Abstract
Indoor radon concentrations constitute a major source of exposure to ionizing radiation for humans. It has been estimated that radon contributes about 10% of deaths from lung cancer in the USA and Europe. In Italy, current legislation establishes that the concentration of radon must be monitored in all workplaces located in a basement and on the ground floor. In this study, the indoor radon concentration of 20 multi-floor buildings on the Cardarelli Hospital was measured during two consecutive semesters. The survey was carried out with CR-39 solid-state nuclear track detectors (SSNTDs). Radon concentrations were found to range from 4 Bq/m3 to 424 Bq/m3, with a median of 24 Bq/m3. The dependence of the radon concentrations on the measurement floor and the room-to-room spatial variation was also analyzed.
1. Introduction
222Rn is a colorless, odorless, and chemically inert radioactive natural gas belonging to the 238U radioactive chain. It is present in many rocks, soils and in well water. When radon is produced by the disintegration of 226Ra in the outdoor atmosphere, it rapidly dilutes. On the contrary, in confined spaces such as homes and office buildings, radon can accumulate to harmful levels for human health. Radon is currently considered an important environmental pollutant because it contributes to more than 50% of the natural background dose to human beings, as reported by UNSCEAR 2000 []. Radon inhalation has been recognized as a risk factor for the onset of lung cancer [].
Several studies [,,,] have shown that exposure to radon is responsible for 3% to 14% of lung cancers in various countries, depending on the national average radon concentration and smoking habits. In France, between approximately 5 and 12% of lung cancers are attributed to radon exposure. In other European countries, such as Germany and Switzerland, the percentage of lung cancer deaths attributable to radon exposure is about 5% and 8.3%, respectively []. In Italy, a study by the National Institute of Health estimated that the lung cancer deaths attributable to radon exposure was about 10% []. In 2013, the European Union, to implement policies for the prevention and control of exposure to radon in confined environments, issued European Directive 2013/59/EURATOM [] with which it indicated 300 Bq/m3 as a reference level for both dwellings and workplaces. The EU Directive was transposed into Italian national legislation in July 2020 through Legislative Decree 101/2020 [].
Today, people spend around 80% of their time in confined environments such as homes and workplaces. Consequently, exposure to radon and its decay products may not be negligible. Furthermore, frequenting public places such as town halls, post offices and hospitals also contribute to increasing the dose of exposure to radon. In the last few decades, in Italy, only a few studies have been conducted in workplaces [,,,,,] on a local scale and with different experimental approaches. It would, therefore, be very useful to launch national radon measurement surveys in workplaces with common measurement methodologies and data analysis to make the measurement results comparable. Furthermore, since indoor radon concentration variations are influenced not only by the structural characteristics of buildings but also by the environment, the investigations should concern homogeneous environments for types of work. To date, the only national study [] dates to 1996, which, however, was conducted in dwellings and not in workplaces.
In the framework of this study, the radon survey was conducted in collaboration between the Medical Physics section of AORN Cardarelli and the Radioactivity Lab.RAD laboratory of the University Federico II of Naples. The radon survey adhered to a quality assurance system as required by Italian legislation, incorporating both quality control and quality assessment programs.
