A Review of Prospective Biocontrol Agents and Sustainable Soil Practices for Bulb Mite (Acari: Acaridae) Management
Abstract
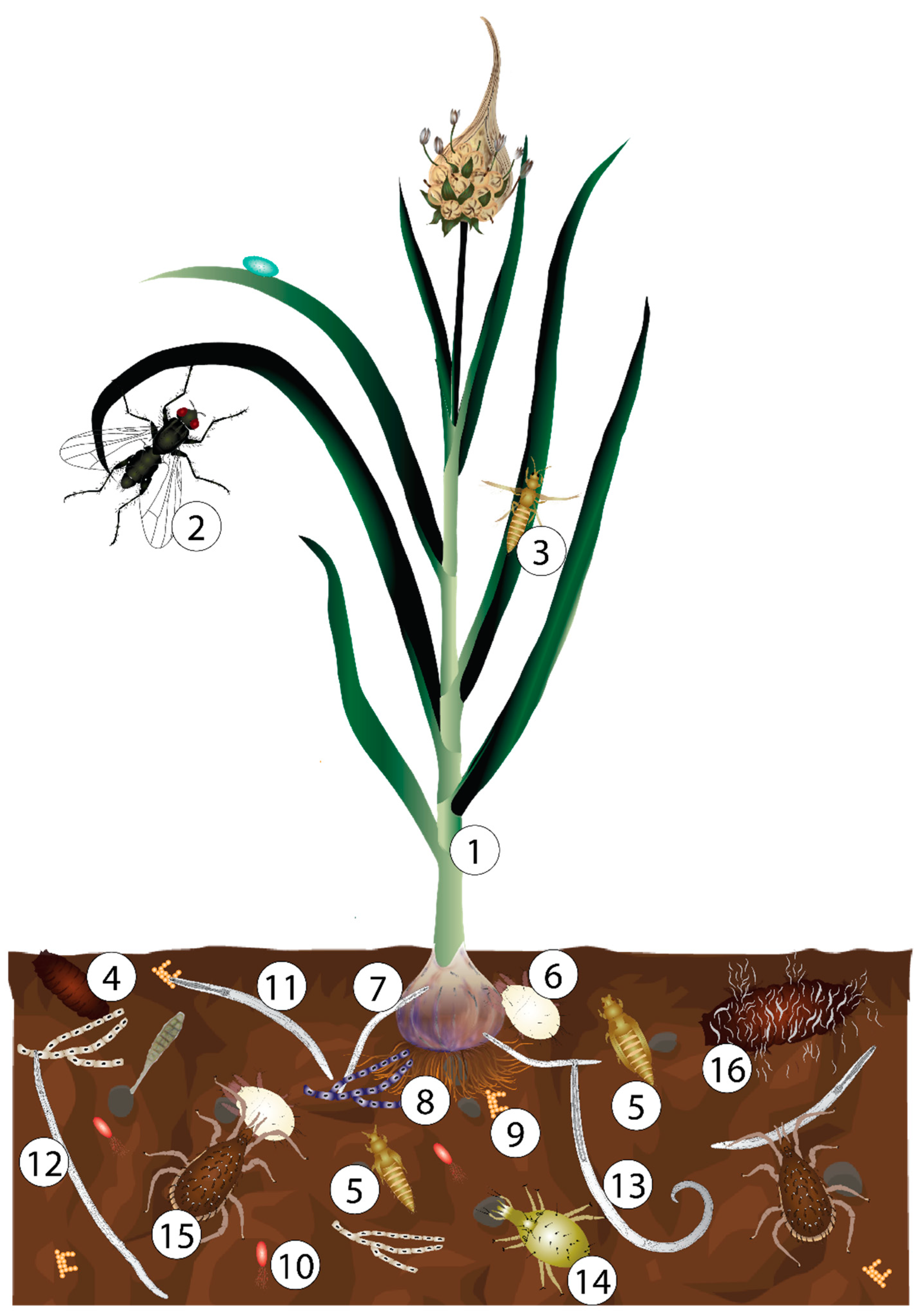
:1. Introduction
2. Bulb Mite Management Using Synthetic Pesticides
3. Biological Control of Bulb Mites
3.1. Bacteria
3.2. Acaropathogenic and Entomopathogenic Fungi
3.3. Entomopathogenic Nematodes
3.4. Predatory Mites
4. The Importance of a Holistic Approach for Better Pest Management
5. Potential Role of Soil Management on Rhizoglyphus Control in Conventional and Organic Systems in Garlic and Onion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawande, K.E.; Khar, A.; Mahajan, V.; Srinivas, P.S.; Sankar, V.; Singh, R.P. Onion and Garlic Research in India. J. Hortic. Sci. 2009, 4, 91–119. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Mnayer, D.; Tabanelli, G.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.Z.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Yousaf, Z.; Vallone, L.; Setzer, W.N.; Iriti, M. Plants of the Genus Allium as Antibacterial Agents: From Tradition to Pharmacy. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.; Saha, P.; Jha, S. Medicinal Bulbous Plants: Biology, Phytochemistry and Biotechnology. In Bulbous Plants: Biotechnology; Ramawat, K., Merillon, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2016; pp. 338–370. ISBN 978-1-4665-8968-1. [Google Scholar]
- Louw, C.A.M.; Regnier, T.J.C.; Korsten, L. Medicinal Bulbous Plants of South Africa and Their Traditional Relevance in the Control of Infectious Diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 82, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, A.; Zia, M.A.B.; Hussain, T.; Tekeli, F.O.; Gokce, A.F. Members of Alliaceae; Better Source of Plant Lectins to Combat Resistance against Sucking Pests of Crops. Acta Hortic. 2016, 1143, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prowse, G.M.; Galloway, T.S.; Foggo, A. Insecticidal Activity of Garlic Juice in Two Dipteran Pests. Agric. Forest Ent. 2006, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, D.W.; Alverson, D.R. Repellency Effects of Garlic Extracts on Twospotted Spider Mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch. J. Entomol. Sci. 2000, 35, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Chakraborti, D.; Das, S. Effectiveness of Garlic Lectin on Red Spider Mite of Tea. J. Plant Interact. 2008, 3, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Tu, H. Bioactivity of Garlic-Straw Extracts against the Spider Mites, Tetranychus urticae and T. viennensis. J. Agric. Urban Entomol. 2014, 30, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Available online: www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- McDonald, M.R.; de los Angeles Jaime, M.; Hovius, M.H.Y. Management of Diseases of Onions and Garlic. In Diseases of Fruits and Vegetables: Volume II; Naqvi, S.A.M.H., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 149–200. ISBN 978-1-4020-1823-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.K.; Jaiswal, K.R.; Kumar, D.; Saabale, P.R.; Singh, A. Management of Major Diseases and Insect Pests of Onion and Garlic: A Comprehensive Review. J. Plant Breed. Crop. Sci. 2014, 6, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebiush-Mordechai, S.; Erlich, O.; Maymon, M.; Freeman, S.; Ben-David, T.; Ofek, T.; Palevsky, E.; Tsror Lahkin, L. Bulb and Root Rot in Lily (Lilium longiflorum) and Onion (Allium cepa) in Israel. J. Phytopathol. 2014, 162, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofek, T.; Gal, S.; Inbar, M.; Lebiush-Mordechai, S.; Tsror, L.; Palevsky, E. The Role of Onion-Associated Fungi in Bulb Mite Infestation and Damage to Onion Seedlings. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2014, 62, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.; Okabe, K.; Eckenrode, C.J.; Villani, M.G.; Oconnor, B.M. Biology, Ecology, and Management of the Bulb Mites of the Genus Rhizoglyphus (Acari: Acaridae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2000, 24, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Q.-H.; Zhang, Z.-Q. Revision of Rhizoglyphus Claparède (Acari: Acaridae) of Australasia and Oceania; Systematic and Applied Acarology Society: London, UK, 2004; ISBN 0-9534144-4-2. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, M.F.C.; Moraes, G.J.D. Rhizoglyphus Mites (Acari: Astigmata: Acaridae) from Brazil, with Complementary Description of Rhizoglyphus vicantus Manson. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2020, 25, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poe, S.L.; Noble, W.E.; Stall, R.E. Acquisition and Retention of Pseudomonas marginata by Anoetus feroniarum and Rhizoglyphus robini. In Recent Advances in Acarology; Rodriguez, J.G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 119–124. ISBN 978-0-12-592201-2. [Google Scholar]
- Okabe, K.; Amano, H. Penetration and Population Growth of the Robine Bulb Mite, Rhizoglyphus robini Claparede (Acari: Acaridae), on Healthy and Fusarium-Infected Rakkyo Bulbs. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1991, 26, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanuny, T.; Inbar, M.; Tsror, L.; Palevsky, E. Complex Interactions between Rhizoglyphus robini and Fusarium oxysporum: Implications on Onion Pest Management. IOBC/WPRS Bull. 2008, 32, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zindel, R.; Ofek, M.; Minz, D.; Palevsky, E.; Zchori-Fein, E.; Aebi, A. The Role of the Bacterial Community in the Nutritional Ecology of the Bulb Mite Rhizoglyphus robini (Acari: Astigmata: Acaridae). FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gencsoylu, I. Toxicity of Acaricides to the Bulb Mite Rhizoglyphus echinopus (Acari: Acaridae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1998, 22, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, M. Resistance of the Bulb Mite, Rhizoglyphus robini Claparede, to Organo-Phosphorus Insecticides. J. Agric. Res. Quart. 1988, 22, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara, M.; Konno, Y.; Shishido, T. Mechanism of Fenitrothion Resistance in the Organophosphate-Resistant Bulb Mite, Rhizoglyphus robini Claparede (Acarina: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1991, 26, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.-S. Genetic Analysis and Effect of Synergists on Diazinon Resistance in the Bulb Mite, Rhizoglyphus robini Claparède (Acari: Acaridae). Pestic. Sci. 1990, 28, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2009/128/EC of the European Parliament and the Council of 21 October 2009 Establishing a Framework for Community Action to Achieve the Sustainable Use of Pesticides; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, L.; Rahman, R.; Khan, M.S. Alternatives of Pesticides. In Pesticide Residue in Foods; Khan, M.S., Rahman, M.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 147–165. ISBN 978-3-319-52681-2. [Google Scholar]
- Poinar, G.; Poinar, R. Parasites and Pathogens of Mites. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.E.; Villani, M.G.; Allee, L.L.; Losey, J.E. Absence of Non-Target Effects of Two Bacillus thuringiensis Coleopteran Active Delta-Endotoxins on the Bulb Mite, Rhizoglypus robini (Claparede) (Acari, Acaridae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2004, 128, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, L.; Song, J.; Cao, W.; Jia, H.; Li, M.; He, Y. Use of Bacillus thuringiensis for Controlling at Least One Rhizoglyphus Insects e.g. Rhizoglyphus echinopus Which Are Harmful to Plants e.g. Pinellia ternata, Water Spinach, Chinese Onion, Adenosma glutinosum, Chives, Leek and. Radish. Patent CN110720470-A, 24 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nermuť, J.; Zemek, R.; Mráček, Z.; Palevsky, E.; Půža, V. Entomopathogenic Nematodes as Natural Enemies for Control of Rhizoglyphus robini (Acari: Acaridae)? Biol. Control. 