Effects of Greenhouse vs. Growth Chamber and Different Blue-Light Percentages on the Growth Performance and Quality of Broccoli Microgreens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
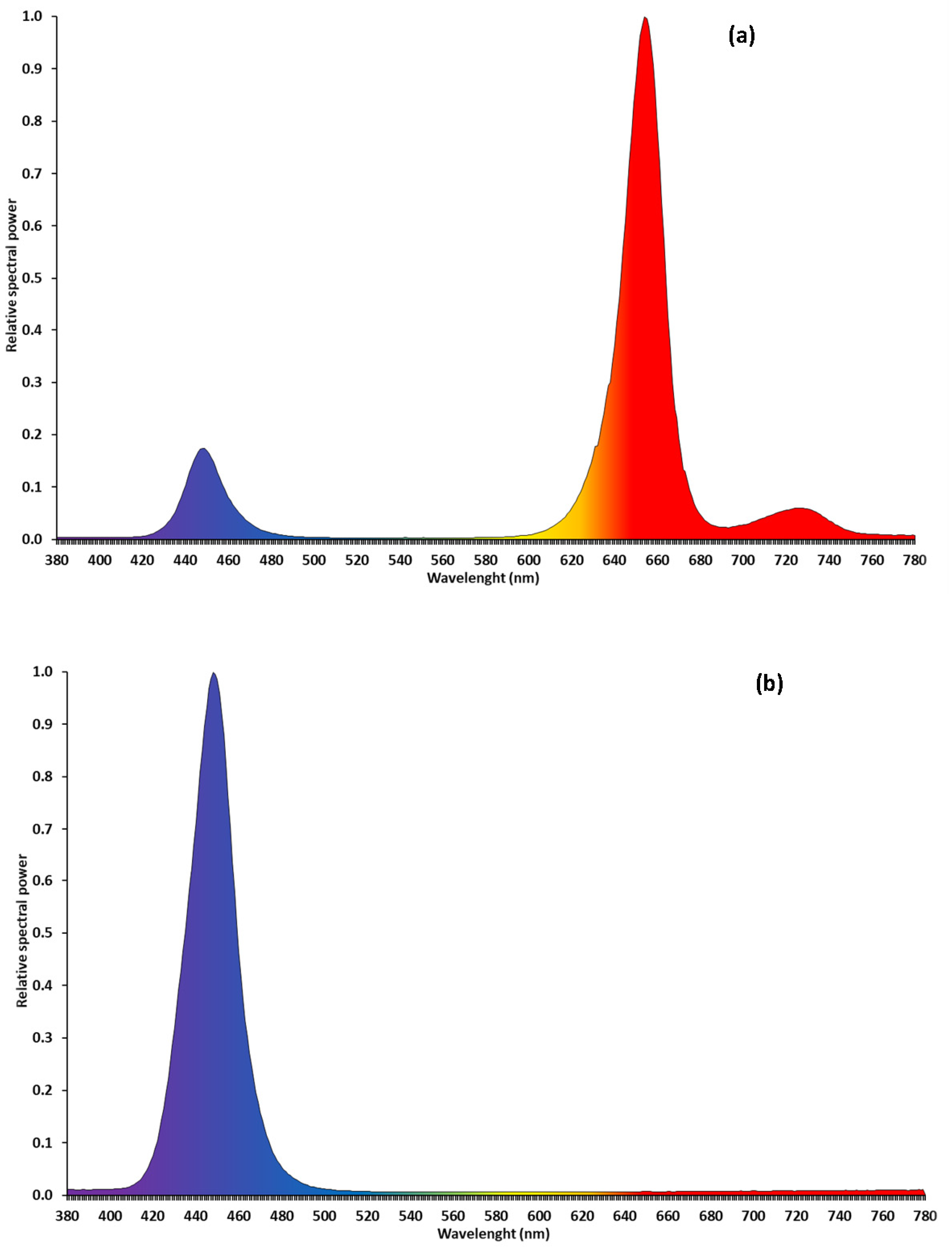
2.2. Light Treatments
2.3. Preliminary Determination of Seed Density
2.4. Biometric Measurements
2.5. Antioxidant Activity and Polyphenols Content
2.6. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Seed Quantities Needed to Produce Broccolo Natalino and Mugnoli Microgreens
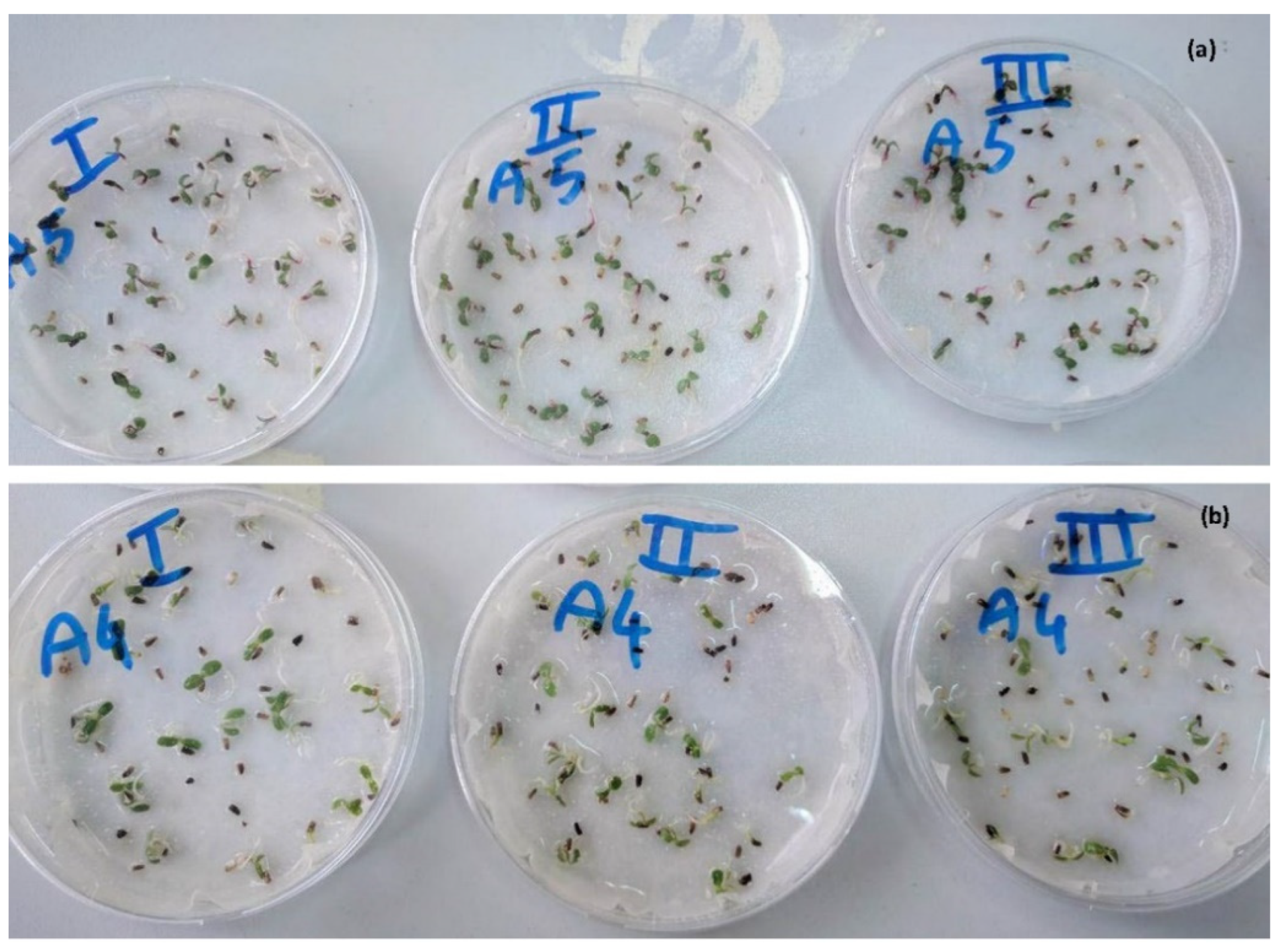
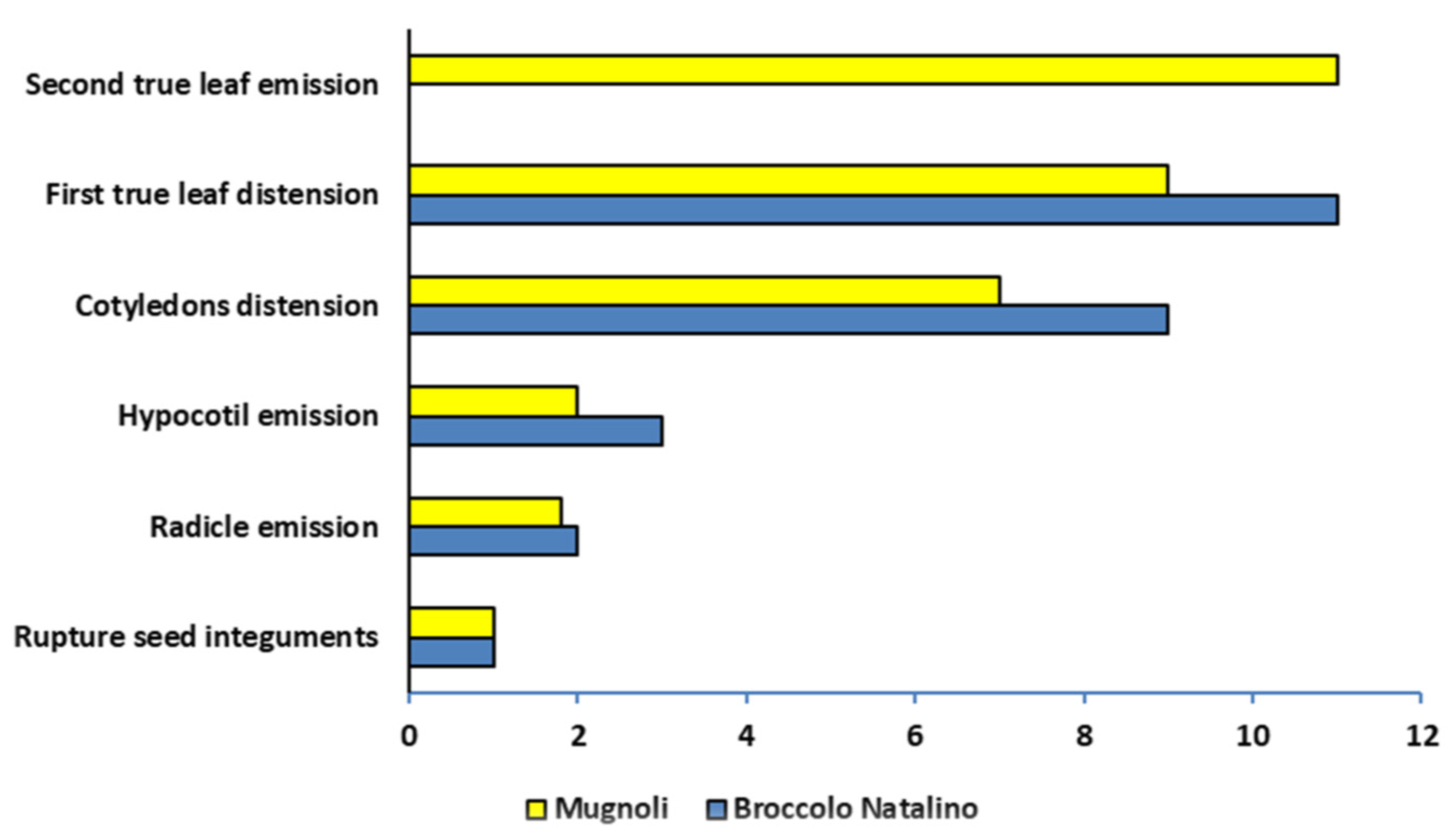
3.2. Seedling Development and Biometric Characteristics
3.3. Microgreens Yield
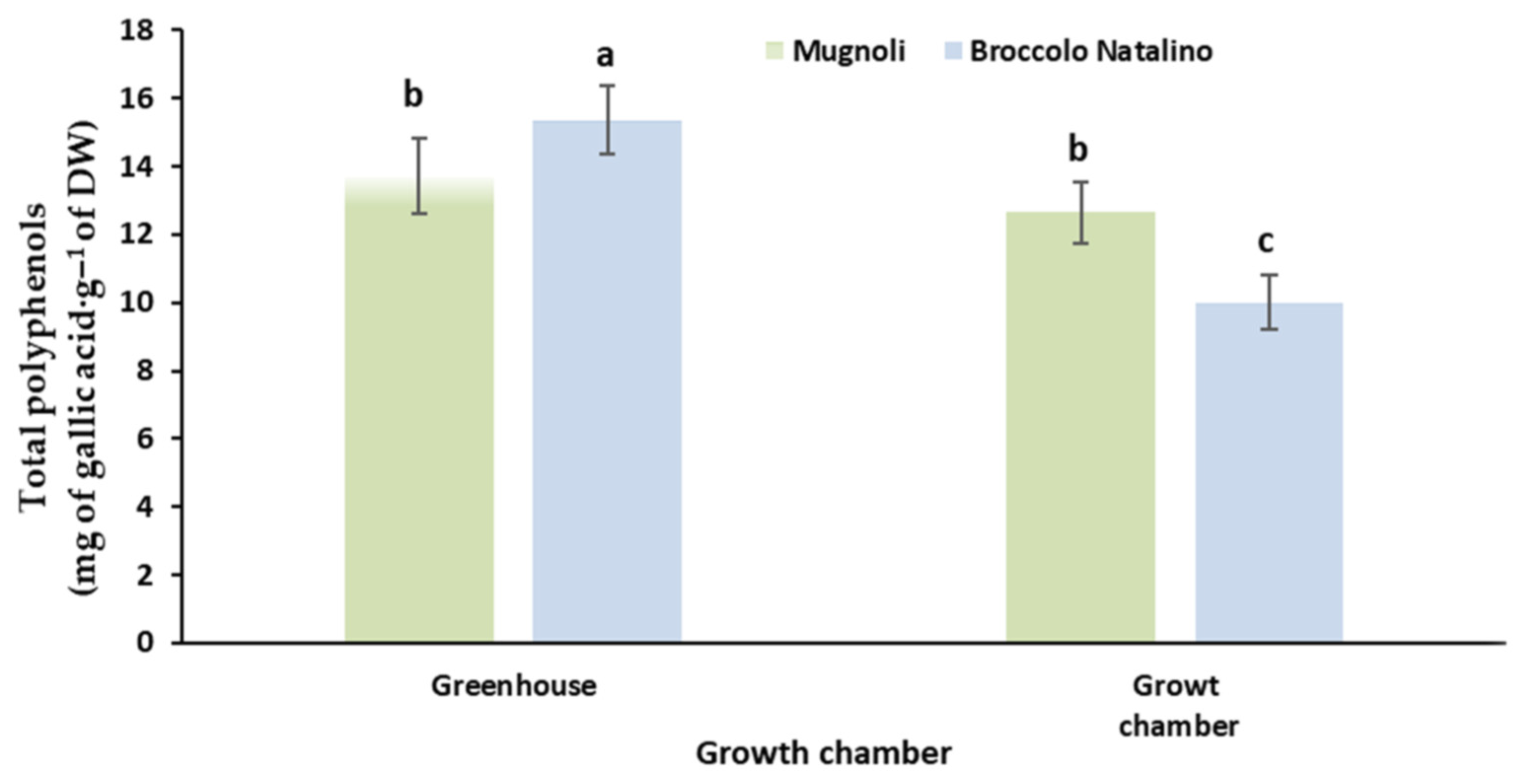
3.4. Total Polyphenols Content and Antioxidant Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teng, J.; Liao, P.; Wang, M. The role of emerging micro-scale vegetables in human diet and health benefits—An updated review based on microgreens. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1914–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, U.; Yu, L.L.; Wang, T.T.Y. The Science behind Microgreens as an Exciting New Food for the 21st Century. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11519–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, F.; Renna, M.; Santamaria, P. Sprouts, Microgreens and “Baby Leaf” Vegetables. In Minimally Processed Refrigerated Fruits and Vegetables; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 403–432. ISBN 978-1-4939-7016-2. [Google Scholar]
- Di Gioia, F.; Santamaria, P. (Eds.) Microgreens, agrobiodiversity and food security. In Microgreens: Novel Fresh and Functional Food to Explore All the Value of Biodiversity; ECO-logica srl: Bari, Italy, 2015; pp. 7–24. ISBN 9788890928932. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriacou, M.C.; Rouphael, Y.; Di Gioia, F.; Kyratzis, A.; Serio, F.; Renna, M.; De Pascale, S.; Santamaria, P. Micro-scale vegetable production and the rise of microgreens. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 57, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgari, R.; Negri, M.; Santoro, P.; Ferrante, A. Quality Evaluation of Indoor-Grown Microgreens Cultivated on Three Different Substrates. