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y. Synthesis of novel zwitterionic polymers and their properties as filtrate reducer for water-based drilling fluid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e54771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chem, S.; Qiu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, F.; Liu, S. Preparation and performance evaluation of a drilling fluid microspherestarch filter loss reducer. Drill. Complet. Fluids 2019, 36, 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.; Ma, J.; Jiang, G.; Sun, J.; An, Y. An inverse emulsion polymer as a highly effective salt-and calcium-resistant fluid loss reducer in water-based drilling fluids. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 16141–16151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Du, H.; Sun, J.; Huang, X.; Shen, H. A thermal-responsive zwitterionic polymer gel as a filtrate reducer for water-based drilling fluids. Gels 2022, 8, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, M. Synthesis and properties of a betaine type copolymer filtrate reducer. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2020, 153, 107953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addagalla, A.; Gad, A.Y.; Sonawane, V. Revolutionary Non-Damaging Liquid Polymeric Fluid Loss Control Agent Eliminates the Use of Conventional Powders in Non-Aqueous Fluid Systems. In Offshore Technology Conference Brasil; OTC: Houston, TX, USA, 2023; p. D031S035R002. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Jiang, G.; Qi, Y.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, L. Nano-fluid loss agent based on an acrylamide based copolymer “grafted” on a modified silica surface. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17246–17255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Sun, J.; Huang, X.; Geng, Y. Development of a Low-Molecular-Weight Filtrate Reducer with High-Temperature Resistance for Drilling Fluid Gel System. Gels 2023, 9, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, R.; Qu, Y.; Liu, F.; Yang, J.; Cheng, R.; Gao, S.; Huang, H. Synthesis of a new high temperature and salt resistant zwitterionic filtrate reducer and its application in water-based drilling fluid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 651, 129730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, B.A.; He, M.; Xu, M.; Liu, W.; Mpelwa, M.; Tang, S.; Jin, L.; Song, J. A novel amphoteric polymer as a rheology enhancer and fluid-loss control agent for water-based drilling muds at elevated temperatures. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8483–8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricky, E.; Mpelwa, M.; Wang, C.; Hamad, B.; Xu, X. Modified corn starch as an environmentally friendly rheology enhancer and fluid loss reducer for water-based drilling mud. SPE J. 2022, 27, 1064–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooripoor, V.; Nazemi, R.; Hashemi, A. Employing nano-sized additives as filtration control agent in water-based drilling fluids: Study on barium sulfate, bentonite, surface-modified bentonite, titanium oxide, and silicon oxide. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 46, 13806–13822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zheng, X.; Bian, J.; Tang, L.; Ye, Z.; Wang, J. Influence of Rigid Side Chains on the Structural Stability of High-Temperature Resistant Fluid Loss Additives for Oil Well Cements: An Experimental Study and Molecular Simulation. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2024, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; You, F.C.; Zhou, S.S. Study of a high-temperature and high-density water-based drilling fluid system based on non-sulfonated plant polymers. Polymers 2022, 14, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.; Liu, W.; Wan, Y.; Kong, X.; Guan, Y.; Qiu, Z.; et al. Application of Psyllium Husk as a Friendly Filtrate Reducer for High-Temperature Water-Based Drilling Fluids. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 27787–27797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Qu, Y.; Wang, P.; Huang, H.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Z. Laponite-polymer composite as a rheology modifier and filtration loss reducer for water-based drilling fluids at high temperature. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 655, 130261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Guan, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Grady, B.P.; Su, J.; Huang, W. Application of carbon coated bentonite composite as an ultra-high temperature filtration reducer in water-based drilling fluid. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 375, 121360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; NI, X.; Li, W.; Quan, X.; Luo, X. Super-amphiphobic, strong self-cleaning and high-efficiency water-based drilling fluids. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Shen, X.; Li, G. Application of tea polyphenols as a biodegradable fluid loss additive and study of the filtration mechanism. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3453–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Khan, I.; Saleh, T.A. Advances in carbon nanostructures and nanocellulose as additives for efficient drilling fluids: Trends and future perspective—A review. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 7319–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Jiang, G.C.; Xu, Y.; Deng, Z.Q.; Wang, K. A new environmentally friendly water-based drilling fluids with laponite nanoparticles and polysaccharide/polypeptide derivatives. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Sun, J.S.; Xie, S.X.; Huang, X.B. Synthesis and Characterization of a Cationic Micro-crosslinking Polymer and its Application as a Fluid Loss Reducer in Water-based Drilling Fluids. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2594, 012058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Qiu, Z.; Shen, Z.; Huang, W. Hydrophobic associated polymer based silica nanoparticles composite with core–shell structure as a filtrate reducer for drilling fluid at utra-high temperature. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 129, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Gao, X.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jin, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, J. Mechanism of filtration loss reduction of environment-friendly β-cyclodextrin polymer microspheres under high temperatures. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 1091. [Google Scholar]
- SY 5490-2016 Standards; Clays for Drilling Fluid Tests. Oil and gas Industry Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 16783.1-2014; Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries-Field Testing of Drilling Fluids-Part 1: Water-Based Fluids. National standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- GB7488-87; Water Quallty-Determination of Biochemicaloxyen Demand After 5 days(BOD5)-Dilutionand Seeding Method. National standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1987.