The purpose of this study is to determine the radon concentration levels to which both workers and patients are exposed in the largest hospital in southern Italy. In addition, another objective is to assess the percentage of environments that exceed the reference level set by Italian law.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Radon Concentration Measurements
In the present study, a radon survey was conducted at the largest public hospital in southern Italy, “AORN Cardarelli” from May 2021 to March 2024. A total of 20 buildings were monitored, and in 589 rooms, the average radon concentration was measured. The buildings differed in terms of construction materials, number of floors and year of construction. According to the requirements of Legislative Decree 101/2020, radon measurements were carried out in all the underground and ground floors, while in only three buildings, measurements were also carried out on mezzanines. The different premises monitored included analysis laboratories, operating rooms, doctors’ offices, emergency rooms, warehouses and reception areas. The long-term measuring technique based on passive alpha detectors (SSNTDs) CR-39 was employed. Each CR-39 was identified by an ID provided by the manufacturer, which was used to ensure its traceability in the process from the laboratory to the measurement site and vice versa. As required by Legislative Decree 203/2022, the radon measurements were carried out by the radioactivity laboratory that has certification according to the ISO 9001:2015 [] standard and accreditation according to the European Standard EN ISO/IEC 17025 [] for the “Integrated measurement method for determining average activity concentration of the radon 222 in the environment air using passive sampling and delayed analysis” (UNI ISO 11665-4: 2021) []. In all monitored rooms, CR-39 detectors were positioned at about 2 m from the floor and at 30 cm from the internal wall in order not to record the contribution from the Thoron. Each CR-39 detector was exposed in the environment to be monitored for six months. After exposure, all CR-39 detectors were chemically etched using a solution of 6.25 M NaOH at (98 ± 1) °C for 60 min. The automatic counting of tracks density was performed using a Politrack system (mi.am s.r.l., Rivergaro, PC, Italy). The radon concentration was calculated using the Equation (1):
where N is the track density corrected by background track density, E is the calibration factor, and T is the exposure time. Background trace density was estimated by chemically attacking and counting the traces of 10 unexposed detectors. The calibration factor was determined by exposing the detectors at certified atmosphere in the range of exposure from 146 kBq h m−3 to 4673 kBq h m−3 at National Metrological Institute (ENEA). The detection limit (LLD) of the method was estimates to be 4 Bq/m3 (with an exposure time of about 4000 h). The associated measurement uncertainty (k = 2) was determined as indicated by UNI ISO 11665-4: 2021 standard and was approximately 14%. The contributions to the standard measurement uncertainty considered were (i) measurement uncertainty associated with the calibration factor, (ii) statistical uncertainty associated with the net trace count, and (iii) the uncertainty associated with the sensitive area of the CR-39 detector. The uncertainty of the sampling duration is considered negligible.
Annual average concentration was then determined from the time-weighted average radon concentration from two consecutive six-month periods using exposure time as the weight, as in the following equation:
where Δt1 and Δt2 are the exposure time of two consecutive semesters, and and are the integrated measured radon concentrations in the two semesters.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with STATA software (Stata Corp, College Station, TX, USA).
Arithmetic mean, median, standard deviation, maximum and minimum were calculated for the entire dataset of radon values of all buildings and for the different datasets of radon values stratified by floor. The normality of log-transformed data was tested using Shapiro–Wilk; the homogeneity of variance was tested by Bartlett’s test. The comparisons between two groups were conducted with the T-test, while the comparison among multiple groups were performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA). The significance of the difference among the groups was evaluated using Bonferroni post hoc test.
2.3. Radon Risk Assessment
To assess radon risk, the effective dose was calculated according to Italian legislation [] using following equation:
where H is is the annual effective dose from radon indoor, CRn is the indoor radon concentration (Bq/m3), O is occupancy time (h/y), and D is the dose conversion factor (Sv Bq−1 h−1 m3).
The estimated cases of lung cancer per million people due to exposure to the average radon concentration level was estimated as:
where H is annual effective dose, and RFLC is risk factor for lung cancer induction expressed in mSv−1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Indoor Radon Concentration
In each semester of measurement, 589 CR39 detectors were used and approximately 84% were returned; the remaining detectors were lost.
Radon concentration measurements in all rooms ranged from 4 Bq/m3 to 424 Bq/m3, with a median of 24 Bq/m3. The geometric mean of radon concentrations was 29 Bq/m3 with a geometric standard deviation of 2. The mean value of radon concentration was 45 Bq/m3. The frequency distribution of all radon concentrations is presented in Figure 1. Although radon activity concentrations appear to follow the lognormal distribution, the Shapiro–Wilk test fails the test of normality (p < 0.0001).