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieth, A.R.; Pinheiro, W.D.; Duarte, T.D.S. Purple cabbage microgreens grown in different substrates and nutritive solution concentrations. Rev. Caatinga 2019, 32, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamal, K.Y.; Khodaeiaminjan, M.; El-Tantawy, A.A.; Moneim, D.A.; Salam, A.A.; Ash-shormillesy, S.M.A.I.; Attia, A.; Ali, M.A.S.; Herranz, R.; El-Esawi, M.A.; et al. Evaluation of growth and nutritional value of Brassica microgreens grown under red, blue and green LEDs combinations. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 169, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannico, A.; El-Nakhel, C.; Graziani, G.; Kyriacou, M.C.; Giordano, M.; Soteriou, G.A.; Zarrelli, A.; Ritieni, A.; De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y. Selenium Biofortification Impacts the Nutritive Value, Polyphenolic Content, and Bioactive Constitution of Variable Microgreens Genotypes. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paradiso, V.M.; Castellino, M.; Renna, M.; Santamaria, P.; Caponio, F. Setup of an Extraction Method for the Analysis of Carotenoids in Microgreens. Foods 2020, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebert, A.W. Sprouts and Microgreens—Novel Food Sources for Healthy Diets. Plants 2022, 11, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renna, M.; Castellino, M.; Leoni, B.; Paradiso, V.M.; Santamaria, P. Microgreens production with low potassium content for patients with impaired kidney function. Nutrients 2018, 10, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Gioia, F.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Rosskopf, E.N. Microgreens: From trendy vegetables to functional food and potential nutrition security resource. Acta Hortic. 2021, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Lester, G.E.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Assessment of vitamin and carotenoid concentrations of emerging food products: Edible microgreens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7644–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renna, M.; Paradiso, V.M. Ongoing Research on Microgreens: Nutritional Innovative Growing and Processing Approaches. Foods 2020, 9, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghetti, G.; Martignano, F.; Falco, V.; Cifarelli, S.; Gladis, T.; Hammer, K. “Mugnoli”: A neglected race of Brassica oleracea L. from Salento (Italy). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2005, 52, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xiao, Z.; Lin, L.; Lester, G.E.; Wang, Q.; Harnly, J.M.; Chen, P. Profiling Polyphenols in Five Brassica Species Microgreens by UHPLC-PDA-ESI/HRMS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10960–10970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmitessa, O.D.; Renna, M.; Crupi, P.; Lovece, A.; Corbo, F.; Santamaria, P. Yield and Quality Characteristics of Brassica Microgreens as Affected by the NH4:NO3 Molar Ratio and Strength of the Nutrient Solution. Foods 2020, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faller, A.L.K.; Fialho, E. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis Polyphenol content and antioxidant capacity in organic and conventional plant foods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010, 23, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Mumper, R.J. Plant Phenolics: Extraction, Analysis and Their Antioxidant and Anticancer Properties. Molecules 2010, 15, 7313–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Baumgardt, C.; Llewellyn, D.; Ying, Q.; Zheng, Y. Intensity of sole-source light-emitting diodes affects growth, yield, and quality of brassicaceae microgreens. HortScience 2019, 54, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusuma, P.; Pattison, P.M. From physics to fixtures to food: Current and potential LED efficacy. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, K.H.; Huang, M.Y.; Huang, W.D.; Hsu, M.H.; Yang, Z.W.; Yang, C.M. The effects of red, blue, and white light-emitting diodes on the growth, development, and edible quality of hydroponically grown lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. capitata). Sci. Hortic. 2013, 150, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuoliene, G.; Brazaitytė, A.; Jankauskienė, J.; Viršilė, A.; Sirtautas, R.; Novičkovas, A.; Sakalauskienė, S.; Sakalauskaitė, J.; Duchovskis, P. LED irradiance level affects growth and nutritional quality of Brassica microgreens. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2013, 8, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meas, S.; Luengwilai, K.; Thongket, T. Enhancing growth and phytochemicals of two amaranth microgreens by LEDs light irradiation. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 265, 109204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazaitytė, A.; Sakalauskienė, S.; Samuoliene, G.; Jankauskienė, J.; Viršilė, A.; Novičkovas, A.; Sirtautas, R.; Miliauskienė, J.; Vaštakaitė, V.; Dabašinskas, L.; et al. The effects of LED illumination spectra and intensity on carotenoid content in Brassicaceae microgreens. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bian, Z.; Yuan, X.; Chen, X.; Lu, C. A review on the effects of light-emitting diode (LED) light on plant nutrients in sprouts and microgreens production. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazaityte, A.; Miliauskienė, J.; Vaštakaitė-Kairienė, V.; Sutuliene, R.; Lauzike, K.; Duchovskis, P.; Malek, S. Effect of Different Ratios of Blue and Red LED Light on Brassicaceae Microgreens under a Controlled Environment. Plants 2021, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Q.; Kong, Y.; Jones-Baumgardt, C.; Zheng, Y. Responses of yield and appearance quality of four Brassicaceae microgreens to varied blue light proportion in red and blue light-emitting diodes lighting. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 259, 108857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmitessa, O.D.; Prinzenberg, A.E.; Kaiser, E. LED and HPS Supplementary light differentially affect gas exchange in tomato Leaves. Plants 2021, 10, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmitessa, O.D.; Pantaleo, M.A.; Santamaria, P. Applications and Development of LEDs as Supplementary Lighting for Tomato at Different Latitudes. Agronomy 2021, 11, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, L.G.; Hay Mele, B.; Vitale, L.; Vitale, E.; Arena, C. The role of monochromatic red and blue light in tomato early photomorphogenesis and photosynthetic traits. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 179, 104195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmardi, J.; Emami, S. Response of Tomato and Pepper Transplants to Light Spectra Provided by Light Emitting Diodes. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2013, 19, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argentieri, M.P.; Accogli, R.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Avato, P. Glucosinolates profile of mugnolo, a variety of Brassica oleracea L. native to southern Italy (Salento). Planta Med. 2011, 77, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Gioia, F.; Mininni, C.; Santamaria, P. (Eds.) How to grow microgreens. In Microgreens: Novel Fresh and Functional Food to Explore All the Value of Biodiversity; Eco-Logica srl: Bari, Italy, 2015; pp. 51–79. ISBN 9788890928932. [Google Scholar]
