Abstract
Pruning residues, which occur every year in orchards and have many different utilization potentials, are an important issue for fruit producers. The shredding process is indispensable and critical for the utilization of these residues. The performance of the shredding process is affected by the operating parameters of the shredding machine as well as the moisture content of the residues to be shredded. In this study, olive pruning residues with three different moisture contents were shredded at three different rotor speeds in the developed shredding system. We determined how the power requirement of the shredder changed under different conditions, and empirical models were developed. The experiments showed that the average power requirement of the shredder ranged from 7.32 to 10.81 kW, and it was found that residues with low moisture content decreased the power values, while higher rotor speeds increased the power requirement. The developed final model has a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.376, a root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.441, and a correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.859. The model serves as a reliable tool for estimating power requirements in the shredding of olive pruning residues, enabling the selection of the optimal rotor speed based on moisture content.
1. Introduction
Spread over a total area of 10.9 million hectares, olives have an important place among fruits grown worldwide. Spain, Tunisia, Morocco, Italy, and Türkiye, which lead olive production, account for 24.07%, 16.43%, 10.97%, 9.83% and 8.23% of the global olive area, respectively [1]. As with all fruit varieties, olive cultivation involves an annual pruning process. During fruit production, orchards produce a significant amount of pruning residue. Romero-García et al. [2] reported that about 1.5 tons/ha of residues were generated after pruning in olive orchards.
Pruning residues represent a valuable resource that can be transformed into energy through shredding and various processes [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. However, to effectively utilize these residues as biomass or raw materials, a series of processes involving multiple machines is necessary [12]. Despite the potential for agricultural residues to serve as sustainable biomass fuel, challenges in storage and logistics persist due to their low thermal energy and density characteristics [13]. Suardi et al. [14] affirm that pruning residues are abundant and of sufficient quality to serve as raw materials for energy production but are underutilized due to supply chain issues and high costs. Furthermore, in addition to their energy potential, pruning residues find application in soil enhancement when shredded and mixed directly into the soil [15,16,17,18]. Holtz et al. [19] observed improvements in soil infiltration, pH regulation, nutrient preservation, and reduction in harmful nematodes by incorporating shredded pruning residues into the soil. Similarly, Repullo et al. [20] found that integrating crop residues into the soil enhances biodiversity and positively impacts harvest yields.
Shredding or size reduction stands out as a crucial stage in all utilization methods and is prioritized due to its significant impact on the quality and economics of the processes [21,22]. The machines used for shredding are diverse, and the choice of shredding machines for agricultural pruning residues depends on several factors, including the type of material, the evaluation criteria and the operating conditions of the machine. There are also specialized shredding machines for the in situ utilization of pruning residues in agricultural areas. Such machines are used for shredding pruning residues from pomegranate, vineyard, avocado and orange orchards [15].
In light of the projected shortage of agricultural labor in the future, the robust development and management of agricultural mechanization and automation technologies will become an imperative trend [23,24,25]. Mechanization management involves the selection, operation and replacement of machinery used in the shredding process [26]. In addition, the power values obtained from these processes are influential in assessing tractor overload rates and fuel consumption. Therefore, it is imperative to use accurate data to develop practical models [27].
The moisture content of pruning residues plays a critical role in shredding performance, but few studies in the literature have comprehensively examined its impact on the process. This lack of research can be attributed to the difficulty and time-consuming nature of monitoring moisture content changes during field experiments. For instance, field trials may require a waiting period of weeks, depending on weather conditions, to obtain pruning residues of the same material with different moisture contents. During this waiting period, the pruning residues left to dry on the land can be an obstacle for other processes in the production line. Furthermore, in practice, when operating machines that shred pruning residues in the orchard, questions such as “When should effective shredding take place? and at what rotor speed should the machine operate?” arise. To fill the gap in the literature and to meet practical needs, this study aimed to determine the power requirement for operating a pruning residue shredder equipped with a collection and screening unit under different conditions. To achieve this objective, a laboratory-based shredding test system was developed, considering the complexities involved in precision and control during orchard trials, such as terrain, climate, and environmental factors. The experiments were conducted using olive pruning residues with different moisture contents, at different rotor speeds and using a specially designed shredding blade. At the end of the experiments, the power values for the shredding machine were determined, and a mathematical model was developed to predict the machine performance under different operating conditions based on the data obtained.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Shredding System
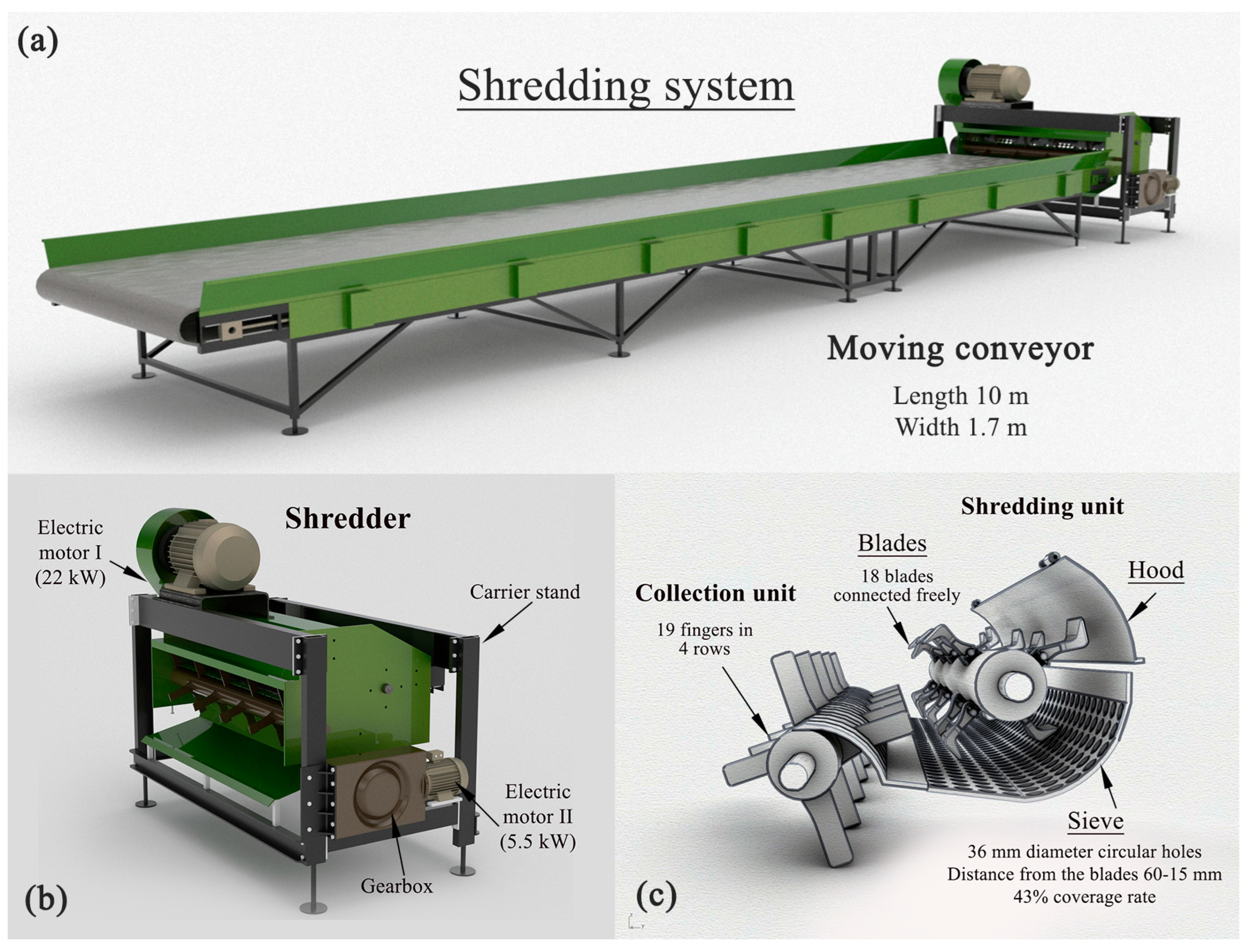
The shredding test system comprises several components, including a shredding machine, a stable stand to support the machine during operation, a mobile conveyor for transporting pruning residues to the shredder, electric motors (I and II) responsible for powering both the shredding machine and conveyor, and a control panel to manage the electric motors’ operations.
