Aggregate-Breaking Mechanism Response to Polyacrylamide Application of Purple Soils in Southwestern China Using Le Bissonnais Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
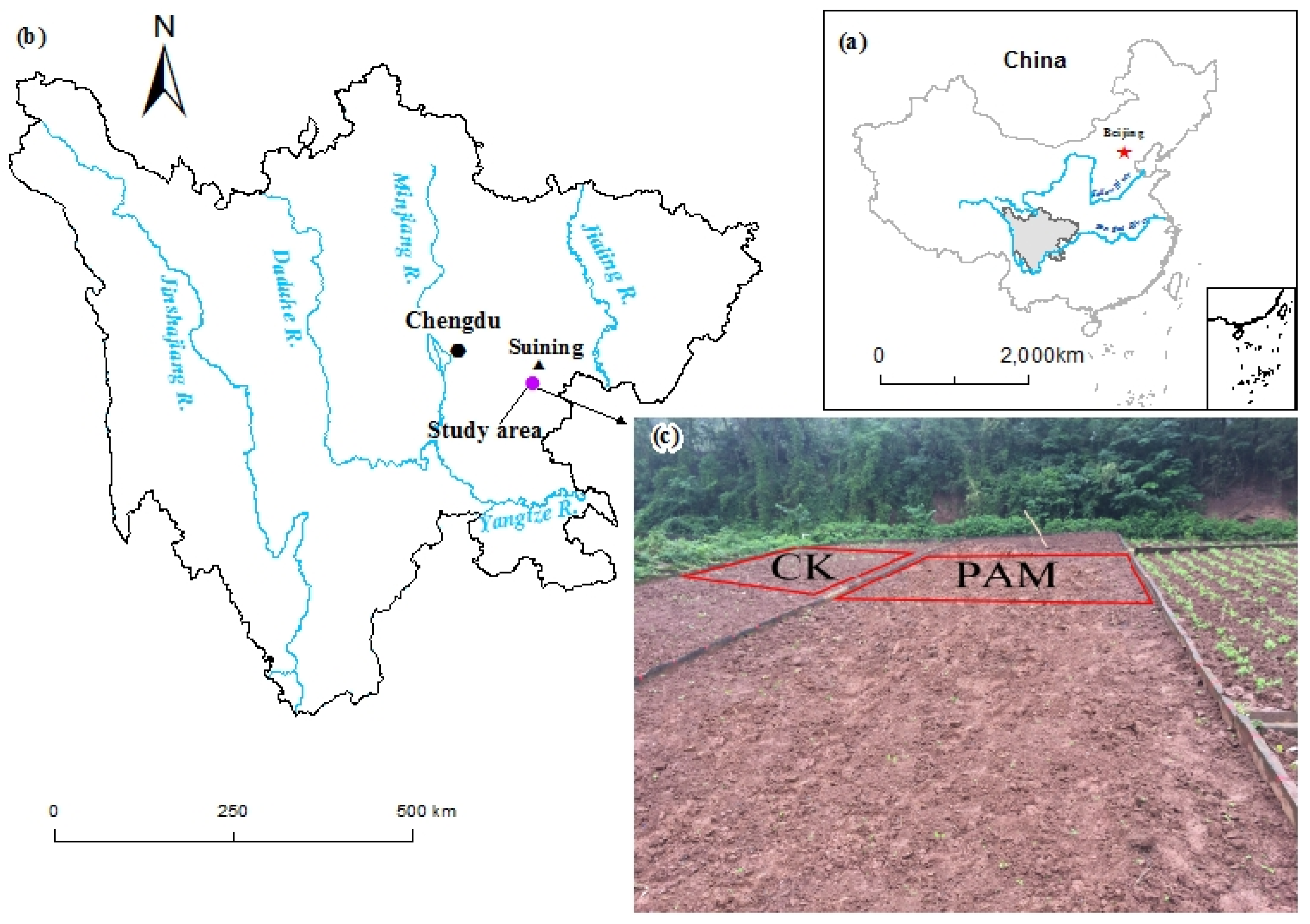
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Methods
2.4. Calculations
3. Results
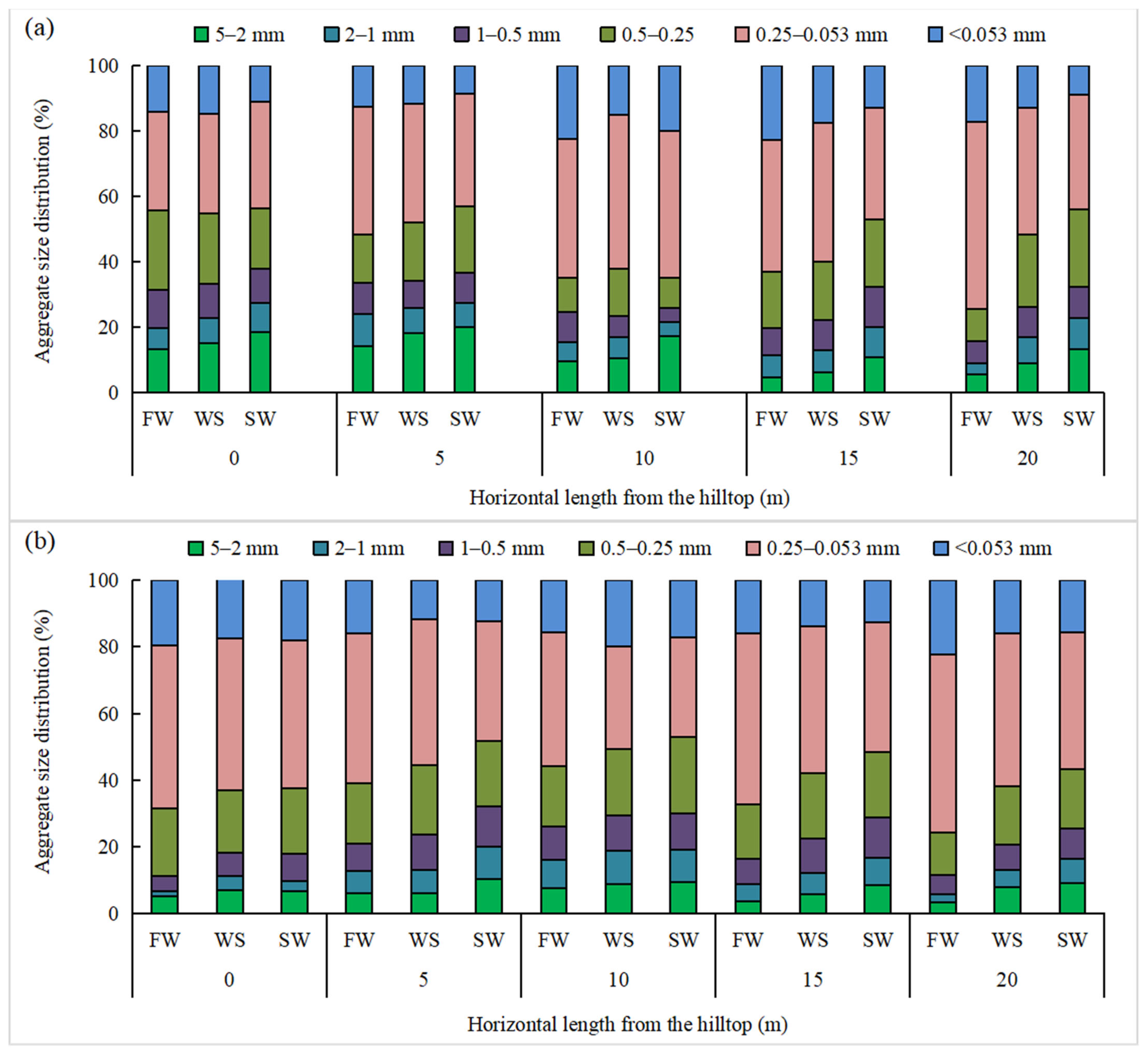
3.1. Aggregates Size Distribution with Three Breakdown Mechanisms at Different Slope Locations
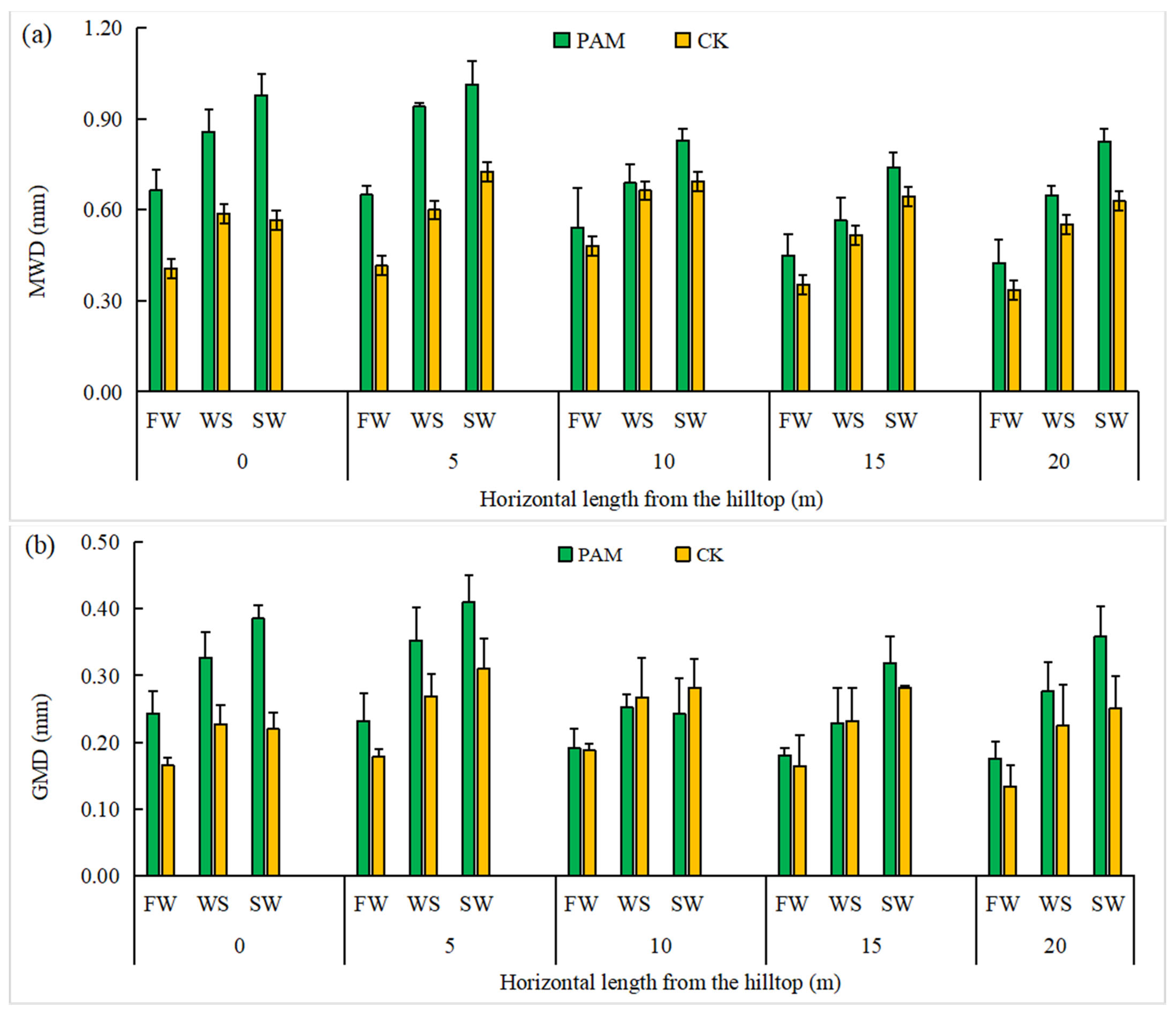
3.2. The MWD and GMD of Soil Water-Stable Aggregates at Different Slope Locations
3.3. Changes in the D Value of Soil Aggregates in Three Breakdown Mechanisms
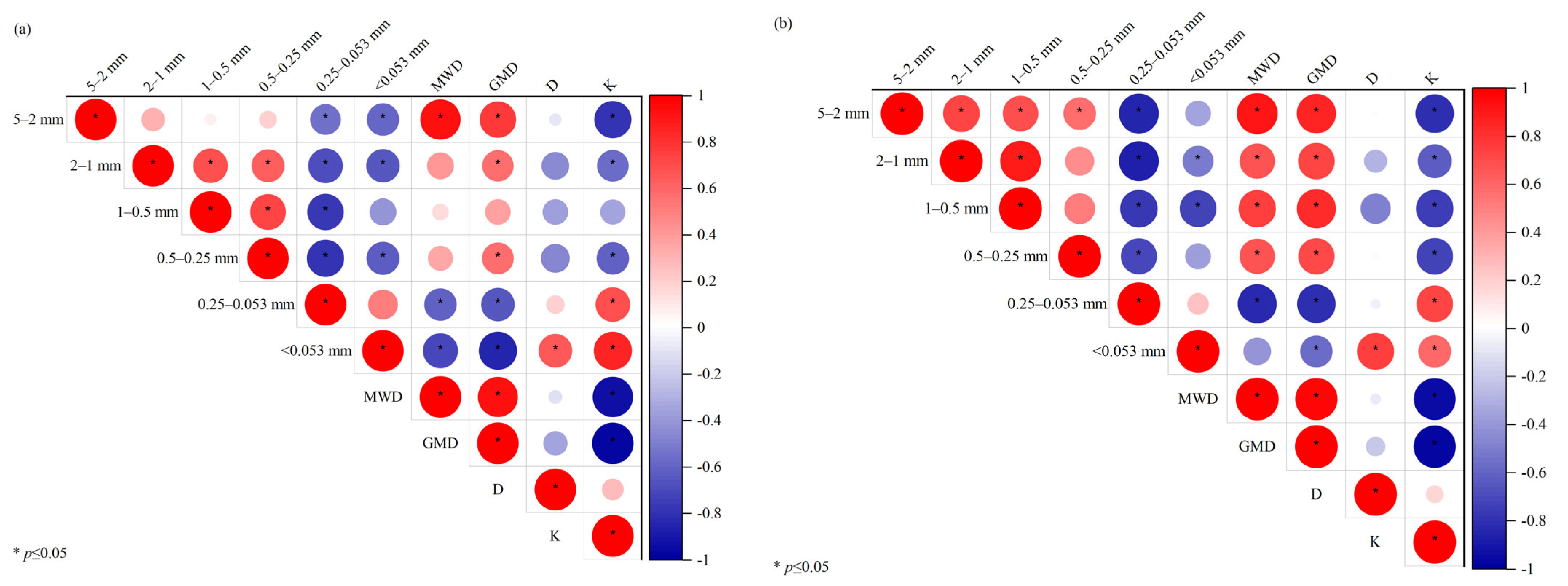
3.4. Change Characteristics of Soil Erodibility under Three Breakdown Mechanisms with LB at Different Slope Locations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, D. High negative surface charge increases the acidification risk of purple soil in China. Catena 2021, 196, 104819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tu, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y. The effect of plant hedgerows on the spatial distribution of soil erosion and soil fertility on sloping farmland in the purple-soil area of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, C.; Pu, Y.; Sun, H. Effects of polyacrylamide on soil erosion and nutrient losses from substrate material in steep rocky slope stabilization projects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554–555, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulaiti, A.; She, D.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, H. Application of biochar and polyacrylamide to revitalize coastal saline soil quality to improve rice growth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 18731–18747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbar, A.; Ben-Hur, M.; Sternberg, M.; Lado, M. Using polyacrylamide to mitigate post-fire soil erosion. Geoderma 2015, 239–240, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Lei, T. Laboratory study on soil erosion of loess convex and concave slopes with application of polyacrylamide. Trans. CSAE 2016, 32, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Wei, C.; He, B.; Wei, S. Influence