- Difonzo, G.; Russo, A.; Trani, A.; Paradiso, V.M.; Ranieri, M.; Pasqualone, A.; Summo, C.; Tamma, G.; Silletti, R.; Caponio, F. Green extracts from Coratina olive cultivar leaves: Antioxidant characterization and biological activity. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 31, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradiso, V.M.; Castellino, M.; Renna, M.; Gattullo, C.E.; Calasso, M.; Terzano, R.; Allegretta, I.; Leoni, B.; Caponio, F.; Santamaria, P. Nutritional characterization and shelf-life of packaged microgreens. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5629–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.S.; Pill, W.G.; Cobb, B.B.; Seed, M.O. Seed treatments to advance greenhouse establishment of beet and chard microgreens. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.X.; Xu, Z.G.; Liu, X.Y.; Tang, C.M.; Wang, L.W.; Han, X.L. Effects of light intensity on the growth and leaf development of young tomato plants grown under a combination of red and blue light. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 153, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Shree, B.; Sharma, D.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, R.; Saini, R. Vegetable microgreens: The gleam of next generation super foods, their genetic enhancement, health benefits and processing approaches. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Effects of Light Intensity and Temperature on the Photosynthesis Characteristics and Yield of Lettuce. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCree, K.J. The Action Spectrum, Absorptance and Quantum Yield of Photosynthesis in Crop Plants. Agric. Meteorol. 1972, 9, 191–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogewoning, S.W.; Trouwborst, G.; Maljaars, H.; Poorter, H.; van Ieperen, W.; Harbinson, J. Blue light dose-responses of leaf photosynthesis, morphology, and chemical composition of Cucumis sativus grown under different combinations of red and blue light. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3107–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougher, T.A.O.; Bugbee, B. Long-term Blue Light Effects on the Histology of Lettuce and Soybean Leaves and Stems. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2004, 129, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samuolienė, G.; Viršilė, A.; Brazaitytė, A.; Jankauskienė, J.; Sakalauskienė, S.; Vaštakaitė, V.; Novičkovas, A.; Viškelienė, A.; Sasnauskas, A.; Duchovskis, P. Blue light dosage affects carotenoids and tocopherols in microgreens. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; De Feo, V.; Battistelli, A.; Da Cruz, A.G.; Coppola, R. Polyphenols, the New Frontiers of Prebiotics, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 94, ISBN 9780128202180. [Google Scholar]
- de Paulo Farias, D.; de Araújo, F.F.; Neri-Numa, I.A.; Pastore, G.M. Antidiabetic potential of dietary polyphenols: A mechanistic review. Food Res. Int. 2021, 145, 110383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Phenolics and polyphenolics in foods, beverages and spices: Antioxidant activity and health effects—A review. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 820–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Radzikowska, D.; Ivanišová, E.; Szwengiel, A.; Kačániová, M.; Sawinska, Z. Influence of abiotic stress factors on the antioxidant properties and polyphenols profile composition of Green Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puccinelli, M.; Maggini, R.; Angelini, L.G.; Santin, M.; Landi, M.; Tavarini, S.; Castagna, A.; Incrocci, L. Can Light Spectrum Composition Increase Growth and Nutritional Quality of Linum usitatissimum L. Sprouts and Microgreens? Horticulturae 2022, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrifai, O.; Hao, X.; Liu, R.; Lu, Z.; Marcone, M.F.; Tsao, R. Amber, red and blue LEDs modulate phenolic contents and antioxidant activities in eight Cruciferous microgreens. J. Food Bioact. 2020, 11, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Stage (1) | Substrate Coverage (2) | Substrate Uniformity (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light treatments (L) | |||
| Blue | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.92 ± 0.23 | 1.92 ± 0.08 b |
