Effects of Peanut Insertion on Soil Dynamics in Fallow Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Presentation of the Experiments
2.1.1. Experiment I—Tests in a Masonry Frame
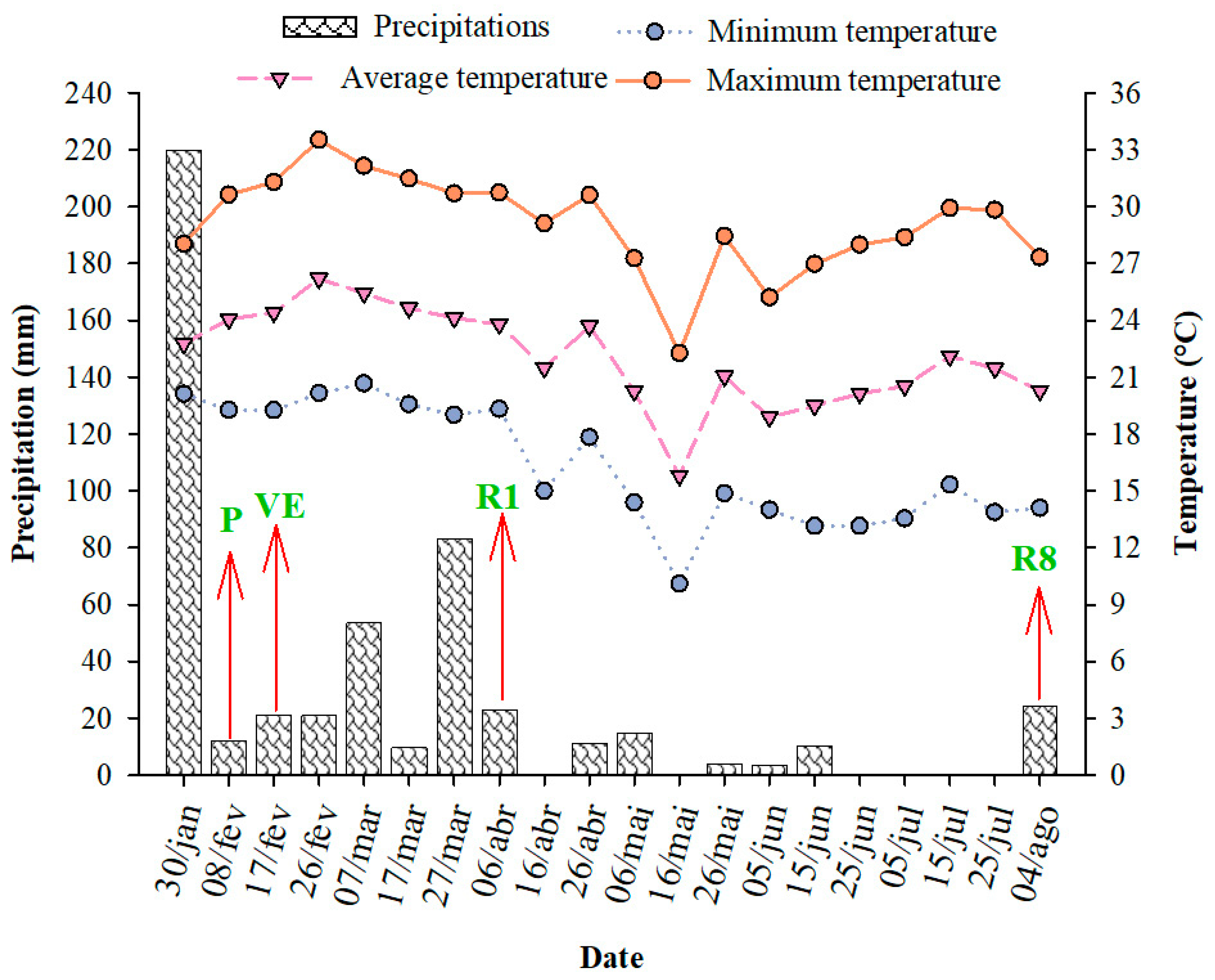
2.1.2. Experiment II—Field
2.2. Variables Analyzed
2.2.1. Soil Chemistry
2.2.2. Activity of β-Glucosidase and Arylsulfatase
2.2.3. Leaf Area and Dry Matter
2.2.4. Productivity
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Experiment I—Tests in a Masonry Frame
3.1.1. Biometric and Productive Evaluation of Peanuts
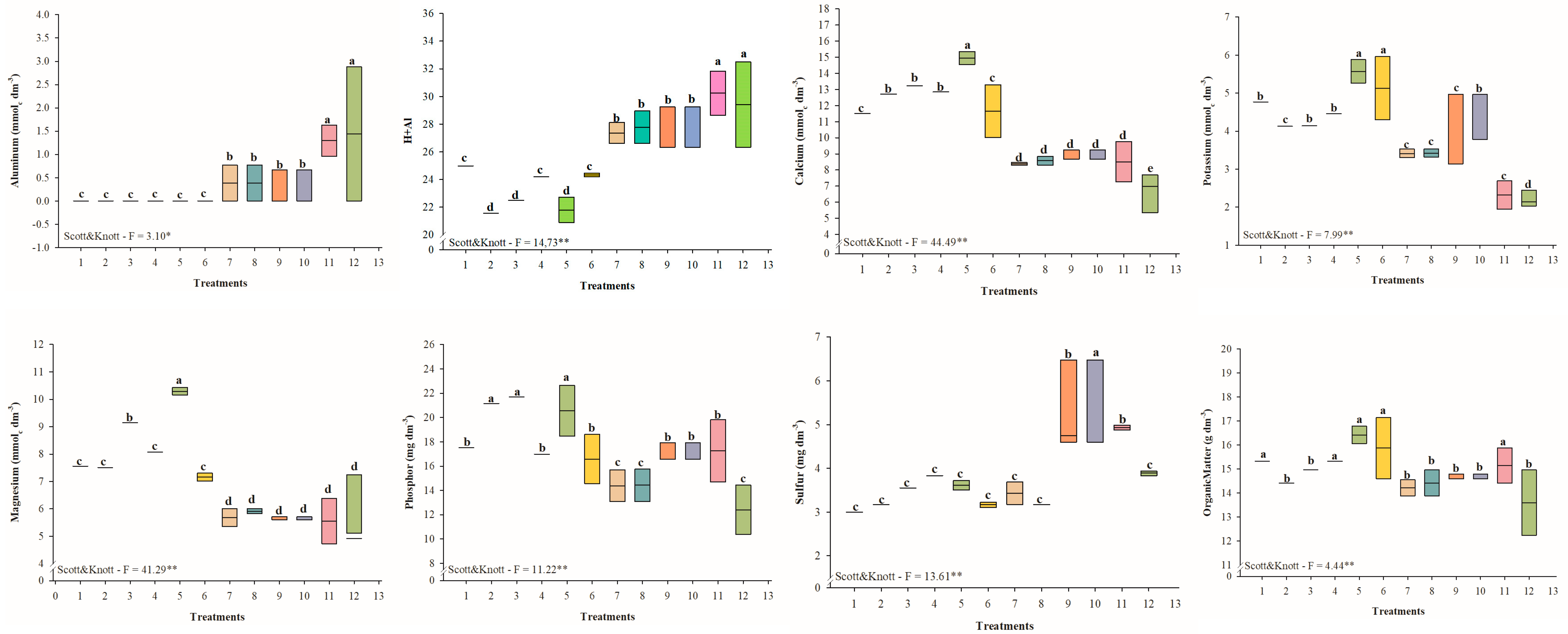
3.1.2. Soil Chemical Assessment
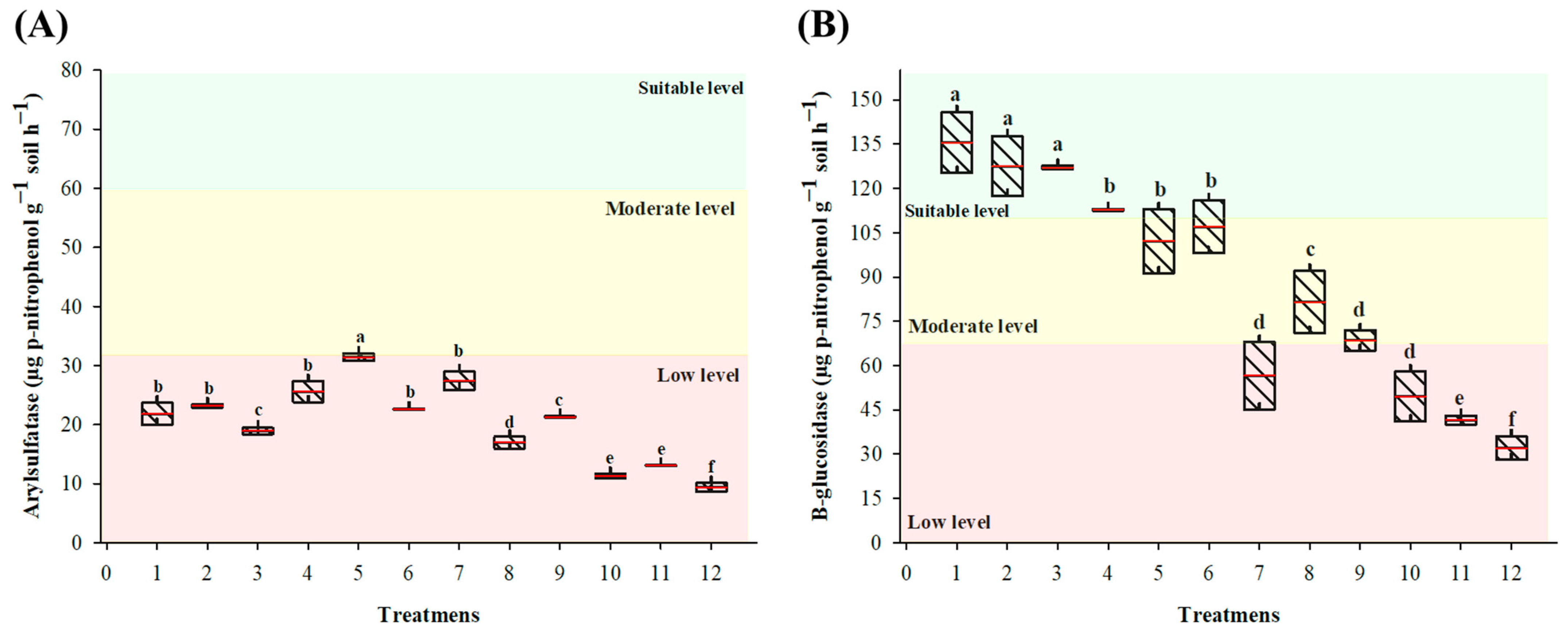
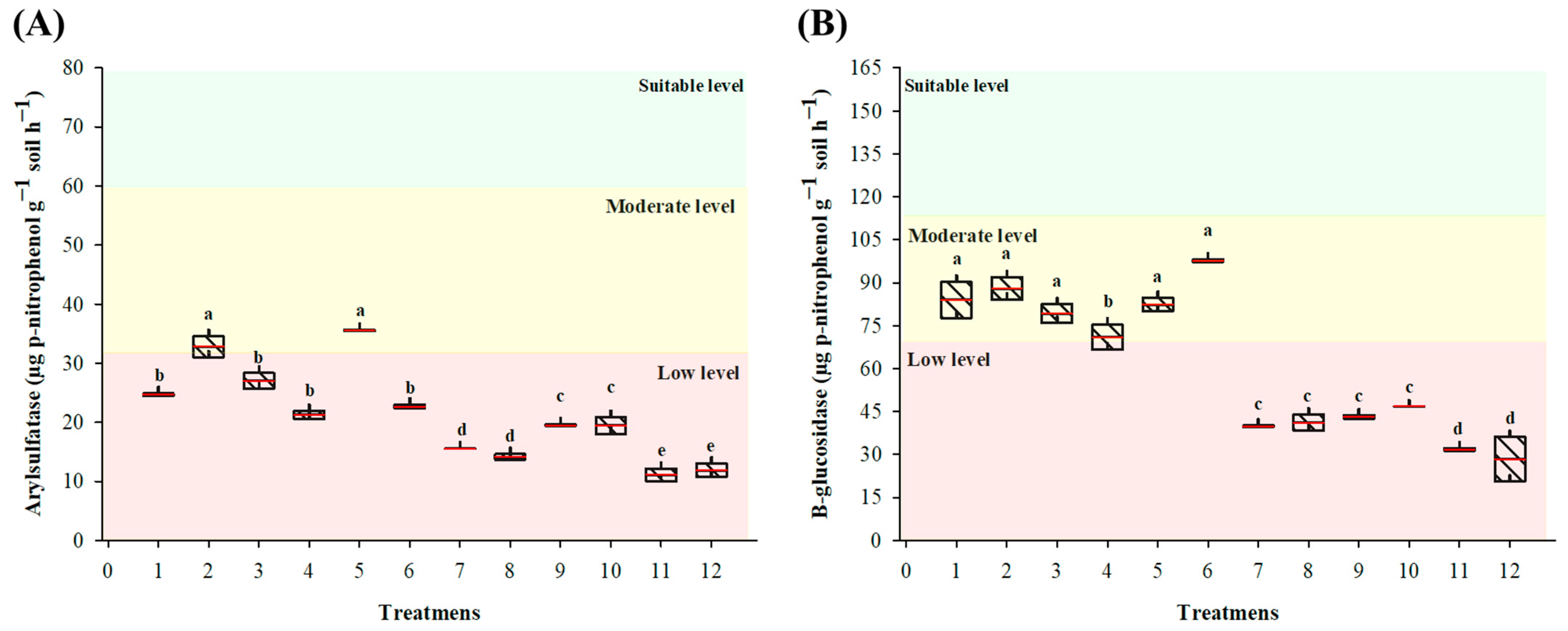
3.1.3. Assessment of Soil Enzyme Activity
3.2. Experiment II—Field
3.2.1. Peanut Evaluation
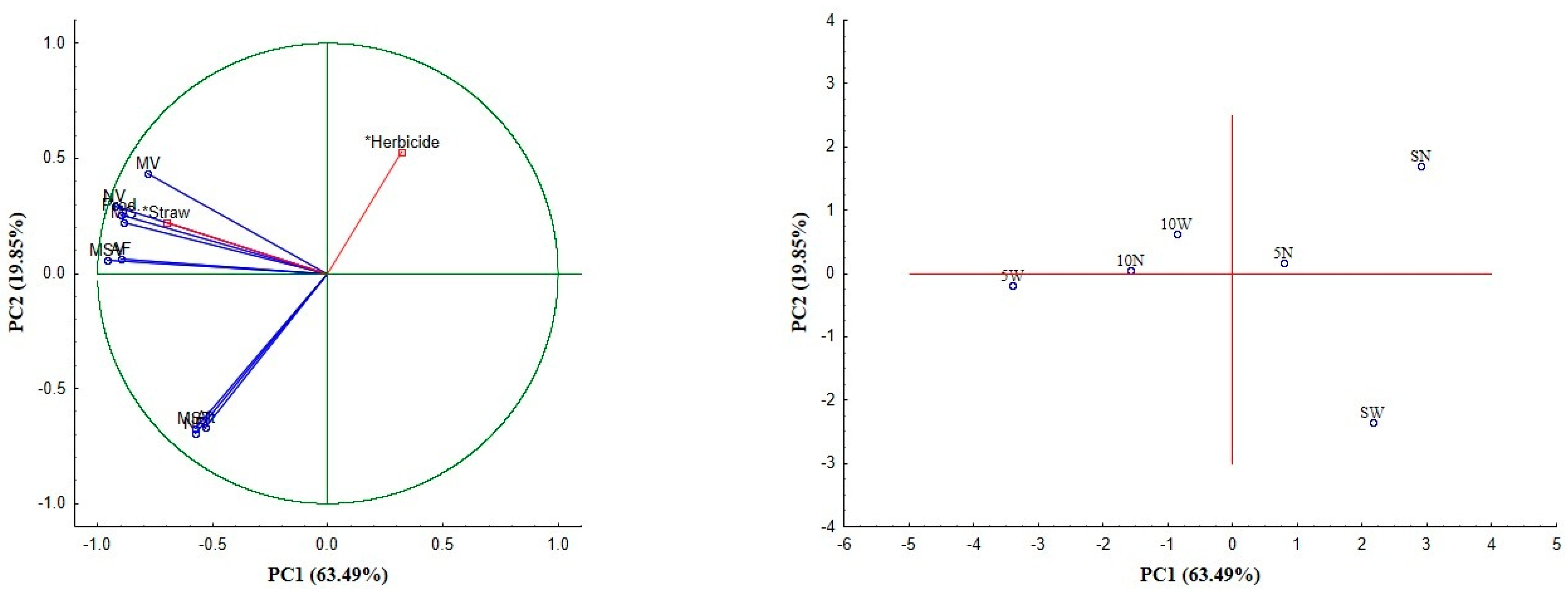
Multivariate Analysis of Plant Data
3.2.2. Soil Chemical Assessment
3.2.3. Assessment of Soil Enzyme Activity
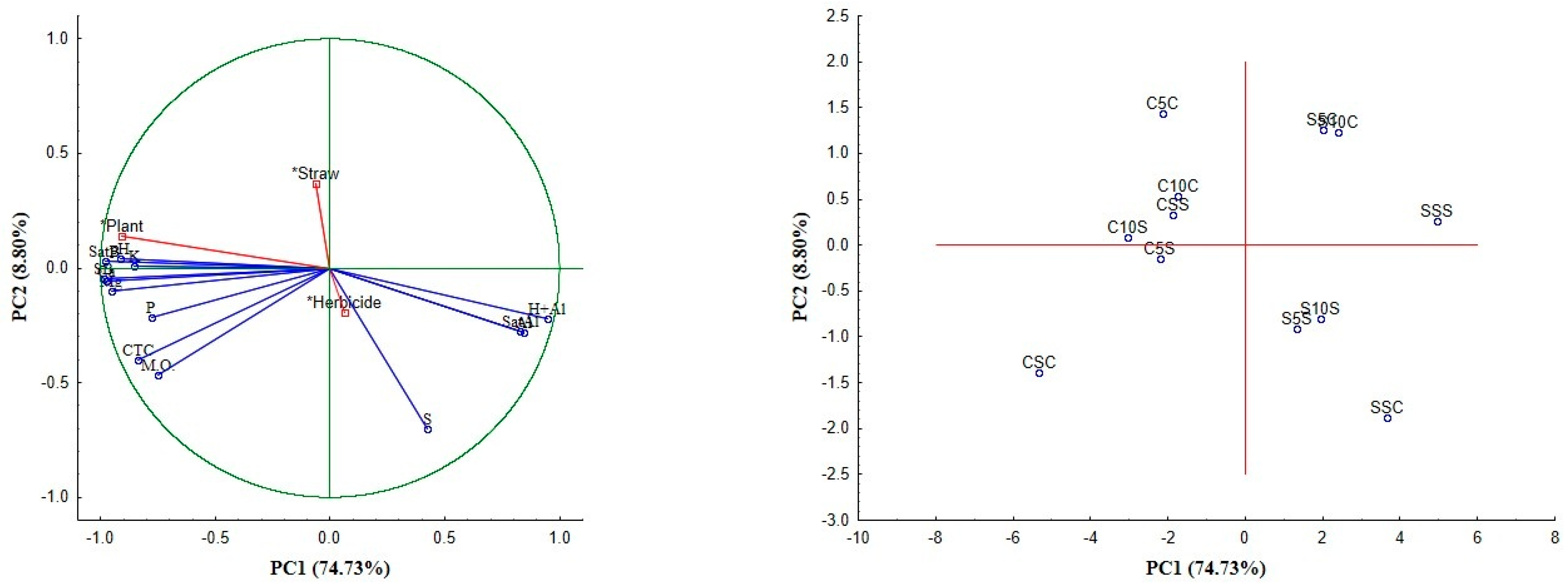
3.2.4. Multivariate Analysis of Soil Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almeida, C.L.; Oliveira, J.G.B.; Araújo, J.C. Impacto da recuperação de área degradada sobre as respostas hidrológicas e sedimentológicas em ambiente semiárido. Water Resour. Irrig. Manag. 2012, 1, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel Vasconcelos, L.G.T.; Kato, O.R.; Vasconcelos, S.S. Matéria orgânica leve do solo em sistema agroflorestal de corte e trituração sob manejo de capoeira. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2012, 47, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherr, C.M.; Scholberg, J.M.S.; McSorley, R. Green Manure Approaches to Crop Production: A Synthesis. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbinot, A.A., Jr.; Moraes, A.; Pelissari, A.; Dieckow, J.; Veiga, M. Formas de uso do solo no inverno e sua relação com a infestação de plantas daninhas em milho (Zea mays) cultivado em sucessão. Planta Daninha 2008, 26, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yao, P.; Na, Z.; Yu, C.; Cao, W.; Gao, Y. Contribution of green manure legumes to nitrogen dynamics in traditional winter wheat cropping system in the Loess Plateau of China. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 72, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T. Aspectos sanitários da cultura do amendoim. Rev. Eletrôn. Biol. 2014, 7, 301–320. [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto, C.P.; Gonçalves, J.A.; de Fátima da Silva Pinto Peixoto, M.; Carmo, D.O.D. Características agronômicas e produtividade de amendoim em diferentes espaçamentos e épocas de semeadura no Recôncavo Baiano. Bragantia 2008, 67, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAB. Acompanhamento da Safra Brasileira de Grãos; Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento: Sobral, Brazil, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosio, L.M.S.; Bolonhezi, D.; Barini, R.T.; Betiol, V.; Gonçalves, L.H.O.; Leal, E.R.P.; Scarpellini, J.R. Análise de Crescimento de Cultivares de Amendoim em Diferentes Sistemas de Manejo do Solo na Palhada de Cana Crua. In Anais; Instituto Agronômico: Campinas, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sholar, J.R.; Mozingo, R.W.; Beasley, J.P., Jr. Peanut cultural practices. In Advances in Peanut Science. Stillwater; American Peanut Research and Education Society: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1995; pp. 354–382. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, F.S.; Porter, D.M. Digging Date and Conservational Tillage Influence on Peanut Production1. Peanut Sci. 1991, 18, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkcom, K.S.; Tubbs, R.S.; Balkcom, K.B. Strip Tillage Implements for Single and Twin Row Peanut. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betiol, O.; Bolonhezi, D.; Leal, É.R.P.; Gruener, C.E.; Michelotto, M.D.; Furlani, C.E.A.; Ruiz, F.F. Conservation agriculture practices in a peanut cropping system: Effects on pod yield and soil penetration resistance. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2023, 47, e0230004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubbs, R.S. The Future of Peanut Agronomic Research–The Sky is Not the Limit. Peanut Sci. 2019, 46, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreefel, L.; Schulte, R.P.O.; de Boer, I.J.M.; Schrijver, A.P.; van Zanten, H.H.E. Regenerative agriculture—The soil is the base. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 26, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, C.C.; Krzywoszynska, A.; Leake, J.R.; Dicks, L.v. Sustainable soil management in the United Kingdom: A survey of current practices and how they relate to the principles of regenerative agriculture. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri-Polizeli, K.M.V.; Guedes Filho, O.; Romanoski, V.S.; Ruthes, B.E.S.; Calábria, Z.P.; de Oliveira, L.B. Conservative farming systems and their effects on soil organic carbon and structural quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 242, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, I.C.; Sousa, D.M.G.; Reis, F.B., Jr.; Kappes, C.; Ono, F.B.; Semler, T.D.; Zancanaro, L.; Lopes, A.A.C. Qualidade biológica do solo: Por que e como avaliar. In Boletim de Pesquisa da Fundação; EMBRAPA: Brasília, Brazil, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, I.C.; Ono, F.B.; Oliveira, M.I.; Silva, R.G.; Kappes, C.; Reis Junior, F.B.; Zancanaro, L. Bioanálise de solo: A mais nova aliada para a sustentabilidade agrícola.Informações Agronômicas. 