In the developed test setup, a commercially available pruning residue shredder machine designed to be powered by the tractor’s PTO and equipped with collection and sieve units was utilized. Modifications were made to adapt the machine for operation in the trials, including the replacement of the original three-point connection and gearbox, which transmit motion from the tractor’s power take-off (PTO), with electric motor I rated at 22 kW. This electric motor, mounted on the machine chassis, drives a pulley with four grooves 30 cm in diameter, which in turn transfers motion to another pulley connected to the rotary unit with an 18 cm diameter belt. Electric motor II also drives the collector unit of the shredder with the double gear mechanism used. Thus, the same motor drives the conveyor belt and the collector unit of the shredding machine, and the number of revolutions of the collector shaft and the feed rate work simultaneously. The shredding machine features a collection unit at the front, with a total of 19 fingers arranged in four rows on the rotary. Additionally, the shredding unit comprises a rotary with 18 freely connected blades. A sieve located beneath the shredding unit has a maximum–minimum clearance between blades of 60–15 mm. The sieve, consisting of circular holes with a diameter of 36 mm, covers 43% of the shredding unit, as shown in Figure 1.
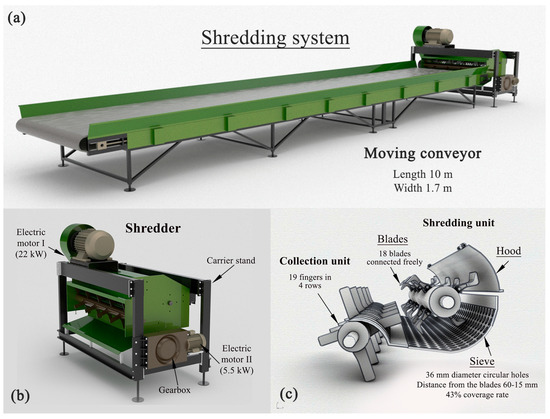
Figure 1.
Schematic views of the shredding system. (a) Overview of the conveyor and shredding machine. (b) Shredding machine and electric motors. (c) Internal components within the shredding machine.
2.2. Shredder Blade
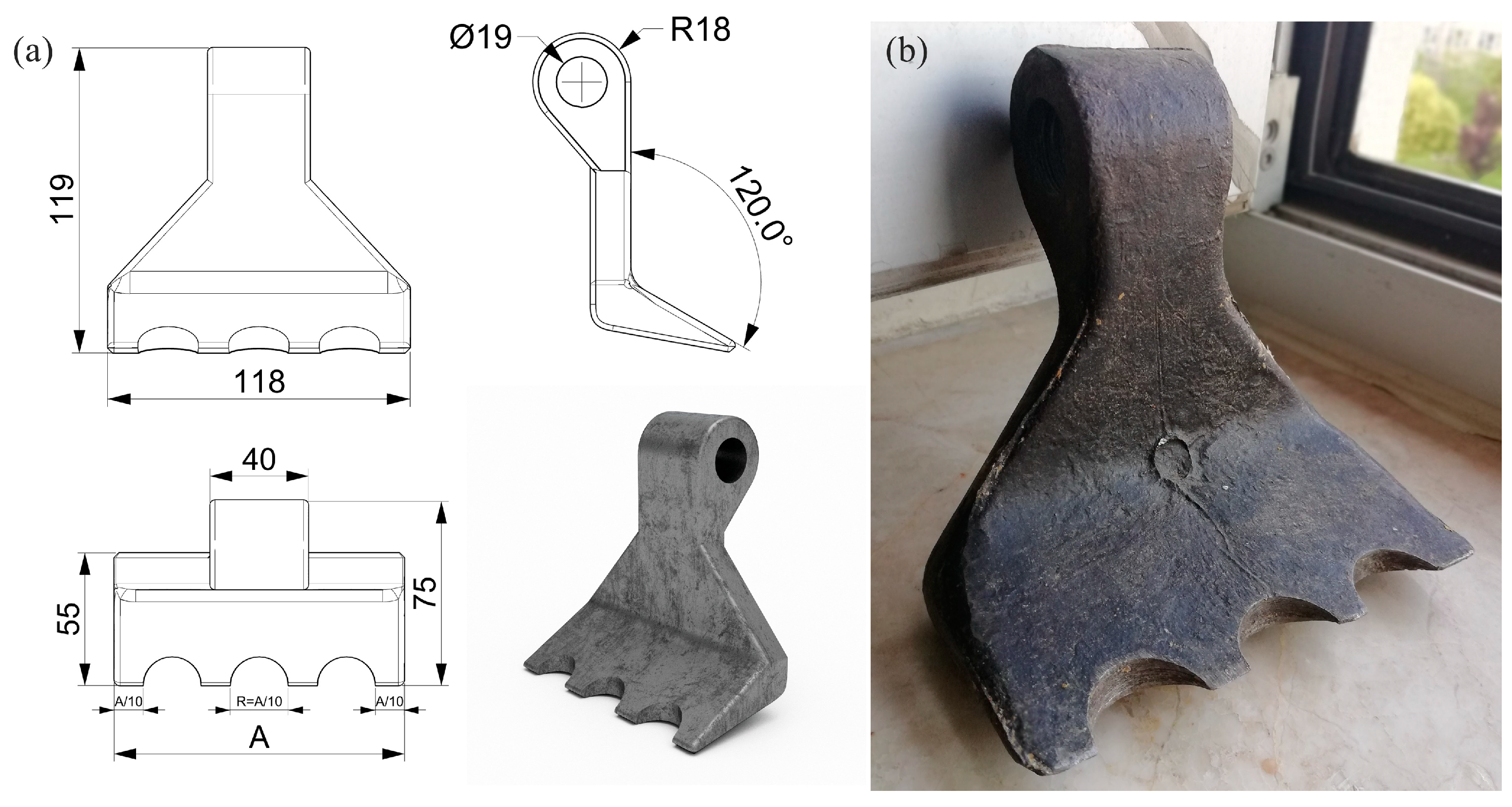
Pruning residue shredders can work with different blades. Çanakcı et al. [12] conducted experiments with a similar shredding machine using hammer, universal (triple) and Y (dual)-type blades and compared the performance of the blades. According to the results obtained, hammer blades provided better shredding efficiency compared to other (segmented) blade types (about 10–20%) but consumed much more power (about 55–70%). Considering this result, a redesigned blade was used in the developed shredding system by modifying the shape of the hammer blade. In the designed toothed hammer blade, the basic dimensions of the hammer blade were retained, and only the shape of the cutting edge was changed. Accordingly, three semicircular grooves were formed on the cutting edge to increase the contact surfaces with the materials to be shredded. The tooted hammer blades are made from forged steel material (30 MgB5), with each individual blade weighing 1270 g. The blades have a material hardness ranging from 46 to 48 HRC. The dimensions of the toothed hammer blade are shown in Figure 2.