of polyacrylamide on loss of purple soil nutrient during simulated rainfall. J. Basic Eng. 2010, 18, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hamdeh, N.H.; Ismail, S.M.; Al-Solaimani, S.G.; Hatamleh, R.I. Effect of tillage systems and polyacrylamide on soil physical properties and wheat grain yield in arid regions differing in fine soil particles. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Influences of intensive tillage on water-stable aggregate distribution on a steep hillslope. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 151, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, F.; Li, G.; Bian, F.; An, J. The effects of raindrop impact and runoff detachment on hillslope soil erosion and soil aggregate loss in the Mollisol region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 161, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fu, Y.; Li, B.; Zheng, T.; Wu, F.; Peng, G.; Xiao, T. Micro-characteristics of soil aggregate breakdown under raindrop action. Catena 2018, 162, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, A.R.; Ahmadi, M.; Cerdà, A. Contribution of raindrop impact to the change of soil physical properties and water erosion under semi-arid rainfalls. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almajmaie, A.; Hardie, M.; Acuña, T.L.B.; Birch, C. Evaluation of methods for determining soil aggregate stability. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 167, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Shi, D.; Guo, Y.; Guo, H.; Peng, X.; Li, Y. Study on soil aggregate stability of mulberry ridge in rocky desertification based on Le Bissonnais treatment. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 5589–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y. Aggregate stability and assessment of soil crustability and erodibility: I. Theory and methodology. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Hu, F.; Mohamed, A.M.; Elbasit, A. Quantifying contributions of slaking and mechanical breakdown of soil aggregates to splash erosion for different soils from the Loess plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 178, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Xiang, R.; Liu, C.; Ye, C.; Gao, F.; Zhang, L.; Xia, Z.; Cui, L. Influence of Polyacrylamide (PAM) on the Sheet Erosion Process of Purple Soil in Three Gorges Reservoir Area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.S. Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis and Description of Soil Profiles; Chinese Standard Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Luo, Y.; Shi, Y. Soil fractal characteristics measured by mass of particle-size distribution. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1993, 38, 1896–1899. [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi, M.A.; Hart, W.J.; Boersma, L. A unifying quantitative analysis of soil texture: Improvement of precision and extension of scale. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1988, 52, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Maity, P.P.; Ray, M.; Chakraborty, D.; Das, B.; Bhatia, A. Inclusion of fractal dimension in four machine learning algorithms improves the prediction accuracy of mean weight diameter of soil. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 74, 101959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Sai, X.; Chun, F.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, H. Grazing altered soil aggregates, nutrients and enzyme activities in a Stipa kirschnii steppe of Inner Mongolia. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 219, 105327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; He, S.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Liang, X. Biochar-blended manure modified by polyacrylamide to reduce soil colloidal phosphorus leaching loss. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2023, 30, 38592–38604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Kiani-Harchegani, M.; Hazbavi, Z.; Sadeghi, P.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R.; Lassabatere, L.; Younesi, H. Field measurement of effects of individual and combined application of biochar and polyacrylamide on erosion variables in loess and marl soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomaz, E.L.; Araujo-Junior, C.F.; Vendrame, P.R.S.; Melo, T.R.D. Mechanisms