2020. Available online: https://www.alice.cnptia.embrapa.br/alice/handle/doc/1128778 (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- de Carvalho Mendes, I.; de Souza, L.M.; de Sousa, D.M.G.; de Castro Lopes, A.A.; dos Reis, F.B., Jr.; Lacerda, M.P.C.; Malaquias, J.V. Critical limits for microbial indicators in tropical Oxisols at post-harvest: The FERTBIO soil sample concept. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 139, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, I.C.; Martinhão Gomes Sousa, D.; Dario Dantas, O.; Alves Castro Lopes, A.; Bueno Reis Junior, F.; Ines Oliveira, M.; Montandon Chaer, G. Soil quality and grain yield: A win–win combination in clayey tropical oxisols. Geoderma 2021, 388, 114880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, R.G.; de Figueiredo, C.C.; Malaquias, J.V.; Mendes, I.C. A soil health assessment tool for vegetable cropping systems in tropical soils based on beta-glucosidase, arylsulfatase, and soil organic carbon. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 198, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.A.C.; Sousa, D.M.G.; Reis, F.B., Jr.; Figueiredo, C.C.; Malaquias, J.V.; Souza, L.M.; Mendes, I.C. Temporal variation and critical limits of microbial indicators in oxisols in the Cerrado, Brazil. Geoderma Reg. 2018, 12, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.A.C.; Sousa, D.M.G.; Chaer, G.M.; Reis Junior, F.B.; Goedert, W.J.; Mendes, I.C. Interpretation of microbial soil indicators as a function of crop yield and organic carbon. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim, M.E.; Zeviani, W.M.; Ono, F.B.; Neves, L.G.; Silva, B.M.; Lal, R. Reference values and soil quality in areas of high soybean yield in Cerrado region, Brazil. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, I.C.; Chaer, G.M.; Reis Junior, F.B.; Dantas, O.D.; Malaquias, J.V.; Oliveira, M.I.L.; Nogueira, M.A.; Hungira, M. Soil Bioanalysis (SoilBio): A Sensitive, Calibrated, and Simple Assessment of Soil Health for Brazil. In Soil Health Series: Volume 3 Soil Health and Sustainable Agriculture in Brazil; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2024; pp. 292–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fávero, A.P.; Pádua, J.G.; Costa, T.S.; Gimenes, M.A.; Godoy, I.J.; Moretzsohn, M.C.; Michelotto, M.D. New hybrids from peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and synthetic amphidiploid crosses show promise in increasing pest and disease tolerance. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 16694–16703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; de Moraes Gonçalves, J.L.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, P.C.; Donagemma, G.K.; Fontana, A.; Teixeira, W.G. Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solo, 3rd ed.; EMBRAPA: Dourados, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Wickham, M.H. Package ‘ggplot2’. Create elegant data visualisations using the grammar of graphics. Version 2016, 2, 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Leonel, C.L. Influência do Preparo do Solo em Área de Reforma de Canavial na Qualidade Física do Solo e na Cultura do Amendoim. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista, Faculdade de Ciências Agrárias e Veterinárias, São José do Rio Preto, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bolonhezi, D.; Leal, R.P. Manejo conservador do solo para amendoim. In A Cultura do Amendoim e Seus Reflexos Econômicos, Sociais e Técnicos; Foundation for Research, Education and Extension Support: Jaboticabal, Brazil, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 30–44. [Google Scholar]
- Anache, J.A.A.; Wendland, E.C.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Flanagan, D.C.; Nearing, M.A. Runoff and soil erosion plot-scale studies under natural rainfall: A meta-analysis of the Brazilian experience. CATENA 2017, 152, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, J.A.; Ramsey, S.; Sandefur, H.N. A Historical Analysis of the Environmental Footprint of Peanut Production in the United States from 1980 to 2014. Peanut Sci. 2016, 43, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiz, L.; Zeiger, E.; Møller, I.M.; Murphy, A. Fisiologia e Desenvolvimento Vegetal; Artmed Editora: São Paulo, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, M.E. Calcium requirements for peanuts. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1975, 6, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, E.A.S. Are calcium oxalate crystals a dynamic calcium store in plants? New Phytol. 2019, 223, 1707–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.R.; Karimi, N. The role of calcium in plants’ salt tolerance. J. Plant Nutr. 2012, 35, 2037–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolonhezi, D.; Mutton, M.Â.; Martins, A.L.M. Sistemas conservacionistas de manejo do solo para amendoim cultivado em sucessão à cana crua. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2007, 42, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolonhezi, D.; Valochi, R.; Zanandrea, P.C.; Scarpelline, J.R.; Ambrosio, L.M.S.; Gonçalves, L.H.O.; Barini, R.T.; Bolonhezi, A.C. Peanut pod yield and soil compaction in conservation agriculture system. In Proceedings in 1st World Conference on Soil and Water Conservation Under Global Change 2017, Lledia, Spain, 12 June–16 June 2017; Spain, L., Simó, I., Poch, R.M., Eds.; pp. 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- D’Amico-Damião, V.; Barroso, A.A.M.; da Costa Aguiar Alves, P.L.; Lemos, L.B. Intercropping maize and succession crops alters the weed community in common bean under no-tillage. Pesqui. Agropecu. Trop. 2020, 50, e65244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Qi, J.; Peng, Z.; Chen, B.; Pan, H.; Liang, C.; Liu, J.; et al. Agricultural tillage practice and rhizosphere selection interactively drive the improvement of soybean plant biomass. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 3542–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, G.; Dhaka, A.K.; Singh, B.; Kumar, A.; Choudhary, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Kamboj, N.K.; Hasanain, M.; Singh, S.; Bhupenchandra, I.; et al. Productivity, soil health, and carbon management index of soybean-wheat cropping system under double zero-tillage and natural-farming based organic nutrient management in north-Indian plains. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorburn, P.J.; Biggs, J.S.; Palmer, J.; Meier, E.A.; Verburg, K.; Skocaj, D.M. Prioritizing crop management to increase nitrogen use efficiency in Australian sugarcane crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmero, F.; Carcedo, A.J.P.; Haro, R.J.; Bigatton, E.D.; Salvagiotti, F.; Ciampitti, I.A. Modeling drought stress impacts under current and future climate for peanut in the semiarid pampas region of Argentina. Field Crops Res. 2022, 286, 108615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovando, G.; Haro, R.J. Uso do modelo CSM-CROPGRO-Peanut para estimar a época ideal de semeadura e produtividade da água da cultura sob diferentes teores de água no solo na Argentina. S. Am. Sci. 2022, 3, e22188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concenço, G.; Leme Filho, J.R.A.; Silva, C.J. O aleiramento do palhiço de cana-de-açúcar agrava a infestação de plantas daninhas. In Embrapa Agropecuária Oeste-Comunicado Técnico; Embrapa: Dourados, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mingotte, F.L.C.; Lemos, L.B.; Jardim, C.A.; Fornasieri Filho, D. Crop systems and topdressing nitrogen on grain yield and technological attributes of common bean under no-tillage. Pesqui. Agropecu. Trop. 2019, 49, e54003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Yi, L.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Lin, C.; Tang, H.; Yang, G.; Xiao, X. Nitrogen release from incorporated 15N-labelled Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) residue and its dynamics in a double rice cropping system. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Wolf, B.; Kiese, R.; Chen, D.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Trade-offs between soil carbon sequestration and reactive nitrogen losses under straw return in global agroecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 5919–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahad, S.; Hussain, S.; Saud, S.; Hassan, S.; Tanveer, M.; Ihsan, M.Z.; Shah, A.N.; Ullah, A.; Nasrullah; Khan, F.; et al. A combined application of biochar and phosphorus alleviates heat-induced adversities on physiological, agronomical and quality attributes of rice. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Feng, J.; Zhai, S.; Dai, Y.; Xu, M.; Wu, J.; Shen, M.; Bian, X.; Koide, R.T.; Liu, J. Long-term ditch-buried straw return alters soil water potential, temperature, and microbial communities in a rice-wheat rotation system. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Lai, H.; Pan, X.; Yang, D.; Li, X. A 2-year study on the effects of tillage and straw management on the soil quality and peanut yield in a wheat–peanut rotation system. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 21, 1698–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J. The effects of pH on phosphate uptake from the soil. Plant Soil 2017, 410, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, E.; Luo, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, C.; Lu, X.; Jiang, L.; Luo, X.; Wen, D. Global meta-analysis shows pervasive phosphorus limitation of aboveground plant production in natural terrestrial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogollón, J.M.; Beusen, A.H.W.; van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Westhoek, H.; Bouwman, A.F. Future agricultural phosphorus demand according to the shared socioeconomic pathways. Glob. Environ. Change 2018, 50, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.W.; Condron, L.M. Chemical nature and potential mobility of phosphorus in fertilized grassland soils. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2000, 57, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessa, C.E.; Mimmo, T.; Deiana, S.; Marzadori, C. Effect of aluminium and pH on the mobility of phosphate through a soil-root interface model. Plant Soil 2005, 272, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asomaning, S.K. Processes and factors affecting phosphorus sorption in soils. In Sorption in 2020s; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; Volume 45, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, R.P. Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment; Doran, J.W., Coleman, D.C., Bezdicek, D.F., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, B.; ur-Rahman, M.; Adnan Ramzani, P.M.; Zubair, M.; Khan, M.A.; Lewińska, K.; Turan, V.; Karczewska, A.; Khan, S.A.; Farhad, M.; et al. Impacts of oxalic acid-activated phosphate rock and root-induced changes on Pb bioavailability in the rhizosphere and its distribution in mung bean plant. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, P.R.; Lal, R. Effects of different mulch materials on soil properties and on the root growth and yield of maize (Zea mays) and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Field Crops Res. 1981, 4, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherene, T. Role of soil enzymes in nutrient transformation: A review. Bio Bull. 2017, 3, 109–131. [Google Scholar]
