A Decision Support System for Irrigation Scheduling Using a Reduced-Size Pan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
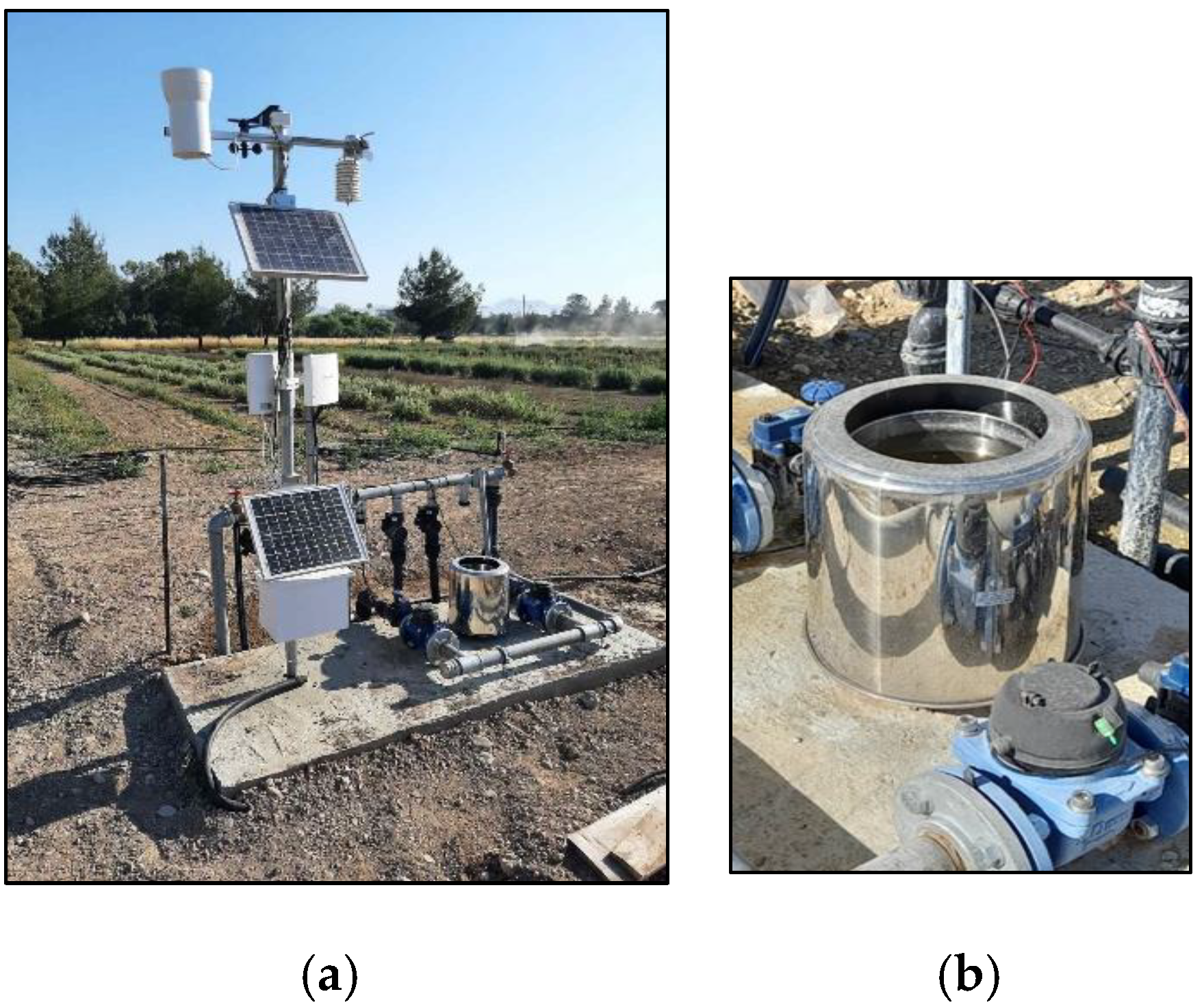
2.1. Study Site and Equipment
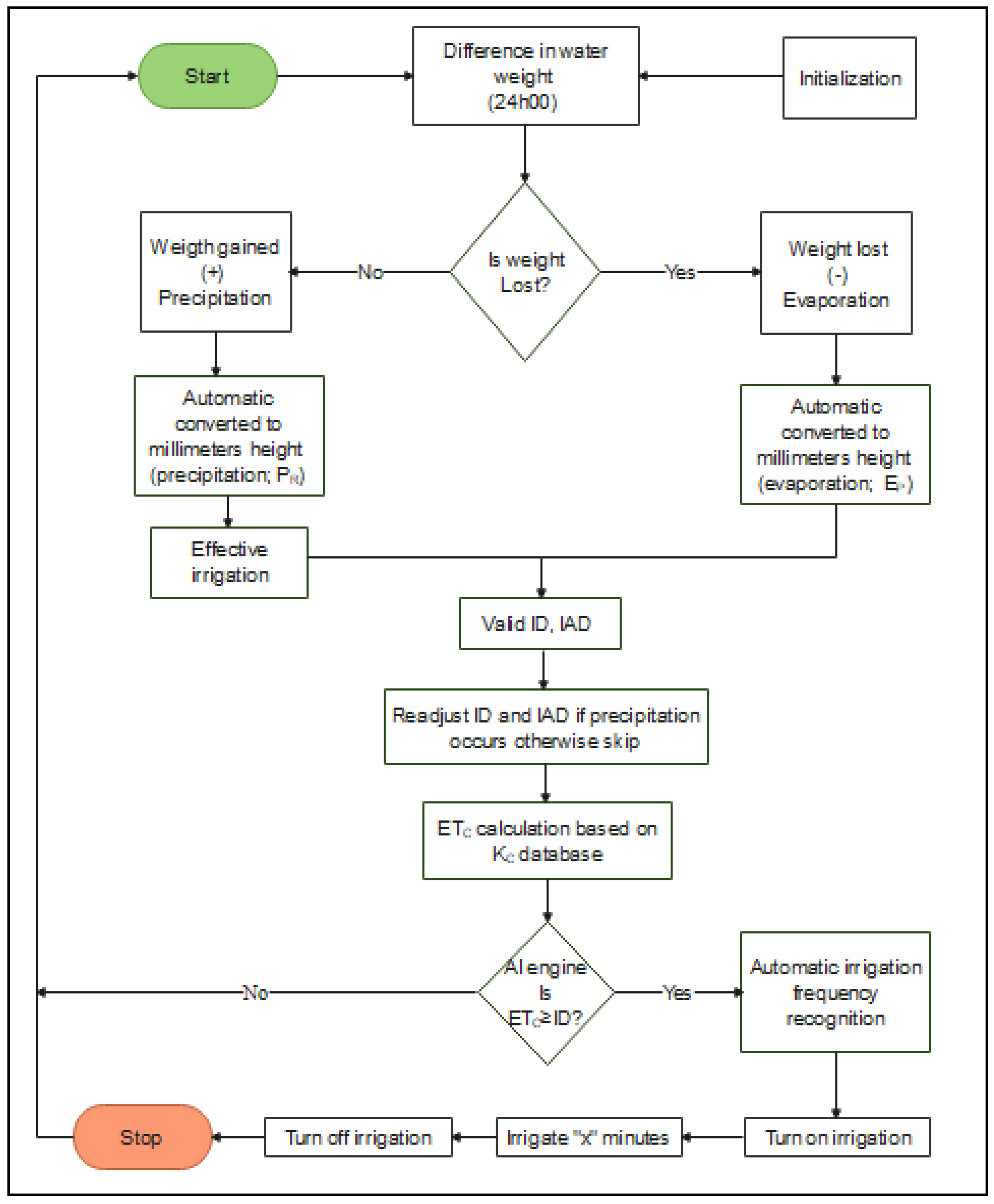
2.2. Theoretical Background of Irrigation Scheduling
2.3. Data Acquisition and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
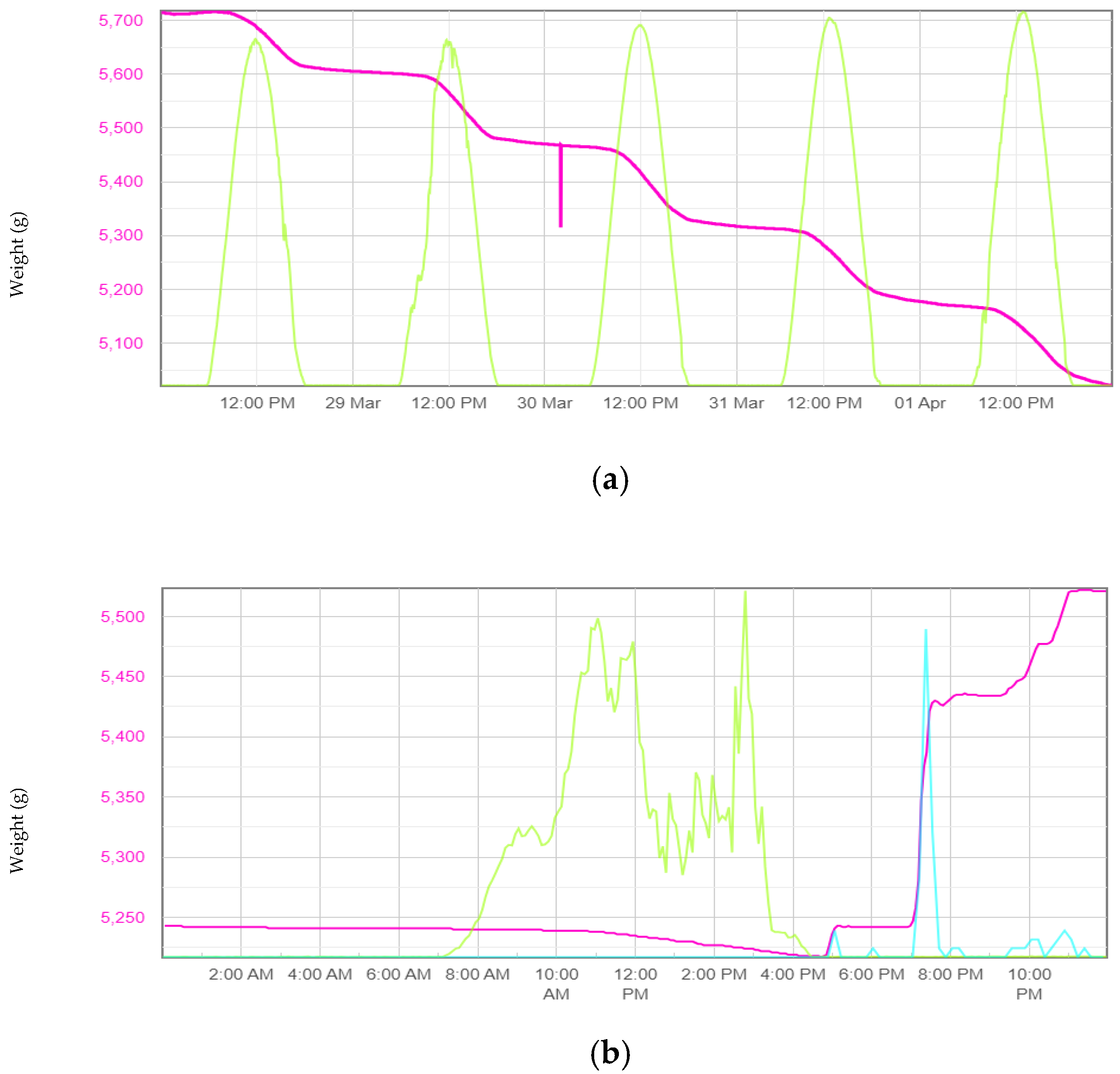
3.1. Pan Evaporation and Climatic Conditions
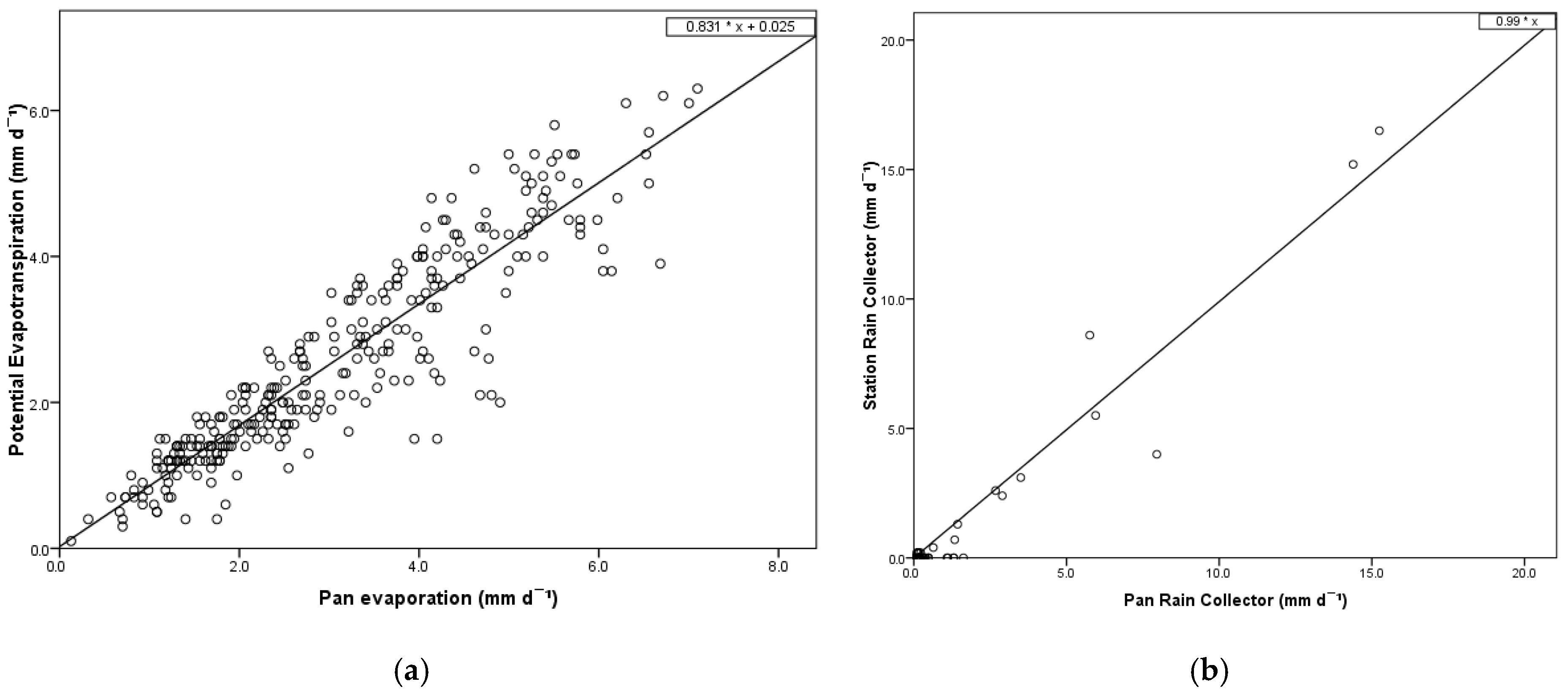
3.2. Model Calibration and Validation
3.3. Irrigation Scheduling Decision Support Tool
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seker, M.; Gumus, V. Projection of Temperature and Precipitation in the Mediterranean Region through Multi-Model Ensemble from CMIP6. Atmos. Res. 2022, 280, 106440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, G.; Neocleous, D.; Christou, A.; Kitta, E.; Katsoulas, N. Implementing Sustainable Irrigation in Water-Scarce Regions under the Impact of Climate Change. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martey, E.; Etwire, P.M.; Adombilla, R.; Abebrese, S.O. Information Constraint and Farmers’ Willingness to Pay for an Irrigation Scheduling Tool. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 276, 108043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boso, A.C.M.R.; Campos, F.S.; Pai, A.D. Calibrated Models to Estimate Referensce Evapotranspiration, for the City of Botucatu/Sp, in Relation to the Weighing Lysimeter. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 6599–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.N.; Tare, V. Assessment of Irrigation Requirement and Scheduling under Canal Command Area of Upper Ganga Canal Using CropWat Model. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 1863–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zereg, S.; Belouz, K. Prediction of Reference Evapotranspiration in Northwestern Africa with Limited Data Using Factorial and SVM Regressions. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 5129–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation. In World Meteorological Organization Volume 8 of Organisation Météorologique Mondiale Issue 8 of WMO (Series) WMO No. 8; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Awe, G.O.; Akomolafe, T.N.; Umam, J.; Ayuba, M.B. Efficiency of Small Pan Evaporimeter in Monitoring Evapotranspiration under Poly-Covered House and Open-Field Conditions in a Hot, Tropical Region of Nigeria. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 32, 100735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56—Crop Evapotranspiration; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.J.; Cohen, S.; Tanny, J.; Lemcoff, J.H.; Huang, G.H. Estimation of Banana (Musa sp.) Plant Transpiration Using a Standard 20 cm Pan in a Greenhouse. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2008, 22, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Patel, Y.; Patel, U.; Patel, V.; Patel, N.; Oza, P.; Patel, U. Towards Automating Irrigation: A Fuzzy Logic-Based Water Irrigation System Using IoT and Deep Learning. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 5235–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalias, P.; Christou, A.; Neocleous, D. Adjustment of Irrigation Schedules as a Strategy to Mitigate Climate Change Impacts on Agriculture in Cyprus. Agriculture 2019, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Shankar, V.; Poddar, A. Investigating the Effect of Limited Climatic Data on Evapotranspiration-Based Numerical Modeling of Soil Moisture Dynamics in the Unsaturated Root Zone: A Case Study for Potato Crop. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 2433–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggi, M.K.; Jain, S. A Survey Towards Decision Support System on Smart Irrigation Scheduling Using Machine Learning Approaches. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 4455–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bencini, L.; Di, D.; Collodi, G.; Manes, A.; Manes, G. Wireless Sensor Networks for On-Field Agricultural Management Process. In Wireless Sensor Networks: Application-Centric Design; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, S.J.T.; Guimarães, C.M.; de Sousa, E.F.; Garcia, R.F.; Marciano, C.R. Application of Artificial Intelligence for Irrigation Management: A Systematic Review. Eng. Agrícola 2022, 42, e20210159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, A.K.; Bhardwaj, A.K.; Verma, C.L.; Mishra, V.K.; Arora, S.; Sharma, N.; Ojha, R.P. Automation in Scheduling Irrigation: A Review of Concepts and Latest Recommendations in Technology. J. Nat. Resour. Conserv. Manag. 2021, 2, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, G.; Neocleous, D.; Manes, A.; Kitta, E. Calibration and Validation of Solar Radiation-Based Equations to Estimate Crop Evapotranspiration in a Semi-Arid Climate. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2024, 68, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacovides, C.P.; Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Tymvios, F.S. Measured on the Island of CyprusSolar Global UV (280–380 nm) Radiation and Its Relationship with Solar Global Radiation. Energy 2006, 31, 2728–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashiardis, S.; Sa, K.; Pelengaris, A. Characteristics of Photosynthetic Active Radiation (PAR) Through Statistical Analysis at Larnaca, Cyprus. SM J. Biom. Biostat. 2017, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Liang, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Zhan, C.; Jiang, S. Encounter Risk Analysis of Crop Water Requirements and Effective Precipitation Based on the Copula Method in the Hilly Area of Southwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 266, 107571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Tian, W.; Li, Y.; Liang, K.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, X. Pan Coefficient Sensitivity to Environment Variables Across China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Kuslu, Y.; Tunc, T.; Kiziloglu, F.M. Determining Crop and Pan Coefficients for Cauliflower and Red Cabbage Crops Under Cool Season Semiarid Climatic Conditions. Agric. Sci. China 2009, 8, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchon, C.E.; Biddle, C.J. Undercatch of Tipping-Bucket Gauges in High Rain Rate Events. Adv. Geosci. 2010, 25, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervos, N.A.; Baltas, E.A. Development of Experimental Low-Cost Rain Gauges and Their Evaluation During a High Intensity Storm Event. Environ. Process. 2024, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.Z.; Bie, Z.L.; Yuan, B.Z. Determination of Optimum Irrigation Water Amount for Drip-Irrigated Muskmelon (Cucumis Melo L.) in Plastic Greenhouse. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Month | T | RH | R | SR | HSR | W | Wm | ETO | EP | KP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 (1.3) | 78 (6.7) | 1.52 (4.0) | 425 (81.4) | 6.42 | 0.82 (0.6) | 3.08 (1.18) | 1.16 (0.35) | 1.32 (0.39) | 0.88 (0.17) |
| 2 | 8 (2.8) | 72 (6.7) | 1.32 (3.4) | 556 (136.2) | 7.21 | 0.68 (0.26) | 2.96 (0.74) | 1.51 (0.56) | 1.67 (0.55) | 0.90 (0.19) |
| 3 | 13 (1.7) | 71 (8.6) | 1.77 (4.8) | 697 (89.5) | 8.48 | 0.88 (0.32) | 3.15 (0.83) | 2.17 (0.70) | 2.31 (0.83) | 0.95 (0.10) |
| 4 | 16 (2.1) | 65 (6.0) | 1.49 (5.6) | 809 (96.6) | 9.73 | 1.01 (0.32) | 3.50 (0.73) | 3.09 (0.96) | 3.30 (1.02) | 0.94 (0.14) |
| 5 | 21 (2.0) | 63 (11.5) | 0.83 (2.9) | 887 (58.7) | 10.74 | 1.15 (0.41) | 3.79 (1.33) | 3.96 (1.04) | 4.17 (1.15) | 0.96 (0.12) |
| 6 | 25 (2.2) | 59 (10.7) | 0.15 (0.8) | 861 (73.6) | 11.67 | 1.10 (0.21) | 3.34 (0.56) | 4.73 (1.00) | 5.13 (1.16) | 0.92 (0.08) |
| 7 | 31 (2.4) | 45 (16.3) | 0.01 (0.1) | 835 (17.8) | 11.97 | 1.14 (0.15) | 3.20 (0.49) | 5.94 (0.68) | 6.99 (1.24) | 0.86 (0.07) |
| 8 | 29 (1.0) | 65 (6.3) | 0.3 (1.6) | 781 (31.2) | 10.68 | 1.01 (0.11) | 2.99 (0.49) | 4.75 (0.54) | 5.80 (0.74) | 0.82 (0.07) |