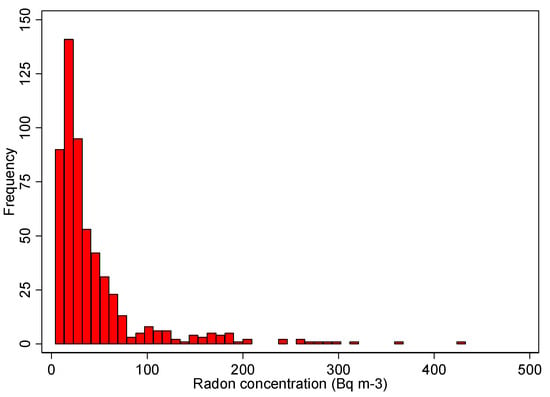
Figure 1.
Frequency distribution of radon measurements in all rooms of AORN Cardarelli.
The average radon activity concentration measured in all buildings was found to be lower than the Italian National average, which is 75 Bq/m3, and the Campanian average, which is 95 Bq/m3 []. Radon concentrations are also lower than those found in other measurement surveys conducted in workplaces in the Campania region [,,].
The European Directive 2013/59/EURATOM to protect workers and the general population from exposure to radon establishes the reference level of radon concentration at 300 Bq/m3 for both workplaces and residential environments. Italy implemented the European Directive in 2020 through Legislative Decree 101 and subsequently issued the National Radon Plan in 2024 []. The reference levels, expressed in terms of the average annual value of the radon activity concentration in the air is set equal to 300 Bq/m3 for workplaces and for homes built before 31 December 2024; for homes built after 31 December 2024, the reference level is lowered to 200 Bq/m3. Interpreting the results according to the Italian legislation, they were divided into smaller than 100 Bq/m3, between 100 Bq/m3 and 300 Bq/m3 e greater than 300 Bq/m3 (Table 1). As shown in Table 1, only three rooms (0.6%) exceeded the 300 Bq/m3 set by Legislative Decree 101/2020. Moreover, in 89.2% of the rooms, an average concentration of radon lower than the WHO reference level (100 Bq/m3) [] was measured.

Table 1.
Levels of radon concentration in relation to the Italian Legislative Decree 101/2020 reference level (300 Bq/m3).
The potential health risk associated with exposure to radon in confined environments depends not only on the concentration of radon activity but also on the duration of exposure. This risk can be estimated through the evaluation of the effective dose and estimating the number of cases of lung cancer per million people due to exposure to the average radon concentration level. Estimating an occupancy factor of 23% for workers, corresponding to 2000 h worked per year, the effective annual dose was found to be 0.61 mSv. Using the risk factor for cancer induction of 18 × 10−6 mSv−1 as reported by ICRP 50 [], the number of cases of lung cancer estimated per million persons resulting from radon exposure was found to be about 11 cases per million persons. Comparing the dose value calculated in this study with the dose limit imposed by the Italian legislature for exposure to radon in the workplace set at 6 mSv, it can be concluded that the risk to which workers are exposed is negligible.
3.2. Annual Radon Concentrations as Function of Floor Level and Room-to Room Variation
Based on the requirements of Legislative Decree 101/2020, radon measurements were conducted in all rooms on underground and ground floors. In this study, an underground floor refers to a floor that is below street level, regardless of the presence of windows. In total, measurements were carried out at ground level in 20 buildings and on underground floors in 12 buildings. Furthermore, radon measurements were carried out in 3 buildings, including on the mezzanine floor. A mezzanine is generally a floor over ground level, and in most cases, it may be considered equivalent to the ground floor. The number of rooms per floor differed for different buildings. Table 2 shows the annual averages of radon per floor, grouping together the measurements carried out in the rooms on the first and second levels below ground, indicated as underground.

Table 2.