- Serafim, M.E.; Mendes, I.C.; Wu, J.; Ono, F.B.; Zancanaro, L.; Valendorff, J.D.P.; Zeviani, W.M.; Pierangeli, M.A.P.; Fan, M.; Lal, R. Soil physicochemical and biological properties in soybean areas under no-till Systems in the Brazilian Cerrado. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; He, J.; Yan, X.; Hong, Q.; Chen, K.; He, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Chuang, S.; Li, S.; et al. Microbial catabolism of chemical herbicides: Microbial resources, metabolic pathways and catabolic genes. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 143, 272–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Factors Affecting Soil Arylsulfatase Activity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1970, 34, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitti, G.C.; Otto, R.; Savieto, J. Manejo do enxofre na agricultura. In Informações Agronômica; Internacional Plant Nutrition Institute: Piracicaba, Brazil, 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Funkler, R.; Pedroso, R.M.; Stein, R.T.; Lazzarini, P.R.C. Ciência do Solo e Fertilidade; Grupo A: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Santos Bastos, T.R.; Barreto-Garcia, P.A.B.; de Carvalho Mendes, I.; Monroe, P.H.M.; de Carvalho, F.F. Response of soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity in coffee-based agroforestry systems in a high-altitude tropical climate region of Brazil. Catena 2023, 230, 107270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, R.P.; Burns, R.G. Methods of Soil Enzymology; Dick, R.P., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjati, S.; Nourbakhsh, F. Effects of cow manure and sewage sludge on the activity and kinetics of l-glutaminase in soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 43, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Trat. | Alt. | PN | LA | TDM | DMG | TRCT | CAN. | Prod. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm | - | cm2 | g | g | UR | % | kg ha−1 | |
| T1 | 30.00 a | 36 a | 1934.42 a | 84.46 a | 21.02 a | 58.7 a | 81.5 a | 3460 a |
| T2 | 28.00 a | 29 a | 1792.12 a | 57.96 b | 14.47 a | 50.30 a | 57.13 b | 2424 b |
| T3 | 24.00 b | 22 b | 1395.48 b | 57.04 b | 6.36 b | 47.75 a | 51.9 b | 2382 b |
| T4 | 23.66 b | 22 b | 1165.30 b | 47.23 b | 5.89 b | 47.40 a | 48.7 b | 1974 b |
| T5 | 23.33 b | 12 c | 607.55 c | 31.79 b | 3.80 b | 27.23 b | 48.63 b | 1048 c |
| T6 | 21.66 b | 11 c | 418.92 c | 26.38 c | 2.45 b | 21.36 b | 46.93 b | 484 c |
| Factor | 8.16 ** | 20.49 ** | 22.31 | 4.88 ** | 8.24 * | 12.21 ** | 1.26 * | 4.0 * |
| CV (%) | 7.68 | 23.08 | 18.43 | 32.12 | 40.10 | 18.45 | 26.18 | 42.28 |
| Treats. | pH | OM | SOC | P | K | SB | CEC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | g dm3 | % | g kg−1 | mg dm3 | mmolc dm3 | - | - | |
| T1 | 6.48 b | 17.15 b | 1.71 | 29.59 b | 71.82 b | 3.41 b | 51.53 c | 65.68 d |
| T2 | 6.70 a | 20.50 a | 2.05 | 35.36 a | 91.72 a | 4.03 a | 60.93 a | 74.92 a |
| T3 | 6.33 c | 15.02 d | 1.50 | 25.92 d | 51.92 c | 3.12 c | 50.00 c | 66.40 d |