| Number | Oil–Water Ratio | Phenomenon |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:4 | turbid |
| 2 | 2:4 | no obvious phase separation |
| 3 | 3:4 | no obvious phase separation |
| 4 | 4:4 | layering |
| 5 | 5:4 | uniform and transparent |
| Dosage of Fluid Loss Reducer | State | AV/ (mPa·s) | PV/ (mPa·s) | YP/ (Pa) | FLAPI /mL | FL(HTHP) /mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Before thermal aging test | 13 | 10 | 3 | ||
| After thermal aging test | 9 | 7 | 2 | 63.7 | - | |
| 1% | Before thermal aging test | 17 | 15 | 2 | ||
| After thermal aging test | 16 | 14 | 2 | 13.8 | 51.2 | |
| 2% | Before thermal aging test | 23 | 18 | 5 | ||
| After thermal aging test | 21 | 18 | 3 | 8.4 | 32.8 | |
| 3% | Before thermal aging test | 26 | 20 | 6 | ||
| Before thermal aging test | 23 | 19 | 4 | 6.3 | 17.6 |
| Fluid Loss Reducer | State | AV/ (mPa·s) | PV/ (mPa·s) | YP/ (Pa) | FLAPI /mL | FL(HTHP) /mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPNH-HT | Before thermal aging test | 20 | 16 | 4 | ||
| After thermal aging test | 8 | 6 | 2 | 62.8 | - | |
| Dristemp | Before thermal aging test | 23 | 17 | 6 | ||
| After thermal aging test | 14 | 11 | 3 | 11.3 | 48.2 | |
| DTEMP | Before thermal aging test | 24 | 21 | 3 | ||
| After thermal aging test | 11 | 9 | 2 | 31.6 | - | |
| EnSipoly-FL | Before thermal aging test | 24 | 20 | 4 | ||
| Before thermal aging test | 25 | 22 | 3 | 7.3 | 18.8 |
| Concentration (%) | COD (mg/L) | BOD5 (mg/L) | BOD5/COD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 23 | 5.1 | 0.221 |
| 0.5 | 126 | 26.9 | 0.213 |
| 1.0 | 281 | 61.1 | 0.217 |
| 2.0 | 608 | 128.6 | 0.211 |
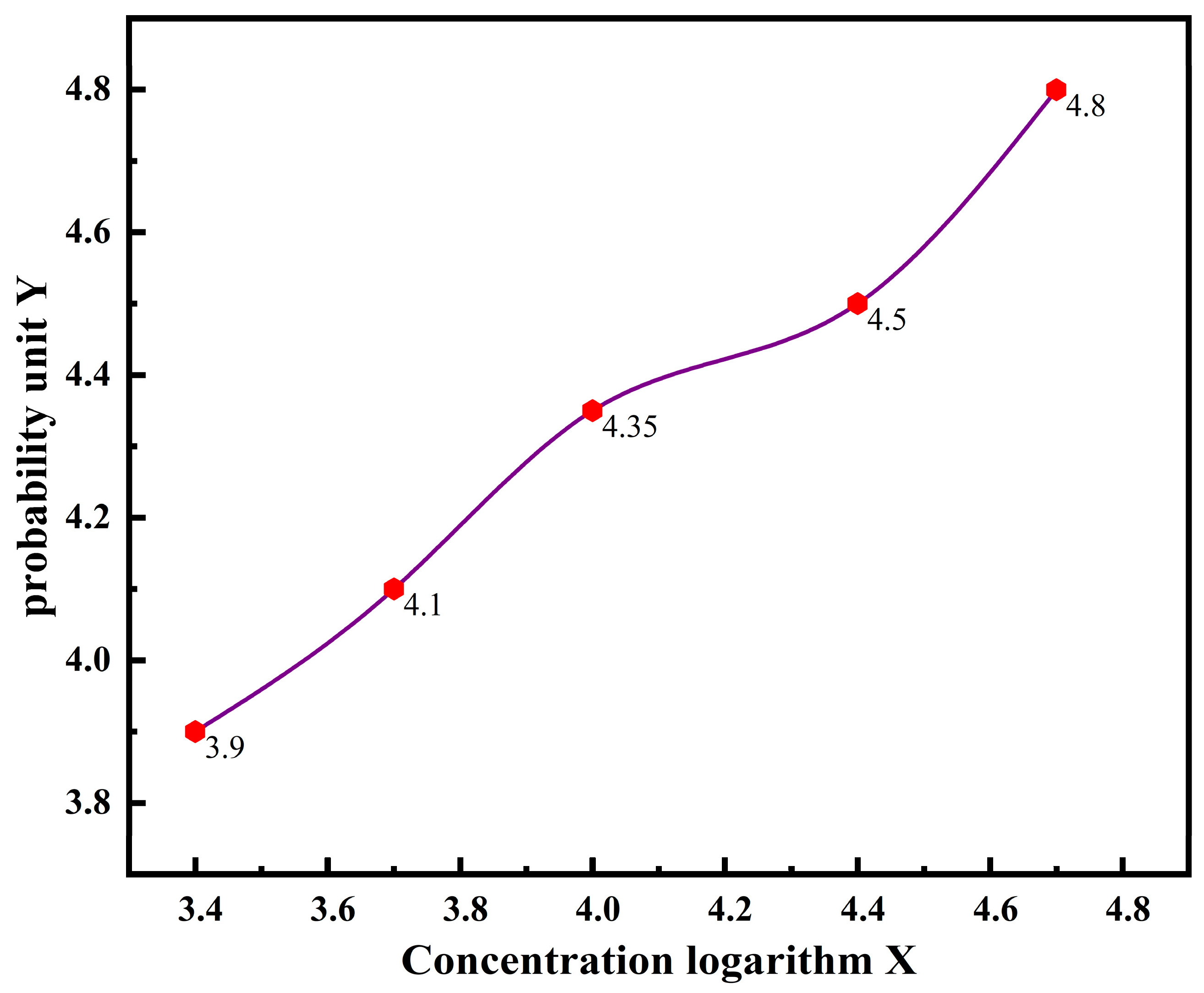