of aggregate breakdown in (sub) tropical soils: Effects of the hierarchical resistance. Catena 2022, 216, 106377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Darboux, F.; Man, C.; Zhu, Z.; An, S. Soil aggregate stability under different rain conditions for three vegetation types on the Loess Plateau (China). Catena 2018, 167, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, G.; Long, K.; Guo, J. Application research of two types of dynamical factors in a vortex rainstorm in Sichuan basin. Plateau Meteor. 2018, 37, 1289–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Albalasmeh, A.A.; Hamdan, E.H.; Gharaibeh, M.A.; El Hanandeh, A. Improving aggregate stability and hydraulic properties of Sandy loam soil by applying polyacrylamide polymer. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 206, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Bi, R.; Chen, W.; Qin, J.; Wang, J. Effect of soil structure conditioner PAM on physical properties of iron tailings in reclaiming. Trans. CSAE 2017, 33, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, R.D. Polyacrylamide and biopolymer effects on flocculation, aggregate stability, and water seepage in a silt loam. Geoderma 2015, 241, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, B.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Tsubo, M.; Mulualem, T.; Mamedov, A.I.; Meshesha, D.T.; Adgo, E.; Fenta, A.A.; Ebabu, K.; et al. Effect of Polyacrylamide integrated with other soil amendments on runoff and soil loss: Case study from northwest Ethiopia. Int. Soil Water Consev. R. 2022, 10, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Saha, A. Effect of polyacrylamide and gypsum on surface runoff, sediment yield and nutrient losses from steep slopes. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Jia, L.Z.; Zhang, Z.H. An interaction between vertical and lateral movements of soil constituents by tillage in a steep-slope landscape. Catena 2017, 152, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Su, Z.; Fan, H. Simulation and 137Cs tracer show tillage erosion translocating soil organic carbon, phosphorus, and potassium. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Item | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Soil Compaction (kPa) | Soil Water Content (%) | Organic Matter (%) | Total Nitrogen (%) | pH | Particle-Size Fraction (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2–0.02 mm | 0.2–0.002 mm | <0.002 mm | |||||||