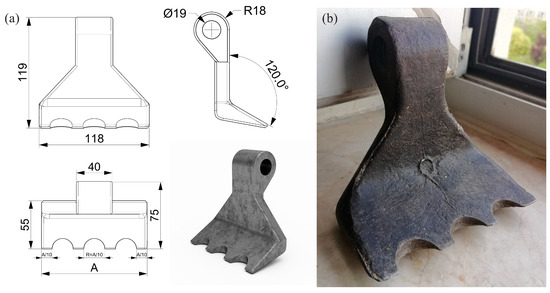
Figure 2.
Toothed-hammer-type blade design: (a) schematic view and dimensions; (b) photograph.
The re-designed toothed hammer blade has been registered as an Industrial Design by the Turkish Patent and Trademark Office (TURKPATENT) with the number 2021 010165 [28].
2.3. Pruning Residues
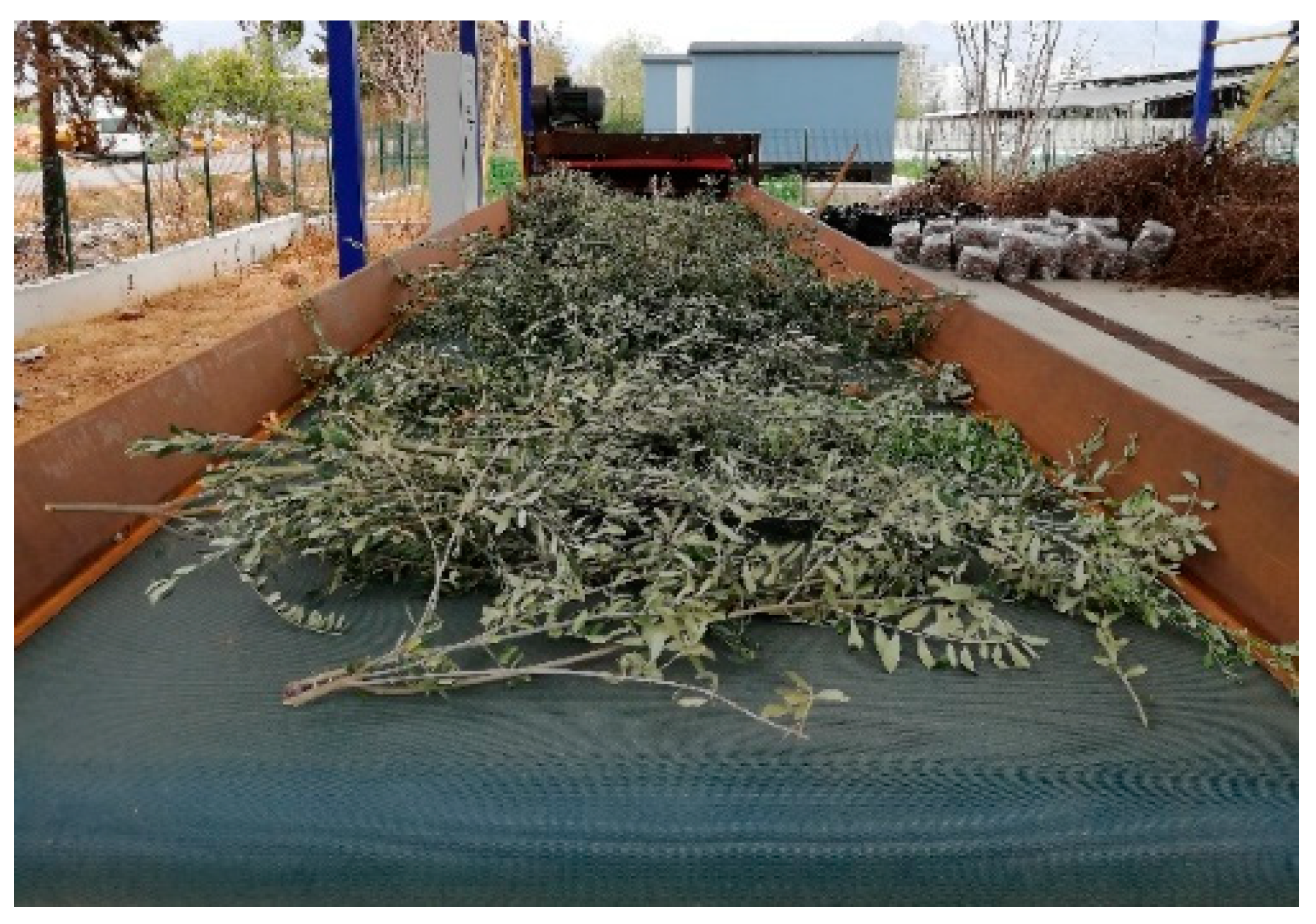
In the experiments, pruning residues obtained from olive trees (Olea europaea L. cv. Ayvalık) located in the campus area of Akdeniz University (Antalya, Turkey) were shredded. An image of the olive pruning residues used in the trials is shown in Figure 3. The average branch thickness of pruning residues was 5.4 ± 1.12 mm, and the branch length was 1.33 ± 0.42 m.

Figure 3.
Image of a sample of olive pruning residues shredded in the trials.
Three different moisture contents of pruning residues were used in the study. The first trials (M1) were conducted immediately after pruning, when the residues had the highest moisture content. In subsequent trials, lower moisture levels were achieved by allowing the residues to dry naturally. Throughout the drying process, samples were periodically collected from the pruning residues at 5-day intervals to follow the reduction in moisture content. The second trials (M2) were carried out when the moisture content of the residues decreased by about 10% compared to the post-pruning period. The third trials (M3) were conducted when the moisture content had decreased by about 20% compared to after pruning and the rate of decrease had slowed down.