2019, 128, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopická, J.; Bohatá, A.; Nermuť, J.; Jozová, E.; Mráček, Z.; Palevsky, E.; Zemek, R. Efficacy of Soil Isolates of Entomopathogenic Fungi against the Bulb Mite, Rhizoglyphus robini (Acari: Acaridae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2021, 26, 1149–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.-H.; Shin, T.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Choi, C.-J.; Woo, S.-D. Screening and Evaluation of Acaropathogenic Fungi against the Bulb Mite Rhizoglyphus robini. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2021, 24, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ment, D.; Raman, S.; Gal, S.; Ezra, D.; Palevsky, E. Interactions of Metarhizium brunneum-7 with Phytophagous Mites Following Different Application Strategies. Insects 2020, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztejnberg, A.; Doron-Shloush, S.; Gerson, U. The Biology of the Acaropathogenic Fungus Hirsutella kirchneri. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 1997, 7, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, A.M.; Hassan, M.F.; Nawar, M.S. Notes on the Biology Feeding Habits of Protogamasellus minutus Hafez, El-Badry & Nasr (Acari: Gamasida: Ascidae). Bull. Entomol. Soc. Egypt 1986, 66, 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Fan, Q. Effects of Five Preys on Growth and Reproduction of Lasioseius Sp. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2009, 38, 581–584. [Google Scholar]
- Mowafi, M.H. Effect of Food Type on Development and Reproduction of Mite Species Lasioseius africanus. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest. Control 2005, 15, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lesna, I.; Sabelis, M.W.; Bolland, H.R.; Conijn, C.G.M. Candidate Natural Enemies for Control of Rhizoglyphus robini Claparède (Acari: Astigmata) in Lily Bulbs: Exploration in the Field and Pre-Selection in the Laboratory. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1995, 19, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreira, G.F.; de Moraes, G.J. The Potential of Free-Living Laelapid Mites (Mesostigmata: Laelapidae) as Biological Control Agents. In Prospects for Biological Control of Plant Feeding Mites and Other Harmful Organisms; Carrillo, D., de Moraes, G.J., Peña, J.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 77–102. ISBN 978-3-319-15041-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lesna, I.; Sabelis, M.; Conijn, C. Biological Control of the Bulb Mite, Rhizoglyphus robini, by the Predatory Mite, Hypoaspis aculeifer, on Lilies: Predator-Prey Interactions at Various Spatial Scales. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedan, M.A.-A. Studies on Predator-Prey Interactions between Hypoaspis aculeifer Canestrini (Acarina: Laelapidae) and Rhizoglyphus echinopus (Fum. & Rob.) (Acarina: Acaridae) under Laboratory Conditions. Rev. Zool. Afric. 1988, 102, 381–387. [Google Scholar]
