Modelling Exposure from Airborne Hazardous Short-Duration Releases in Urban Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Statement of the hypotheses connecting the short-release ensemble average dosage and its standard deviation with the corresponding continuous-release mean concentration and its standard deviation (Section 2).
- Theoretical establishment of the relationship between short duration release ensemble average dosage and corresponding continuous release mean steady-state concentration (Section 2.1).
- Theoretical establishment of the relationship between short duration release dosage standard deviation and corresponding continuous release concentration standard deviation (Section 2.2).
- Experimental evidence in support of the proposed relationships (Section 3.1).
- Experimental evidence of the relationship between peak concentration and dosage statistics for short-duration releases (Section 3.2).
- Experimental evidence supporting that the probability/cumulative density function for puff ensemble average dosage and peak concentration can be approximated by the beta function (Section 3.3).
- Conclusions (Section 4).
2. Methodology
2.1. Finite Duration Release Ensemble Average Dosage () vs. Corresponding Continuous Release Mean Steady-State Concentration ()
2.2. Short Release Dosage Standard Deviation () vs. Corresponding Continuous Release Concentration Standard Deviation ()
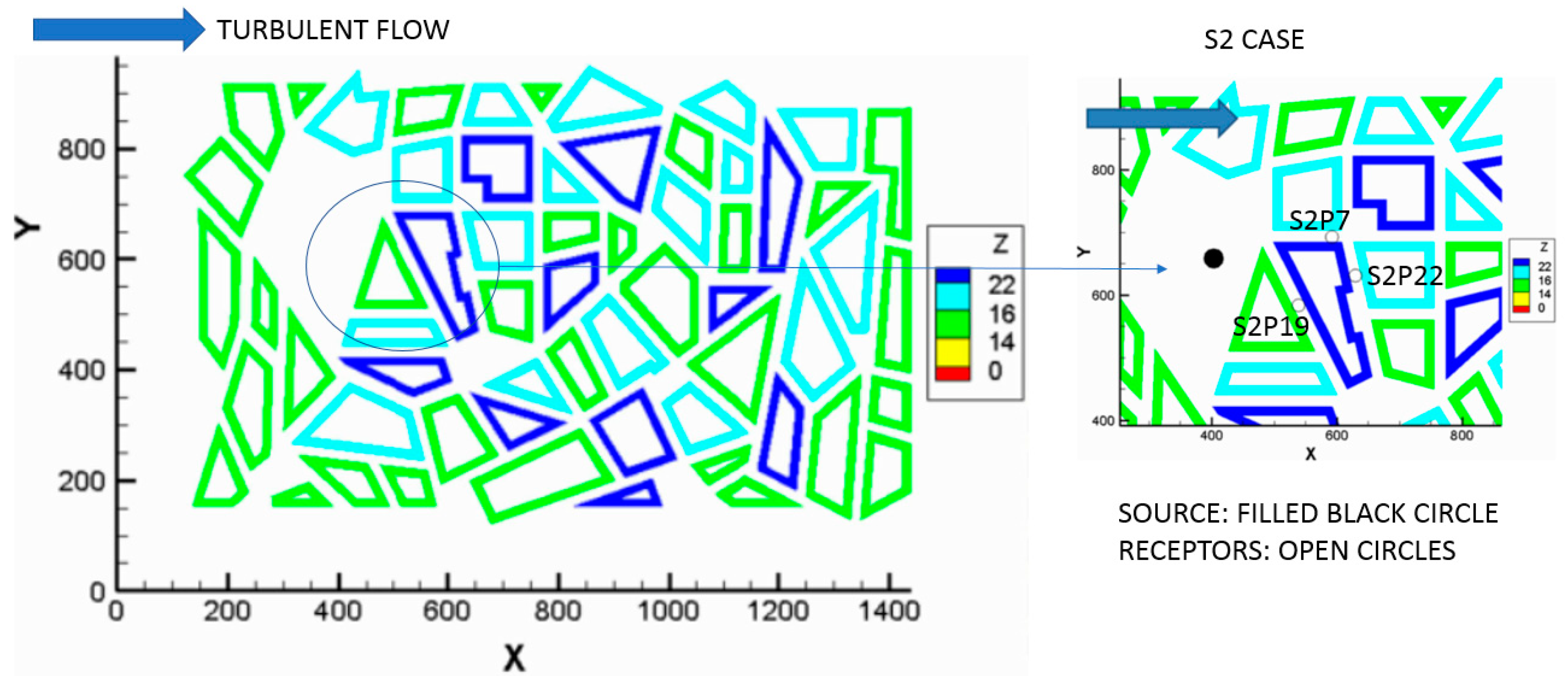
3. The Experimental Evidence: The S2 Michelstadt Experiment for Puff and Continuous Releases
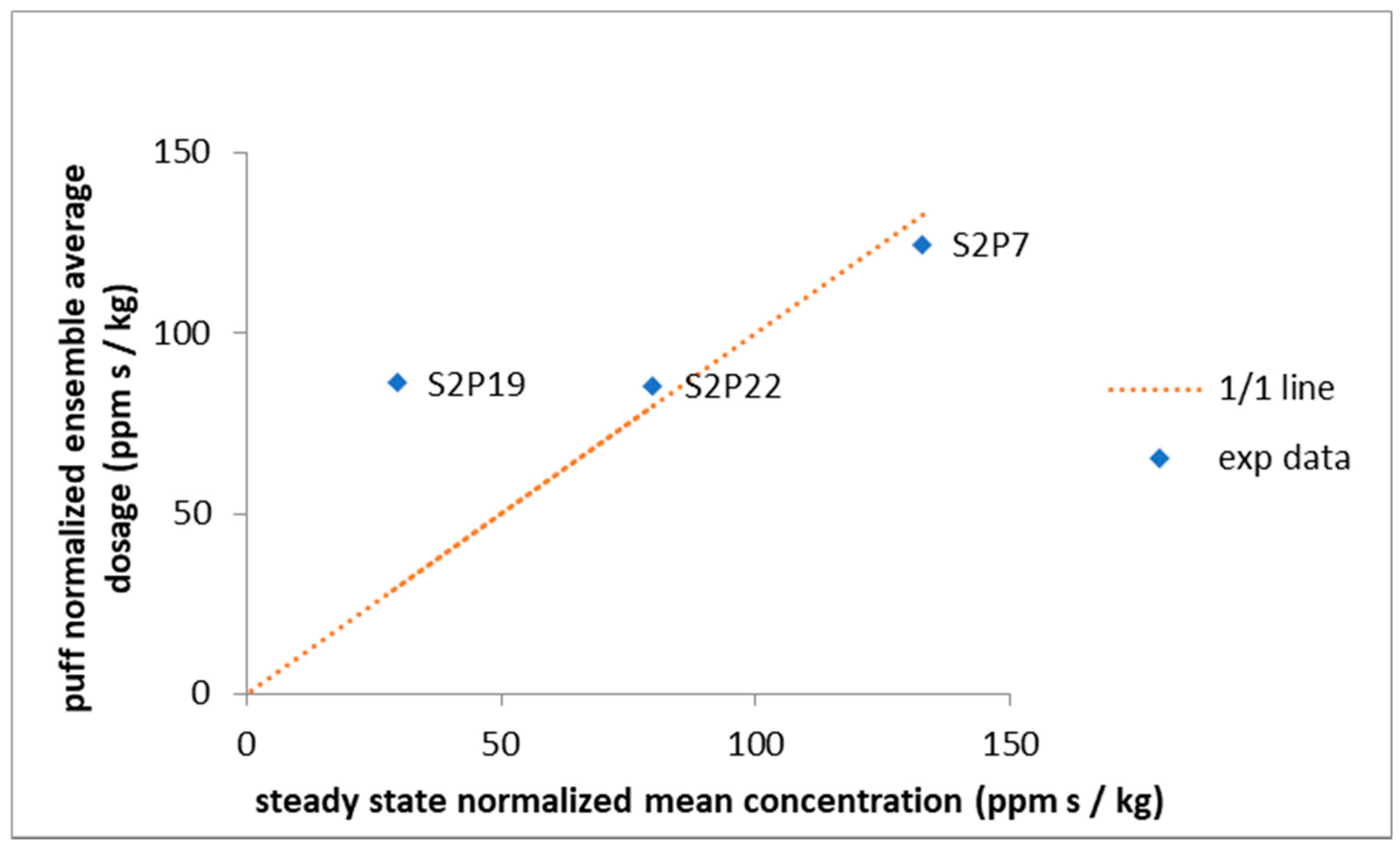
3.1. The Puff Releases vs. the Continuous Release Comparisons
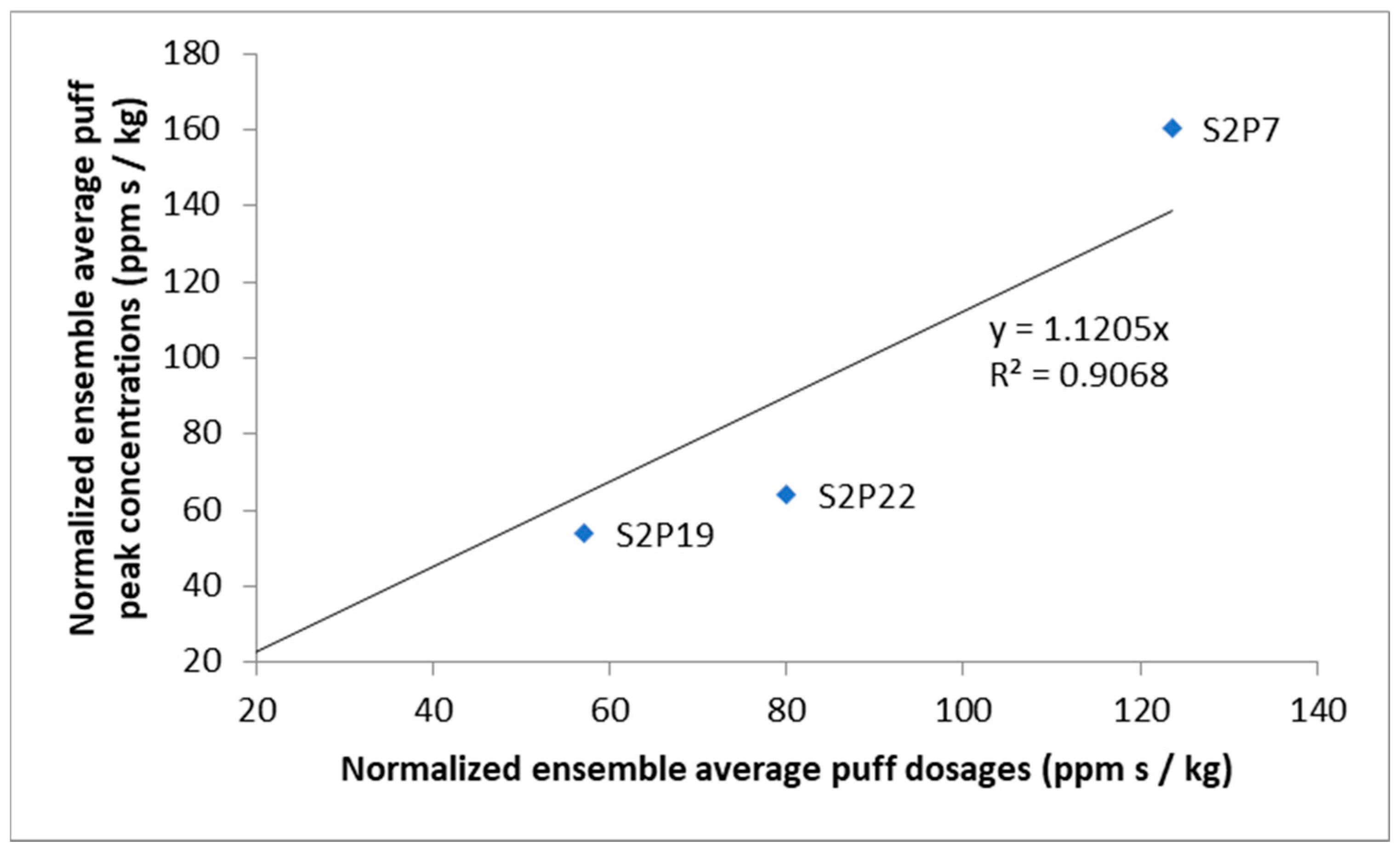
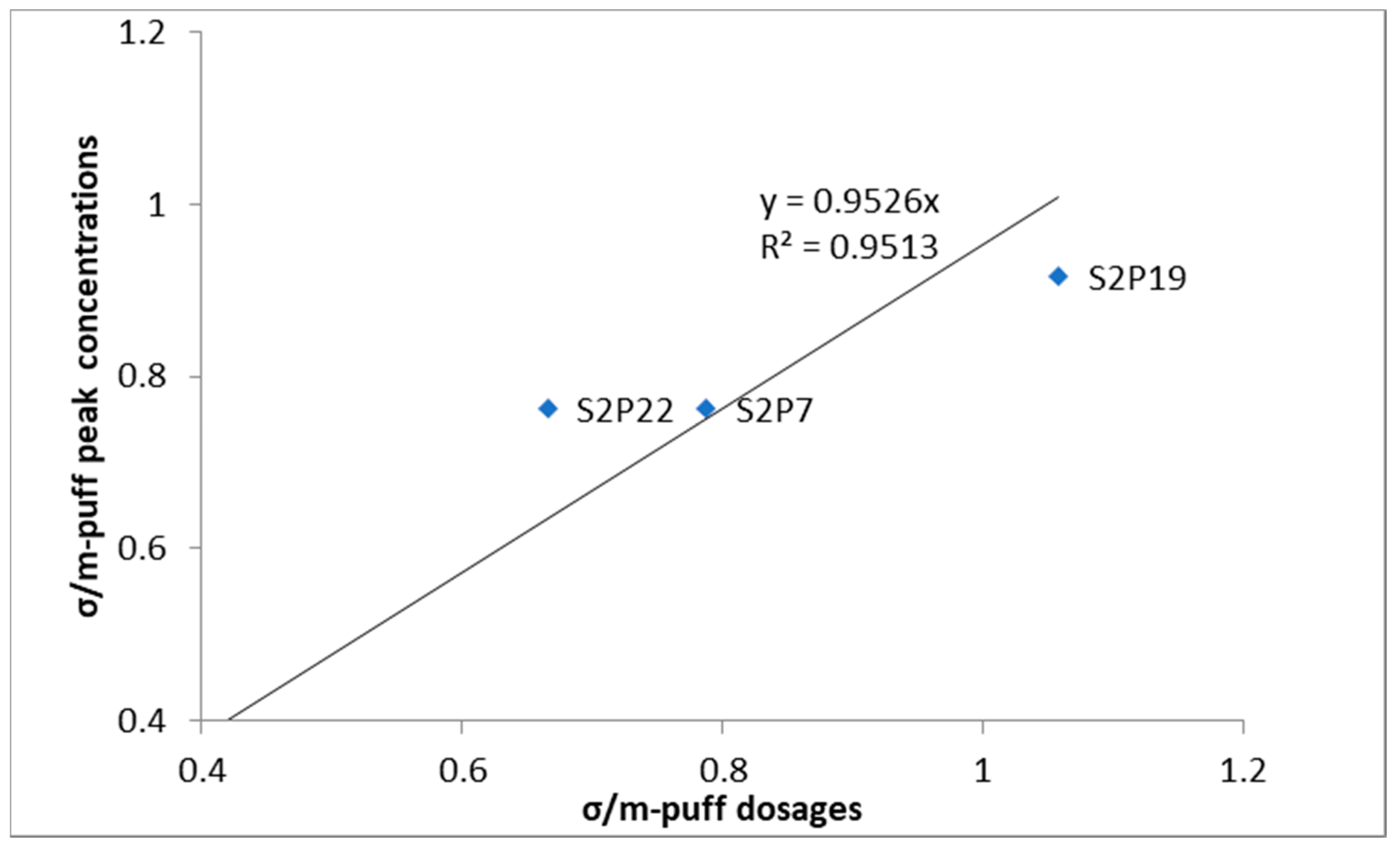
3.2. The Puff Release Experiment Peak Concentrations
3.3. Dosage/Peak Concentrations Pdf/Cdf for Puff Releases
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andronopoulos, S.; Bartzis, J.G.; Efthimiou, G.C.; Venetsanos, A.G. Puff-dispersion variability assessment through Lagrangian and Eulerian modelling based on the JU2003 campaign. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2019, 171, 395–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbekar, E.; Harms, F.; Leitl, B. Dosage-based parameters for characterization of puff dispersion results. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, S.; Chang, J.; Mazzola, T. Comparison of an Analytical Urban Puff-Dispersion Model with Tracer Observations from the Joint Urban 2003 Field Campaign. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2019, 171, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ceballos, M.A.; Hanna, S.; Bianconi, R.; Bellasio, R.; Chang, J.; Mazzola, T.; Andronopoulos, S.; Armand, P.; Benbouta, N.; Čarný, P.; et al. UDINEE: Evaluation of Multiple Models with Data from the JU2003 Puff Releases in Oklahoma City. Part II: Simulation of Puff Parameters. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2019, 171, 351–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldrini, O.; Armand, P. Validation and Sensitivity Study of the PMSS Modelling System for Puff Releases in the Joint Urban 2003 Field Experiment. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2019, 171, 513–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trini Castelli, S.; Armand, P.; Tinarelli, G.; Duchenne, C.; Nibart, M. Validation of a Lagrangian particle dispersion model with wind tunnel and field experiments in urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 193, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloupecká, H.; Jakubcová, M.; Janour, Z.; Jurcáková, K.; Kellnerová, R. Equations of a new puff model for idealized urban canopy. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.R.; Brown, M.J.; Camelli, F.E.; Chan, S.T.; Coirier, W.J.; Hansen, O.R.; Huber, A.H.; Kim, S.; Reynolds, R.M. Detailed simulations of atmospheric flow and dispersion downtown Manhattan: An application of five computational fluid dynamics models. Bull Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, S.T.; Leach, M.J. A validation of FEM3MP with Joint Urban 2003 data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2007, 46, 2127–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flaherty, J.E.; Stock, D.; Lamb, B. Computational fluid dynamic simulations of plume dispersion in urban Oklahoma City. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2007, 46, 2110–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, E.A.; Diehl, S.R.; Burrows, D.A.; Keith, R. Evaluation of a fast-running urban dispersion modeling system using Joint Urban 2003 field data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2007, 46, 2165–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, S.; Platt, N.; Urban, J.T.; Heagy, J.F. Comparisons of transport and dispersion model predictions of the Joint Urban 2003 field experiment. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2008, 47, 1910–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.R.; White, J.M.; Troiler, J.; Vernot, R.; Brown, M.; Kaplan, H.; Alexander, Y.; Moussafir, J.; Wang, Y.; Williamson, C.; et al. Comparisons of JU2003 observations with four diagnostic urban wind flow and Lagrangian particle dispersion models. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4073–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Stanzer, K.; Andronopoulos, S.; Armand, P.; Berbekar, E.; Efthimiou, G.; Fuka, V.; Gariazzo, C.; Gasparac, G.; Harms, F.; Hellsten, A.; et al. COST ES1006-Model Evaluation Case Studies: Approach and Results; COST Office: Brussels, Belgium, 2015; ISBN 987-3-9817334-2-6. [Google Scholar]
- Trini Castelli, S.; Tinarelli, G.; Reisin, T.G. Comparison of atmospheric modelling systems simulating the flow, turbulence and dispersion at the microscale within obstacles. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2017, 17, 879–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatwin, P.C. The use of statistics in describing and predicting the effects of dispersing gas clouds. J. Hazard. Mater. 1982, 6, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogen, K.T.; Gouveia, F.J. Impact of spatiotemporal fluctuations in airborne chemical concentration on toxic hazard assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, N.; Clarke, E.D. Relationships between higher moments of concentration and of dose in turbulent dispersion. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1995, 73, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilderman, T.L.; Hrudey, S.E.; Wilson, D.J. A model for effective toxic load from fluctuating gas concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 1999, 64, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.R. The exponential probability density function and concentration fluctuations in smoke plumes. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1984, 29, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, E. The shape of the probability density function of short-term concentration fluctuations of plumes in the atmospheric boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1990, 51, 269–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, J.C.; Sykes, R.I.; Venkatram, A. Evaluating air-quality models: Review and outlook. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1992, 31, 1121–1145. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/26186554 (accessed on 4 January 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yee, E.; Wilson, D.J.; Zelt, B.W. Probability distributions of concentration fluctuations of a weakly diffusive passive plume in turbulent boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1993, 64, 321–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, E.; Kosteniuk, P.R.; Chandler, G.M.; Biltoft, C.A.; Bowers, J.F. Statistical characteristics of concentration fluctuations in dispersing plumes in the atmospheric surface layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1993, 65, 69–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, T.; Müller, H.-J.; Gläser, M.; Möller, B. Measurements and modelling of full-scale concentration fluctuations. Agratechnische Forsch. 2002, 8, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Csanady, G.T. Concentration fluctuations in turbulent diffusion. J. Atmos. Sci. 1967, 24, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andronopoulos, S.; Grigoriadis, D.; Robins, A.; Venetsanos, A.; Rafailidis, S.; Bartzis, J.G. Three-dimensional modelling of concentration fluctuations in complicated geometry. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2001, 1, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, K.-J.; Lien, F.-S.; Yee, E. Numerical modeling of passive scalar dispersion in an urban canopy layer. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2007, 95, 1611–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroidis, I.; Andronopoulos, S.; Bartzis, J.G.; Griffiths, R.F. Atmospheric dispersion in the presence of a three-dimensional cubical obstacle: Modelling of mean concentration and concentration fluctuations. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2740–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliez, M.; Carissimo, B. Computational Fluid Dynamical Modelling of Concentration Fluctuations in an Idealized Urban Area. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2008, 127, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, E.; Wang, B.