| 9 | 27 (0.9) | 58 (8.9) | 0.01 (0.1) | 703 (59.2) | 9.53 | 0.87 (0.18) | 3.01 (0.60) | 3.93 (0.53) | 4.94 (0.77) | 0.80 (0.13) |
| 10 | 22 (1.0) | 64 (7.8) | 0.18 (0.4) | 531 (84.3) | 7.94 | 0.65 (0.18) | 2.91 (0.83) | 2.22 (0.52) | 3.49 (0.86) | 0.64 (0.13) |
| 11 | 17 (3.5) | 71 (6.2) | 0.35 (1.0) | 459 (60.1) | 6.63 | 0.72 (0.38) | 2.91 (0.74) | 1.63 (0.37) | 2.46 (0.60) | 0.67 (0.11) |
| 12 | 13 (1.5) | 78 (4.9) | 1.05 (3.4) | 369 (68.0) | 6.13 | 0.55 (0.31) | 2.57 (1.08) | 1.08 (0.33) | 1.49 (0.35) | 0.73 (0.18) |
| AVG | 20 (7.5) | 66 (12.5) | 0.75 (3.0) | 660 (191.9) | 8.94 | 0.88 (0.37) | 3.12 (0.89) | 3.02 (1.70) | 3.61 (1.95) | 0.84 (0.16) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolaou, G.; Neocleous, D.; Evangelides, E.; Kitta, E. A Decision Support System for Irrigation Scheduling Using a Reduced-Size Pan. Agronomy 2025, 15, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040848
Nikolaou G, Neocleous D, Evangelides E, Kitta E. A Decision Support System for Irrigation Scheduling Using a Reduced-Size Pan. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040848
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolaou, Georgios, Damianos Neocleous, Efstathios Evangelides, and Evangelini Kitta. 2025. "A Decision Support System for Irrigation Scheduling Using a Reduced-Size Pan" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040848
APA StyleNikolaou, G., Neocleous, D., Evangelides, E., & Kitta, E. (2025). A Decision Support System for Irrigation Scheduling Using a Reduced-Size Pan. Agronomy, 15(4), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040848