Randomly selected branches weighing approximately 200 g were used to determine the moisture content of pruning residues. These samples were initially weighed and then placed in a drying oven set at 105 °C for 24 h [29]. After the drying period, the samples were re-weighed to determine their moisture content.
2.4. Determination of Power Values
The power values of the shredding machine were determined using a Chauvin Arnoux CA 8332B 3-phase portable energy analyzer. The analyzer measured the phase-to-phase voltage (V), active–reactive (capacitive and inductive) current (A), and apparent power factor values (cosφ and tanφ) of the electric motor responsible for powering the machine. Power (W) values were recorded at 1-second intervals during the trials.
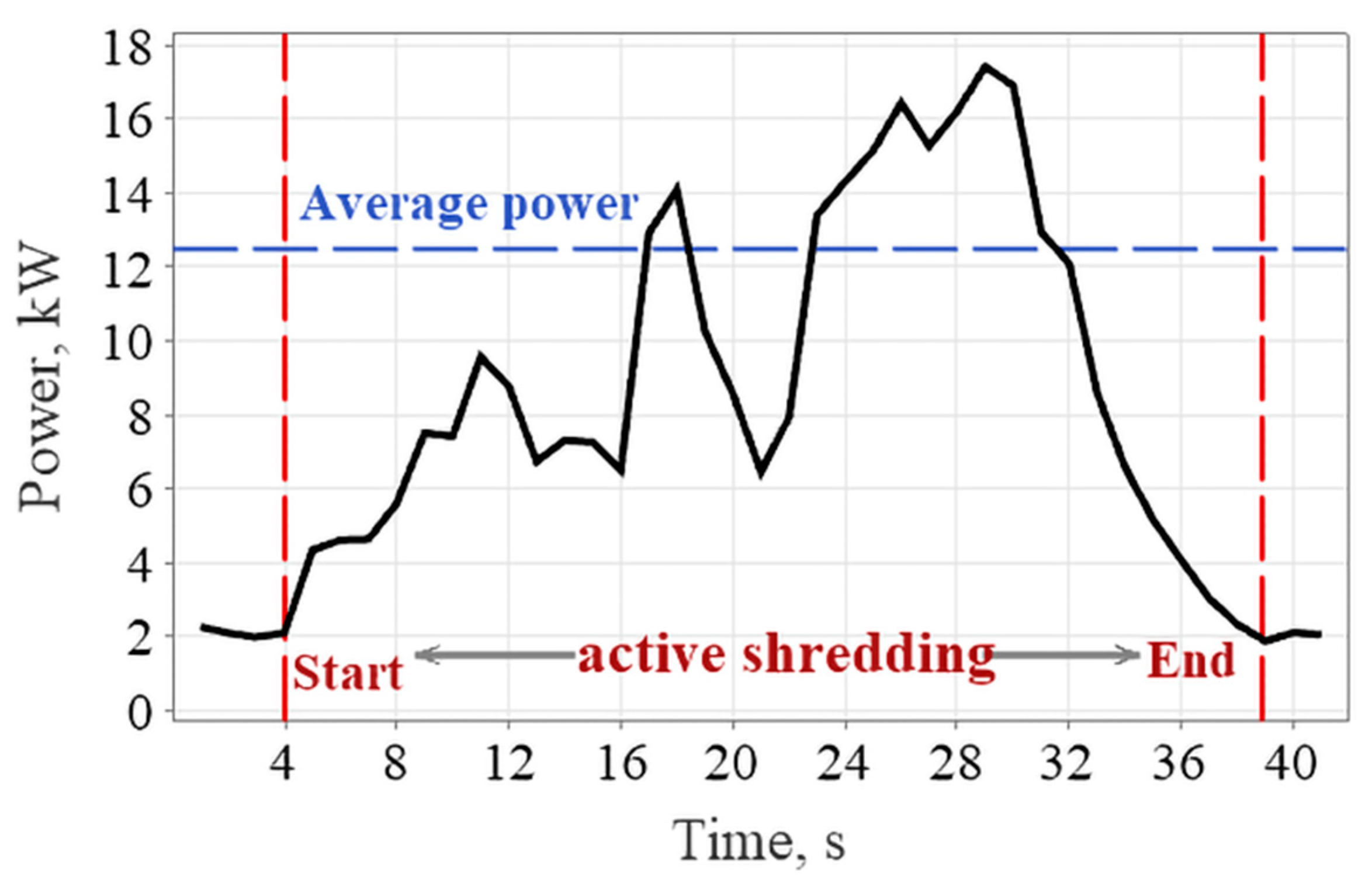
Throughout the experiments, the energy analyzer started recording when the shredding system was activated and ended when all pruning residues had passed through the sieves in the shredding unit and settled on the ground. By reviewing the recorded data, the focus of the analysis was on the data captured during the “active shredding” interval when shredding starts and ends, as shown in Figure 4. The power requirement of the shredder was determined by averaging the data collected during this time period [30,31,32].
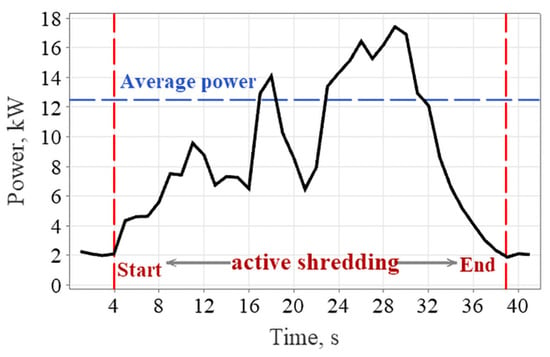
Figure 4.
Determining the average power values of shredding.
2.5. Experiment Conditions
To operate the shredding system, two (Driver I and II) AC motor speed control drivers (FRENIC-Ace series, Fuji Electric, Tokyo, Japan) and a control panel with potentiometers were used. The rotary speeds of the shredding machine were adjusted by altering the frequency (Hz) of the electric energy supplied to the electric motors using AC motor speed control drivers. Potentiometers linked to both drivers facilitated this adjustment. Tachometer measurements were conducted on the collector, shredder rotary, and conveyor belt to monitor the changes in frequency. The experiments maintained a consistent collector speed of 45 rpm while varying the shredder rotary speed to three different values: 1200 rpm, 1500 rpm, and 1800 rpm.
The experiments were carried out at three different rotor speeds and material moisture contents, with three replicates for each different combination. In this way, a total of 27 experiments were conducted.
The feeding process of the shredding machine ensured consistent dry matter content for each experiment, as shown in Table 1. Material density was maintained at a constant value of 1 kg (dry mass) per meter throughout all experiments, regardless of variations in moisture content, drawing from insights gained in previous studies.

Table 1.
The moisture content of olive pruning residues, material density values, and operating conditions of the shredding system.