Mean of radon activity concentration, minimum and maximum by floor of monitored rooms.
One-way analysis of variance on the log-transformed experimental data presents a statistically significant dependence on the floor (p < 0.0005). The results obtained agree with other studies [,,,,]. In contrast, Ivanova et al. [] found no statistically significant difference between radon concentrations measured on different floors at a large rehabilitation hospital. Our result is attributable to the fact that the lower floors are more affected by the infiltration of radon produced by the soil. Furthermore, the lower floors also have less ventilation, and this can favor the accumulation of radon in the rooms.
In each building, the radon concentration variation among rooms of the same floor, was also studied. To analyze this effect, SD and the coefficient of variation of radon concentrations (COV), defined as the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean, was determined for each floor and building (Table 3). The average COVs of the annual radon measurements per floor obtained were equal to 66%, 60% and 53% for the measurements carried out on the underground floors, ground floor and mezzanine floor, respectively. As observed, the variability between rooms is not negligible and decreases as the floor increases, although the differences are not statistically significant. This variability can be associated with the different characteristics of the rooms and with the different behavior of the occupants. In fact, rooms belonging to the same floor and building were often intended for very different uses.

Table 3.
COV and SD distribution in relation to floor.
It is well known that radon concentrations have wide diurnal and seasonal variability as demonstrated by many studies [,,]. This variability is usually attributed to weather conditions and changes in lifestyles in different seasons. In the present study, seasonal variability was studied starting from a subset of 289 measurements taken in the 6-month autumn–winter period and in the 6-month spring–summer period. As expected, radon concentrations measured from March to September were generally lower than those in autumn–winter (p < 0.001).
This finding agrees with the results of other authors who measured radon activity concentrations in confined spaces [,,]. For each room, the winter/summer ratio of indoor radon concentrations was also computed, and their distribution of values ranged from 0.24 to 4.65 with a mean value of 1.36. The difference in average concentrations between summer and winter periods can presumably be attributed to the greater ventilation due to air conditioning and the opening of windows during the summer months.
It is known that indoor radon concentrations are affected by several factors such as building materials, occupant lifestyles, and frequency and type of aeration. Unfortunately, it was not possible to explain the effect of these factors on the distribution of the experimental data because this information could not be collected during the study. This aspect certainly deserves further study and will be the subject of a future study which will concern the analysis of factors affecting radon concentration. Through ad hoc questionnaires, information will be collected on the main construction characteristics of the buildings and the lifestyle of the workers who use the monitored environments. This will allow us to analyze the impact that these factors have on radon concentrations.
Despite this limitation, this study has many positive aspects. The radon measurements, including the sampling phase, were carried out at the Lab.RAD radioactivity laboratory accredited according to the EN ISO/IEC 17025 standard and the UNI ISO 11665-4:2021 test method. This aspect certainly provides a guarantee regarding the quality assurance of the experimental data obtained. Furthermore, it is one of the few studies conducted systematically in an Italian hospital. Now, in fact, only a few studies have been conducted in hospital or healthcare facilities in a broader sense [,,,]. Moreover, it contributes to increasing information on radon concentrations in workplaces in the Campania region, as required by the National Radon Plan.
4. Conclusions
The present study represents the first systematic measurement campaign at a hospital in the Campania region, Italy. The results show that the percentage of premises that exceed the reference level of 300 Bq/m3 is 0.6%. A non-negligible room-to-room variation was observed. Furthermore, a statistically significant difference was observed between the measurements performed in the cold and warm semesters. The main merit of the present study can contribute to providing information on radon levels in hospital environments which have so far been little investigated in Italy. It would be extremely useful to perform national campaigns, organized by workplace type, to measure radon levels in workplaces using standardized measurement methodologies. This would ensure the comparability of measurement results in workplaces of the same type. Such campaigns would not only raise awareness of the potential health risks associated with radon exposure but would also facilitate the implementation of effective mitigation strategies based on reliable data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Q. and F.L.; methodology, M.Q. and F.L.; formal analysis, M.Q.; investigation, T.C., F.D.M. and F.L.; writing—review and editing, M.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- UNSCEAR-2000; United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation Report to the General Assembly: Sources, Effects and Risks of Ionizing Radiation. United Nations: New York, NY, USA; Beirut, Lebanon, 2000.