| Control | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 2.00 ± 0.14 | 2.00 ± 0.00 a |
| Control + Blue | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.84 ± 0.28 | 2.11 ± 0.13 a |
| Genotype (G) | |||
| Broccolo Natalino | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.86 ± 0.31 | 2.07 ± 0.14 |
| Mugnoli | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.94 ± 0.24 | 2.08 ± 0.11 |
| Significance | |||
| L | NS | NS | ** |
| G | NS | NS | NS |
| L × G | NS | NS | NS |
| Stage (1) | True Leaf Presence | First True Leaf Length | Substrate Coverage (2) | Substrate Uniformity (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth system (S) | % | cm | |||
| Growth chamber | 1.00 ± 0.00 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 1.93 ± 0.26 | 2.08 ± 0.38 |
| Greenhouse | 2.50 ± 0.52 a | 85.00 ± 10.00 a | 0.68 ± 0.21 a | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 2.00 ± 0.00 |
| Genotype (G) | |||||
| Broccolo Natalino | 1.29 ± b | 20.00 ± 2.50 b | 0.14 ± 0.05 b | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 2.19 ± 0.33 |
| Mugnoli | 1.50 ± a | 25.00 ± 2.00 a | 0.22 ± 0.08 a | 1.92 ± 0.33 | 2.04 ± 0.43 |
| Significance | |||||
| S | *** | *** | *** | NS | NS |
| G | *** | *** | *** | NS | NS |
| S × G | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Fresh Weight | Dry Weight | Hypocotil Lenght | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light treatments (L) | g·m−2 | g·100 g−1 FW | cm |
| Blue | 1174 ± 80 c | 5.11 ± 0.31 a | 8.11 ± 0.95 b |
| Control | 1358 ± 64 a | 4.78 ± 0.28 b | 9.31 ± 1.34 a |
| Control + Blue | 1236 ± 76 b | 4.91 ± 0.23 ab | 8.54 ± 0.38 b |
| Genotype (G) | |||
| Broccolo Natalino | 1181 ± 112 | 5.92 ± 0.36 | 8.52 ± 3.62 |
| Mugnoli | 1255 ± 91 | 5.44 ± 0.37 | 8.84 ± 3.48 |
| Significance (1) | |||
| L | ** | *** | *** |
| G | NS | NS | NS |
| L × G | NS | NS | NS |
| Fresh Weight | Dry Weight | Hypocotil Lenght | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth system (S) | g·m−2 | g·100 g−1 FW | cm |
| Growth chamber | 1426 ± 99 b | 4.87 ± 0.35 b | 9.65 ± 0.94 b |
| Greenhouse | 1742 ± 87 a | 7.46 ± 0.51 a | 6.75 ± 0.35 a |
| Genotype (G) | |||
| Broccolo Natalino | 1481 ± 93 | 5.63 ± 1.04 | 8.31 ± 0.67 |
| Mugnoli | 1504 ± 92 | 5.70 ± 1.01 | 9.19 ± 0.64 |
| Significance (1) | |||
| S | ** | *** | *** |
| G | NS | NS | NS |
| S × G | NS | NS | NS |