For each experiment, the olive pruning residues of the determined weight were laid on the conveyor, and the particles formed after the shredding process were collected in the hopper placed under the sieve unit. After the hopper was emptied, the same procedures were repeated for the next experiment.
2.6. Model Development and Statical Analysis
The effect of rotor speed and material moisture content changes on machine power requirement was evaluated using multiple analysis of variance (MANOVA). Subsequently, the Tukey test was employed for multiple comparisons of significant factors. GraphPad Prism 9 software was used to generate graphs for both the analysis of variance and multiple comparisons. In the graphs, the distinctions between the means of the analyzed parameters were indicated based on their significance levels (p ≤ 0.05; *, p ≤ 0.01; **, p ≤ 0.001; ***).
Regression analyses were performed to predict the power requirement of the pruning residue shredder in relation to the variation of shredder rotor speed and material moisture content. Minitab 20.3 software was used for regression analysis and graphing.
Regression models were developed to predict the machine power requirement by considering the following operating conditions;
- i.
- Effect of moisture content variation for each rotor speed;
- ii.
- Effect of rotor speed variation for each moisture content;
- iii.
- Combined effect of rotor speed and moisture content variation.
In order to evaluate the performance of the developed model, the following three statistical indices were calculated: mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE), and correlation coefficient (R2). R-squared (R2) showcases the total variance explained by the model, and values close to 1 or −1 indicate that the relationship is strong [33]. Mean absolute error (MAE) provides the most meaningful measures of the absolute and relative errors in the developed model, and it is required to reach zero. root mean square error (RMSE) quantifies the remaining variance unaccounted for by the model. These calculations are derived using the following equations.
where; Ow = observed value of power, Pw = predicted value of power, N = number of observations, n = number of constants.
3. Results and Discussion
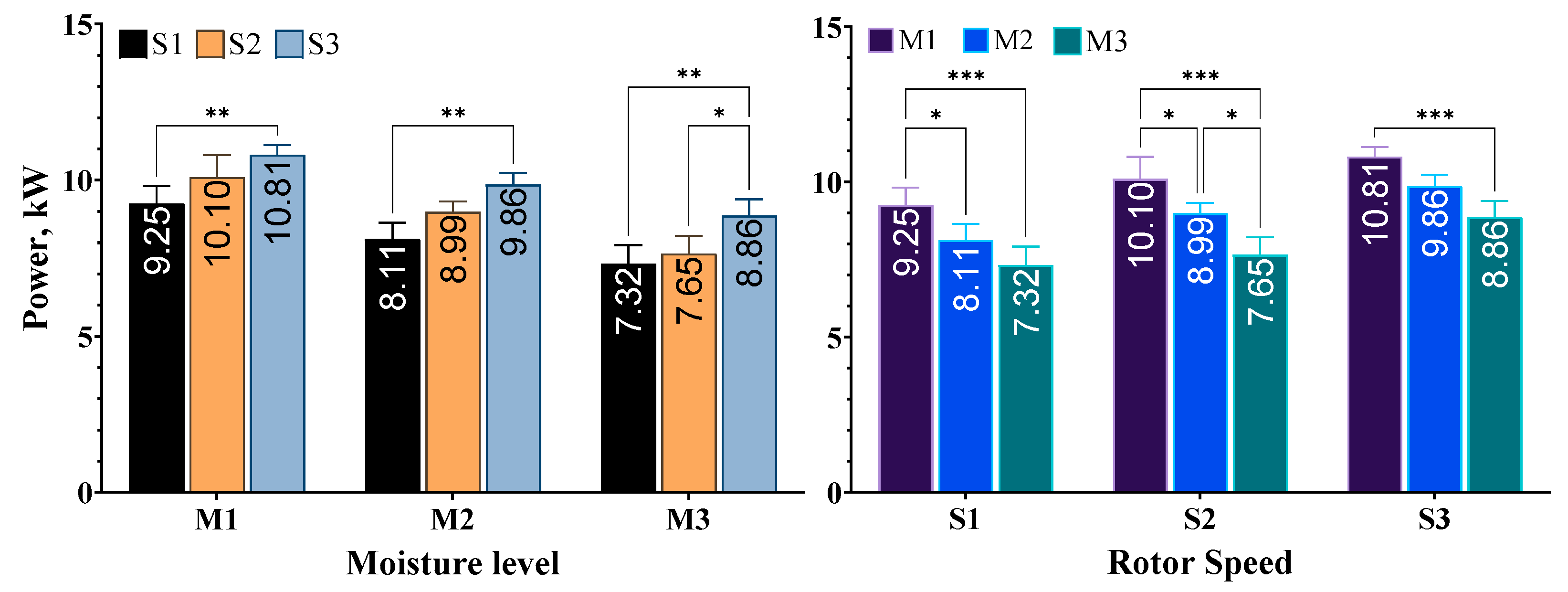
The experiments resulted in average power requirement values for the shredder ranging from 7.32 kW to 10.81 kW. According to the analysis of variance results, variations in rotor speed and material moisture content affected the power consumption values of the shredding machine (p < 0.05).
At all moisture levels, higher rotor speed increased the power requirements of the shredder. The increase in rotor speeds from S1 to S3 showed a statistically significant difference. Additionally, at the lowest moisture level, M3, increasing the speed from S2 to S3 prompted a significant increase in power values. This finding is consistent with research conducted by Flizikowski et al. [34], who reported that rotor speed is a key factor affecting power levels. According to the relational equation between speed and instantaneous power, when speed increases, instantaneous power also increases. Similar findings were reported by Johnson et al. [35] in their studies on mango and licorice root, respectively. Xue et al. [36] also reached similar results in the shredding of silage corn with disc cutters [37].
At all rotor speeds, decreasing the material moisture content from M1 to M3 led to a decrease in power consumption. In particular, at rotor speed S1, the power decrease in M1-M2 and M1-M3 changes of moisture levels was statistically significant. Similarly, at rotor speed S2, all changes in moisture levels resulted in a significant reduction in power requirement. At rotor speed S3, only the decrease in moisture content from M1 to M3 had a significant effect on power values, as shown in Figure 5.
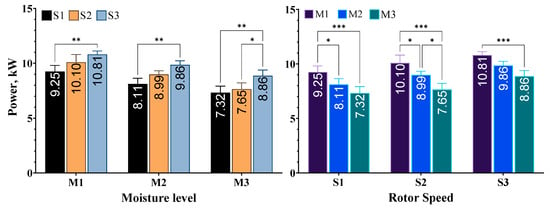
Figure 5.
Average power values determined according to varying rotor speed and material moisture level. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001.
There are few studies in the literature that examine the effects of different moisture contents on the shredding process during the shredding of the same plant material with the same feed density. Savoie and Gagnon [31] shredded willow branches with different moisture contents under different rotor speeds, counter blade usage, hood openings and feed density conditions in the shredding process; they tested these factors under laboratory conditions However, they did not directly indicate the effects of varying the moisture content of plant residues.