-C.; Lien, F.-S. Probabilistic Model for Concentration Fluctuations in Compact-Source Plumes in an Urban Environment. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2009, 130, 169–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuzzi, G.; Amicarelli, A.; Monti, P.; Thomson, D.J. A 3D Lagrangian micromixing dispersion model LAGFLUM and its validation with a wind tunnel experiment. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, H.; Santos, J.M.; Reis, N.C., Jr.; Mavroidis, I. Development of a fluctuating plume model for odour dispersion around buildings. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, A. A Stochastic Single-Particle Lagrangian Model for the Concentration Fluctuations in a Plume Dispersing Inside an Urban Canopy. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2014, 150, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroidis, I.; Andronopoulos, S.; Venetsanos, A.; Bartzis, J.G. Numerical investigation of concentrations and concentration fluctuations around isolated obstacles of different shapes. Comparison with wind tunnel results. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2015, 15, 999–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, G.C.; Berbekar, E.; Harms, F.; Bartzis, J.G.; Leitl, B. Prediction of high concentrations and concentration distribution of a continuous point source release in a semi-idealized urban canopy using CFD-RANS modeling. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 100, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, G.C.; Andronopoulos, S.; Tolias, I.; Venetsanos, A. Prediction of the upper tail of concentration distributions of a continuous point source release in urban environments. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2016, 16, 899–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, G.C.; Andronopoulos, S.; Bartzis, J.G. Evaluation of probability distributions for concentration fluctuations in a building array. Physica A 2017, 484, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, G.C. Prediction of four concentration moments of an airborne material released from a point source in an urban environment. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2019, 184, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.J.; Snyder, W.H.; Lawson, R.E., Jr.; Hunt, J.C.R. Wind tunnel simulations of plume dispersion through groups of obstacles. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3715–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavageau, M.; Schatzmann, M. Wind tunnel measurements of concentration fluctuations in an urban street canyon. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3961–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, E.; Biltoft, C.A. Concentration fluctuation measurements in a plume dispersing through a regular array of obstacles. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2004, 111, 363–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Griffiths, R.F.; Roberts, I.D.; Reis, N.C., Jr. A field experiment on turbulent concentration fluctuations of an atmospheric tracer gas in the vicinity of a complex-shaped building. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4999–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailis, R.M.; Hill, A. A wind-tunnel simulation of plume dispersion within a large array of obstacles. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 119, 289–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, E.; Chan, R.; Kosteniuk, P.R.; Chandler, G.M.; Biltoft, C.A.; Bowers, J.F. Concentration fluctuation measurements in clouds released from a quasi-instantaneous point source in the atmospheric surface layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1994, 71, 341–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, E.; Kosteniuk, P.R.; Bowers, J.F. Study of concentration fluctuations in instantaneous clouds dispersing in the atmospheric surface layer for relative turbulent diffusion: Basic descriptive statistics. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1998, 87, 409–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, M.; Bertagni, M.B.; Marro, M.; Salizzoni, P. Concentration fluctuations from localized atmospheric releases. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2020, 177, 461–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andronopoulos, S.; Bartzis, J.G.; Würtz, J.; Asimakopoulos, D. Modelling the effects of obstacles on the dispersion of denser-than-air gases. J. Hazard. Mater. 1994, 37, 327–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatram, A. The expected deviation of observed concentrations from predicted ensemble means. Atmos. Environ. 