- Zeeb, H.; Shannoun, F. WHO Handbook in Indoor Radon: A Public Health Perspective; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, S.; Hill, D.; Auvinen, A.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Baysson, H.; Bochicchio, F.; Deo, H.; Falk, R.; Forastiere, F.; Hakama, M.; et al. Radon in homes and risk of lung cancer: Collaborative analysis of individual data from 13 European case-control studies. Br. Med. J. 2005, 330, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNSCEAR-2006; United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation Report to the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes: Effect of Ionizing Radiation. United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2006.
- Tirmarche, M.; Harrionson, J.D.; Laurier, D.; Paquet, F.; Blanchardon, E.; Marsh, J.W. ICRP 115, International Commission on Radiological Protection: Lung Cancer Risk from Radon and Progeny and Statement on Radon; Annals ICRP: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- ICRP 126; International Commission on Radiological Protection: Radiological Protection against Radon Exposure. Annals ICRP: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2014.
- Bochicchio, F.; Antignani, S.; Venoso, G.; Forastiere, F. Quantitative evaluation of the lung cancer deaths attributable to residential radon: A simple method and results for all the 21 Italian Regions. Radiat. Meas. 2013, 50, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Council. Council Directive 2013/59/Euratomon basic safety standards for protection against the dangers arising from exposure to ionising radiation. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2014, 57, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Italian Governement. Decreto Legislativo n. 241 del 26maggio 2000, Attuazione Della Direttiva 96/29/EURATOM in Materia di Protezione Sanitaria Della Popolazione e Dei Lavoratori Contro i Rischi Derivanti Dalle Radiazioni Ionizzanti. Official Gazette No. 203, 31, Rome, August 2000. Available online: https://www.mase.gov.it/sites/default/files/archivio/normativa/gu_43_2024_radon.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2024). (In Italian)
- Loffredo, F.; Quarto, M. Indoor radon concentration measurements in workplaces and their impact on health risk assessment. Indoor Built Environ. 2022, 32, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avino, V.; Pugliese, M.; Ambrosino, F.; Bifulco, M.; La Commara, M.; Roca, V.; Sabbarese, C.; La Verde, G. Radon Survey in Bank Buildings of Campania Region According to the Italian Transposition of Euratom 59/2013. Life 2021, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venoso, G.; Ampollini, M.; Antignani, S.; Caprio, M.; Carpentieri, C.; Di Carlo, C.; Bochicchio, F. Short-time annual variation of radon concentration in workplaces: Some results in a research institute. Rad. Prot. Dos. 2020, 191, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, F.; Savino, F.; Amato, R.; Irollo, A.; Gargiulo, F.; Sabatino, G.; Serra, M.; Quarto, M. Indoor Radon Concentration and Risk Assessment in 27 Districts of a Public Healthcare Company in Naples, South Italy. Life 2021, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maria, L.; Sponselli, S.; Caputi, A.; Delvecchio, G.; Giannelli, G.; Pipoli, A.; Cafaro, F.; Zagaria, S.; Cavone, D.; Sardone, R.; et al. Indoor Radon Concentration Levels in Healthcare Settings: The Results of an Environmental Monitoring in a Large Italian University Hospital. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, F.; Botti, T.; Buresti, G.; Caricato, A.P.; Chezzi, A.; Pepe, C.; Spagnolo, S.; Tonnarini, S.; Veschetti, M.; Trevisi, R. Radon Spatial Variations in University’s Buildings Located in an Italian Karst Region. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochicchio, F.; Campos Venuti, G.; Nuccetelli, C.; Piermattei, S.; Risica, S.; Tommasino, L.; Torri, G. Results of the representative Italian national survey on radon indoors. Health Phys. 1996, 71, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9001:2015; Quality Management Systems–Requirements. International Organization for Standardization: Genewa, Switzerland, 2015.