- Ragusa, S.; Zedan, M.A. Biology and Predation of Hypoaspis aculeifer (Canestrini) (Parasitiformes, Dermanyssidae) on Rhizoglyphus echinopus (Fum. & Rob.) (Acariformes, Acaridae). Redia 1988, 71, 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakkoli-Korghond, G.; Sahebzadeh, N. A Modified Method for Mass Production of Generalist Predatory Edaphic Mite Gaeolaelaps aculeifer as a Candidate for Biological Control of the Saffron Corm Mite. Int. J. Acarol. 2022, 48, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesna, I.; Conijn, C.G.M.; Sabelis, M.W.; van Straalen, N.M. Biological Control of the Bulb Mite, Rhizoglyphus robini, by the Predatory Mite, Hypoaspis aculeifer, on Lilies: Predator-Prey Dynamics in the Soil, under Greenhouse and Field Conditions. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, L.H.; Ferreira, M.P.; Castilho, R.C.; Cançado, P.H.D.; de Moraes, G.J. Potential of Macrocheles Species (Acari: Mesostigmata: Macrochelidae) as Control Agents of Harmful Flies (Diptera) and Biology of Macrocheles embersoni Azevedo, Castilho and Berto on Stomoxys calcitrans (L.) and Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae). Biol. Control 2018, 123, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castilho, R.C.; de Moraes, G.J.; Silva, E.S.; Silva, L.O. Predation Potential and Biology of Protogamasellopsis posnaniensis Wisniewski & Hirschmann (Acari: Rhodacaridae). Biol. Control 2009, 48, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G. Options of Control of Pests Affecting Roots and Bulbs. Sci. Pap. Ser. Manag. Econ. Eng. Agric. Rural Dev. 2018, 18, 483–487. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, A.J.; Whipps, J.M. Beneficial Microorganism Survival on Seed, Roots and in Rhizosphere Soil Following Application to Seed during Drum Priming. Biol. Control 2008, 44, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunbury-Blanchette, A.L.; Walker, A.K. Trichoderma Species Show Biocontrol Potential in Dual Culture and Greenhouse Bioassays against Fusarium Basal Rot of Onion. Biol. Control 2019, 130, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, H.; Azis, A.A.; Jumadi, O. Antagonistic Activity and Characterization of Indigenous Soil Isolates of Bacteria and Fungi against Onion Wilt Incited by Fusarium Sp. Arch. Microbiol 2022, 204, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mougy, N.S.; Abdel-Kader, M.M. Biocontrol Measures against Onion Basal Rot Incidence under Natural Field Conditions. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 101, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erban, T.; Nesvorna, M.; Erbanova, M.; Hubert, J. Bacillus thuringiensis var. tenebrionis Control of Synanthropic Mites (Acari: Acaridida) under Laboratory Conditions. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2009, 49, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahyane, H.; El Alaoui, A.; Abousaid, H.; Aimrane, A.; Atibi, Y.; Oufdou, K.; El Messoussi, S. Biological Activity of Some Native Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner Strains against Eutetranychus orientalis Klein (Acari: Tetranychidae). Appl. Ecol. Env. Res. 2019, 17, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, T.M.; Goettel, M.S. Bioassays of Entomogenous Fungi. In Bioassays of Entomopathogenic Microbes and Nematodes; Navon, A., Ascher, K.R.S., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2000; pp. 141–195. ISBN 978-0-85199-422-2. [Google Scholar]
- Meyling, N.V.; Eilenberg, J. Ecology of the Entomopathogenic Fungi Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae in Temperate Agroecosystems: Potential for Conservation Biological Control. Biol. Control 2007, 43, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- der van Geest, L.P.S. Diseases of Mites. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2000, 24, 497–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vänninen, I. Distribution and Occurrence of Four Entomopathogenic Fungi in Finland: Effect of Geographical Location, Habitat Type and Soil Type. Mycol. Res. 1996, 100, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vänninen, I.; Tyni-Juslin, J.; Hokkanen, H. Persistence of Augmented Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana in Finnish Agricultural Soils. BioControl 2000, 45, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemek, R.; Konopická, J.; Bohatá, A. Inoculation of Sphagnum-Based Soil Substrate with Entomopathogenic Fungus Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae). In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1954, p. 030009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopická, J.; Bohatá, A.; Palevsky, E.; Nermuť, J.; Půža, V.; Zemek, R. Survey of Entomopathogenic and Mycoparasitic Fungi in the Soil of Onion and Garlic Fields in the Czech Republic and Israel. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2022, 129, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D.; Davidson, G.; Pell, J.K.; Ball, B.V.; Shaw, K.; Sunderland, K.D. Fungal Biocontrol of Acari. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 357–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S.; Kuwahara, Y.; Suzuki, T. Hexyl 2-Formyl-3-Hydroxybenzoate, a Fungitoxic Cuticular Constituent of the Bulb Mite Rhizoglyphus robini. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1990, 54, 2593–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal, W.S.; Kuwahara, Y.; Suzuki, T. Robinal, a Highly Conjugated Monoterpenoid from the Mite Rhizoglyphus robini. Naturwissenschaften 1990, 77, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, T.; Kuwahara, Y.; Kurosa, K. 4-Isopropenyl-3-Oxo-l-Cyclohexene-l-Carboxyaldehyde, Isorobinal: A Novel Monoterpene from the Mite Rhizoglyphus Sp. (Astigmata: Rhizoglyphinae). Naturwissenschaften 1996, 83, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askary, T.H.; Ahmad, M.J. Entomopathogenic Nematodes: Mass Production, Formulation and Application. In Biocontrol Agents: Entomopathogenic and Slug Parasitic Nematodes; Abd-Elgawad, M.M.M., Askary, T.H., Coupland, J., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2017; pp. 261–286. ISBN 978-1-78639-000-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lacey, L.A.; Georgis, R. Entomopathogenic Nematodes for Control of Insect Pests above and below Ground with Comments on Commercial Production. J. Nematol. 2012, 44, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Vashisth, S.; Chandel, Y.S.; Sharma, P.K. Entomopathogenic Nematodes—A Review. Agri. Rev. 2013, 34, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppenhöfer, A.M.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Hiltpold, I. Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Sustainable Food Production. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nermuť, J.; Konopická, J.; Zemek, R.; Kopačka, M.; Bohatá, A.; Půža, V. Dissemination of Isaria fumosorosea Spores by Steinernema feltiae and Heterorhabditis bacteriophora. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.K.; Koppenhöfer, A.M.; Johnson, M. Natural Enemies of Entomopathogenic Nematodes. Jpn. J. Nematol. 1998, 28, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, U.; Yathom, S.; Katan, J. A Demonstration of Bulb Mite Control by Solar Heating of the Soil. Phytoparasitica 1981, 9, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.M. Potency of Solarization and Fumigation of Some Pesticides on Predacious Soil Mites Associated with Cantaloupe in Egypt. In Modern Acarology, Proceedings of the VIII International Congress of Acarology, České Budĕjovice, Czechoslovakia, 6–11 August 1990; Dusbábek, F., Bukva, V., Eds.; SPB Academic Publishing: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1991; Volume 2, pp. 719–723. [Google Scholar]