| Group | Concentration (mg/L) | Logarithm of Concentration (X) | Number of Experimental Organisms (ind) | Number of Deaths (r) | Mortality Rate (%) | Corrected Mortality Rate (%) | Probability Unit (Y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | / | / | 40 | 6 | 15 | / | / |
| A2 | 2500 | 3.3979 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 11.8 | 3.8150 |
| A3 | 5000 | 3.6990 | 40 | 12 | 30 | 17.6 | 4.0693 |
| A4 | 10,000 | 4 | 40 | 14 | 35 | 23.5 | 4.2775 |
| A5 | 20,000 | 4.3010 | 40 | 17 | 42.5 | 32.4 | 4.5435 |
| A6 | 40,000 | 4.6021 | 40 | 20 | 50 | 41.2 | 4.7776 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, M.; Yang, C.; Huang, Q.; Wang, R.; Su, X.; Xu, P.; Peng, T. Synthesis and Evaluation of High-Temperature-Resistant and Environmentally Friendly Polymer Filter Loss Additives. Polymers 2025, 17, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060792
Tian M, Yang C, Huang Q, Wang R, Su X, Xu P, Peng T. Synthesis and Evaluation of High-Temperature-Resistant and Environmentally Friendly Polymer Filter Loss Additives. Polymers. 2025; 17(6):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060792
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Ming, Chuan Yang, Qian Huang, Ruixue Wang, Xiaoming Su, Peng Xu, and Tao Peng. 2025. "Synthesis and Evaluation of High-Temperature-Resistant and Environmentally Friendly Polymer Filter Loss Additives" Polymers 17, no. 6: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060792
APA StyleTian, M., Yang, C., Huang, Q., Wang, R., Su, X., Xu, P., & Peng, T. (2025). Synthesis and Evaluation of High-Temperature-Resistant and Environmentally Friendly Polymer Filter Loss Additives. Polymers, 17(6), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060792