- UNI CEI EN ISO/IEC 17025:2018; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. International Organization for Standardization: Genewa, Switzerland, 2018.
- UNI ISO 11665-4:2021; Measurement of Radioactivity in the Environment—Air: Radon-222—Part 4: Integrated Measurement Method for Determining Average Activity Concentration Using Passive Sampling and Delayed Analysis. Ente Nazionale Italiano di Unificazione: Rome, Italy, 2021.
- Bochicchio, F.; Campos Venuti, G.; Piermattei, S.; Nuccetelli, C.; Risica, S.; Tommasino, L.; Torri, G.; Magnoni, M.; Agnesod, G.; Sgorbati, G.; et al. Annual average and seasonal variations of residential radon concentration for all the Italian Regions. Radiat. Meas. 2005, 40, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano Nazionale d’Azione per Il Radon 2023–2032. Supplemento Ordinario n. 10 alla Gazzetta Ufficiale; Gazzetta Ufficiale: Milan, Italy, 2024. (In Italian)
- ICRP 50, International Commission on Radiological Protection. Lung Cancer Risk from Exposures to Radon Daughters; ICRP Publication 50, ICRP: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Gisbert, L.; Candal-Pedreira, C.; San Miguel, M.G.-T.; Perez-Ríos, M.; Barros-Dios, J.; Varela-Lema, L.; Ruano-Ravina, A. Radon exposure and its influencing factors across 3,140 workplaces in Spain. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reste, J.; Pavlovska, I.; Martinsone, Z.; Romans, A.; Martinsone, I.; Vanadzins, I. Indoor Air Radon Concentration in Premises of Public Companies and Workplaces in Latvia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, K.; Dzhunakova, D.; Stojanovska, Z.; Djounova, J.; Kunovska, B.; Chobanova, N. Analysis of exposure to radon in Bulgarian rehabilitation hospitals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 19098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves-Kirkby, C.J.; Denman, A.R.; Phillips, P.S. Lorenz Curve and Gini Coefficient: Novel tools for analysing seasonal variation of environmental radon gas. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2480–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun Park, J.; Min Lee, C.; Young Lee, H.; Ryong Kang, D. Estimation of Seasonal Correction Factors for Indoor Radon Concentrations in Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşköprü, C.; İçhedef, M.; Saç, M.M. Diurnal, monthly, and seasonal variations of indoor radon concentrations concerning meteorological parameters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 195, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoo, F.; Darko, E.O.; Garavaglia, M.; Giovani, C.; Pividore, S.; Andam, A.B.; Amoako, J.K.; Adukpo, O.K.; Tandoh, J.B.; Inkoom, S. Seasonal indoor radon studies in buildings of Accra Metropolis of Greater Accra region of Ghana. Radioprotection 2018, 53, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimercati, L.; Fucilli, F.; Cavone, D.; De Maria, L.; Birtolo, F.; Ferri, G.M.; Soleo, L.; Lovreglio, P. Radon Levels in Indoor Environments of the University Hospital in Bari-Apulia Region Southern Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarto, M.; Pugliese, M.; Loffredo, F.; La Verde, G.; Roca, V. Indoor radon activity concentration measurements in the great historical museums of University of Naples, Italy. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2016, 168, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiana, G.; Dettori, M.; Masia, M.D.; Spano, A.L.; Piana, A.; Arghittu, A.; Castiglia, P.; Azara, A. Monitoring Radon Levels in Hospital Environments. Findings of a Preliminary Study in the University Hospital of Sassari, Italy. Environments 2021, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).