| T4 | 6.36 c | 14.12 d | 1.41 | 24.35 d | 41.71 c | 1.80 f | 42.19 f | 60.02 f |
| T5 | 6.37 c | 17.52 b | 1.75 | 30.22 b | 66.69 b | 2.22 e | 50.31 c | 68.72 c |
| T6 | 6.44 b | 16.47 c | 1.64 | 28.41 b | 46.57 c | 3.63 b | 51.87 c | 66.65 d |
| T7 | 6.25 d | 17.53 b | 1.75 | 30.25 b | 41.58 c | 4.00 a | 51.07 c | 68.72 c |
| T8 | 6.17 d | 14.72 d | 1.47 | 25.40 d | 29.42 d | 2.78 d | 45.05 e | 64.45 e |
| T9 | 6.21 d | 17.02 b | 1.70 | 31.43 b | 34.04 d | 3.96 a | 46.33 d | 64.36 e |
| T10 | 6.11 e | 15.94 c | 1.59 | 27.50 c | 51.56 c | 3.31 c | 47.23 d | 64.33 e |
| T11 | 6.05 e | 4.72 e | 0.47 | 4.84 e | 35.88 d | 2.77 d | 53.86 b | 71.14 b |
| T12 | 6.10 e | 2.80 f | 0.28 | 5.14 e | 28.44 d | 2.33 e | 37.52 g | 55.26 g |
| Causes of variation | ||||||||
| Ftrat | 31.51 ** | 92.10 ** | 92.25 * | 16.42 ** | 51.26 ** | 64.86 ** | 108.39 ** | |
| CV (%) | 0.91 | 6.62 | 6.61 | 15.63 | 5.79 | 2.07 | 1.27 | |
| Trat. | Alt. | PN | DPM | LA | TDM | DMG | Prod. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm | - | - | cm2 | g | g | kg ha−1 | |
| T1 | 28.00 a | 18 a | 14.81 a | 1341.92 a | 42.28 a | 7.81 a | 1722 a |
| T2 | 29.33 a | 15 a | 10.40 a | 1917.95 a | 45.97 a | 7.77 a | 1381 a |
| T3 | 29.66 a | 13 a | 8.64 b | 826.73 b | 36.96 a | 8.12 a | 1430 a |
| T4 | 30.00 a | 14 a | 4.27 b | 667.38 b | 36.16 a | 6.10 a | 1084 a |
| T5 | 24.33 b | 6 b | 2.14 c | 470.21 b | 34.51 a | 1.65 b | 562 b |
| T6 | 20.00 c | 3 b | 1.89 c | 408.92 b | 29.16 a | 1.23 b | 457 b |
| Causes of variation | |||||||
| Ftrat | 3.43 * | 11.58 ** | 3.43 * | 8.86 ** | 0.25 ns | 4.09 * | 3.45 * |
| CV (%) | 13.32 | 29.17 | 30.50 | 36.03 | 42.92 | 20.10 | 42.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, H.L.; Korasaki, V.; Campalle, A.N.; Zanqueta, J.F.D.; de Oliveira, A.B.; Parreira, M.C.; Alves, P.L.d.C.A. Effects of Peanut Insertion on Soil Dynamics in Fallow Areas. Agronomy 2025, 15, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040912
Martins HL, Korasaki V, Campalle AN, Zanqueta JFD, de Oliveira AB, Parreira MC, Alves PLdCA. Effects of Peanut Insertion on Soil Dynamics in Fallow Areas. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040912
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Heytor Lemos, Vanesca Korasaki, Arthur Nardi Campalle, João Francisco Damião Zanqueta, Andrey Batalhão de Oliveira, Mariana Casari Parreira, and Pedro Luís da Costa Aguiar Alves. 2025. "Effects of Peanut Insertion on Soil Dynamics in Fallow Areas" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040912
APA StyleMartins, H. L., Korasaki, V., Campalle, A. N., Zanqueta, J. F. D., de Oliveira, A. B., Parreira, M. C., & Alves, P. L. d. C. A. (2025). Effects of Peanut Insertion on Soil Dynamics in Fallow Areas. Agronomy, 15(4), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040912