- Van De Bund, C.F. Some Observations on Predatory Action of Mites on Nematodes. Zesz. Probl. Postepow Nauk. Rol. 1972, 129, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- McSorley, R.; Seal, D.; Klassen, W.; Wang, K.; Hooks, C. Non-Target Effects of Sunn Hemp and Marigold Cover Crops on the Soil Invertebrate Community. Nematropica 2009, 39, 235–245. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.-H.; Radovich, T.; Pant, A.; Cheng, Z. Integration of Cover Crops and Vermicompost Tea for Soil and Plant Health Management in a Short-Term Vegetable Cropping System. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 82, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirling, G.R. Surrounding the Swollen Roots of Sweetpotato with a Decomposing Band of an Organic Amendment Enhances Nematode-Suppressive Services and Reduces Damage Caused by Root-Knot Nematode. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2021, 50, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udalova, Z.; Ushakova, N.; Butorina, N.; Zinovieva, S. Influence of Insectocomposts through Hermetia illucens Larvae on Nematodes of Various Ecological-Trophic Groups. Res. Crops 2021, 22, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cássia Neves Esteca, F.; Rodrigues, L.R.; de Moraes, G.J.; Júnior, I.D.; Klingen, I. Mulching with Coffee Husk and Pulp in Strawberry Affects Edaphic Predatory Mite and Spider Mite Densities. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 76, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla-Tornel, M.A.; Wang, K.-H.; Tavares, J.; Hooks, C.R.R. Effects of Mulching on above and below Ground Pests and Beneficials in a Green Onion Agroecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 224, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rueda-Ramírez, D.; Rios-Malaver, D.; Varela-Ramírez, A.; Moraes, G.J. Biology and Predation Capacity of Parasitus bituberosus (Acari: Mesostigmata: Parasitidae) on Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae), and Free-living Nematodes as Its Complementary Prey. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, L.H.; Leite, L.G.; Chacon-Orozco, J.G.; Moreira, M.F.P.; Ferreira, M.P.; González-Cano, L.M.; Borges, V.; Rueda-Ramírez, D.; de Moraes, G.J.; Palevsky, E. Free Living Nematodes as Alternative Prey for Soil Predatory Mites: An Interdisciplinary Case Study of Conservation Biological Control. Biol. Control 2019, 132, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, L.H.; Moreira, M.F.P.; Pereira, G.G.; Borges, V.; de Moraes, G.J.; Inomoto, M.M.; Vicente, M.H.; de Siqueira Pinto, M.; Peres, L.E.P.; Rueda-Ramírez, D.; et al. Combined Releases of Soil Predatory Mites and Provisioning of Free-Living Nematodes for the Biological Control of Root-Knot Nematodes on ‘Micro Tom Tomato’. Biol. Control 2020, 146, 104280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T. Bulb Mites-UMass Extension Greenhouse Crops and Floriculture Program. Available online: https://ag.umass.edu/greenhouse-floriculture/fact-sheets/bulb-mites (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Brust, G. Garlic Bulb Mites. Available online: https://extension.umd.edu/resource/garlic-bulb-mites (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Kaur, N. Pacific Northwest Insect Management Handbook-Onion Bulb Mites. Available online: https://pnwhandbooks.org/node/7803 (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- California Garlic & Onion Research Advisory Board A Pest Management Strategic Plan for Garlic Production in California. Available online: https://ipmdata.ipmcenters.org/documents/pmsps/2019%20Garlic%20PMSP.