| Total Polyphenols | Antioxidant Activity | |
|---|---|---|
| Light treatments (L) | mg of gallic acid·g−1 DW | μmol Trolox equivalents (TE)·g−1 DW |
| Blue | 10.3 ± 0.44 b | 25.0 ± 2.20 |
| Control | 12.2 ± 0.95 a | 63.6 ± 7.89 |
| Control + Blue | 11.6 ± 1.05 ab | 40.9 ± 8.63 |
| Genotype (G) | ||
| Broccolo Natalino | 10.0 ± 1.1 b | 38.2 ± 7.51 |
| Mugnoli | 12.7 ± 0.9 a | 48.1 ± 7.66 |
| Significance (1) | ||
| L | *** | *** |
| G | ** | ** |
| L × G (2) | NS | ** |
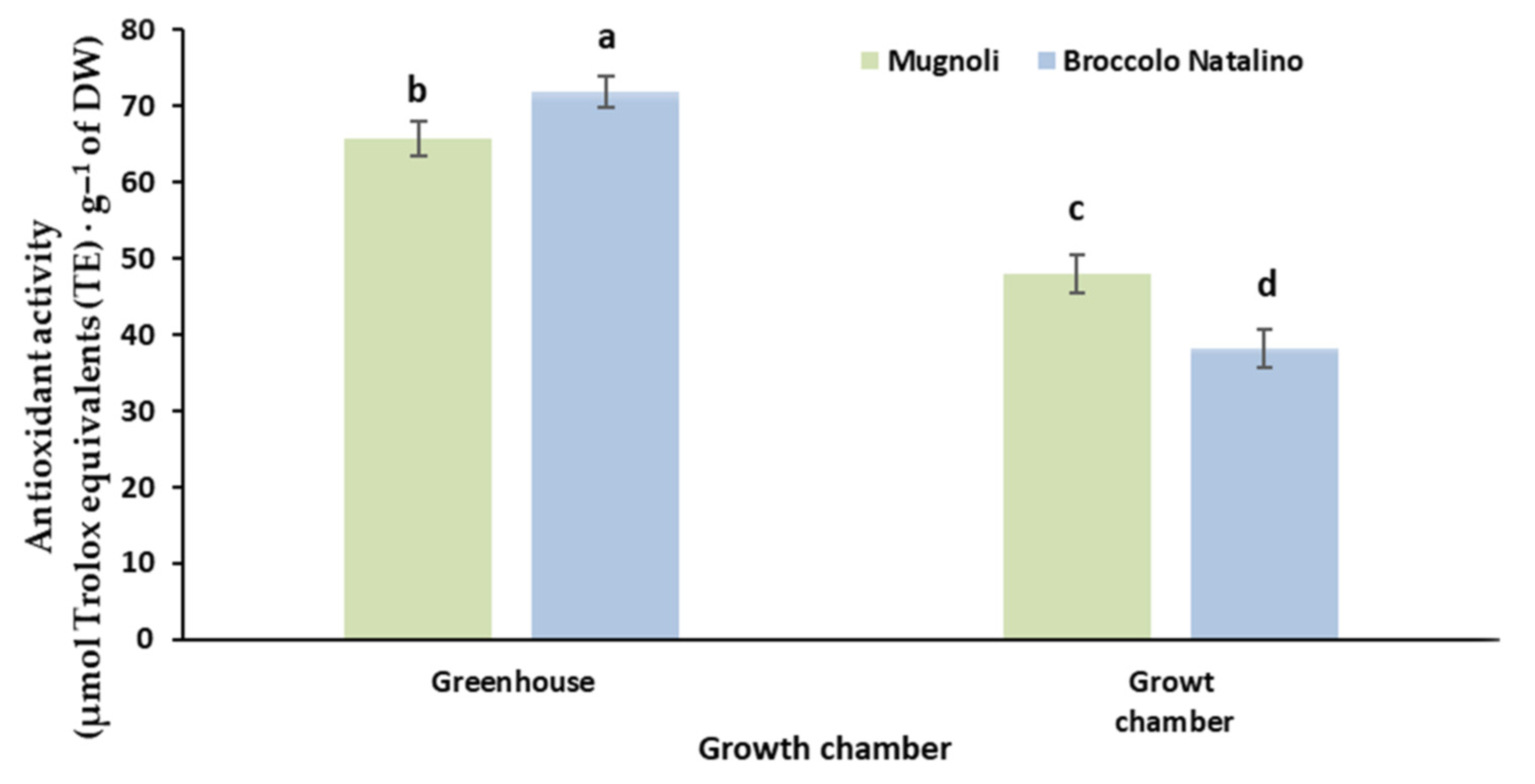
| Polyphenols | Antioxidant Activity | |
|---|---|---|
| Growth system (S) | mg of gallic acid·g−1 DW | μmol Trolox equivalents (TE)·g−1 DW |
| Growth chamber | 12.1 ± 0.86 | 46.7 ± 0.33 |
| Greenhouse | 14.5 ± 0.45 | 68.8 ± 1.66 |
| Genotype (G) | ||
| Broccolo Natalino | 11.3 ± 1.03 | 46.7 ± 6.5 |
| Mugnoli | 12.9 ± 0.95 | 52.5 ± 4.6 |
| Significance (1) | ||
| S | *** | *** |
| G | ** | ** |
| S × G (2) | ** | *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palmitessa, O.D.; Gadaleta, A.; Leoni, B.; Renna, M.; Signore, A.; Paradiso, V.M.; Santamaria, P. Effects of Greenhouse vs. Growth Chamber and Different Blue-Light Percentages on the Growth Performance and Quality of Broccoli Microgreens. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051161
Palmitessa OD, Gadaleta A, Leoni B, Renna M, Signore A, Paradiso VM, Santamaria P. Effects of Greenhouse vs. Growth Chamber and Different Blue-Light Percentages on the Growth Performance and Quality of Broccoli Microgreens. Agronomy. 2022; 12(5):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051161
Chicago/Turabian StylePalmitessa, Onofrio Davide, Alessio Gadaleta, Beniamino Leoni, Massimiliano Renna, Angelo Signore, Vito Michele Paradiso, and Pietro Santamaria. 2022. "Effects of Greenhouse vs. Growth Chamber and Different Blue-Light Percentages on the Growth Performance and Quality of Broccoli Microgreens" Agronomy 12, no. 5: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051161
APA StylePalmitessa, O. D., Gadaleta, A., Leoni, B., Renna, M., Signore, A., Paradiso, V. M., & Santamaria, P. (2022). Effects of Greenhouse vs. Growth Chamber and Different Blue-Light Percentages on the Growth Performance and Quality of Broccoli Microgreens. Agronomy, 12(5), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051161