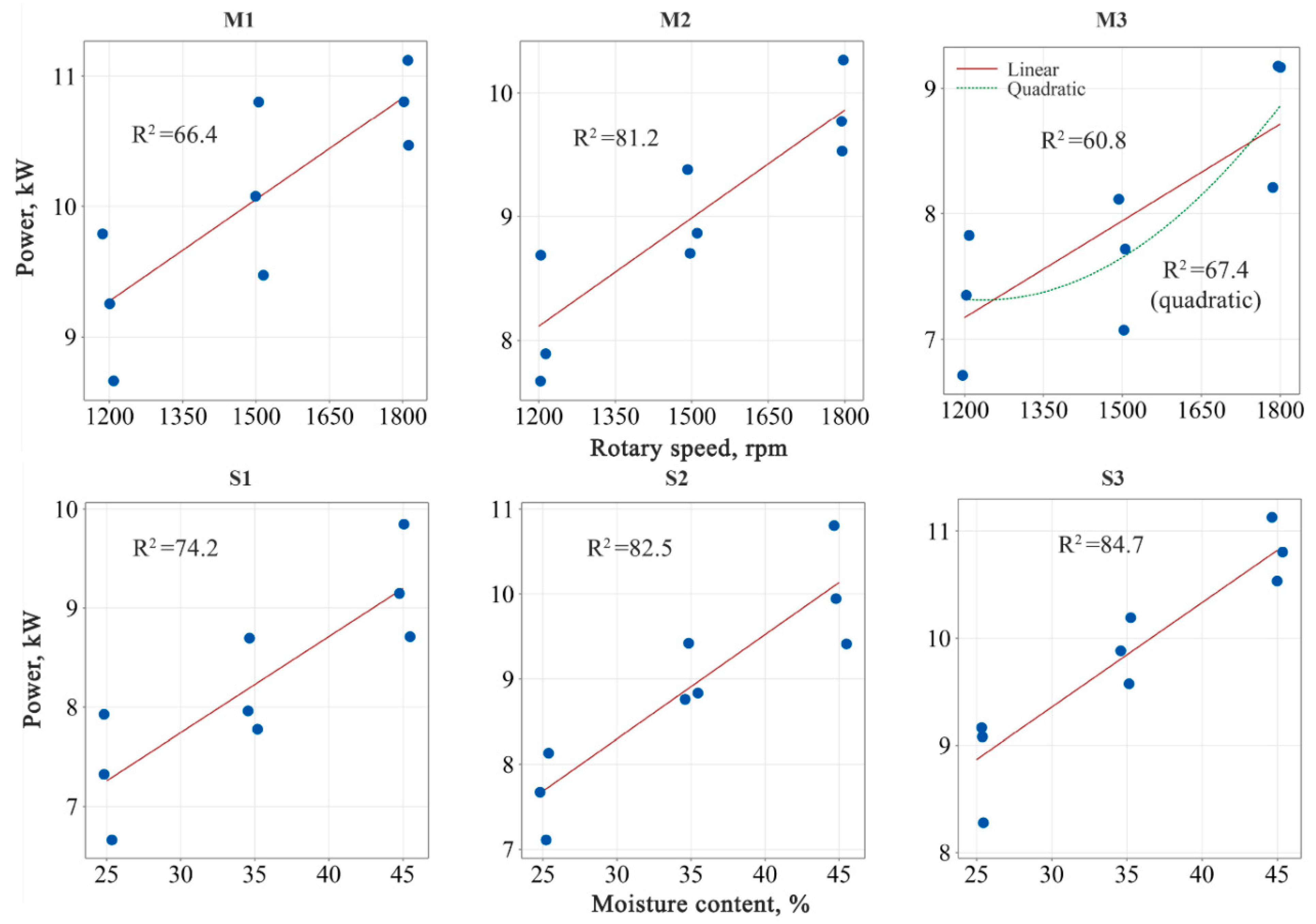
By evaluating the data obtained as a result of the experiments, regression models were formulated in which the dependent variables were assumed to be rotor speed and material moisture content, as shown in Figure 6.
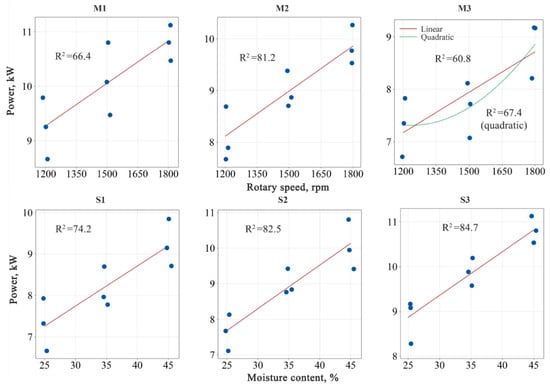
Figure 6.
Power value of the shredding machine as a function of rotary speed and moisture content of materials. R2: correlation coefficient. • = average power value measured in experiments; — = linear slope line of the calculated equation.
The lowest correlation coefficient at the end of the regression analysis was calculated for the model in which rotor speed was considered the effective factor at the M3 moisture level. A polynomial model was also developed for this model to increase its prediction success. Using this method, the correlation coefficient reached 0.67. Except for the models developed for the M1 and M3 moisture levels, all other models were highly correlated (R2 > 0.70).
In all models where rotor speed and material moisture content are independent variables, the power requirement of the shredder shows a linear trend. Considering this trend and aiming for a more practical and transferable model, multiple linear regression analysis was performed to estimate the combined effect of rotor speed and moisture content variation on the power requirement of the shredder.
There are modelling studies on different types of shredding machines other than the machines used in shredding agricultural residues. In these studies, mechanistic models based on basic principles and including the characteristics of the machine were developed. Liang et al. [37] developed a model to predict, through regression analysis and analysis of variance, the shredding power consumption of a machine shredding a mixture of residual mulch and foreign matter, taking into account the number of toothed cutters and fixed blades, the gap between them, and the shredder speed. The error between the predicted value of shredding power consumption obtained from the model and the measured value in the validation test was 9.76%. In the developed model, the power values increase linearly with the increasing rotational speed of the shredder rollers.
Igboayaka et al. [38] developed a basic model using fundamental principles to predict the specific energy consumption and efficiency of a motorized cassava grinder. When the simulation results were compared with the experimental results, the prediction accuracy of each model was found to be above 98% on average. Increasing the shredder speed similarly increased the predicted power requirement.
Savioe and Ganon [31] developed an empirical model to predict the energy requirement of a willow branch shredder in a laboratory test study. The model was built by considering rotor speed, counter blade position, and the mass of material shredded in 5 s as variables affecting the energy requirement. The correlation coefficient (R2) value of the model was calculated as 0.890.
As an improvement beyond the aforementioned studies, this paper introduces an empirical model developed to predict the power requirement of a pruning residue shredder. The model encompasses important factors such as rotor speed, which is considered the primary variable affecting the shredding process, and includes the parameter of material moisture content, which was not considered in previous studies. In this way, an easily applicable formula can be obtained and can predict the effect of olive pruning residues with different moisture contents on the shredding process. The developed models and performance evaluation measurements are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Performance evaluation measurements of the developed model.