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- European Commission; Directorate-General for Research and Innovation; Veerman, C.; Pinto Correia, T.; Bastioli, C.; Biro, B.; Bouma, J.; Cienciala, E.; Emmett, B.; Frison, E.; et al. Caring for Soil Is Caring for Life: Ensure 75% of Soils Are Healthy by 2030 for Food, People, Nature and Climate: Report of the Mission Board for Soil Health and Food; Publications Office: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dara, S.K.; Natwick, E.T.; Orloff, S.B.; Bulb Mites. Agriculture: Onion and Garlic Pest Management Guidelines. Available online: https://www2.ipm.ucanr.edu/agriculture/onion-and-garlic/Bulb-Mites/ (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Woodrow, J.E.; LePage, J.T.; Miller, G.C.; Hebert, V.R. Determination of Methyl Isocyanate in Outdoor Residential Air near Metam-Sodium Soil Fumigations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8921–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P. Overview of Cover Crops and Green Manures. Available online: https://attra.ncat.org/product/overview-of-cover-crops-and-green-manures/ (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Adam, K. Organic Allium Production. Available online: https://attra.ncat.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/allium.pdf? (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Bachmann, J.; Hinman, T. Garlic: Organic Production. Available online: https://attra.ncat.org/garlic-organic-production-page/ (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Bonanomi, G.; Cesarano, G.; Antignani, V.; Di Maio, C.; De Filippis, F.; Scala, F. Conventional Farming Impairs Rhizoctonia solani Disease Suppression by Disrupting Soil Food Web. J. Phytopathol. 2018, 166, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshel, G.; Egozi, R.; Goldwasser, Y.; Kashti, Y.; Fine, P.; Hayut, E.; Kazukro, H.; Rubin, B.; Dar, Z.; Keisar, O.; et al. Benefits of Growing Potatoes under Cover Crops in a Mediterranean Climate. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 211, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanarella, L.; Pennock, D.J.; McKenzie, N.; Badraoui, M.; Chude, V.; Baptista, I.; Mamo, T.; Yemefack, M.; Singh Aulakh, M.; Yagi, K.; et al. World’s Soils Are under Threat. Soil 2016, 2, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unc, A.; Eshel, G.; Unc, G.A.; Doniger, T.; Sherman, C.; Leikin, M.; Steinberger, Y. Vineyard Soil Microbial Community under Conventional, Sustainable and Organic Management Practices in a Mediterranean Climate. Soil Res. 2021, 59, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshel, G.; Unc, A.; Egozi, R.; Shakartchy, E.; Doniger, T.; Steinberger, Y. Orchard Floor Management Effect on Soil Free-Living Nematode Communities. Soil Res. 2021, 60, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, S.; Gil, E.; Doniger, T.; Applebaum, I.; Steinberger, Y. Abundance and Community Composition of Free-Living Nematodes as a Function of Soil Structure under Different Vineyard Managements. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Prill, P.; Ruess, L. Disentangling Nematode-Bacteria Interactions Using a Modular Soil Model System and Biochemical Markers. Nematology 2016, 18, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.L.; Caldwell, K.N.; Beuchat, L.R.; Williams, P.L. Interaction of a Free-Living Soil Nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans, with Surrogates of Foodborne Aathogenic Bacteria. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.-X.; Sun, B. Nematode Grazing Promotes Bacterial Community Dynamics in Soil at the Aggregate Level. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2705–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erktan, A.; Or, D.; Scheu, S. The Physical Structure of Soil: Determinant and Consequence of Trophic Interactions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Conservation Agriculture. Available online: https://www.fao.org/conservation-agriculture/en/ (accessed on 28 April 2022).