1979, 13, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.W.; Lee, S.J. The effects of bottom gap and non-uniform porosity in a wind fence on the surface pressure of a triangular prism located behind the fence. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2001, 89, 1137–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, G.C.; Bartzis, J.G. Atmospheric dispersion and individual exposure of hazardous materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartzis, J.G.; Efthimiou, G.C.; Andronopoulos, S. Modelling Short Term Individual Exposure from Airborne Hazardous Releases in Urban Environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efthimiou, G.C.; Kovalets, I.V.; Argyropoulos, C.D.; Venetsanos, A.; Andronopoulos, S.; Kakosimos, K. Evaluation of an inverse modelling methodology for the prediction of a stationary point pollutant source in complex urban environments. Build. Environ. 2018, 143, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, G.C.; Andronopoulos, S.; Bartzis, J.G. Prediction of dosage-based parameters from the short-duration release of airborne materials in urban environments. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2018, 130, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakai, A.; Franke, J. Validation of two RANS solvers with flow data of the flat roof Michelstadt case. Urban Clim. 2014, 10, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroney, R.N.; Leitl, B.M.; Rafailidis, S.; Schatzmann, M. Wind-tunnel and numerical modeling of flow and dispersion about several building shapes. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1999, 81, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnew, A.K.; Bitsuamlak, G.T. Computational evaluation of wind loads on buildings: A review. Wind Struct. Int. J. 2013, 16, 629–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwig, D.; Efthimiou, G.C.; Bartzis, J.G.; Leitl, B. CFD-RANS model validation of turbulent flow in a semiidealized urban canopy. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2012, 111, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Stathopoulos, T. Numerical simulation of dispersion around an isolated cubic building: Model evaluation of RANS and LES. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tominaga, Y.; Mochida, A.; Murakami, S.; Sawaki, S. Comparison of various revised k-ε models and LES applied to flow around a high-rise building model with 1:1:2 shape placed within the surface boundary layer. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, N.G.; Easom, G.J. Non-linear k-ε turbulence model results for flow over a building at full-scale. Appl. Math. Model. 2003, 27, 1013–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


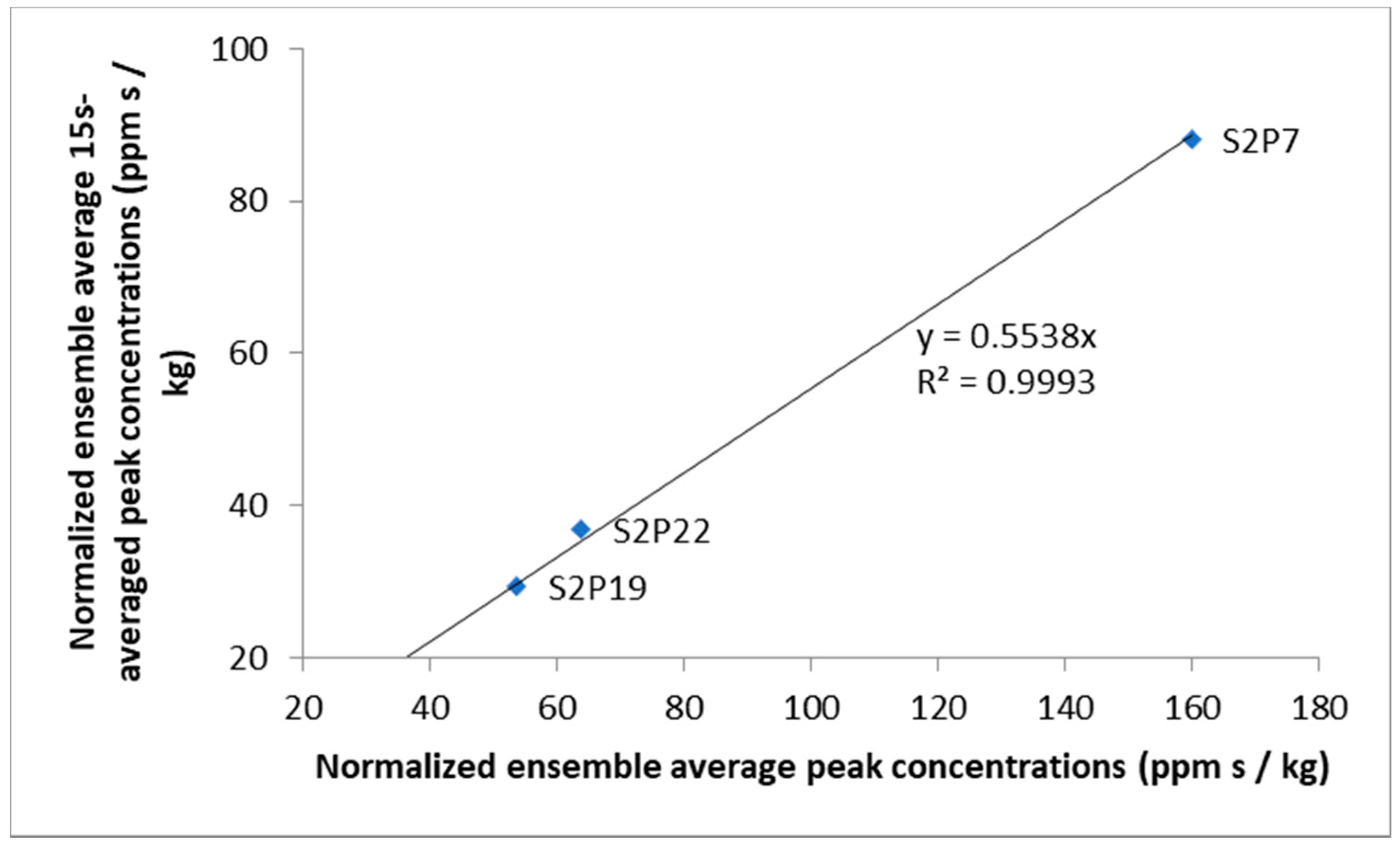
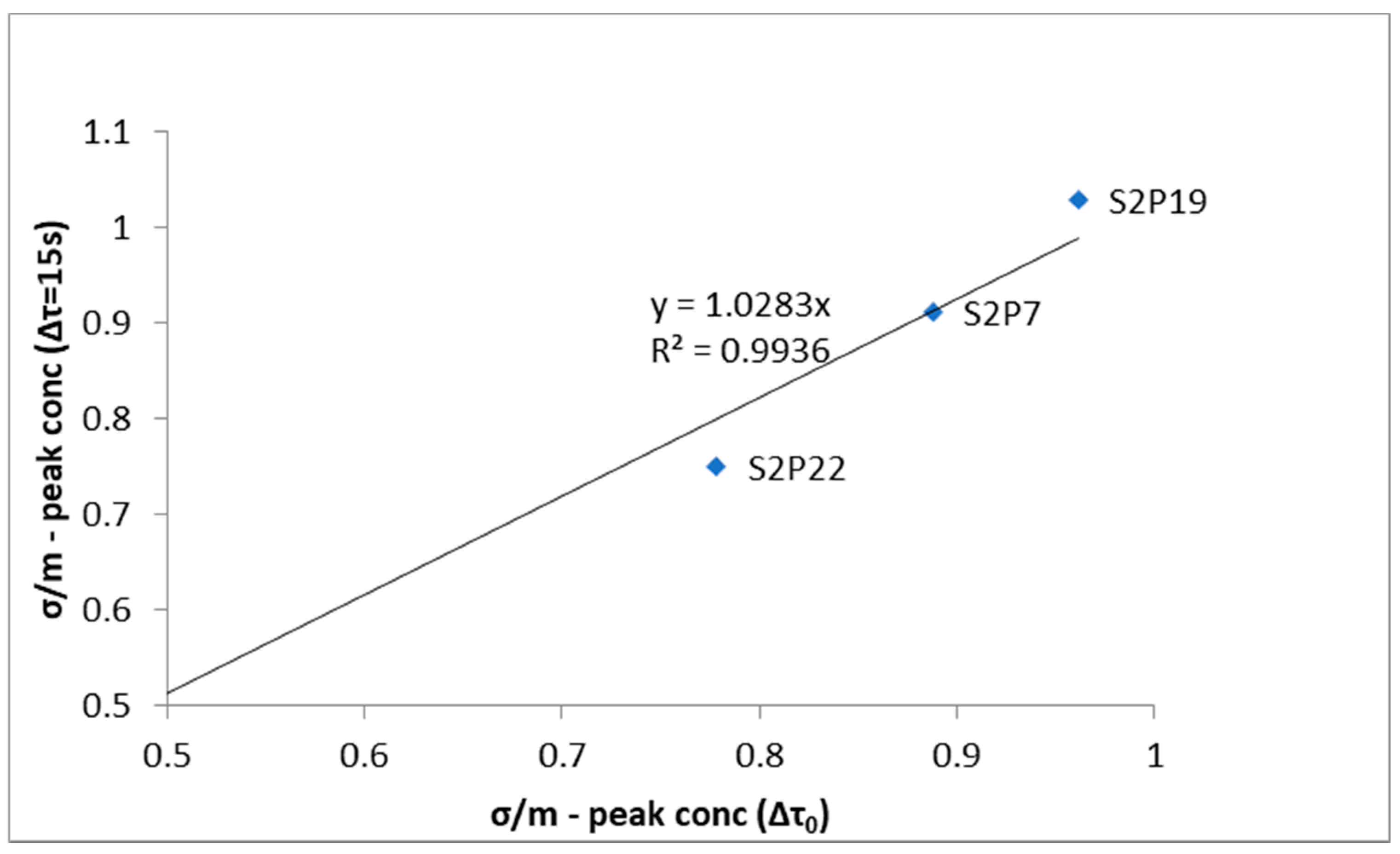
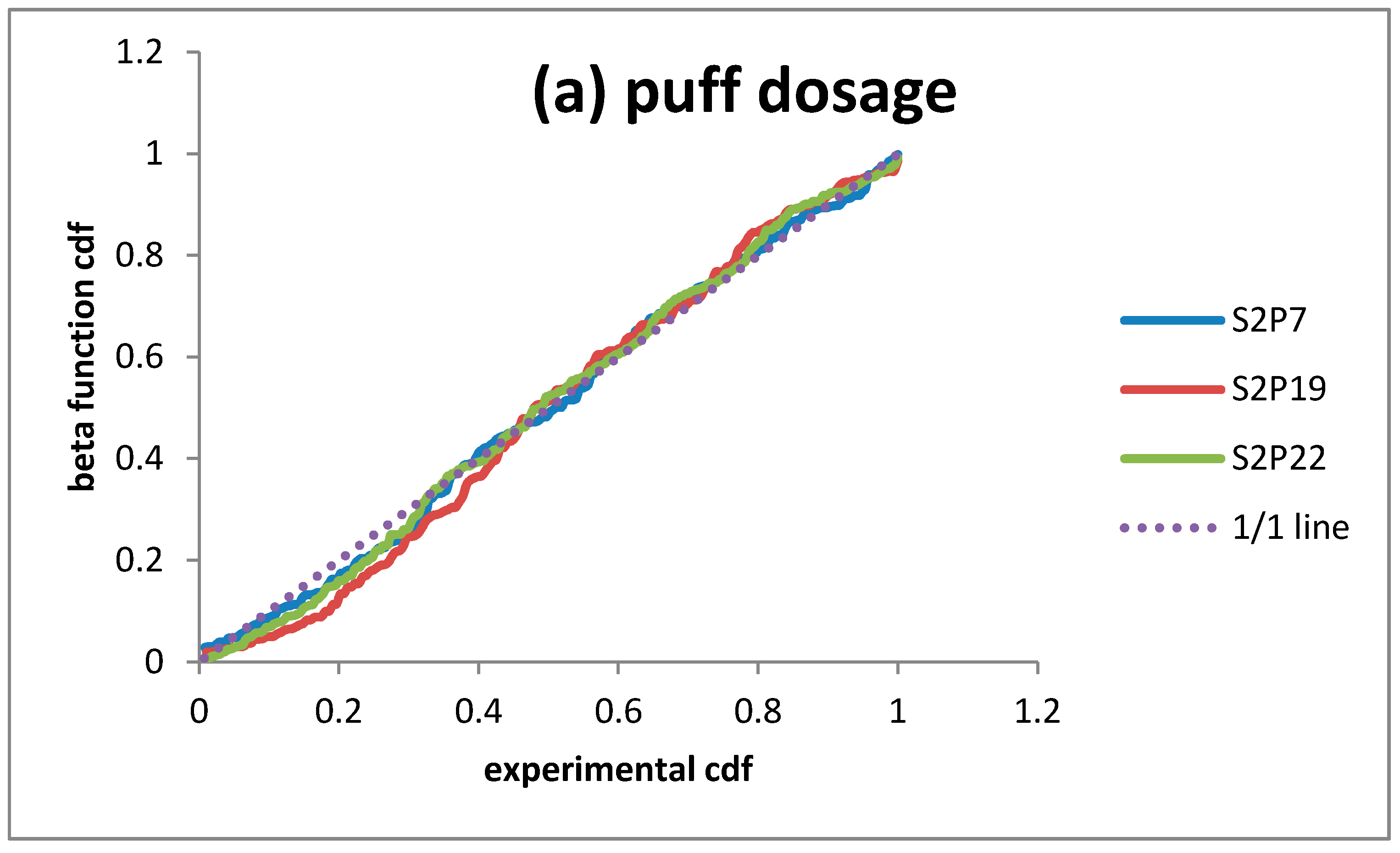
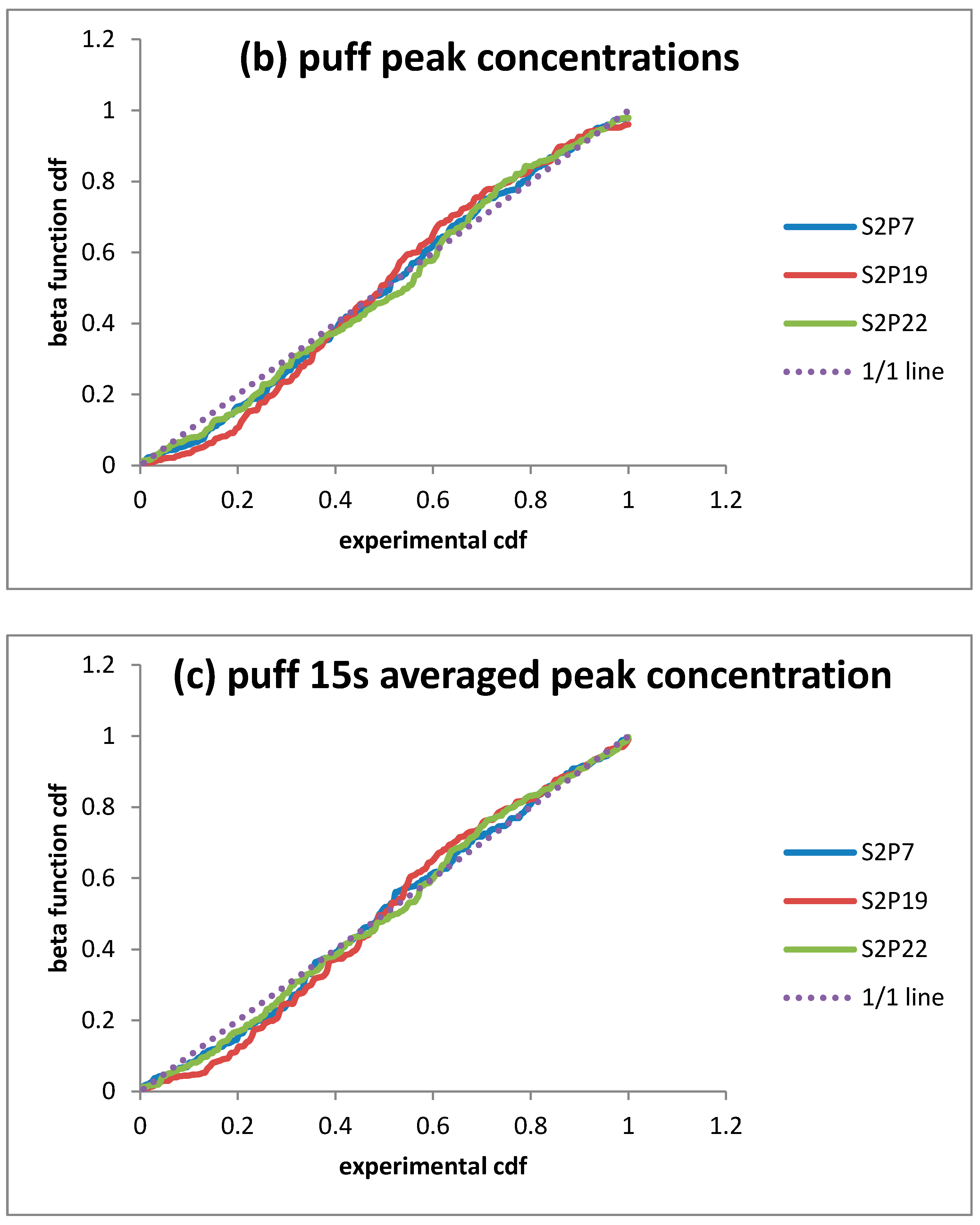
| Sensors | Puff Releases | Continuous Release | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non Detected Puffs | Normalised Dosage (ppm s/kg) | Normalised Concentrations (ppm s/kg) | Turbulence Time Scales (s) | ||||
| m | σ | m | σ | σ (29 s)(*) | |||
| S2P7 | 31/286 | 124.73 | 116.60 | 125.85 | 145.06 | 114.36 | 19.20 |
| S2P19 | 44/286 | 86.42 | 88.99 | 32.27 | 43.44 | 39.58 | 59.54 |
| S2P22 | 4/286 | 85.49 | 62.56 | 78.79 | 56.20 | 49.31 | 40.69 |
| Sensor | Normalised Peak Concentration (ppm·s/kg) | 15-s Time-Averaged Normalised Peak Concentration (ppm·s/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | σ | m | σ | |
| S2P7 | 160.00 | 121.92 | 88.05 | 69.26 |
| S2P19 | 53.66 | 49.21 | 29.51 | 29.08 |
| S2P22 | 63.80 | 48.67 | 36.91 | 27.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartzis, J.G.; Efthimiou, G.C.; Andronopoulos, S. Modelling Exposure from Airborne Hazardous Short-Duration Releases in Urban Environments. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020130
Bartzis JG, Efthimiou GC, Andronopoulos S. Modelling Exposure from Airborne Hazardous Short-Duration Releases in Urban Environments. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(2):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020130
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartzis, John G., George C. Efthimiou, and Spyros Andronopoulos. 2021. "Modelling Exposure from Airborne Hazardous Short-Duration Releases in Urban Environments" Atmosphere 12, no. 2: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020130
APA StyleBartzis, J. G., Efthimiou, G. C., & Andronopoulos, S. (2021). Modelling Exposure from Airborne Hazardous Short-Duration Releases in Urban Environments. Atmosphere, 12(2), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020130