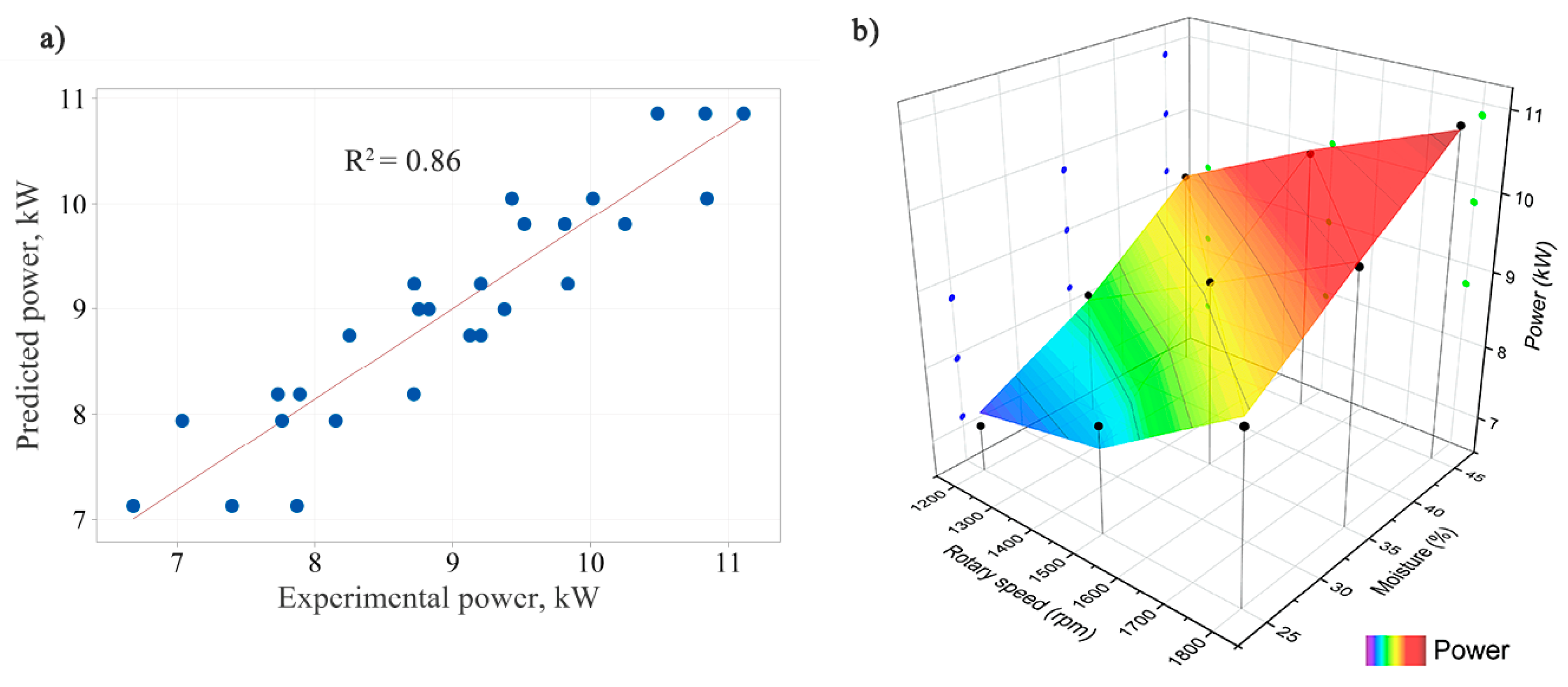
To validate the final model, the predicted power values were compared with the observed power values. The performance of the model is depicted in Figure 7a. The predicted data cluster closely around the straight line, suggesting that the final model accurately predicts the power requirement of the shredder across different variations of rotor speed and material moisture content. The observed and predicted power values depending on variation in rotor speed and material moisture content are shown in Figure 7b.
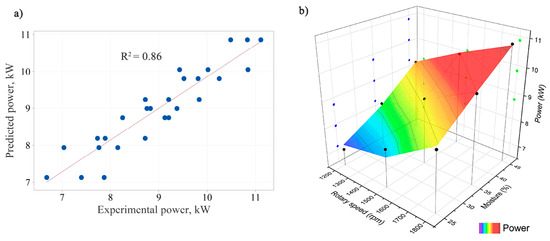
Figure 7.
(a) Experimental versus predicted power values according to the final model; R2: correlation coefficient. • = average power value measured in experiments; — = linear slope line of the calculated equation. (b) Three-dimensional surface plot of predicted power values.
Comparisons with previous studies highlight the novelty of our approach, which incorporated moisture content, a factor often neglected in similar investigations.
4. Conclusions
As a result of these experiments, the average power requirement values of the shredding machine were found to be in the range of 7.32–10.81 kW. The analysis of variance results revealed significant effects of both rotor speed and material moisture content on the power consumption values (p < 0.05). A decrease in material moisture content decreased the power values, while an increase in rotor speed increased the power values. The empirical model developed in this study successfully predicts the power requirement of the shredding machine by considering both rotor speed and material moisture content. Unlike previous models with varying correlation coefficients, our model exhibits high correlations across different moisture levels. The final model had a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.376, a root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.441, and a correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.859. The validation results confirm the model’s accuracy, further supporting its practical utility in optimizing shredding operations. It can be concluded that the experimental shredding system examines different parameters affecting shredding and has the potential to be used in future studies with different crop residues.
Based on the results from the shredding of olive pruning residues, it can be concluded that such shredding machines should be operated at low rotor speeds for all moisture contents to achieve low power requirements. Furthermore, given that the reduction in material moisture content also reduces power consumption, the most efficient shredding process can be achieved with a low moisture content and a high rotor speed. Trials conducted in Antalya, Turkey between April and June showed that it took about 6 weeks to reduce the moisture content of olive pruning residues from 45% to 20%. For effective shredding in regions with similar climatic conditions, it is recommended that the pruning residues are left to dry in the field for this period of time before being shredded at low rotor speeds.