| Group | Family | Species | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Bacillaceae | Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner | [29,30] |
| Morganellaceae * | Xenorhabdus bovienii Akhurst and Boemare | [31] | |
| Xenorhabdus budapestensis Lengyel et al. | |||
| Xenorhabdus cabanillasii Tailliez et al. | |||
| Xenorhabdus doucetiae Tailliez et al. | |||
| Xenorhabdus griffiniae Tailliez et al. | |||
| Xenorhabdus kozodoii Tailliez et al. | |||
| Xenorhabdus magdalenensis Tailliez et al. | |||
| Xenorhabdus nematophila (Poinar and Thomas) Thomas and Poinar | |||
| Xenorhabdus poinarii (Akhurst) Akhurst and Boemare | |||
| Xenorhabdus stockiae Tailliez et al. | |||
| Xenorhabdus sp. | |||
| Photorhabdus sp. | |||
| Entomo- pathogenic fungi | Clavicipitaceae | Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch.) Sorokin | [32,33] |
| Metarhizium brunneum Petch | [34] | ||
| Metarhizium indigoticum (Kobayasi and Shimizu) Kepler, S.A. Rehner and Humber | [32] | ||
| Metarhizium pemphigi (Driver and R.J. Milner) Kepler, S.A. Rehner and Humber | [33] | ||
| Metarhizium pinghaense Q.T. Chen and H.L. Guo | [33] | ||
| Cordycipitaceae | Beauveria bassiana (Bals.-Criv.) Vuill. | [32] | |
| Beauveria brongniartii (Sacc.) Petch | [32] | ||
| Cordyceps fumosorosea (Wize) Kepler, B. Shrestha and Spatafora | [32] | ||
| Ophiocordycipitaceae | Hirsutella kirchneri (Rostrup) Minter, Brady and Hall | [35] | |
| Entomo- pathogenic nematodes | Steinernematidae | Steinernema carpocapsae (Weiser) | [31] |
| Steinernema huense Phan, Mráček, Půža, Nermuť and Jarošová | |||
| Steinernema surkhetense Khatri-Chhetri, Waeyenberge, Spiridonov, Manandhar and Moens | |||
| Steinernema sp. | |||
| Heterorhabditidae | Heterorhabditis amazonensis Andaló, Nguyen and Moino | [31] | |
| Heterorhabditis bacteriophora Poinar | |||
| Heterorhabditis beicherriana Li, Liu, Nermuť, Půža and Mráček | |||
| Heterorhabditis floridensis Nguyen, Gozel, Koppenhöfer and Adams | |||
| Heterorhabditis indica Poinar et al. | |||
| Heterorhabditis taysearae Shamseldean | |||
| Heterorhabditis sp. | |||
| Predatory mites | Ascidae | Protogamasellus minutus Nasr | [36] |
| Blattisociidae | Lasioseius sp. | [37] | |
| Lasioseius africanus Nasr | [38] | ||
| Lasioseius allii Chant (mentioned as Lasioseius bispinosus Evans) | [39] | ||
| Laelapidae | Cosmolaelaps barbatus Moreira, Klompen and Moraes | [40] | |
| Cosmolaelaps jaboticabalensis Moreira, Klompen and Moraes | [40] | ||
| Gaeolaelaps aculeifer (Canestrini) | [39,41,42,43,44,45] | ||
| Stratiolaelaps miles (Berlese) | [39] | ||
| Macrochelidae | Macrocheles embersoni Azevedo, Berto and Castilho | [46] | |
| Macrocheles muscaedomesticae (Scopoli) | [46] | ||
| Macrocheles robustulus (Berlese) | [46] | ||
| Parasitidae | Parasitus fimetorum (Berlese) | [39] | |
| Rhodacaridae | Protogamasellopsis zaheri Abo-Shnaf, Castilho and Moraes (mentioned as Protogamasellopsis posnaniensis Wisniewski and Hirschmann) | [47] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palevsky, E.; Konopická, J.; Rueda-Ramírez, D.; Zemek, R. A Review of Prospective Biocontrol Agents and Sustainable Soil Practices for Bulb Mite (Acari: Acaridae) Management. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071491
Palevsky E, Konopická J, Rueda-Ramírez D, Zemek R. A Review of Prospective Biocontrol Agents and Sustainable Soil Practices for Bulb Mite (Acari: Acaridae) Management. Agronomy. 2022; 12(7):1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071491
Chicago/Turabian StylePalevsky, Eric, Jana Konopická, Diana Rueda-Ramírez, and Rostislav Zemek. 2022. "A Review of Prospective Biocontrol Agents and Sustainable Soil Practices for Bulb Mite (Acari: Acaridae) Management" Agronomy 12, no. 7: 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071491
APA StylePalevsky, E., Konopická, J., Rueda-Ramírez, D., & Zemek, R. (2022). A Review of Prospective Biocontrol Agents and Sustainable Soil Practices for Bulb Mite (Acari: Acaridae) Management. Agronomy, 12(7), 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071491