| PAM | 1.43 ± 0.10 | 993.94 ± 116.27 | 14.19 ± 1.43 | 1.24 ± 0.15 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 8.28 ± 0.05 | 39.80 ± 2.37 | 49.08 ± 1.50 | 11.13 ± 1.00 |
| CK | 1.41 ± 0.08 | 1007.51 ± 296.77 | 12.78 ± 1.95 | 1.15 ± 0.29 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 8.16 ± 0.09 | 36.40 ± 3.74 | 53.43 ± 4.77 | 10.17 ± 1.18 |
| Item | Breakdown Mechanism | Paired Difference (PAM–CK) | t | df | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference | ||||||
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| MWD | FW | 0.148 | 0.139 | 0.036 | 0.071 | 0.225 | 4.107 | 14 | 0.001 |
| WS | 0.156 | 0.209 | 0.054 | 0.040 | 0.272 | 2.888 | 14 | 0.012 | |
| SW | 0.225 | 0.191 | 0.049 | 0.119 | 0.330 | 4.555 | 14 | 0.000 | |
| GMD | FW | 0.039 | 0.055 | 0.014 | 0.008 | 0.070 | 2.746 | 14 | 0.016 |
| WS | 0.042 | 0.091 | 0.023 | –0.007 | 0.093 | 1.819 | 14 | 0.090 | |
| SW | 0.075 | 0.099 | 0.026 | 0.020 | 0.129 | 2.926 | 14 | 0.011 | |
| Slope Location | FW | WS | SW | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAM | CK | PAM | CK | PAM | CK | |
| 0 | 2.37 ± 0.13 | 2.54 ± 0.01 | 2.47 ± 0.03 | 2.47 ± 0.04 | 2.38 ± 0.13 | 2.51 ± 0.04 |
| 5 | 2.32 ± 0.07 | 2.37 ± 0.08 | 2.42 ± 0.05 | 2.40 ± 0.09 | 2.33 ± 0.07 | 2.39 ± 0.10 |
| 10 | 2.59 ± 0.05 | 2.46 ± 0.10 | 2.49 ± 0.03 | 2.55 ± 0.07 | 2.59 ± 0.05 | 2.48 ± 0.09 |
| 15 | 2.40 ± 0.12 | 2.46 ± 0.01 | 2.51 ± 0.02 | 2.38 ± 0.03 | 2.41 ± 0.12 | 2.40 ± 0.06 |
| 20 | 2.32 ± 0.05 | 2.47 ± 0.08 | 2.41 ± 0.10 | 2.48 ± 0.05 | 2.29 ± 0.06 | 2.47 ± 0.09 |
| Mean | 2.40 ± 0.11 | 2.46 ± 0.06 | 2.46 ± 0.04 | 2.46 ± 0.07 | 2.40 ± 0.12 | 2.45 ± 0.05 |
| CV (%) | 4.65 | 2.46 | 1.77 | 2.77 | 4.83 | 2.04 |
| Item | III Sum of Square | df | Mean Square | F Value | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAM | CK | PAM | CK | PAM | CK | PAM | CK | ||