5. Patents
M. Pruning Machine Blade. Design Registration. Turkish Patent and Trademark Office, 25 October 2021. No: 2021 010165.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Y., M.Ç. and D.K.; methodology, M.Y., M.Ç. and D.K.; software, M.Y.; validation, M.Ç. and D.K.; formal analysis, M.Y. and D.K.; investigation, M.Y. and M.Ç.; resources, M.Ç.; data curation, M.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Y.; writing—review and editing, M.Ç. and D.K.; visualization, M.Y.; supervision, M.Ç.; project administration, M.Ç.; funding acquisition, M.Ç. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by project number FDK-2017-2561 of the Scientific Research Projects Administration Unit of Akdeniz University, Antalya, Türkiye.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- FAOSTAT. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- García, J.M.; Nino, L.; Martínez-Patiño, C.; Álvarez, C.; Castro, E.; Negro, M.J. Biorefinery based on olive biomass. State of the art and future trends. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalos, G.A.; Grigoriou, A.H. Characterization and utilisation of vine pruning as a wood substitute for particleboard production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2002, 16, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, R.; Magagnotti, N.; Nati, C. Harvesting Vineyard Pruning Residues for Energy Use. Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 105, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Marti, B.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, E. Analysis of the process of biomass harvesting with collecting chippers fed by pick up headers in plantations of olive trees. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 104, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrizzi, M.; Sperandio, G.; Pagano, M.; Pochi, D.; Fanigliulo, R.; Recchi, P. A prototype machine for harvesting and chipping of pruning residues: First test on hazelnut plantation (Corylus avellana L.). In Proceedings of the International Conference of Agricultural Engineering, CIGR-Ageng, Valencia, Spain, 8–12 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bilandzija, N.; Voca, N.; Kricka, T.; Matin, A.; Jurisic, V. Energy potential of fruit tree pruned biomass in Croatia. SJAR 2012, 10, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, R.A.; Al-Mefarrej, H.A. Evaluation of using midribs of date palm fronds as a raw material for wood-cement composite panels industry in Saudi Arabia. Acta Hortic 2010, 882, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyjakon, K.; Boer, J.D.; Bukowskı, P.; Adamczyk, F.; Frąckowıak, P. Wooden biomass potential from apple orchards in Poland. Drewno 2016, 59, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorio, C.; Pizzini, S.; Marchiori, E.; Piazza, R.; Grigolato, S.; Zanetti, M.; Cavalli, R.; Simoncin, M.; Soldà, L.; Badocco, D.; et al. Sustainability of using vineyard pruning residues as an energy source: Combustion performances and environmental impact. Fuel 2019, 243, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Sarria, A.; Lopez-Cortes, I.; Estornell, J.; Velazquez-Marti, B.; Salazar, D. Estimating residual biomass of olive tree crops using terrestrial laser scanning. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 75, 163170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakci, M.; Topakci, M.; Karayel, D.; Agsaran, B.; Kabas, O.; Yigit, M. The effect of different blades on the performance values of a pruning chopper used to improve soil properties. BJAS 2019, 25, 1052–1059. Available online: https://www.agrojournal.org/25/05-29.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Margaritis, N.; Grammelis, P.; Karampinis, E.; Kanaveli, I. Impact of Torrefaction on Vine Pruning’s Fuel Characteristics. J. Energy Eng. 2020, 146, 04020006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suardi, A.; Saia, S.; Alfano, V.; Rezaei, N.; Cetera, P.; Bergonzoli, S.; Pari, L. Pruning harvesting with modular towed chipper: Little effect of the machine setting and configuration on performance despite strong impact on wood chip quality. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çanakci, M.; Topakci, M.; Karayel, D.; Ağsaran, B. Determination of basic machinery management data for PTO driven pruning residue chopper. JAS 2010, 16, 46–54. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatrava, J.; Franco, J.A. Using pruning residues as mulch: Analysis of its adoption and process of diffusion in Southern Spain olive orchards. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Jimenez, F.; Blanco-Roldan, G.L.; Marquez-Garcia, F.; Castro-Garcia, S.; Aguera-Vega, J. Estimation of soil coverage of chopped pruning residues in olive orchards by image analysis. SJAR 2013, 11, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanares, P.; Ruiz, E.; Ballesteros, M.; Negro, M.J.; Gallego, F.J.; Lopez-Linares, J.C.; Castro, E. Residual biomass potential in olive tree cultivation and olive oil industry in Spain: Valorisation proposal in a biorefinery context. SJAR 2017, 15, e0206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, B.A.; McKenry, M.V.; Caesar-TonThat, T.C. Wood chipping almond brush and its effect on the almond rhizosphere, soil aggregation and soil nutrients. Acta Hortic 2004, 638, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repullo, M.A.; Carbonell, R.; Hidalgo, J.; Rodrı’guez-Lizana, A.; Ordóñez, R. Using olive pruning residues to cover soil and improve fertility. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 124, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çanakcı, M. Chopping and mechanization of the pruning residues. Hasad (Harvest) J.—Plant Prod. 2014, 29, 70–78. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Valencia, L.; Camenzind, D.; Wigmosta, M.; Garcia-Perez, M.; Wolcott, M. Biomass supply chain equipment for renewable fuels production: A review. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 148, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Luo, L.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wei, H.; Wang, J. Dynamic visual servo control methods for continuous operation of a fruit harvesting robot working throughout an orchard. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 219, 108774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, C.; Han, Q.; Wu, F.; Zou, X. A Performance Analysis of a Litchi Picking Robot System for Actively Removing Obstructions, Using an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Z.; Tang, Y. A Study on Long-Close Distance Coordination Control Strategy for Litchi Picking. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witney, B. Choosing and Using Farm Machines; Land Technology Ltd.: Edinburgh, Scotland, 1996; p. 412. [Google Scholar]
- Rotz, C.A.; Muhtar, H.A. Rotary power requirements for harvesting and handling equipment. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1992, 8, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiğit, M.; Çanakcı, M. Pruning Machine Blade. Design Registration; Turkish Patent and Trademark Office: Ankara, Turkey, 25 October 2021; No: 2021 010165. [Google Scholar]
- ASABE S358.2; Moisture Measurement—Forages. ASABE Standards: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2006.
- Spinelli, R.; Magagnotti, N.; Paletto, G.; Preti, C. Determining the impact of some wood characteristics on the performance of a mobile chipper. Silva Fenn. 2011, 45, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoie, P.; Gagnon-Bouchard, M. High-speed processing of woody stems with a flail hammer shredder. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2012, 27, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecenka, R.; Lenz, H.; Jekayinfa, S.O.; Hoffmann, T. Influence of Tree Species, Harvesting Method and Storage on Energy Demand and Wood Chip Quality When Chipping Poplar, Willow and Black Locust. Agriculture 2020, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuero, A.G.; Sayago, A.; González, A.G. The Correlation Coefficient: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2006, 36, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flizikowski, J.; Kruszelnicka, W.; Macko, M. The Development of Efficient Contaminated Polymer Materials Shredding in Recycling Processes. Polymers 2021, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.C.; Clementson, C.L.; Mathanker, S.K.; Grift, T.E.; Hansen, A.C. Cutting energy characteristics of Miscanthus × giganteus stems with varying oblique angle and cutting speed. Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 112, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Han, S.; Ren, L. Optimization experiment on parameters of chopping device of forage maize harvester. J. Jilin Univ. 2020, 50, 739–748. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, P.; Li, Y.; Meng, H.; Kan, Z. Power consumption analysis of the multi-edge toothed device for shredding the residual film and impurity mixture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 196, 106898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igboayaka, E.C.; Ndukwu, M.C.; Ernest, I.C. A Modelling approach for determining the throughput capacity and energy consumption of a cassava tuber shredder. JCAMS 2018, 6, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).