| Correction model | 0.373 a | 0.285 b | 14 | 0.027 | 0.020 | 5.261 | 3.629 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| Intercept | 275.816 | 281.915 | 1 | 275.816 | 281.915 | 54,427.680 | 50,221.861 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Slope location | 0.189 | 0.182 | 4 | 0.094 | 0.091 | 18.647 | 16.212 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Sieving test | 0.116 | 0.077 | 2 | 0.029 | 0.019 | 5.706 | 3.416 | 0.002 | 0.020 |
| Slope location × sieving test | 0.069 | 0.026 | 8 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 1.691 | 0.589 | 0.142 | 0.779 |
| Error | 0.152 | 0.168 | 30 | 0.005 | 0.006 | ||||
| Total | 276.342 | 282.369 | 45 | ||||||
| Total correction | 0.525 | 0.454 | 44 | ||||||
| Breakdown Mechanism | Paired Difference (PAM–CK) | t | df | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference | |||||
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| FW | –0.027 | 0.035 | 0.009 | –0.047 | –0.008 | –3.004 | 14 | 0.009 |
| SW | –0.019 | 0.033 | 0.008 | –0.037 | –0.001 | –2.220 | 14 | 0.043 |
| WS | –0.022 | 0.032 | 0.008 | –0.040 | –0.005 | –2.710 | 14 | 0.017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, Z.; Liang, X. Aggregate-Breaking Mechanism Response to Polyacrylamide Application of Purple Soils in Southwestern China Using Le Bissonnais Method. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092222
Wang Y, Wang J, Ma Z, Liang X. Aggregate-Breaking Mechanism Response to Polyacrylamide Application of Purple Soils in Southwestern China Using Le Bissonnais Method. Agronomy. 2023; 13(9):2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092222
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yong, Jiaqi Wang, Zhenzhen Ma, and Xinlan Liang. 2023. "Aggregate-Breaking Mechanism Response to Polyacrylamide Application of Purple Soils in Southwestern China Using Le Bissonnais Method" Agronomy 13, no. 9: 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092222
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, J., Ma, Z., & Liang, X. (2023). Aggregate-Breaking Mechanism Response to Polyacrylamide Application of Purple Soils in Southwestern China Using Le Bissonnais Method. Agronomy, 13(9), 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092222






